E2: ortho practice questions
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
b. Valgus stress test
Which of the following tests is performed by pushing on the lateral aspect of the knee & trying to open the MCL?
a. Varus stress test
b. Valgus stress test
c. McMurray's Test
d. Clarke sign
c. LCL injury
What does a + Varus stress test indicate?
a. ACL injury
b. MCL injury
c. LCL injury
d. Meniscus injury
a. ACL tears/injuries
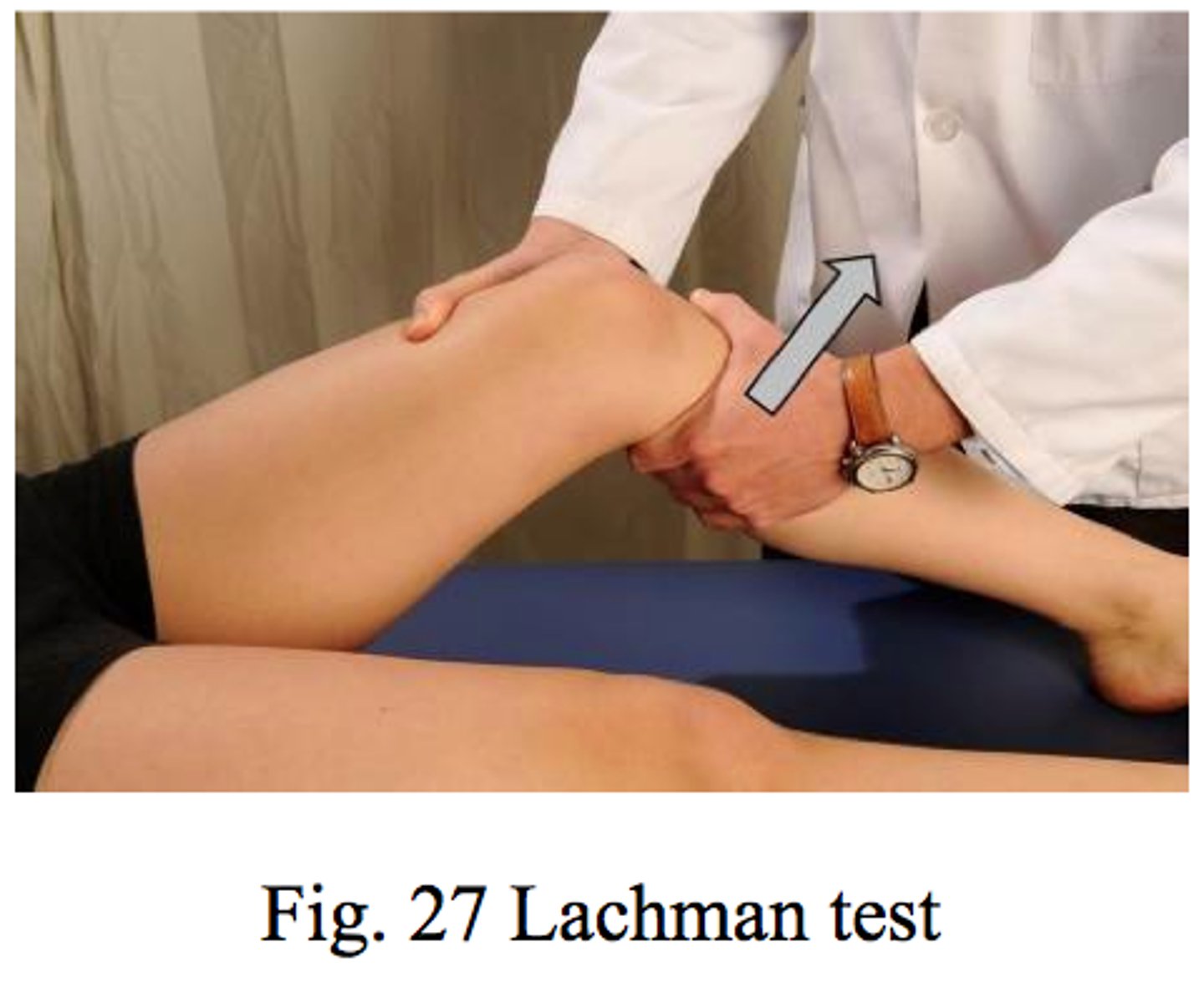
What does the Lachman test look for?
