Groundwater
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Equation for Head
Head = Energy / Weight
Energy: (J, ft-lbs)
Weight: (N, lbf)
Bernoulli’s Law
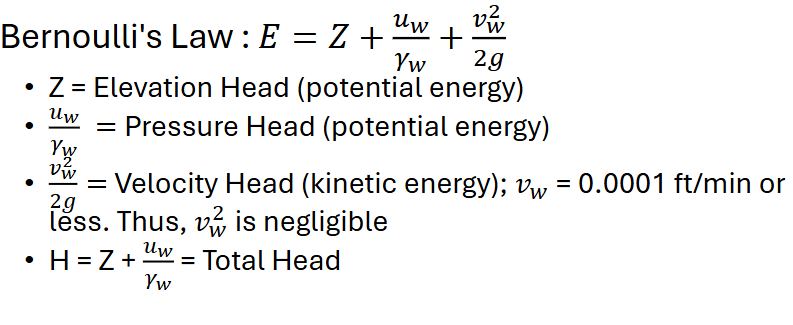
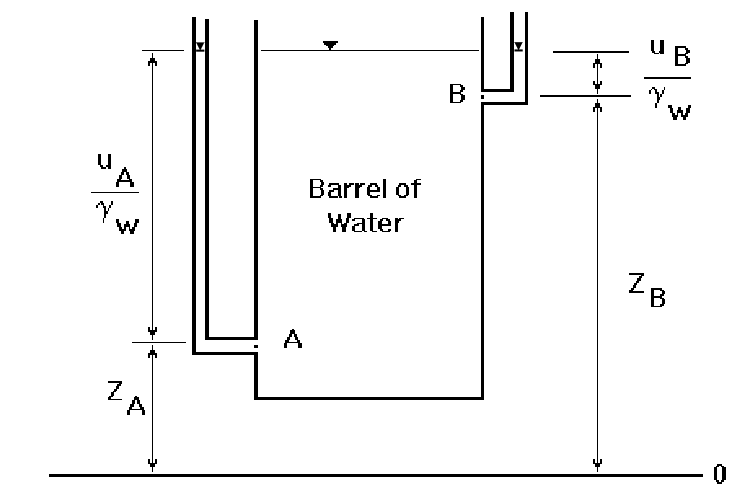
Will the water flow through the barrel?
No. Flow is not possible because the Head of A and the Head of B are equal.
Define Aquifer
A layer in which water can flow easily such as sand and gravel
Define Aquitard
A layer in which water flow is greatly restricted, such as sand or clay
Define Aquiclude
A layer in which water cannot flow such as bed rock
Piezometric surface
A conceptual surface that represents the level to which water will rise (in wells) due to ground water pressure in aquifer
Types of Aquifers
Phreatic, Water Table or Unconfined Aquifer
Top of Water in Aquifer and at Atmospheric Pressure
Phreatic Surface
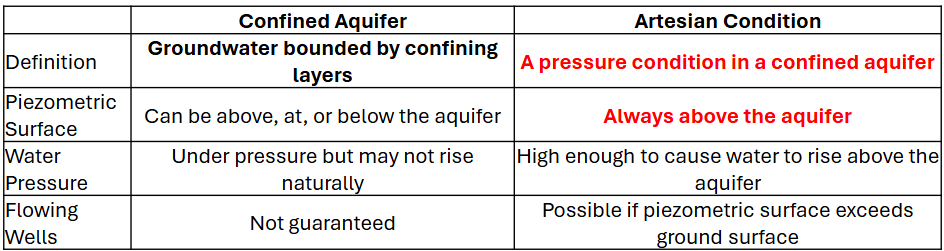
Confined Aquifer or Artesian Condition
Top of Water Against a Confining Layer and Water Pressure is greater than zero
Piezometric Surface
Well vs. Piezometer
Well: Used to Pump Water
Piezometer: Used to determine Water Pressure at a specific depth
Confined aquifer vs. Artesian
What is Darcy’s Law?
Flow rate or discharge (Q) was proportional to A
and ∆h, and inversely proportional to L.
