The Bio 102 Mega Review
1/259
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Every single one of my bio 102 review knowts, merged into one super knowt set. Good luck, have fun, you got this for the final...
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
260 Terms
All living things are made of…
cells
cell
membrane bound units filled with aqueous chemicals and organelles and can make copies of itself
micrometer
unit of measurement at the cellular level
Cells are made of…
carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids
genes
instructions in the DNA that code for proteins
4 DNA nucleotides
Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G)
Central dogma
DNA → RNA → protein
amino acids
monomers that make up proteins
mutation
DNA copies incorrectly and changes or removes sequences of nucleotides, changing proteins that are made
Evolution
mutations over billions of cell generations that permanently change species
Microscope
Instrument that allows us to zoom incredible amounts and see cells
Electron microscope
microscope that uses beams of electrons instead of light (shorter wavelength) so see much more zoomed in than conventional light microscopes
Robert Hooke
First person to observe and name cells
Cell Theory
All cells come from growth and division of preexisting cells
Extracellular Matrix
Protein fibers that connect cells together in multicellular organisms
Plasma Membrane
Barrier Enclosing Cell
Nucleus
Organelle containing DNA, in center of Eukaryotes
Cytoplasm
Transparent substance filling the inside of a cell
Ribosome
Small organelle that assembles proteins
Fluoresence Microscopy
Light microscope with fluorescent dyes that give off light when illuminated, help distinguish organelles
Prokaryotes
Cells without nuclei
Eukaryotes
Cells with nuclei
Archaea
Ancient prokaryotes adapted to live in extreme conditions that normal cells cannot
Mitochondria
worm shaped organelle that converts food into ATP (usable energy)
Chloroplasts
large green organelle in plants and algae that convert sunlight and CO2 and H2O into sugar and oxygen
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Rough version synthesizes proteins
Smooth version synthesizes lipids
Golgi Apparatus
packages and modifies molecules made in the ER for export
Lysosomes
intercellular digestion
Peroxisomes
detoxifies peroxides in cell
cytosol
aqueous portion of the cytoplasm
Cytoskeleton
system of protein filaments that help with movement and maintain shapes
Actin
thinnest cytoskeleton filaments for contractions
Microtubules
thickest cytoskeleton filaments that are tube like and pull chromosomes apart
intermediate filaments
part of cyctoskeleton that maintain cell shape and strengthen it
transport vesicles
shuttle from one organelle to others
E.coli
Model Organism for studying basic prokaryote cell properties
S. cerevisiae
yeast, model organisms for studying single celled, simple eukaryotic processes
Arabidopsis
Plant model organism used for studying plant development
Drosphilia Melongaster
Fly, idea organism for studying genetics
C. elegans
worm for studying tissue specialization
Zebrafish
ideal for studying vertebrate development, transparent for first two weeks of development
Mouse
Ideal for studying mammals, useful in medicine
Organic Chemistry
Chemistry of life based on carbon compounds
aqueous
watery environment
polymers
molecules made of subunits connected end to end
Avogadro’s Number
6.022×10²3 atoms or 6×10²3
Dalton
Unit of molecular weight
Electronegativity
tendancy of atom to attract electrons
Bond Strength
energy needed to break bond
Catabolism
break down food into smaller molecules to create usable energy and building blocks
anabolism
use energy created in catabolism to drive synthesis of new molecules that form cell
First Law of Thermodynamics
Energy neither created nor destroyed, only changed from one form to another
Second law of thermodynamics
entropy always increases
entropy
measures disorder in universe
Activated carrier
stores usable energy in chemical bonds to use later
Oxidation
lose electrons in reaction
reduction
gain electrons in reaction
free energy
energy available that can do work
activation energy
energy boost required to start a reaction
Standard free energy change
change in free energy independent of concentration
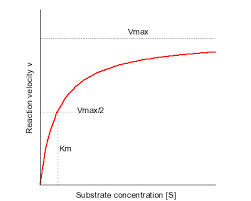
Michaelis Constant
concentration of substrate where enzyme works at half minimum speed
Michaelis Menten Graph
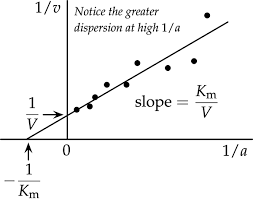
Lineweaver Burk Graph
Fatty Acids Comprise of:
Hydrophillic head with a hydrophobic tail
Saturated Fatty Acids
Filled with single bonds, no double bonds, solid at room temperature
Unsaturated Fatty Acid
Have at lease one double bond, liquid at room temperature.
Phospholipid Bilayer
make up membrane of the cell, head contains phosphate group
Plasma membrane
thin yet durable membrane that holds the cell together
amphipathic
contains a hydrophilic and hydrophobic portion
How are membranes made more fluid?
Unsaturated fatty acids
sterols for rigidity (ex. cholesterol)
temperature
length of fatty acid tails
Membrane proteins
proteins scattered throughout the cell membrane in a fluid mosaic model that have a variety of purposes
glycolipids
lipids that have sugars attached to them
transporters
shift small organic molecules by changing shape - passive
channels
pores to facilitate ion diffusion
simple diffusion
transport of molecules without energy from high to low concentration
facilitated diffusion
form of passive transport that moves molecules across the cell membrane with the help of a protein
Active Transport
uses energy to transport large molecules and/or against their concentration gradient
Concentration gradient
gradual high concentration to low concentration across a membrane
the lipid bilayer is penetrable to:
small nonpolar molecules
uncharged polar molecules
membrane potential
tiny gradient in electrical charge across a membrane
resting membrane potential
non zero voltage diffence that is steady
threshold voltage in humans
-55 mV
peak of depolarization voltage
40 mV
transmembrane domain
nonpolar region of membrane protein that is lodged in hydrophobic tails of membrane
transmembrane protein
membrane protein that completely passes through membrane
monolayer associated protein
membrane protein directly attacked to membrane, but only on one side
lipid anchored protein
membrane protein attached purely by a lipid
peripheral membrane protein
protein loosely associated with the membrane and purely attached by another protein
tight junction
prevents protein from moving past it and creates seal between cells
Aquaporins
channels for water to freely enter
osmosis
movement/diffusion of water, toward higher solute concentration
hyposmotic
more water inside cell than outside
hyperosmotic
less water outside cell than inside cell
isosmotic
equal concentrations of water inside and outside cell
gap junctions
pores between two or more cells
Nernst Equation
V = 62log(Co/Ci)
Patch-Clamp Recording
fine glass microelectrode records voltage of cell membrane
ligand gated channel
needs allosteric binding of ligand to open
mechanically gated channel
mechanical force needed to open
voltage gated channel
opens only to a certain membrane potential