PAthomorph- Lect 5 Pathology of Nasal Cavity | Quizlet
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Equine Ethmoidal Progressive Hematomes is common in, what does it cause/characterisation, what's the origin and pathomorph
-C in older horses
-Characterised by chronic, progressive, often unilateral nasal bleeding
-Unknown origin
-PM: single, soft, tumour like dark red mass arising from mucosa of ethmoid bine

Nasal cavity inflammation-Rhinitis usually occurs w what? what is it caused by? what does it result in?
Panasal sinus inflam sinusitis
-changes in balance b/w normal flora of nasal cavity and potential pathogens in nasal cavity
-Disruption of defensive mechanisms and nasal discharge
Serous Rhinitis results in, causes of it are?
-Mildest form
-only hyperemia and swelling with synthesis of watery fluid abundant in protein produced by serous gland present in nasal mucosa
-CAUSES: mild irritants, cold air, early phases of viral infections, mild allergic reactions
Catarrhal Rhinitis results in
-besides hyperemia and swelling also synthesis of exudates abundant in mucus bc of increased activity of goblet cells and mucous glands
-Exudates is thick, translucent, slightly turbid viscous fluid, containing few exfoliated cells, leukocytes and cellular debris
PURULENT RHINITIS, characterised by and causes of it
- characterized by presence of neutrophilic exudates
-exudates is thick, opaque, vary from white to green to brown depending on the cause
-neutrophils can be present within mucosa, submucosa, blood vessels, between epithelial cells and on the mucosal surface
CAUSES: more severe injury usually connected with secondary bacterial infections and tissue necrosis
Fibrinous RHINITIS, characterised by and causes of it
-characterized by presence of exudates abundant in plasma fibrinogen->fibrin
-fibrin=yellow, tan or gray rubbery mat on nasal mucosa and can forms= pseudomembrane (distinct film of exudates
CAUSES: injury that cause a severe increase in vascular permeability to plasma protein
Types of rhinitis
1. serous
2. cattarrhal
3. Purulent
4.Fibrinous
5. Granulomatous
Granulomatous RHINITIS, characterised by and causes of it
-Characterizing by presence of activated macrophages mixed w lymphocytes and plasma cell in nasal mucosa and submucosa
-often inflammatory response lead to formation tumoral lesions that can protrude from nares or to cause obstruction of nasal passage
CAUSES: chronic allergies, infection with specific organisms or foreign bodies
sinusitis characterisation and causes if it
– usually connected or sequel of rhinitis rarely as single entity
-bc of poor drainage exudates often accumulate and cause distension of the sinus and facial deformity
Mucocele- catarrhal inflam
Empyema-purulent inflam
-CAUSES: penetrating wounds, improper dehorning that exposes the frontal sinus, tooth infection in horses and dogs
Nasal tumours occurence
_ Not common in companion animals
-Median Age= 10
PAthomorph of nasal tumours
-usually malignant types with low tendency to metastasis but locally invasive
=adenocarcinomas, fibrosarcomas, osteosarcomas,
chondrosarcomas, lymphomas
- rarely benign types
=papillomas, adenomas
Clinical signs of nasal tumours
-signs attributable to rhinitis but w/out /minimal response to therapy
-chronic progressive unilateral (rarely bilateral) nasal bleeding or/and discharge
-facial deformity, sneezing, dyspnea or difficulties and sound in breathing
-Possible neuro signs
Endemic Ethmoidal Carcinoma occurs in , what is cause, what is pathomorph?
