Growth hormone
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
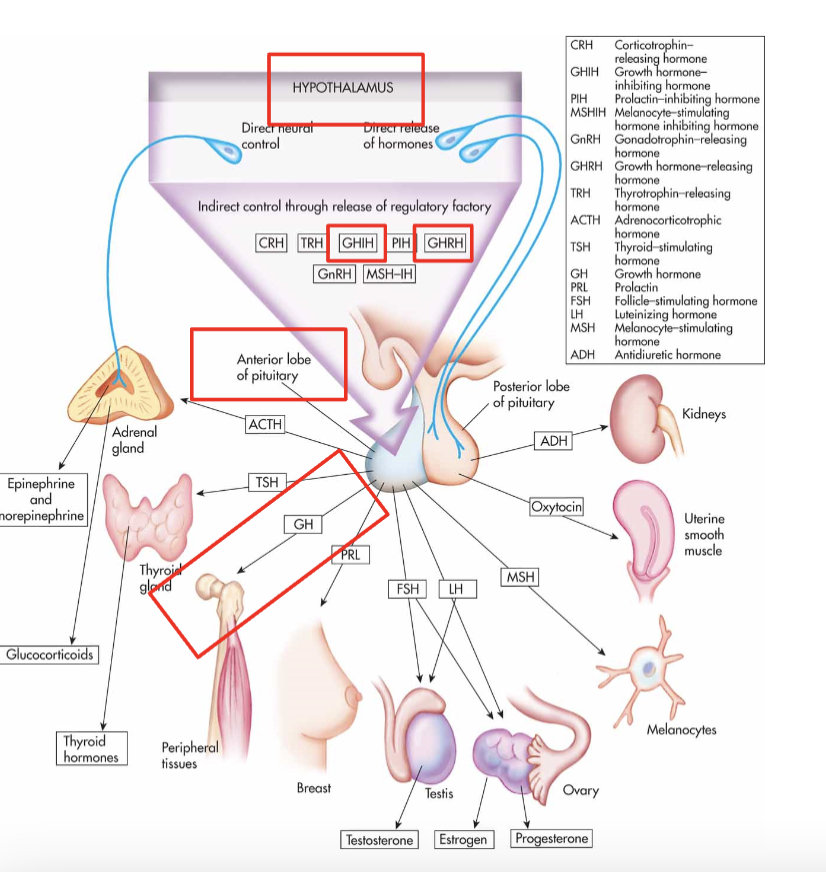
GH regulatory pathway
Hypothalamus released GHRH (stimulates GH release) and GHIH (inhibits GH release)
These act on the adenohypophysis with secretes GH
GH acts on target tissues
GH overview
GH is a protein hormone, and acts on membrane receptors
Main targets include liver, muscles, bones and adipose tissue
Circulates blood bound to GH binding protein
Non tropic hormone → acts directly on tissues
Synthesis and regulation
Synthesied by somatotropic cells in anterior pituitary
Release stimulated by GHRH (produced in hypothalamus) → somatocrinin
Release inhibited by GHIH (from hypothalamus) → somatostatin
Indirect actions of GH
Growth promoting
On bones → lengthening (chondrocyte proliferation) and thickening of bones
On muscles → muscle hypertrophy (reduce protein breakdown, increase protein synthesis and amino acid uptakes)
On organs → stim growth of visceral organs and tissue regeneration
Direct actions of GH
Metabolic
Increase blood glucose → less glucose uptake by muscles and fat
Lipolysis → mobilise fatty acids from adipose tissue, provide energy during fasting
Protein syntheis → increase amino uptake, less protein breakdown
Somatomedins
Group of peptide homrones produced in response to GH
They are better known as Insulin-like Growth Factors because of their structural similarity to insulin
GH stimulates liver to produce IGF1 which then acts on tissues
Types include IGF-1 and IGF-2
IGF-1
Primary mediator of GH growth promoting effects
Produced mainly by liver, circulation bound to IGF binding proteins
Stimulation → GH, insulin, thyroid hormones, adequate nutrition
Inhibition → malnutrition, insulin deficiency, chronic illness…
IGF-1 actions
Bone - chondrocyte profileration and osteoblast activity
Muscle - increase amino uptake and protein synthesis
Organs - cell profileration and organ enlargment
Cell cycle - promotes cell division, G1 to S phase
Apoptosis - support tissue survival and regeneration
Stimulators of GH secretion
Low blood glucose - triggers GHRH
High amino acids - signal protein uptake, protein synthesis → fat for energy
Stress/exercise/sleep - increase GHRH
Puberty - enhance GH release and increase liver IGF
Neurotransmitters - serotonin and alpha adrenergic stimulare GHRH
Hormones - TRH, thyroid hormones, androgens, glucocorticoids
Inhibitors of GH secretion
High glucose - increases somatostatin
IGF 1 - negative feedback, increase hypothalamic GHIH
Glucocorticoids - high cortisol supresses GH synthesis
Excess estrogen
GH deficiency
In children → leads to dwarfism
May result from pituitary dysfunction, hypothalamic diseases and endocrine disorders
GH excess
Before puberty → leads to gigantism
After puberty → acromegaly (bones thicken and don’t lengthen)
Can also lead to insulin resistance → diabetes mellitus