1.4 Cholinergic Med Chem
1/173
Earn XP
Description and Tags
El Sayed
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
174 Terms
what are the two types of cholinergic receptors
muscarinic and nicotinic
where are most of the cholinergic receptors located in the body
PNS
are nicotinic receptors inhibitory or excitatory
excitatory
what are the muscarinic receptor subtypes
M1, M2, M3, M4, M5
which muscarinic receptors are excitatory
M1, M3, M5
which muscarinic receptors are inhibitory
M2 and M4
are nicotinic receptors GPCRs or ligand gated?
ligand gated
how many transmembrane domains does a nicotinic receptor have
5
which nicotinic transmembrane domain is responsible for opening and closing in response to ACh
TM2
is the neurotransmitter binding region of nicotinic receptors intracellular or extracellular
extracellular
how many transmembrane domains do muscarinic receptors have
7
are muscarinic receptors GPCRs or ligand gated?
GPCRs
which transmembrane domain of muscarinic receptors is responsible for binding to ACh
TM3
why is TM3 of muscarinic receptors responsible for binding to ACh
it has Asp 105 in it which acts as an anionic group to directly bind to the quaternary ammonium on the ACh
cholinergic neurons release ____
ACh
cholinergic receptors respond to _____
ACh
cholinergic ____ release ACh and cholinergic ____ respond to ACh
neurons, receptors
muscarinic agonists are also called
parasympathomimetics
what are some acetylcholine like structures
methacholine, carbachol, and bethanechol
what has a non-acetylcholine like structure
pilocarpine
AChE (acetylcholinesterase) is responsible for…
hydrolysis of ACh to form acetate and choline
what controls the action of ACh
AChE
ACh that is not bound to receptors is ______ which terminates its action
hydrolyzed by AChE
if AChE were inhibited it would lead to…
increased ACh concentration and prolong its actions on neurons
inhibition of AChE can be useful for which diseases
myasthenia gravis, glaucoma, alzheimers
AChE has an ____ site that can bind to the charged choline of ACh
anionic
active esteratic site contains a ___residue that is involved in the hydrolysis of the ester bond
nucleophilic serine
how does ACh get metabolized
the nucleophilic serine hydroxy group attacks the ester carbonyl group of ACh which forms a tetrahedral intermediate, which breaks down resulting in a release of choline intermediate acetylated serine which hydrolyses to release ACH E and acetic acid
why cant ACh be used as a drug
no selectivity between receptors
poorly absorbed
hydrolyzed in gut (inactivated)
not orally active
True or false:
ACh is selective for nicotinic receptors
false
why is ACh poorly absorbed thru cell membranes
contains a quaternary ammonium salt
why is ACh not orally active
hydrolysis in the gut
why does ACh undergo rapid enzymatic hydrolysis in the blood and tissues
because of its ester group
does ACh have any chiral centers
nah fam
the torsion angle of ACh is between which areas
ester oxygen atom and quaternary nitrogen
which structure of ACh is the most common and active
synclinal
which conformation of ACTM was more potent for muscarinic receptors
trans-ACTM
compounds that have a positive charge on the atom in place of the N on ACh are _____
active
removal of a methyl group on ACh causes…
decreased activity
removal of a ____ on ACh leads to decreased activity
methyl
there should be no more than ___ atoms between N and the terminal hydrogen atom for maximal muscarinic potency
5
there should be no more than 5 atoms between N and the terminal hydrogen atom for maximal ____ potency
muscarinic
replacing the nitrogen on ACh with which 4 atoms leads to less activity than ACh
S, As, P, and Se
if ACh’s methyl group was replaced with larger and bulkier groups then it was ____
inactive
when three methyl groups were replaced by _____ it formed a cholinergic antagonist
ethyl
when three methyl groups were replaced with ethyl groups instead it formed…
cholinergic antagonists
successive removal of methyl groups and replacement with hydrogen makes them…
primary, secondary, and tertiary amines with decreasing muscarinic activity
Acetic acid esters of quaternary ammonium alcohols of greater length than choline led to a series of compounds with rapid ____ in activity
decreases
Acetic acid esters of quaternary ammonium alcohols of ____ length than choline led to a series of compounds with rapid decrease in activity
greater
ing rule of 5
There should not be more than 5 atoms between the N & terminal H atom for maximal muscarinic potency
Ethylene bridge replaced by alkyl groups _____ than methyl led to less active compounds with agonist activity 1/10 as active as ACh
larger
Ethylene bridge replaced by alkyl groups larger than methyl led to _____ active compounds
less
Addition of a methyl group on β-carbon to quaternary nitrogen atom led to a compound with activity similar to AcCh, but more selective to ______ receptors
muscarinic
Addition of a methyl group on ____-carbon to quaternary nitrogen atom led to a compound with activity similar to AcCh, but more selective to muscarinic receptors
beta
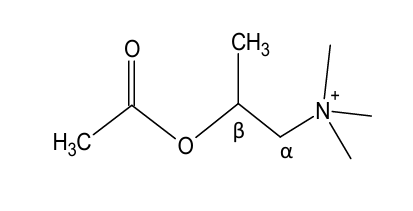
would this structure be more selective for nicotinic or muscarinic receptors?
