Chemistry FINAL
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/272
Last updated 9:36 PM on 6/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
273 Terms
1
New cards
AXl
linear
2
New cards
AX3
trigonal planar
3
New cards
AX2E
bent
4
New cards
AX4
tetrahedral
5
New cards
AX3E
trigonal pyramidal
6
New cards
AX2E2
bent
7
New cards
AX5
trigonal byprimidal
8
New cards
AX4E
seesaw
9
New cards
AX3E2
t-shaped
10
New cards
AX2E3
linear
11
New cards
AX6
octahedral
12
New cards
AX5E
square based pyramid
13
New cards
AX4E2
square planar
14
New cards
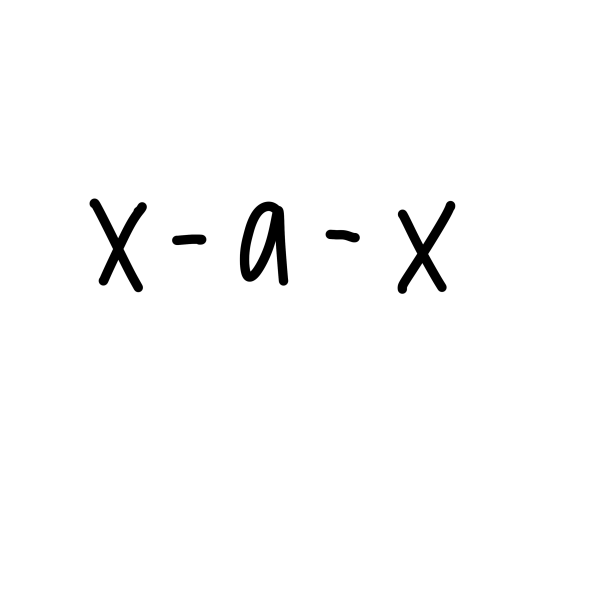
linear
15
New cards
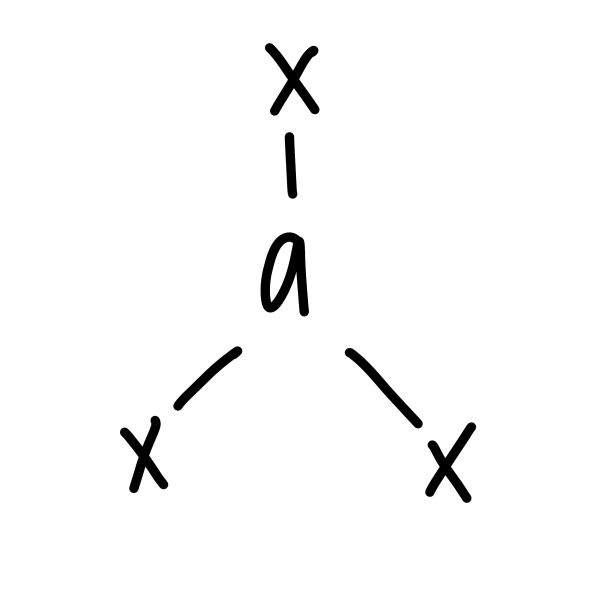
trigonal planar
16
New cards
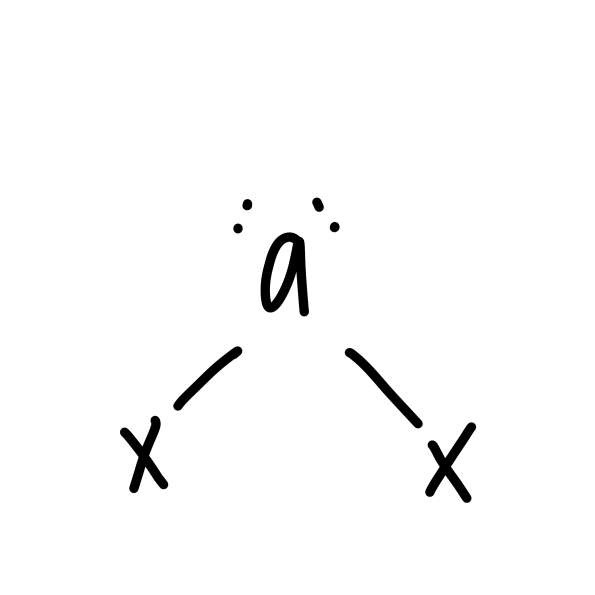
bent
17
New cards
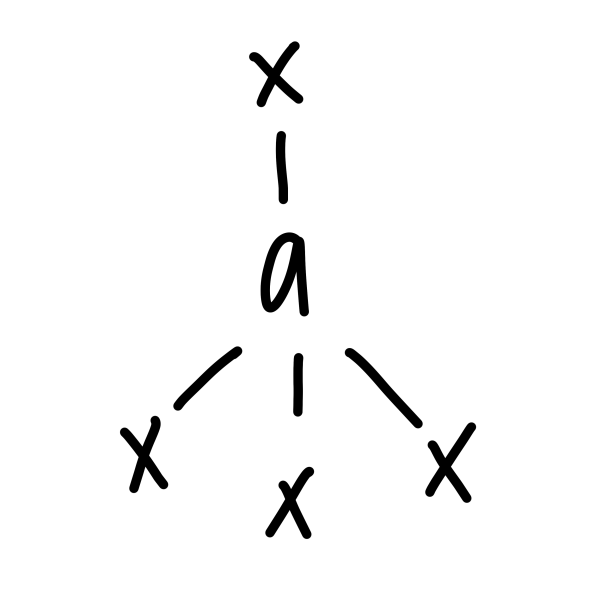
tetrahedral
18
New cards
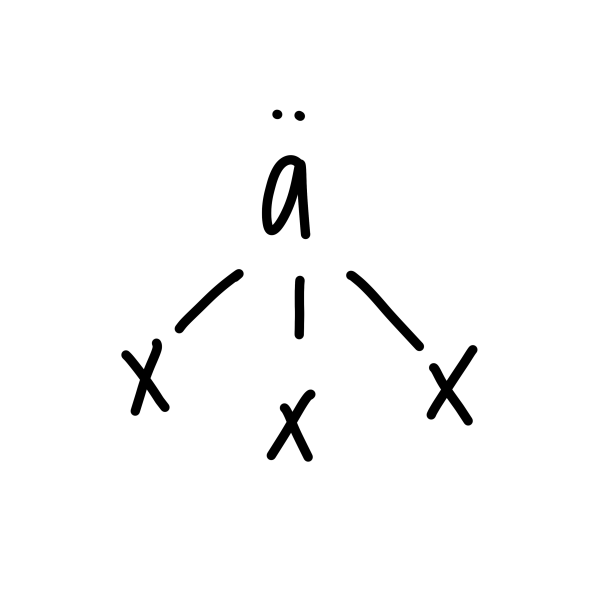
trigonal pyramidal
19
New cards
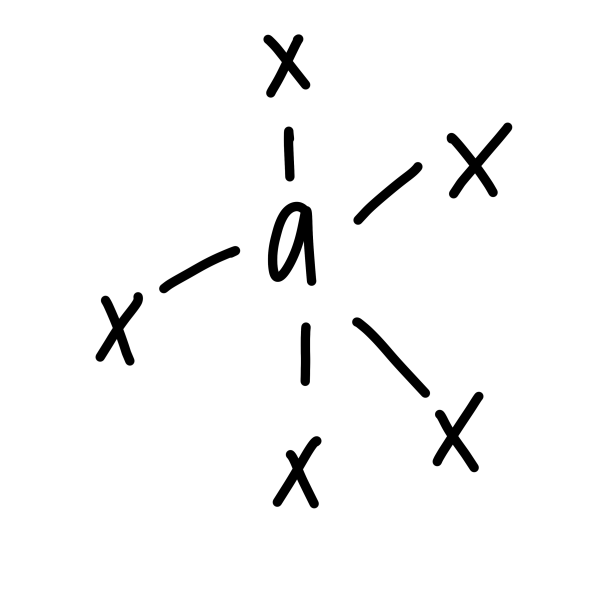
trigonal byprimidal
20
New cards
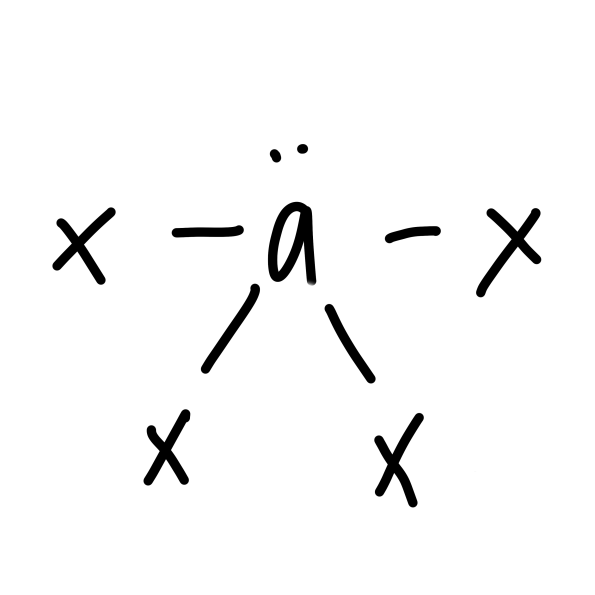
\
seesaw
21
New cards
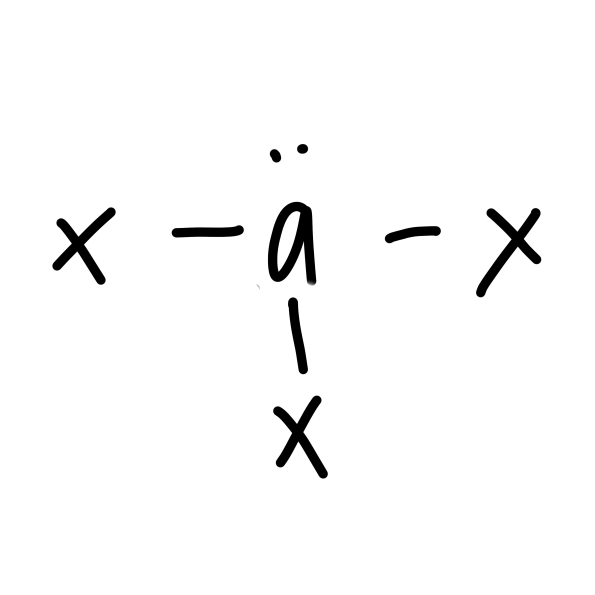
\
t-shaped
22
New cards
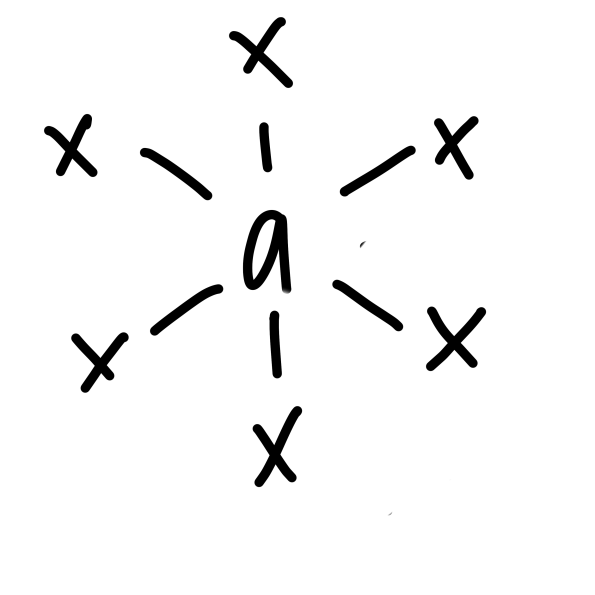
\
octahedral
23
New cards
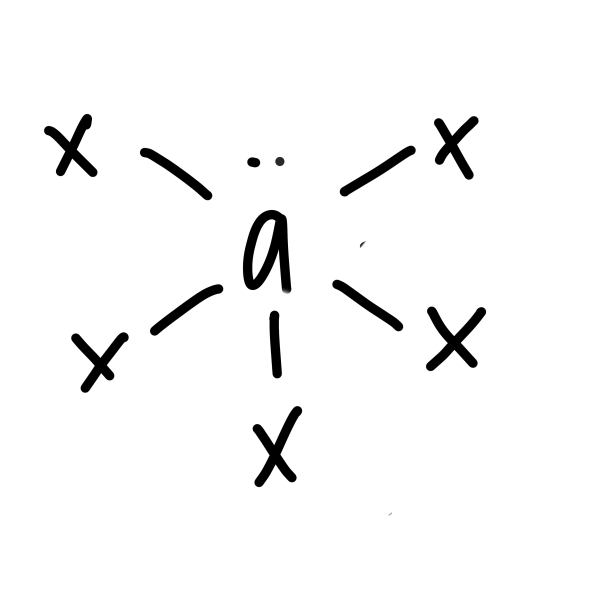
\
