Module 4: Cerebral cortex - Organization and Anatomy
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Behavior occurs…
through neural network processing and neural processing is a system of connectivity and modularity
Neurons in different regions….
behave differently
2 cerebral hemispheres
right
left
Cerebrum
the largest segment of the CNS; most complex
split into 2 symmetrical regions called the cerebral hemispheres by the longitudinal cerebral fissure
possesses characteristic grooves and hills, called sulci and gyri
serves as information processing hub and center of all integrative operations of the cerebrum
Hemispheres are joined together via…
a massive tract of axons located at the bottom of the longitudinal fissure called the corpus callosum
4 lobes of the cerebral hemisphere
frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal
subcortical structures also part of the cerebrum
basal ganglia
hippocampus
amygdala
insula
white matter associated with afferent and efferent signals passing to and from regions of gray matter
Cerebral cortex diagram
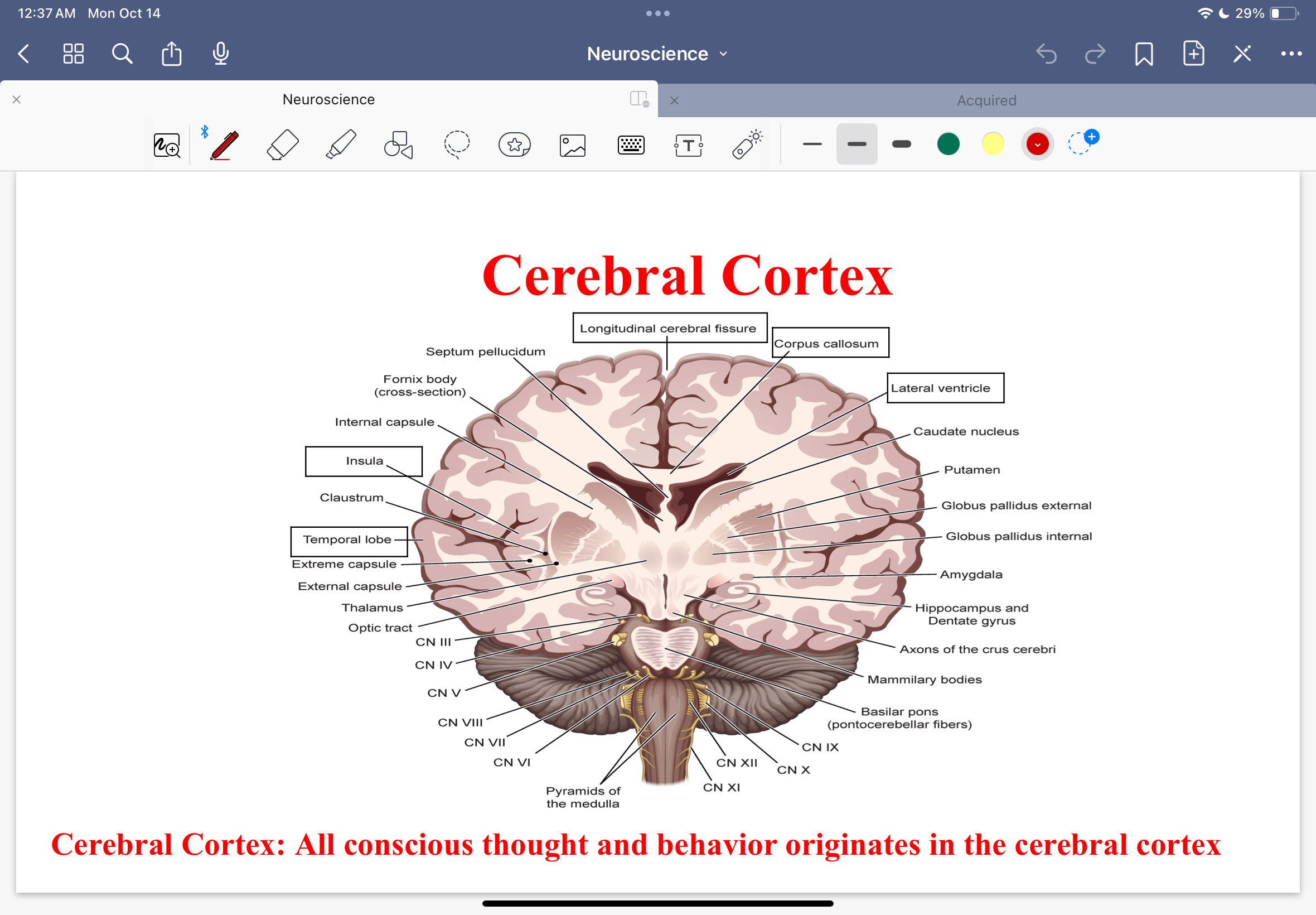
Cerebral cortex
All conscious thought and behavior originates in the cerebral cortex
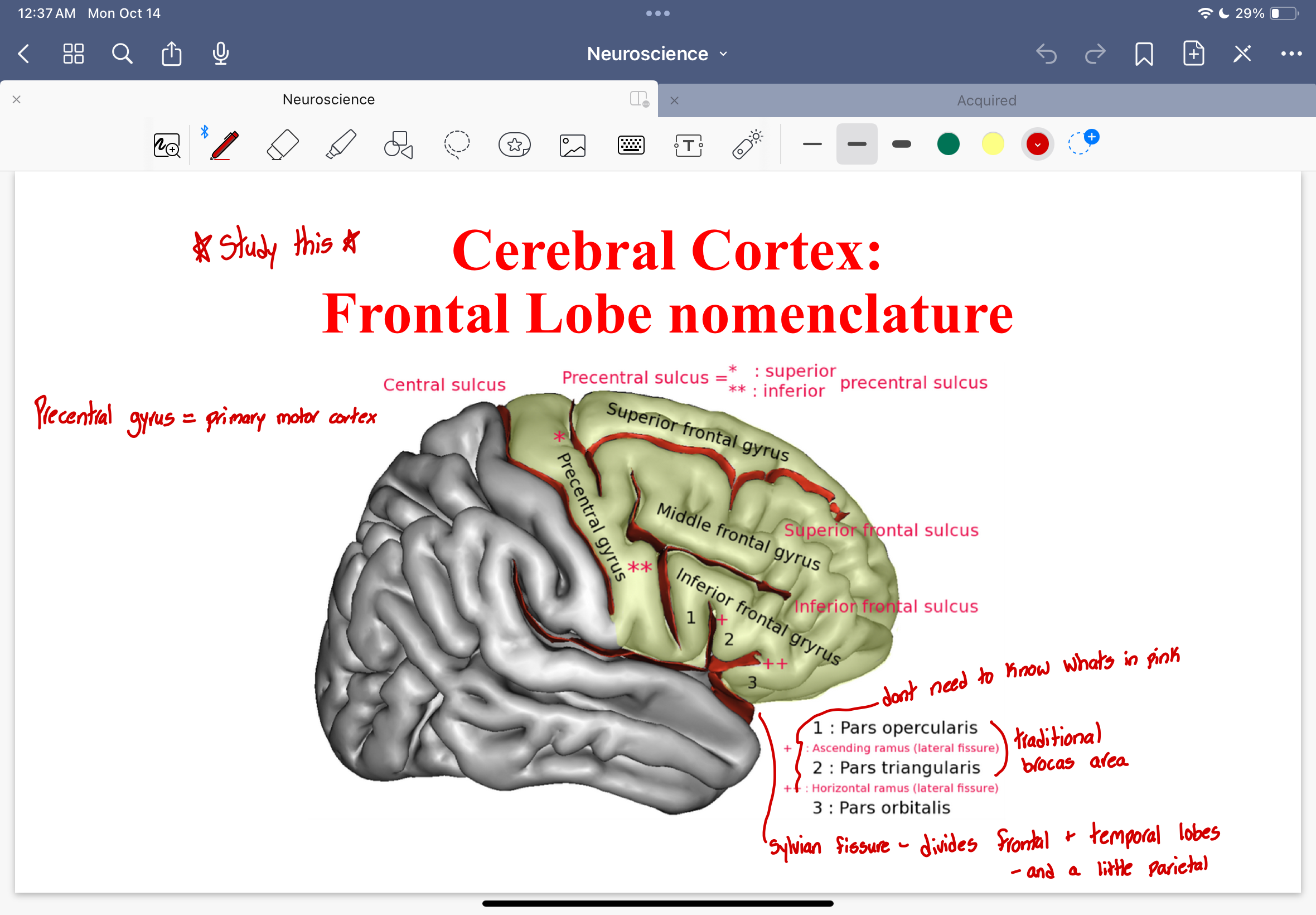
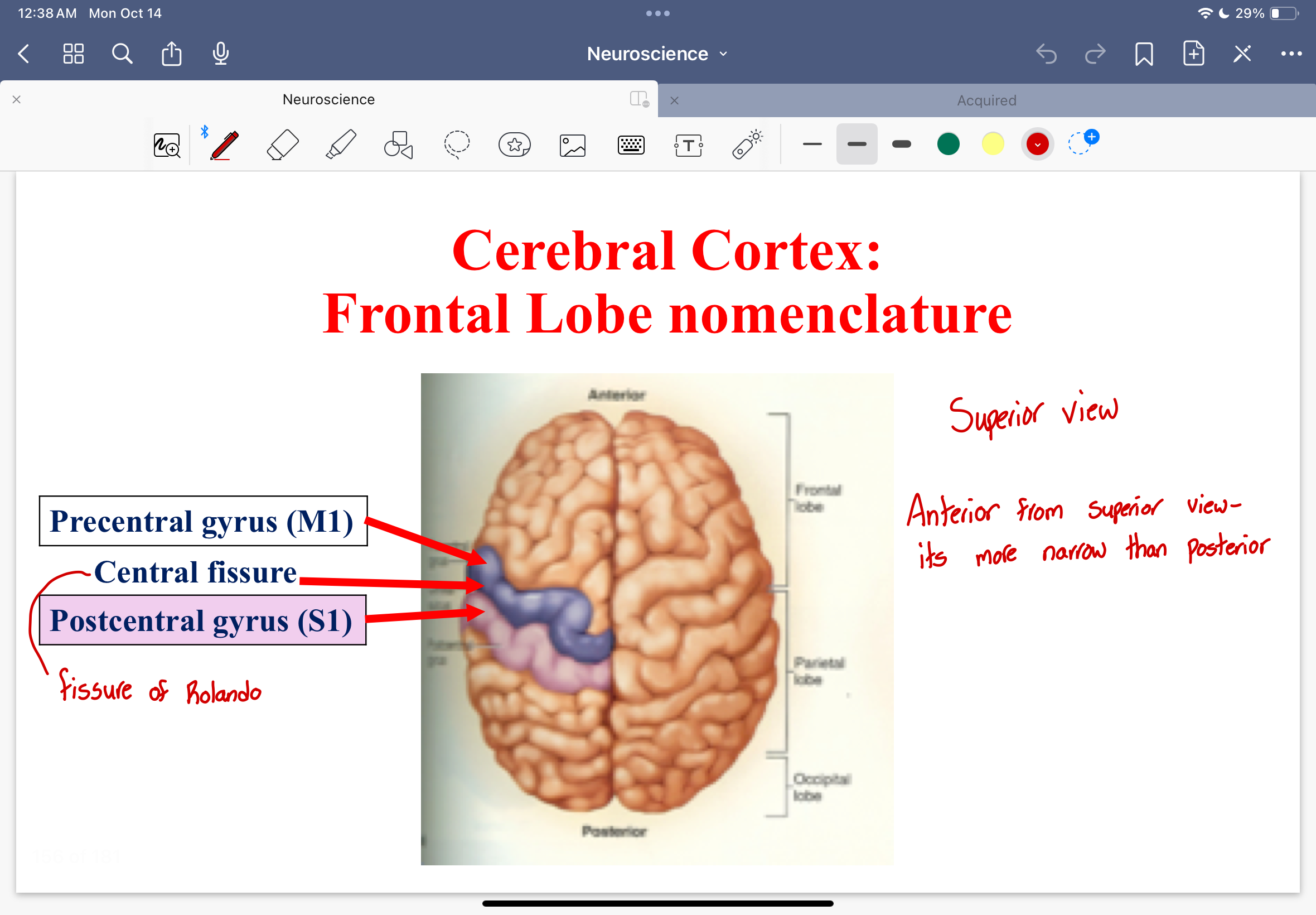
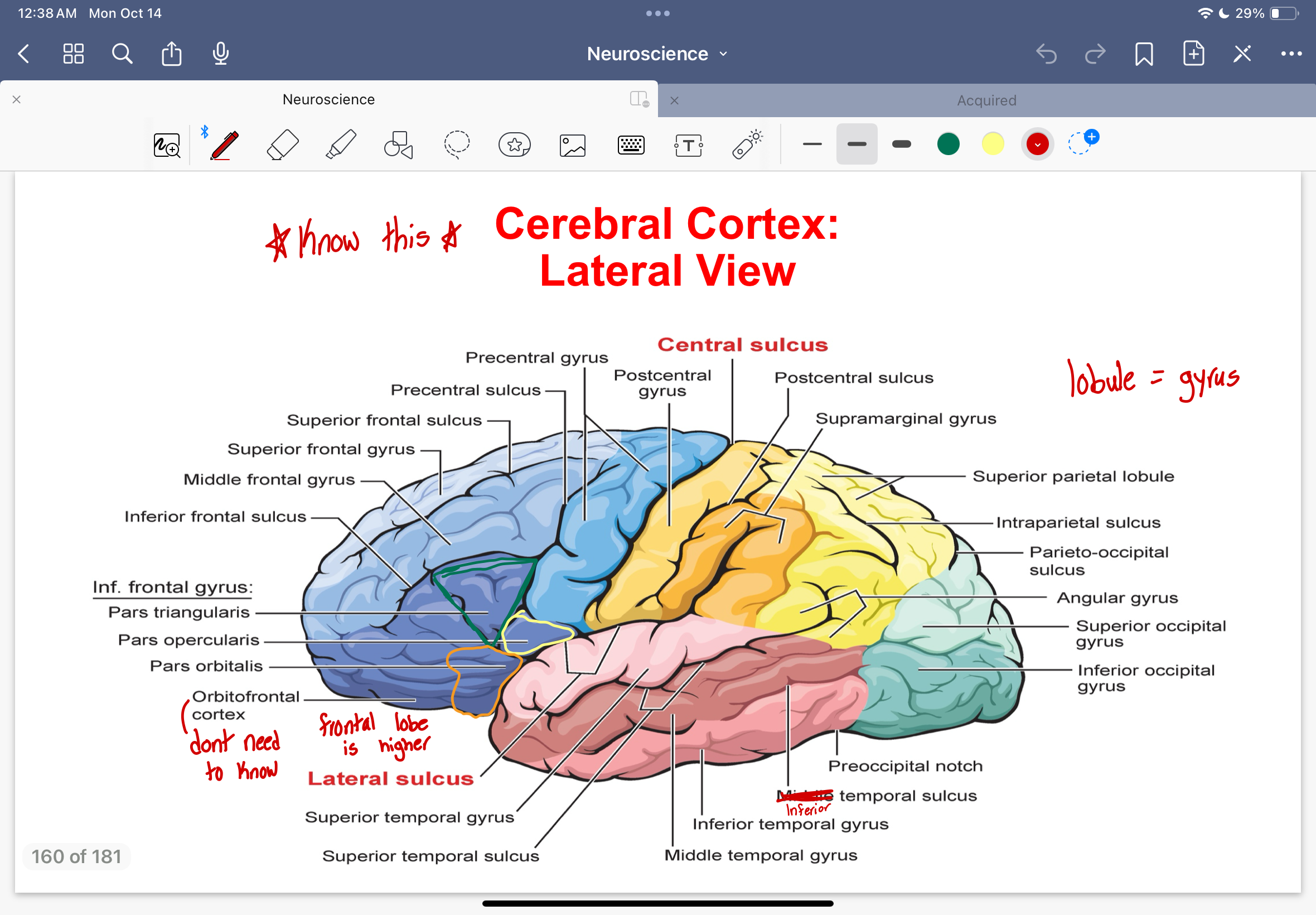
Cerebral Cortex: Frontal Lobe nomenclature
precentral gyrus
superior, middle, and inferior frontal gyrus
superior, inferior frontal sulcus
3 parts of the inferior frontal gyrus
pars opercularis
pars triangularis
pars orbitalis
Traditional brocas area
Pars opercularis and Pars triangularis
Sylvian fissure
