Antibodies and Immune Responses Overview
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Ligand
A molecule that binds specifically to a protein.
Immune Response
Reaction to unrecognized substances in the body.
-distinguishes molecular "self" from "nonself" and destroys "nonself"
-Eliminated viruses, bacteria, and other pathogens and molecules
-Coordinated interactions among many classes of proteins, molecules, and cell types
Primary Immune Response
First exposure to an antigen.
Secondary Immune Response
Response after subsequent exposures to an antigen.
Humoral Immune System
directed at extracellular bacterial infections and viruses
-antibodies
-Memory B cells
Cellular Immune System
Destroys intracellular pathogens and cancers from infected host cells, parasites, and foreign tissues.
-Antigen presentation
-Cytotoxic T-cells
-Memory T cells
Antigen
Substance that elicits an immune response.
-could be a virus, a bacterial cell wall, an individual protein, or other molecule
antibodies
bind to an epitope (antigenic determinant) within the antigen
-interaction is strong and specific
Epitopes
Specific regions on antigens recognized by antibodies.
Haptens
Small molecules that elicit immune responses when covalently bound to large proteins.
Helper T Cells
A type of T lymphocyte that have CD4+ receptor on their surface
-Activated when their TCR binds to an antigen presented by an APC in combination with MHC class II molecules
-Do not directly kill infected cells
-"Help" by activating other immune cells via cytokines
Cytokines
small signaling proteins released by cells that regulate inflammation, immune responses, and intercellular communication
B cell activation
Key function of Th cells
-The B cell presents and antigen to t a helper T cell
-Th can recognize the antigen and secrete cytokines that trigger B cell differentiation into a plasma cell
Activation of Cytotoxic T cells
Key function of Th cells
-Helper T cells release cytokines that promote the differentiation and proliferation of cytotoxic T cells, which can then kill infected cells directly
Macrophage Activation
Key function of Th cells
-Macrophages present antigens to helper T cells, which then secrete cytokines to enhance the macrophages' ability to destroy pathogens
Regulation
Key function of Th cells
-Intensity and duration of immune responses
-The balance between humoral response and cellular responses
Th1 Cells
Promote cellular immune response by activating macrophages and cytotoxic T cells to eliminate intracellular pathogens (viruses and bacteria)
Th2 Cells
Promote humoral immune response, particularly in response to extracellular pathogens (like parasites)
-B cell activation and antibody production
Th17 Cells
Target extracellular bacteria and fungi, associated with inflammation.
T Regulatory Cells
Help regulate or suppress immune responses
-important for preventing autoimmune diseases by maintaining immune tolerance
Cytotoxic T Cells
(Tc cells or CD8+ cells) recognize and directly destroy infected or abnormal cells upon recognition of antigens bound to MHC class I molecules
-leads to the production of cytokines that stimulate the selective production of Tc cells that can bind to a particular antigen
Helper T eclls
(Th or CD4+ cells) recognize antigens presented on MHC class II molecules by antigen-presenting cells (i.e., macrophages or B cells)
-leads to production of cytokines that simulate the selective proliferation of B cells that can bind to a particular antigen
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)
Molecules presenting antigens on cell surfaces.
Clonal Selection
Process of selecting specific immune cells for response.
Leukocytes
immune cells that protect against infections, foreign invaders, and diseases
-Circulate in the blood and can migrate into tissues
leukocyte functions
-Defend against infection by identifying, engulfing and destroying pathogens
-Initiate immune responses (recognize foreign antigens and activate a response)
-Remove dead or damaged cells (phagocytosis)
-Mediate inflammation and allergic reactions (release signaling molecules such as cytokines and histamine)
Granulocytes
Leukocytes with granules, including neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils.
Neutrophils
-The most abundant WBC
-First responders to infections
-Phagocytose pathogens
type of granulocyte
Eosinophils
type of granulocyte that is primarily involved in parasitic infections and allergic reactions
Basophils
least common type of granulocyte
-release histamine during allergic responses
-Help mediate inflammation
Agranulocytes
Leukocytes without granules, including lymphocytes and monocytes.
