General Biology 2 Exam 2
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Of the following choices, the epithelium with the shortest diffusion distance is __.
A. Simple squamous epithelium
B. Simple columnar epithelium
C. Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
D. Stratified squamous epithelium
A. Simple squamous epithelium
Which type of muscle is the basis for voluntary movement and must be stimulated by the nervous system in order to contract?
A. Smooth muscle
B. Adipose tissue
C. Cardiac muscle
D. Squamous epithelium
E. Skeletal muscle
E. Skeletal muscle
Which behavior leads to a reduction in the body temperature of an animal as a result of evaporative cooling?
A. Fluffing feathers
B. Piloerection
C. Non-shivering thermogenesis
D. Huddling together
E. Panting
E. Panting
Which statement about counter-current heat exchangers is correct?
A. Relatively cool arterial blood is next to relatively warm venous blood
B. They are mechanism for animals to dissipate excess body heat
C. Relatively warm arterial blood is next to relatively cool venous blood
D. Arterial blood and venous blood flow in the same direction
E. None of the above
E. None of the above
True or false. For an endotherm and an ectotherm that are the same weight, the ectotherm has a higher metabolic rate than the endotherm.
A. True
B. False
B. False
Consider the energy budgets for a human, an elephant, a penguin, a mouse, and a snake. The ___ would have the highest total annual energy expenditure, and the __ would have the highest energy expenditure per unit mass.
A. Elephant; mouse
B. Elephant; human
C. Human; penguin
D. Mouse; snake
A. Elephant; mouse
The temperature-regulating center of vertebrate animals is located in the ___.
A. Thyroid gland
B. Hypothalamus
C. Subcutaneous layer of the skin
D. Liver
B. Hypothalamus
There are advantages and disadvantages to adaptations. Animals that are endothermic are likely to be at the greatest disadvantage in ___.
A. Very cold environments
B. Very cold environments
C. Environments with a constant food source
D. Environments with variable and limited food sources
D. Environments with variable and limited food sources
In a cool environment, an ectotherm is more likely to survive an extended period of food deprivation than would an equally sized ectotherm because the ectotherm ___.
A. Maintains a higher basal metabolic rate
B. Expends more energy per kilogram of body mass than does the endotherm C. Invest little energy in temperature regulation
D. Has greater insulation on its body surface
C. Invest little energy in temperature regulation
Chemical digestion of which type of macromolecule begins in the stomach?
A. Nucleic acids
B. Carbohydrates
C. Proteins
D. Lipids
C. Proteins
Essential organic molecules that are required in the diet in much smaller quantities than essential amino acids and essential fatty acids are called ___.
A. Minerals
B. Vitamins
C. Local regulators
D. Amines
E. Steroids
B. Vitamins
Most minerals are required in small quantities in the diet, but two minerals that are required in large quantities for the formation of the extracellular matrix of bone are:
A. Iodine and zinc
B. Calcium and zine
C. Sodium and phosphorus
D. Calcium and phosphorus
E. Chlorine and magnesium
D. Calcium and phosphorus
Which statement is true about the group of mammals known as "ruminants"?
A. The endothelium of their stomach produces specialized digestive enzymes that break down cellulose
B. They have an enlarged gizzard that stores large populations of microbes that can digest cellulose
C. They have enlarged livers to de-toxify high levels of toxic compounds (secondary compounds) that occur in leaves
D. After initial digestion of cellulose in one of the four chambers of their stomach, they regurgitate the partially digested food and chew it a second time
D. After initial digestion of cellulose in one of the four chambers of their stomach, they regurgitate the partially digested food and chew it a second time
Which secretion of accessory glands in the mammalian alimentary canal acts as an emulsifying agent, breaking large fat globules into small globules?
A. Pepsinogen
B. Salivary amylase
C. HCl
D. Pancreatic juice
E. Bile
E. Bile
he osmoregulatory challenge facing freshwater fish is that the water flows from their surroundings into their bodies. How do freshwater fish maintain appropriate solute concentrations in the cells in spite of this continuous inflow of water?
A. They excrete large amounts of dilute urine
B. They excrete small amounts of highly concentrated urine
C. They drink large amounts of freshwater
D. Transport epithelia in their gills actively transport Cl ions out of their bodies
A. They excrete large amounts of dilute urine
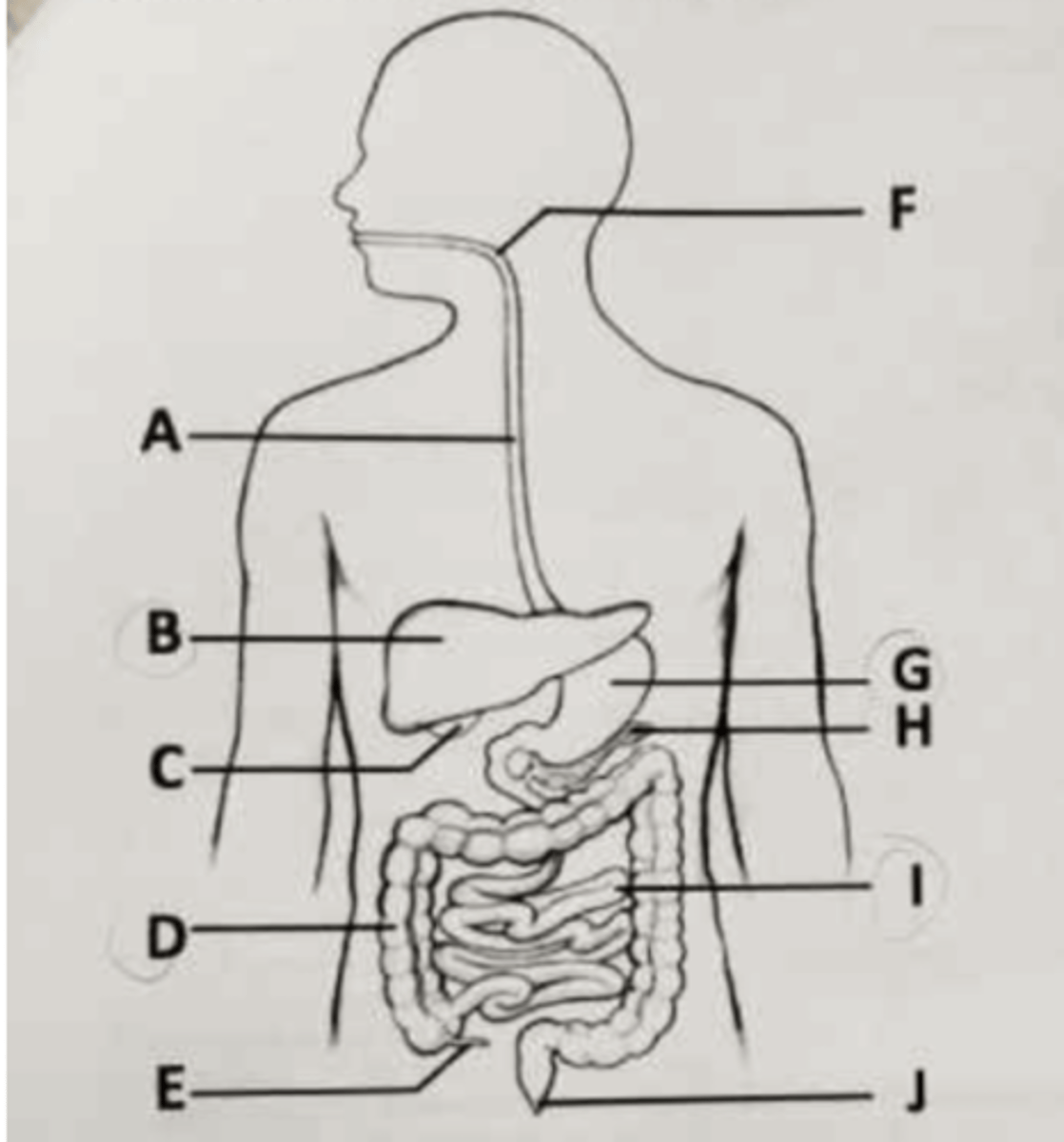
Villi and microvilli help promote absorption of nutrients in the part labeled ___.