a. ACL tears/injuries
b. MCL tears/injuries
c. LCL tears/injuries
d. Meniscus tears/injuries
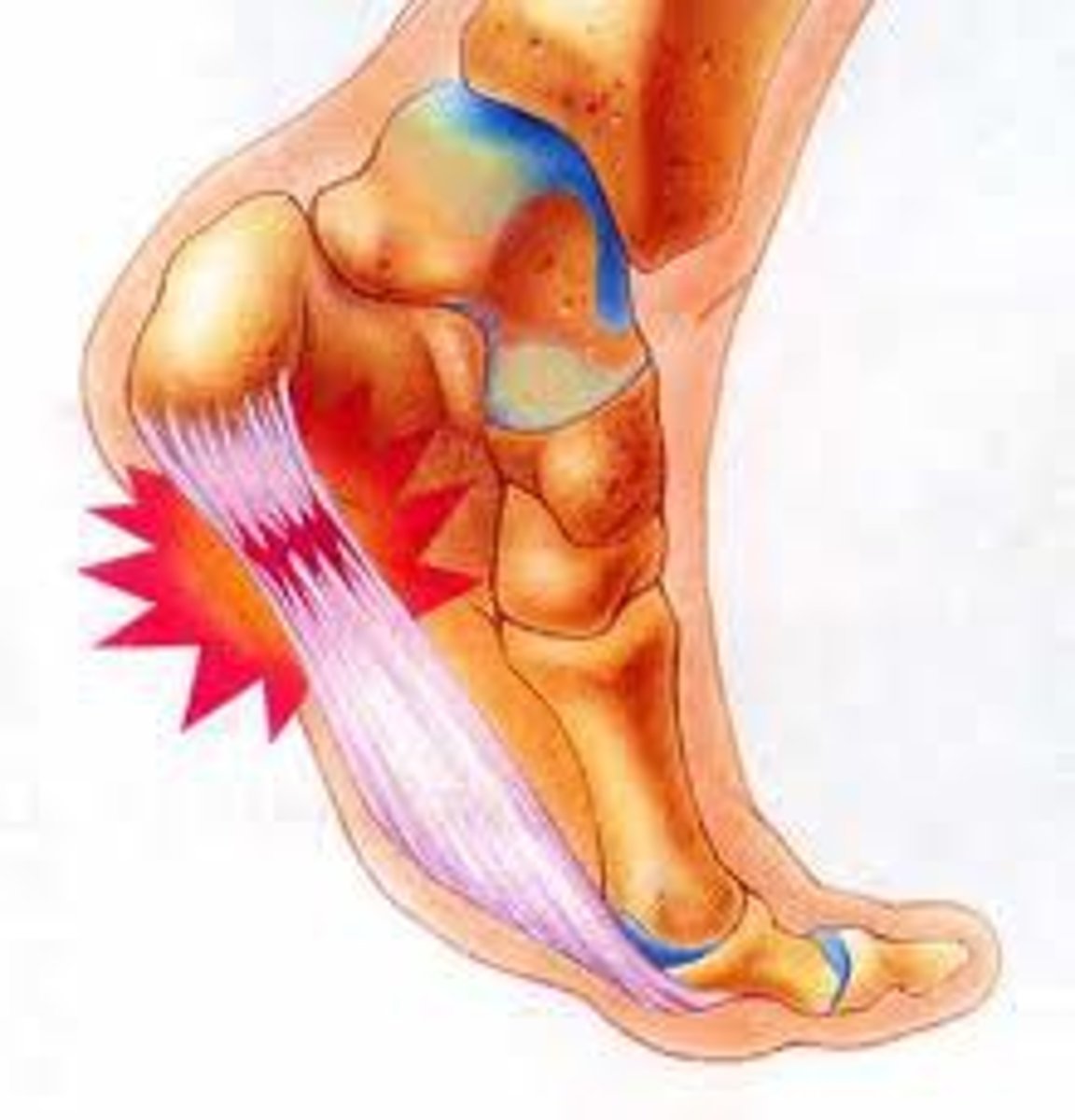
d. Pain in the AM with 1st step
How do pts with plantar fasciitis present?
a. Pain with exercise
b. Pain going downstairs
c. "Freezing" phase of pain
d. Pain in the AM with 1st step
b. ACL, MCL, meniscus
Which of the following describes the unhappy triad?
a. MCL, LCL, meniscus
b. ACL, MCL, meniscus
c. ACL, MCL, LCL
d. ACL, LCL, meniscus
d. MRI
(Stress fx = hairline or microscopic break in a bone caused by microtraumatic, cumulative overload on bone)
What type if imaging is best for viewing stress fractures?
a. DEXA
b. X-ray
c. CT
d. MRI
b. MRI
What type if imaging can confirm the dx of a rotator cuff injury?
a. CT
b. MRI
c. X-ray
d. DEXA
a. Patellofemoral syndrome
(also will have edema behind the knee)
Which of the following is associated with "pain going downstairs?"
a. Patellofemoral syndrome
b. Shin splints
c. Stress fractures
d. Osgood schlatter's
c. Base of the 5th metatarsal
Where does a Jones fracture occur?
a. Distal portion of the 5th metatarsal
b. Distal portion of the 5th metacarpal
c. Base of the 5th metatarsal
d. Base of the 5th metacarpal
tennis; extension
Lateral epicondylitis is also known as (golfer's/tennis) elbow; these pts feel pain with (flexion/extension)
golfer's; flexion
Medial epicondylitis is also known as (golfer's/tennis) elbow; these pts feel pain with (flexion/extension)
c. Apley's test
(this test assesses for meniscus damage)
Which of the following is NOT a special test that can be performed for carpal tunnel syndrome?
a. Phalen's test
b. Durkin's test
c. Apley's test
d. Tinel's sign
c. Nursemaid's elbow
(most common in preschool age kids 1-4 y/o; radial head subluxation)
A 2 year old female presents crying with pain in her elbow & refusing to move her arm. She was holding hands with her dad while walking in the park, but then she decided that she wanted to pull away to pet a dog (don't blame her), which led to her injury. What dx are you thinking?