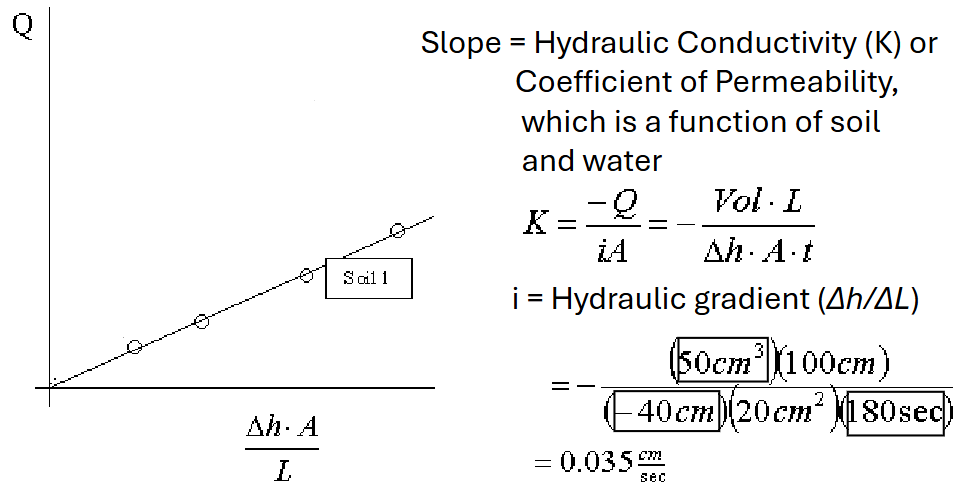
Hydraulic Conductivity Formula
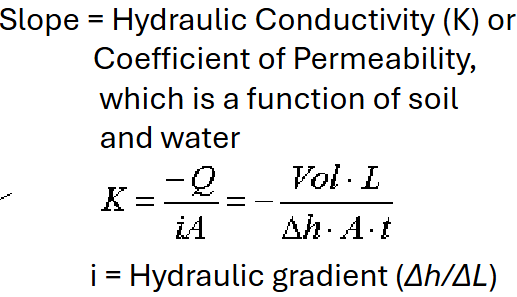
Determination Hydraulic Conductivity in the field
• Most accurate of the various in-situ procedures:
Account for layering in the soil, temperature, soil/water chemistry, hydrologic boundaries, and minimal sample disturbance
• Extremely expensive: It can usually be justified only on the largest projects where the information is fundamentally important, for example, dams and tunnels.
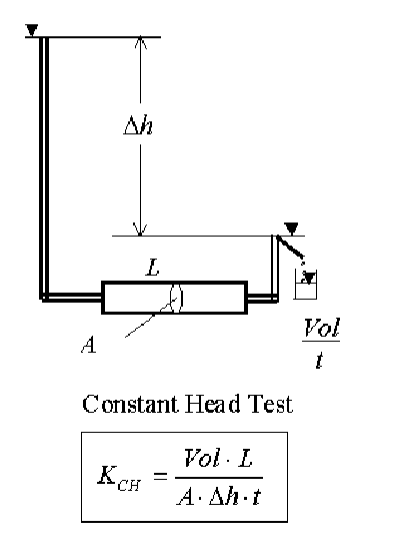
How is the constant head test conducted for the determination of hydraulic conductivity?
Constant Head Test: used for coarse-grained soils where upstream and downstream heads are maintained at a constant difference during the test.
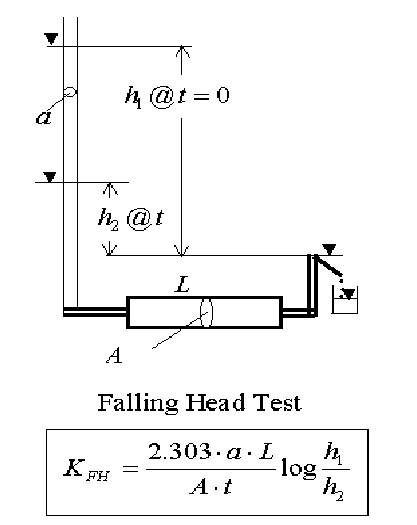
How is the falling head test conducted for the determination of hydraulic conductivity?
Typically used with finer-grained soils that have lower conductivities. Downstream water does not have to be collected and is not subject to evaporation losses during long-scale test
How to solve head problems step by step:
Select a Zero Elevation Datum
Determine Heads at known points (usually at water surfaces where the pressure head is zero)
Zero Total Head Loss in Piping
a) Total Head is the same all through the piping
b) Some simple justifications
i. Flow rate is usually very low in piping (head loss due to
turbulence is negligible)
ii. Flow velocity is very low in piping (hf ∝ v2)
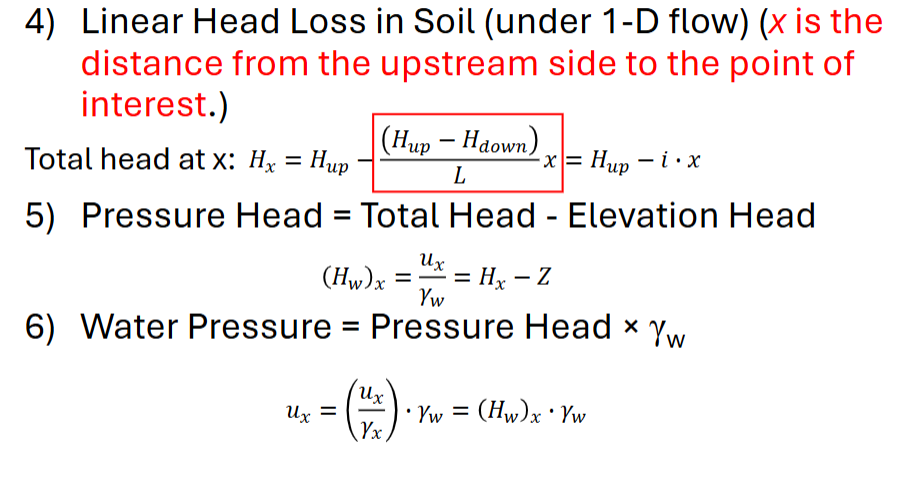
iii. Friction is very low in piping compared to soilLinear Head Loss in Soil (under 1-D flow) (x is the
distance from the upstream side to the point of
interest.) Formula on ImagePressure Head = Total Head - Elevation Head
Water Pressure =Pressure Head * unit weight of water