square based pyramid
24
New cards
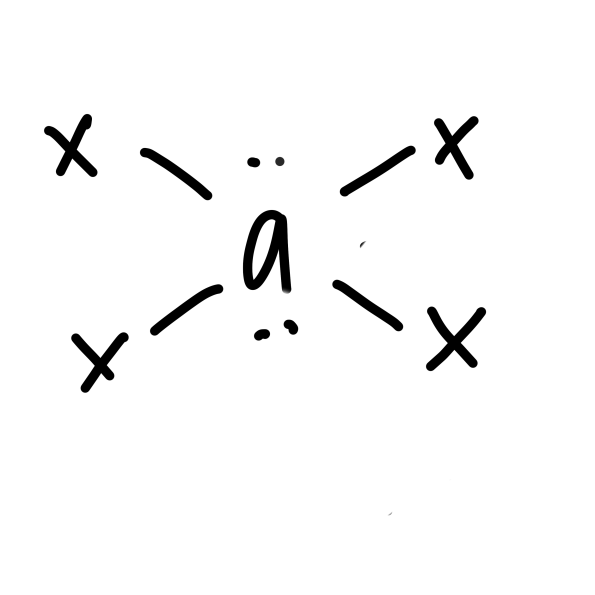
\
square planar
25
New cards
what is chemistry
Science that deals with the composition, structures, and properties of matter, how matter interacts with another, and energy changes that result when matter in transformed
26
New cards
what is matter
anything that has mass and takes up space
27
New cards
what is composition
the makeup of matter what kinds of and the number of particle in a substance
28
New cards
what is structure
how particles are bonded together in a substance
29
New cards
what are properties
characteristics of matter used to identify the substance
30
New cards
what is responsible for the properties of a substance
composition and structure
31
New cards
what are the different types of properties
physical
chemical
qualitative
quantitative
extensive
intensive
chemical
qualitative
quantitative
extensive
intensive
32
New cards
what is a physical property
characteristics of a substance that pertain to its appearance or physical state; measurable characteristics
33
New cards
what is a chemical property
characteristics that allow the substance to change to something new or alter the internal makeup of the substance