muscarinic
Addition of methyl group on α-carbon to quaternary N atom led to compound with slightly less activity than AcCh, but more selective to ______ receptors
nicotinic
Addition of methyl group on ____ carbon to quaternary N atom led to compound with slightly less activity than AcCh, but more selective to nicotinic receptors
alpha
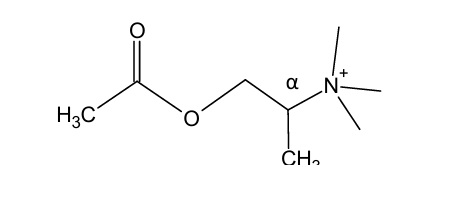
would this structure be more selective for muscarinic or nicotinic receptors?
nicotinic
When acetyl group were replaced with higher homologues (propionyl, butyryl) activity was ____ vs ACh
decreased
Choline esters of aromatic acids or higher molecular weight acids possess cholinergic _____ activity.
antagonist
In acetylcholine, ____ group is susceptible for hydrolysis.
acetyloxy
In acetylcholine, acetyloxy group is susceptible for ____.
hydrolysis
carbachol and bethanechol are both ____ active
orally
Modifications of carbachol resulted in ____
bethanechol
Modifications of ____ resulted in bethanechol
carbachol
Bethanechol is orally available potent ______ agonist
muscarine
Bethanechol is orally available potent muscarinic ______
agonist
Bethanechol has almost no activity on ____ receptors
nicotinic
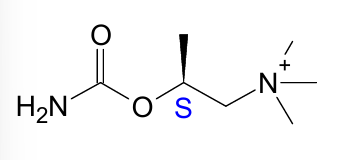
which enantiomer of bethanechol has greater binding affinity for muscarine receptors than the other
S
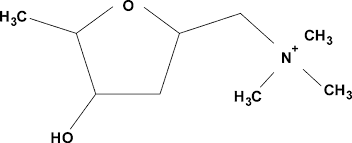
where are the three chiral centers on muscarine
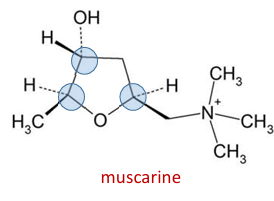