A. B
B. D
C. G
D. I
D. I
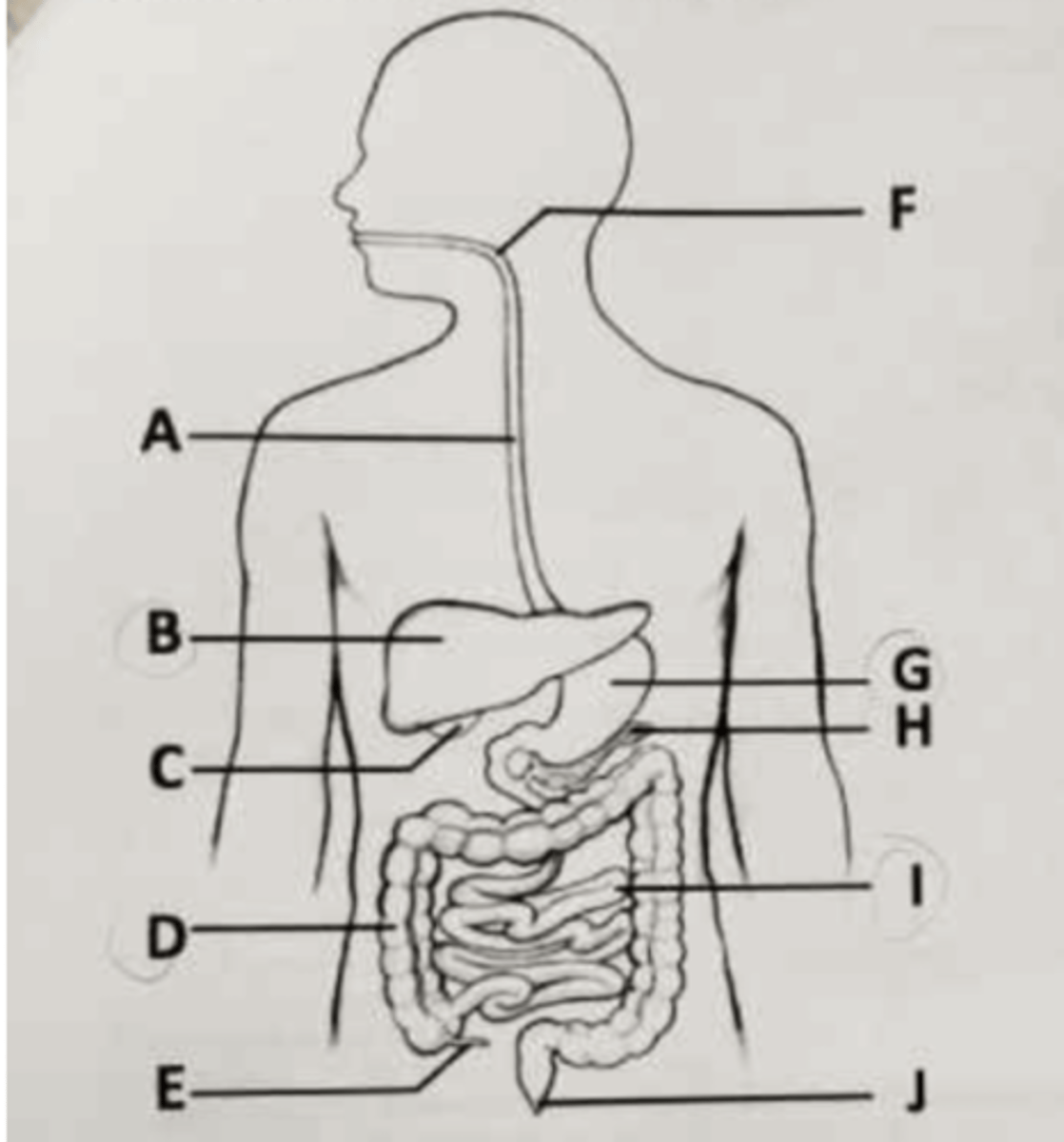
Water reabsorption occurs in the part labeled ___.
