Bootcamp.com - Diversity of Life
1/253
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
254 Terms
what is taxonomy?
the science of classifying organisms
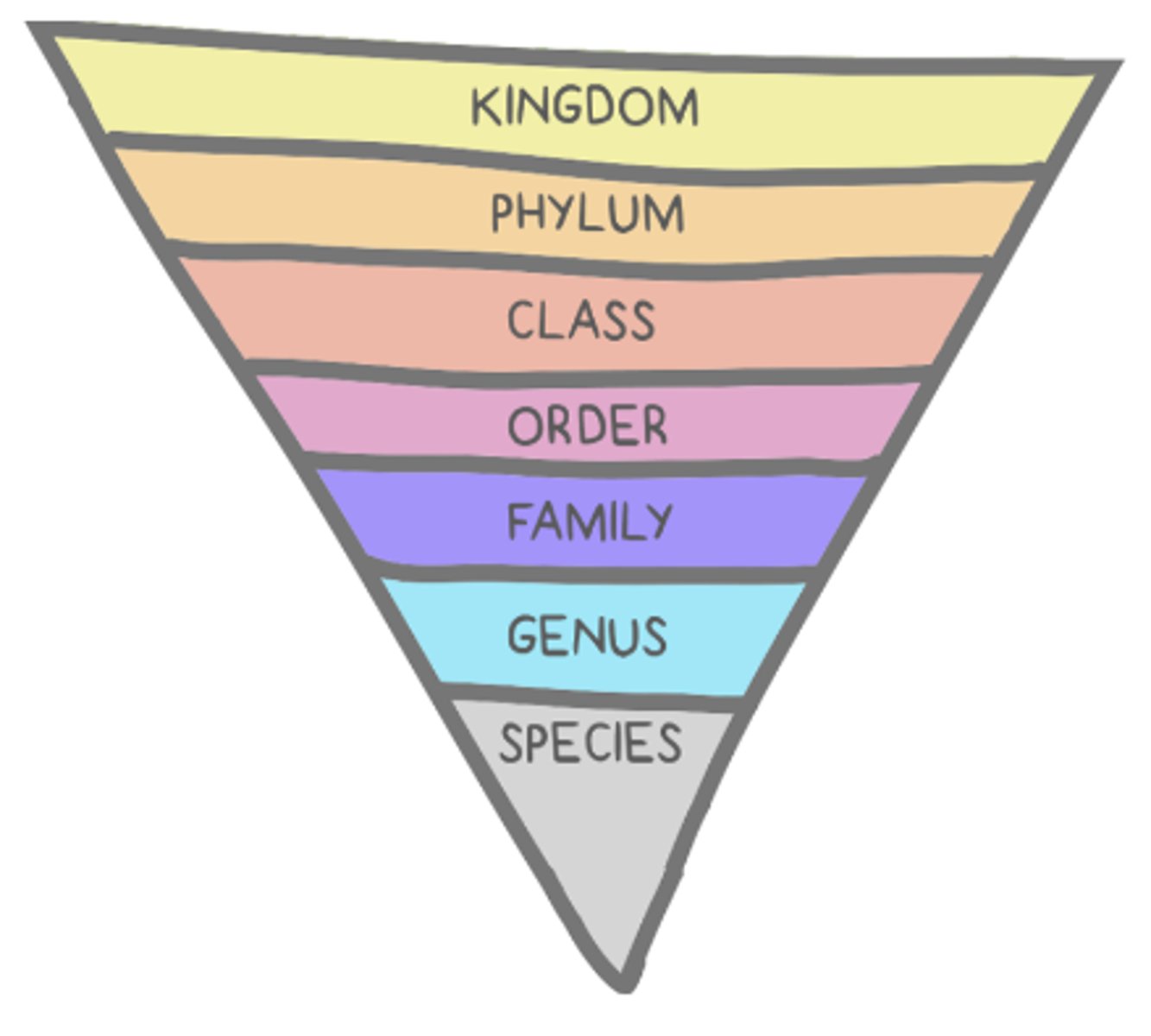
list the broadest to most specific taxonomic ranks:
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
list the six kingdoms:
1. Archaea
2. Eubacteria
3. Protista
4. Fungi
5. Plantae
6. Animalia
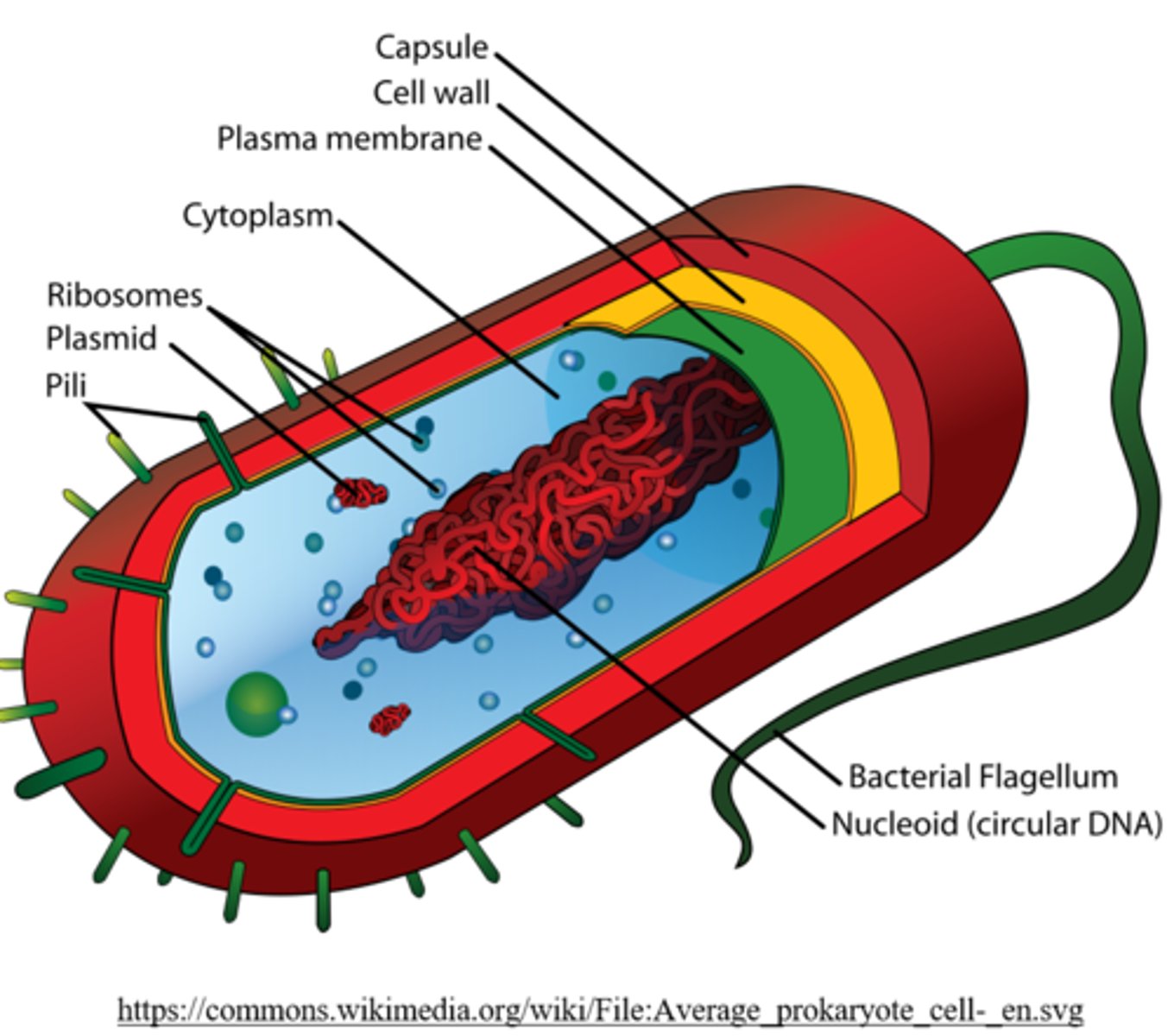
eubacteria and archaea are _____ cells
prokaryotic
_____ do not have membrane-bound nuclei (or organelles for the most part)
prokaryotes
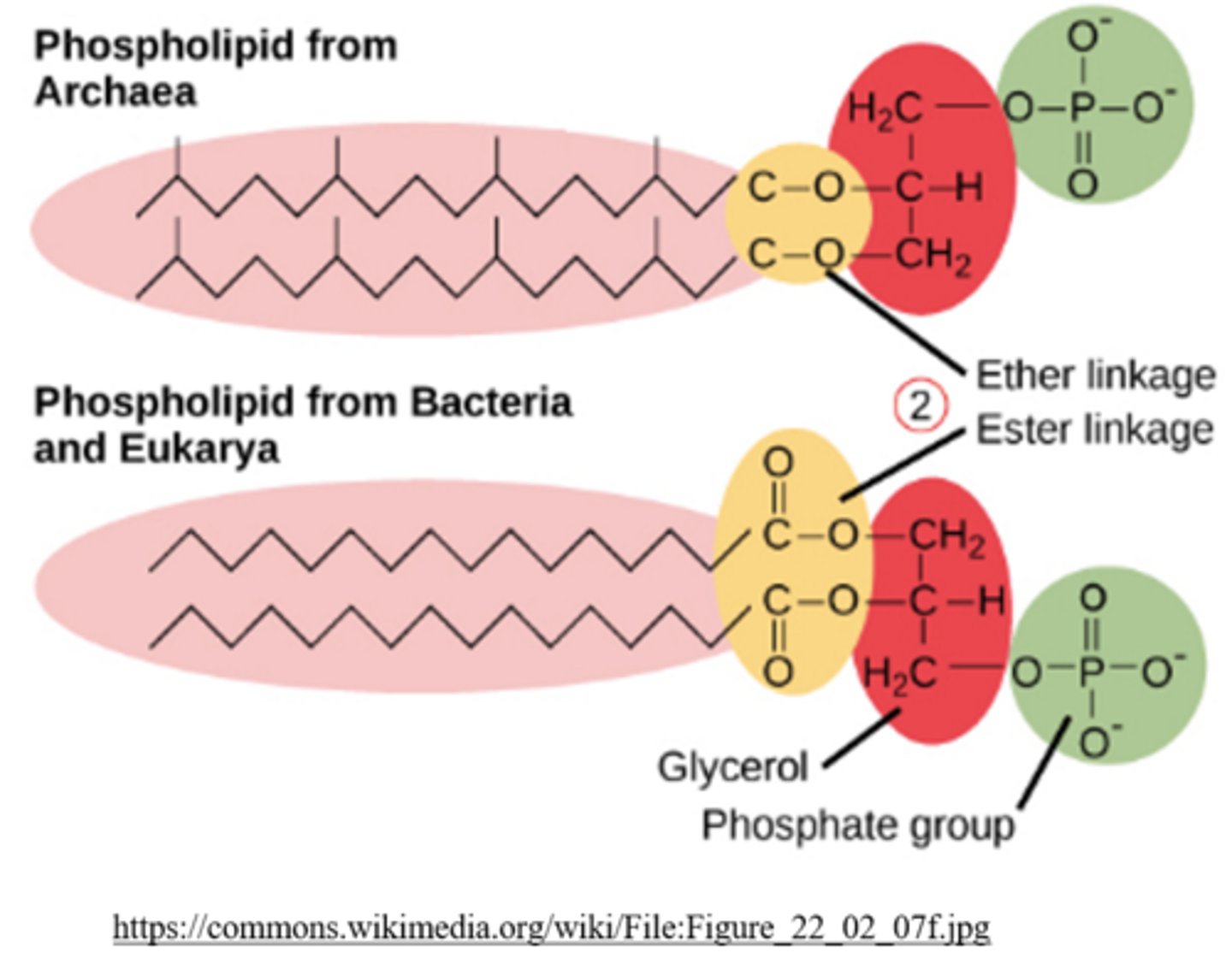
_____ have cell walls with peptidoglycan and esters
eubacteria
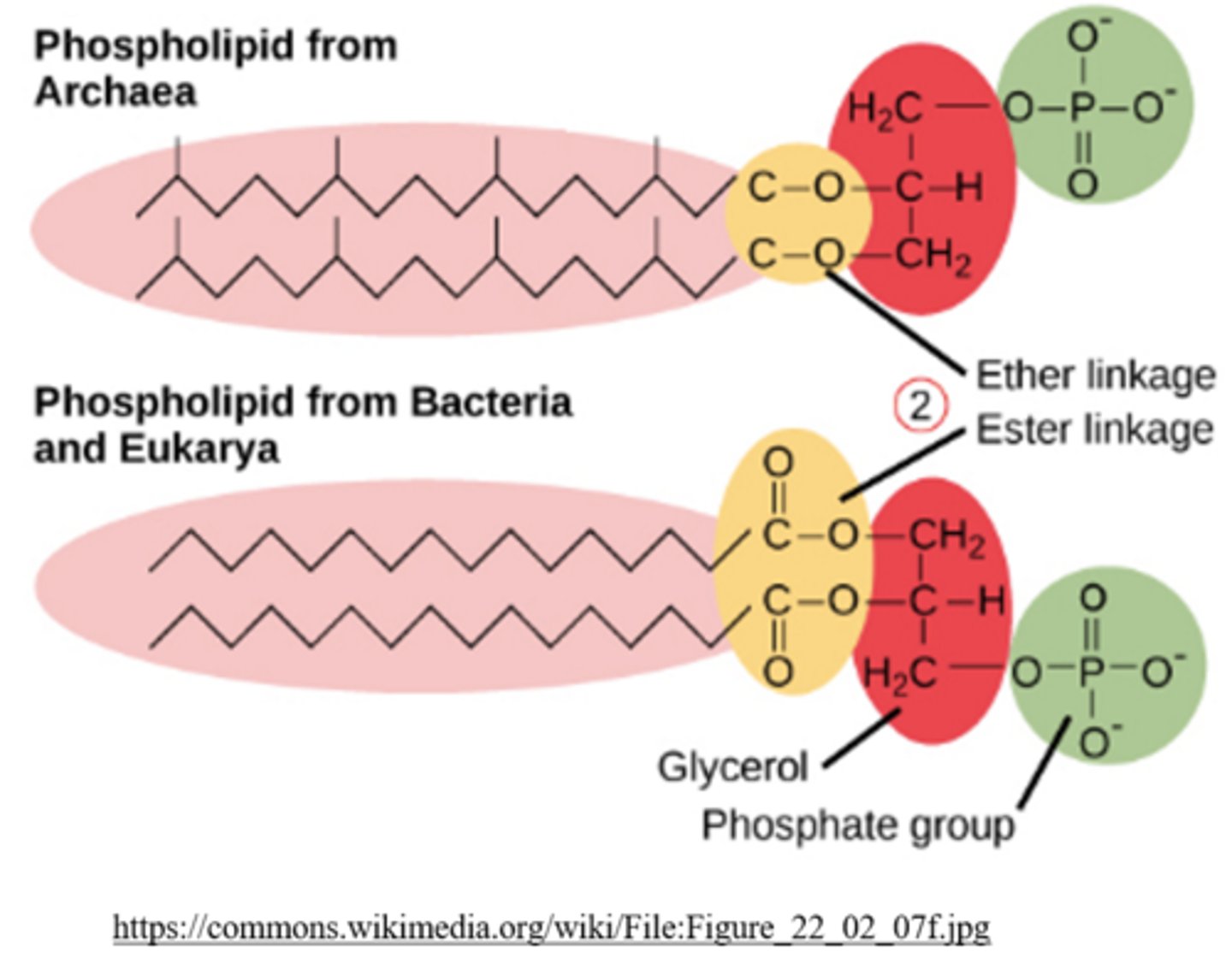