a. Lateral epicondylitis
b. Medial epicondylitis
c. Nursemaid's elbow
d. Monteggia fracture
d. Colles fracture
(this is the most common distal wrist injury)
A 70 y/o female falls on her outstretched hand, leading to the dorsal angulation of her distal radius. X-ray shows a "dinner fork" deformity. What type of fracture has occurred?
a. Scaphoid fracture
b. Smith fracture
c. Boxers fracture
d. Colles fracture
b. Anatomical snuffbox tenderness is present
Which of the following is associated with a scaphoid fracture?
a. Can be limb threatening
b. Anatomical snuffbox tenderness is present
c. Can be diagnosed using Phalen's test
d. Caused by falling on an outstretched hand
c. Reduce
(if fracture is OPEN --> immediate ortho surgery consult)
A 25 y/o male presents to the clinic with extreme pain & swelling in his hand. He got in a fight with his sister & was so angry that he couldn't help himself, so he punched a wall. He is diagnosed with a boxer fx with >25-30 degrees of angulation. What should we do for this pt?
a. Amputation
b. Place rods & screws (surgery)
c. Reduce
d. Refer to PT
b. 50 y/o female with T1DM
(W>M; 40-60 y/o; Type 1 DM)
Which of the following pts is most likely to present with adhesive capsulitis?
a. 50 y/o male with HTN
b. 50 y/o female with T1DM
c. 55 y/o male with T2DM
d. 70 y/o female with HTN
a. Thompson's test
(dx is an Achilles tendon rupture)
A 35 y/o male presents after playing a long soccer game & reports that he felt a "pop." Now he can't stand on his tip toes of the affected side. What special test should we perform on him?
a. Thompson's test
b. Lachman test
c. Anterior Drawer test
d. Posterior Drawer test
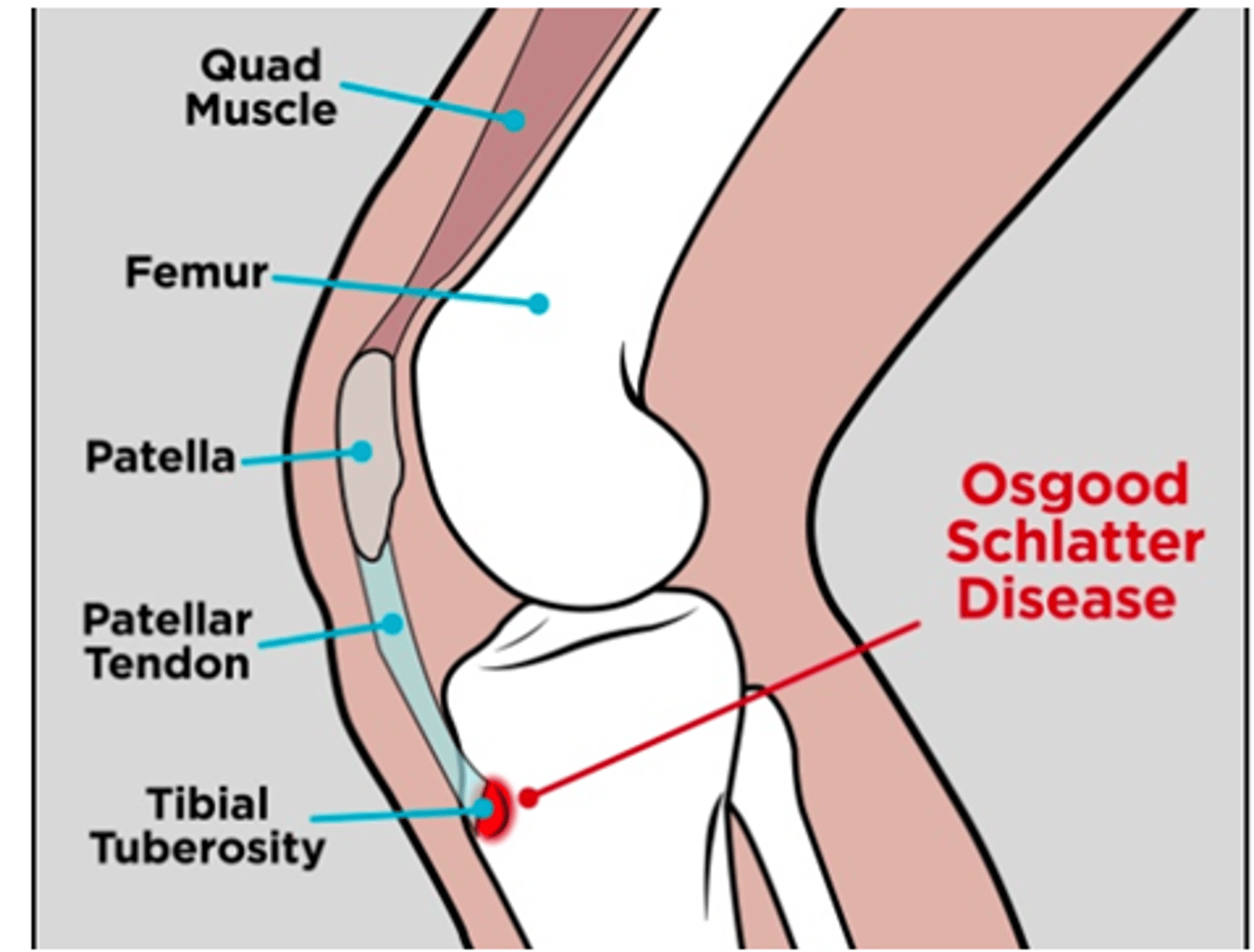
d. An 18 year old male who plays soccer
(adolescent athlete)
Who is most likely to have Osgood Schlatter's?