Lymphocytes
B cells, T cells, and natural killer cells, which are crucial for adaptive immunity
-B cells produce antibodies, T cells are involved in cell-mediated immunity, and NK cells target virus-infected or cancerous cells
Monocytes
The largest type of leukocyte
-Circulate in the bloodstream and migrate into tissues where they differentiate into macrophages and dendritic cells
-Macrophages phagocytose pathogens and dead cells
-Dendritic cells are critical for antigen presentation to T cells
Antibody mediated immunity
-Antibody = immunoglobulin = (Ig)= quaternary proteins that bind bacteria, viruses, or large molecules identified as foreign and target them for destruction
-Produced by B lymphocytes or B cells
B Cells Activation
activated by an antigen and helper T cells
-Activated B cells turn into plasma cells that mass produce antibodies
Memory cells
permit a rapid response to pathogens previously encountered
Vaccines
-Often consist of weakened of killed virus or isolated proteins from a viral or bacterial protein coat
-Presents viral particle to the immune system, "teaching" it what the viral particles look like, thus stimulating the production of memory cells
Immunization
Process of building protection against diseases.
Evidence-Based Medicine
Practice of using research to inform clinical decisions.
Immunoglobulin Classes
Five antibody (Ig) classes identified by heavy chain type.
IgA
Antibody that protects against pathogens in mucosal linings (gut, lungs, urogenital tract), saliva, tears, and breast milk
IgD
-A B-cell surface receptor
-Has potential role in cell differentiation
IgE
-Triggers histamine release from mast cells and basophils
-Also protects against parasitic worms
-AllergiEs & and Asthma ...E
IgG
Primary antibody responsible for antibody-based immunity
-The only antibody able to cross the placenta and protect a fetus
-G for Gestation
IgM
-A B-cell surface receptor
-Can be a monomer or pentamer
-First line of defense before IgG can be produced in sufficient quantities
Immunoglobulin G (IgG)
One of the most abundant blood serum proteins
-4 polypeptide chains: 2 heavy and 2 light chains
-Cleavage with protease papain releases the basal fragment Fc and two Fab branches (each with a single antigen-binding site)
