Molecular Geometry & Shapes
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
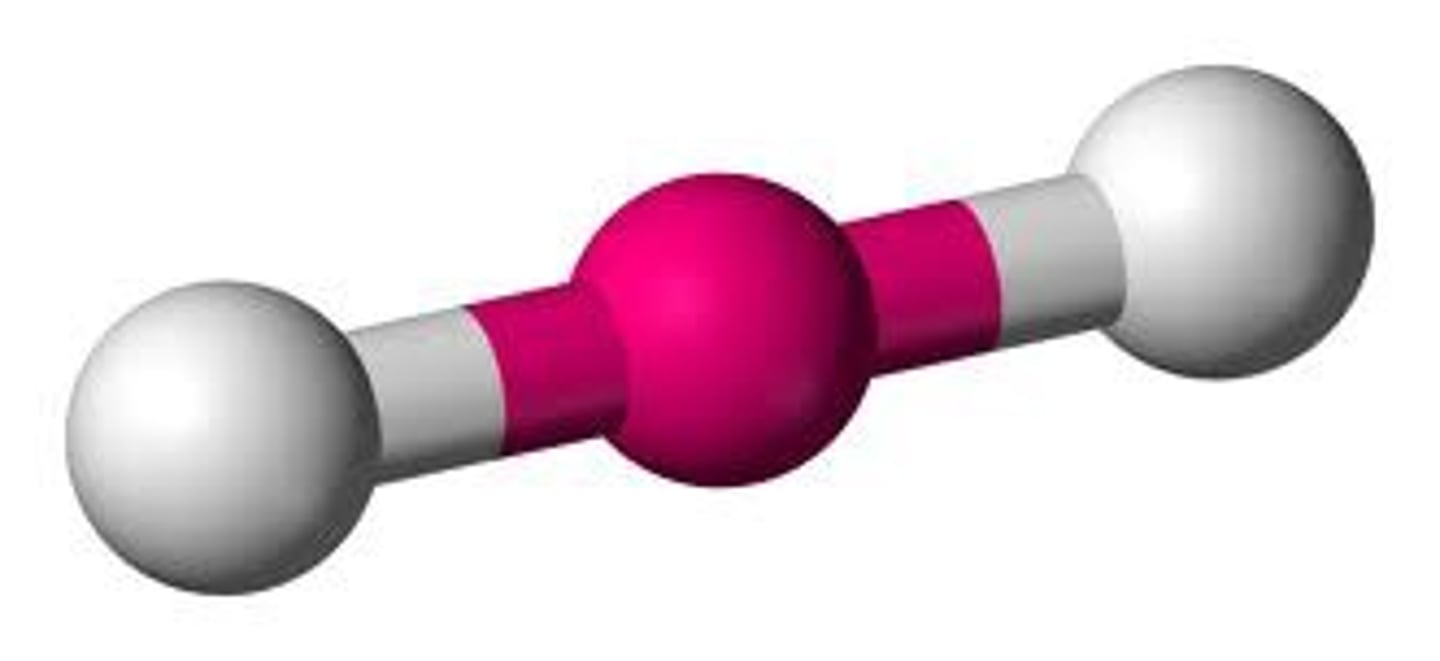
Molecular Shape - Linear
-angle of 180°.
- such as acetylene (HC≡CH).
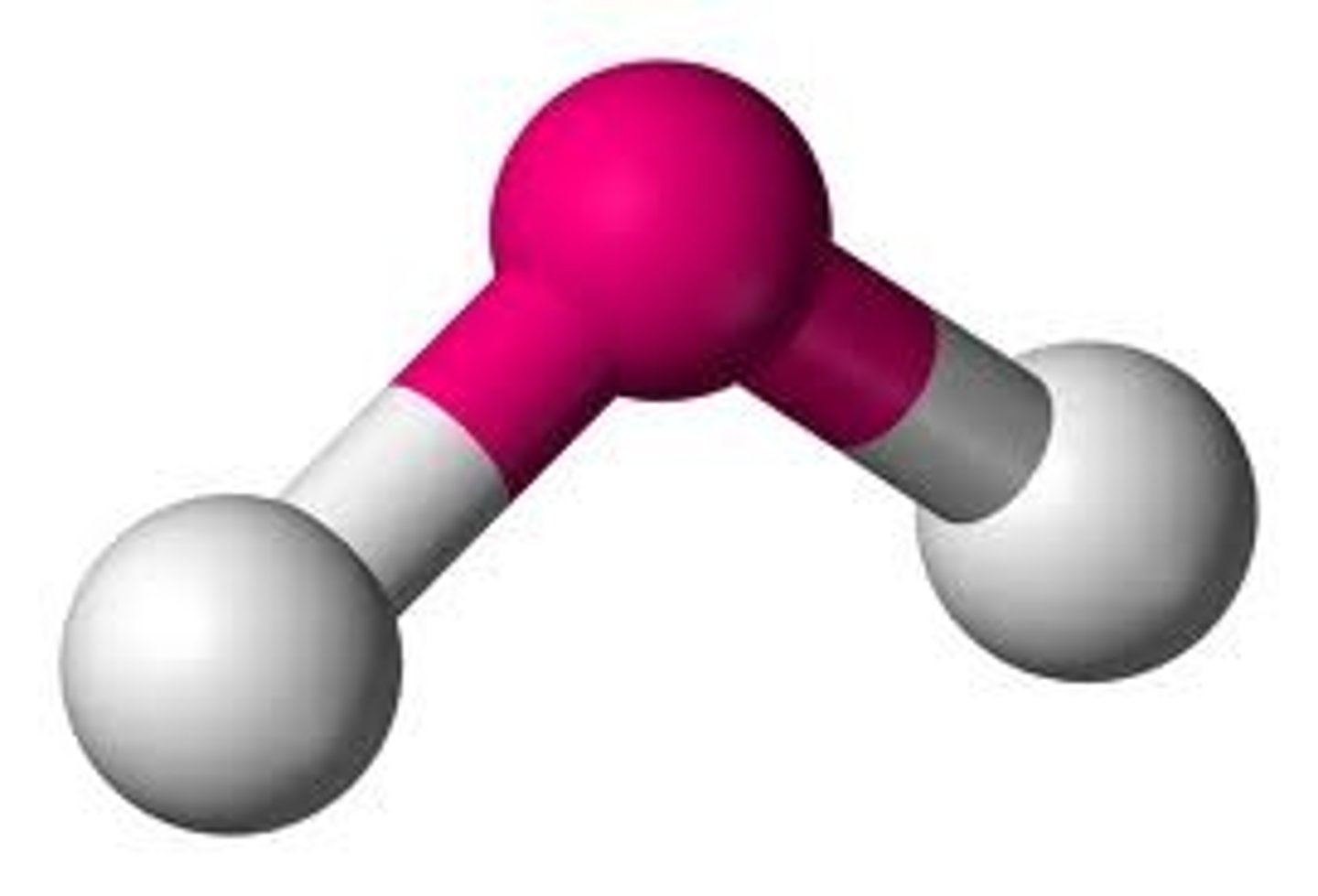
Molecular Shape - Bent
- In chemistry, the term "bent" can be applied to certain molecules to describe their molecular geometry.
- Water (H2O) is an example of a bent molecule, as well as its analogues.
- The bond angle between the two hydrogen atoms is approximately 104.45°.
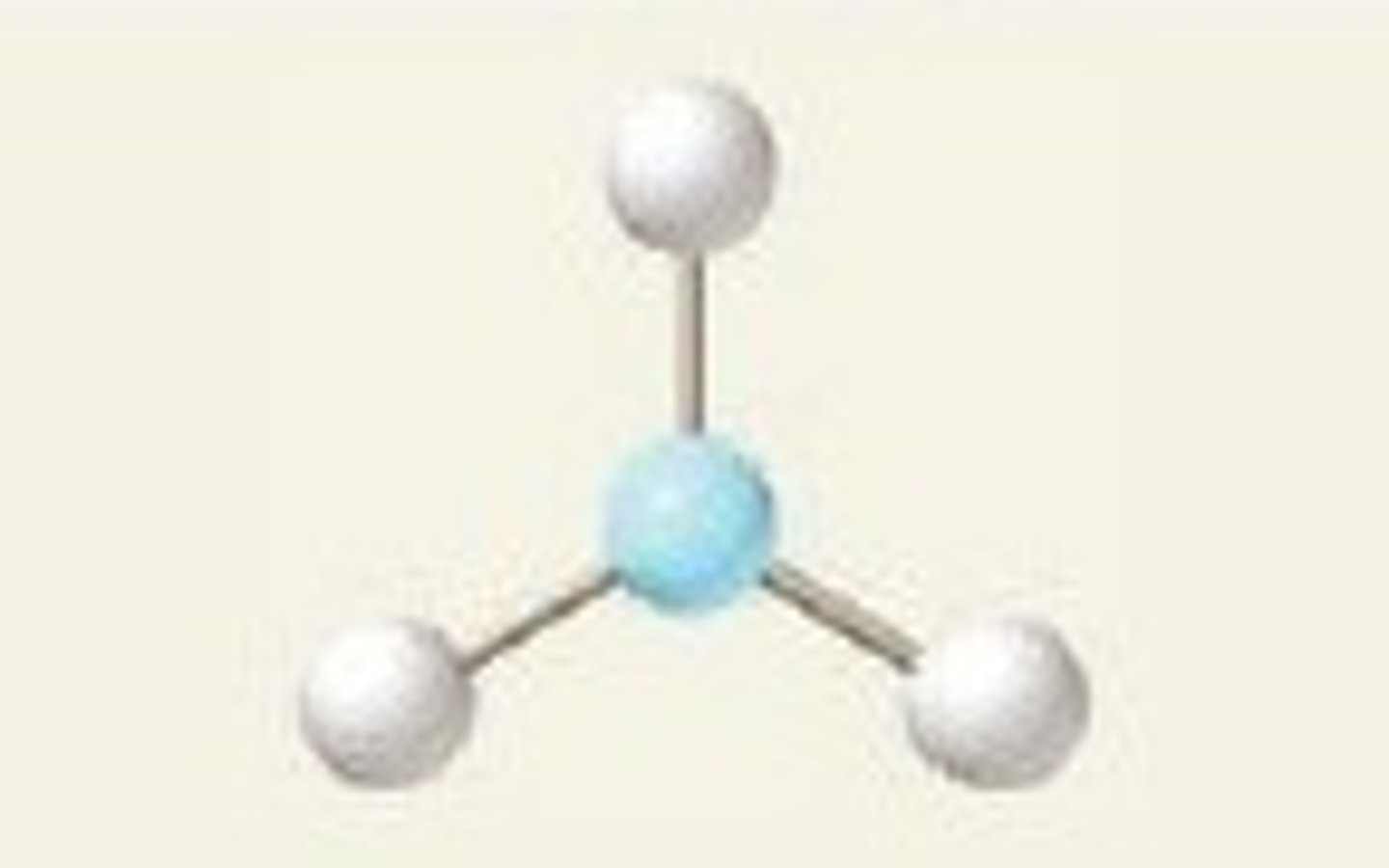
Molecular Shape - Trigonal Planar
- Trigonal planar is a molecular shape that results when there are three bonds and no lone pairs around the central atom in the molecule. - The pairs are arranged along the central atom's equator, with 120° angles between them.
- The carbonate ion (CO32-) has a trigonal planar geometry.