a. A 75 y/o female who is a retired basketball player
b. A 66 y/o male who plays at the park with his grandchildren
c. A 25 y/o female who is a PA
d. An 18 y/o male who plays soccer
d. Pilon fx
Which of the following is defined as an oblique, comminuted fx of the distal tibia that extends through the tibiotalar articular surface (into the joint)?
a. Jones fx
b. Fibula fx
c. Monteggia fx
d. Pilon fx
a. I
AC ligaments are partially disrupted & the CC ligaments are intact. What grade of AC separation does this describe?
a. I
b. II
c. III
d. IV
b. II
AC ligaments are torn & the CC ligaments are intact. Partial separation of the clavicle from the acromion. There's AP & vertical instability. What grade of AC separation does this describe?
a. I
b. II
c. III
d. IV
c. III
CC ligaments are completely disrupted & there's complete separation of the clavicle from the acromion. What grade of AC separation does this describe?
a. I
b. II
c. III
d. IV
b. De Quervain's tenosynovitis
A + Finkelstein's test indicates which of the following?
a. Radial head fx
b. De Quervain's tenosynovitis
c. Dupuytren's contracture
d. Distal radius fx
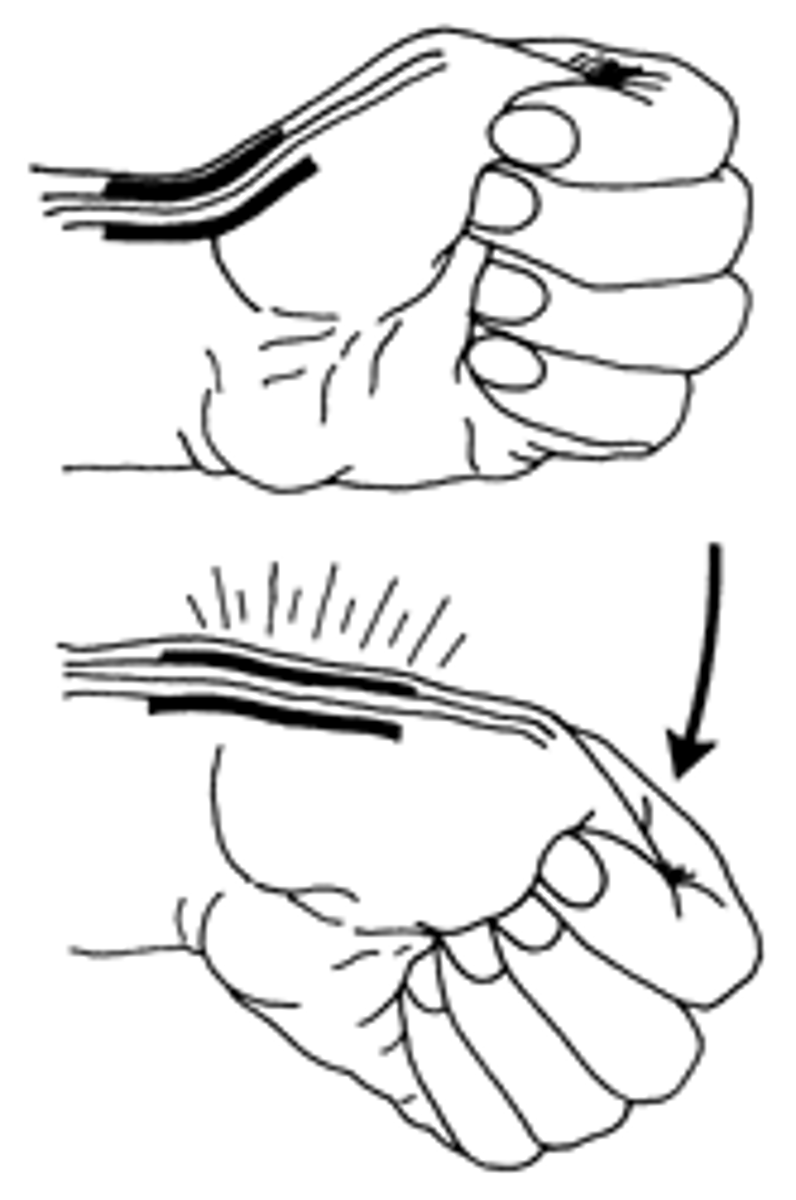
c. Anterior drawer has knee flexed at 90, Lachman has knee flexed at 30
What is the main difference b/t the Lachman test & the Anterior Drawer test?
a. Anterior drawer has knee flexed at 90, Lachman has knee flexed at 45
b. Anterior drawer has knee flexed at 45, Lachman has knee flexed at 90
c. Anterior drawer has knee flexed at 90, Lachman has knee flexed at 30
d. Anterior drawer has knee flexed at 30, Lachman has knee flexed at 90
a. Fasciotomy
Acute Compartment syndrome is a medical EMERGENCY. What is a tx option for this condition?
