Enzymes and Metabolism
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What are enzymes?
Biological catalysts involved in biological reactions that speed them up without being used up in the reaction.
What is the composition of enzymes?
Enzymes are globular proteins composed of one or more polypeptides.
How do changes in temperature and pH affect enzymes?
Affects their structure
What is the rate of reaction?
The rate of reaction is the amount of product produced per unit of time.
What is metabolism?
Metabolism is the complex network of interdependent and interacting biochemical reactions occurring in living things.
Are enzymes specific to their substrates?
Yes, enzymes are specific to their particular substrate.
What are anabolic reactions?
Anabolic reactions are involved with the building of large molecules from smaller ones.
What is required for anabolic reactions?
Energy (ATP) is required for anabolic reactions.
What happens in a condensation reaction?
In a condensation reaction, H2O is released.
Name one example of an anabolic reaction.
Photosynthesis is an example of an anabolic reaction.
What are catabolic reactions?
Catabolic reactions are involved with breaking down large molecules into smaller, simpler ones.
What is released during catabolic reactions?
Energy is released during catabolic reactions.
What happens in hydrolysis reactions?
In hydrolysis reactions, H2O is needed.
Name one example of a catabolic reaction.
Cellular respiration is an example of a catabolic reaction.
How are enzyme-catalyst reactions measured?
Record the amount of substrate that has disappeared or the amount of product that has accumulated in a unit in time
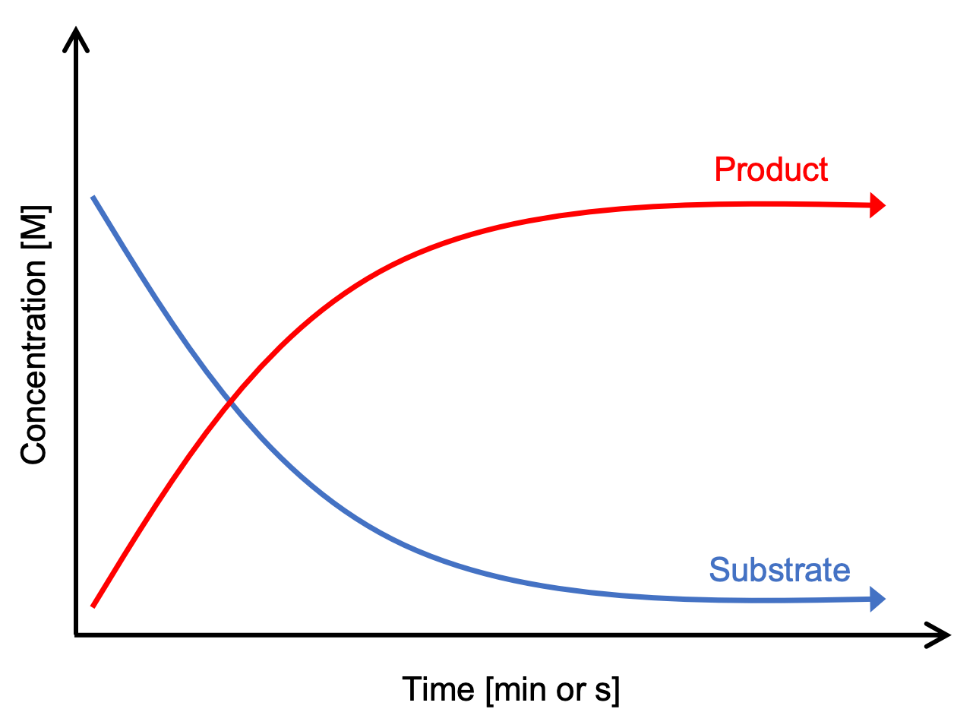
What isn’t constant?
The rate of reaction indicated by the shape of the curve
How can the rate be measured?
Drawing a tangent to the curve at the specific time and dividing the change in product by the change in time
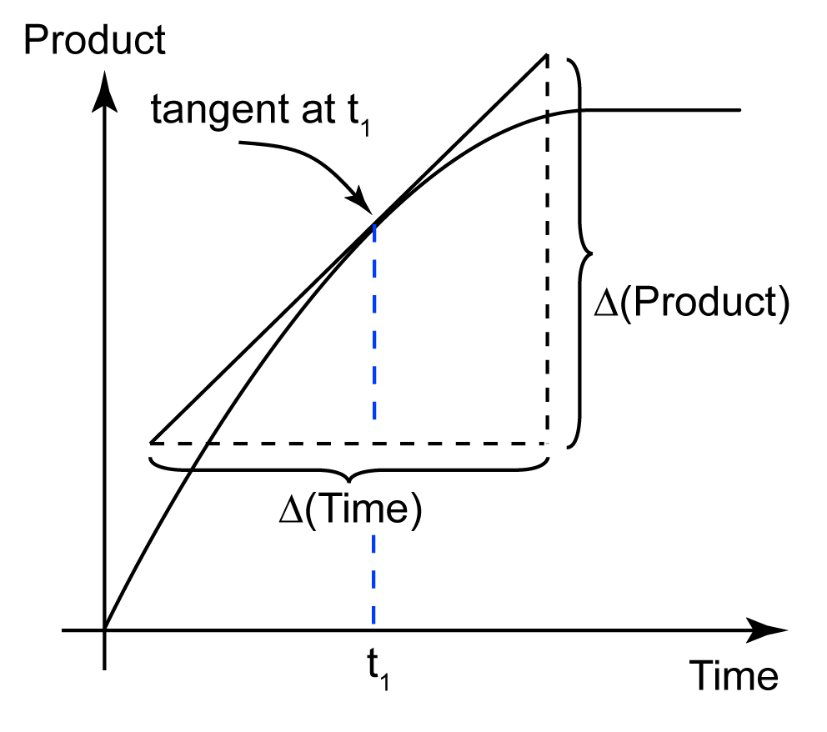
What do we call it when the instantaneous rate of reaction is calculated at t=0?
The initial rate of reaction