_____ have polysaccharide cell walls and ethers
archaea
_____ is a combination of carbohydrate and amino acids in bacterial cell walls
peptidoglycan
what is a gram stain?
a test to determine the amount of peptidoglycan content in a eubacteria cell wall
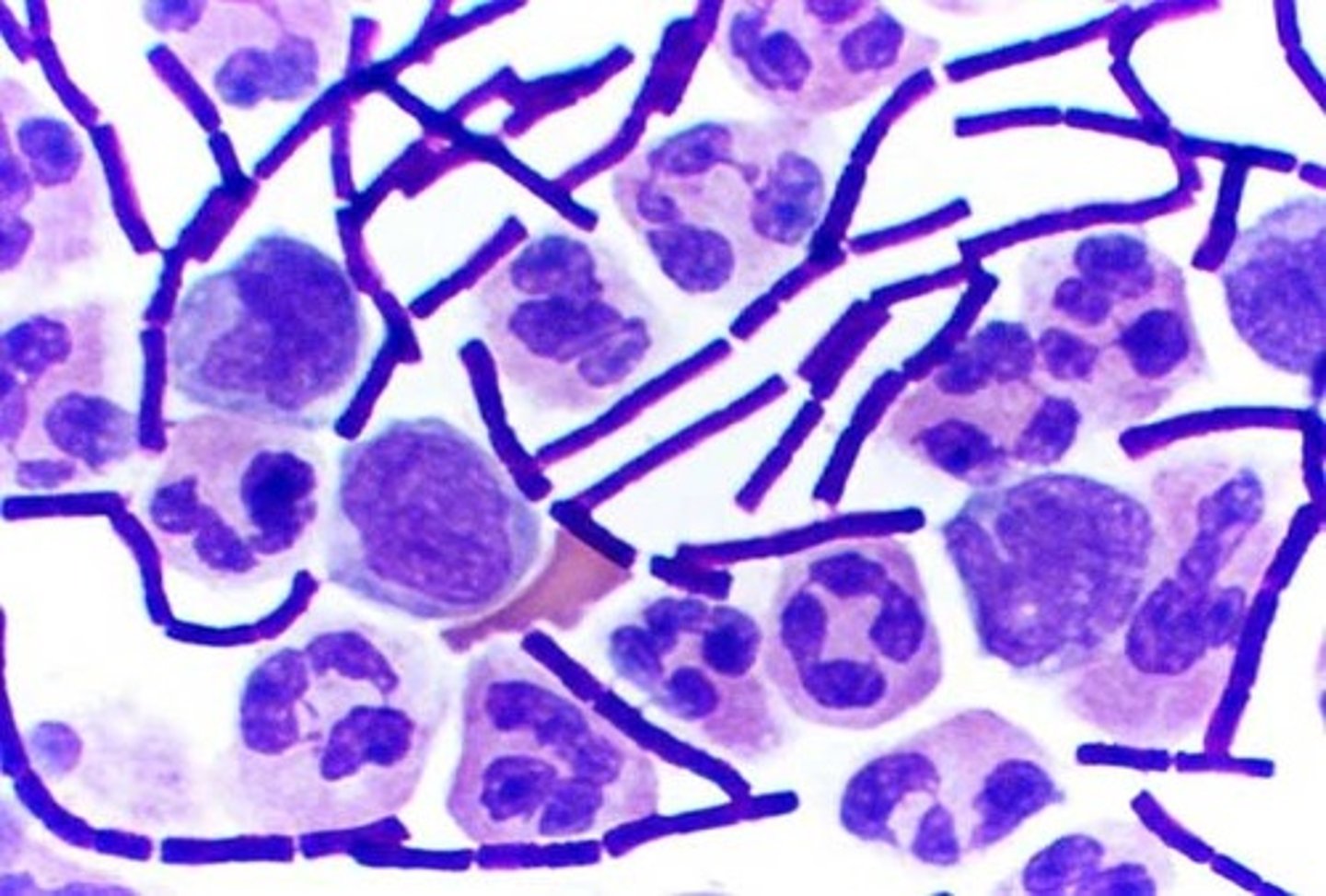
_____ bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer, and they appear dark purple
gram positive
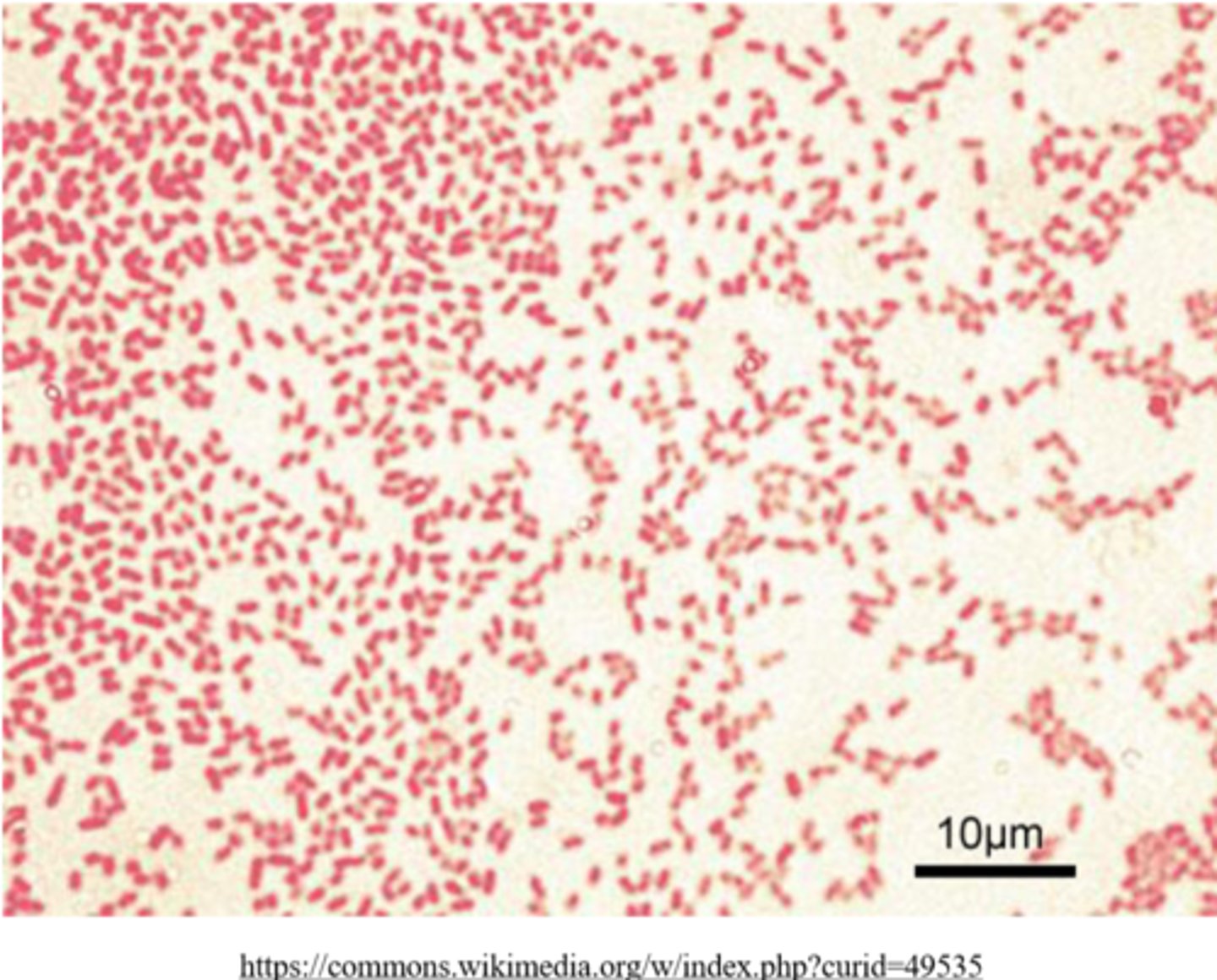
_____ bacteria have a thin peptidoglycan layer between two membranes, and they appear pink
gram negative
the _____ makes gram negative bacteria visible during staining
counterstain
the _____ is the gel located in the periplasmic space (predominantly in gram negative bacteria)
periplasm