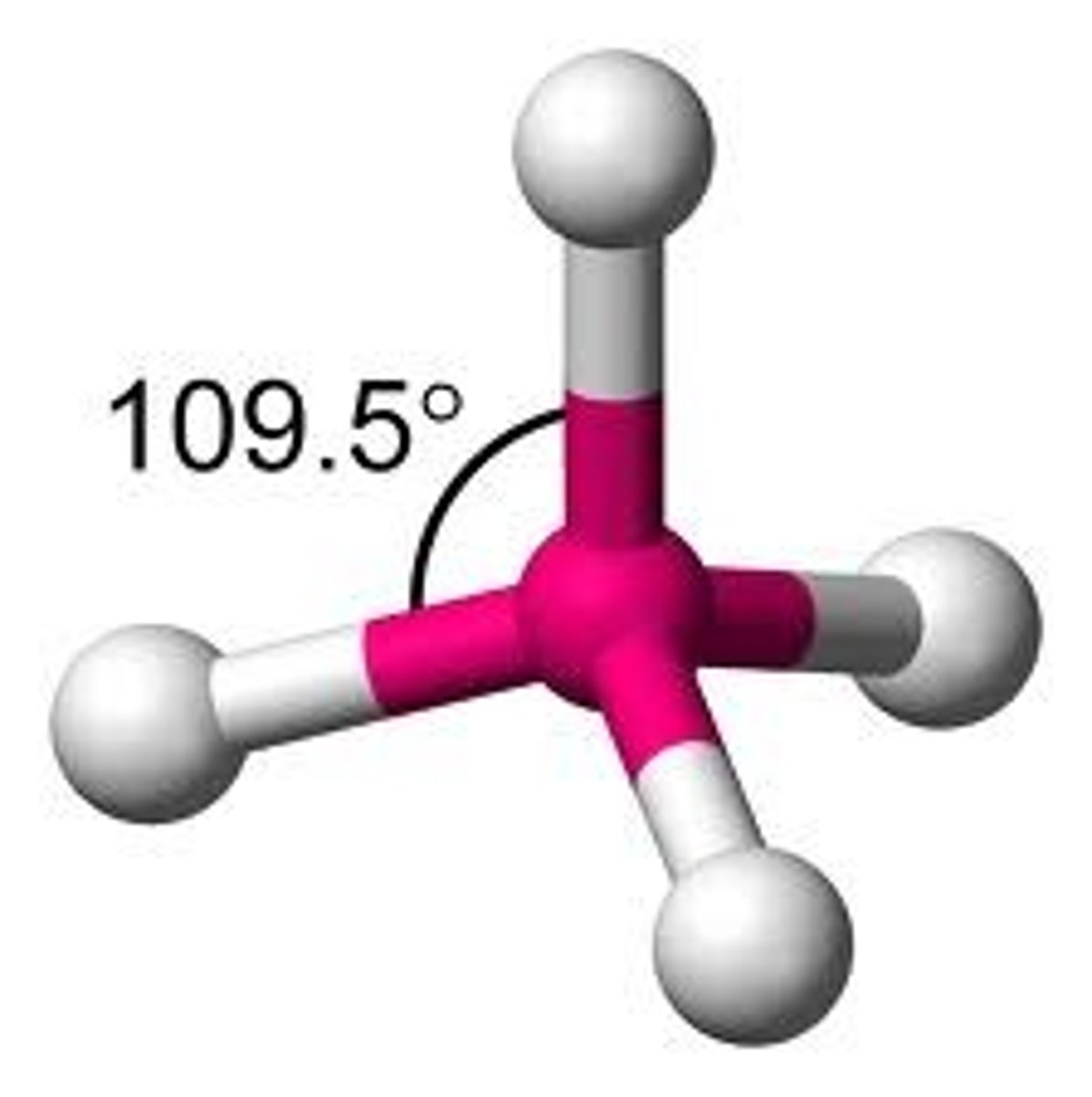
Molecular Shape - Tetrahedral
- Tetrahedral is a descriptor of the geometry of a molecule in which a central atom forms four bonds which are directed toward the corners of a regular tetrahedron.
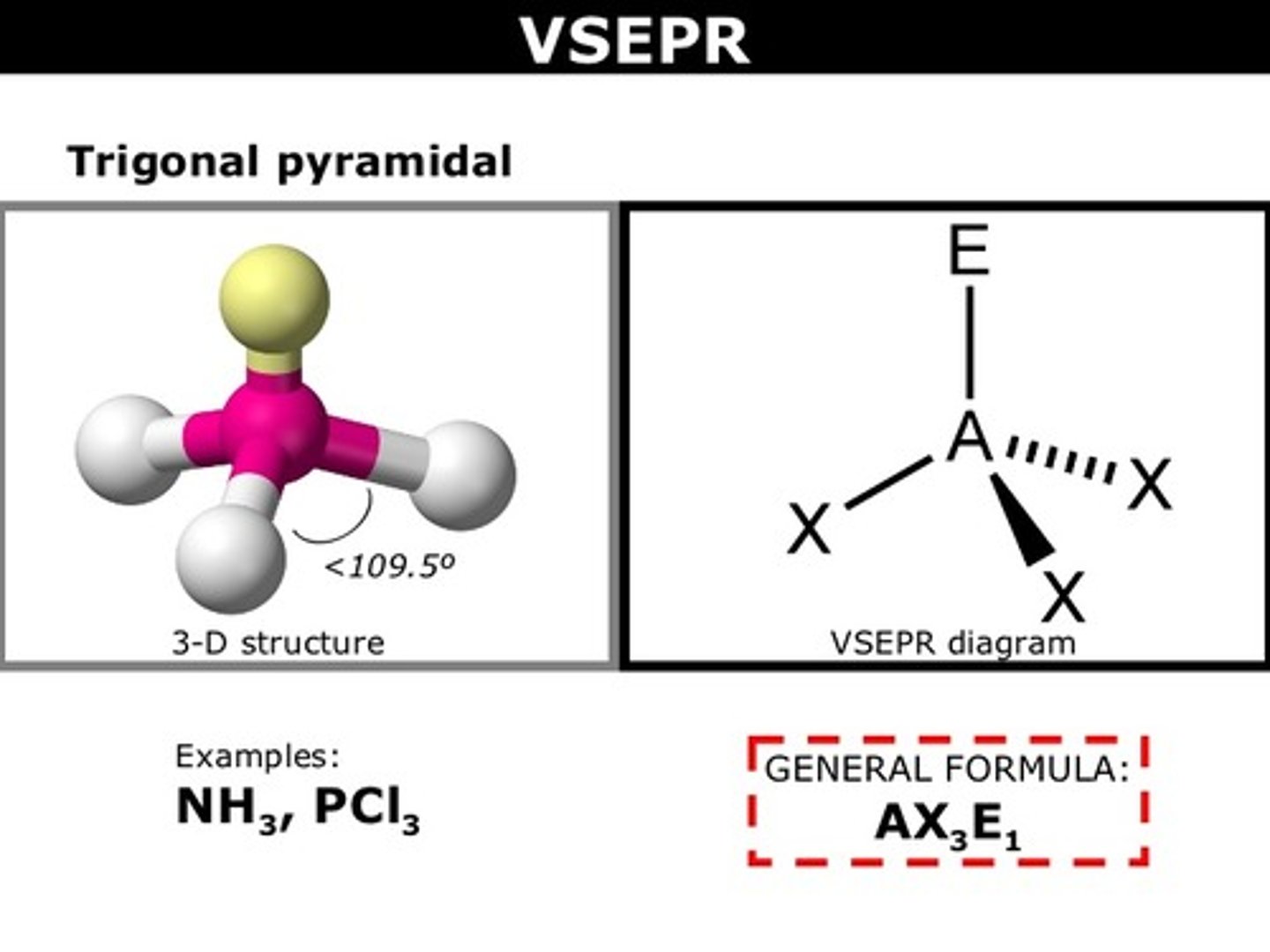
Molecular Shape - Trigonal Pyramidal
- Trigonal pyramidal is a molecular shape that results when there are three bonds and one lone pair on the central atom in the molecule.
