Incomplete Dominance and Codominance
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Exceptions to Mendel’s principles
Some alleles are neither dominant nor recessive
Instead show “blending,” or differential expression in different parts of the organism.
Polygenic traits
Incomplete dominance
No allele is dominant over the other
Both alleles are expressed in each and every cell that carries them
When both alleles are present a “new” phenotype appears that is a blend of each allele.
Alleles will be represented by capital letters with superscripts.
According to Mendel, What happens when a red flower is crossed with a white flower?
Some white and some red or
All offspring red (if red is dominant) or
All offspring white (if white is dominant)
Sickle Cell Anemia
An inherited blood disorder
Oxygen circulation is diminished due to defective haemoglobin (Hb)
Haemoglobin is coded for by 2 different alleles
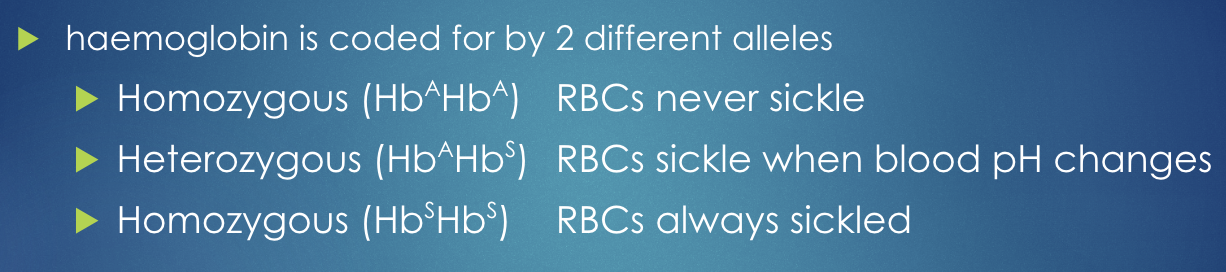
Codominance
ONE allele is expressed in each and every cell that carries the two alleles but which allele is expressed alternates between cells
Produces patches, stripes, variegation in colour
Alleles will be represented by capital letters with superscripts.
Multiple Allele Inheritance
One gene for the characteristic BUT two or more alleles exist in the population.
The alleles continue to be related:
dominant,
recessive,
incompletely dominant, or
codominant
The human blood types (phenotypes)
A
B
AB
O
A and B are codominant to each other
Both A and B are dominant over O

How are human blood types classified?
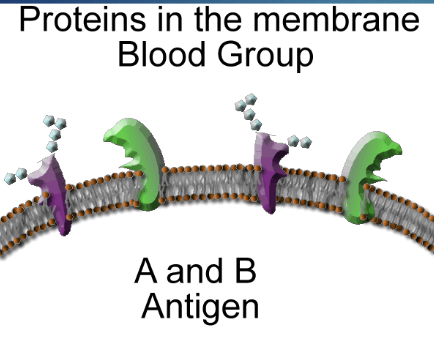
Classified based on the specific agglutinogens on the surface of red blood cells (erythrocytes)
We designate agglutinogens as A or B
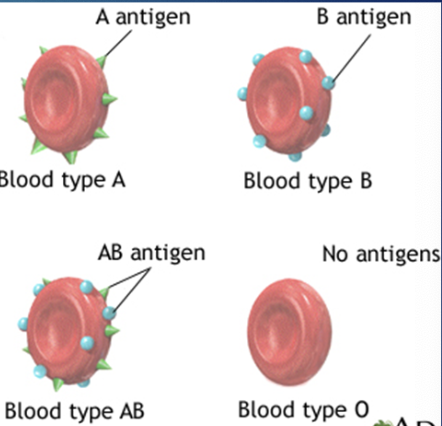
Agglutinogens
Antigens found on the surfaces of red blood cells
Antigens
Structures on cells surfaces that can cause a immune response in the body
Antibody
A large, Y-shaped protein made by plasma cells that is used by the immune system to neutralize foreign pathogens like bacteria or viruses
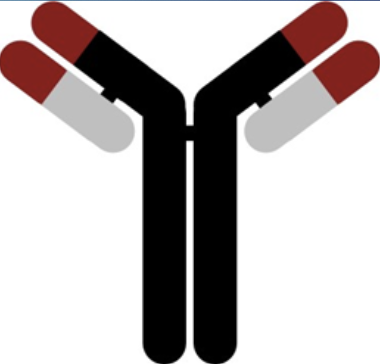
Human blood types- how do humans develop antibodies against antigens not on their own red blood cell?
someone with:
blood type A will develop anti-B antibodies
blood type B will develop anti-A antibodies
Blood type AB will develop neither antibody
type O will develop both anti-A and anti-B antibodies
What happens if incompatible blood is given in a transfusion?
Donor cells are treated as foreign invaders (since plasma antibodies attach to matching surface proteins) and the patient's immune system attacks them accordingly.
Blood transfusion is useless and a potentially massive activation of the immune system and clotting system (agglutination) can cause shock, kidney failure, circulatory collapse, and death.
Type A Blood
Allele = IA
Blood cells have small antigens on the surface.
Type B Blood
Allele = IB
Cells coated with type B antigens
Type AB Blood
genotype = IAIB
Blood cells contain both types of antigens
Known as universal recipient
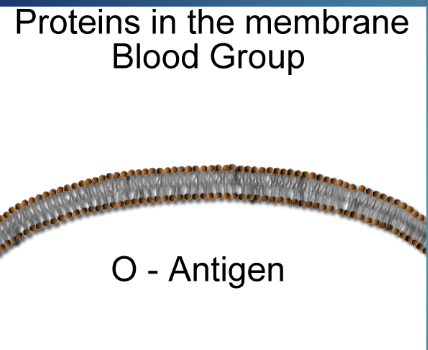
Type O Blood
Allele = i
No antigens on the surface of the blood cells
Known as universal donor
Polygenic Traits
Traits controlled by two or more genes.
(I.e. Human height, eye and skin colour)