auto ganglionic blockers
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
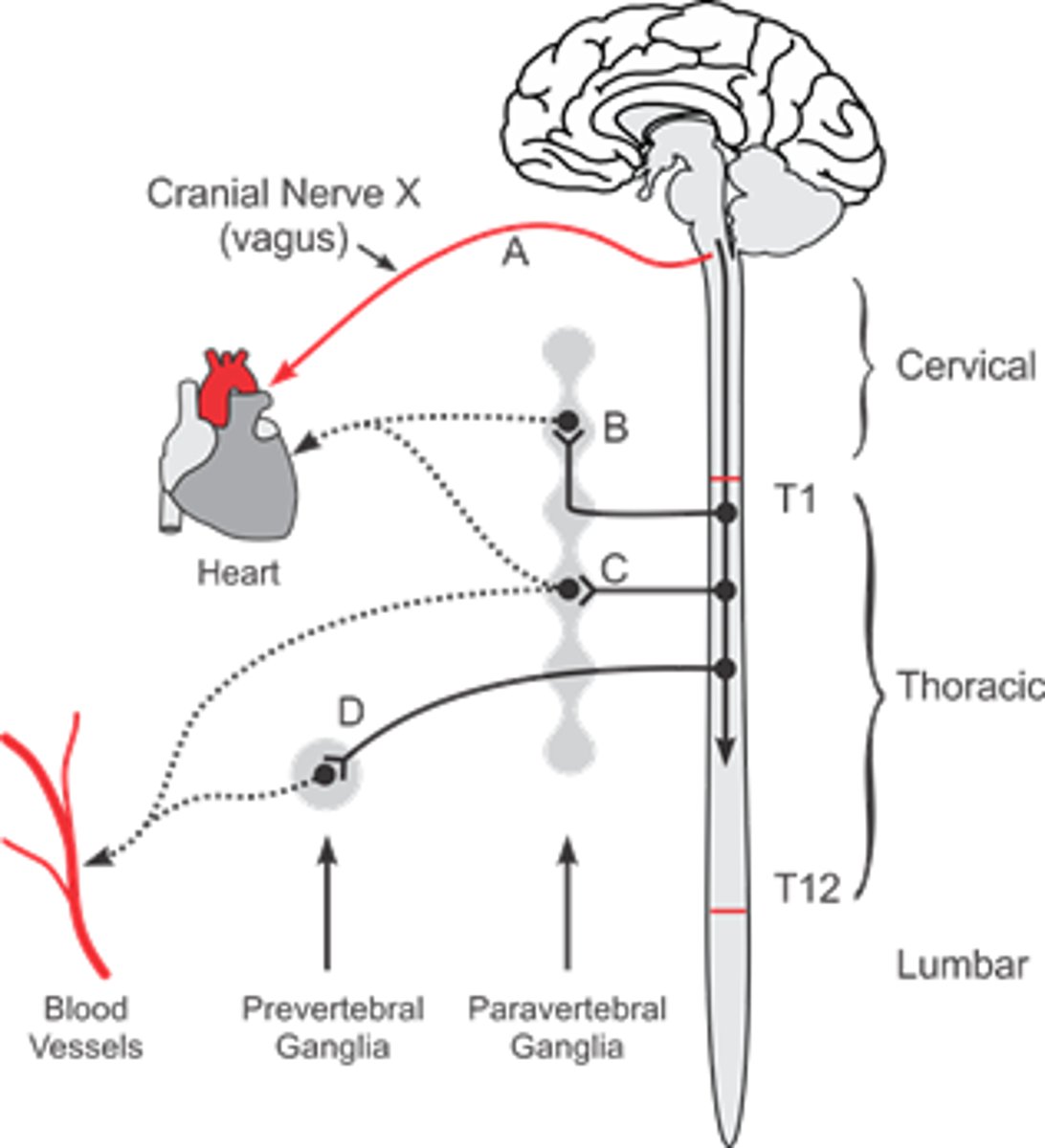
sympathetic NS has _________ outflow, with ganglia ________ from target organs
parasympathetic NS has __________ outflow, with ganglia ________ from target organs
symp= thoracolumbar; far from target/ close to spine
para= cranial sacral; close to target organ/ further from spine
paravertebral vs prevertebral ganglia
- both sympathetic
Paravertebral ganglia= close to spinal cord (sympathetic chain) give rise to post ganglionic fibers
prevertebral= front of aorta/ abdomen; "collateral" ganglia
what kind of receptors are found in ganglia?