a. Fasciotomy
b. NSAIDS
c. RICE
d. Cast immobilization
d. Dupuytren's contracture
Which of the following is a genetic predisposed fibrosing disorder that causes contracture of the palmar fascia due to nodules & cords at the MCPs & PIPs?
a. Carpal tunnel syndrome
b. De Quervain's tenosynovitis
c. Boutonniere deformity
d. Dupuytren's contracture
b. 40
With a Boxer's fracture, ____ degrees of volar angulation is the greatest amount consistent with a good functional result.
a. 30
b. 40
c. 70
d. 90
d. Drop arm test
Which of the following special tests assesses for supraspinatus muscle tendonitis or tear?
a. Empty can test
b. Lift off test (IR lag sign)
c. ER lag sign
d. Drop arm test
a. Cast immobilization of the finger
(with corticosteroid injections, be sure to AVOID THE TENDON; can offer a 2nd injection if sx persists; surgery = last resort)
Which of the following is NOT a tx option for trigger fingers?
a. Cast immobilization of the finger
b. Corticosteroid injections into the tendon sheath
c. Surgical release
d. NSAIDS
d. Tinel's test
Which special test is being described?
Percussion of the median nerve at the carpal tunnel may reproduce pain & tingling along the median nerve distribution
a. Phalen's test
b. Drop arm test
c. Durkin's test
d. Tinel's test
d. Rotator cuff tear
A 62 y/o male presents to the clinic with shoulder pain that's worse at night. Yesterday he tried throwing a ball with his son, but he felt an uncomfortable catching sensation, so he decided to stop. What dx does this pt likely have?
a. Carpal tunnel syndrome
b. Proximal shoulder dislocation
c. Distal shoulder dislocation
d. Rotator cuff tear
a. Gradual onset of pain in the anteromedial aspect of the proximal ⅓ of leg
(not proximal-- distal!)
Which of the following is NOT true about shin splints?
a. Gradual onset of pain in the anteromedial aspect of the proximal ⅓ of leg
b. Associated with pes planus with overpronation
c. Tx includes rest & ice, massage, analgesic creams, exercises
d. Commonly results from running on hard, uneven surfaces
c. Transtibial
(= below knee or BKA)
If you cannot avoid amputation, what type of amputation is the better one to have?
a. Knee Disarticulation
b. Hindfoot
c. Transtibial
d. Transfemoral
c. Diabetes
(Other leading causes: severe infxns, PVD)
Which of the following is a leading cause of amputation?
a. Congenital deformities
b. Trauma
c. Diabetes
d. Tumors
b. ulnar
Which of the following nerve injuries is most commonly associated with a distal humeral fx?
a. radial
b. ulnar
c. median
d. axillary
d. axillary
Which of the following nerves is most commonly injured with a shoulder dislocation?
a. radial
b. ulnar
c. median
d. axillary
b. Hawkin's & Neer's
Which 2 special tests are used to detect shoulder impingement?
a. Phalen's & Tinel's
b. Hawkin's & Neer's
c. Neer's & Phalen's
d. Durkin's & Phalen's
radial head
A nursemaid's elbow is described as a pulled elbow, annular ligament entrapment, & _____ _____ subluxation.
b. Ankle sprains
What is the most common injury in sports?
a. Ankle strains
b. Ankle sprains
c. ACL tears
d. Meniscus tears
d. Popliteal artery injury
(any vascular compromise --> consult vascular surgery stat)
What is the most dangerous potential complication following a tibiofemoral dislocation (aka knee dislocation)?
a. MCL tear
b. Osgood Schlatters
c. Axillary artery injury
d. Popliteal artery injury
b. Stress fxs
(plain films used to r/o fx)
What do you expect to see on a bone scan of someone with Osgood Schlatters?
a. Multiple tibiofemoral fxs
b. Stress fxs
c. Medially displaced patella
d. Laterally displaced patella
b. Distal fibula fx
A sprained ankle is the result of a...
a. Proximal fibula fx
b. Distal fibula fx
c. Proximal tibial fx
d. Distal tibial fx
a. B/t the 3rd & 4th metatarsal head
Morton's neuroma is a painful neuroma that causes severe burning pain, which increases with activity & decreases with removal of shoes. Where is it MOST COMMONLY located?
a. B/t the 3rd & 4th metatarsal head
b. B/t the 4th & 5th metatarsal head
c. B/t the 3rd & 4th metacarpal head
d. B/t the 2nd & 3rd metacarpal head
b. Refer to ortho for surgical repair
How do we tx an achilles tendon rupture?
a. NSAIDS
b. Refer to ortho for surgical repair
c. Cast immobilization
d. Wrap tightly in a compression bandage
ECRB
Lateral epicondylitis produces pain over the _____ muscle at the lateral epicondyle of the humerus.
a. Fat pad & sail sign
What will you see in the x-ray of a pt with a radial head fx?
a. Fat pad & sail sign
b. Lateral displacement of the radius
c. Arthritis of the nearby joints
d. Nothing, it should be WNL
b. MCL rupture
Which of the following is NOT involved in the terrible triad of elbow dislocations?