- Molecules with an tetrahedral electron pair geometries have sp3 hybridization at the central atom.
- Ammonia (NH3) is a trigonal pyramidal molecule.
Molecular Shape - Really Bent
- In chemistry, the term "really bent" can be applied to certain molecules to describe their molecular geometry.
- The bond angle between the two hydrogen atoms is less than 109°.
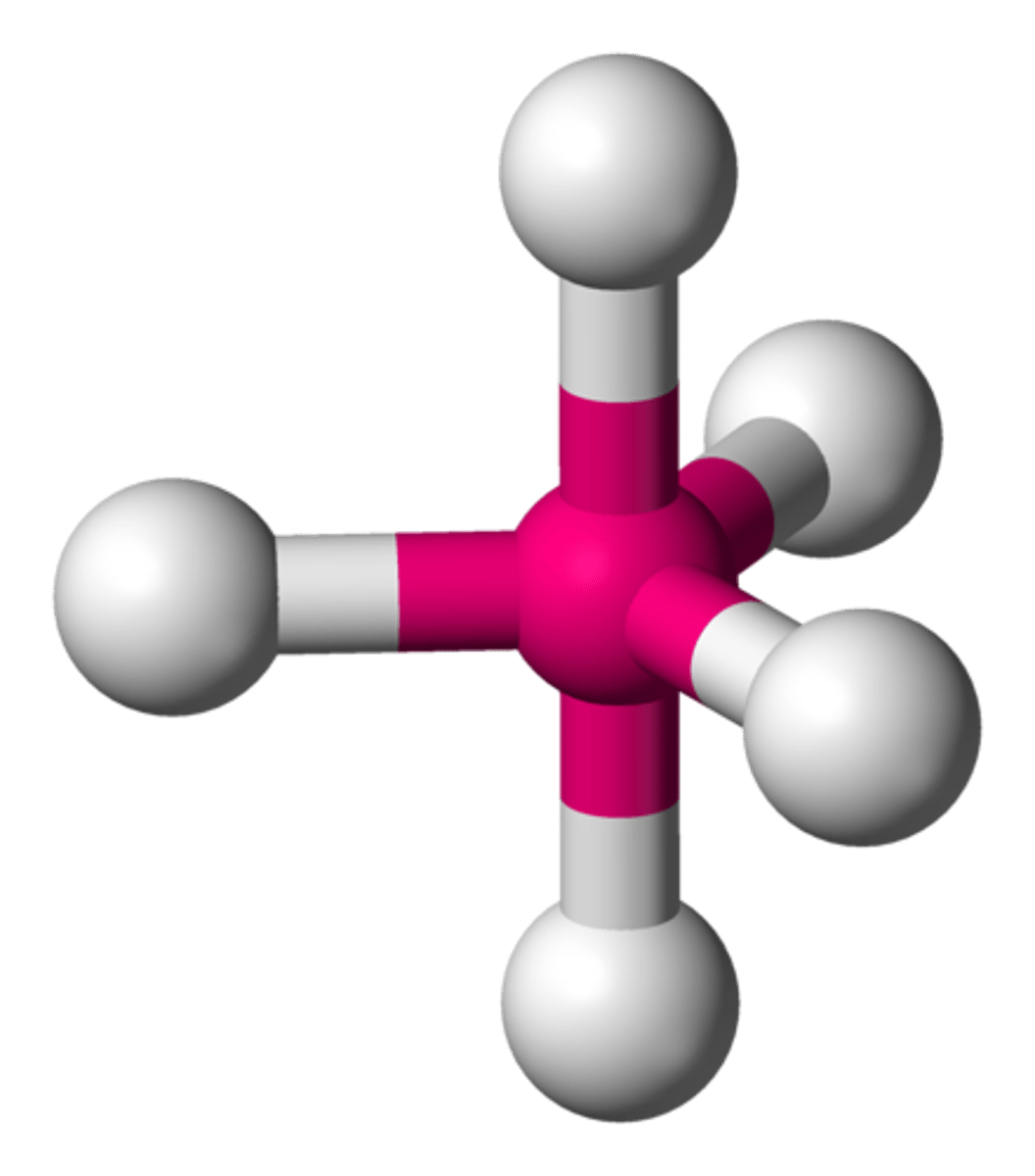
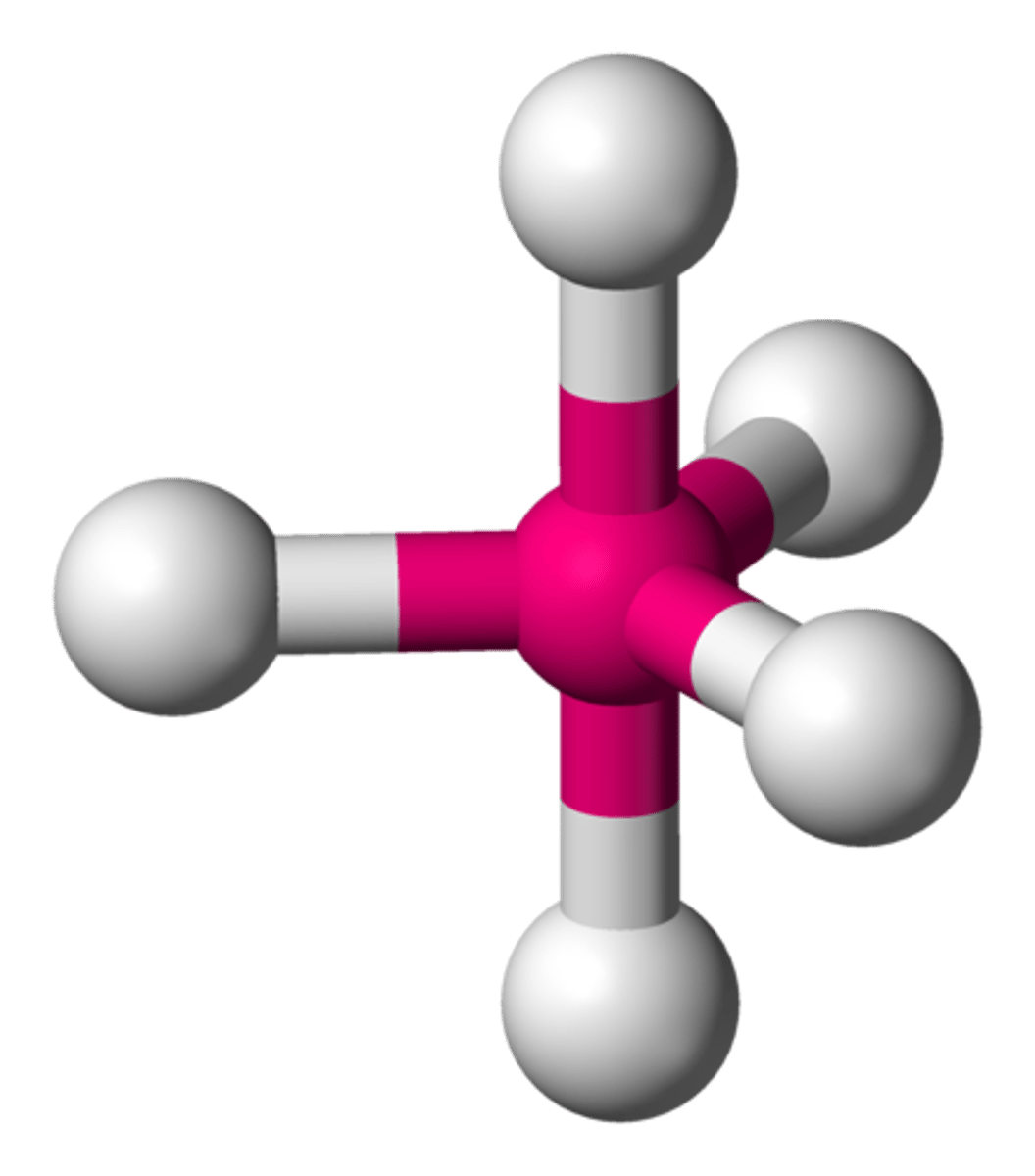
Molecular Shape - Trigonal Bi-pyramidal