-Sheep, goat, cattle horse pig
-oncogenic retrovirus that cause malignant transformation of surface nasal mucosa epithelium and glands of ethmoidal conchae
PM
-locally invasive, not metastasize
-often occludes the nasal passage and
-deformed facial part of the head
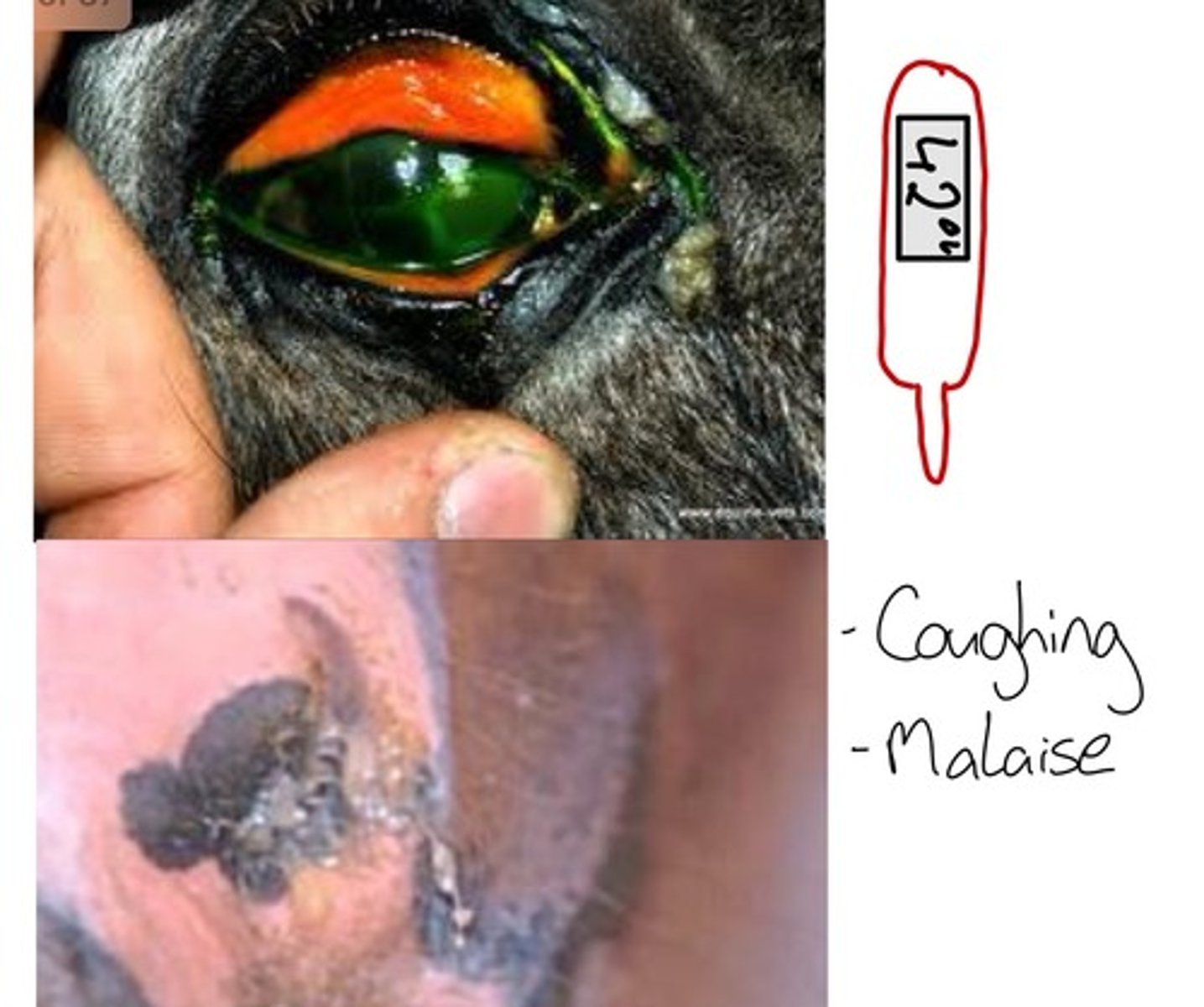
EQUINE VIRAL NASAL INFECTIONS causes, clinically and PM
CAUSES -via aerogenous route
-rhinopneumonitis virus
-influenza virus type A
-adenovirus
-rhinovirus
CLINICALLY
-usually mild and transient infections
-conjunctivitis
-nasal discharge
-malaise, fever, coughing
PM
lesions can be absent
after secondary bacterial infections
Equine Bacterial Nasal Infections include
1. Strangles
2. Glanders
(usually systemic w nasal involvement)
Strangles is causes by, occurrence, clinically
-Streptocoocus equi
-Foals and young Eq
-Cough
-nasal discharge
-Conjunctivitis
-Painful swelling of regional lymph nodes
Strangles Pathomorph
-purulent rhinitis and lymphangitis
-often fistulas at the base of the head
-Inflammation and pus accumulation in guttural pouches
-Poss dissemination of internal organs

Glanders is causes by, occurrence, clinically
-Burkholderia Mallei
-Eq, mules donkeys and carnivores
Glanders Pathomorph
-Pyogranulomatous nodules/ulcers on nasal mucosa
