BIO 2.1 - 2.5 (NO TRANSCRIPTION OR TRANSLATION)
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
What is a codon?
A triplet of bases which encodes a particular amino acid.
How many different codon combinations are there?
64 different codon combinations.
What does it mean that the genetic code is said to be degenerate?
Codons can translate 20 amino acids.
What determines the amino acid sequence for a protein?
The order of codons.
What codon does the coding region always start with?
A START codon (AUG).
What signals the termination of the coding region in mRNA?
A STOP codon, which causes the release of the polypeptide.
What does mRNA do in protein synthesis?
mRNA brings code from DNA in the nucleus in its base sequence, which has instructions for polypeptide production.
Where does mRNA bind during translation?
mRNA binds to the small ribosomal subunit at an mRNA binding site.
What codon does tRNA carrying methionine bind to?
tRNA carrying methionine binds at the start codon 'AUG'.
What happens after the tRNA binds to the start codon?
The large ribosomal subunit then binds to the small ribosomal subunit.
Where is the initial tRNA located in the ribosome?
The initial tRNA is located in the P site.
What happens to DNA when RNA Polymerase binds to it?
DNA uncoils
What does RNA Polymerase catalyze during transcription?
The formation of nucleotide bonds in mRNA
Where does RNA Polymerase bind to start transcription?
At the start of the gene to be transcribed
What does RNA Polymerase do to the DNA strands during transcription?
Splits the DNA into two strands
How does RNA Polymerase move during transcription?
Along the template strand
How does RNA Polymerase link RNA nucleotides together?
By covalent sugar-phosphate bonds
What happens to RNA after it is synthesized by RNA Polymerase?
It detaches, allowing DNA to reform its helix
What ensures the correct sequence of RNA is produced during transcription?
Complementary base pairing
How many hydrogen bonds form between adenine and thymine/uracil?
Two hydrogen bonds
How many hydrogen bonds form between cytosine and guanine?
Three hydrogen bonds
What are polysaccharides?
Carbohydrates that are made up of more than two monosaccharides.
What is a characteristic of polysaccharides in terms of solubility?
They are insoluble storage molecules.
How are excess sugars stored in the liver?
Excess sugars are converted by insulin for storage in the liver.
