Quiz 8: Sadness
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
A researcher hypothesizes that there will be brain areas associated with valence and arousal, but they will not be regions that are specific to only one emotion. Which viewpoint does this hypothesis align with?
a. basic emotion b. biological c. core affect d. natural-kinds
c. core affect
A researcher hypothesizes that sadness, anger, and fear all rely on distinct neural systems that do not overlap. Which viewpoint does this hypothesis align with?
a. appraisal b. core affect c. natural-kinds d. valence
c. natural-kinds
Barrett and her colleagues have conducted numerous studies to test the conceptual act model. In the one presented in class, the … was associated with subjective ratings of valence, regardless of the specific emotion tested.
a. medial orbital frontal cortex b. amygdala c. dorsolateral PFC d. hippocampus
a. medial orbital frontal cortex
Barrett and her colleagues have conducted numerous studies to test the conceptual act model. In the one presented in class, the … was associated with subjective ratings of arousal, regardless of the specific emotion tested.
a. medial orbital frontal cortex b. amygdala c. dorsolateral PFC d. hippocampus
b. amygdala
Applying the conceptual act model, if I encounter a snake, my core affect is negative, and my arousal is high, I am likely to label or categorize my emotional experience in that moment as
a. excitement b. frustration c. happiness d. fear
d. fear
A researcher wants to track cerebral blood flow to different regions of the brain. They could use either the BOLD signal of an fMRI or the
a. time signature of EEG b. amplitude of ERPs c. radioactive water tracer in PET d. lesion method
c. radioactive water tracer in PET
George et al (1995) noted several brain regions with greater activity following a sad memory compared to a neutral or happy memory. The list of structures with greater activity for sad memory did not include the
a. ACC b. basal ganglia c. PFC d. temporal gyrus
d. temporal gyrus
George et al (1995) found significantly less activity in the sadness condition in which brain structure?
a. visual cortex b. thalamus c. insula d. fornix
a. visual cortex
Short Answer: The articles we discussed used very different methods to induce/provoke sadness in their participants. Compare/contrast their methods by telling me a) how they induced sadness, b) a benefit of each methods, and c) a drawback of each method.

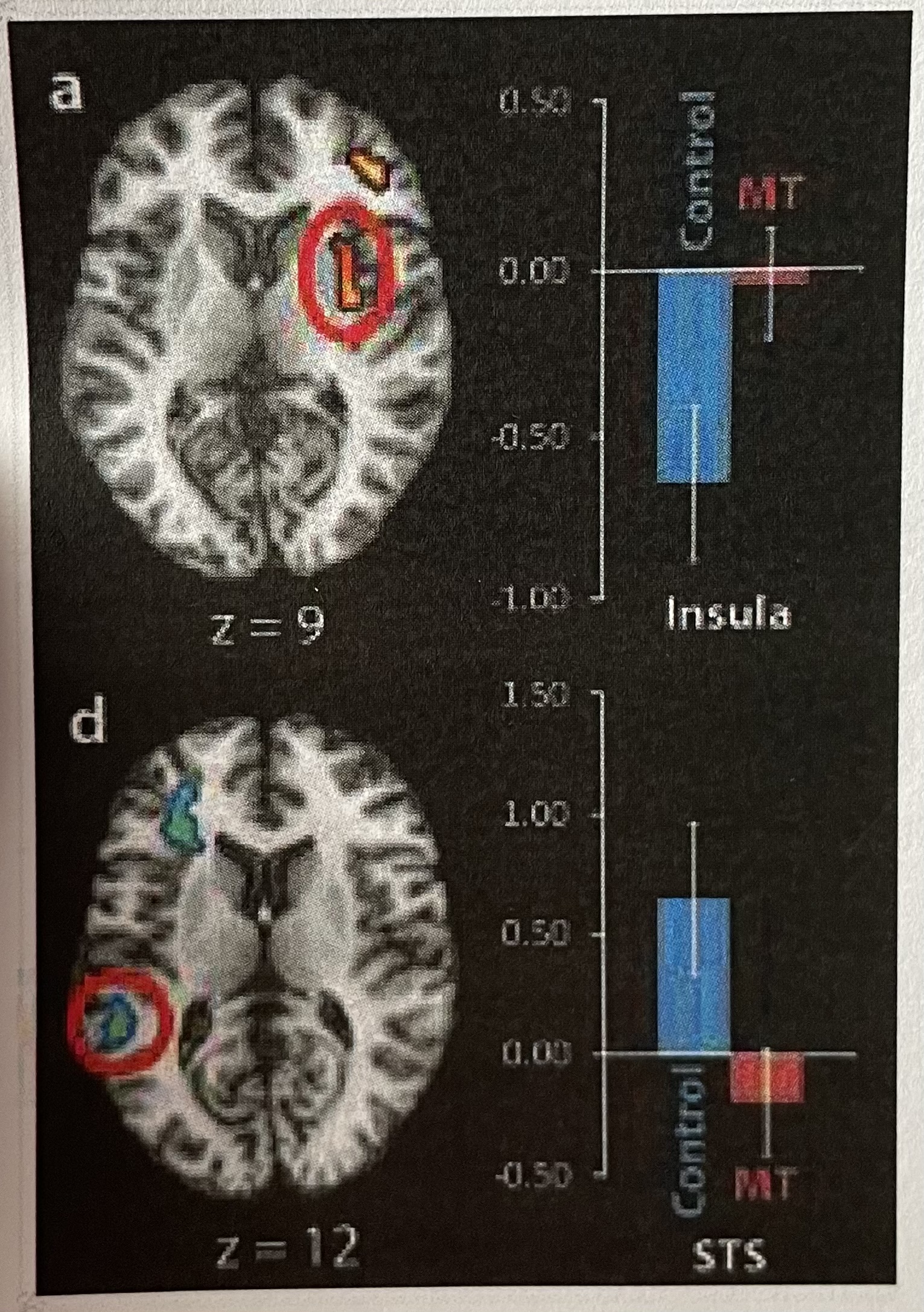
Short Answer: This figure from Farb et al. (2010) represents the difference in the BOLD signal for sad minus the neutral conditions in the control group and the mindfulness training (MT) group. Is the insula activated or deactivated for sad compared to neutral in the controls?