nicotinic ACh receptors= ligand-gated (ACh) channels that become permeable to sodium (major) and calcium (minor) when activated
when nicotinic receptors are activated by a ligand (ACh), what do they become permeable to
1. primarily sodium
2. secondarily calcium
t/f: nicotinic receptor subunits have low diversity amongst ganglia
false. subunit composition is very diverse among nicotinic receptors in CNS and ganglia
when ACh is released from pregang neurons, it activates nicotinic receptors leading to _________ of postgang neurons and ______
a. hyperpolarization
b. depolarization
c. repolarization
b. depolarization
= excitatory post synaptic potential (EPSP)
Excitatory post synaptic potential (EPSP)
after ACh activates nicotinic receptor-> small post synaptic potential that makes the neurons more likely to fire an action potential (decays over time, need large EPSP for AP)
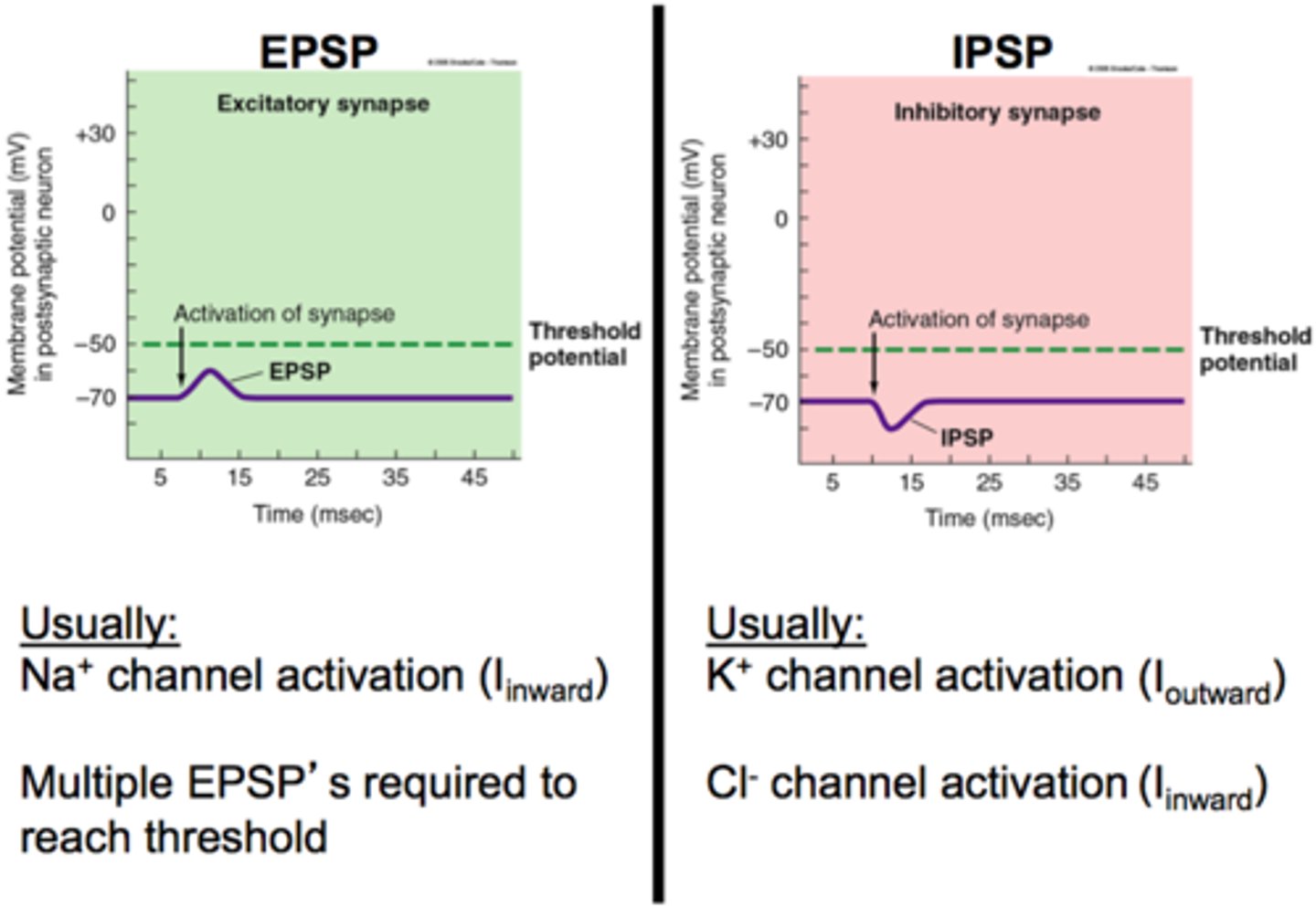
t/f: IPSP and secondary slow EPSPs are not mediated by nicotinic neuronal receptors
true, mediated by M2 and neuropeptides
summarize the electrophysiology of ganglionic transmission (how is neuronal electricity mediated? one receptor or multiple?)
- negative resting potential
- ACh binds= depolarization= EPSP may lead to action potential if threshold reached (mediated by Nn)
- IPSP follows action potential (mediated by M2, then EPSP follows (mediated by M1)
- late slow EPSP mediated by neuropeptides
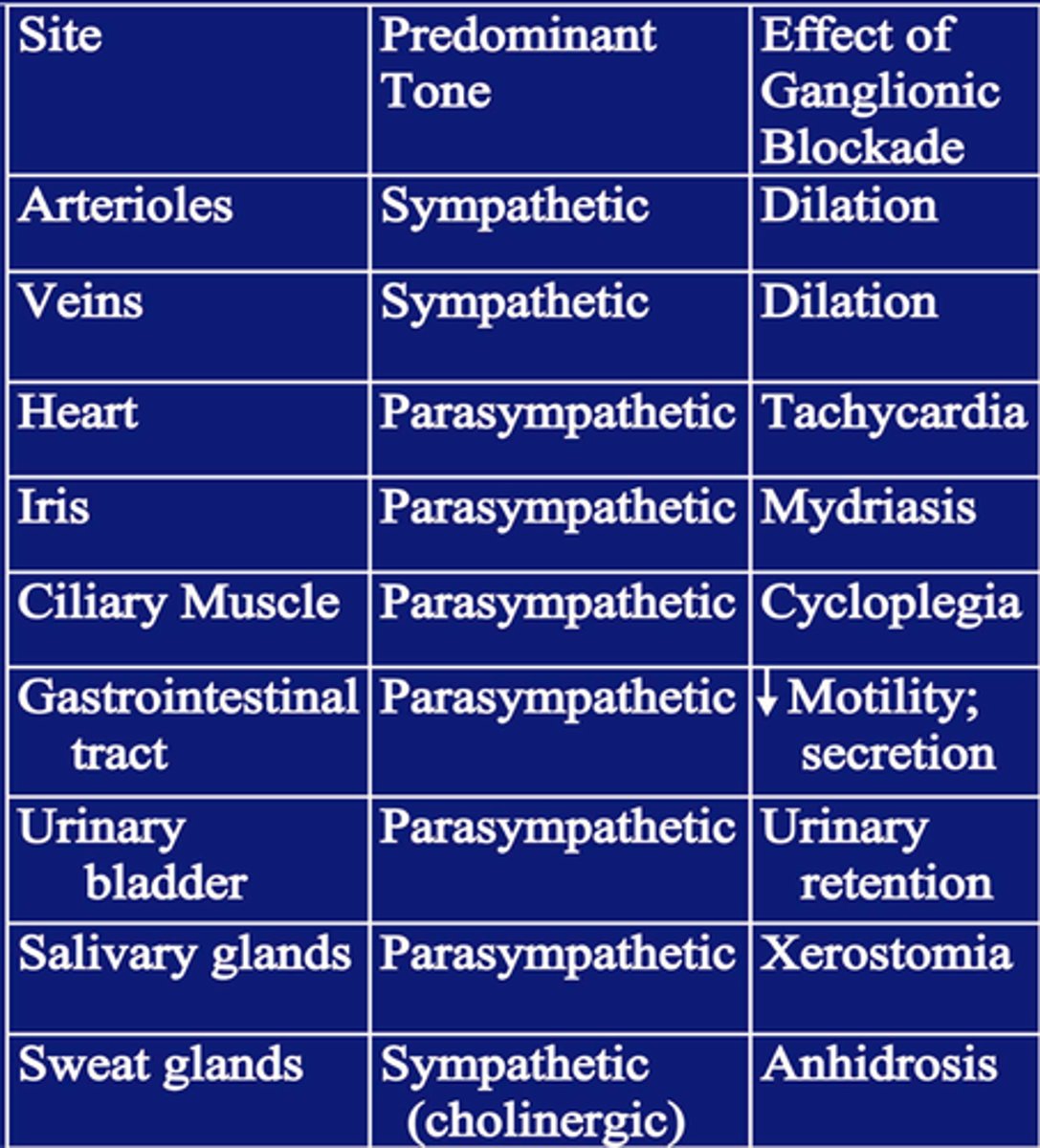
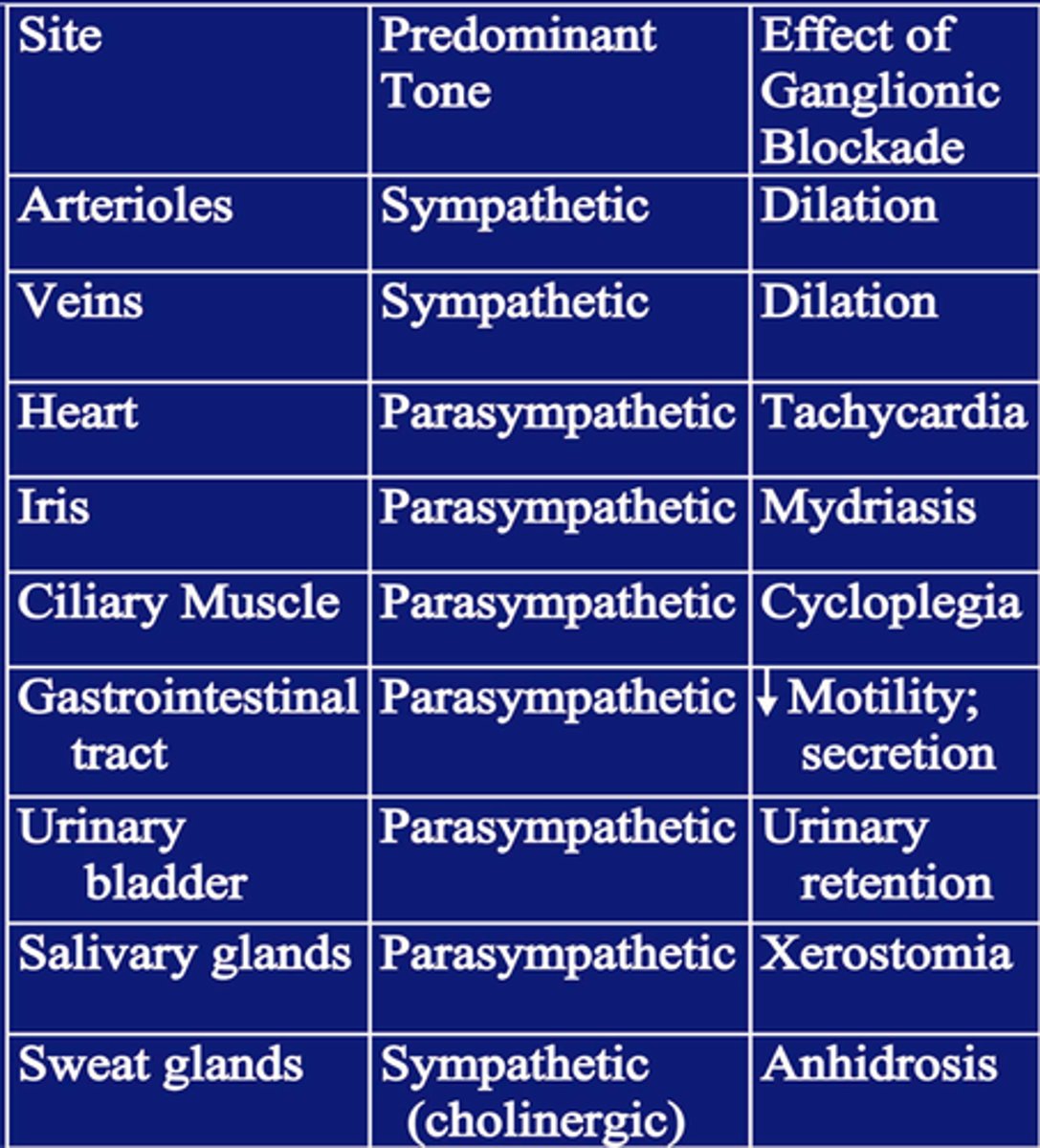
predominant tone of arterioles/veins
sympathetic
predominant tone of heart, eye, GI, urinary bladder
parasymp
hexamethonium