Divides frontal and temporal lobes, and a little parietal
Cerebral Cortex: Frontal Lobe Nomenclature diagram
Prefrontal Cortex
Remainder of the frontal lobe rostral (front) to the premotor areas
Executive function of prefrontal cortex
Judgement, future planning, the sense of purpose in action (ex: stopping yourself from cursing), the notion of personal responsibility, adherence to social norms and constructs
Massive interconnections of the prefrontal corex
*motor-related regions: premotor areas, cerebellum, basal ganglia
*sensory-related regions: parietal and temporal association areas
thalamus, memory systems, limbic systems, neuromodulatory systems
Cerebral Cortex: Parietal Lobe Nomenclature
postcentral gyrus
postcentral sulcus
intraparietal sulcus
parieto-occipital sulcus
superior temporal sulcus
superior and inferior parietal lobe
Cerebral Cortex: Parietal Lobe Nomenclature diagram
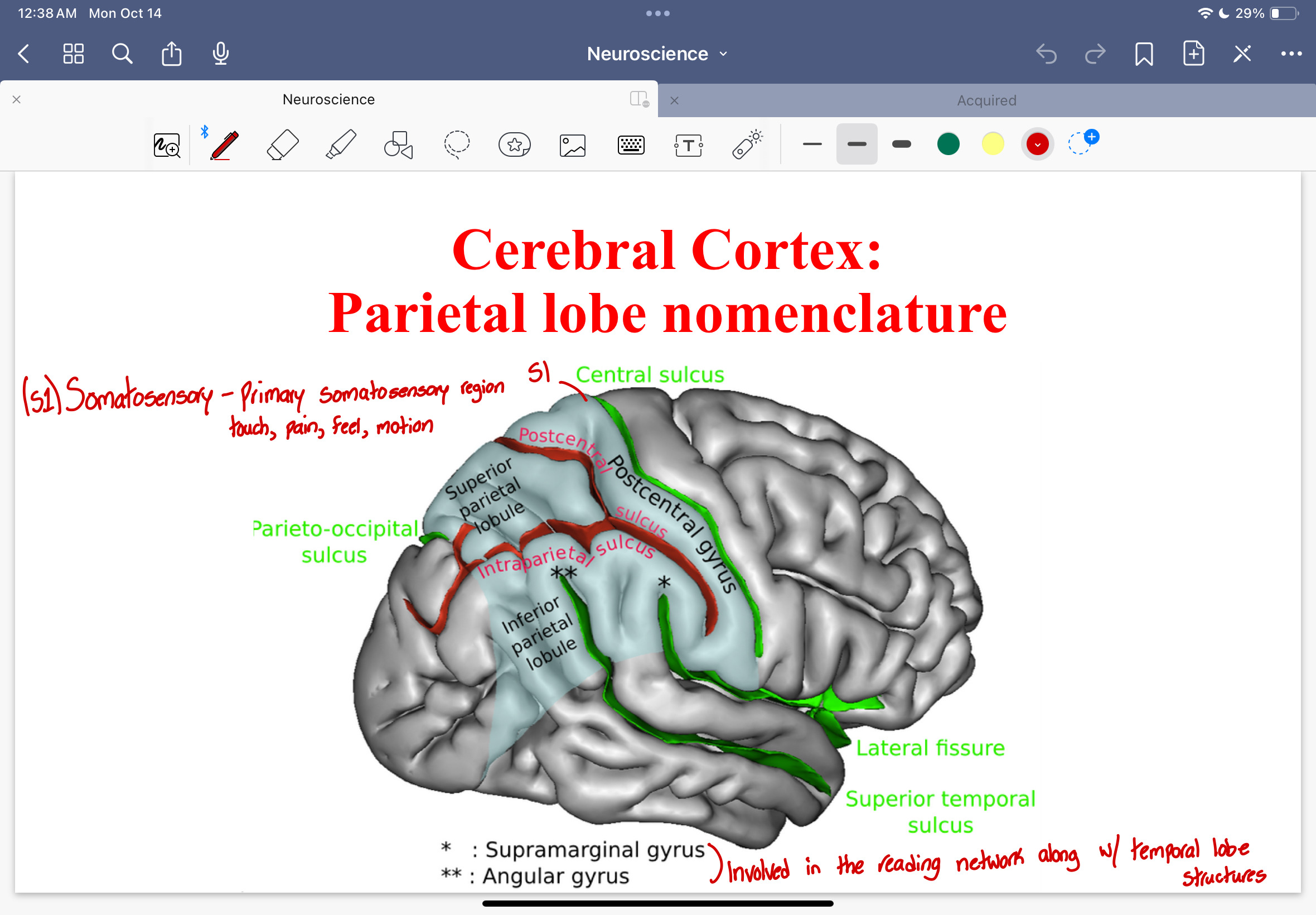
2 parts within the inferior parietal lobule
supramarginal gyrus
angular gyrus
They are involved in reading network along with the temporal lobe structures
Superior view of cerebral cortex diagram
Somatopic Organization of M1 and S1 diagram
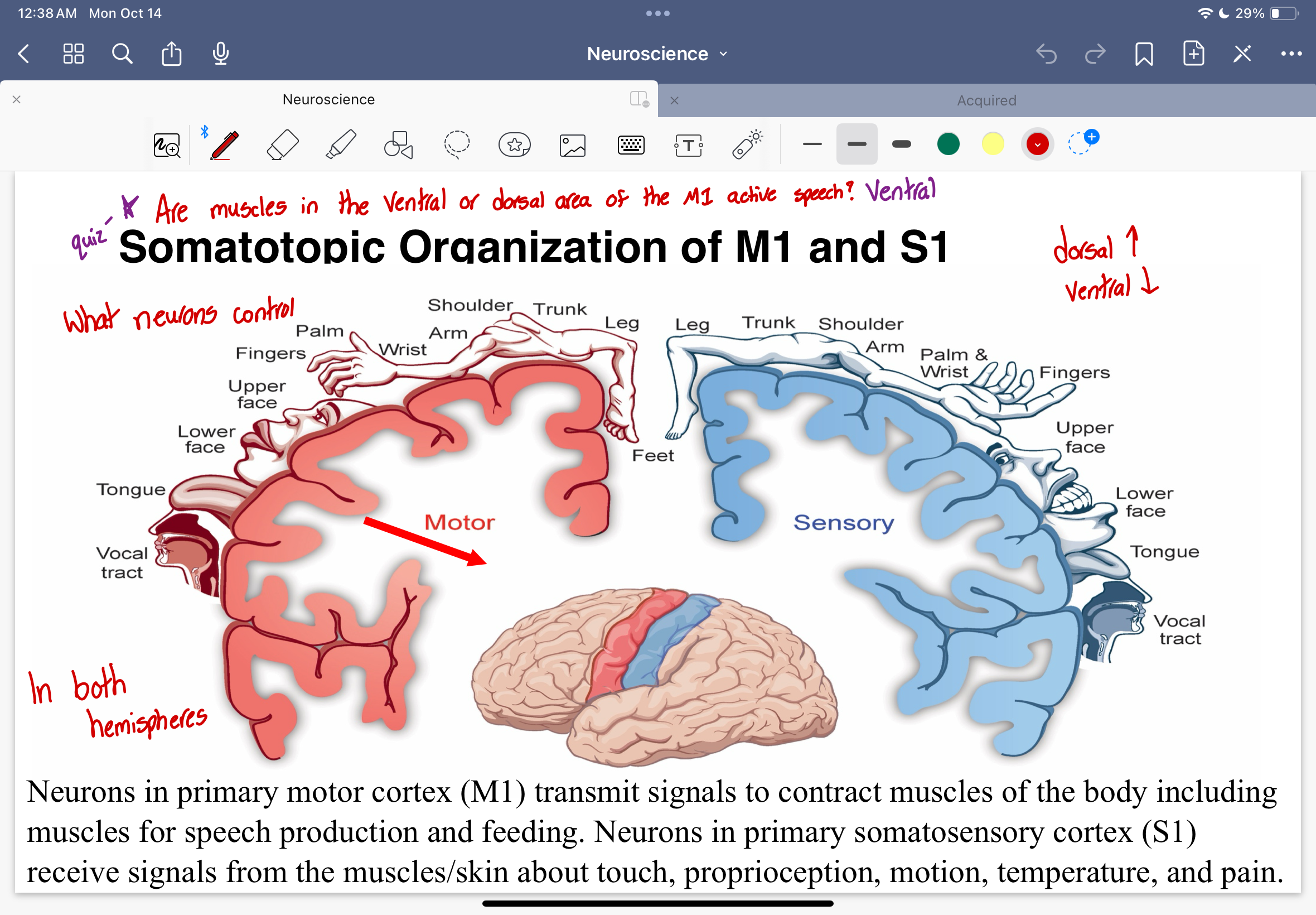
Dorsal
towards the top
Ventral
towards the bottom
Neurons in the M1
Neurons in the primary motor cortex transmit signals to contract muscles of the body including muscles for speech production and feeding
Neurons in the S1
Neurons in the primary somatosensory cortex receive signals from the muscles/skin about touch, proprioception, motion, temperature, and pain
Are muscles in the ventral or dorsal area of the M1 that active speech?