a. Radial head fx
b. MCL rupture
c. Coronoid fx
d. LCL rupture
d. If open fx
When is an immediate ortho surgery consult necessary with a Boxer's fx?
a. If >25 degree angulation
b. If >40 degrees angulation
c. If 70-90 degrees angulation
d. If open fx
b. Buckle fx
What type of distal radius fx is common in peds?
a. Barton fx
b. Buckle fx
c. Chauffeur's fx
d. Die-punch fx
d. Avulsion of the extensor tendon at the distal insertion
Which of the following describes a mallet finger?
a. Hyperextension of PIP Joint with flexion of DIP joint
b. Flexion of PIP joint from unopposed pull of flexor tendon
c. Avulsion of the extensor tendon at the proximal insertion
d. Avulsion of the extensor tendon at the distal insertion
c. EMG/NCV
What is the most useful diagnostic test for carpal tunnel syndrome?
a. X-ray
b. MRI
c. EMG/NCV
d. Bone scan
shoulder
Hill-Sachs lesion is commonly associated with a ________ dislocation.
b. Leads to wrist drop
(correct answers:
a. Also called Saturday night palsy
c. Results in loss of function in the extensors
d. Caused by a fx to the midshaft of the humerus)
Which of the following is TRUE about radial nerve palsy?
a. Also called Friday night palsy
b. Leads to wrist drop
c. Results in loss of function in the flexors
d. Caused by a fx to the midshaft of the radius
b. Eliminating or modifying activities
What is the most important tx for lateral epicondylitis?
a. Ortho consult for surgery
b. Eliminating or modifying activities
c. Splting/Casting
d. NSAIDS
a. anterior compartment syndrome
acute --> emergency fasciotomy
A 29 year old male patient presents to the ortho clinic with pain in his shin after a tibia fracture. He reports paresthesias down his leg. On exam you note paleness and a diminished tibia pulse. There is pain on passively stretching the extensor hallucis longus muscle. What is the diagnosis?
a. anterior compartment syndrome
b. lateral compartment syndrome
c. deep posterior compartment syndrome
d. superficial compartment syndrome
d. increased exercise
shin splints
What is the most common cause of medial tibia stress syndrome?
a. decreased exercise
b. sitting long periods of time
c. acute trauma
d. increased exercise
d. surgery
What treatment option is not indicated for shin splints?
a. RICE
b. NSAIDs
c. orthotics
d. surgery
c. MRI
MRI confirms stress fractures. plain films may not show anything until 3 weeks after injury, bone scan shows inc uptake but MRI confirms!!! shin splints have normal xray
A marathon runner presents to the clinic complaining of pain on the anteromedial aspect of the distal 1/3 of the leg. On PE there is pain with resisted plantar flexion and inversion. What imaging modality will differentiate between stress fracture and shin splints?
a. plain films
b. CT
c. MRI
d. bone scan
a. Valgus stress test
varus tests LCL by placing pressure medially
Which special test assess the MCL by applying pressure to the lateral aspect of the knee to check for instability?
a. Valgus stress test
b. Varus stress test
c. McMurray's test
d. Lachman test
c. MRI
meniscal tear tx w/ PT, bracing, NSAIDs, surgery if severe
A 41 year old female presents to the clinic with right knee pain for 2 days. On history she states that she turned awkwardly the other day and since then her medial aspect of her right knee has been hurting. On exam you note tenderness when palpating the medial aspect of her knee joint. Forced flexion elicits pain as well. What test would you want that is most accurate for meniscal injuries?
a. plain films
b. CT
c. MRI
d. bone scan
d. McMurray
McMurray's test is performed with the patient supine and relaxed. The knee is flexed maximally, with external tibial rotation (medial meniscus) or internal tibial rotation (lateral meniscus)
What special test would you suspect be positive in a patient with a meniscal tear?
a. posterior drawer
b. anterior drawer
c. Lachman test
d. McMurray
c. PCL tear
ACL + MCL + meniscus
Which of the following is not part of the unhappy triad?
a. ACL tear
b. MCL tear
c. PCL tear
d. meniscal tear
b. Lachmans, ACL
A 23 year old on a ski trip presents to the urgent care clinic after having what he describes as trauma to his knee while skiing. He states that he noticed a popping like feeling and his knee gave out. On exam you note swelling and pain when the patient walks. You have the patient lie supine, flex their knee to about 30 degrees, stabilize the femur and pull the tibia anteriorly. The tibia translates anteriorly of the femur. What special test is this and what injury does the patient have?
a. anterior drawer, ACL
b. Lachmans, ACL
c. posterior drawer, PCL
d. Lachmans, PCL
a. posterior drawer
PCL injury
A football player presents to the clinic with severe knee pain after getting taken out at the knee in a football game. When you gather history he says "the guy just ran at me head on and took me out at the knee." On exam you note swelling and pain on the posterior portion of the knee. What special test would you expect to be positive based on his presentation?
a. posterior drawer
b. anterior drawer
c. Lachman test
d. McMurray
b. male sex
more common in females
lateral dislocation MC
+ apprehensive test
Which of the following does not put someone at risk for a patellar dislocation?
a. excessive Q angle
b. male sex
c. ligament laxity
d. pes planus
d. vascular compromise can threaten the limb
A 46 year old male was in a MVA. He sustained severe trauma to his knee. On exam he cannot bear weight on his right leg. There is visible deformity and decreased pulses distally. What is the MOST important reason to start immediate treatment?