_____ is found (predominantly) between membranes of gram negative bacteria
periplasmic space
(very small in gram positive bacteria)
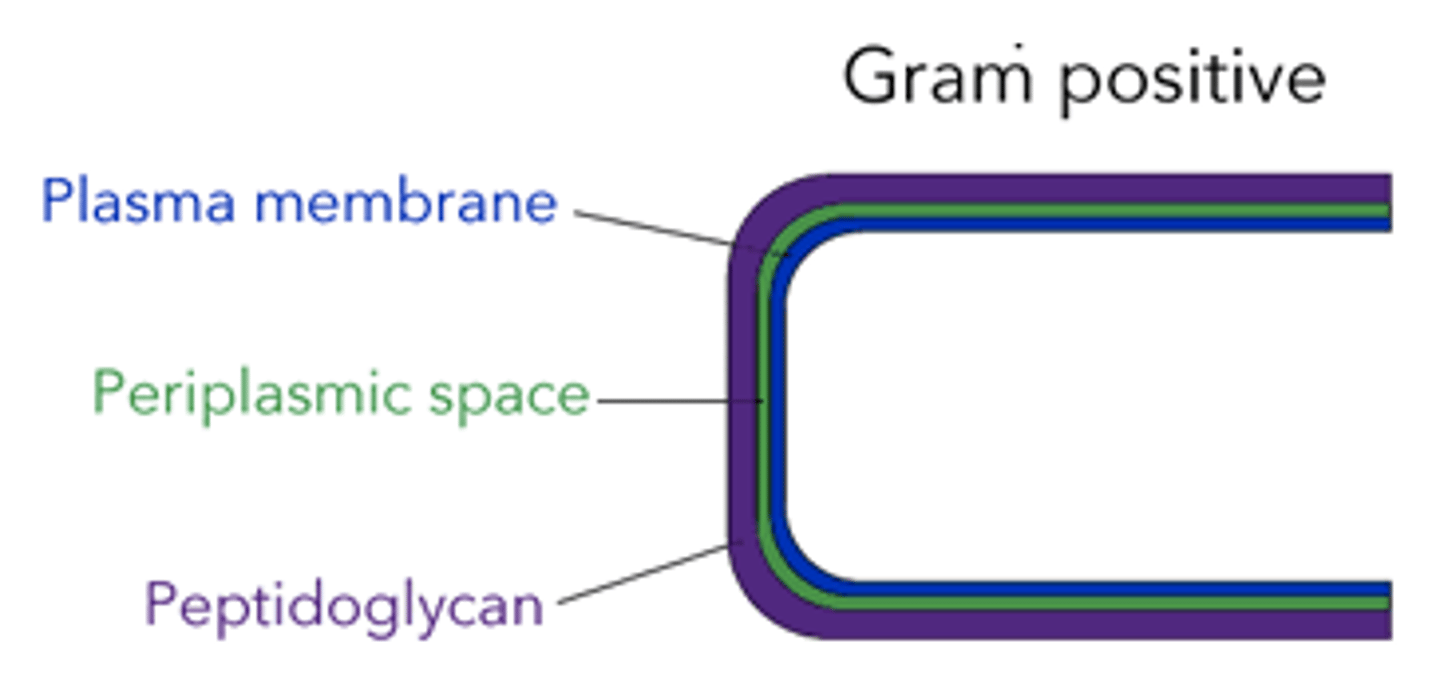
list the layers of gram positive bacterial membrane (from inside to outside)
plasma membrane > periplasmic space > peptidoglycan
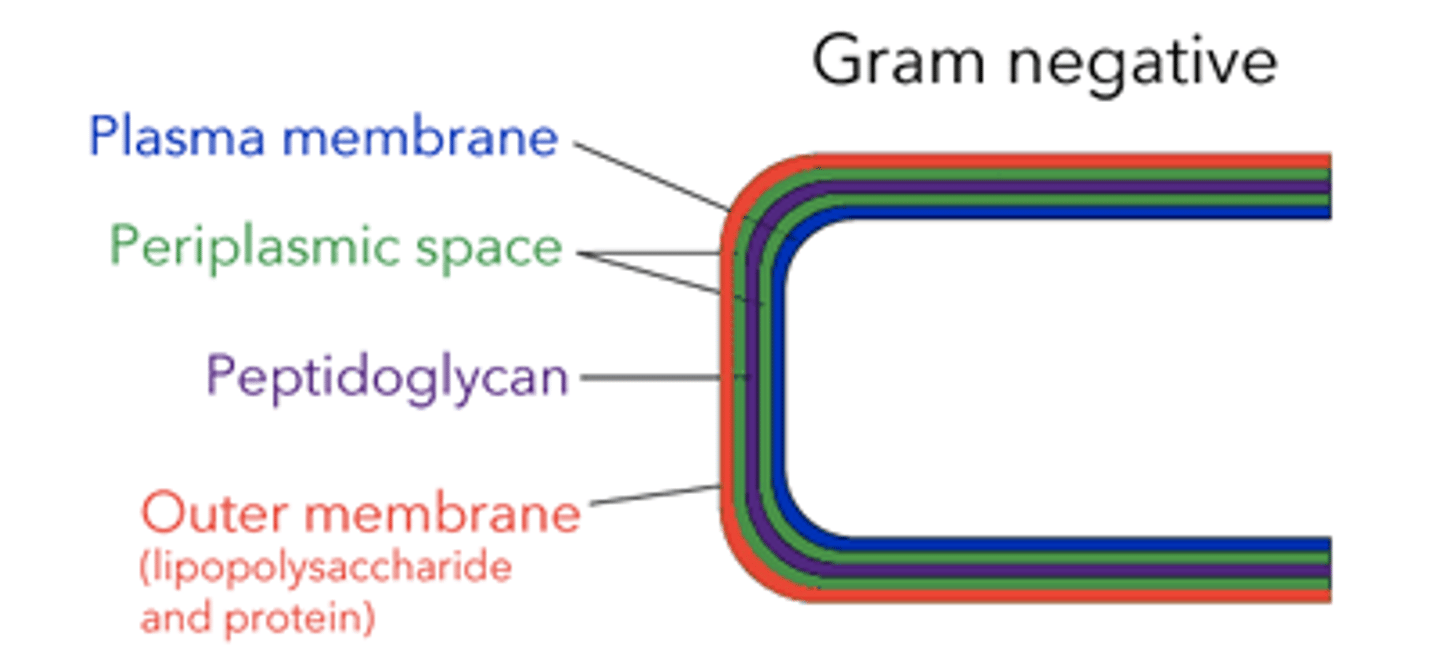
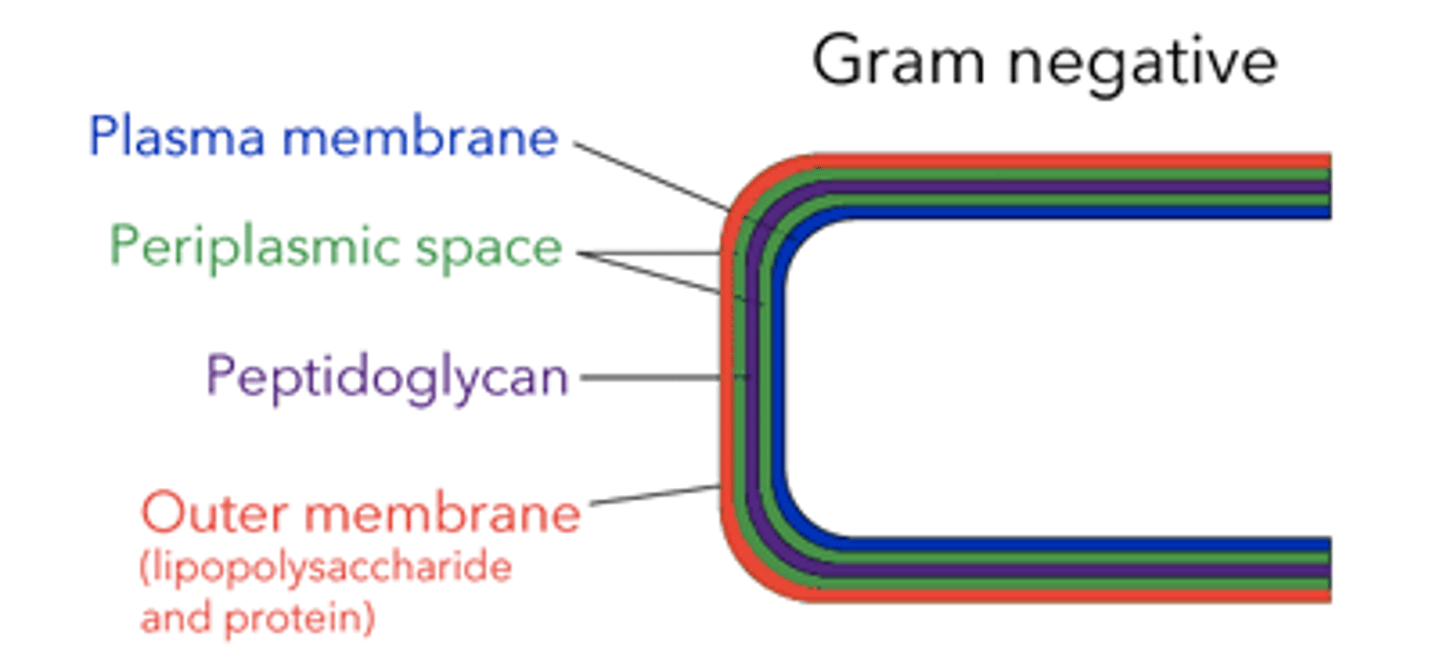
list the layers of gram negative bacterial membrane (from inside to outside)
plasma membrane > periplasmic space > peptidoglycan > outer membrane (LPS and protein)
lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is an _____ found in gram _____ bacteria only
endotoxin; negative
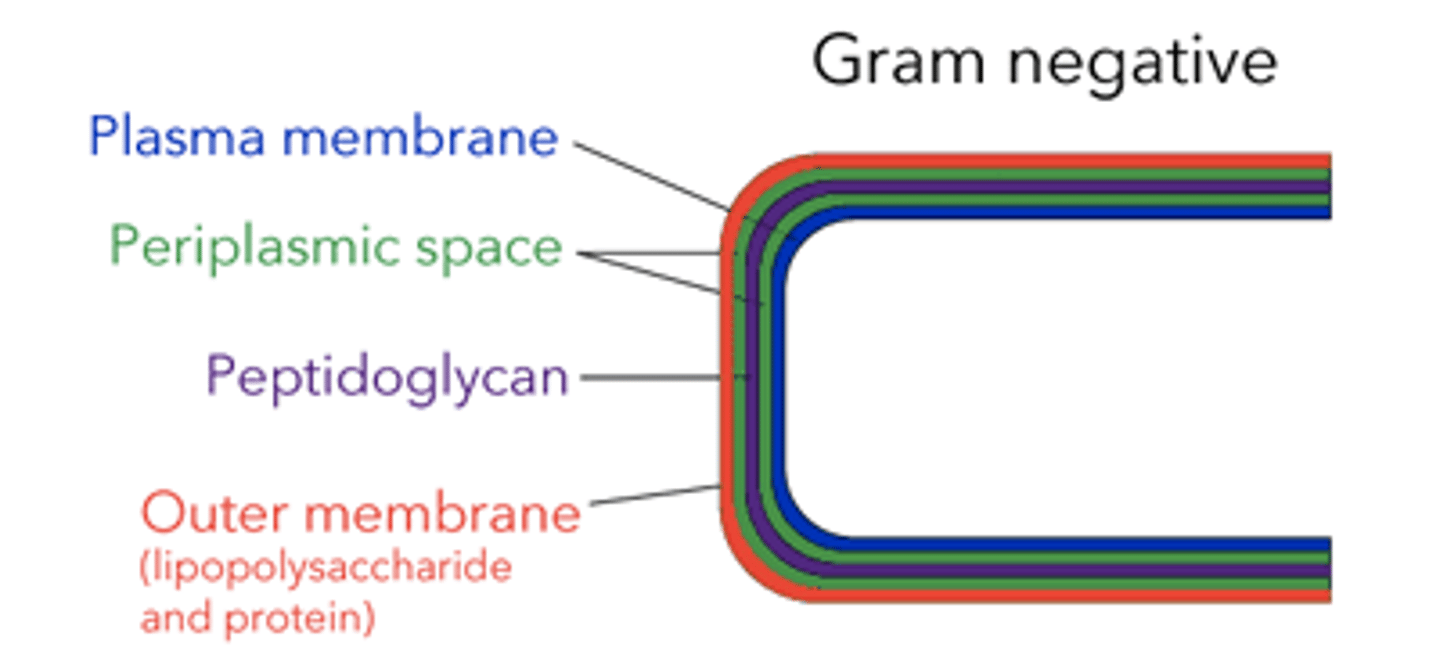
where is LPS found in gram negative cells, and when is it released?