Ventral
Electrical stimulation of M1 neurons
low level electrical stimulation of M1 neurons produces contraction of discrete muscles in the body
high level electrical stimulation of M1 neurons begins coordinated and purposeful actions such as reaching or grabbing
M1 characteristics
somotopically organized in a gross manner along the precentral gyrus
integrative hub for inputs related to movement from cerebellum, basal ganglia and pre-motor area
obtains somotosensory input from thalamus and S1
combinations of inputs from associated motor and somotosensory structures is thought to provide M1 with required info to produce skilled and goal directed actions
Cerebral cortex: temporal lobe nomenclature diagram
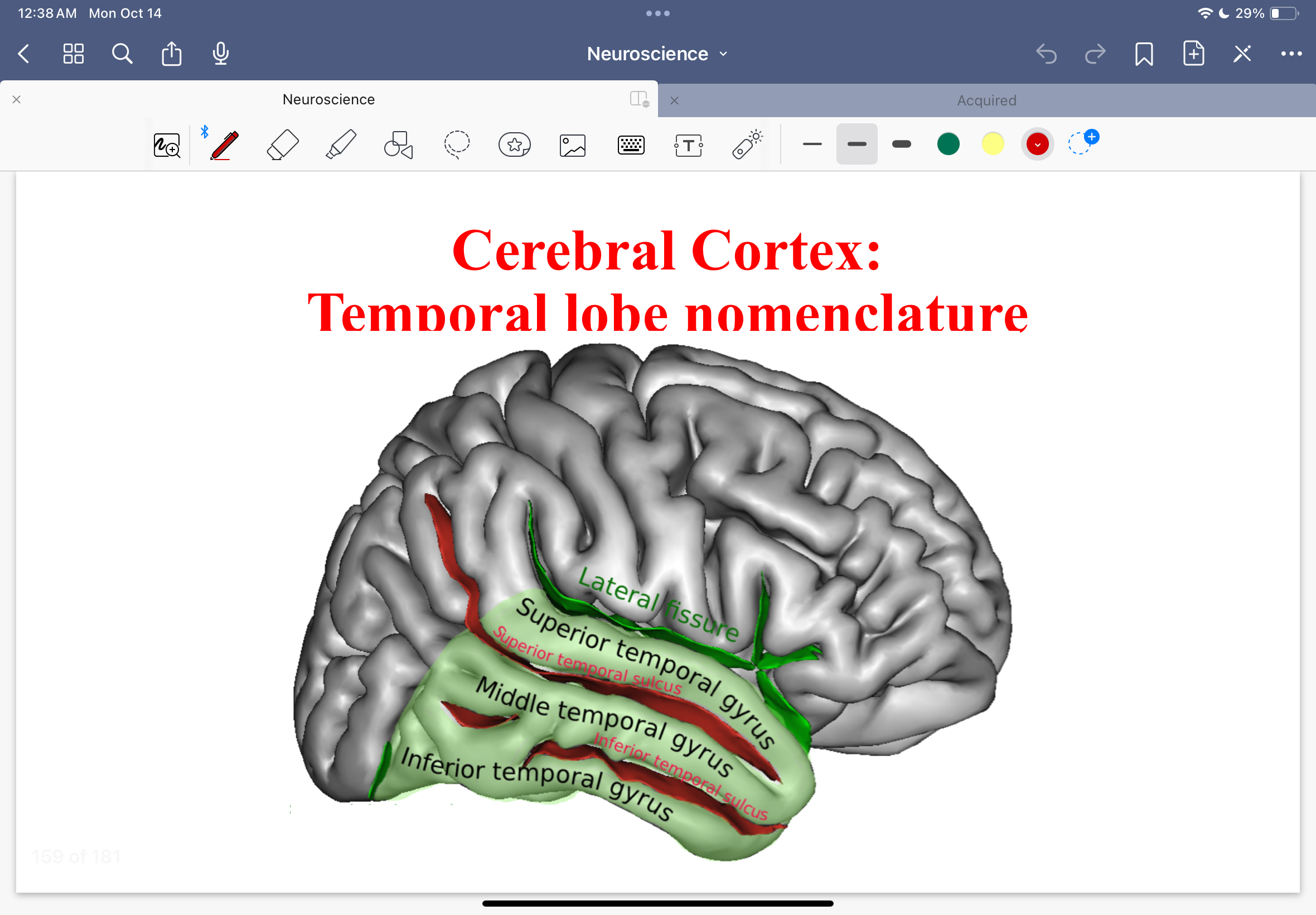
Cerebral cortex: temporal lobe nomenclature
superior, middle, inferior temporal gyrus
superior and inferior temporal sulcus
Cerebral Cortex: lateral view diagram
Thalamus diagram