A. D
B. E
C. G
D. I
A. D
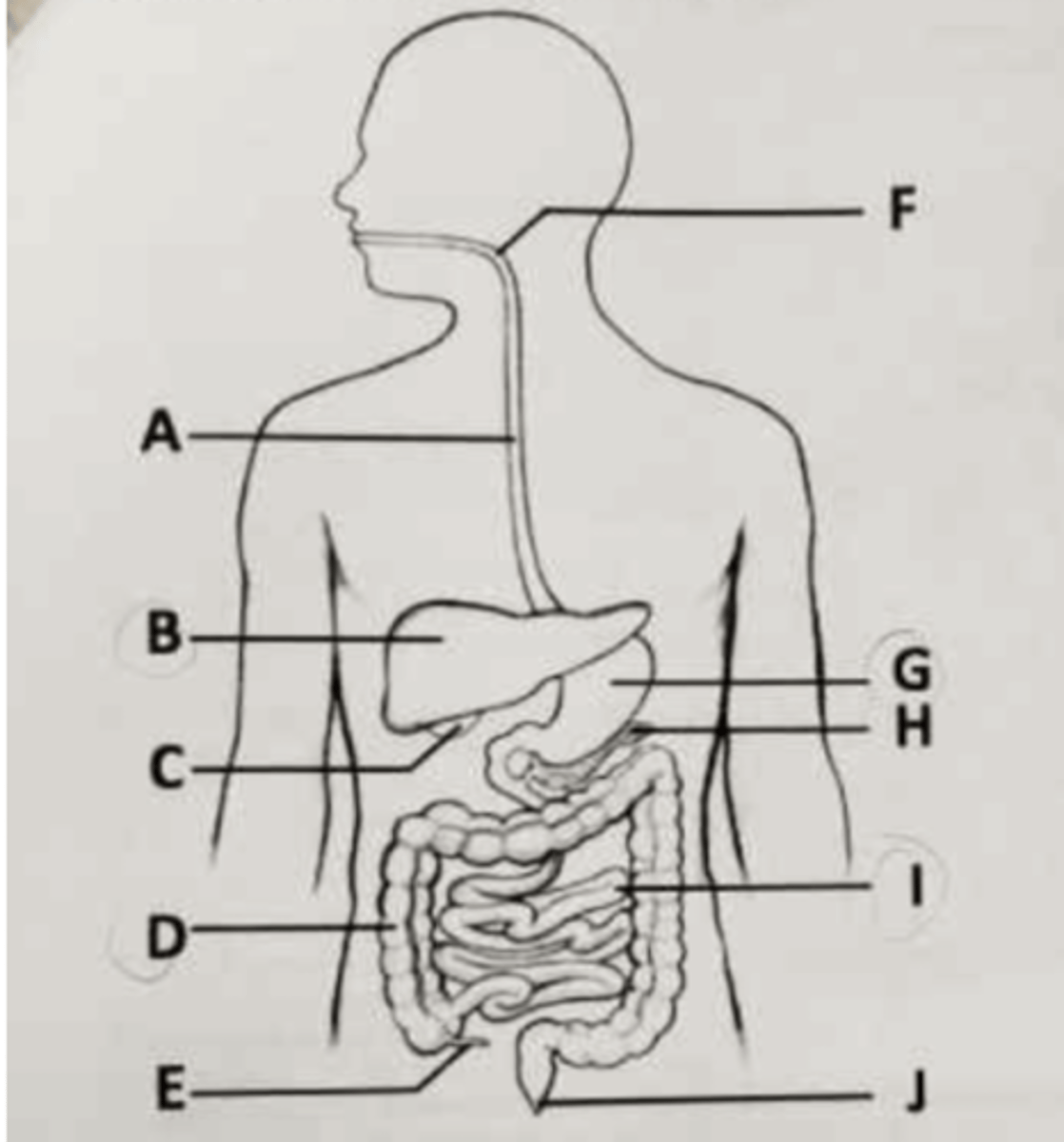
The mammalian trachea and the esophagus both connect to the part labeled ___.
A. A
B. C
C. F
D. G
C. F
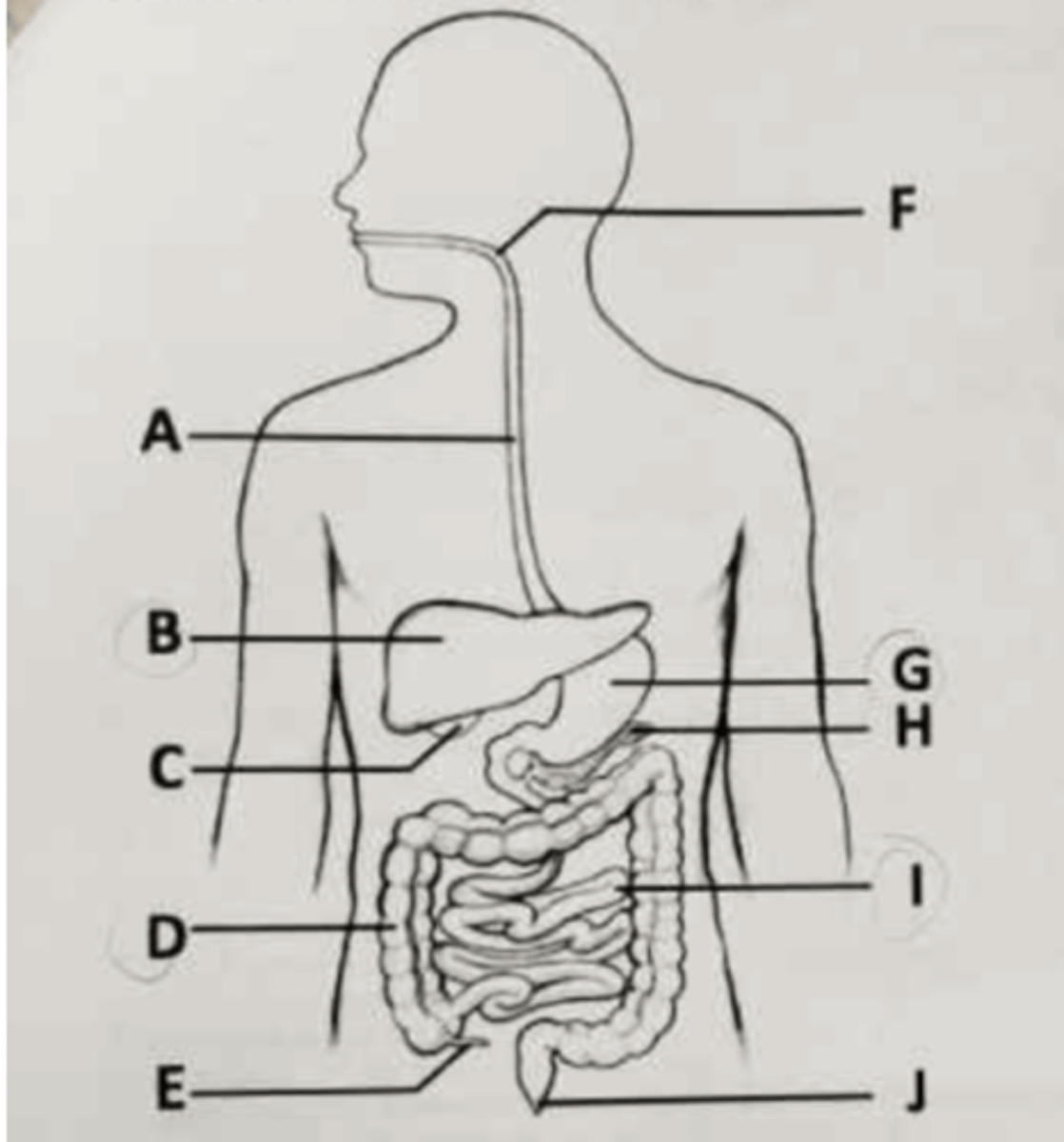
Hormones that assist with glucose regulation are produced in the part labeled ___.