-after healing they form typical star-shaped fibrous scars
-numerous military nodules randomly scattered in the lung parenchyma
-pymogranulomas, draining sinuses in regional lymph nodes
Canine Infectious Tracheobronchitis is also called what and what is it
-Highly contagious infection that manifest by acute onset of coughing
Porcine atrophic Rhinitis causes and clinically
-complex etiology
-Synergist of numerous pathogens that inhibit osteoblastic activity
-Rhinitis w nasal mucopurulent discharge
-Conchae atrophy and assymetry
-Nasal + facial deformity
Oestrosis occurence, cause
-sheep, sporadically goats, dogs and humans
-Oestrus ovis deposit larvae in nostril- large maggot in nasal passage/sinuses- dropped by nares onto the ground--->adult
Oestrosis clinically and PM
-presence of maggot in nasal cavity, sinuses
-purulent and erosive rhinitis and sinusitis
mucopurulent nasal discharge
-sneezing, breath difficulties
-sometimes neurologic signs
Canine rhinitis causes and PM and clinically
-Viruses, bact, fungi, hypersensitivity
PM
-acute to chronic or transient clinical signs
-sneezing, stretor, dyspnea
-serous to mucopurulent and bloody discharge
-lacrimation
-inflammatory lesions in nasal cavity
-Turbinates deformity
NAsal Mycoses causes, manifestation
Aspergilus fumigatus in dogs more common