the outer membrane; when the bacteria is destroyed
an _____ is a toxin that both gram positive and gram negative bacteria secrete
exotoxin
endotoxins are only secreted by gram _____ bacteria
negative
_____ are acidic polysaccharides that provide significant rigidity and structure only in gram _____ bacteria
teichoic acids; positive
how do teichoic acids confer rigidity and structure?
they connect the cell wall peptidoglycan to the cell membrane
a _____ covers both gram negative and gram positive bacterial cell walls
capsule
bacterial capsules are _____ because they decrease the capacity for bacteria to be phagocytosed by immune cells
virulence factors
in prokaryotes, the small ribosomal subunit is _____ and the large ribosomal subunit is _____ - these combine to form a _____ ribosome
30S; 50S; 70S
prokaryotic ribosomal subunits are made in the _____, and they are assembled into a 70S ribosome in the _____
nucleoid/cytosol; cytosol
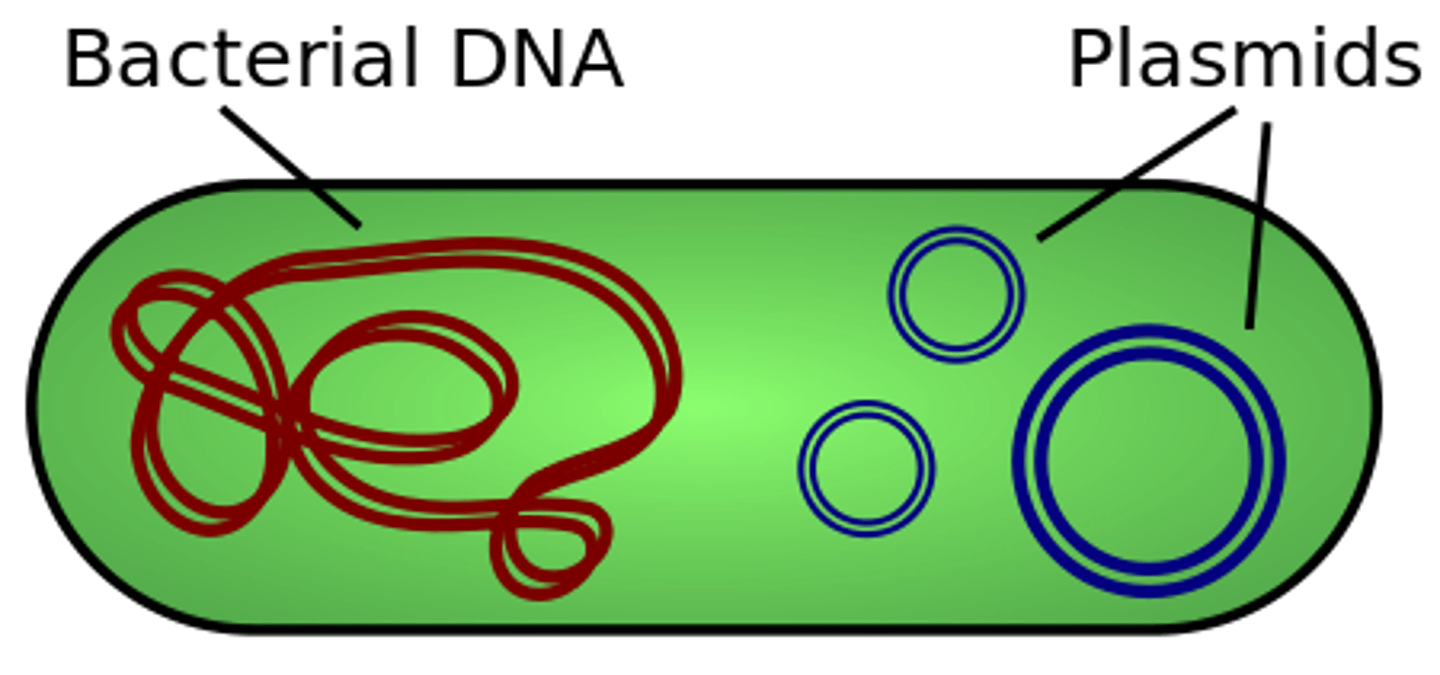
eubacteria and archaea can contain extrachromosomal pieces of DNA called _____
plasmids
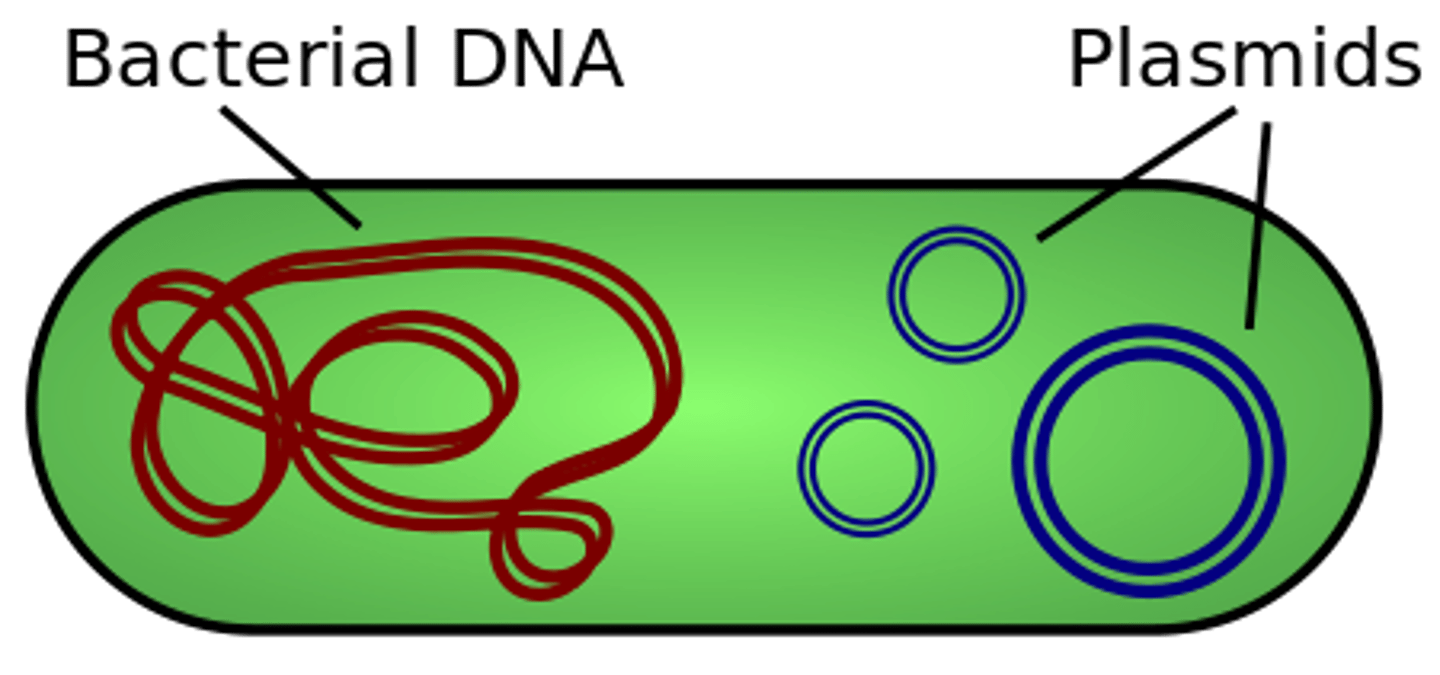
plasmids are segments of _____ DNA that may pass _____ between cells
extrachromosomal; horizontally
_____ have histone proteins and introns, but _____ lack both
archaea; bacteria
archaea and bacteria both have _____ and _____ (structural features)
pili; flagella
both archaea and bacteria undergo _____ to reproduce
binary fission (asexual reproduction)
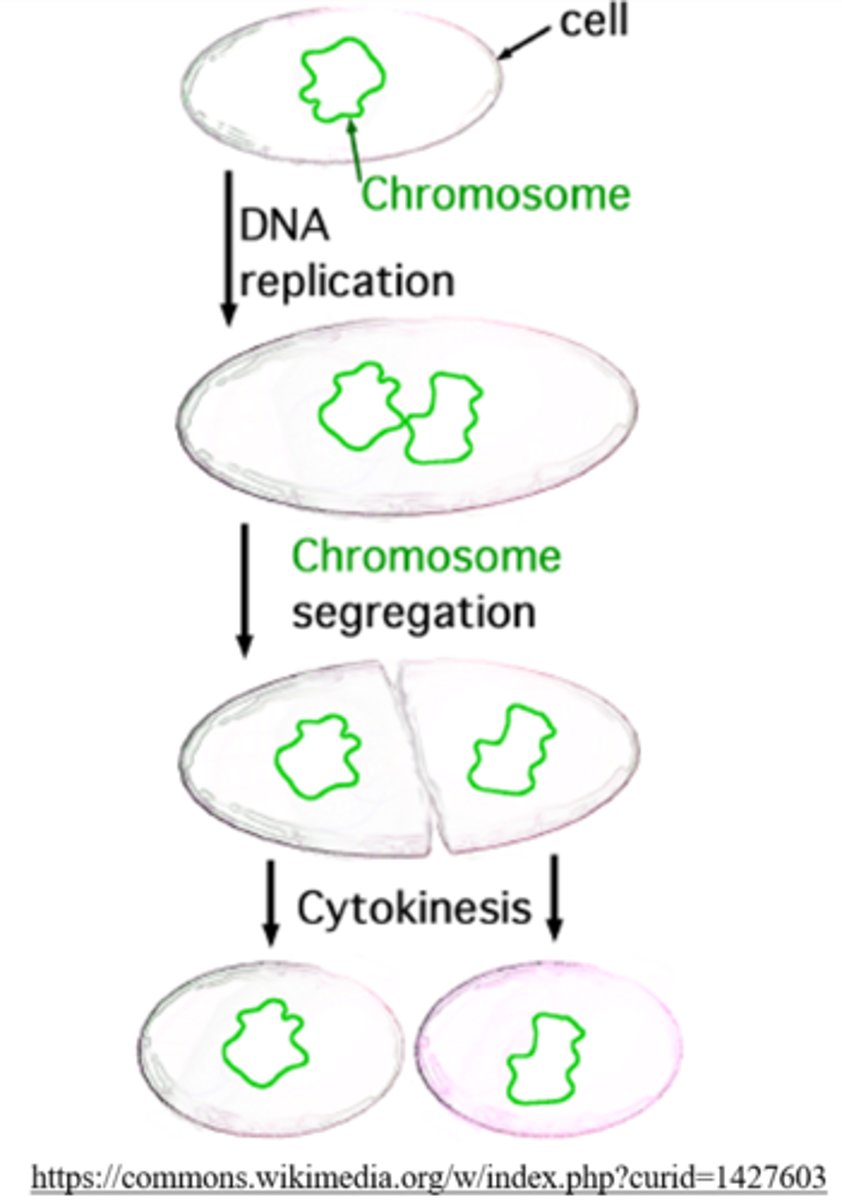