A. B
B. C
C. H
D. I
B. C
Constipation can result from the consumption of a substance that ___.
A. Promotes water reabsorption in the large intestine
B. Speeds up movement of material in the large intestine
C. Decreases water reabsorption in the small intestine
D. Stimulates peristalsis
A. Promotes water reabsorption in the large intestine
Which of the following develops the greatest pressure on the blood in the mammalian aorta?
A. Systole of the part labeled A
B. Diastole of the part labeled A
C. Systole of the part labeled E
D. Diastole of the part labeled E
C. Systole of the part labeled E
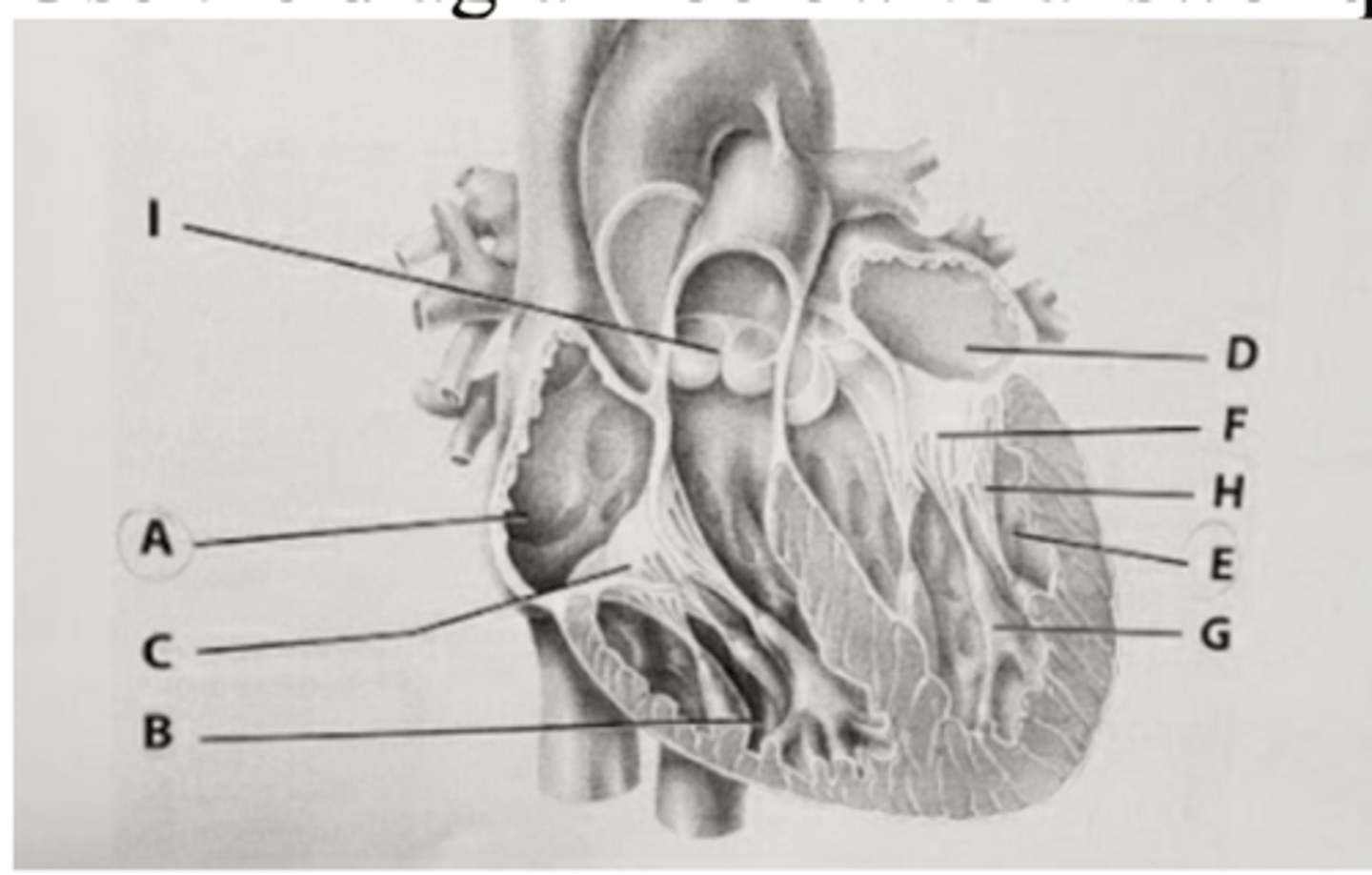
Deoxygenated blood is pumped from the part labeled ___ to the lungs.
