Maternal Physiology
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Enlargement (hyperplasia, myogenesis, hypertrophy) that is stimulated by estrogen, progesterone, and mechanical distention (No longer in the pelvis by 12 weeks), Increased blood flow
What happens to the uterus in pregnancy?
Softens, a dusky blue violet hue (Chadwicks), cervical gland proliferation, thicken mucus
What happens to the cervix in pregnancy?
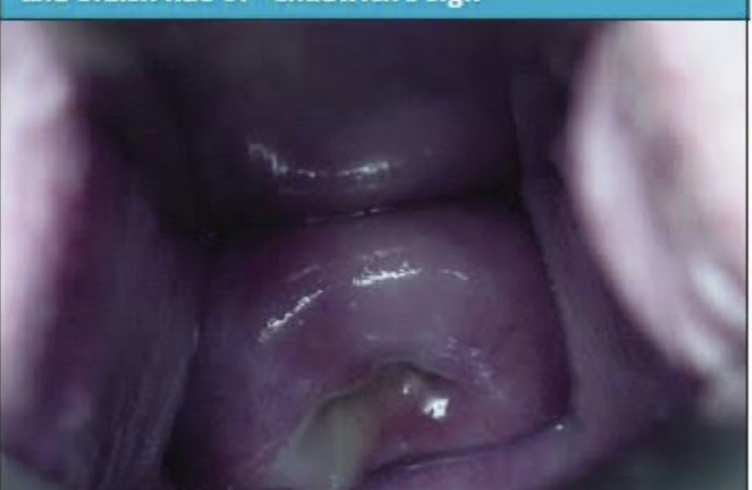
Increased vascularity, thickening of the mucosa, muscular hypertrophy, increased in vaginal secretions (leukorrhea)
What happens to the vagina in pregnancy?
Cessation of ovulation (progesterone secretion by the corpus luteum (6-7 weeks) and then the placenta)
What happens to the ovaries in pregnancy?
luteoma, hyperreactio luteinalis
Ovarian tumors specific to pregnancy?
Luteoma of pregnancy
Which type of ovarian tumor is characterized by a solid, benign exaggeration of normal reaction of the ovary and leads to maternal virilization
Hypereactio Luteinalis
Which type of rare ovarian tumor is characterized by a benign bilateral cystic tumor (functional multicystic ovarian enlargement) that is commonly seen in the 3rd trimester and leads to maternal virilization?
linea nigra (vertical line along the abdomen), chloasma, vulva, breast
Where are the changes in pigmentation associated with pregnancy?
Spider angiomas, palmer erythema
What are the changes in cutaneous vascular areas - caused by hyperestrogenemia of pregnancy and regresses post-partum
Chloasma (melasma)
Symmetrical patches of dark skin, commonly seen on the cheeks, upper lip, forehead, and chin that can resemble a mask pattern
Increased volume, Increased skin erectility of the nipple, colostrum production, increased skin and pigmentation of the areolae
Changes in the breast during pregnancy
Alveolar hypertrophy, ductal growth, growth and branding of terminal glands
What causes the increase in breast volume during pregnancy?
3400 g
How much should the fetus weight at birth
25-35 lbs (11-16 kg)
What is the suggested weight gain for a normal BMI pregnancy?
23-40 lbs
What is the suggested weight gain for an underweight BMI pregnancy?
15-25 lbs
What is the suggested weight gain for an overweight BMI pregnancy?
11-20 lbs (5-9.1 kg)
What is the suggested weight gain for an obese BMI pregnancy?
get glucose to the fetus
What is the goal of carbohydrate metabolism in pregnancy?
fasting hypoglycemia (symptomatic at 4 hours), postprandial hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, peripheral insulin resistance (due to HPL)
Normal Characteristics of pregnancy metabolism
Human placental lactogen (HPL, human chorionic somatomammotropin), progesterone, estrogen
What hormones control Carb Metabolism
Increased plasma volume (45%), Increased fibrinogen, VII, VIII, IX, X, prothrombin, plasminogen; Decreased platelets (220,000), XI, XIII
Hematologic changes in pregnancy
Dilutional Anemia (Hgb of 12 is normal)
What is a complication of the increase in plasma volume?
Increased resting pulse (10-15), displaced heart left and upward, increased cardiac silhouette, lateral displacement of the apex, exaggerated S1 split, S3, Murmurs (systolic is most common), LAD on EKG, increased CO (40%), decreased vascular resistance
Cardio changes in pregnancy
supine hypotension phenomenon (compression of the vena cava, throw ‘em in left lateral), Decreased BP (if elevated think pre-eclampsia)
What is a complication of the cardio changes in pregnancy?
Compensated Respiratory Alkalosis, increased upper airway vasodilation, diaphragm rises 4cm, Increased tidal volume, minute ventilation (20-40%), physiologic dead space; decreased residual volume, functional residual capacity, expiratory reserve
Respiratory changes in pregnancy?
O2 consumption increases (20%), ventilation increases (40%), PaCO2 falls (30 mmhg is normal), Minute volume (1st trimester), alveolar ventilation (50-70%), increased metabolic CO2 production, increased respiratory drive, increased tidal volume
How does ventilation change in pregnancy - mediated by progesterone?
RR, airway resistance (FEV1, peak flow), vital capacity, functional vital capacity, peek expiratory flow reserve PEFR
What does NOT change in pregnancy (respiratory wise)?
Shifts the O2-Hgb dissociation curve to the right (decreases O2 affinity, increases unloading)
What is the result of the acid base changes in pregnancy?
lower pH, increased temp, more 2,3-dphosphoglycerate (2,3-DPG), increased CO2
What factors influence the shift of the O2-Hgb Curve
dilation of the collection system (more common on the right), increased urinary stasis, increased GFR (2nd trimester), sodium and water retention, glycosuria
Changes in the urinary tract during pregnancy?
asymptomatic bacteriuria, Proteinuria (NEVER physiologic)
What is a complication of the changes in the urinary tract?
Delayed gastric emptying, decreased LES tone, cholestasis, increase ALP
Changes in the GI tract in pregnancy?
Cholesterol gallstones
Complications of GI tract changes in pregnancy
Enlarges (135%), increased prolactin secretion (due to pit and uterine decidua)
Changes in the pituitary during pregnancy
enlarges, hCG acts like TSH → increased total T3 and T4 (free is normal)
Changes in the thyroid during pregnancy
Fetus is completely dependant on maternal supply
Why is iodine supplementation important in pregnancy?

Increased cortisol (decreased clearance), Increased aldosterone, Increased androstenedione and testosterone (converted to estradiol by placenta)
What changes occur in the Adrenals during pregnancy?