binary fission is an _____ mechanism where cells simultaneously grow, replicate their genome, and divide into 2 genetically identical cells
asexual reproduction
protista, fungi, plantae, and animalia are _____ kingdoms
eukaryotic
eukaryotes have membrane bound _____ and _____
nuclei; organelles
some _____ have cell walls, whereas most _____ will have them
non-mamalian eukaryotes: prokaryotes
(mammals have an extracellular matrix with collagen fibrils instead of a cell wall)
prokaryotic cells are _____ (size) than eukaryotes
smaller
prokaryotes tend to have _____ chromosome(s) in their _____, while eukaryotes tend to have _____ chromosome(s) in their _____
a single, circular; nucleoid; multiple, linear; nucleus
plasmids are frequently in _____, but they only occur sometimes in _____
bacterial prokaryotes; eukaryotes
(plasmids occur sometimes in archaeal prokaryotes)
histone proteins are present in _____ and _____, but they are absent in _____
eukaryotes; archaeal prokaryotes; bacterial prokaryotes
DNA replication is _____ (speed) in prokaryotes, but it is _____ (speed) in eukaryotes
fast; slow
introns are present in _____ and _____, but they are absent in _____
eukaryotes; archaeal prokaryotes; bacterial prokaryotes
prokaryotes have _____ ribosomes, while eukaryotes have _____ ribosomes
70S (30S and 50S subunits); 80S (40S and 60S subunits)
prokaryotes are _____ (ploidy), while eukaryotes are _____ (ploidy)
haploid; diploid
(prokaryotes/eukaryotes) do not have telomeres, but (prokaryotes/eukaryotes) do
prokaryotes; eukaryotes
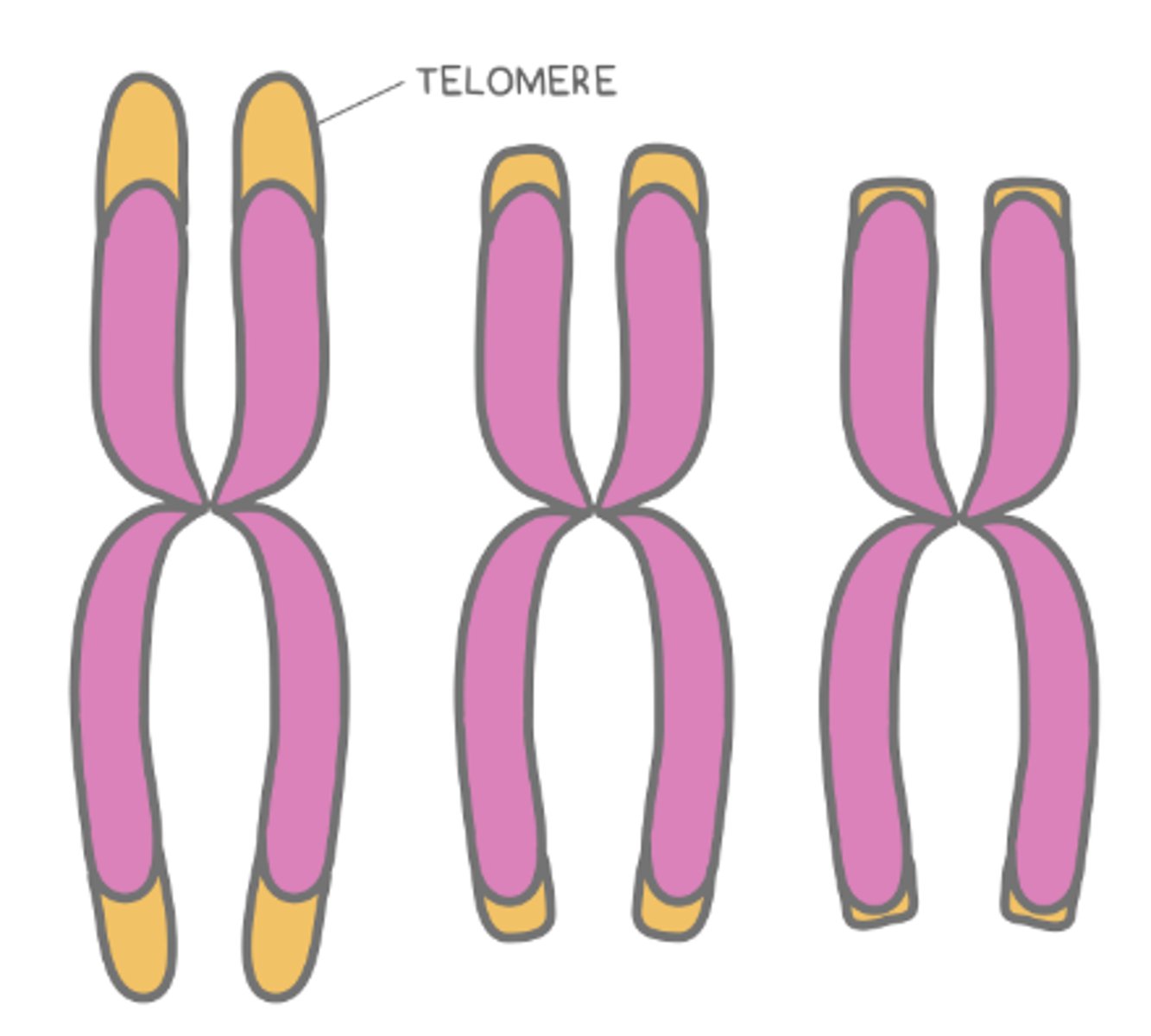