Deactivated
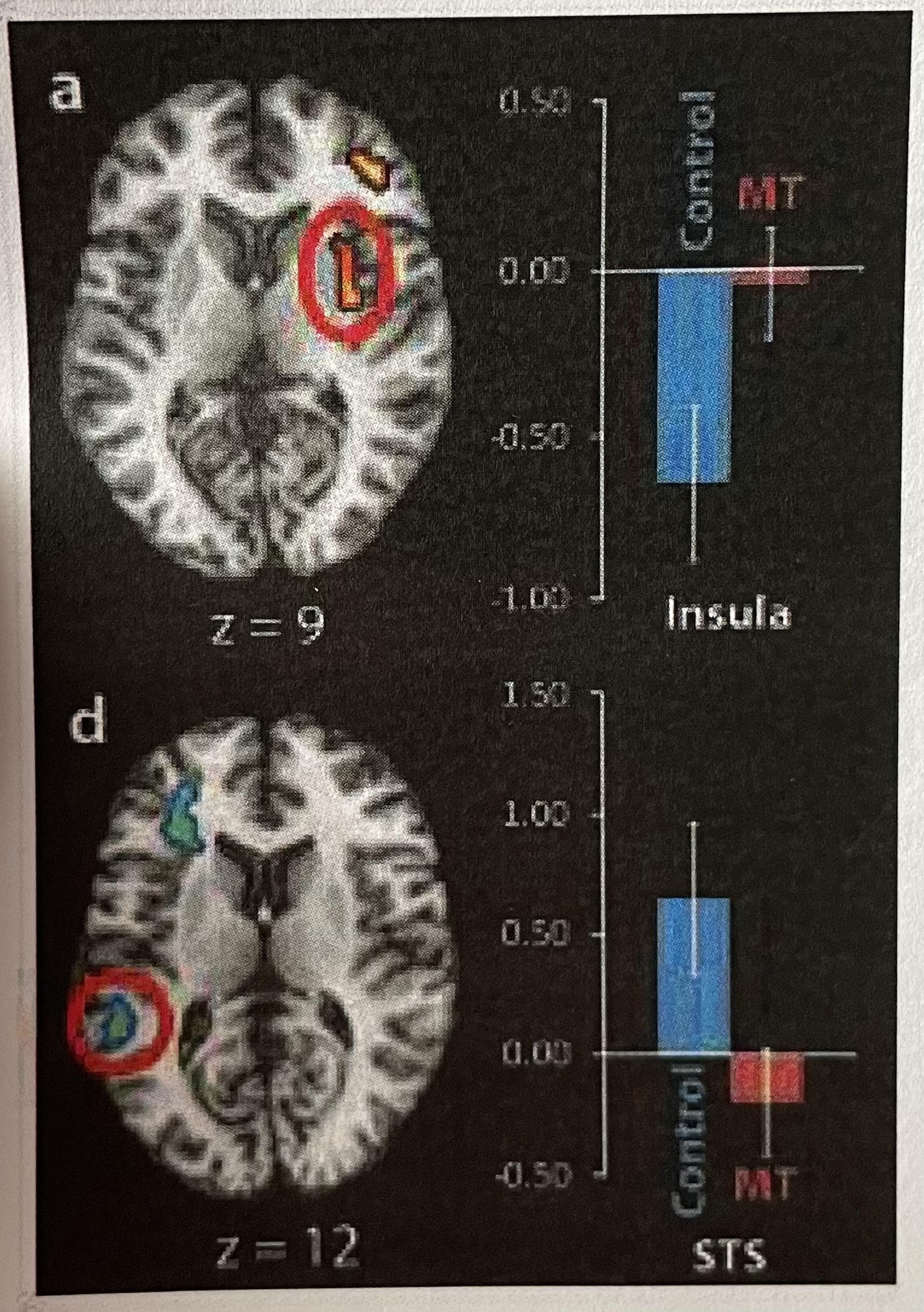
Short Answer: Are there any differences between sad and neutral conditions in either of these brain areas for the mindfulness training (MT) group (i.e., is there any activation or deactivation)?
