Unit 6: Knee Injuries
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Anterior Cruciate Ligament
- prevents the femur from moving posteriorly during weight bearing and limits anterior translation of tibia in non-weight bearing
- stabilizes tibia against excessive internal rotation
Posterior Cruciate Ligament
- resists internal rotation of tibia, prevents hyperextension of knee
Prevention of Knee Injuries
- total body conditioning (strength, flexibility, endurance, agility, speed & balance
- muscles around condition to maximize stability
- avoid abnormal action
Decreasing the risk of ACL injury
- focus on strength, neuromuscular control, and balance
Shoe type Affecting the Knee
- change in football footwear has drastically reduced injuries
- more short cleats do not allow the foot to become fixes, still allows for control with running
Functional and prophylactic knee braces
- Used to prevent and reduce severity of knee injuries
- protects MCL and ACL
Medial Collateral Ligament Sprain (MCL)
- result of severe blow from lateral side (valgus force)
- different grades
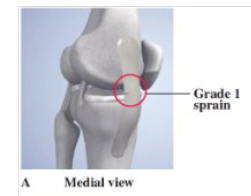
Grade 1 Medial Collateral Ligament Sprain
- little fiber tearing/stretching
- stable valgus test
- normal ROM
- tx: POLICE (24 hrs), crutches, cryokinetics, 3 weeks recovery
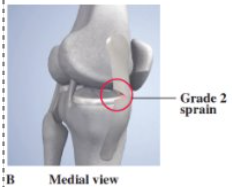
Grade 2 Medial Collateral Ligament Sprain
- complete tear of deep ligament, partial tear of superficial layer
- slight swelling, laxity at 30 degrees of flexion, joint tightness, decreased ROM
- tx: POLICE (48-72 hrs), crutches, brace/casts, gradual progression to closed kinetic chain exercises
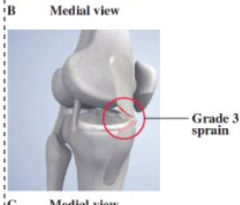
Grade 3 Medial Collateral Ligament Sprain
- complete loss of medial stability, minimum swelling, immediate pain, loss of motion, positive valgus stress test
- tx: POLICE, limited immobilization (brace), progressive weight bearing, increased ROM
Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL)
- result of varus force, generally with tibia internally rotated
- severe damage, pain/tenderness, swelling, irritation to fibular (peroneal) nerve
- tx: depends on severity follows the same as MCL
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Sprain
- caused by direct contact/noncontact mechanism (80% more likely)
- experience a pop, severe pain/disability, rapid swelling
- tx: POLICE, crutches surgery depending on severity (4-6 months of rehab)
Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Sprain
- caused by fall on bent knee (most common), rotational force
- feel a pop, tenderness, swelling
- tx: POLICE, surgery (6 weeks of immobilization) (ROM after 6 weeks)
Meniscal Lesions
- medial meniscus is more common injured
- ruptured edges harden and may atrophy
- joint line pain, loss of motion, knee locking, pain squatting
- tx: unlock the knee with surgery, repair meniscus (immobilization with gradual return to activity over 12 weeks)
Knee plica
- irritation of the plica
- recurrent episodes of painful pseudolocking, possible snapping/locking, pain with bending knee, little swelling
- tx: RICE, if recurrent may require surgery
Bursitis
- prepatellar: continued kneeling
- infrapatellar: overuse of patellar tendon
- swelling above or behind knee, can be painless, little disability
- tx: RICE, steroid injection (chronic)
Patellar Fracture
- direct/indirect trauma (severe pull of tendon)
- hemorrhaging, swelling, capsular tearing, little bone separation
- tx: x-ray, RICE, splinting, immobilize for 2-3 months
Acute Patella Subluxation/Dislocation
- deceleration with simultaneous cutting in opposite direction, quad pulls patella out of alignment
- subluxation, pain, swelling, restricted ROM, tenderness, total loss of function
- tx: reduction (flex hip, move patella medially, and slowly extend knee), immobilization for 4 weeks, crutches, horseshoe pad after immobilization, muscle rehab
Chondromalacia patella
- softening/deterioration of the articular cartilage
- pain with moving knee (walking, running, stairs), swelling, pain at inferior border during palpation
- tx: RICE, orthotics, surgery
Patellofemoral Stress Syndrome
- Result of lateral deviation of patella while tracking in femoral groove
- tenderness of lateral facet, swelling, dull ache, crepitus with compression
- tx: correct imbalances (strength/flexibility), McConnell taping
Osgood-Schlatter disease
- apophysitis occurring at tibial tubercle
- resolves with aging
- swelling, hemorrhaging, gradual degeneration, point tenderness, pain (kneeling, jumping, running)
- tx: reduce stressful activity (6-12 months), possible casting, ice before/after activity
Larsen-Johansson disease
- result of excessive pulling on the inferior pole of the patella
- swelling, hemorrhaging, gradual degeneration, point tenderness, pain (kneeling, jumping, running)
- tx: reduce stressful activity (6-12 months), possible casting, ice before/after activity
Patellar tendinitis (Jumper’s/Kicker’s knee)
- placing tremendous stress/strain on patellar/quad tendon, sudden or repetitive extension
- pain, tenderness, goes through pain phases
- tx: ice, exercise, patellar tendon bracing, transverse friction massage
Patellar Tendon Rupture
- sudden/powerful quad contraction (occurs commonly at point of attachment
- generally does not occur unless chronic inflammation condition results in tissue degeneration
- palpable defect, lack of knee extension, swelling, pain
- tx: surgical repair needed, proper conservative care can minimize changes of occurring
Iliotibial Band Friction Syndrome (Runner’s/Cyclist’s Knee)
- repetitive/overuse condition attributed to malalignment and structural asymmetries
- irritation at band’s insertion, positive Ober’s test
- tx: correction of malalignments, ice before/after activity, proper warmup/stretches, avoidance of activities, orthotics
Pes Anserine Tendinitis/Bursitis
- result of excessive genu valgum (knees inward) and weak vastus medialis
- occurs due to running with one leg higher than the other (slope)