the electron transport chain (ETC) is located along the _____ of prokaryotes, and it is located along the _____ of eukaryotes
cell membrane; mitochondrial inner membrane (cristae)
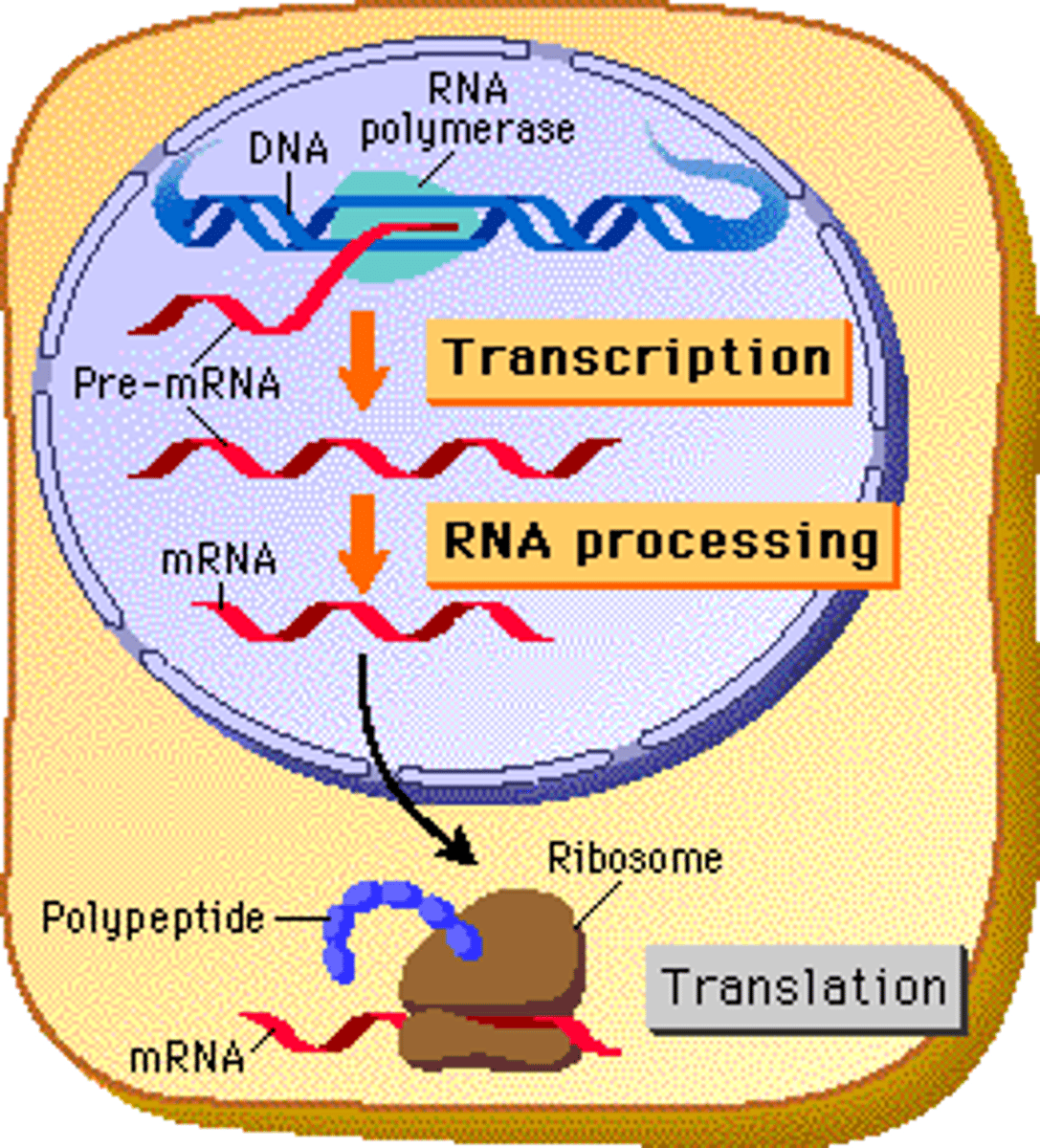
transcription + translation occurs simultaneously for the same mRNA transcript in _____
prokaryotes
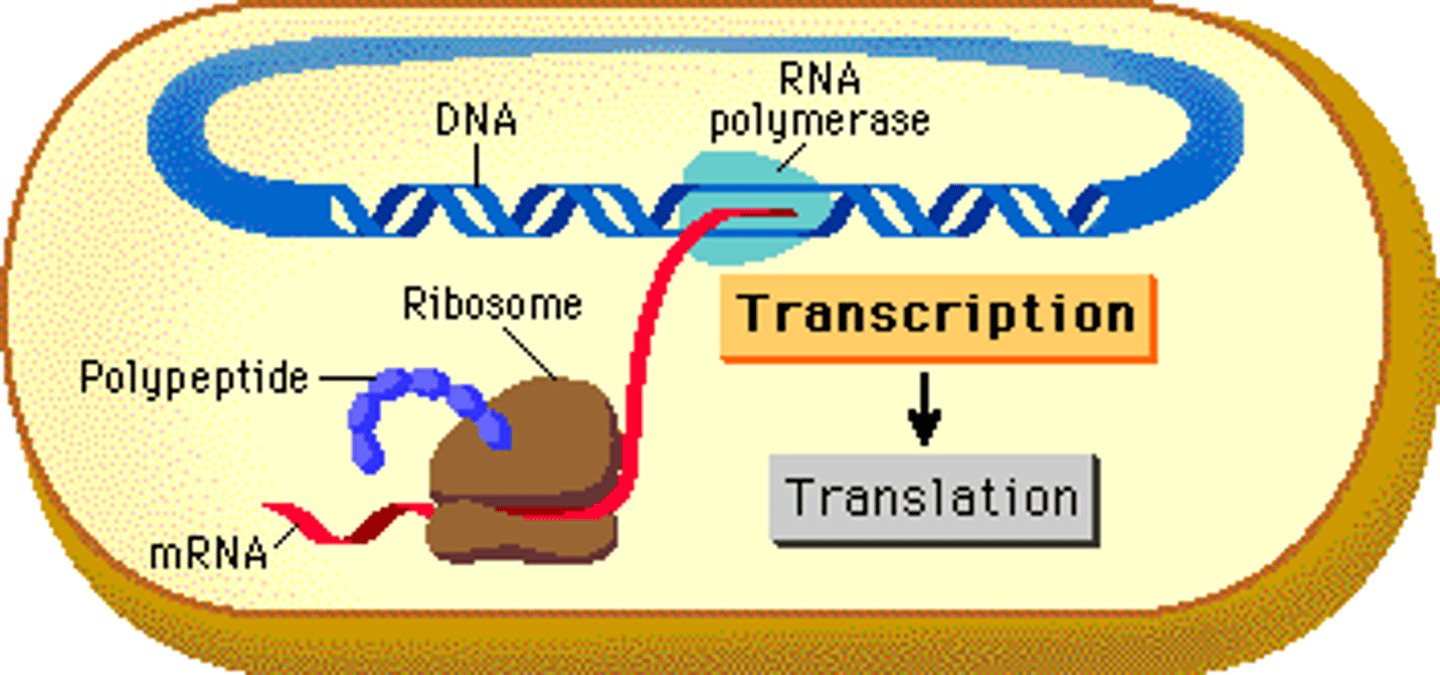
transcription + translation does not occur simultaneously for the same mRNA transcript in _____
eukaryotes
(transcription occurs first in the nucleus, then translation occurs when the mRNA moves to the cytoplasm)
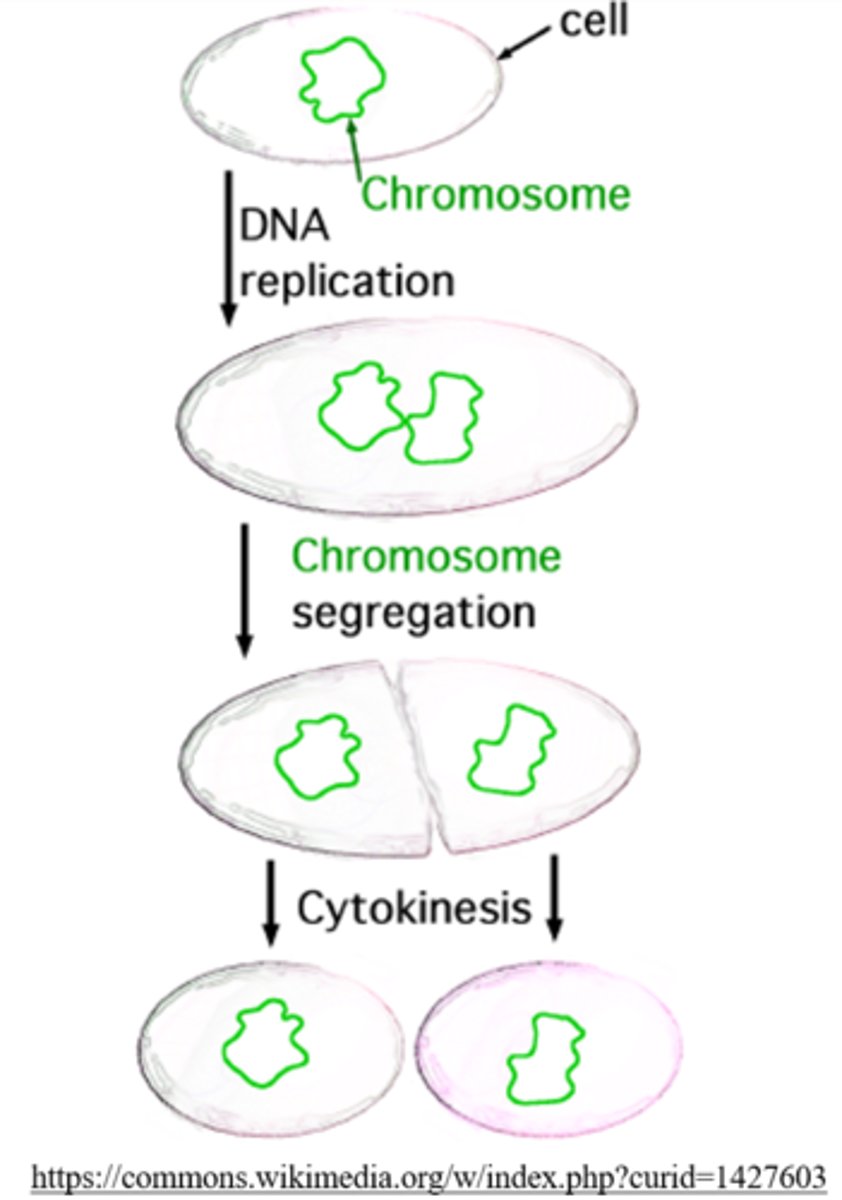
prokaryotes have a (short/long) cell cycle, and they divide by _____
short; binary fission
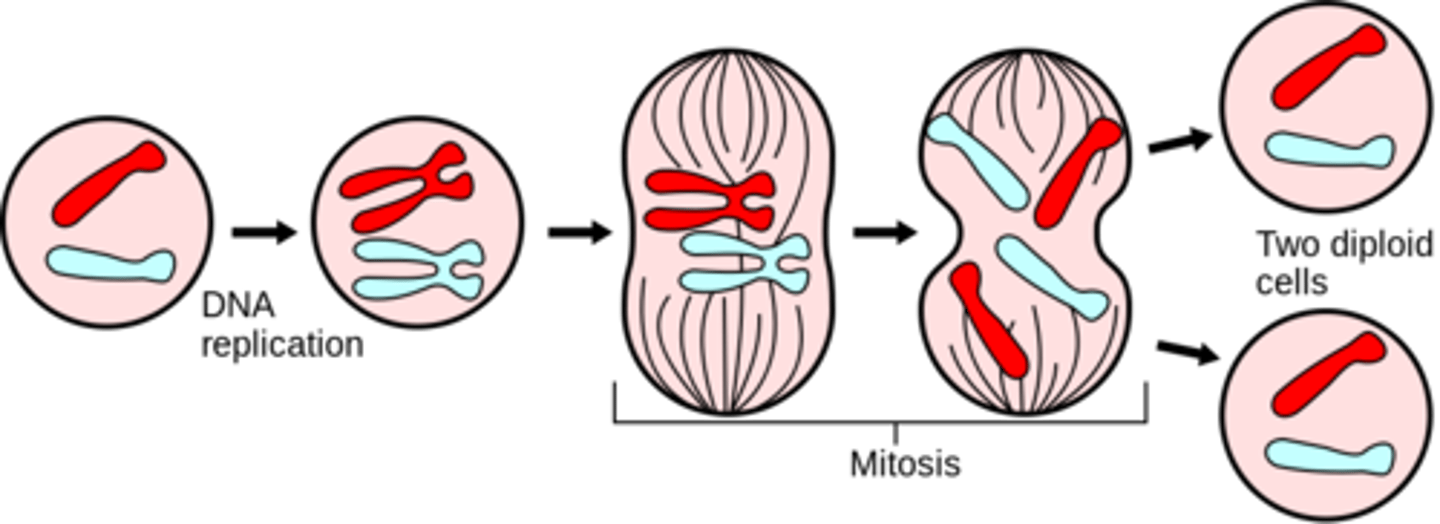
eukaryotes have a (short/long) cell cycle, and they divide by _____
long; mitosis/meiosis
(mitosis for somatic cells and meiosis to make gametes)
_____ are usually unicellular organisms, which can be fungus like, animal like, or plant like
protists
fungus-like protists (slime mold) do not have a cell wall made of _____ and they can move via _____
chitin; flagella or cilia

_____ organisms feed on decaying matter
saprophytic
how do fungus-like protists reproduce?
asexual reproduction and sporulation
_____ protists are photosynthetic primary producers
plant-like
dinoflagellates, diatoms, and euglenoids are unicellular, _____ protists that live in aquatic environments, reproduce asexually
plant-like
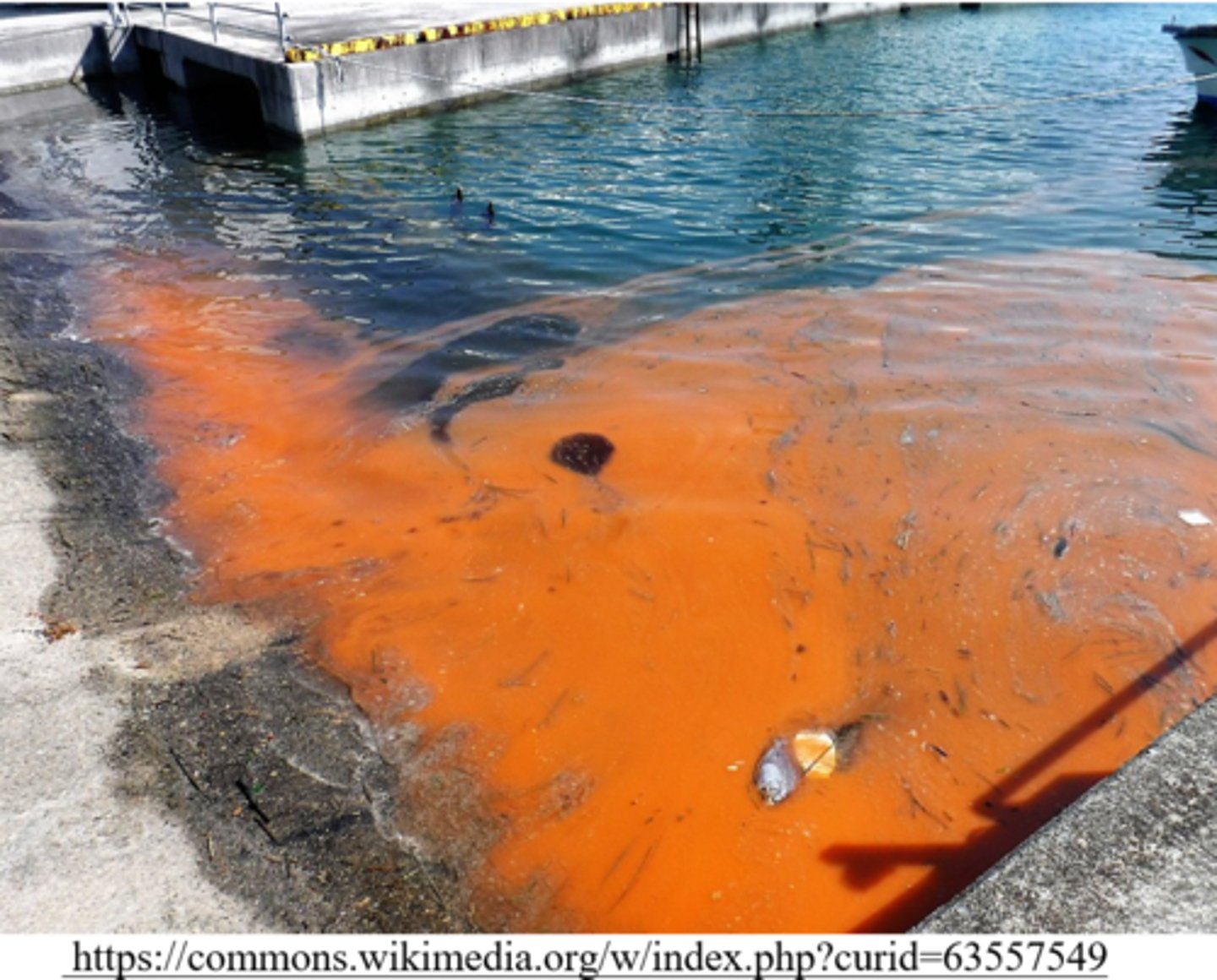