What is the structure of polysaccharides?
They are very long and may be branched.
What types of glycosidic bonds can be found in polysaccharides?
Glycosidic bonds can be 1-4 or 1-6.
How can glucose be transported in the body from polysaccharides?
1 glucose can be hydrolyzed by breaking a 1-4 bond to allow glucose to transport elsewhere in the body.
What is the purpose of starch and glycogen in cells?
They are used to store large amounts of glucose without swelling the cell.
foundation of organic molecules
carbon and hydrogen
hydrogen ions
1+, used in active transport, photosynthesis, cell respitation (through chemiosmosis)
-the pH of a solution is measure of activity of dissolved H+ ions
-low pH (1-6) = high concentrate H+
-high pH (7,14) = low H+
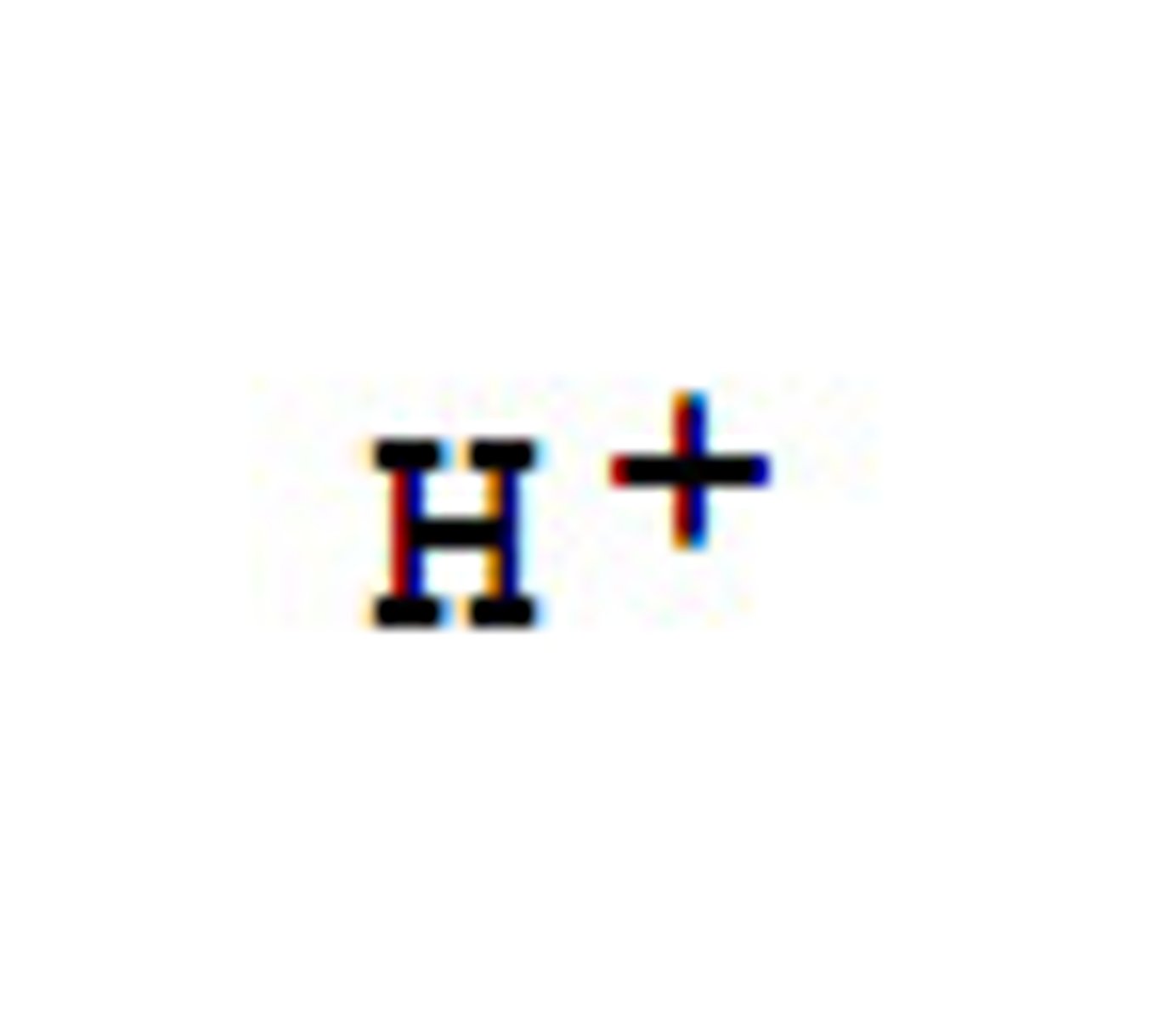
covalent bond
•chemical bond involves sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms.
• Carbon atoms form covalent bonds with other atoms (one of the strongest types of bonds)
• For many molecules, sharing of electrons allows each atom to attain equivalent of a full valence shell, corresponding to stable electronic configuration.
• In organic chemistry, covalent bonding is more common than ionic bonding.
Role of carbon
•Carbohydrates, lipids and proteins are composed of carbon.
•Organic compounds - contain carbon (living things).
•Relatively small atom.
•Able to form 4 strong, stable covalent bonds
•form covalent bonds with other atoms, one of the strongest types of all bonds
groups of organic compounds (4)
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
Metabolism
The sum of all reactions that occur in an organism
-all living things carry out chem reactions -> which catalysed by enzymes
-consist of pathways which one typa molecule is transformed into another (in series of steps)
Condensation and hydrolysis
condensation MAKES bonds (water releasing)
[ANABOLIC reactions BUILD molecules (e.g. photosynthesis)]
hydrolysis BREAKS bonds (water splitting)
[CATABOLIC reactions break down molecules (e.g. digestion)]
![<p>condensation MAKES bonds (water releasing)</p><p>[ANABOLIC reactions BUILD molecules (e.g. photosynthesis)]</p><p>hydrolysis BREAKS bonds (water splitting)</p><p>[CATABOLIC reactions break down molecules (e.g. digestion)]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/00a266d2-e6b5-4187-b3eb-a72bcffe5b65.jpg)
What is the chemical composition of water?