34
New cards
what is a qualitative property
what can be identified by the 5 senses; identifiable qualitites
35
New cards
what is a quantitative property
amounts or how much it is in the substance and requires tools for measuring; measurable quantities
36
New cards
what is an intensive property
independent of the amount of substance at hand; only depends on the type of matter
37
New cards
example of intensive property
density, boiling point
38
New cards
what is extensive property
dependent on amount of substance at hand
39
New cards
example of extensive property
volume, mass
40
New cards
what are transformations
changes in matter will alwayss involve changes in energy
41
New cards
what are the 3 types of transformations
physical
chemical
nuclear
chemical
nuclear
42
New cards
what is a physical change
only the state or the appearance of the substance changes. the type of matter of atoms is still the same as before
43
New cards
what is a chemical change
involves change to the makeup of the substance. the same atoms are arranged differently in the final substance. also called a chemical reaction
44
New cards
what is a nuclear change
produces entirely different atoms
45
New cards
what is energy
whatever it takes to generate heat, produce electricity, or move an object
46
New cards
what is enthalpy
a quantity of heat (energy) that has to do with a system that absorbs or releases energy during a chemical change
(delta H)
(delta H)
47
New cards
what is an exothermic reaction
energy in the form of heat or light is released to the surroundings after a reaction occurs; heat is a product
48
New cards
what is the equation of an exothermic reaction
nrgprod - nrg reac = -delta H
49
New cards
what is an endothermic reaction
energy from surroundings and system is absorbed during the reaction; heat is a reactant
50
New cards
what is the equation of an endothermic reaction
product - reactant = +delta H
51
New cards
what are significant figures
digits in a numeral that are known to be exact, plus a digit that is doubtful in the measurement
52
New cards
what are measurements always recorded to
a certain degree of certainty (sig figs) and always have a value and a unit
53
New cards
what is a hypothesis?
a tentative or unconfirmed explanation of certain facts that provides as a basis for further experimentation; an educated guess
54
New cards
what is a theory?
