Module 4: Protein Function
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Myoglobin
Binds oxygen through ‘simple’ behavior (unlike hemoglobin...)
Monomer
First X-ray crystal structure determined
Myoglobin function
Improves oxygen solubility to facilitate diffusion in the muscle
Prevents heme oxidation
Prevents carbon monoxide binding
1. Distal His blocks CO, which normally binds heme 25,000x stronger than O2
Heme group
Prosthetic group (permanently attached molecule)
• NOT proteins
• Fe (II) with a porphoryin ringBinds oxygen reversibly
• Protein enables this
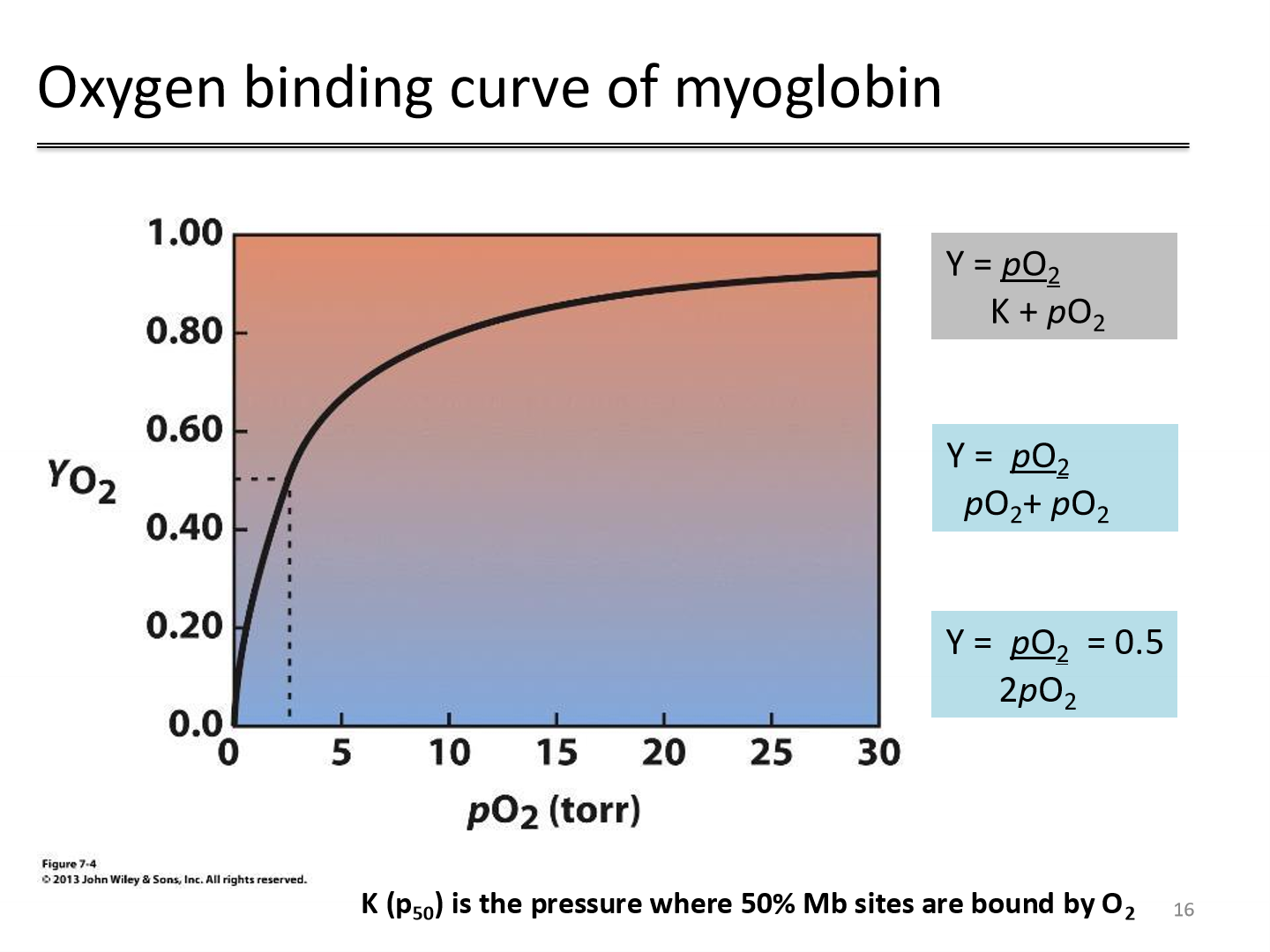
Oxygen binding curve of myoglobin
P50 is when 50% of Myoglobin binding sites are occupied
high P50 implies low affinity for oxygen
low P50 implies high affinity for oxygen
P50 for myoglobin in blood is 2.8 torr
Myoglobin acts as an oxygen reservoir — it stores O₂ and releases it when tissue pO₂ is low; constant high affinity for oxygen
Ligand binding to protein
hyperbolic binding observed at multiple biding sites ONLY WHEN binding at each site is independent of binding at other sites
Kd is concentration at which 50% binding sites are occupied by ligand
Cooperativity
the binding of a ligand to one site affects the binding of additional ligands to additional sites
requires multiple subunits, so myoglobin's O2-binding is NOT sigmoidal (has rectangular hyperbola)
Myoglobin cannot transport O2 because it has a high O2 affinity and would NOT release O2 in the tissues
Threshold effect in hemoglobin allows it to release more O2 in tissues that work "harder" and have lower O2
Hemoglobin
Dimer of dimers
• Two αβ dimers
• α2β2 tetramer
• Each subunit binds one heme
• Thus, Hb binds 4 hemes!
alpha and beta subunits
The globin fold
• Sequences only ~18% identical at amino acid level
• Important principle: sequences diverge much more rapidly than
structures