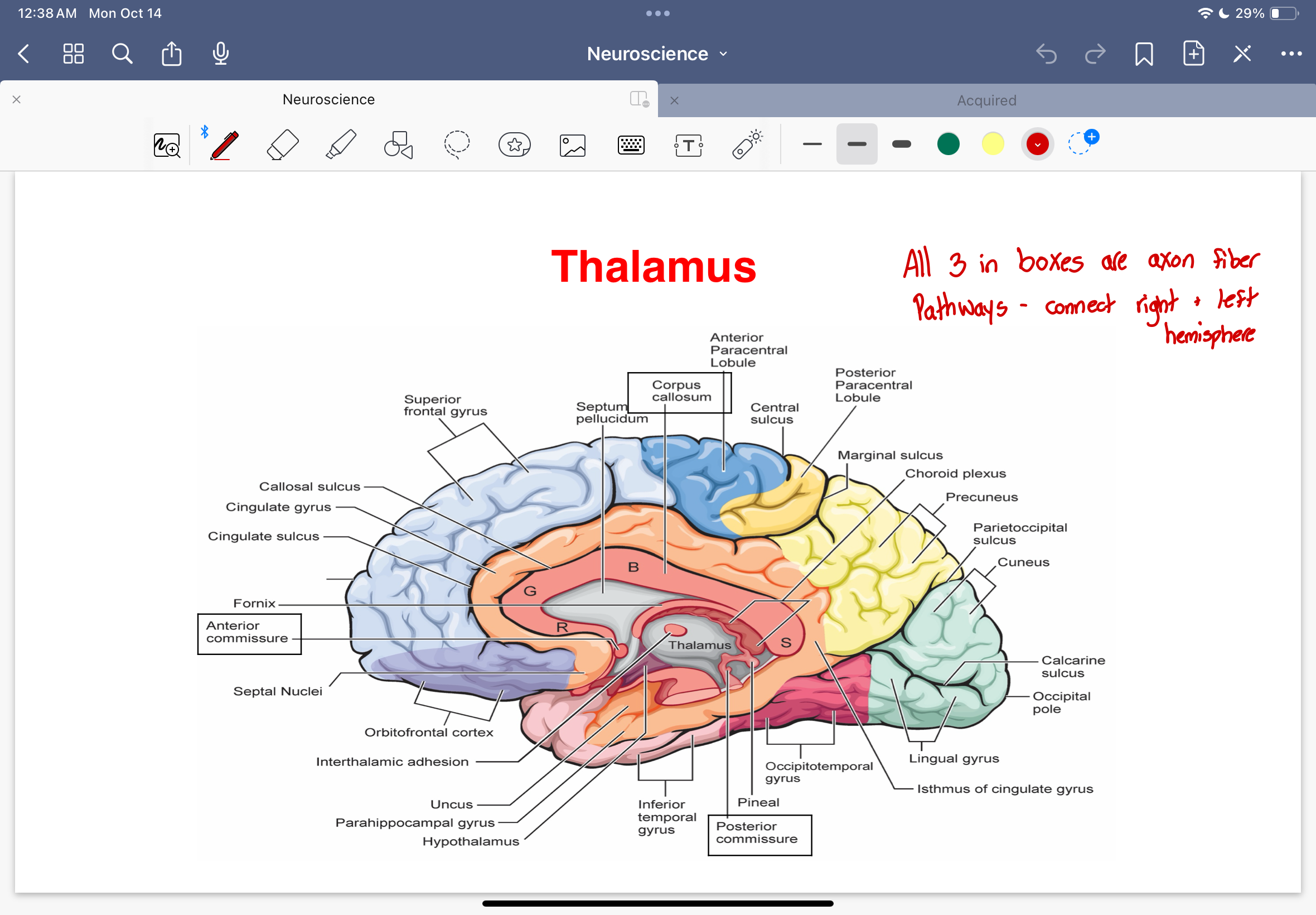
Axon fiber pathways
corpus callosum
anterior commisure
posterior commisure
Connect right and left hemispheres
Thalamus
has connections to ALL cortical regions
thalamo-corticol fibers transmit signals from all senses except smell
modulates incoming sensory info and influences attentiveness of the cerebral cortex to specific features of incoming sensory info
important in motor control, emotional regulation, memory, and autonomic functions
Organization of nervous system
anatomic approach
developmental approach
Anatomical approach
Based on the gross anatomy of the nervous system
CNS
PNS - cranial and spinal nerves
Developmental Approach
Based on the development of the nervous system and neurodevelopmental terms
Developmental approach example
Diencephalon: thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus
Cortical (cortex) organization
primary sensory and motor regions to association cortex