A. A
B. B
C. D
D. E
A. A
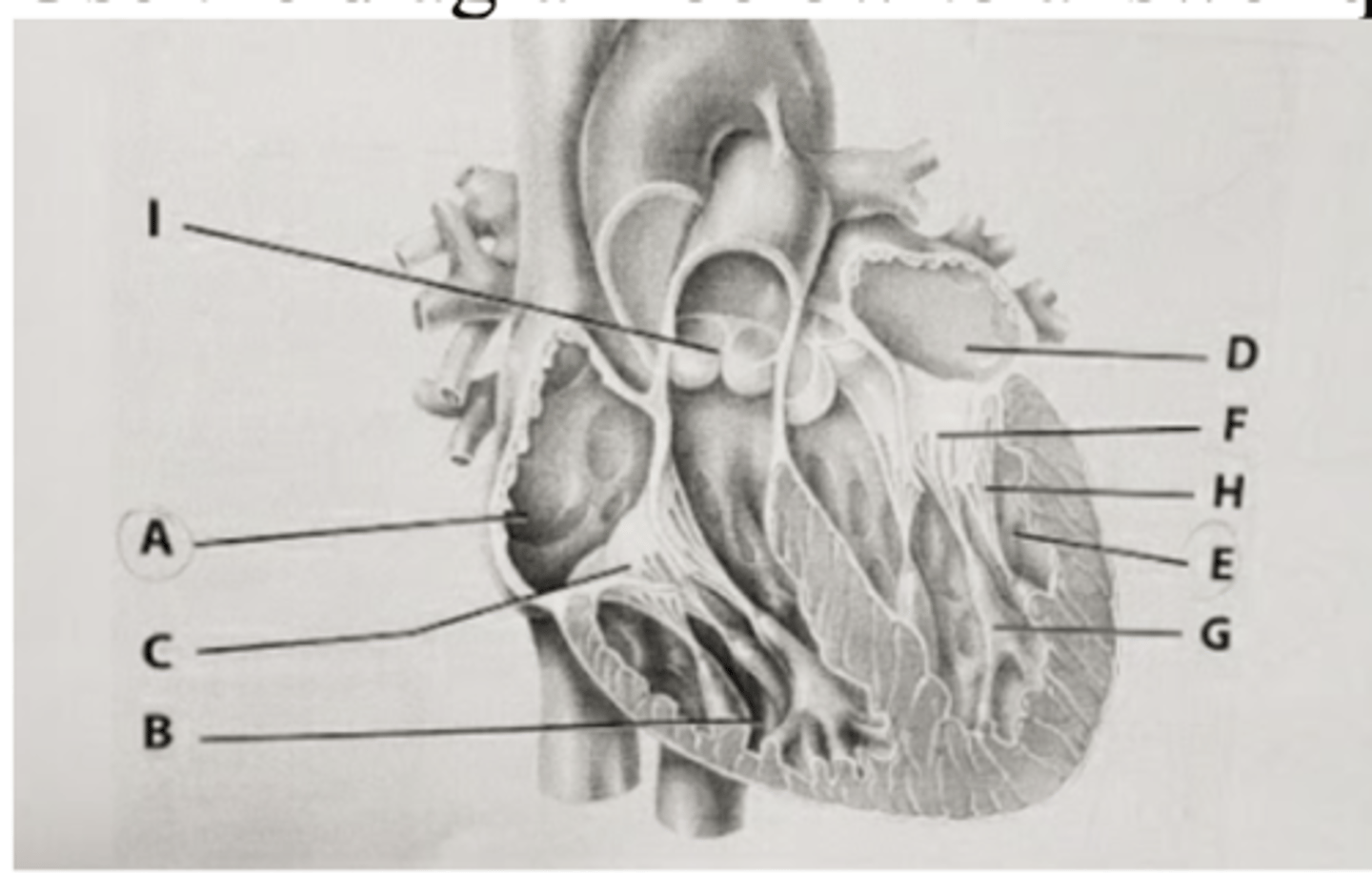
The region of the heart that sets the rate and timing of contractions is located in the area of the heart labeled ___.
A. A
B. B
C. D
D. E
E. F
A. A
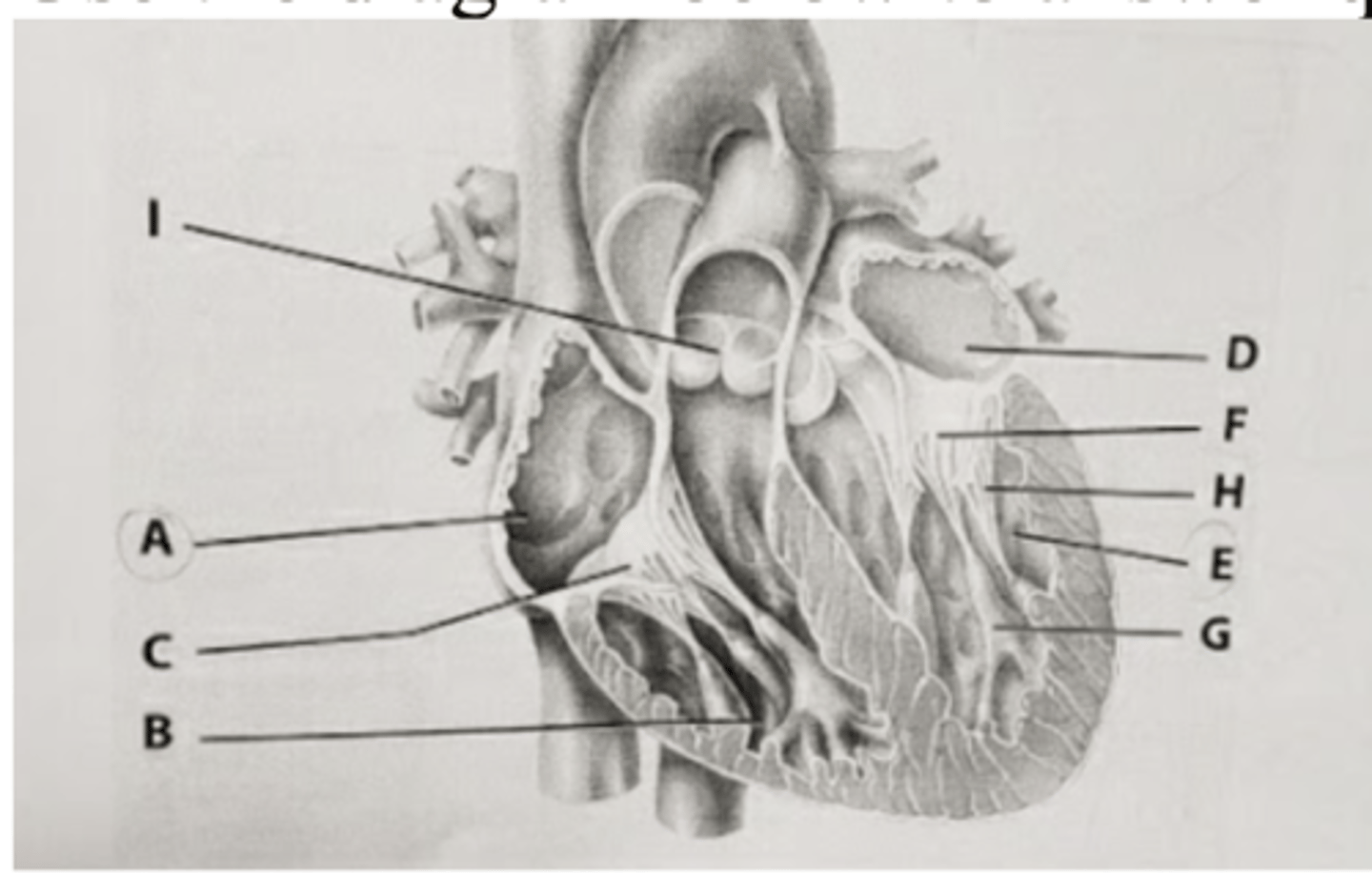
The heart valves labeled ___ close due to pressure and produce the "dup" or "dup" sound of your heart.