to be a muscarinic agonist, the molecule must have a quaternary N with a ______
positive charge
to be a muscarinic agonist, the molecule must have a ____ with a positive charge
quaternary N
to be a muscarinic agonist, the size of the alkyl groups on the N should NOT excess the size of a ______
methyl group
to be a muscarinic agonist, there should be an ____ atom preferably…
oxygen; ester-like and participating in a hydrogen bond
to be a muscarinic agonist there should be ____ carbons between the oxygen and nitrogen
2
examples of muscarinic agonists
methacholine, carbachol, bethanechol, pilocarpine, donepezil
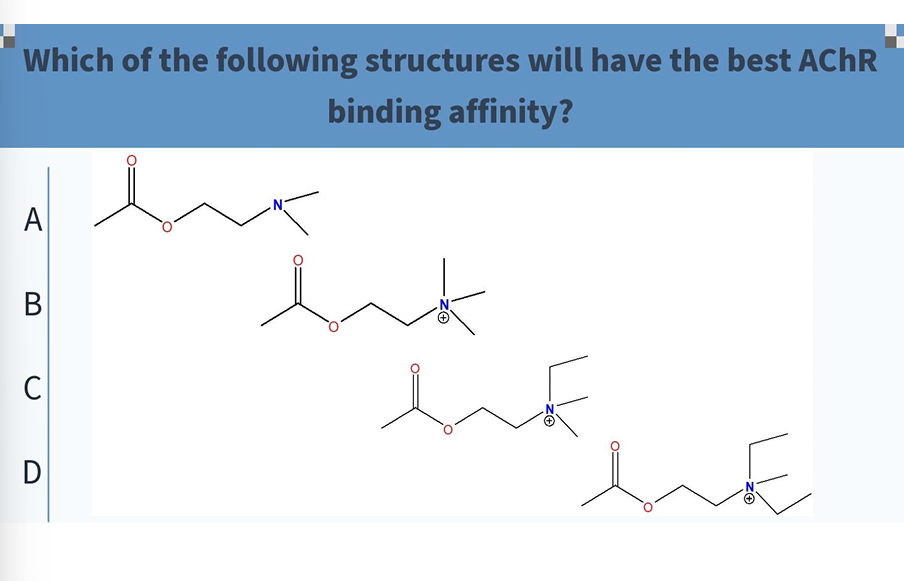
B
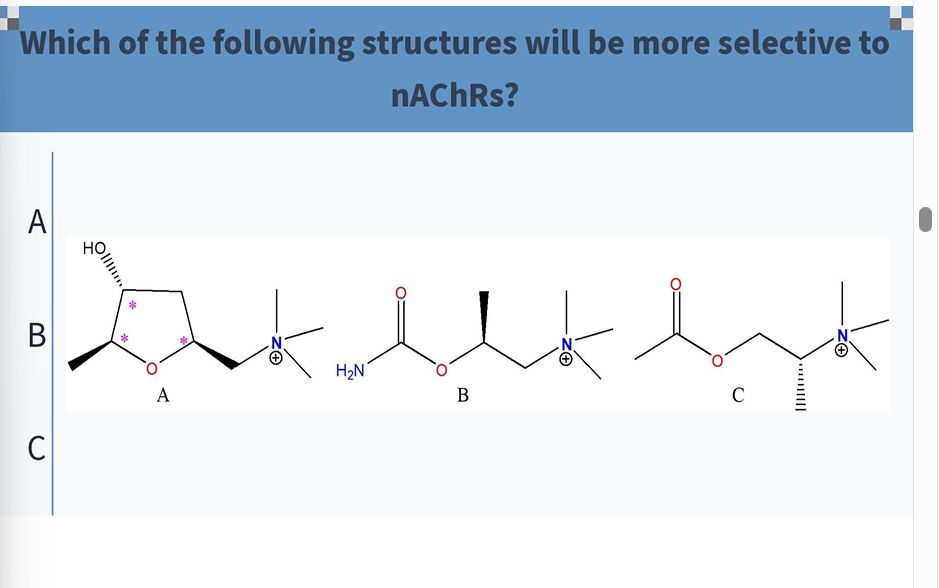
C
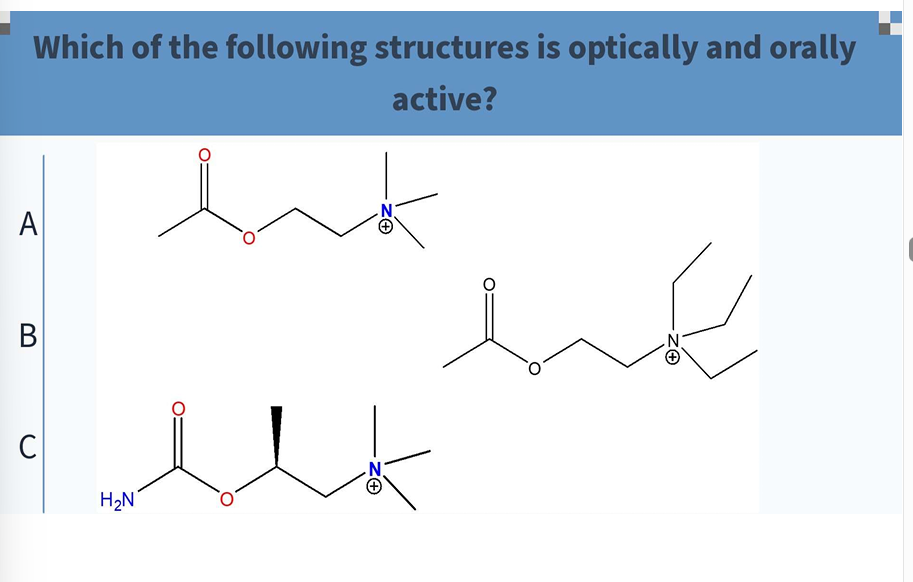
C
pilocarpine has high affinity for ____ receptors
muscarinic
how many chiral centers does pilocarpine have
2
due to pilocarpines lactone group, it undergoes ____ to the inactive pilocarpic acid
hydrolysis
pilocarpine is hydrolyzed to the inactive…
pilocarpic acid
is pilocarpic acid active or inactive
inactive
due to pilocarpines lactone group, base catalyzed epimerization occurs to make _____ which is inactive
isopilocarpine
due to pilocarpines lactone group, ______ occurs to make isopilocarpine which is inactive
base catalyzed epimerization
pilocarpine has issues with…
drug storage and shelf life
AChE inhibitors lead to…
increases the concentration of acetylcholine in the synapse, inducing both muscarinic & nicotinic effects.
