fluids part 1
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
functions of fluids
-transportation of nutrients, electrolytes, and oxygen to the cells
-excretion of waste products
-regulation of body temperature
-lubrication of joints, organs and tissues
-medium for food digestion
primary fluid compartments
-intracellular
-extracellular
intracellular
fluid within the cell (potassium)
extracellular
around/outside the cell (sodium)
interstitial
between tissue
intravascular
within the vessels (plasma)
transcellular
around the cells in a certain fluid. (cerebral spinal fluid)
extracellular fluid compartments
-interstitial
-intravascular
-transcelluar
adipose tissue
takes up space of fluids in the body, repels water
fluid shifts
third spacing
third spacing
fluids become trapped into areas where they cannot be utilized by body
third spacing
ascites, edam, peritonitis. sings of fluid volume deficit and increased weight
colloid osmotic pressure
proteins keep fluids within vascular space where they can be utilized
serum albumin
3.5-5.5
when proteins levels drop
fluids leak out of intravascular space to interstitial space (edema)
ascites
fluid that collects in the abdomen
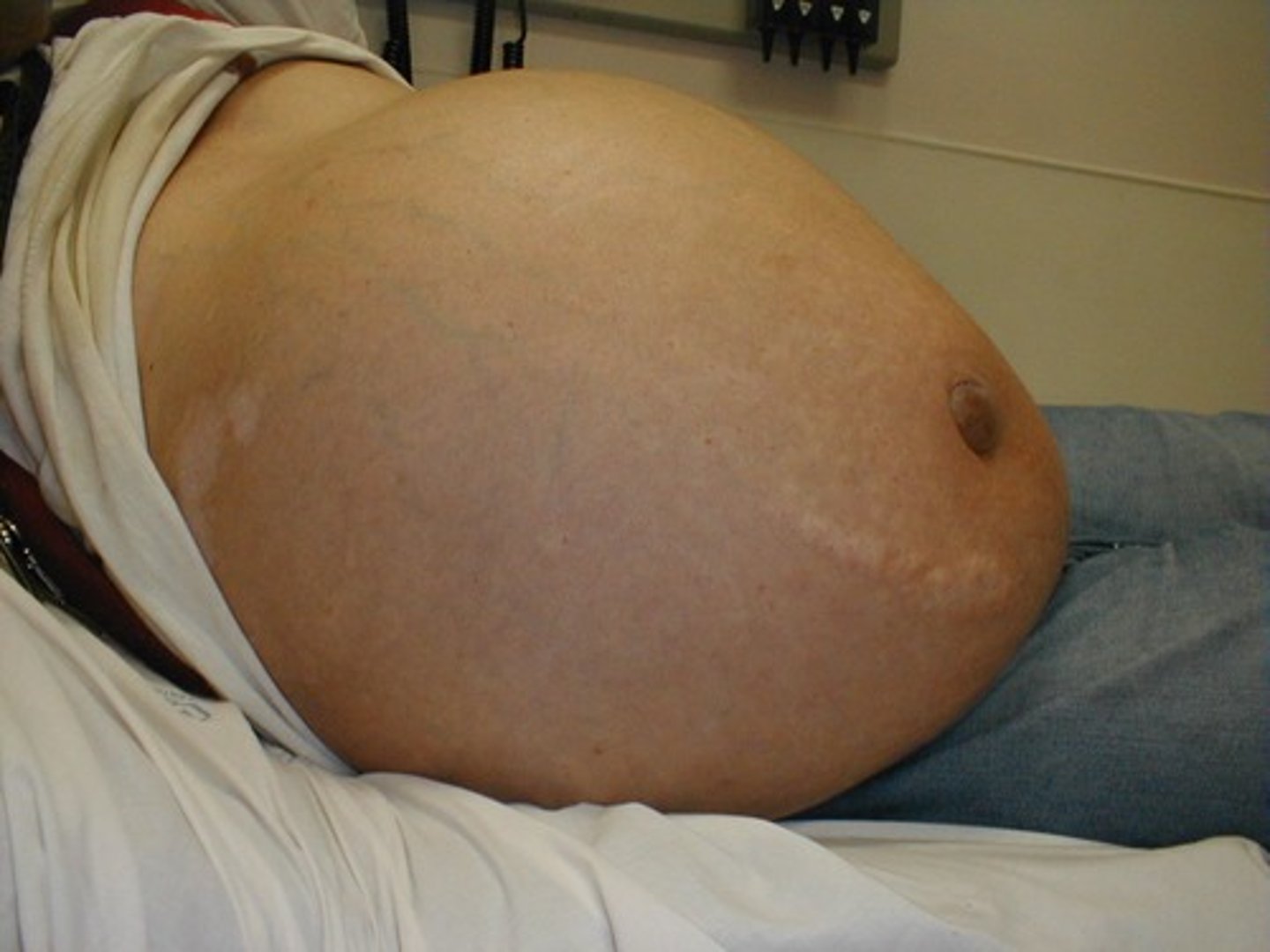
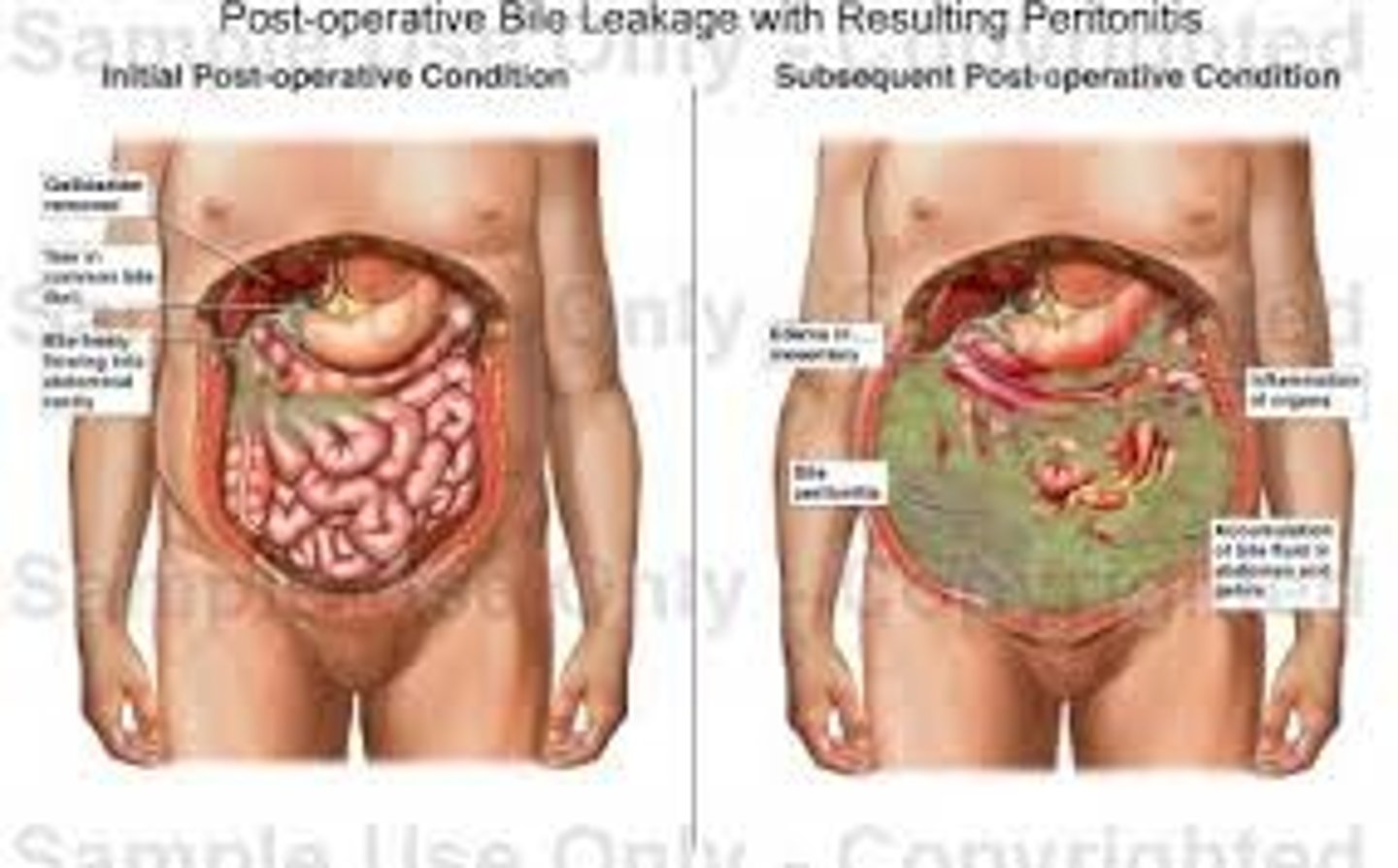
peritonitis
fluid in the abdominal cavity that becomes infected
blood volume is directly to
blood pressure
higher blood volume
bloop pressure increase, creates higher pressure
decreased blood volume (even is misplaced fluid) causes
blood pressure would decrease. to compensate the heart speeds up, causing increase pulse
to get rid of fluid this is prescribed
diuretics
hemtocrit
the ratio of the volume of red blood cells to the total volume of blood
Buffy coat
white blood cells, platelets
plasma
water, proteins, nutrients, hormones,
hematocrit levels
males 42%-52%; females 37%-47%
low albumin
low nutritional value, causes holes in blood vessels, leading to fluid leaking out of the