No. They both show nonsignificant deactivation.
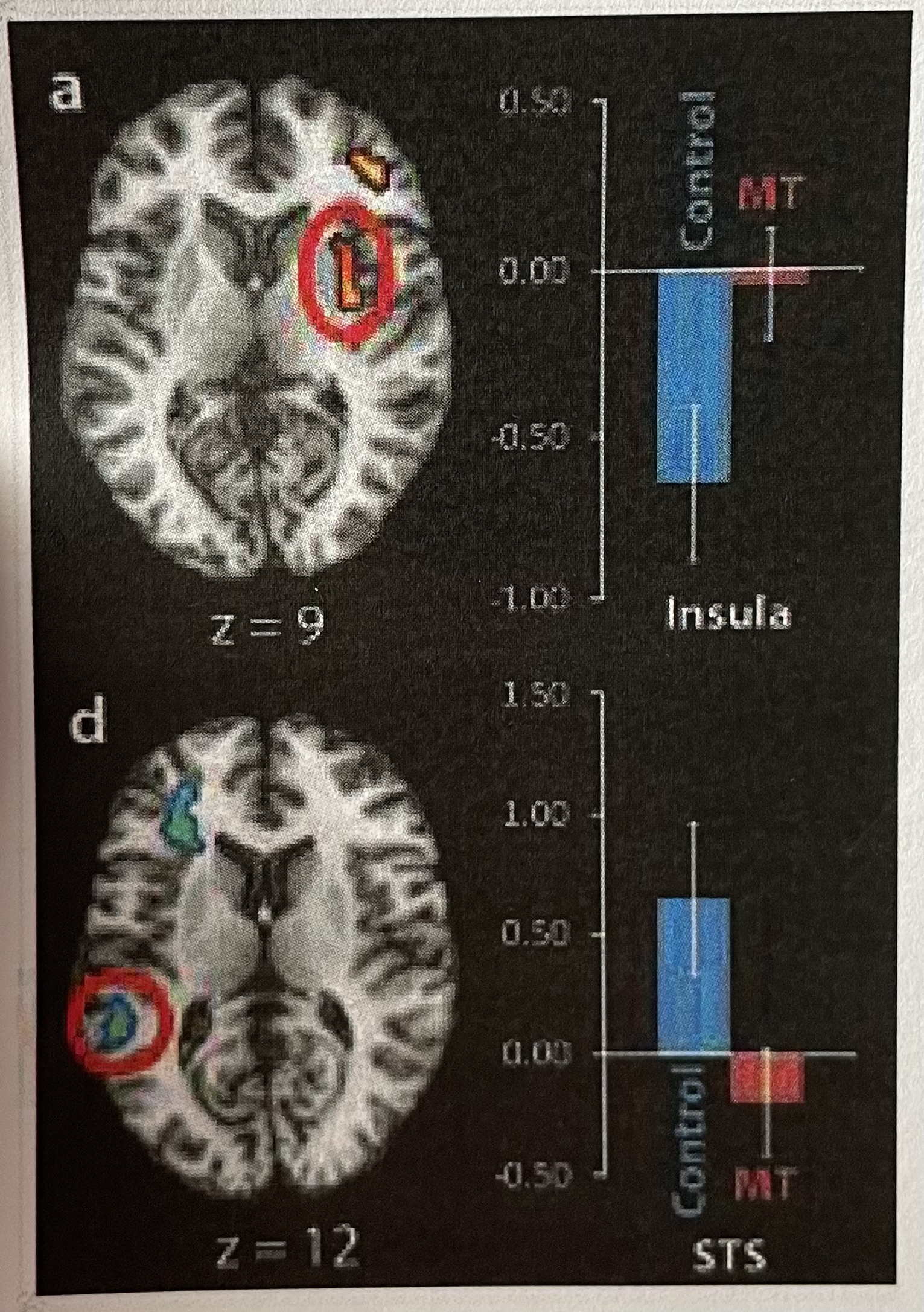
Short Answer: What can you conclude about the effect of mindfulness training on brain activity related to sadness based on these data?
Mindfulness training reduces brain reactivity to sadness in regions involved in emotional processing.