a. immediate immobilization with save the joint
b. prevent future osteonecrosis
c. delayed treatment increases chance of not being able to bear weight on the joint
d. vascular compromise can threaten the limb
b. patellofemoral syndrome
-generalized pain behind knee cap, overuse injury, pain going up or down stairs, dx of exclusion, tendons are tight
-patellar dislocation can have positive apprehensive test too but look at pt history
A 34 year old female training for a triathlon presents with dull aching pain that she describes is "behind her knee cap." Her pain is worse when she goes up and down stairs. On exam she has patellar tenderness and swelling and a positive apprehensive test. What is the likely diagnosis?
a. patellar dislocation
b. patellofemoral syndrome
c. Osgood-schlatter
d. tibiofemoral dislocation
a. tall male
Which patient would you most likely see Ogood Schlatter's disease in?
a. tall male
b. tall female
c. short male
d. short female
b. immobilize with splint
splint first then cast
ortho f/u you decide on surgery
A 38 year old female is walking downtown and accidentally steps in a pothole and hurts her ankle. She cannot bear weight on the joint. There is visible deformity and ecchymosis. Xray shows fracture of the distal fibula. What is the next appropriate step?
a. cast the patient at the affected ankle
b. immobilize with splint
c. immediate surgery
d. RICE and no splint
d. Thompson
What special test would be positive if a patient had a ruptured Achilles tendon?
a. Homan's
b. Anterior drawer
c. Posterior drawer
d. Thompson
b. plantar fasciitis
A 21 year old male training for the summer olympics in long jumping presents with heel pain and pain in the morning of his right foot when he takes his first step. There is no history of trauma. On exam he has tenderness on palpation. What is the likely diagnosis?
a. heel spurs
b. plantar fasciitis
c. achilles tendonitis
d. calcaneous fracture
c. Pilon fracture
What type of fracture is a comminuted fracture of the distal tibia that extends through the tibiotalar articular surface and can have fibula involvement?
a. Lisfranc fracture
b. Morton's fracture
c. Pilon fracture
d. Jone's fracture
d. Jone's fracture
Mikie Driscoll got dunked on in a basketball game. When the opposing player came down, he stepped on Mikie's right foot. He has pain and tenderness over the base of his 5th metatarsal. Before plain films are obtained what fracture is high on your differential?
a. Lisfranc fracture
b. Morton's fracture
c. Pilon fracture
d. Jone's fracture
c. neuroma is located between 2nd and 3rd metatarsal
located b/w 3rd and 4th metatarsals
Which of the following statements about Morton's neuroma is incorrect?
a. severe burning pain that increases with activity
b. decreased pain with removal of shoes
c. neuroma is located between 2nd and 3rd metatarsal
d. treatment includes steroid injections
c. fell forward and landed on an outstretched hand
If a patient has a Colle's fracture, how did they break it?
a. fell forward and landed on a flexed wrist
b. fell forward on hand and sprained wrist
c. fell forward and landed on an outstretched hand
d. landed on an outstretched hand with hyperpronated forearm
a. radial head subluxes out of the annular ligament
Nursemaid's elbow
tx: closed reduction, ice, NSAIDs
A mom is holding her 3 year old's hand at Disney world when he yanks his arm away from to run towards Winnie the Pooh. She notices he acts funny the rest of the day and she brings him to the urgent care. The child refuses to to use his arm. What is the pathogenesis of this injury?
a. radial head subluxes out of the annular ligament
b. ulnar head subluxes out of the annular ligament
c. medial collateral ligament is torn
d. there is a fracture at the proximal ulna
c. median
Which nerve are you worried about in a posterior elbow dislocation?
a. ulnar
b. radial
c. median
d. musculocutaneous
d. fracture of the radial head
A patient falls on an outstretched hand. They have pain and swelling over the lateral aspect of their elbow and loss of elbow ROM. Xray shows fat pad and sail sign. What is most likely fractured?
a. fracture of the olecranon
b. fracture of the proximal humerus
c. fracture of the ulnar head
d. fracture of the radial head
a. splinting and slow progressive AROM
type II - rule of 3s (less than 1/3 of articular surface, less than 30 degrees of angulation, less than 3 mm displaced --> if doesnt meet criteria tx w/ ORIF)
type III & IV - early excision of the bone fragments and ORIF
What is the treatment for a type 1 radial head fracture?
a. splinting and slow progressive AROM
b. open reduction internal fixation
c. rule of 3s
d. early excision of the bone fragments and ORIF
a. ulnar
Which nerve would likely be compressed in an olecranon fracture?
a. ulnar
b. radial
c. median
d. musculocutaneous
d. olecranon
A patient suffers from a blow to his elbow. He has swelling, ecchymosis, no deformity, and signs and symptoms of ulnar nerve compression (paresthesias/numbness of 4th and 5th digits). Flexing his elbow decreases his pain. What is likely fractured?
a. radial head
b. ulnar head
c. distal humerus
d. olecranon
a. Monteggia
A patient falls on an on a hyperpronated forearm. Xray shows proximal ulnar fracture and radial head dislocation. What type of fracture is this?