Cyptocoocus neoformans- in cats more common
-Chronic signs of rhitis
-pain, sneezing
-Ulceration & depigmentation of nares dogs
-Deformity and masses cats
NAsal Mycoses
- Possible destruction of nasal septa
-Masses
Cause of kennel cough, Clinically and PM
Synergism between
-environmental factors
- microbes
Clinical + PM
-catarrhal to purulent rhinitis
-catarrhal to purulent tracheobronchitis
-conjunctivitis
-enlargement of tonsils and regional lymph nodes
- bronchopneumonia or pneumonia after secondary bacterial infection
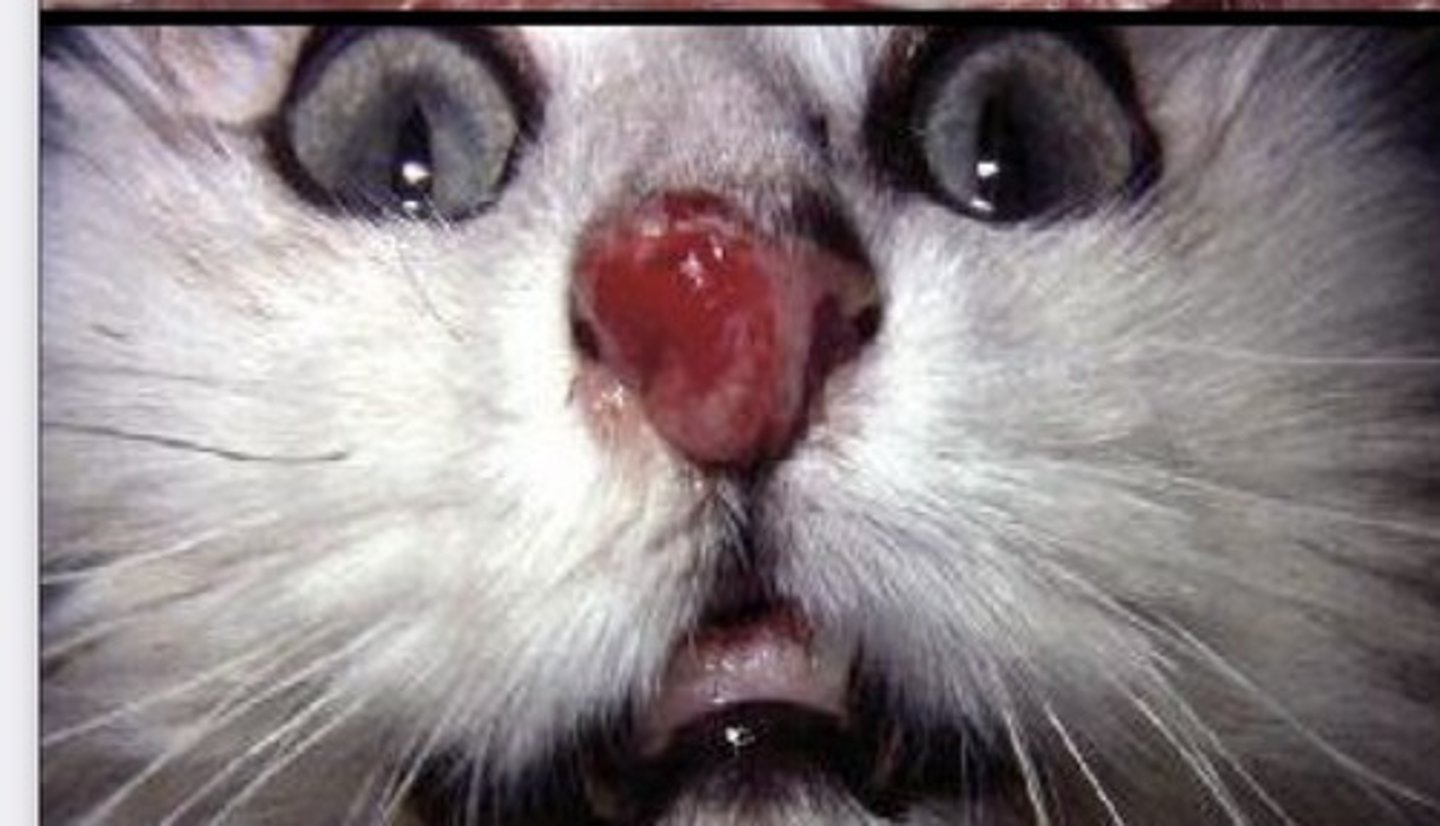
Feline Viral Rhinotracheitis is common in, caused by
-Young kittens
-FHV1, FCV, chlamydia felis, mycoplasma felis
-Ocular and nasal discharge
-Sneezing, lethargy & anorexia
-Corneal ulcers
-Bronchopneumonia
Laryngeal Paralysis/Hemiplegia is, cause and pathomorph
-Roaring atrophy of lateral and dorsal crico-arytenoid muscles, esp on left side
Causes- denervation, secondary nerve damage, unknown
Clinically- roaring during exercise
-Laryngeal muscles smaller and paler
Tracheal collapse and stenosis is, occurrence, PM
-Segmental reduction of tracheal lumen or narrowing of entire length of trachea
Occurence
-Toy, horse, cattle & goats
PM in dog
-Dorsalventral flattening of tracheal lumen
-Horse narrowing is lateral