Water (H2O) is made up of 2 hydrogen (H) atoms covalently bound to 1 oxygen (O) atom.
How are electrons shared in a water molecule?
In a water molecule, electrons are shared between hydrogen and oxygen atoms, but they are not shared equally.
What is the difference in the number of protons between oxygen and hydrogen in water?
Oxygen has 8 protons, while each hydrogen atom has 1 proton.
Why does the oxygen end of a water molecule become slightly negative?
The oxygen end of a water molecule becomes slightly negative because it has more protons and attracts electrons more strongly than hydrogen.
What type of bonds form between water molecules?
Hydrogen bonds form between water molecules.
What type of bonds form within a water molecule?
Covalent bonds form within a water molecule.
Which atom is always positively charged in hydrogen bonds between water molecules?
The positively charged atom in hydrogen bonds between water molecules is always a hydrogen atom.
How many hydrogen bonds can each hydrogen atom of a water molecule form?
Each hydrogen atom of a water molecule can form a hydrogen bond with a nearby partially negative oxygen atom of another water molecule.
How many hydrogen bonds can the negative (oxygen) pole of a water molecule form?
The negative (oxygen) pole of a water molecule can form hydrogen bonds to two hydrogen atoms.
Hydrophilic
water loving
-all substances dissolving in water or water adheres to are hydrophilic
e.g. polar molecules like glucose or particles with + and -such as ions
Hydrophobic
water fearing
substances that are insoluble in water
e.g. lipids, (including fats n oils)
-hydrophobic molecules can dissolve in other solvents like propanone
Cohesion
-occurs as a result of polarity of water molecule and its ability to form H bonds
-although H bonds are weak the large # of bonds present gives cohesive force great strength