_____ is an algal bloom created by dinoflagellates, which leads to a build up of toxins and depletion of oxygen in the water
red tide

amoeba and paramecium are _____ protists (protozoa)
animal-like
amoeba and paramecium are protozoa (animal-like protists) that move via _____
cilia/flagella
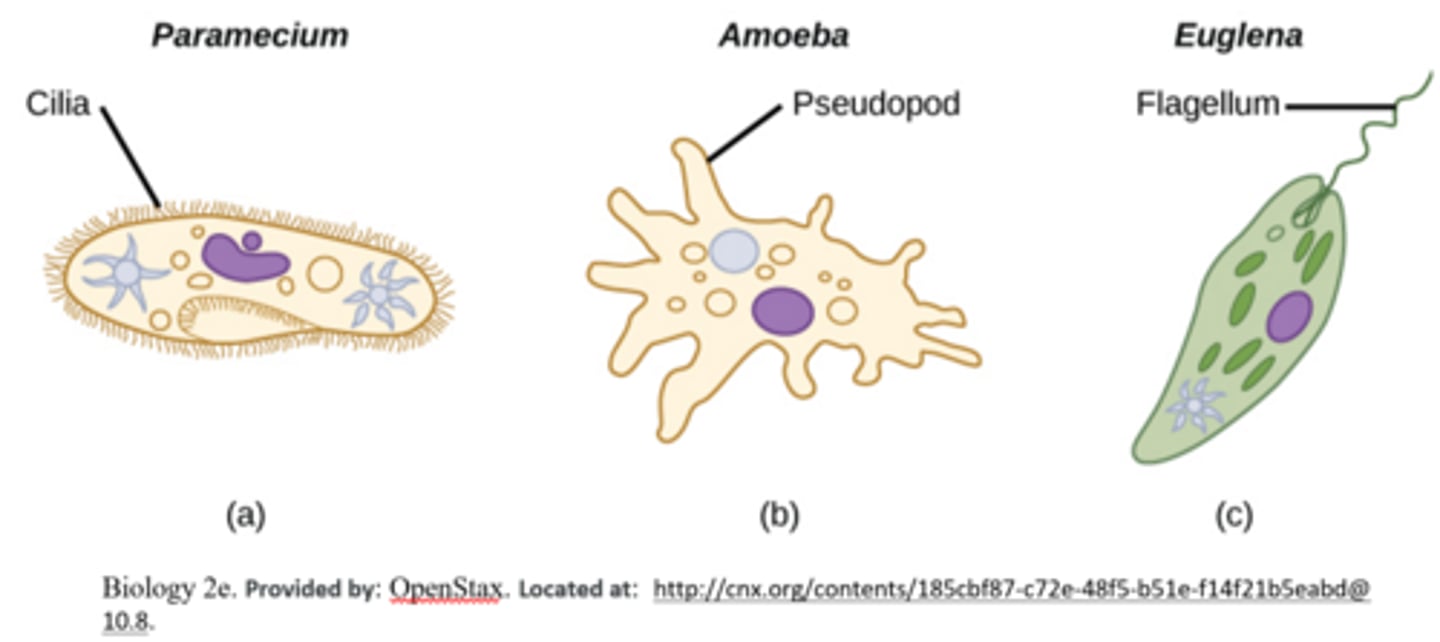
_____ are protozoa (animal-like protists) that are heterotrophic and act as parasitic pathogens
amoeba and paramecium
fungi are heterotrophic _____, and they are (prokaryotic/eukaryotic)
saprophytes; eukaryotic
_____ are unicellular, eukaryotic, non-filamentous fungi
yeasts
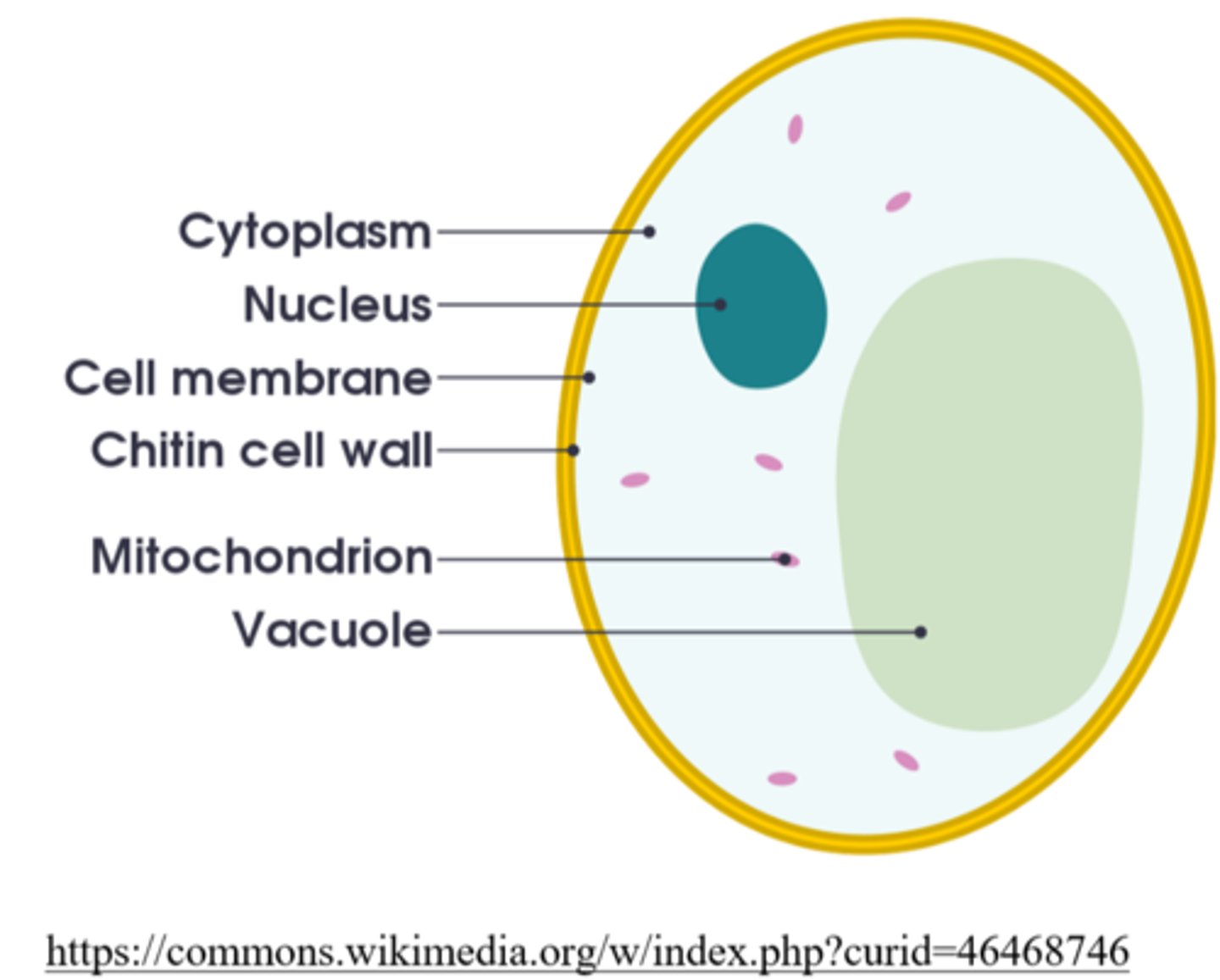
yeast are _____ (metabolism), and they reproduce asexually, by _____
facultatively anaerobic; budding
_____ are multicellular, eukaryotic, filamentous fungi
molds
molds form hyphae, and they are _____(metabolism)
aerobic
_____ are long branching network with nearby fungi
hyphae
a _____ is a whole group of hyphae
mycelium
_____ hyphae are separated into sections
septate
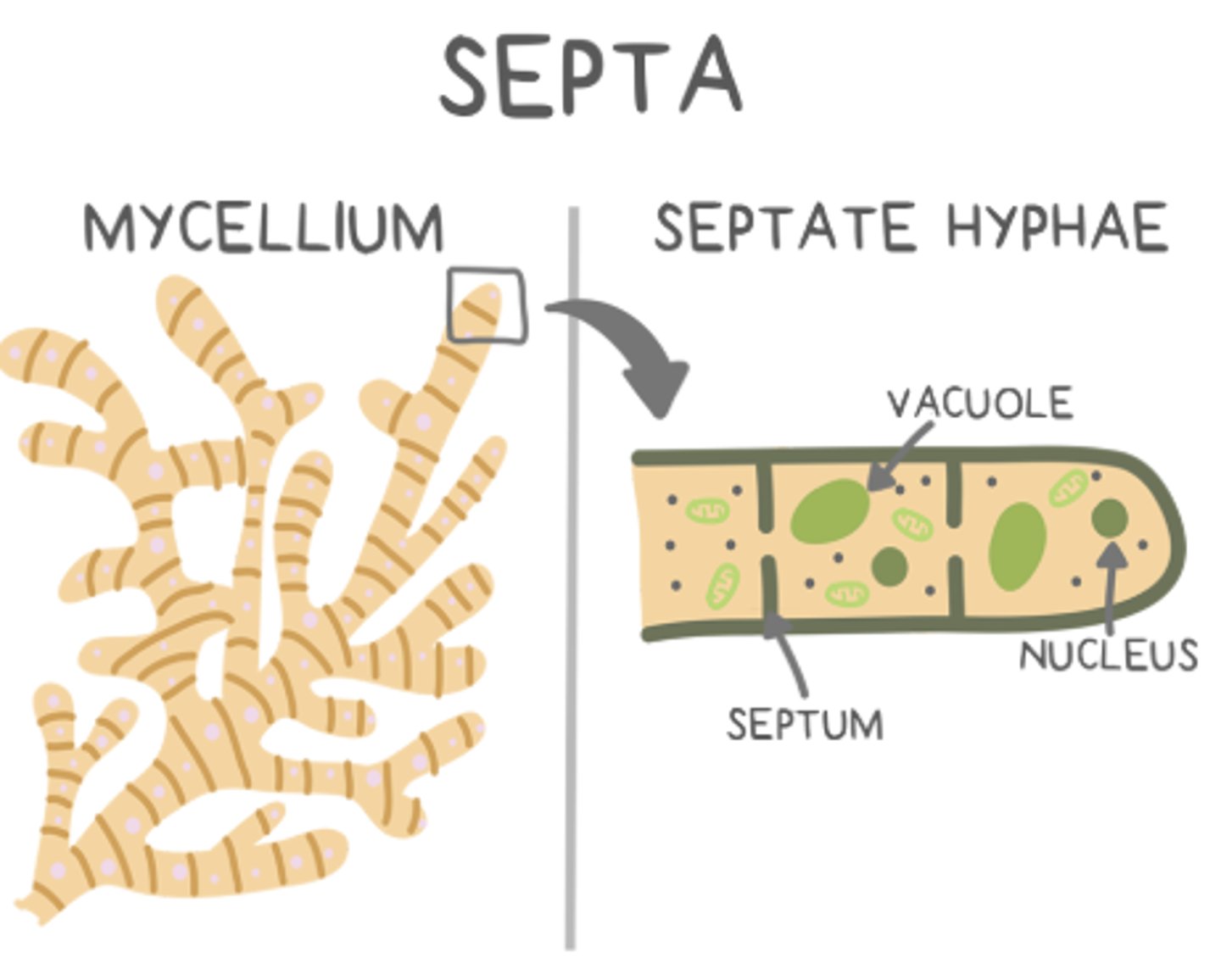
_____ hyphae are not separated into sections
coenocytic

fungi reproduce _____ when environmental conditions are good, and _____ when environmental conditions are bad
asexually; sexually
what is plasmogamy and how does it occur?
initiating step of sexual reproduction for filamentous fungi; two hyphae of a mycelium fuse their cytoplasm
following plasmogamy, the single fused cell now contains two haploid nuclei known as _______
pronuclei
what is the process of fusing pronuclei to form a single diploid cell in fungi?
