Adolescence
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 9; PSYC 2007
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Adolescence
Age 10-24
Period of significant change
Early; Middle; Late Stages
Early adolescence
11- 14 years
Rapid pubertal change
Middle adolescence
14 - 16 years
Pubertal changes nearly complete
Late adolescence
16- 18 years
Young person achieves full adult appearance
Begins to assume adult roles
Types of changes in adolescence
Biological
Psychological
Social
Grow spurts
Occurs approx. 2 yrs earlier for girls
Beginng of growth spurt
9 Yrs- Girls
11Yrs- Boys
Peak Rate of Pubertal Change
11 yrs- Girls
13 yrs- Boys
Approximate increase in height for Girls
3 inches per year
Approximate increase in height for Boys
4 iches per year
Brain Regions affected during Adolescence
cortical and subcortical
During adolescence imbalance b/t connections within limbic and PFC regions result in...
Heightened sensitivity to peer influence
Impulsivity
Risk taking
Emotional volatility
Risks during adolescent brain development
peer influence
impulsive/risky behaviours
emotional volatility
Opportunities during adolescent brain development
Exploration, experimentation, creativity
Responsive to reward
Plasticity=capacity for learning
Reasons for the psychosocial developments in adolescence
Cognitive capacity
Improved mentalising
Perspective taking
Social status awareness
Adolescent Peer Relations: Sullivans Interpersonal Theory
Development is motivated by fulfilment of interpersonal needs
Infancy = tenderness
Childhood = companionship
Juvenile = acceptance
pre-adolescence (pre-teen) = friendship
Adolescence + Adulthood= romantic
How to measure adolescent popularity
Sociometric technique-
Peer nominations:
popular
controversial
neglected
rejected
behaviour profile of popular adolescent
leader
cooperative
doesnt seek help, fight, disrupt
Behaviour profile of controversial adolescent
seeks help
fights
disrupts
doesn't lead or cooperate
2 Skills as Predictors of social status-
Cognitive skills
Social skills:
initiation of interactions
communication
responsivity
cooperation
Superficial characteristics affecting peer relationships
Attractiveness, gender, age
Continuity of relationships on peer status
Secure attachment - more likely to be popular
Factors for Harmonious Interactions with peers
Joint attention
Emotional regulation
Inhibitory control
Imitation
Causal understanding
Language
Social Information Processing
Model explaining individual differences in interpreting social situations.
Dodge's (1986) social information processing model
Shows biases in social processing that contribute to aggression in adolescence.
Peer Group Structure in adolescence- Dunphy 1963
CLIQUES = small group with strong affectional bonds
CROWDS = large group loosely made up of cliques joined together.
characteristics of cliques
small
later childhood
same gender
powerful influence
Characteristics of crowds
large
reputation based
shared attitudes
less important with age
4 behavioural systems of romantic relationships
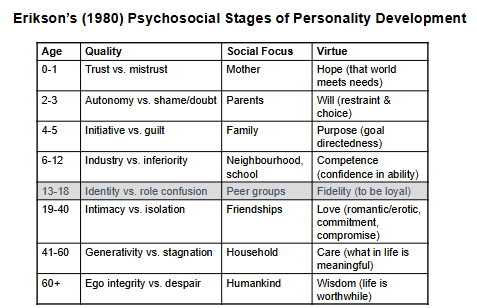
Erikson’s (1980) Psychosocial Stages of Personality Development- Adolescence
13-18 YRS
IDENTITY VS ROLE CONFUSION
SOCIAL FOCUS= Peer Groups
Virtue= Fidelity( Loyality)
4 Idenity type- Marcia’s Theory of Idenity Achievement
Identity achievers
Identity moratoriums
Identity foreclosurers
Identity diffusers
Identity Achievers
Extensive soul-searching/ exploration has produced
stable identity.
Identity Moratoriums
Engaging in self-exploration but not yet formed stable identity.
Experiencing anxiety/worry
Frequent identity crisis
Uncertainty of belonging/full commitment
Identity Foreclosurers
Automatically adopt others’ values without extensive critical reflection.
Identity Diffusers
Lack firm commitments
Not actively engaged in self-exploration, apathetic.
Lack of anxiety/worry about themselves and others
Adolescent rites of passage STEPS
Separation
Training
Initiation
Induction
Adolescent rites of passage- Functions:
Sense of adult responsibility
Lessen ambiguity
Bond
What does Quinn et al 1985 say about rites of passage?
No formal equivalent in UK
It would help adolescents through the difficult transition into adulthood.
Psycho-social changes
Greater autonomy and less dependence on parents.
Increased age-appripriate indepence/freedom
Parental support still necesary
Parental/Adolence create relational dialogue (i.e., Balance b/t autonomy and curfew)
What are 3 ways relationship with parents changes in adolescence?
As cognitive ability increases, their perceptions of parents change. View as individuals/parents.
Less time spent with parents/families.
More conflict with parents: Rapid/ situational mood swings & increased irritability.
Erik Erikson’s theory- Psycho-social stages of personality development
8 Pyscho stages
Social/environmental influences
Ego identity: developing a sense of inner self-continuity (Crucial for optimal persnality/functioning)
Adolescent Sexuality
time of sexual exploration and experimentation.
concerned about managing sexuality in social
relationshipsuncertainty about partner’s expectations/body-image concerns.
Improved cognitive capacities influence sexuality
self-reflection and perspective taking
Psychological effects of puberty
Early-maturing girls and late-maturing boys suffer lower self-esteem
Puberty brings boys closer to ideal physical image (muscle definition, strength, stamina).
Girls have increased body fat and weight gain, plus menstruation- takes them away from the Western cultural ideal.
Late maturing girls
Retain their ‘girly behaviours’
Perceived as attractive, lively, and sociable.
Late maturing boys
Come across as more anxious, overly talkative, and attention seeking to compensate.
Western- Ideals of females Evidence
Heterosexual men value lower to medium Waist-to-Hip ratios (WHR) in females.
Adolescence and early adulthood- Brain development
Late-maturing prefrontal cortex ( PFC)
abstract thought, metacognition, mentalising,
emotion- and self-regulation.Continued myelination of axons
Structural changes in the brain underpin adolescents….
- cognitive development
- social and emotional development
Functional changes: Cognitive development
Higher-order cognitive processes- cognitive control/inhibition ( suuported by PFC)
Become more fine tuned during Adolescence; posterior regions become reduced….
Increased activation of slow maturing prefrontal
cortex from childhood to young adulthood.Decreased activation of lower-level sensory and parietal regions from childhood to young adulthood
Stroop Task
Name colour not the actual word
measure of inhibition of PFC
Stroop Tasks Findings
Young adults show greater PFC recruitment than adolescence.
adolescents respond quicker, but at the expense of accuracy
Social brain responsibilities
social cognition
mentalising
social cognition brain regions
late developing areas
dorsomedial PFC
inferior frontal gyrus
amygdala
mentalising brain regions
precuneus
temporal parietal junction
superior temporal sulcus
anterior temporal cortex
Mentalising network connectivity associated with peer-relationships
- Schmalzle et al 2017
Stronger connectivity in mentalising network during social exclusion than inclusion.
Social cognition:
recognising, understanding, and interpreting social cues from others
ability to perceive and adapt to social cues
Mentalizing:
ability to interpret mental states, feelings and actions of other.
perspective-taking, empathy and prosocial behaviours
understanding manipulative and rejective behaviours
What improves social cognition, mentalizing, and emotion regulation skills?
The functional maturation and connectivity between fronto-parietal and limbic regions.