the cortex is organized into layers (rows) or columns for organized signal transmission
Brodmann’s organization: cell architecture
Each lobe possess…
segments that function as primary sites of raw information input & direct output to effectors of the body
M1, S1, V1, A1
primary motor cortex, primary somatosensory cortex, visual primary cortex, auditory cortex
Association Cortices diagram
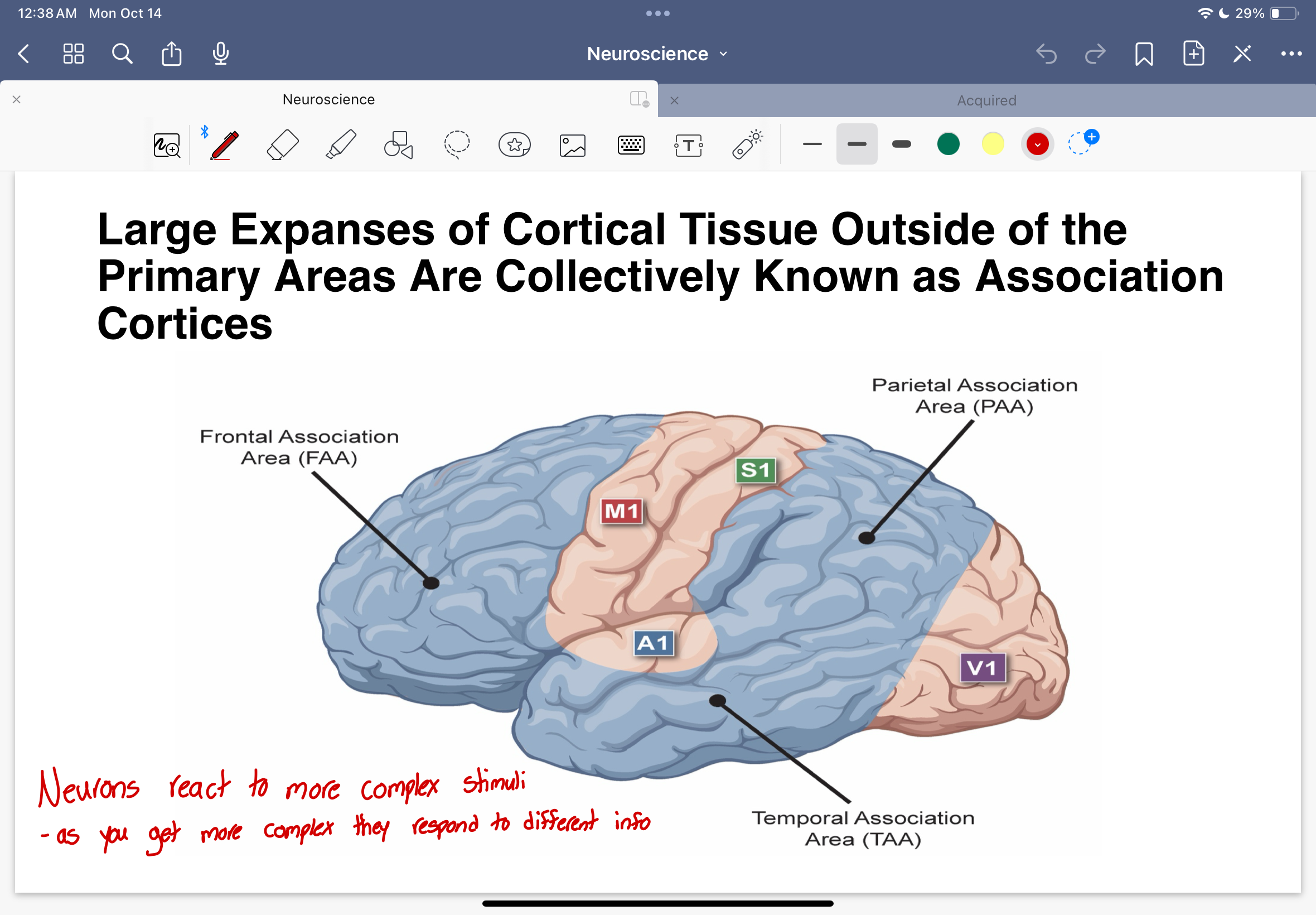
Neurons react to more complex stimuli…
as you get more complex, they respond to different info
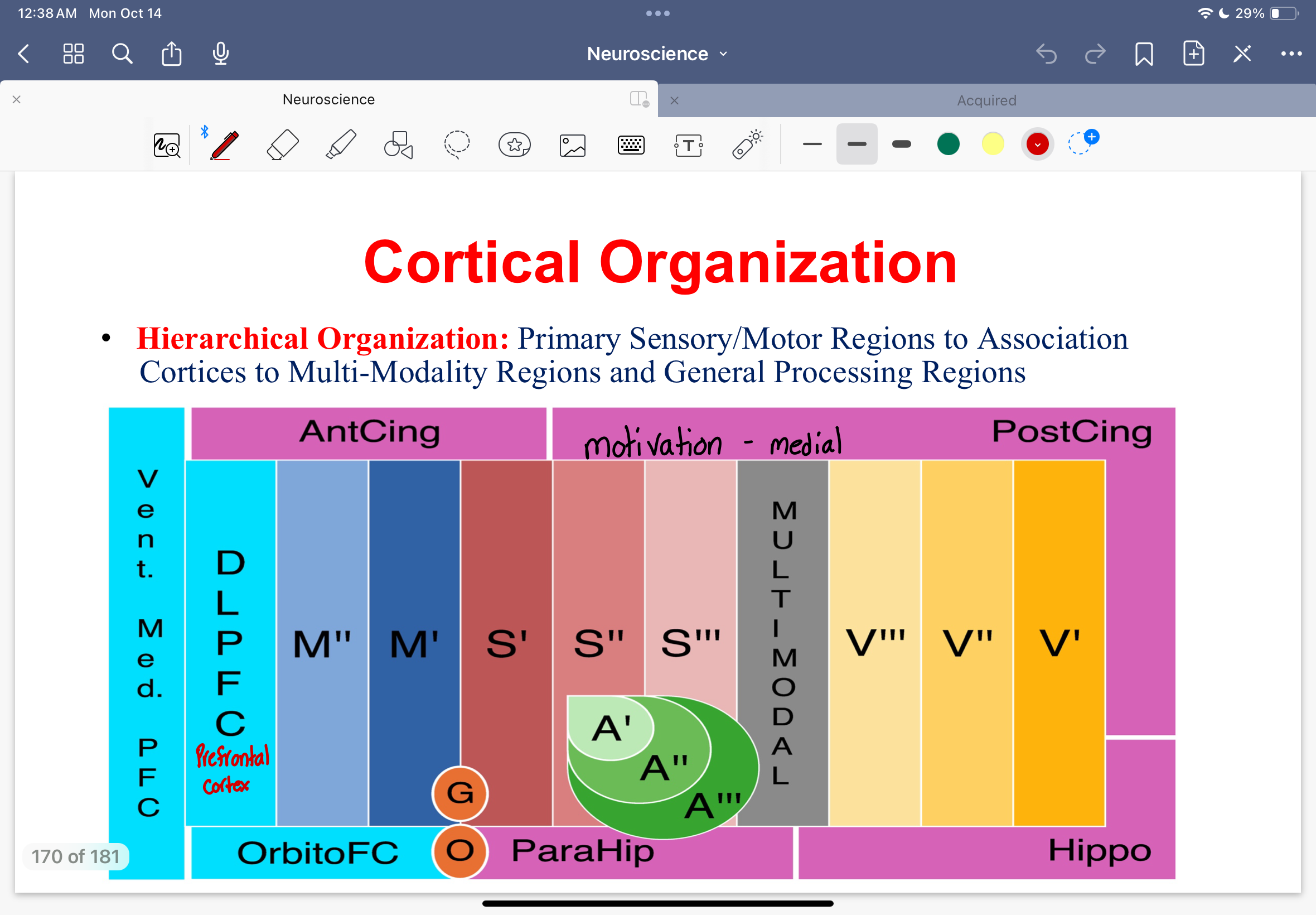
Hierarchical organization
Primary sensory/motor regions to association cortices to multi-modality regions and general processing regions
Hierarchial organization diagram
6 layers
Cerebral cortex is a grouping of 6 layers of cell bodies
6 layers of cerebral cortex diagram
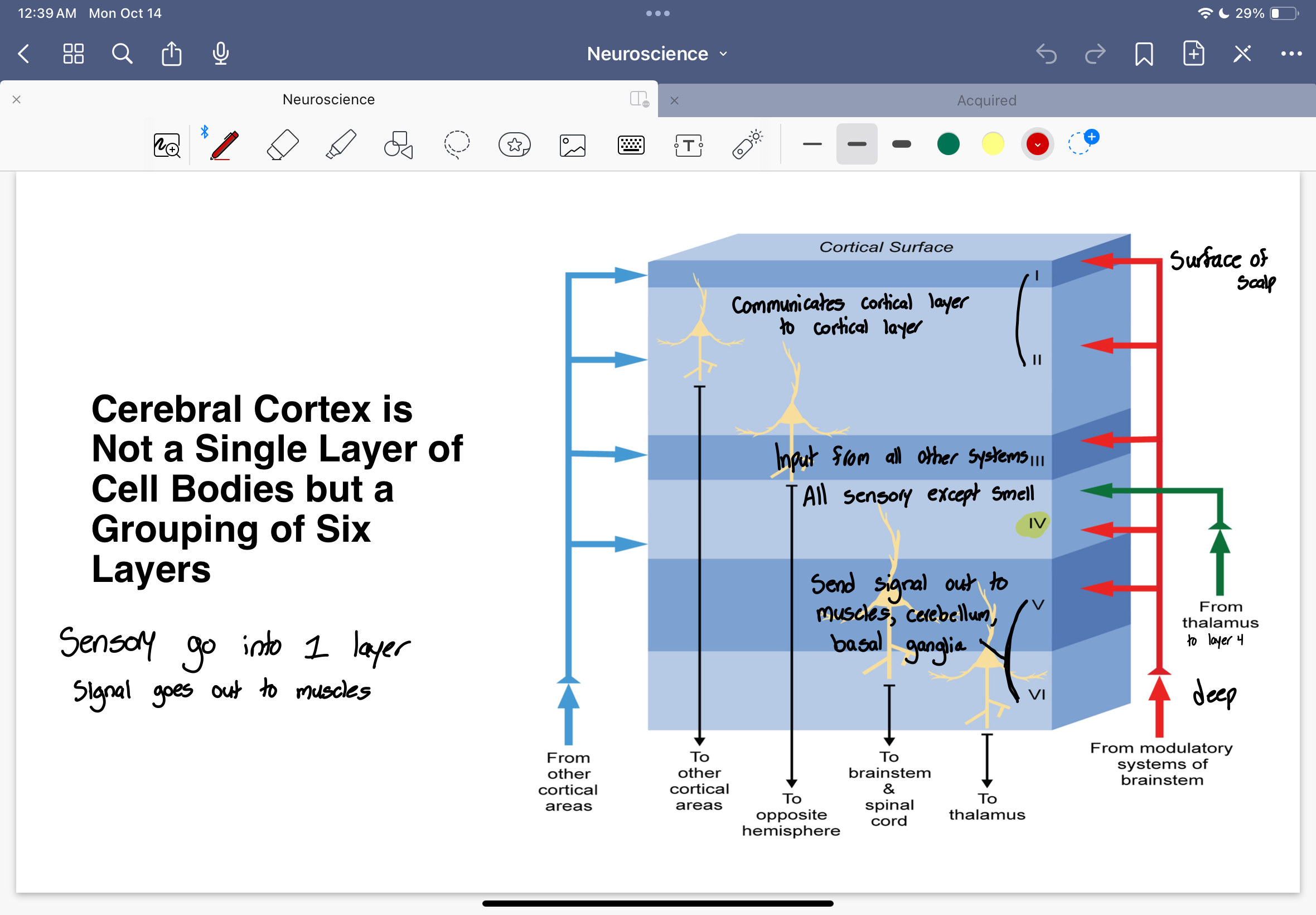
Layer 1 and 2
Layer 1 is surface of scalp
They both communicate cortical layer to other cortical areas
Layer 3
receives input from all other systems
sends to opposite hemisphere
Layer 4
information comes from thalamus to layer 4
all sensory except smell
Layer 5 and 6
Sends signals out to muscles, cerebellum, basal ganglia
layer 5 - to brainstem and spinal cord
layer 6 - to thalamus
Cortical Columns
fundamental processing and computational unit of the cortex is the cortical column
Korbinian Brodmann
He created cytoarchitectonic maps
cross sections of cortical tissue
cell staining
cells looked different across regions
Brodmann’s map of the lateral and medial cerebral cortex
Major Brodmann’s areas associated with speech, language and sensorimotor behavior
BA maps do NOT account for
hidden regions (ex: within fissures)
left - right asymmetries
individual differences
BA4 and BA3
BA4 - primary motor cortex
BA3 - primary somatosensory cortex