- Trigonal bipyramidal molecular geometry.
- In chemistry a trigonal bipyramid formation is a molecular geometry with one atom at the center and 5 more atoms at the corners of a triangular di-pyramid.
- Example of this molecular geometry are phosphorus pentafluoride (PF5)
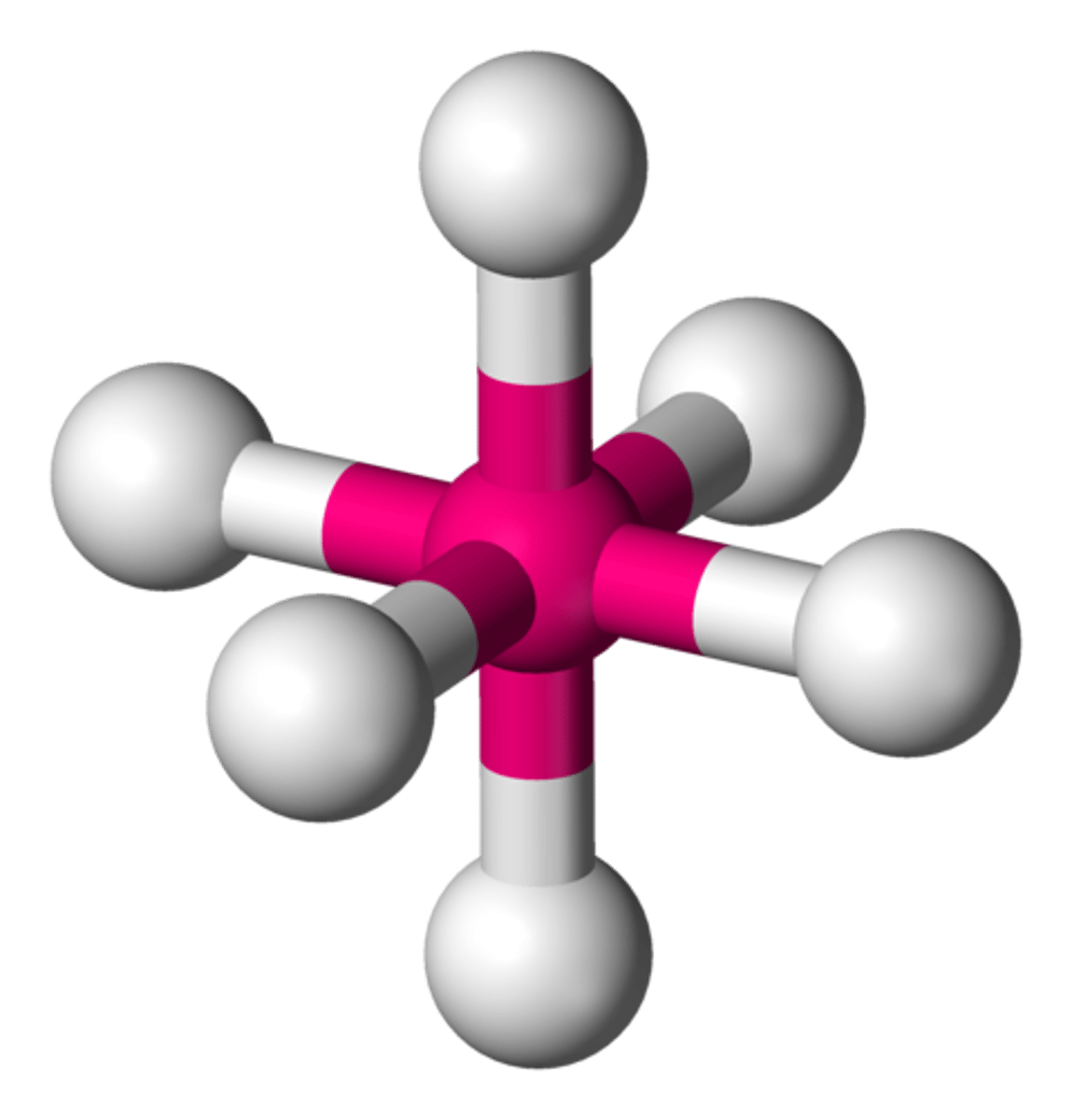
Molecular Shape - Octahedral
- In chemistry, octahedral molecular geometry describes the shape of compounds with six atoms or groups of atoms or ligands