classes of physostigmine
AChE inhibitor AND a muscarinic agonist
physostigmine is used to treat
glaucoma and antimuscarinic poisoning
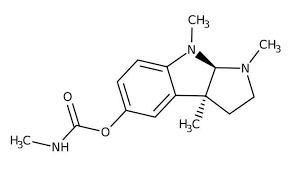
which N of Physostigmine is most basic
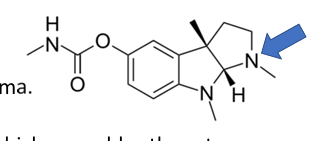
physostigmine is protonated at physiological pH so it can…
bind to the anionic site of AChE
the ____ residue of AChE can attack physostigmine carbamate group & serine OH is carbamoylated
serine
physostigmine inhibition of AChE is an example of
slowly-reversible inhibition (pseudo-irreversible inhibition)
what occurs in slowly-reversible inhibition (pseudo-irreversible inhibition) of AChE via physostigmine
involving covalent bond formation & slow cleavage
When ______ such as physostigmine bind to AChE, hydrolysis of carbamate occurs forming a carbamoylated enzyme
aryl carbamates
The rate of hydrolysis of carbamoylated enzyme is much _____ than hydrolysis of acetylated enzyme
slower
compounds that reversibly bind AChE & slow its AChE hydrolytic reaction can act as _____
AChE reversible inhibitors
which has better AChE binding, alkyl carbamates or aryl carbamates?
aryl carbamates
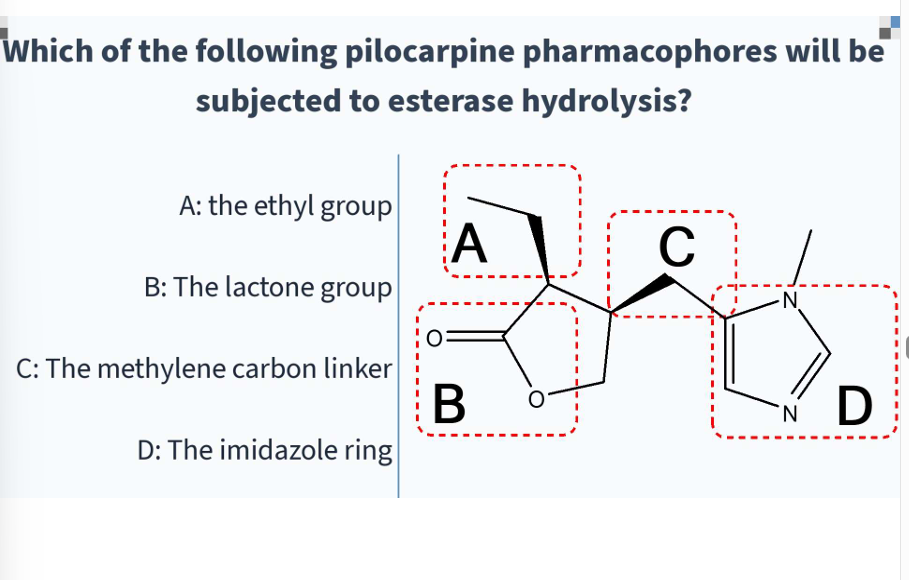
B