A. C
B. F
C. G
D. H
E. I
E. I
Which changes in the diameters of blood vessels in the skin would increase transfer of heat form an animal's warm body to the surrounding cooler environment?
A. Non-shivering thermogenesis
B. Vasoconstriction
C. Piloerection
D. Vasodilation
D. Vasodilation
Which group of vertebrates has a single circulation circulatory system?
A. Amphibians
B. Birds
C. Mammals
D. Reptiles
E. Fish
E. Fish
Blood traveling through the pulmonary vein is ___.
A. Returning from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart
B. Deoxygenated
C. Returning from the systemic circuit to the right atrium of the heart
D. Returning from the lungs to the right atrium of the heart
E. Leaving the heart and headed toward the systemic capillaries
A. Returning from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart
Which statement is true about the tissue layers found in human blood vessels?
A. Capillaries have a thicker layer of smooth muscle than do arteries
B. The endothelia of arteries have flaps of tissue that allow blood flwo in only one direction
C. The walls of capillaries lack layers of smooth muscle
D. Veins have thicker layers of smooth muscle than do arteries
E. B & C
C. The walls of capillaries lack layers of smooth muscle
Which change is sensed by breathing control centers in the medulla oblongata and causes the medulla oblongata to increase the rate and depth of breathing?
A. Increased pH of the blood
B. Decreased pH of the cerebrospinal fluid
C. Decreased CO2 concentrations in the blood
D. Increased O2 concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid
E. Decreased O2 concentration in the blood
E. Decreased O2 concentration in the blood
Drinking alcohol inhibits production of the anti-diuretic hormone by the posterior pituitary. Therefore, which change would you predict as a result of alcohol consumption?
A. More water is absorbed from the collecting ducts in the kidneys
B. The ascending limb of the Loop of Henle regulate NaCl and K+
C. The descending limb of the Loop of Henle reabsorbs bicarbonate ions
D. Less water is absorbed from the collecting duct in the kidneys
E. Erythrocytes pass from the glomerulus in the nephron
D. Less water is absorbed from the collecting duct in the kidneys
Which statement is true of osmoconformers?
A. All else being equal, they have higher metabolic rates than osmoregulators
B. They include many terrestrial and fresh water species
C. They maintain a constant internal solute concentration in spite of fluctuating solute concentration in their surroundings
D. None of the above are true
D. None of the above are true
The force driving simple diffusion is ___, while the energy source for active transport is ___.
A. The concentration gradient; ADP
B. The concentration gradient; ATP
C. Transmembrane pumps; electron transport
D. Phosphorylated protein carriers; ATP
B. The concentration gradient; ATP
What is the function of the osmotic gradient found in the kidney? The osmotic gradient allows for ___.
A. Electrolytes to move from low to high concentration in the absence of ATP
B. The precise control of the retention of water and electrolytes
C. The Loop of Henle to deliver water to the renal vein
D. The filtration of large cells at the glomerulus
B. The precise control of the retention of water and electrolytes
This part of the nephron establishes an osmotic gradient, an important feature of osmoregulation in terrestrial vertebrates.
A. A and E
B. D and F
C. G
D. B
B. D and F
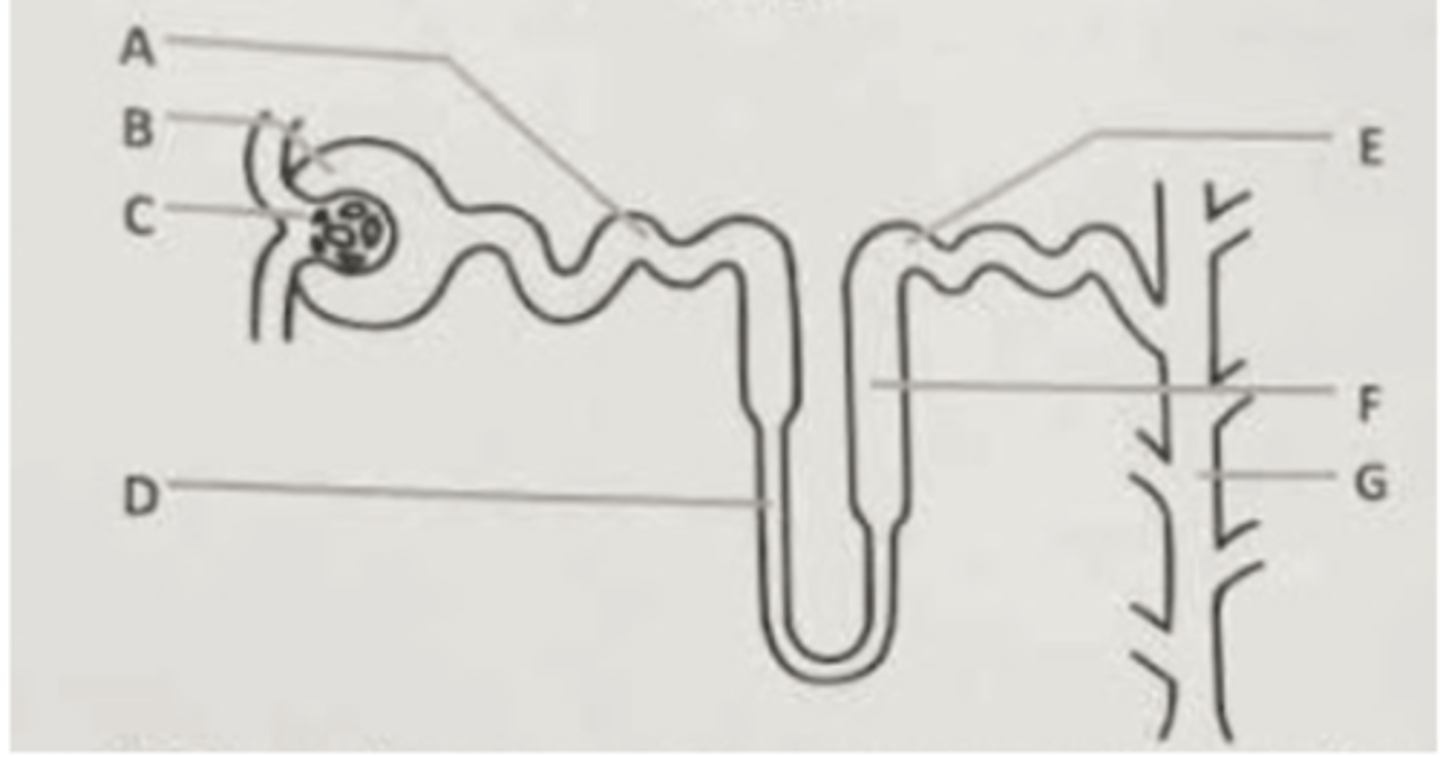
High pressure forces solutes out of the blood in the structure labeled ___.