karyogamy
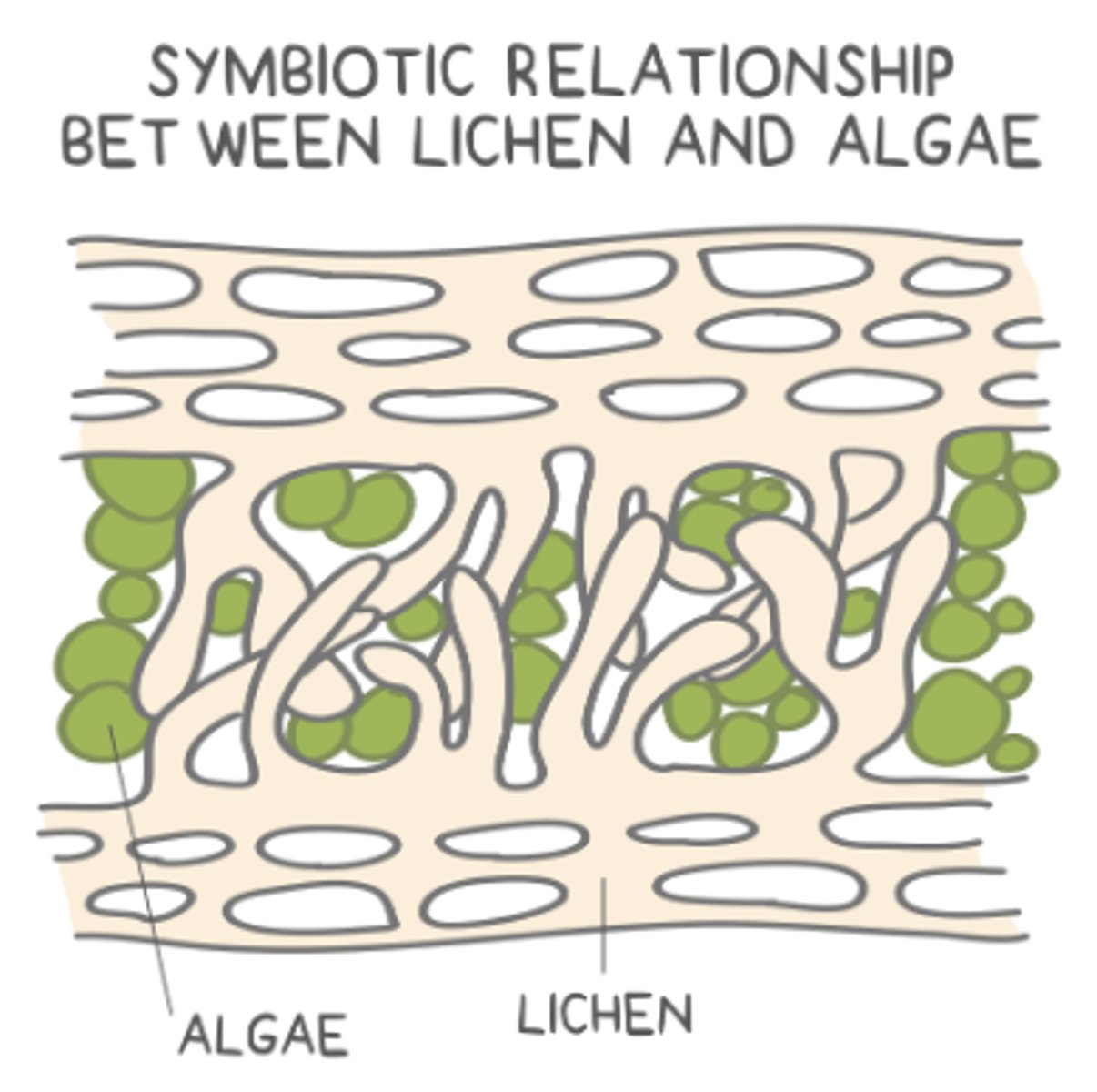
lichens are _____ containing fungi
symbiotic autotrophs
fungi can be paired with _____ or _____ in a lichen
algae; cyanobacteria
what are some of the most common features that animals share?
eukaryotic; diploid; multicellular; heterotrophic aerobes; usually motile; nervous and muscular systems
what are the ten most important phyla?
Porifera
Cnidaria
Platyhelminthes
Nematoda
Rotifera
Annelida
Mollusca
Arthropoda
Echinodermata
Chordata
_____ is a cavity fully lined by mesoderm
coelom
_____ have no cavity between the mesoderm and endoderm
acoelomates
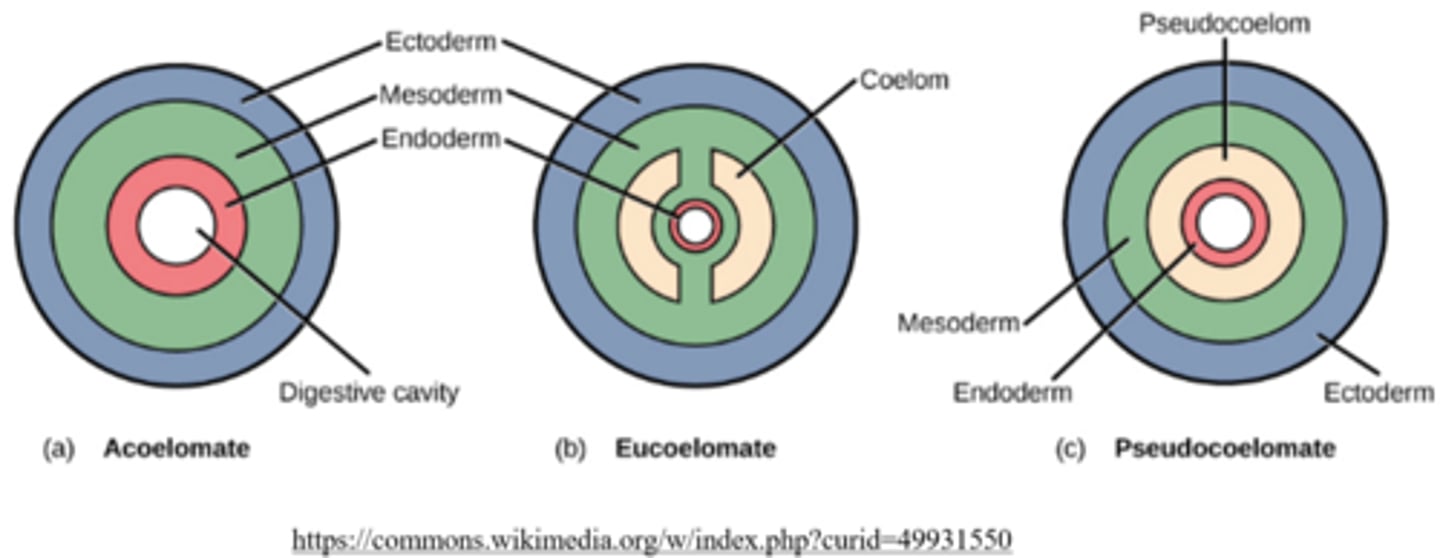
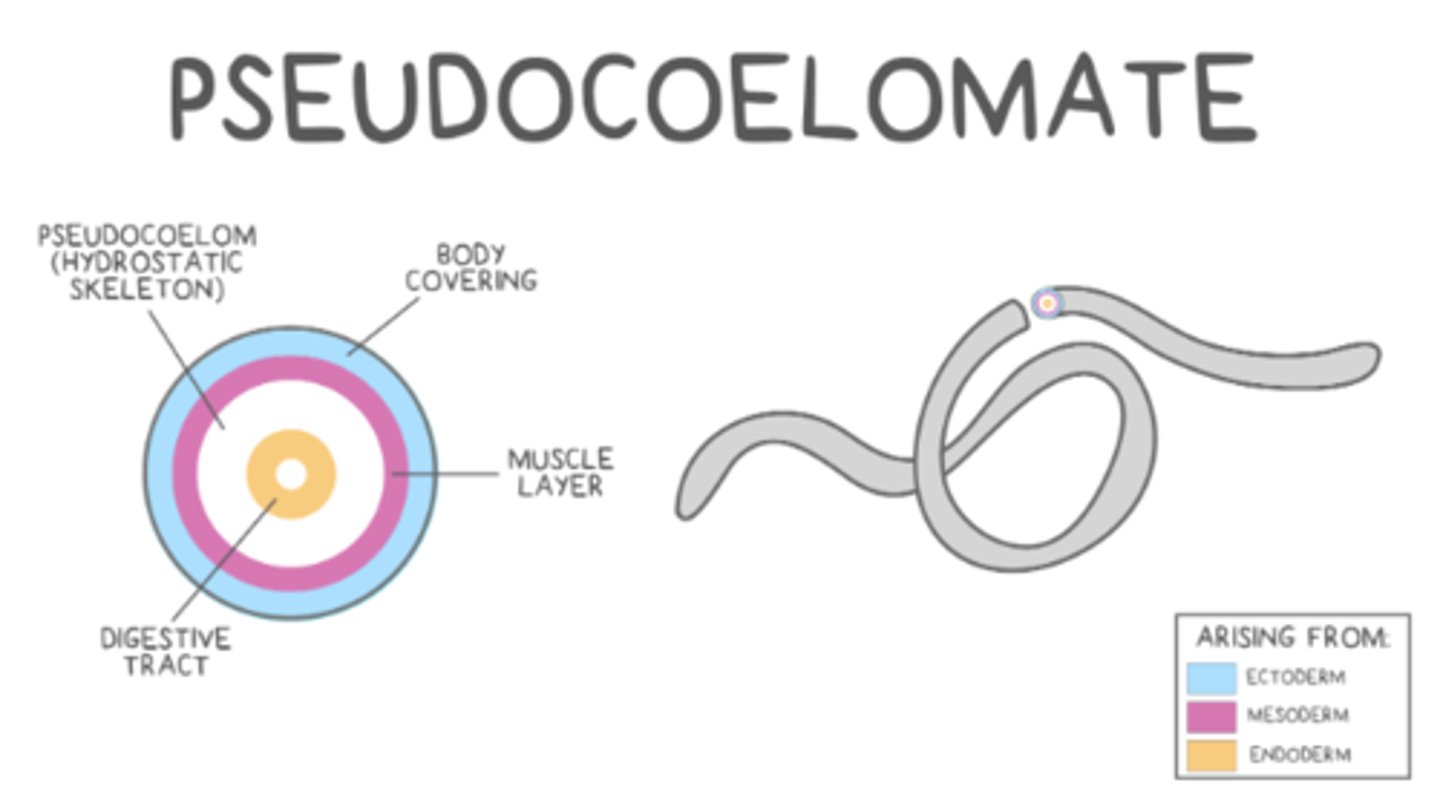
the coelom is only partially surrounded by mesodermal tissue in _____
pseudocoelomates
which of the nine phyla are acoelomate (lack a coelom)?
Platyhelminthes are acoelomate. Cnidaria and Porifera are not triploblastic are are unable to be classified by coelom.
which two phyla are considered pseudocoelomate?
nematoda, rotifera
a _____ provides rigidity through fluid pressure
hydrostatic skeleton

what are the five coelomate phyla?
annelids, mollusca, arthropoda, echinodermata, and chordata
_____ is a form of asexual reproduction, where an outgrowth from an old organism produces a new organism
budding
_____ have both male and female sexual structures, so they can produce both male and female gametes
hermaphrodites
_____ are organisms without true tissues
parazoa
_____ organisms are fixed in one place
sessile
_____ organisms have endoderm and ectoderm (no mesoderm)
diploblastic
_____ are organisms that have true tissues
eumetazoans
_____ are digestive systems with just one opening
gastrovascular cavities
_____ are cells that shoot poisonous barbs for protection and hunting
cnidocytes
nerve nets are primitive central nervous systems found in organisms without _____ and _____ symmetry
cephalization; radial
_____ symmetry refers to symmetry around the central axis
radial
what are some examples of platyhelminthes?
flatworms, trematoda, flukes, tapeworm, planaria
platyhelminthes have _____ symmetry and cephalization (a head)
bilateral

how are tissues organized in platyhelminthes?
triploblasts, eumetazoa
describe the circulatory system of platyhelminthes:
none (diffusion)
describe the nervous system of platyhelminthes:
two nerve cords with an anterior centralized ganglia (brain)
describe the respiratory system of platyhelminthes:
none (diffusion)
describe the digestive system of platyhelminthes:
gastrovascular cavity with two-way digestion