-water molecules are strongly cohesive
e.g. water droplets and surface tension
Adhesion
-occurs as result of polarity of H2O and ability to form H bonds
-H2O tend to stick to other molecules that r charged or polar (for similar reasons they stick to eachother
Capillary action
caused by combination of adhesive forces -> cause water to bond to a surface
-useful in movement of water of water during transpiration
Xylem vessels
are thin narrow tubes with transport water from the roots to the leavs of plants
-the cohesive nature of water molecules allow H2O to form continuous column of H2O moving up the xylem/stem of plants
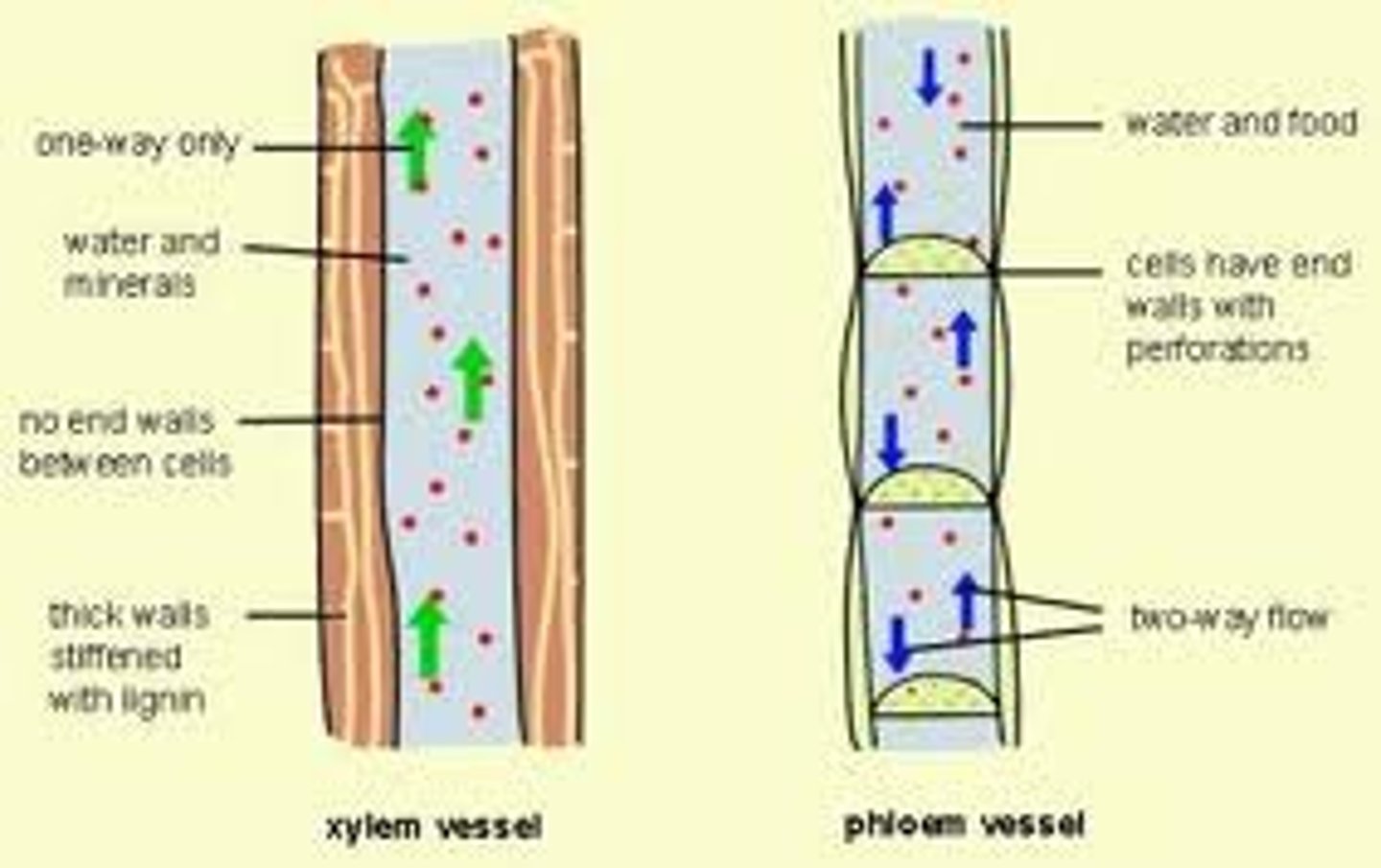
SOLVENT
-water can dissolve many organic + inorganic substances with charged or polar regions
-polar attraction of large quantity of water can interrupt intramolecular forces (like ionic bonds), resulting in dissociation of atoms
+ atoms end up being surrounded my - O regions, and - atoms surrounded by + H regions of water
-
Condensation
Two sugars are joined by condensation
Hydrolysis
A chemical process that splits a molecule by adding water.
sucrose
glucose + fructose
lactose
glucose + galactose
maltose
glucose + glucos
example of monosaccharides
glucose, galactose, fructose
example of dissacharides
maltose, lactose sucrose
example of polysaccharides
starch, glycogen, cellulose
monosaccharide
-A single sugar molecule such as glucose or fructose, the simplest type of sugar.
-small, easily absorbed sugars
-fast releases for respiration
-are monomers of polysaccharides
disaccharide
Carbohydrates that are made up of two monosaccharides
-quickly digested into their monosaccharides
how starch forms
alpha-glucose molecules joined chemically to form a polymer
how cellulose forms
when beta-glucose molecules are joined to form a polymer
Properties of Lipids
large class of organic compounds.
