8- rotary instrumentation systems
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Why are the 3 parts of the rotary system?
Rotary instruments
Motor- continuous or reciproc
Obturation material
What 2 techniques to do RCT?
Apicoronal- step back- start in apex
Coronoapical- can use continuous and reciprocal techniques
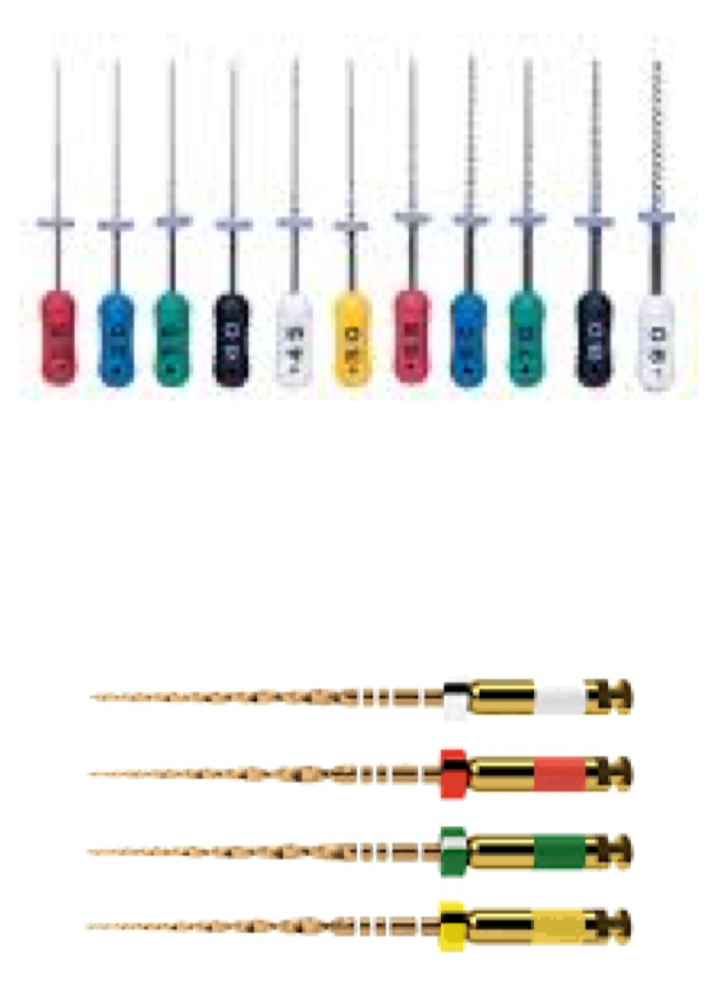

What are the objectives of access cavity prep?
Remove all caries
Preserve sound structure
Unroof pulp chamber
Remove all coronal pulp tissue
Locate canal orifices
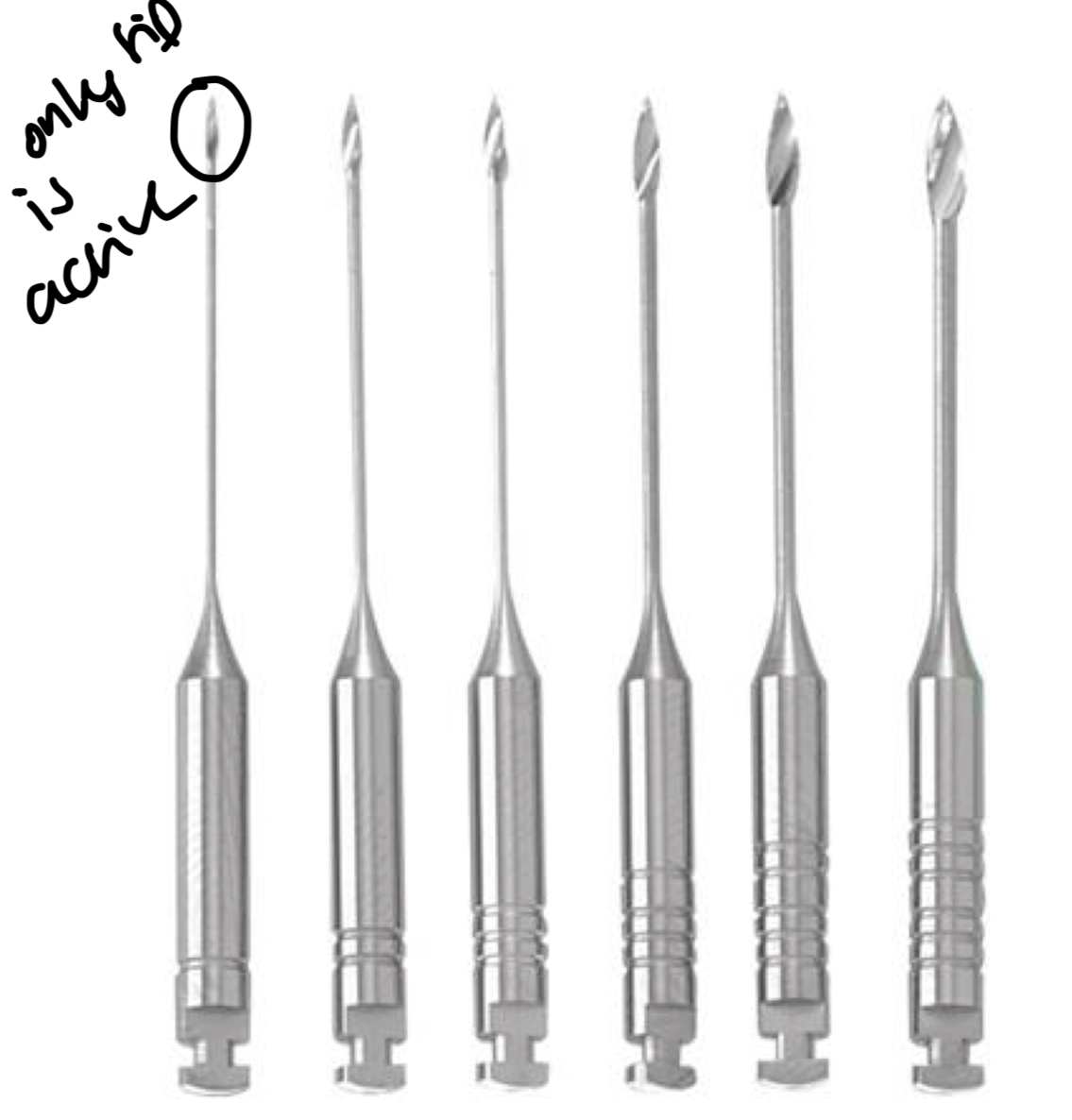
What is the function of Gates Glidden Bur and its characteristics?
Widen coronary thirds
Stainless steel- 6 diff sizes
Tip is only active part- has cutting capacity- can fracture but is rigid

What is ni ti rotary files made of and its characteristics?
Nicker and titanium
How much is the speed of the electric motor of ni ti rotary files?
150-300rpm
What are characteristics of ni ti rotary files?
Super elastic and flexible
Resist plastic deformation
Fracture resistance
Good cutting and inactive tip- use lateral movements
Use flexible NiTi files in curved canals
Explore coronal 2/3- with K-files 10-20 to create a glide path
Prepare coronal 2/3- with rotary files- continuous rotation
Determine WL- tactile, electronic apex locator, radiograph
Continue shaping- coronoapically with rotary files
Maintain patency- recapitulate with small K-file (#10) between files