symmetrically arranged around a central atom, defining the vertices of an octahedron.
- The octahedron has eight faces, hence the prefix octa.
Linear
AB2
Example: N2O Nitrous oxide
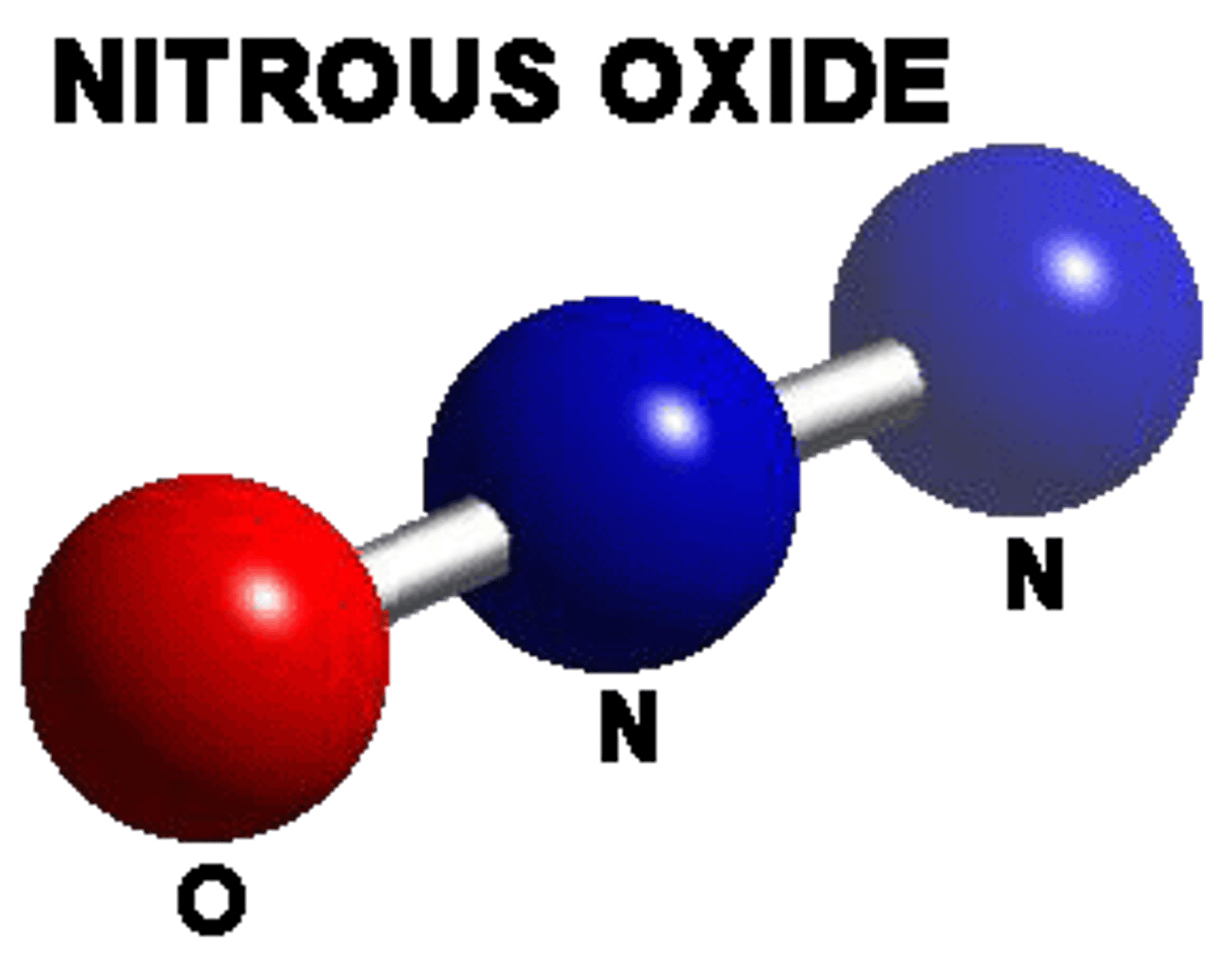
Bent
AB2E
Example: O3 - ozone
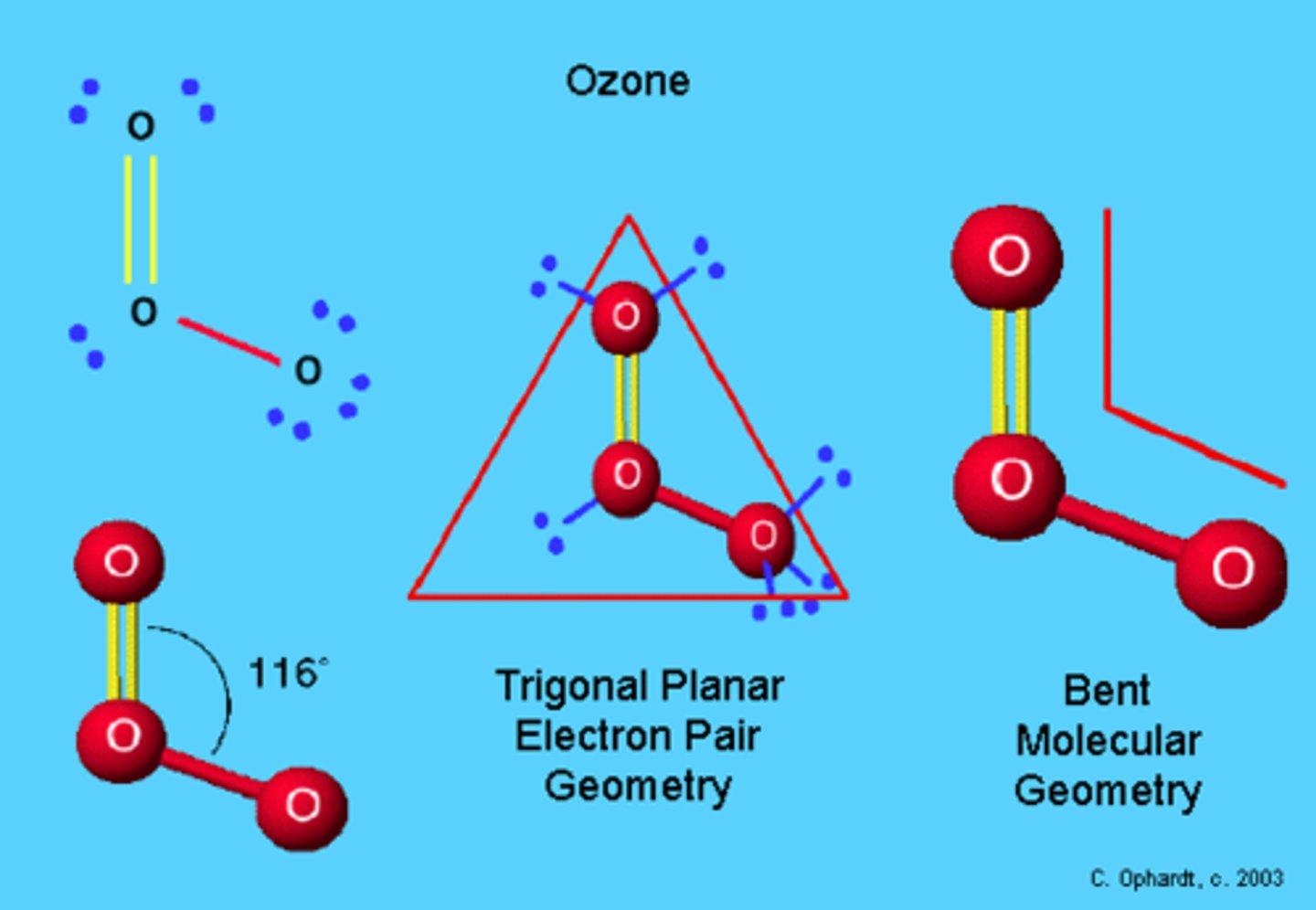
Trigonal Planar
AB3
Example: NO3 - nitrate ion
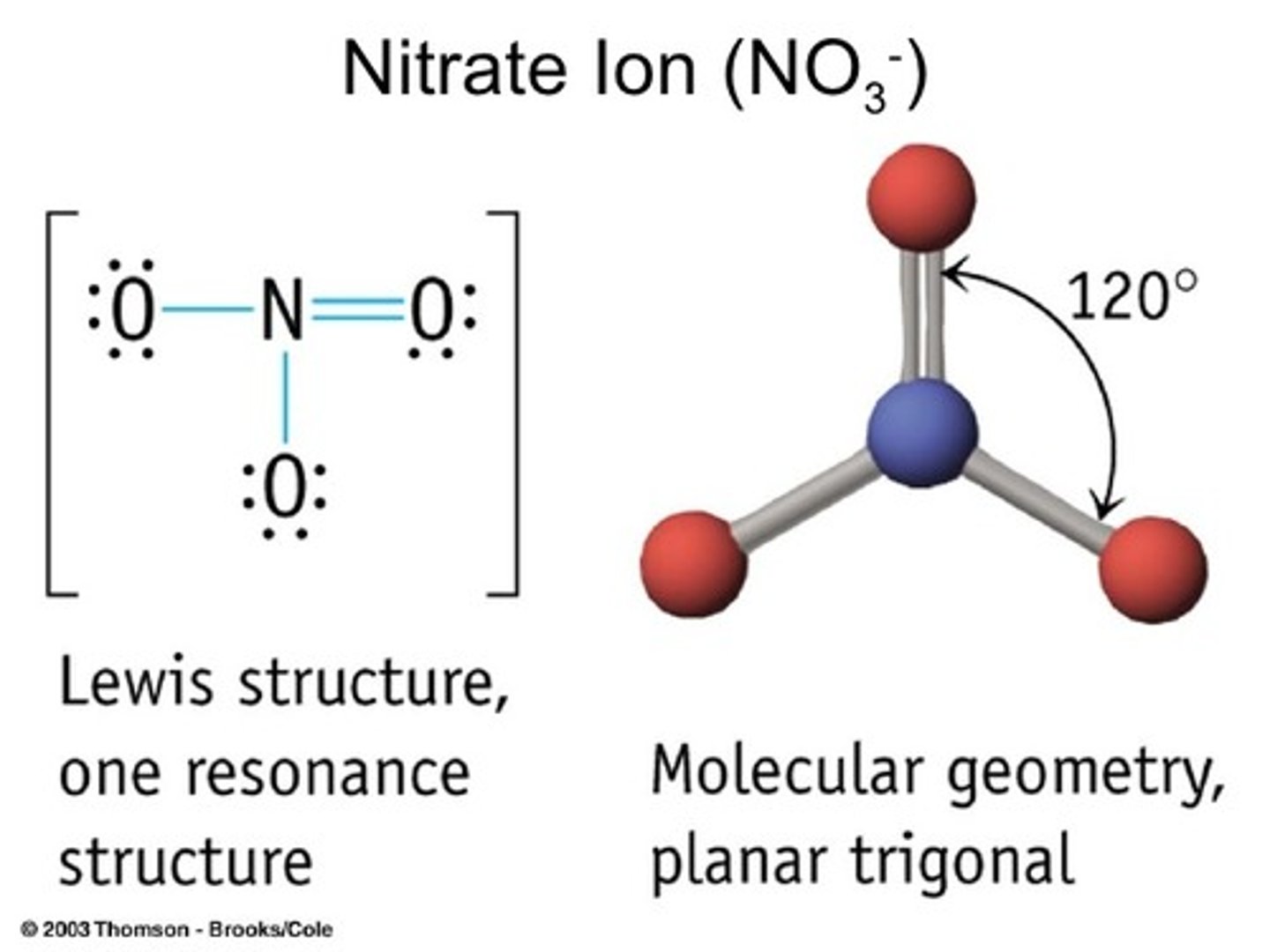
Tetrahedral
AB4
Example: NH4+ - ammonium ion
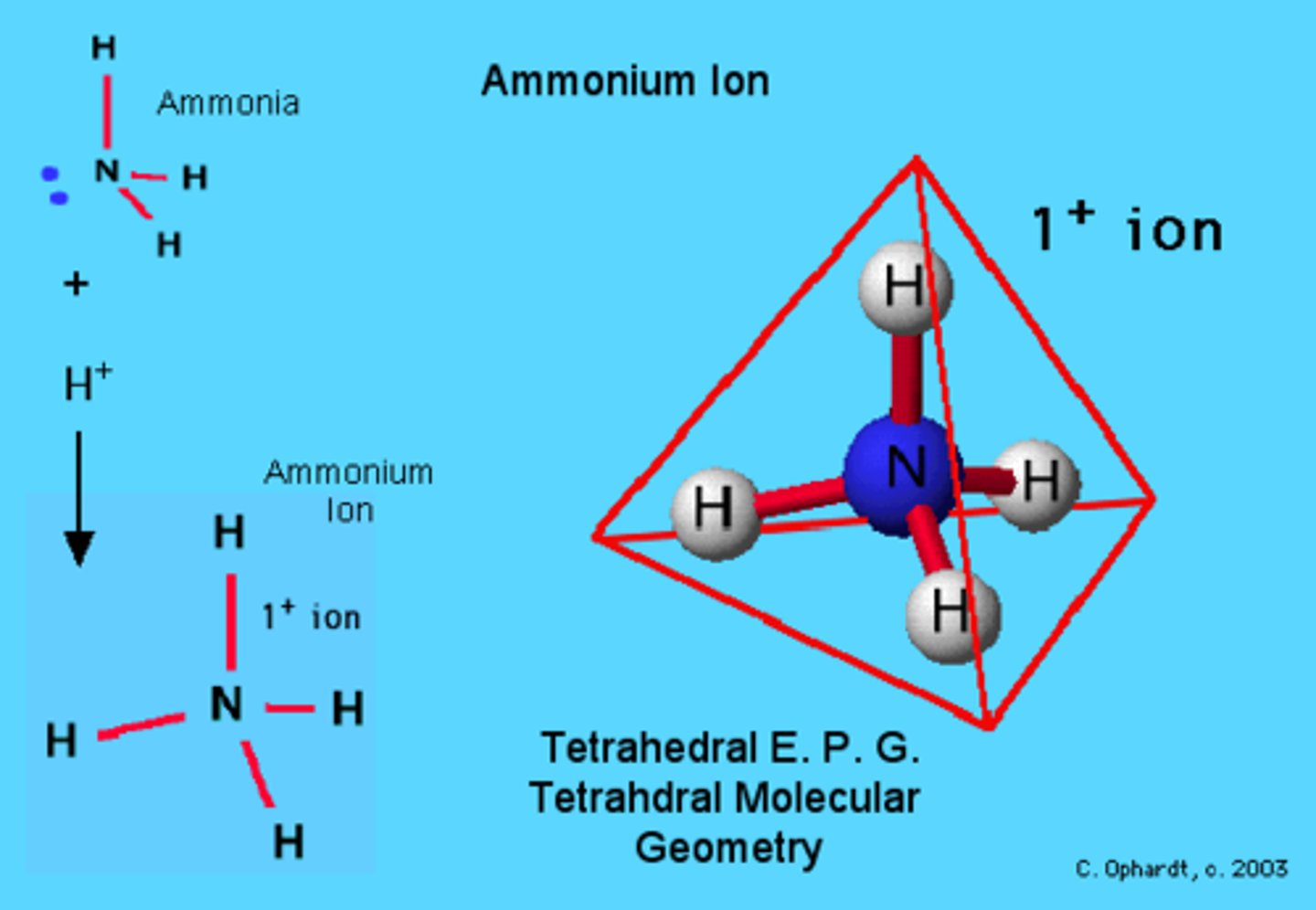