A. A
B. C
C. D
D. G
B. C
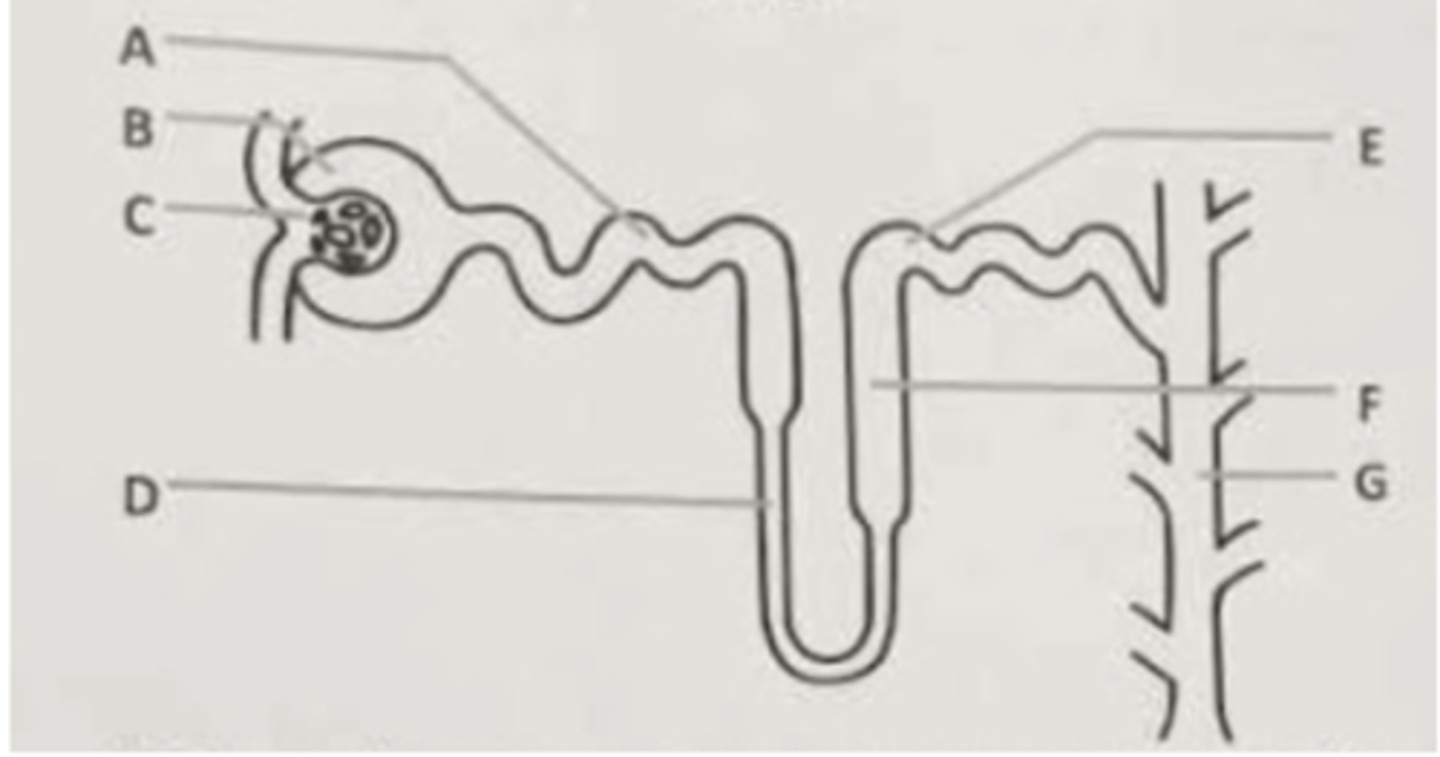
The filtrate (not urine) is collected in the structure labeled ___.
A. B
B. D
C. F
D. G
B. D
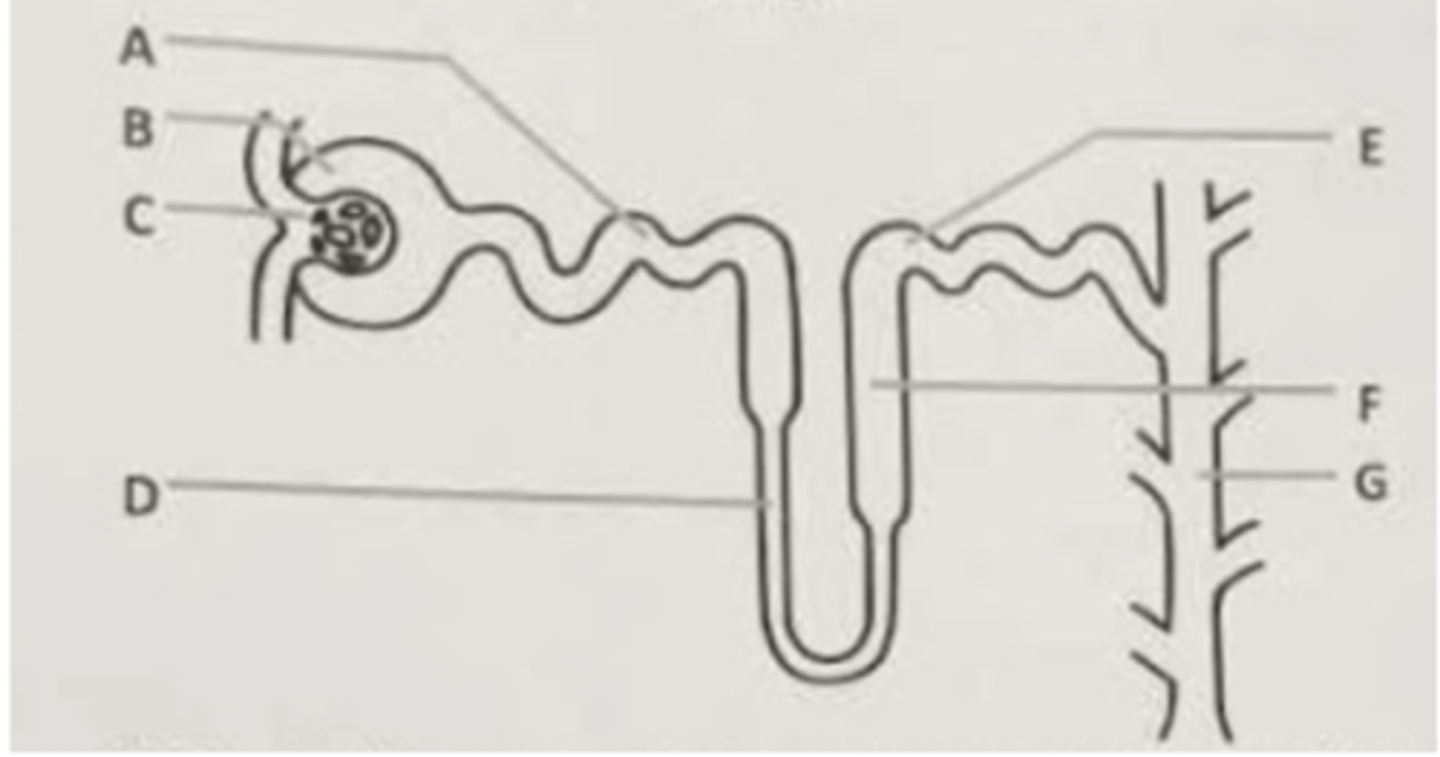
In response to low blood volume due to dehydration or blood loss the enzyme renin initiates a complex feedback circuit that involves the peptide angiotensin II. Angiotensin II stimulates which of the following responses that increase blood pressure?