Use pecking motion- advance 1 mm, withdraw 2–3 mm, clean
What types of irrigating solutions are used?
2.5-5% sodium hypochlorite- to dissolve pulp tissue (organic)
15-17% EDTA- treat calcified canals (inorganic) and removes smear layer
0.2% chlorhexidine gluconate- antimicrobial
What may the interaction between Naocl and EDTA cause?
EDTA increases effectiveness of naocl
But too much damages dentin
What other devices can be used to disinfect?
Laser systems
Gaseous ozone
Passive ultrasonic irrigation
Photo activation disinfection
What are advantages of rotary instruments?
Reduces apical transportation, steps and perforations
Centre the duct
Less apical extrusion- so less inflammation and post op pain
What are disadvantages of rotary instruments?
Hard if patient doesn’t open mouth far
Can’t pre curve files
Easy to fracture if pressure forced on
What are the general principles of technique of rotary systems?
Preop x ray
Remove caries
Open canal and only isolate once canal is localised
Root canal permeabilisation to find apex
Conductometry with apex locator and x ray
Root instrumentation and irrigate
Conometry x ray
Obturate canals
Final x ray
How to find apex with files?
PathFile (Dentsply Maillefer) – taper 2% and gauge 13,16,19
ProGlider (Dentsply Maillefer): Newer and just one filePathFile

4 x rays for RCT
Initial
Preop
Conductometry and conometry x ray
Post op
What movements are conducted in root instrumentation?