Trigonal Pyramidal
AB3E
Example: PCl3 - phosphorus tri-chloride
Really Bent
AB2E2
Example: OF2 - oxygen di-fluoride
Trigonal Bipyramidal
AB5
Example: AsF5 - Arsenic pentafluoride

Octahedral
AB6
Example: SeF6 - Selenium hexafluoride
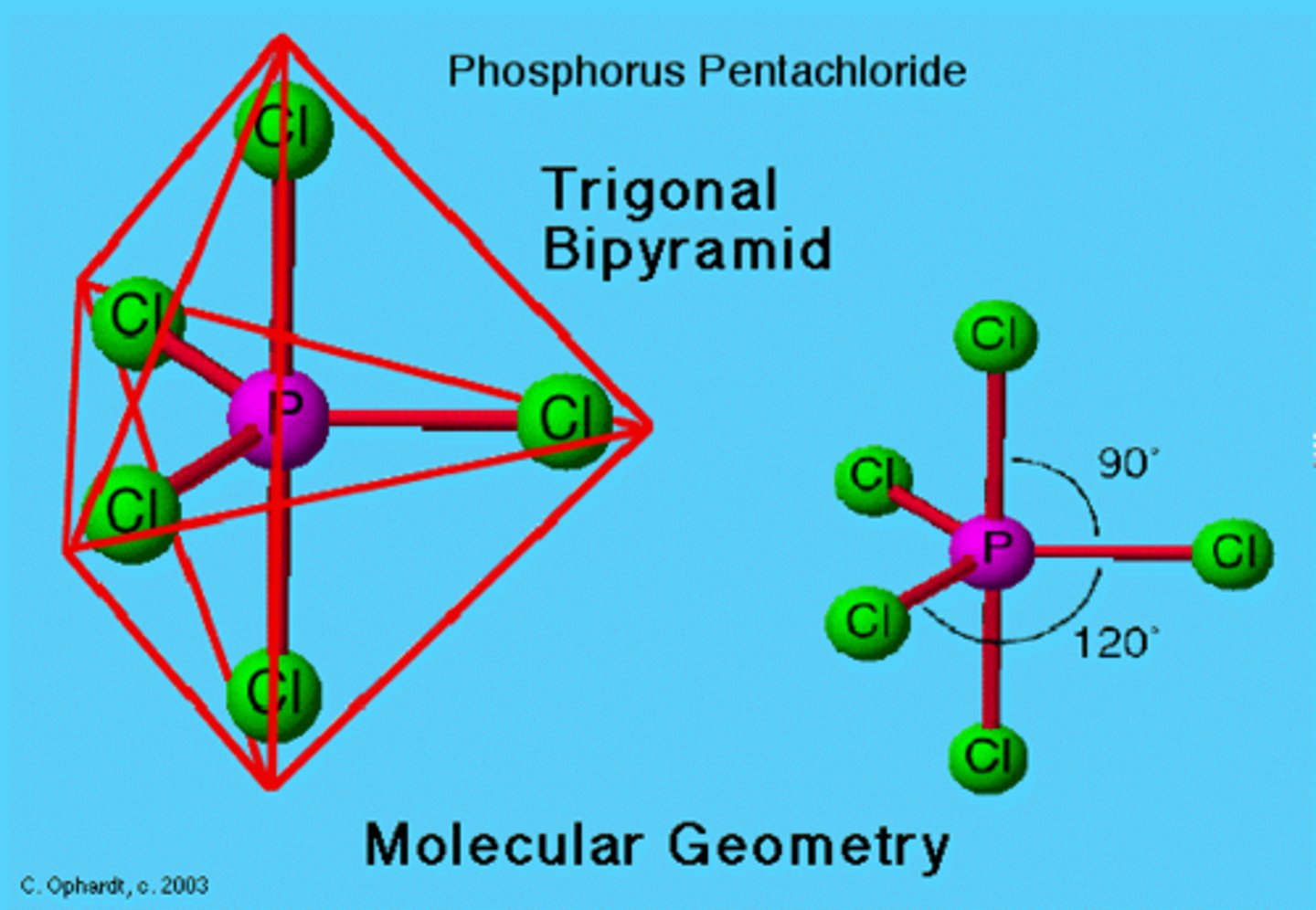
Name the Compound
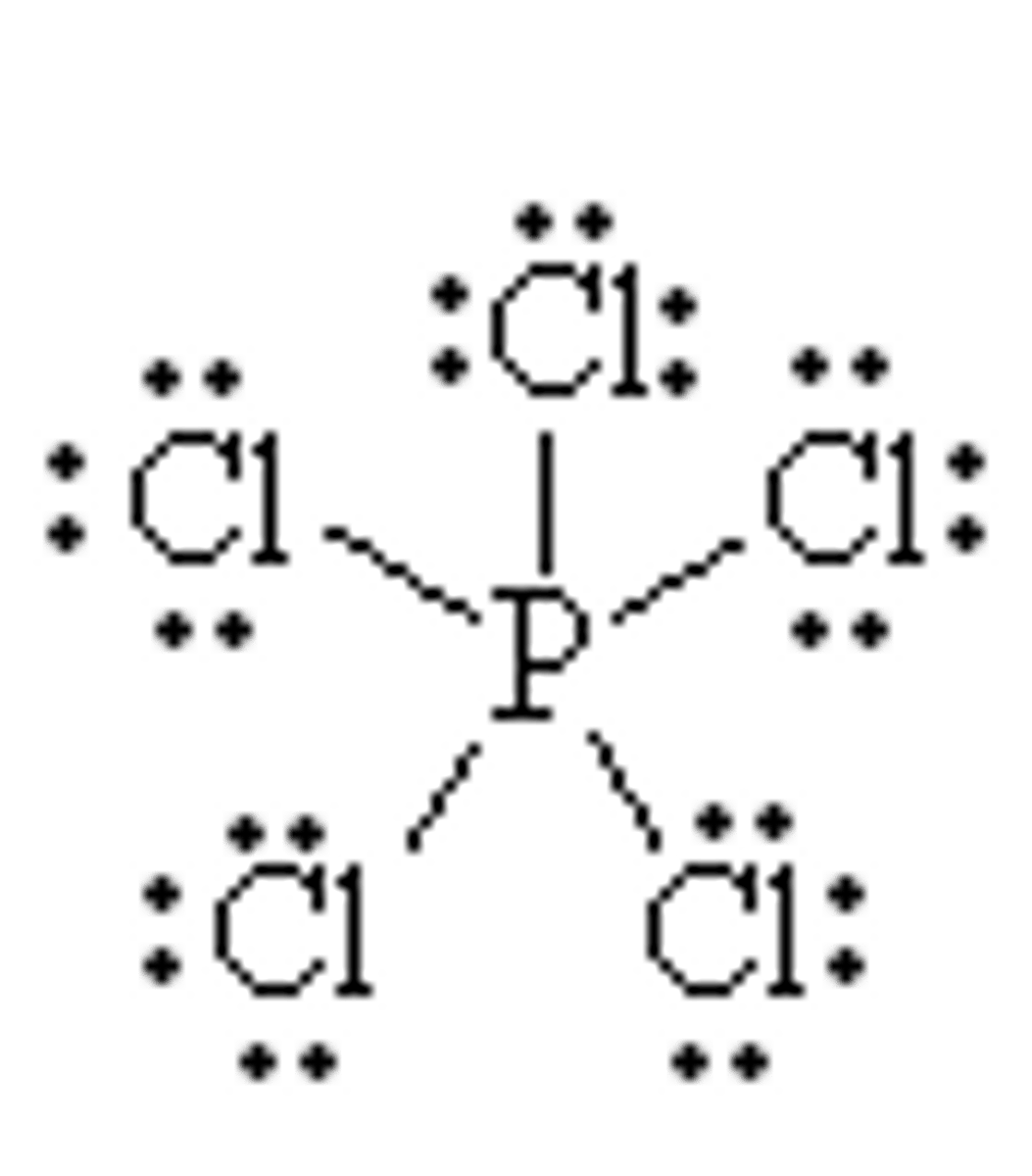
PCl5
Phosphorus Pentachloride; Phosphorus(V) chloride
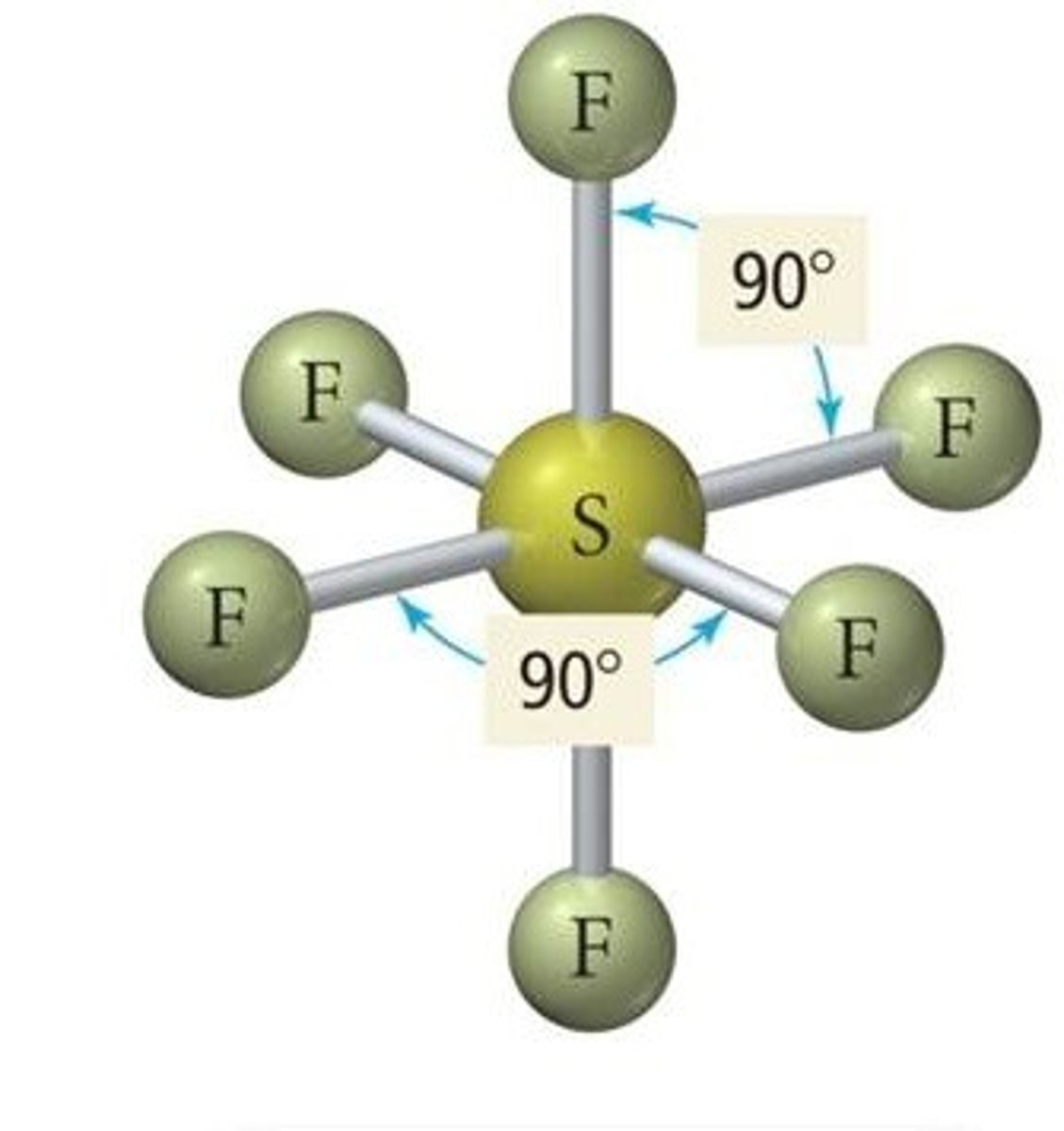
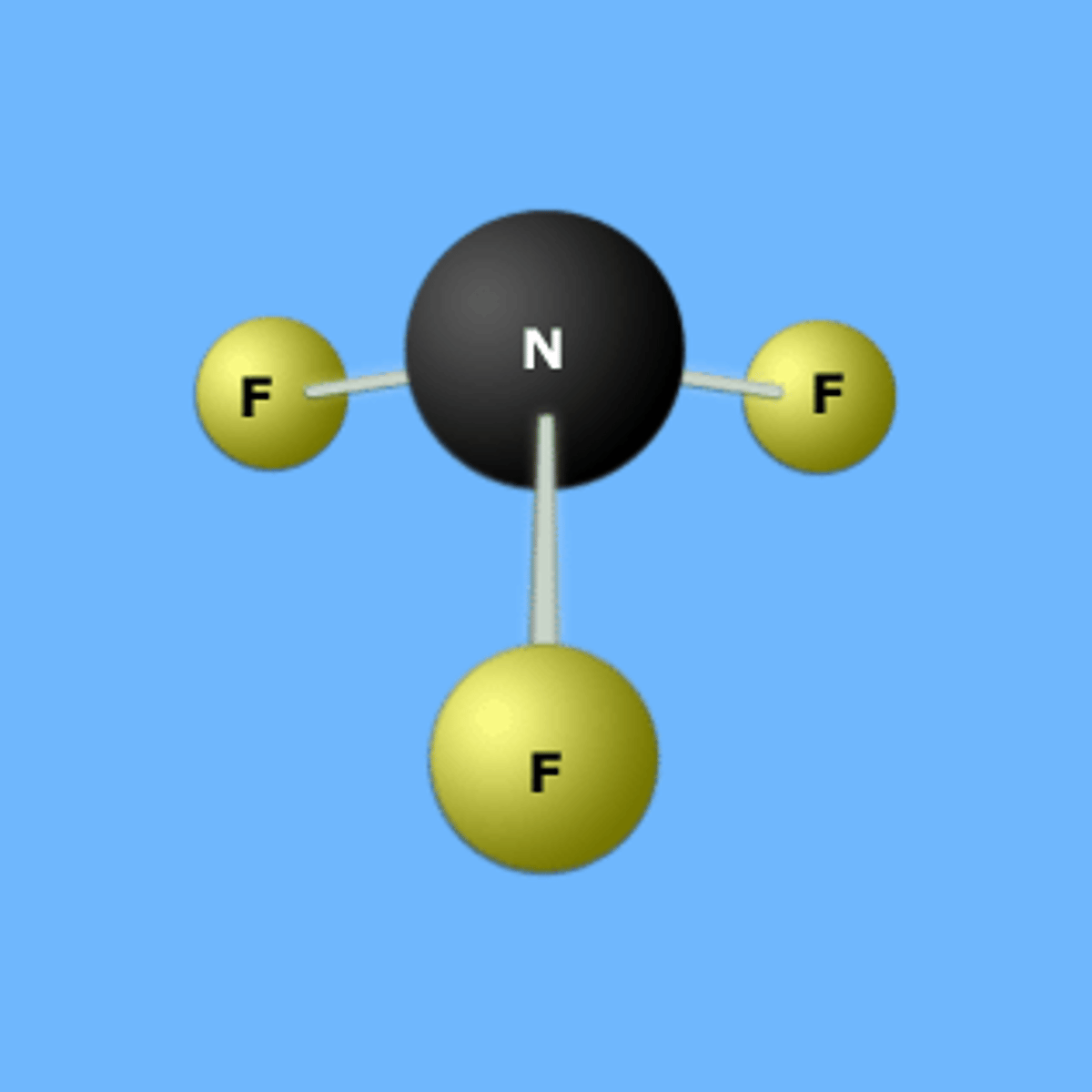