They are all hydrophobic and insoluble in water
Saturated Lipid
No double bonds
-high density energy store
-solid at room temp
-animal products, palm and coconut oil
-high risk of CHD (coronary heart disease)
Unsaturated Lipid
Some carbon double bonds in fatty acid
mono-unsaturated is 1 double bond, poly-unsaturated is 2+
usually oils at room temp
-usually from plant sources
-ollive oil
-less risk of CHD
-molecule bends due to double bond
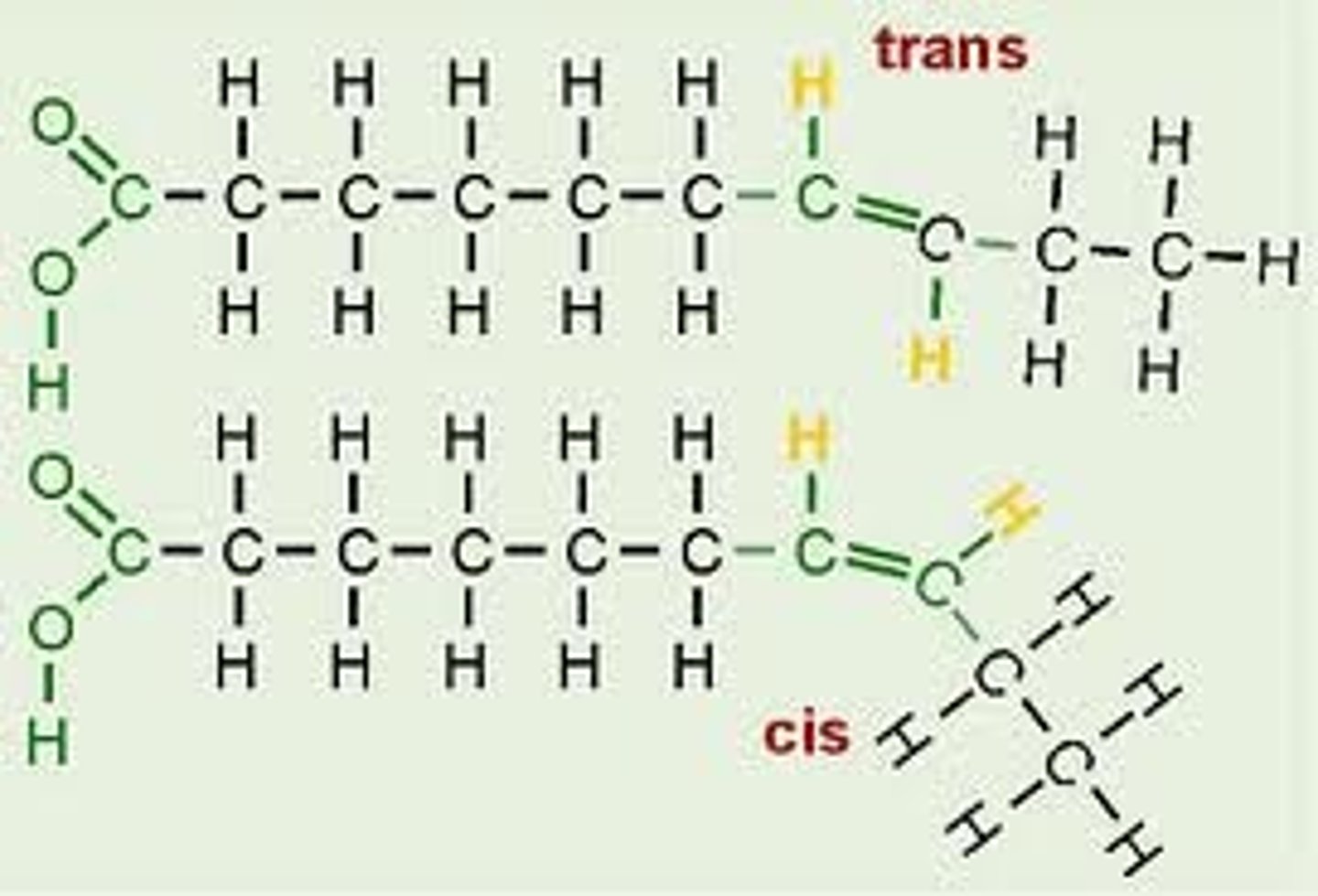
Cis Fat
An unsaturated fat
Hydrogens on the same side of the double bond
-oil at room temp
-usually from plant sources
-less risk of CHD
-almost all in nature
-cause molecule to bend (less good at packing together than saturated due to bends, therefore oil at room temp)
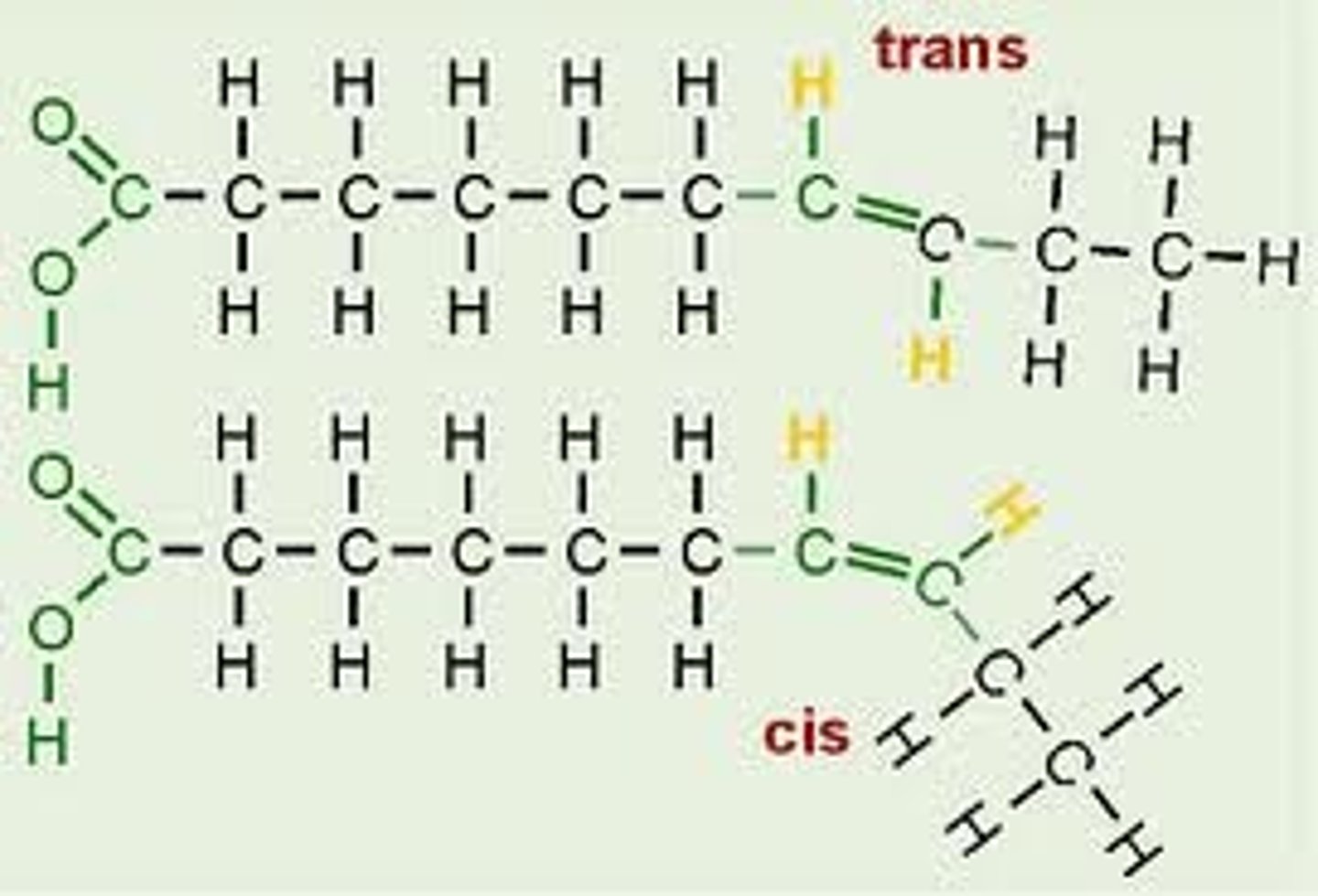
Trans Fat
An unsaturated fat
containing one or more trans double bonds.