a. Monteggia
b. Galeazzi
c. Smith's
d. Colle's
c. eliminating or modifying activities
What is the most important treatment for lateral epicondylitis?
a. NSAIDs
b. commerical tennis elbow brace
c. eliminating or modifying activities
d. heat/ice
a. Golfer's elbow test
What positive test indicates medial epicondylitis?
a. Golfer's elbow test
b. Mills test
c. Cozens test
d. Tinel test at the elbow
c. Scaphoid view
A patient falls on an outstretched hand and lands on the palm of their hand. They come into the clinic complaining of pain on the radial side of their wrist with tenderness of their anatomical snuffbox. What type of xray view do you need to visualize what is highest on your differential?
a. oblique view
b. PA view of the wrist
c. Scaphoid view
d. AP view of the wrist
d. 40
ulnar gutter splint 2-3 weeks, if >40 refer to surgeon
if open fx immediate ortho surg consult
boxer fx w/ >25-30 degrees angulation neeeds to be reduced (closed or open)
At what degree of volar angulation is the greatest amount consistent with a good functional result in a Boxer's fracture?
a. 25
b. 30
c. 35
d. 40
d. Colle's
A patient falls on an outstretched hand. There is visible deformity of the wrist and pain. Xray shows distal radius fracture with dorsal displacement. What type of fracture is this?
a. Monteggia
b. Galeazzi
c. Smith's
d. Colle's
c. Smith's
What type of fracture is when the distal radius fragment tilts volarly?
a. Monteggia
b. Galeazzi
c. Smith's
d. Colle's
c. Finkelstein
What special test is positive in DeQuervain's tenosynovitis?
a. Phalen
b. Grind
c. Finkelstein
d. Durkin's
b. thenar hypertrophy
thenar atrophy
What sign and symptom would you not see in Carpal Tunnel syndrome?
a. paresthesias in median nerve distribution
b. thenar hypertrophy
c. weakness in the hand
d. inability to open jars
a. Durkin's test
A pregnant woman presents with wrist pain. The examiner places one thumb over carpal tunnel and other thumb and applies gentle, sustained pressure which causes pain in the woman. What positive test is this?
a. Durkin's test
b. Phalens test
c. Tinels test at the wrist
d. Finkelstein test
c. carpal tunnel release
conservative measures are not helping
A patient with carpal tunnel syndrome has had a volar splint for 3 months, takes NSAIDs, and steroid injections. They are still suffering from weakness, thenar atrophy, and severe pain. What would be the best next management of this patient?
a. another steroid injection
b. ergonomic modification
c. carpal tunnel release
d. opioids
b. European male with diabetes in his 60s
Europeans, M > F, 40-60s, common in diabetics, alcoholics, pts w/ manual labor and vibration exposure
Who would you MOST likely see Dupuytren's contracture in?
a. African american female in her 50s
b. European male with diabetes in his 60s
c. Asian female in her 30s thats an alcoholic
d. European female in her 40s no PMHx
a. Trigger finger
tx w/ NSAIDs or corticosteroid injection (avoid tendon), surgical release if necessary
A 45 year old woman presents with complaints of painful snapping when she flexes her right ring finger. There is stiffness, swelling, and anodule distal to the palmar crease that moves. What is the likely diagnosis?
a. Trigger finger
b. Dupuytren's contracture
c. Game keeper's finger
d. Boutonneire finger
b. Boutonnieres
Mallet is DIP flexion & unable to extend due to avulsion of the extensor tendon
Swan neck is PIP hyperextension and DIP flexion
What finger deformity is characterized by PIP flexion and DIP extension?
a. Mallet
b. Boutonnieres
c. Swan neck
d. Jersey finger
b. Teres major
SITS
subscap, infraspinatus, supraspinatus, teres MINOR
Which muscle is not part of the rotator cuff?
a. Teres minor
b. Teres major
c. Subscapularis
d. Supraspinatus
c. Rotator cuff tear
MRI confirms dx
similar pain in shoulder impingement but AROM is preserved
A 60 year old male presents with shoulder pain that increases at night. He states his shoulder "catches" when he lifts it overhead. On exam you note weakness in abduction and lateral rotation and decreased active ROM. The back of his shoulder appears sunken. Neer's test and drop arm test are positive. There are no paresthesias. What is the diagnosis?
a. Shoulder impingement
b. Frozen shoulder
c. Rotator cuff tear
d. Thoracic outlet syndrome
b. Adhesive capsulitis
co morbidities: hypothyroidism, dupuytrens, cervical disk herniation, parkinsons, cerebral hemorrhage & tumors
non surg tx: NSAIDs, nonnarcotic analgesics, moist heat, stretching exercises, intraarticular steroid injections, TENS unit
A 57 year old female with DM type 1 presents with insidious shoulder pain. She notes that her ROM has progressively been worsening. She states shell have a phase of pain and loss of ROM that is followed by a phase of decreasing discomfort. What is the likely dx?
a. Shoulder impingement
b. Adhesive capsulitis
c. Rotator cuff tear
d. Thoracic outlet syndrome
b. type II
What grade of AC separation occurs when AC ligaments are torn and the CC ligaments are intact with partial separation o the clavicle from the acromion?
a. type I
b. type II
c. type III
d. type IV