• Some residues are absolutely conserved among Mb, Hb a, and Hb
Oxygen binding curve of hemoglobin p50
the oxygen pressure at which hemoglobin is 50% saturated
hemoglobin has a p50 of 26 torr, meaning hemoglobin is half-saturated with oxygen at a partial pressure of 26 torr
A lower p₅₀ means less oxygen is needed to reach 50% saturation ⇒ oxygen binds more easily (higher affinity for oxygen)
A higher p₅₀ means more oxygen is needed to reach 50% saturation ⇒ oxygen binds less easily (lower affinity for oxygen)
this causes oxygen release
Fractional saturation (Y)
Y = (pO2) / (p50) + (pO2)
Hill plot
• How do we determine n and p50 for hemoglobin?
• Ratio of oxy-Hb (Y) to deoxy-Hb (1-Y)
• Re-arrange Hill equation and take log to get linear equation
log (Yo2/1-Yo2)= nlogpO2 – nlogp50
Structural basis of functional hemoglobin
Deoxy-hemoglobin: Tense state (T)
Oxy-hemoglobin: Relaxed state (R)
Oxygen binding drives structural changes T to R
One heme bound to oxygen triggers the other three subunits into the R state (allostery)
Structural Basis of Hemoglobin
Step 1
Oxygen pulls iron into heme plane, which pulls on proximal His
F8, which pulls entire Helix F
Step 2
As a result, Tertiary structure changes between subunits
1. At the a1—b2 and a2—b1 interfaces
2. Ion pairs ‘break’ at C-terminus of a and b subunits
How to lower affinity of Hemoglobin for oxygen
important to facilitate R —> T transition
• increase H+ (Bohr effect)
• increase CO2 (Bohr effect part 1 and part 2)
• increase Bisphosphoglycerate (BPG)
Bohr Effect for protons
as pH goes down (e.g. from increasing CO2), [H+] goes up.
Protonation (deoxygenation/T-state) is favorable
T-state ionic interactions are REFORMED
O2 affinity decreases, causing a shift of the O2 binding curve to the right
O2 binding is therefore pH dependent
lower pH promotes T state (oxygen release)
higher pH promotes R state (oxygen binding)