-oil or solid
-artificially produced
-very high CHD risk
-'mimic' saturated fats
formation of triglyceride
Each fatty acid forms an ester bond with glycerol in a condensation reaction
(reaction between hydroxyl of glycerol and carboxyl group or fatty acid as only hydrophilic part an used make water)
+1 water molecule produced
ALL TRIGLYCERIDE HYDROPHOBIC
comparing carbohydrates and lipids as energy
[lul if u want this flashcard u need the knowt so i can input the image]
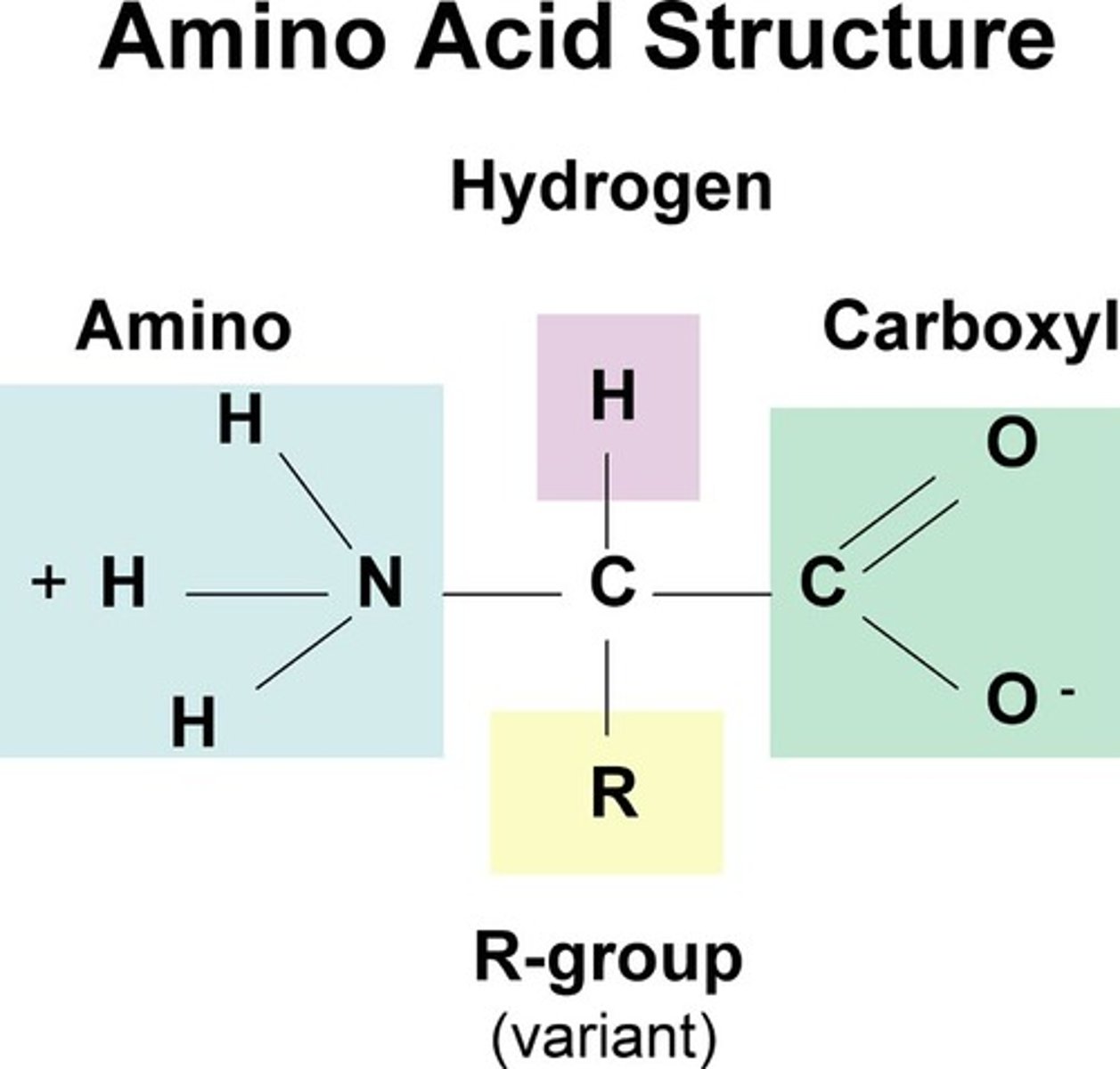
structure of proteins
amino acids create proteins through either simple chain or complex subunit
-protein may consist of single polypeptide or more than 1 polypeptide linked
-R group changes
Formation of Dipeptide
ribosome condenses 2 amino acids into dipeptide, forming a peptide bond
[key to understand amino acids linked by condensation to form polypeptides]