an explanation of general principles of certain phenomena backed with considerable evidence as support
55
New cards
what is a scientific law
simple states of natural phenomena to which no exceptions are known under the given conditions
56
New cards
what has a definite shape and volume
solid
57
New cards
what has definite volume but no shape
liquid
58
New cards
what has an indefinite shape and slight compressibility
gas
59
New cards
what is a phase
homogeneous part of a system separated from other parts by physical boundaries
60
New cards
what is a system
refers to two substances that have come together in a container and allowed heat to flow from the hotter substance to the cooler substance
61
New cards
what is another name for homogenous mixture
solution
62
New cards
When a stopper is removed from a partially filled bottle containing solid and liquid acetic acid at 16.7 C, a strong vinegar odor is noticeable immediately. How many acetic phases must be present in the bottle? Explain. Is this system homogenous or heterogenous?
3 phases; solid and liquid acidic acid (liquid) + vinegar odor (gas)
heterogenous system because there are 3 phases present
heterogenous system because there are 3 phases present
63
New cards
what is the difference between homogenous and heterogenous mixture
homogenous: one phase
heterogenous more than one phase
heterogenous more than one phase
64
New cards
full metric scale
P T G M k h da BASE d c m u n p f
65
New cards
what is volume
the amount of space occupied by matter or the amount of matter that a container can hold
66
New cards
addition or subtracting sig figs
same number of decimal places
67
New cards
multiplying or dividing sig figs
round to least number of sig figs
68
New cards
volume of a box
LWH
69
New cards
volume of a cylinder
πr²h
70
New cards
volume of a sphere
4/3πr³
71
New cards
what are capacity units
volume in terms of how much a container can hold
72
New cards
how much L is in a gallon?
1 gallon \= 3.785 L
73
New cards
how much L is in a quart?
1 quart \= 0.946 L
74
New cards
how much quarts in a gallon?
1 gallon \= 4 quarts
75
New cards
how much cm are in an inch
1 inch \= 2.54 cm
76
New cards
how much mL are in a fl. oz?
2.96 mL
77
New cards
how much cm^3 are in a mL?
1 cm^3 \= 1 mL
78
New cards
how much 1m^3 in cm?
1m^3 \= 100 cm^3
79
New cards
how much inches are in a ft?
12 inch \= 1 ft
80
New cards
how much cm is in a m?
1 m \= 100 cm
81
New cards
what are derived units
when a measurement is the result of a certain relationship between variables
82
New cards
what is the relationship in density
mass and volume of a substance
83
New cards
what is the relationship in specific heat
mass, delta T, and the amount of energy involved
84
New cards
what is a mol
a special unit in chemistry used to clump together a particular number of particles
85
New cards
when we say particles we mean
an atom of Na
molecule of H2O
ion of Na+ or SO4^-2
a formula unit of NaCl
a phonton of light from electrons
molecule of H2O
ion of Na+ or SO4^-2
a formula unit of NaCl
a phonton of light from electrons
86
New cards
what is molar mass
the total mass of all atoms in a compound in grams per mol (g/mol)
87
New cards
what is density
the mass of a substance per unit volume
88
New cards
what properties does density have
intensive property because the amount of substance does not affect its value
physical property because it can be studied without changing the identity of the substance
physical property because it can be studied without changing the identity of the substance
89
New cards
what is accuracy
how close you get to a target value
90
New cards
what is precision
how close your trial results are to each other
91
New cards
what is percentage error
experimental - theoretical/theoretical x 100
92
New cards
what is random error
erratic errors that may come from many sources like human error and calculation error, mainly affecting precision
93
New cards
what is systematic error
often comes from errors due to equipment limitations that affect the accuracy of measurements are reptitious
94
New cards
how to convert celsiuis to fahrenheit
F = C x 1.8 + 32
95
New cards
how to convert fahrenheit to celsius
C = (F - 32)/1.8
96
New cards
how to convert celsius to kelvin
K \= C + 273
97
New cards
what is fahrenheit
a scale commonly used in the US to representing boiling point at 212 degrees F and freezing point at 32 degrees F
98
New cards
What is Avogadro's number?
6.02 x 10^23
99
New cards
what is celsius
also called centrigrade, commonly used in canada to represent freezing point at 0 degrees and boils at 100 degree celsius
100
New cards
what is kelvin
uses the same degree measure as celsius but has zero set to absolute zero