Name the Compound
NF3
Nitrogen trifluoride
Name the Compound
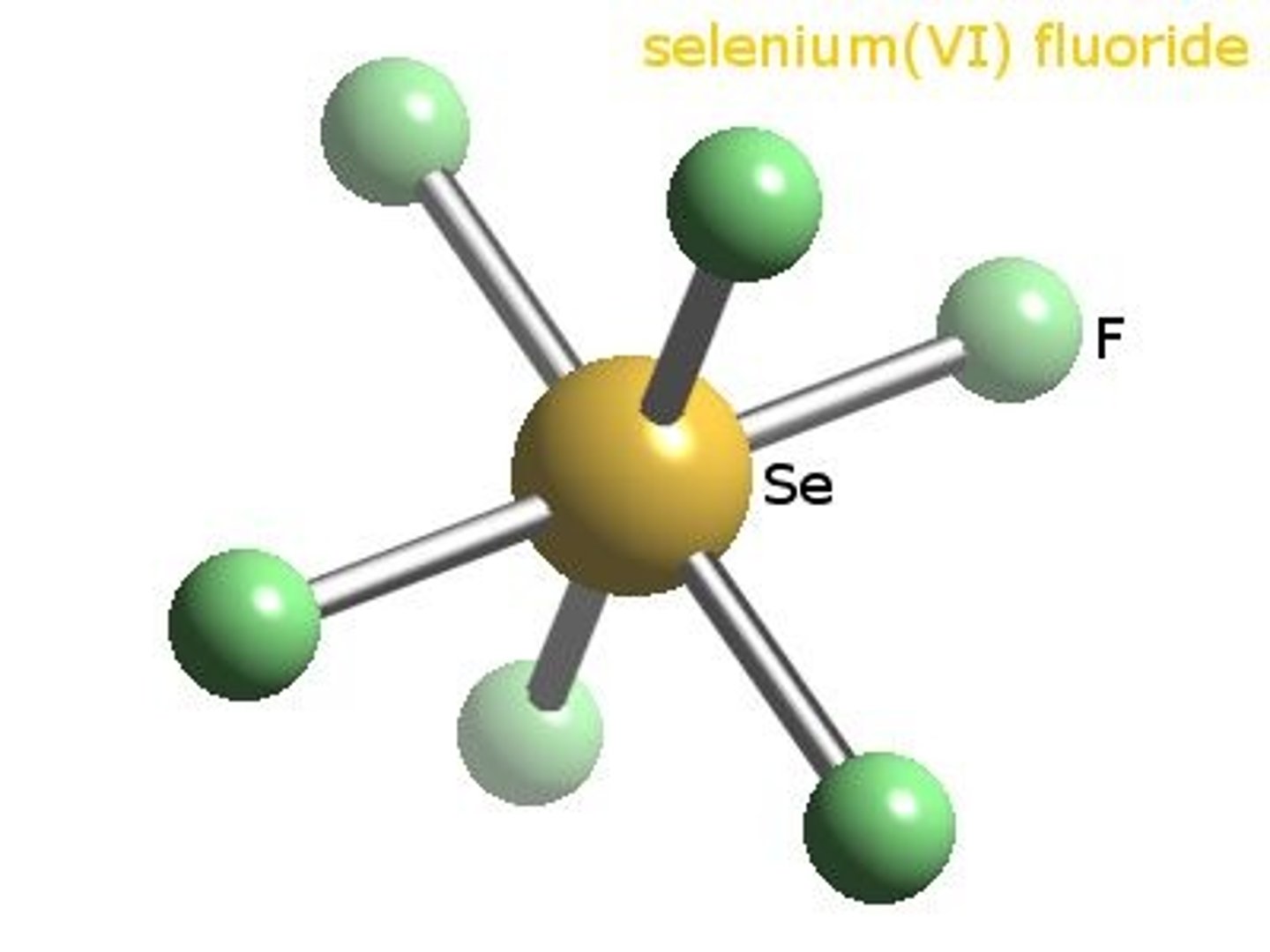
SeF6
Selenium hexafluoride
Name the Compound
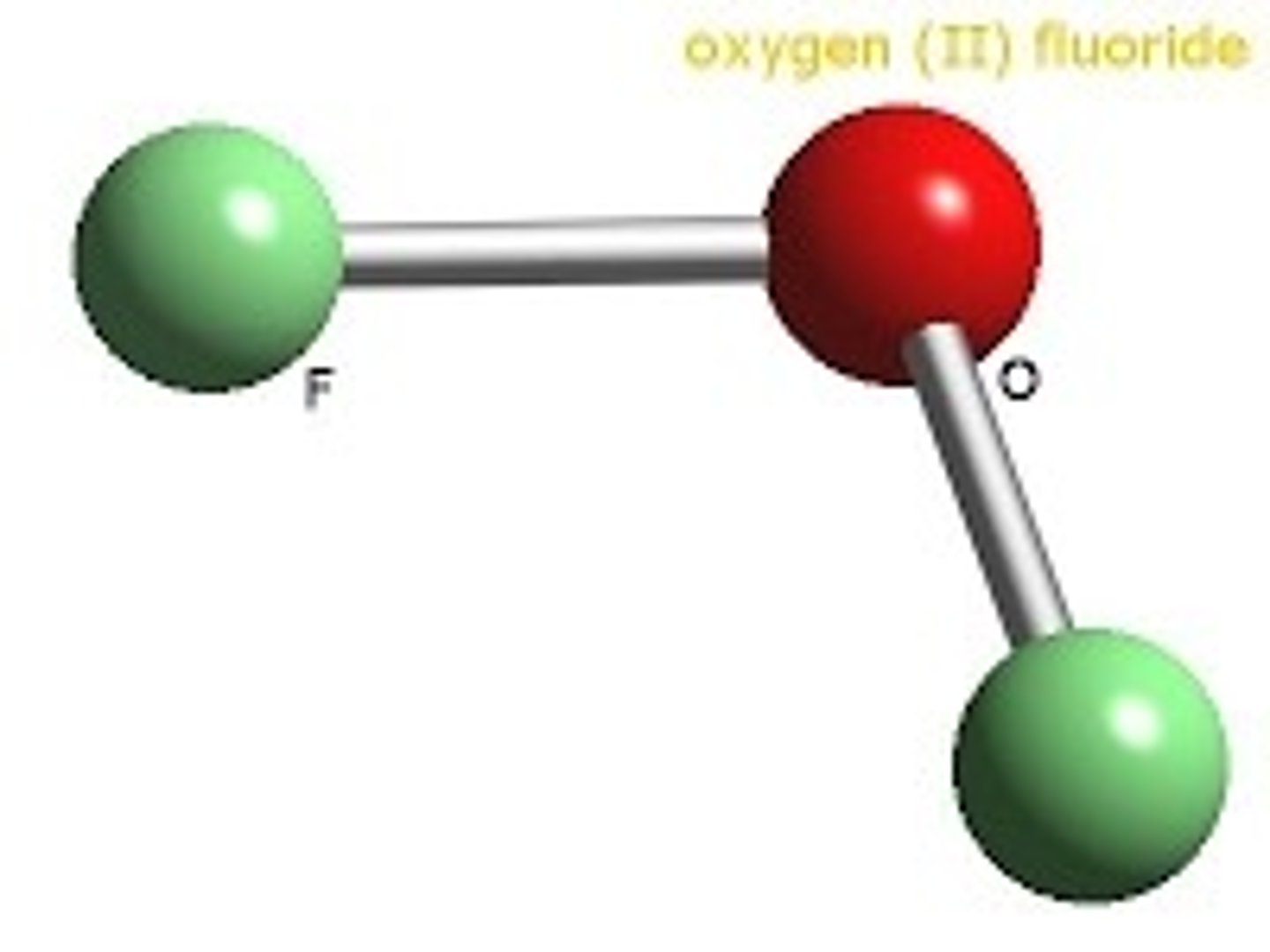
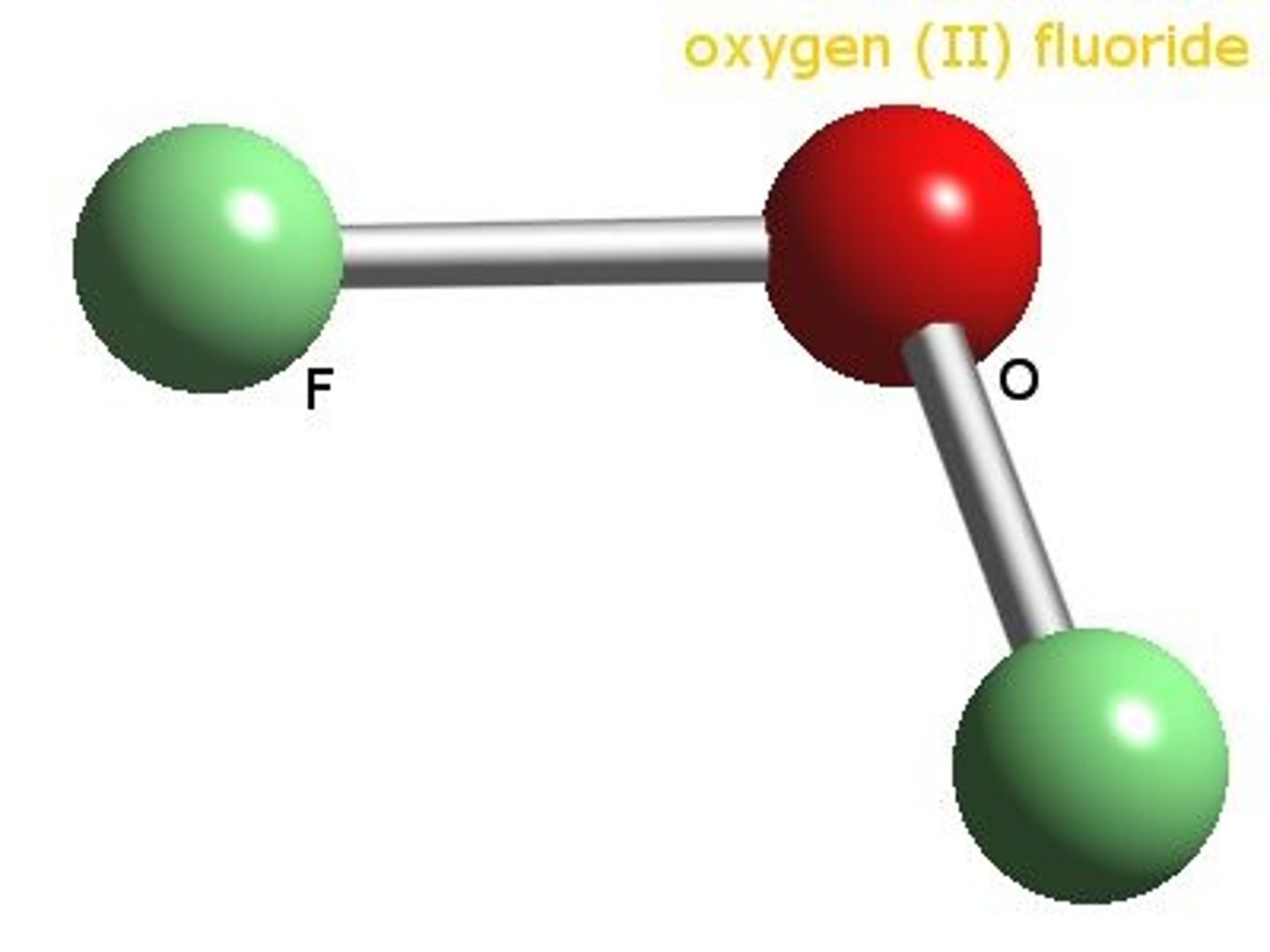
OF2
Oxygen difluoride
Name the Compound
CBr2O
Carbonyl dibromide
Lewis Structure:
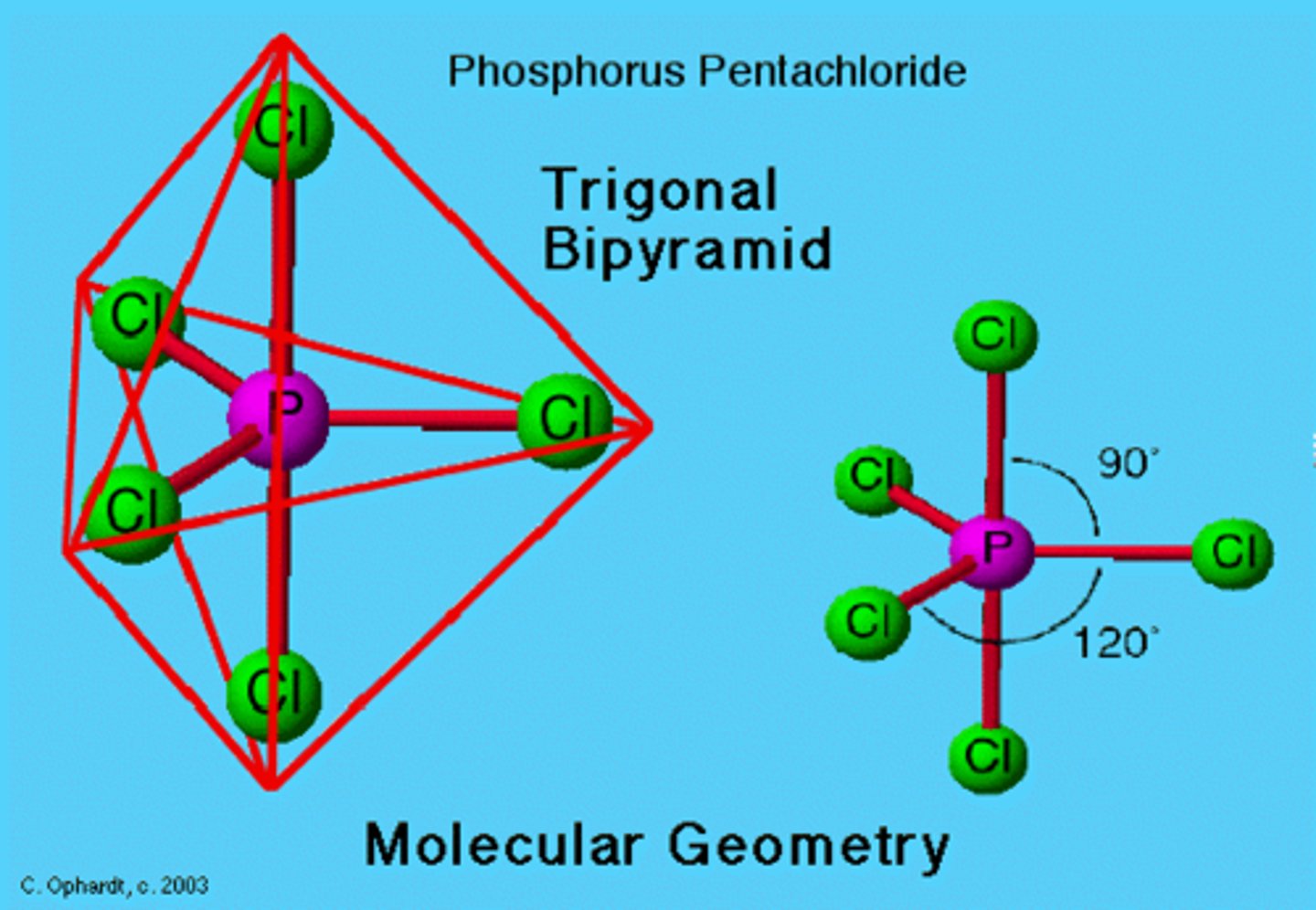
Phosphorus Pentachloride
Lewis Structure:
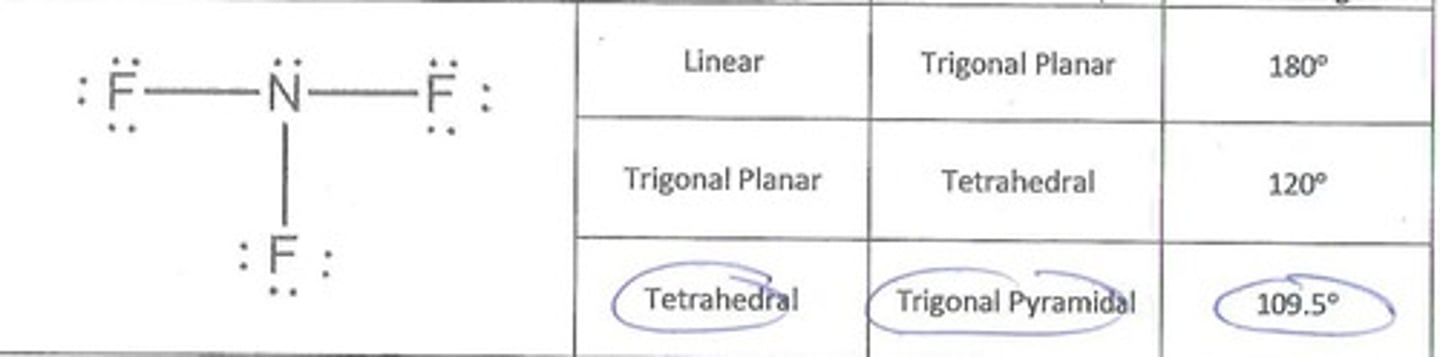
Nitrogen trifluoride