A. Increase reabsorption of NaCl and water from the Loop of Henle
B. Production of aldosterone by the adrenal gland
C. Dilation of the arterioles
D. All of the above
A. Increase reabsorption of NaCl and water from the Loop of Henle
Analysis of a blood sample from a fasting individual who had not eaten for twenty-four hours would be expected to reveal high levels of ___.
A. Insulin
B. Glucagon
C. Gastrin
D. Glucose
B. Glucagon
Which endocrine gland is produced by the hypothalamus and contains neurosecretory cells that extend into it from the hypothalamus
A. Anterior pituitary
B. Pineal gland
C. Adrenal gland
D. Posterior pituitary
E. Thyroid
A. Anterior pituitary
Which endocrine disorder is correctly matched with the malfunctioning gland?
A. Dwarfism - the adrenal cortex
B. Gigantism - the anterior pituitary gland
C. Goiter - the adrenal medulla
D. Diabetes mellitus - the parathyroid glands
B. Gigantism - the anterior pituitary gland
In regulation metabolism, two endocrine glands detect levels of the thyroid hormones, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), and in response to high levels of these thyroid hormones reduce their production of thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). What are two endocrine glands, other than the thyroid gland, that are involved in negative feedback loops to regulate metabolism?
A. Pineal gland, hypothalamus
B. Hypothalamus, anterior pituitary
C. Anterior pituitary, adrenal gland
D. Hypothalamus, gonads
E. Anterior pituitary, parathyroid gland
B. Hypothalamus, anterior pituitary
Osteoporosis is a condition in which the density of bones is decrease so much that the individual is at a higher risk of fractures. The more calcium in bones, the better the bone density. Which of the following would produce the greatest increase in bone calcium levels?
A. Calcitonin injection
B. Calcitonin receptor blocker
C. Parathyroid hormone injection
D. Glucagon receptor blocker
A. Calcitonin injection
One symptom of untreated diabetes is severe dehydration. People whose bodies do not produce sufficient insulin may suffer dehydration because ___.
A. Osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus are non-functional
B. Concentrations of glucose in the urine are high preventing water reabsorption in collecting ducts in the kidneys
C. Dysfunctional production of glucagon
D. Concentrations of glucose in the urine are low preventing water reabsorption in the Bowman's capsule in the kidneys
B. Concentrations of glucose in the urine are high preventing water reabsorption in collecting ducts in the kidneys
Increasing the temperature of the human scrotum by 2° (that is, above the normal body core temperature) would most likely ___.
A. Reduce the fertility of the man by impairing the production of gonadal steroid hormones
B. Reduce the fertility of the man by impairing spermatogenesis
C. Reduce the man's sexual interest
D. Increase the fertility of the affected man by enhancing the rate of steroidogenesis
B. Reduce the fertility of the man by impairing spermatogenesis
A physician finds that a eight-year-old male patient is entering puberty much earlier than is usual. Such a condition is most likely the result of a tumor in the ___.
A. Hypothalamus, producing elevated levels of testosterone
B. Anterior pituitary, producing elevated levels of testosterone
C. Testes, producing elevated levels of estrogen
D. Hypothalamus, producing elevated levels of gonadotropin-stimulating hormone
D. Hypothalamus, producing elevated levels of gonadotropin-stimulating hormone
Which of the following structure in females is analogous in function to the vas deferens in males?
A. Urethra
B. Oviduct (fallopian tube)
C. Uterus
D. Vagina
B. Oviduct (fallopian tube)
Asexual reproduction results in offspring that are genetically identical to their parent. What type of cell process occurs to generate this type of offspring?
A. Mitosis
B. Meiosis
C. Cell fusion
D. Cross over
A. Mitosis
External fertilization occurs in which group of vertebrates?
A. Birds
B. Mammals
C. Amphibians
D. A & B
C. Amphibians
In the human female reproductive tract, fertilization occurs in the ___.
A. Vagina
B. Cervix
C. Uterus
D. Fallopian tube (oviduct)
E. Ovaries
D. Fallopian tube (oviduct)
In humans, oogenesis differs from spermatogenesis in that ___.
A. A man has all the spermatogonia that he will ever have when he is born, but women produce oogonia throughout their lives
B. Oogenesis a continuous process, but in spermatogenesis the developing sperm goes through a resting period in the middle of meiosis 1 and then again in the middle of meiosis 2
C. Oogenesis produces haploid egg cells, but spermatogenesis produces diploid sperm
D. In oogenesis one egg cell is produced from each oogonium, but in spermatogenesis four sperm are produced from each spermatogonium
D. In oogenesis one egg cell is produced from each oogonium, but in spermatogenesis four sperm are produced from each spermatogonium