blocks the CHANNEL associated with Nn receptors, blocking ganglionic transmission
(does not reach CNS)
trimethaphan
competes w ACh for ACh binding site on Nn receptors, blocking ganglionic transmission
(does not reach CNS)
mecamylamine
competes w ACh for ACH binding site on Nn receptors, blocking ganglionic transmission (same as trimethaphan)
BUT this can get through BBB and enter CNS!!!
which ganglionic blocker can get past BBB and reach CNS due to its lipophilicity?
mecamylamine
what would happen to a patient with normal cardiovasc function if given a ganglionic blocker?
- ganglionic blocker would stop transmission of both parasymp and symp
arterioles, veins, sweat glands (sympathetic)= vasodilation, drop in bp, postural hypotension, blood pooling= lower CO, anhidrosis
heart, GI, bladder, salivary, eye (para)= tachycardia, atony in GI/bladder, xerostomia, cycloplegia
why would ganglionic blockers lead to mild tachycardia and lower cardiac output
-heart has parasympathetic predominant tone, so blocking it would increase HR
- veins have symp tone, blood pooling means not enough reaching heart= lower CO
t/f: ganglionic blockers block both Nn and Nm
false. only Nn (neuronal)
t/f: nicotine has potential opposing effects on Nn seen as receptor stimulation and receptor desensitization
true. if too much nicotine, it may desensitize Nn receptors (protective effect), or it may work and stimulate receptors
(remember ACh has AChE to prevent too much, but nicotine is exogenous so we can have too much)
what were ganglionic blockers initially used as?
lower bp, treat acute hypertensive crisis (but too many side effects, not rlly used now)