Lewis Structure:
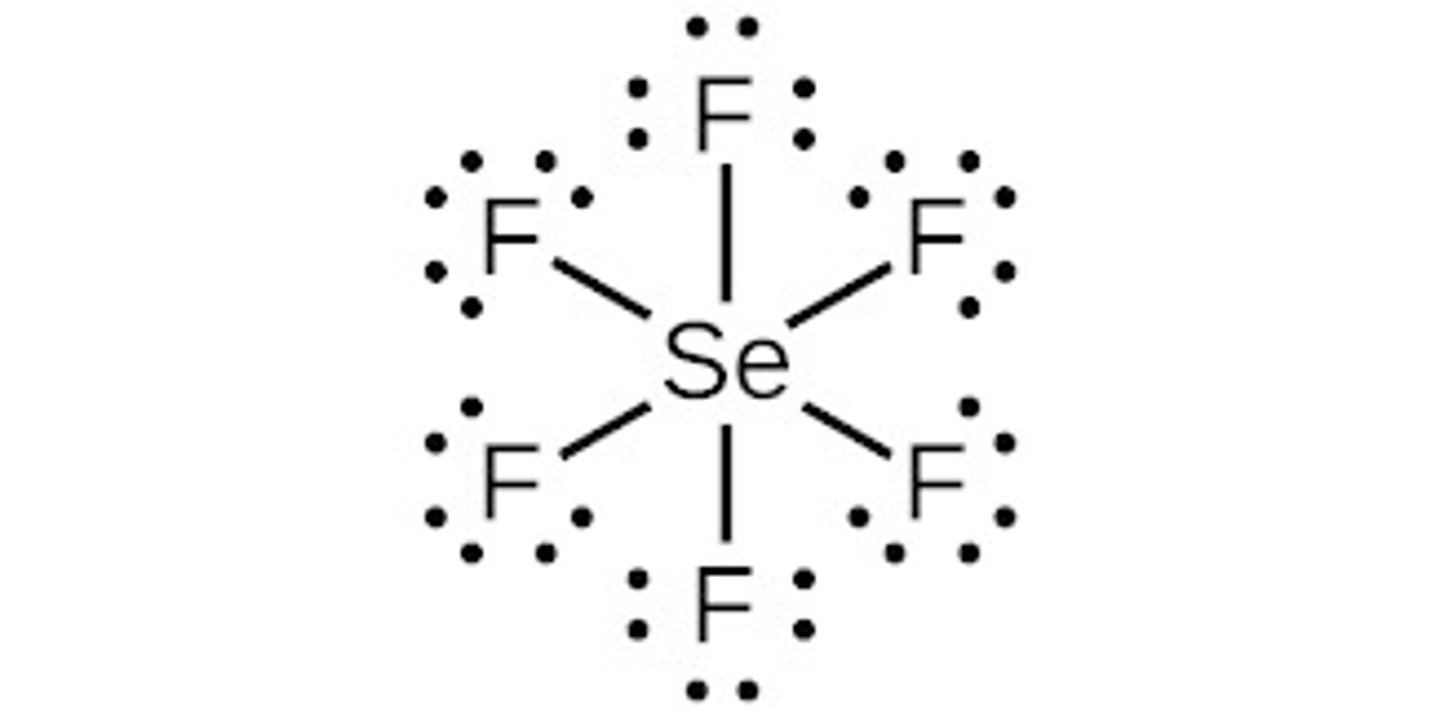
Selenium hexafluoride
Lewis Structure:
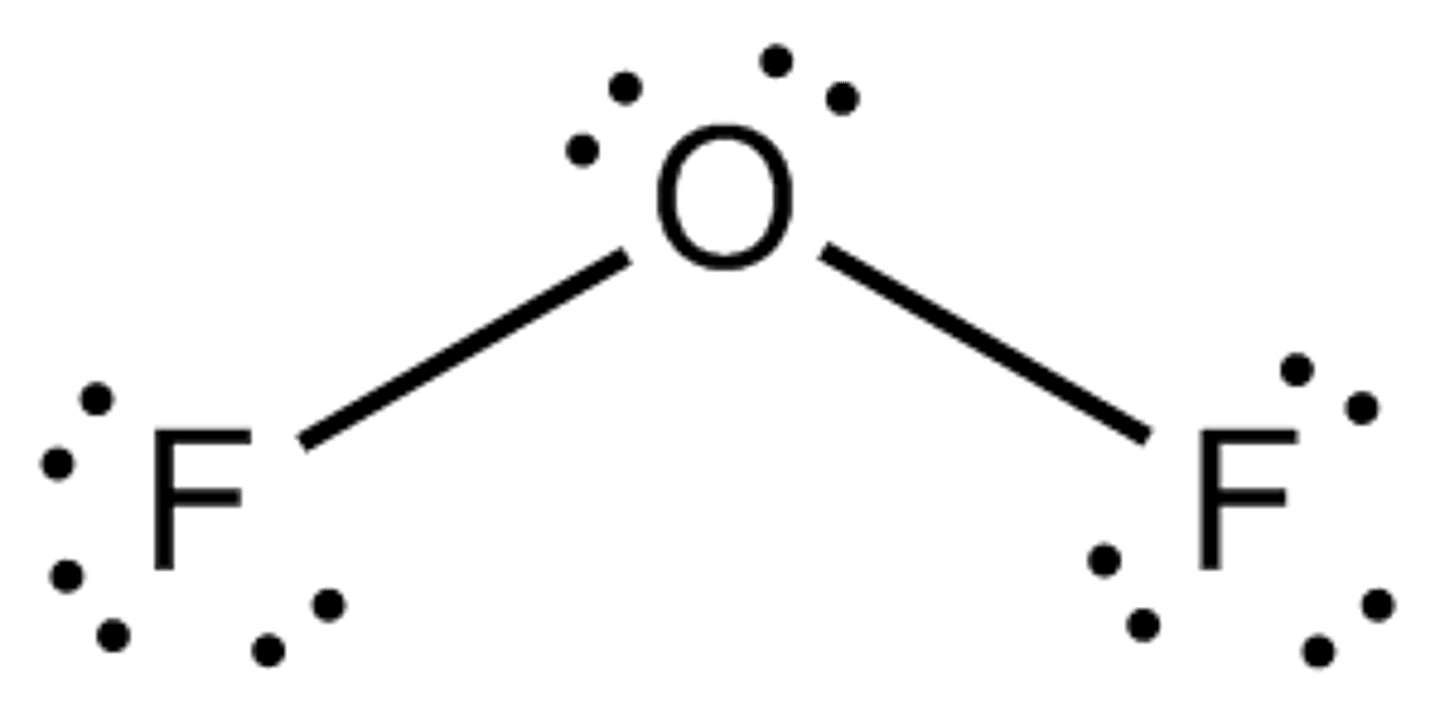
Oxygen difluoride
Molecular Shape:
PCl5
AB5
trigonal bipyramidal
non polar molecule
Molecular Shape:
NF3
AB3E
trigonal pyramidal
tetrahedral
polar
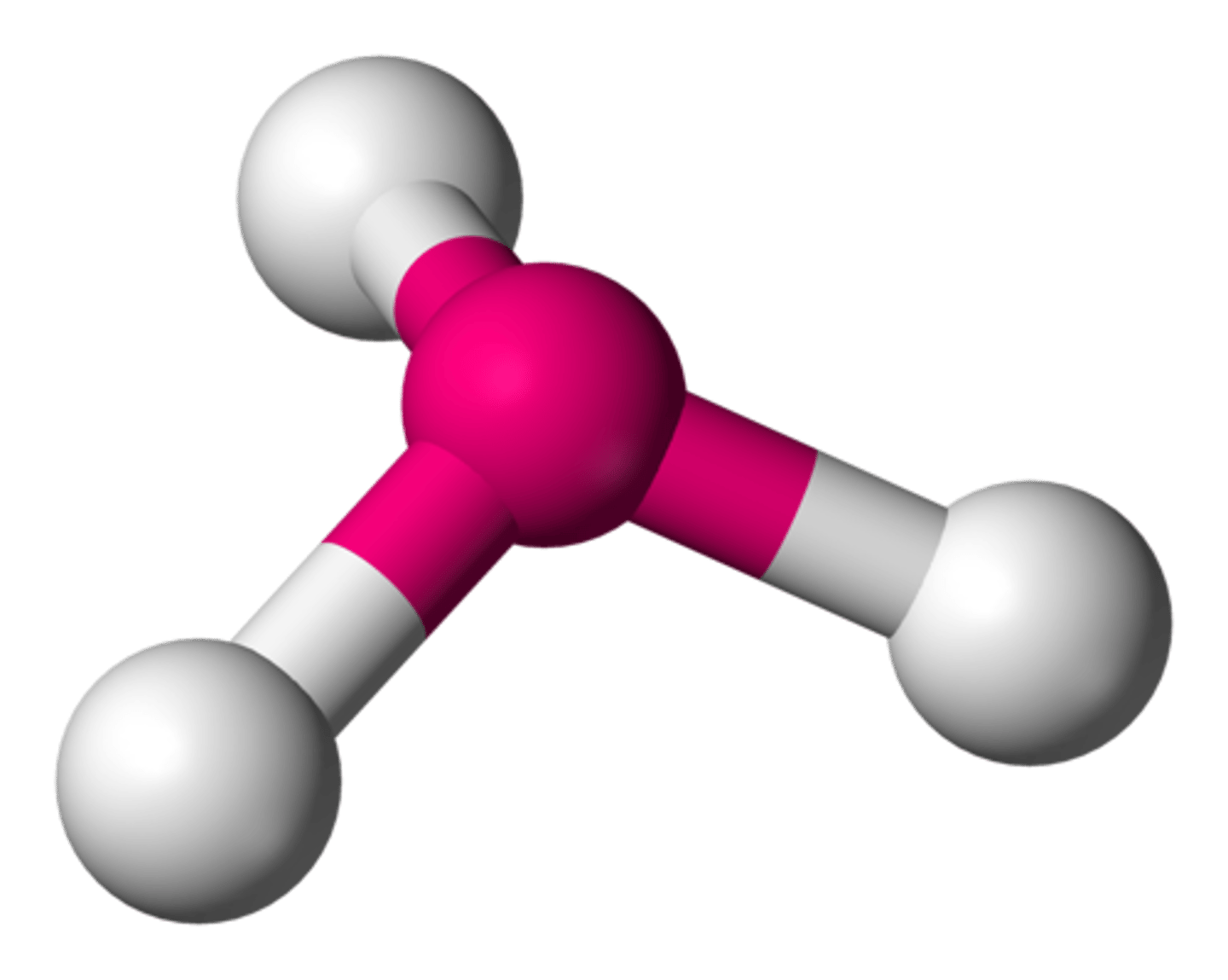
Molecular Shape:
SeF6
AB6
octahedral
nonpolar
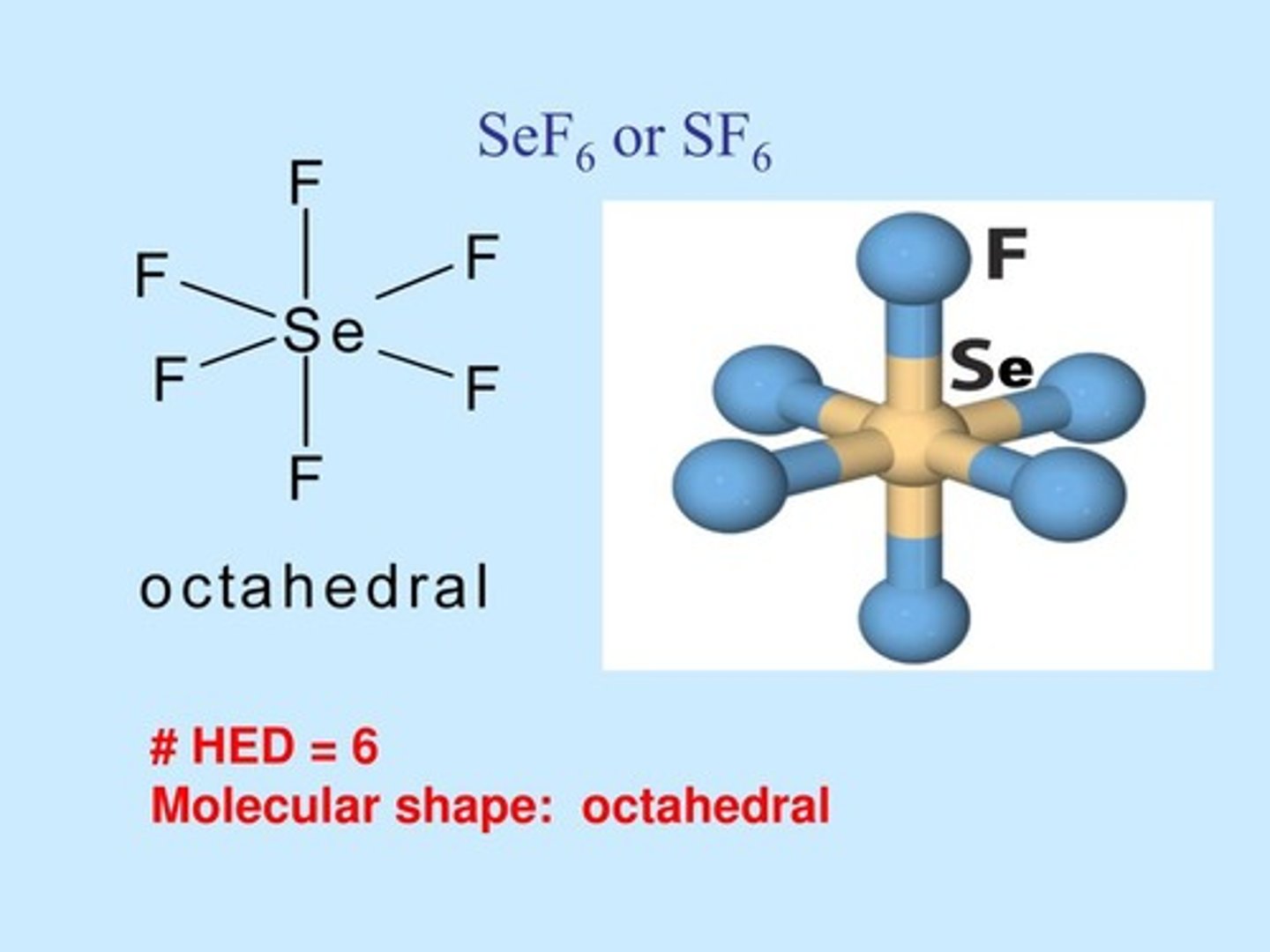
Molecular Shape:
OF2
AB2E2
bent 109.5 degrees
polar molecule