-Constant domains contain the immunoglobulin fold structural motif
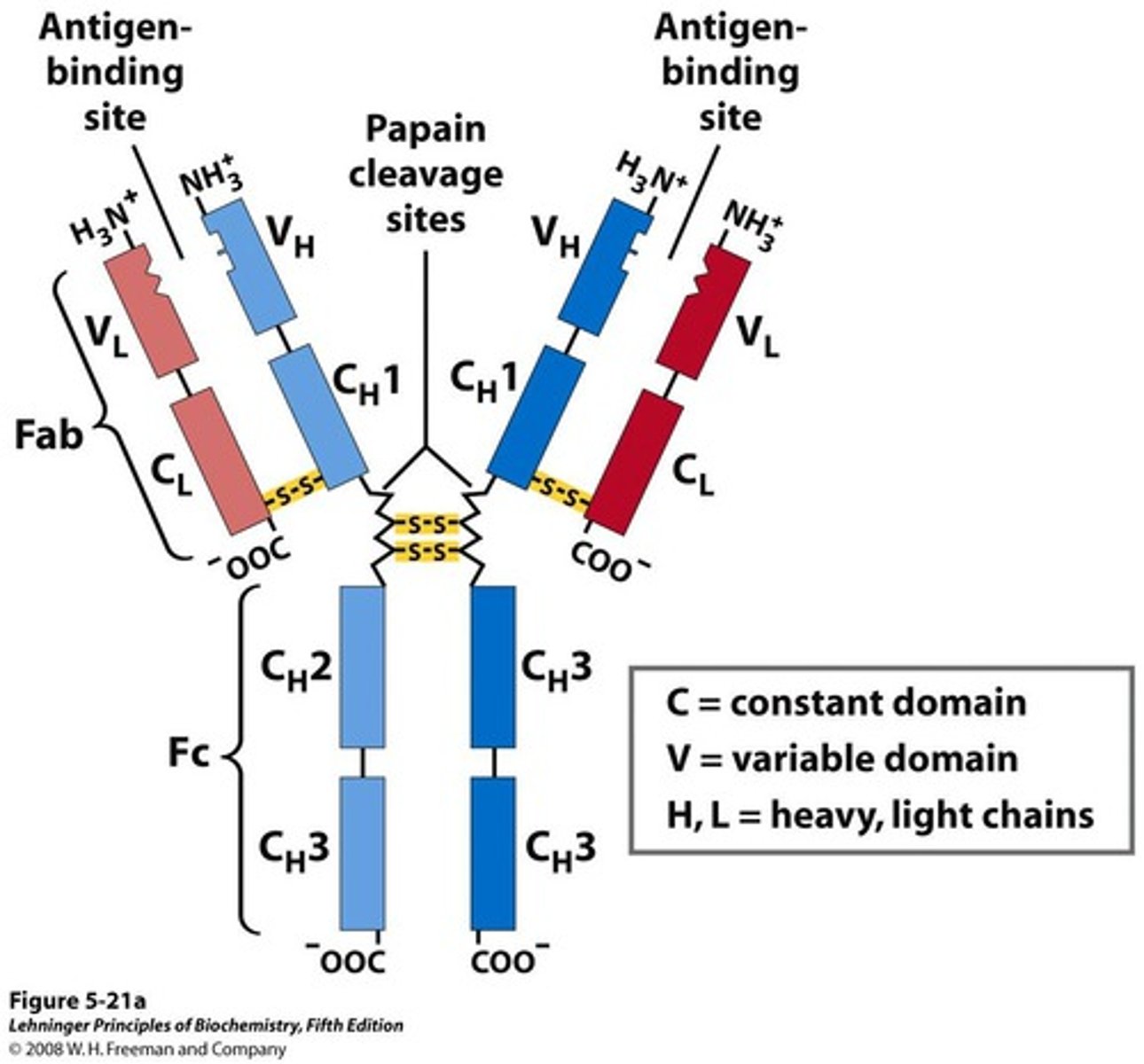
Antigen-Binding Sites
Antibodies have two identical sites for binding.
Variable Domain of IgG
-Associate to create the antigen-binding site
-VDJ recombination allows for unique paratope generation
-Allows formation of an antigen-antibody complex
VDJ Recombination
Process generating diverse antibody binding sites.
Phagocytosis of Antibody-Bound viruses
When Fc receptors bind and antibody pathogen complex, macrophages engulf the complex
Induced fit
the antibody and/or antigen change structures to make a better fit
-Kd values as low as 10^-10 M
Polyclonal antibodies (pAbs)
-Inject an antigen into a subject
-Different B cells will recognize different epitopes of the same antigen
-Different antibodies will be made against the same antigen
-pAbs are heterogenous; recognize different epitopes
Monoclonal Antibodies
Homogeneous antibodies from a single B cell clone.
Western Blot
Technique using antibodies to detect specific proteins.
Immunoaffinity
Strong, selective binding between antibody and antigen.
Autoimmune Disease
Immune system mistakenly attacks body's own tissues.
Molecular Mimicry
Foreign antigens resemble self-antigens, triggering autoimmunity.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Chronic inflammation targeting synovial joints.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Autoimmune disease affecting multiple organ systems.
Type 1 Diabetes
Immune attack on insulin-producing pancreatic beta cells.
Multiple Sclerosis
Immune system attacks myelin in the CNS.
Graves' Disease
Autoantibodies stimulate thyroid, causing hyperthyroidism.
Celiac Disease
Immune reaction to gluten damaging the small intestine.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Autoimmune attack on the gastrointestinal tract.
Myasthenia Gravis
Antibodies block acetylcholine receptors, causing weakness.
Lateral Flow Assays
Diagnostic tests using antibodies for analyte detection.
Anti-VEGF Therapy
Monoclonal antibodies inhibit VEGF to reduce angiogenesis.
Ranibizumab
Antibody fragment targeting VEGF-A for eye treatment.
Aflibercept
Fusion protein trapping multiple angiogenic factors.