Progression and relief- not too much pressure, only for 2/3 secs
Rotate on entry and exit
Don’t force
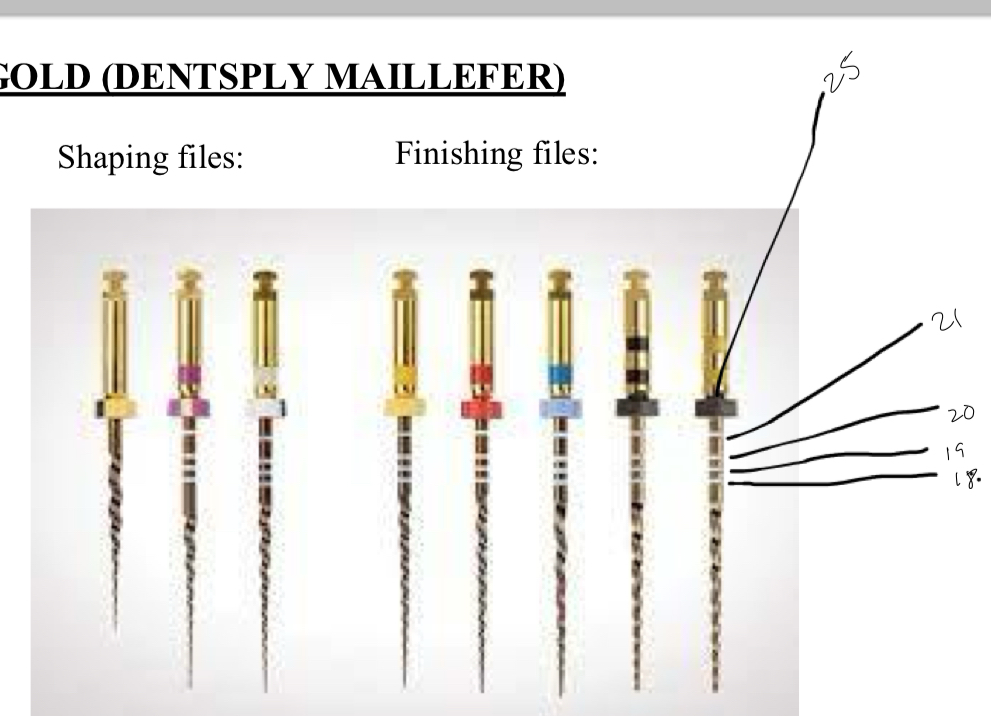
What is the sequence of use of shaping and finishing files of protaper gold?
S- yellow, purple, white, F- yellow, red, blue

What are the features of protaper gold files?
Variable taper
Inactive tip
First line always measures 18mm
1mm diff between each line
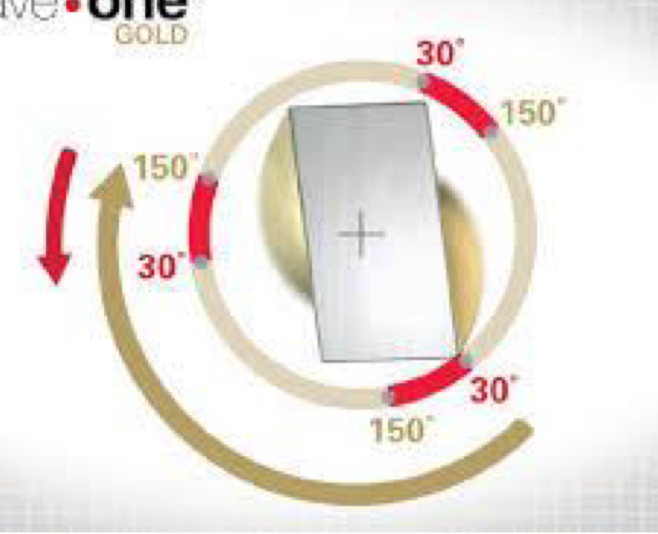
In the reciprocal system how many movements complete one full cycle?
3 movements- 150 degree, then goes back 30
What are the 2 types of fractures?
Torsion- part of instrument remains immobilised, rest keeps turning
Flexural- cyclic fatigue- rotates freely in curved duct until max curvature
How do we prevent the fracture of rotary instrument?
Control speed and torque
Progression and relief movements
No pressure
Control number of file uses
Irrigate and lubricate
What anatomical factors contributes to the wear of rotary files?
More curved
Narrow ducts
Confluent ducts
More ducts, more wear