osmosis
water is going to move from low concentration to high concentration to achieve homeostasis. equalizes porportions
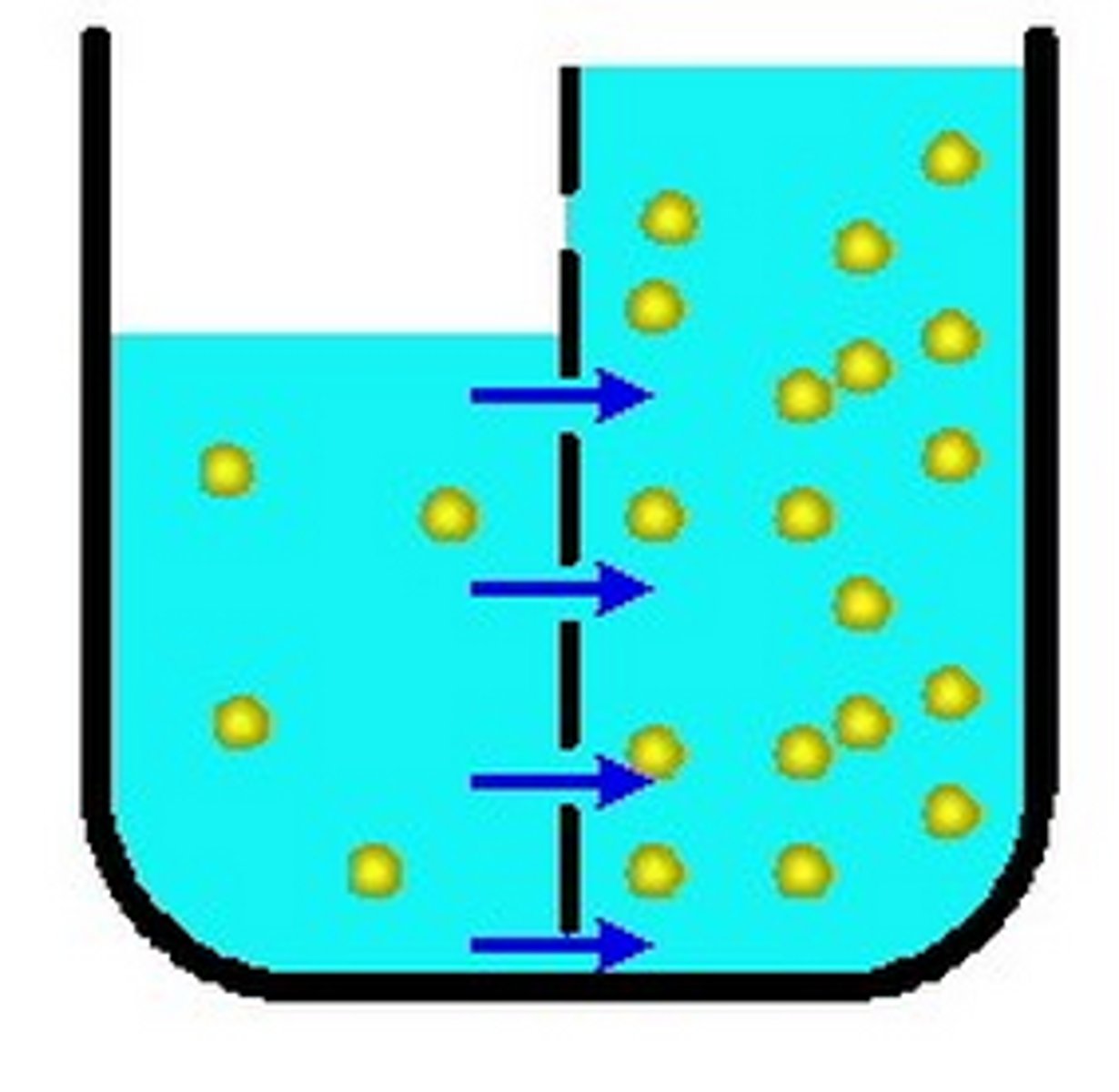
water follows
salt
serum osmolality
concentration in the blood
urine osmolarity (urine specific gravity)
concentration of urine
serum osmolality
275-300
urine specific gravity
1.010-1.030
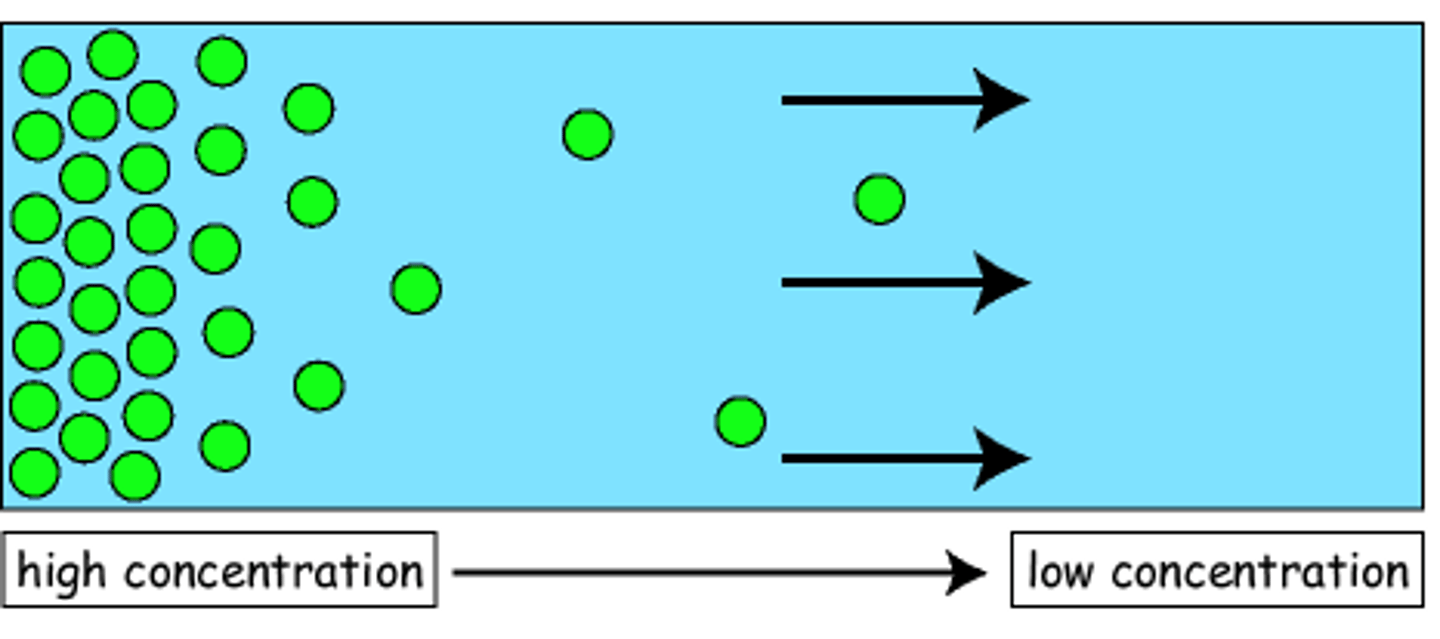
diffusion
the movement of solutes (opposite of osmosis). high concentration to low concentration
filtration
water and solutes move. from high pressure to low pressure
sodium potassium pumps
on the cell membrane
organs that regulate
-kidneys
-heart
-lungs
-pituitary gland
-adrenal gland
-parathyroid gland
hormonal regulation of fluid
-antidiuretic hormone
-renin angiotensin system
-aldosterone
antidiuretic hormone
stops the body from getting rid of fluid,
aldosterone
takes slat so water will follow
intake of water per day
2.5 liters
healthy people should have an output
equal to input
once a shift
check I and o's unless otherwise ordered every hour
creatinnine
0.7-1.4
blood urea nitrogen
10-20
all hypertonic solutions
go thru central line
given with blood
only normal saline
all electrolytes/given in labor and delivery
lactated ringers
monitor blood sugar with
5% dextrose in water
half normal saline
hypotonic fluids, free water
FVD causes
-sweating
-GI fluid loss
-decreased oral intake
-hemorrhage
-diuretics
-third spacing
FVD signs
-acute weight loss
-decreased skin turgor
-oliguria
-concentrated urine
-postural hypotension
-thirst/dry mucous membranes
FVD treatment
-PO fluids
-isotonic IVF
-monitors I/os
FVE causes
-heart failure
-excessive ingestion of salt
-renal failure
-excessive/rapid IV infusion
FVE signs
-edema
-crackles, SOB, wheezing
-JVD
-hypertension and tachycardia
-weight gain
FVE treatment
-diuretics
-fluid restriction
-daily weights
-dialysis
diuretics
-thiazide diuretics
-loop diuretics
-potassium sparing diuretics