protein synthesis
ribosomes synthesze polypeptide chains
ribosome role in synthesis of protein
facilitate the formation of peptide bonds and hence where polypeptides are synthesized
Polypeptide
chain of amino acids linked by peptide bonds
-amino acid sequence determines the 3-D conformation of a protein
how many amino acids are there
20 different amino acids
-each can be combined any order and have unique properties:
-polar(hydrophilic) or non-polar(hydrophobic)
-positive/negative charge
-some contain sulphur
-the proterties determine how a polypeptide folds up into a protein
4 Levels of protein structure
what level protein conforms to is determined by amino acid sequence:
primary
secondary
tertiary
quaternary
primary protein structure
sequence of chain of amino acids
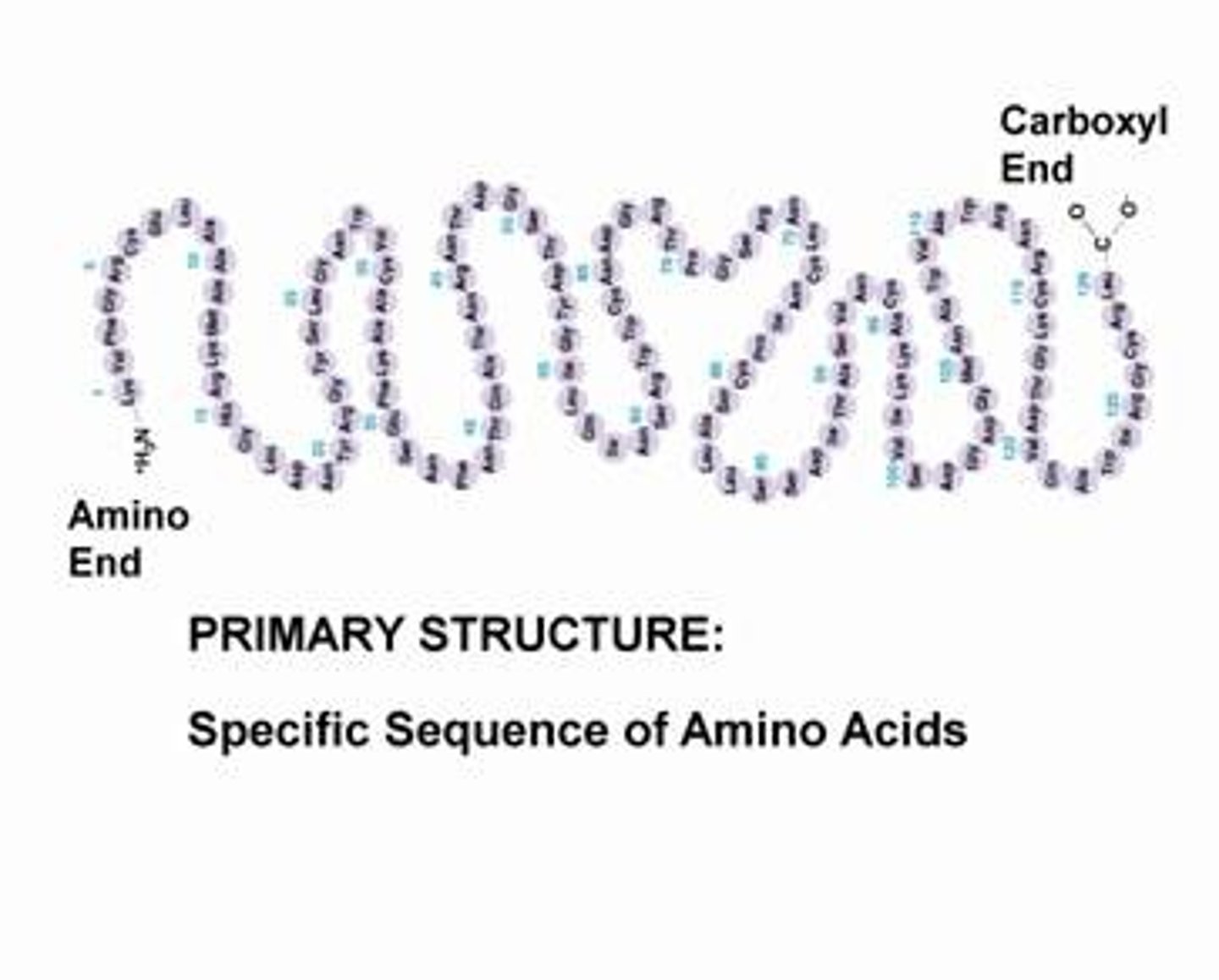
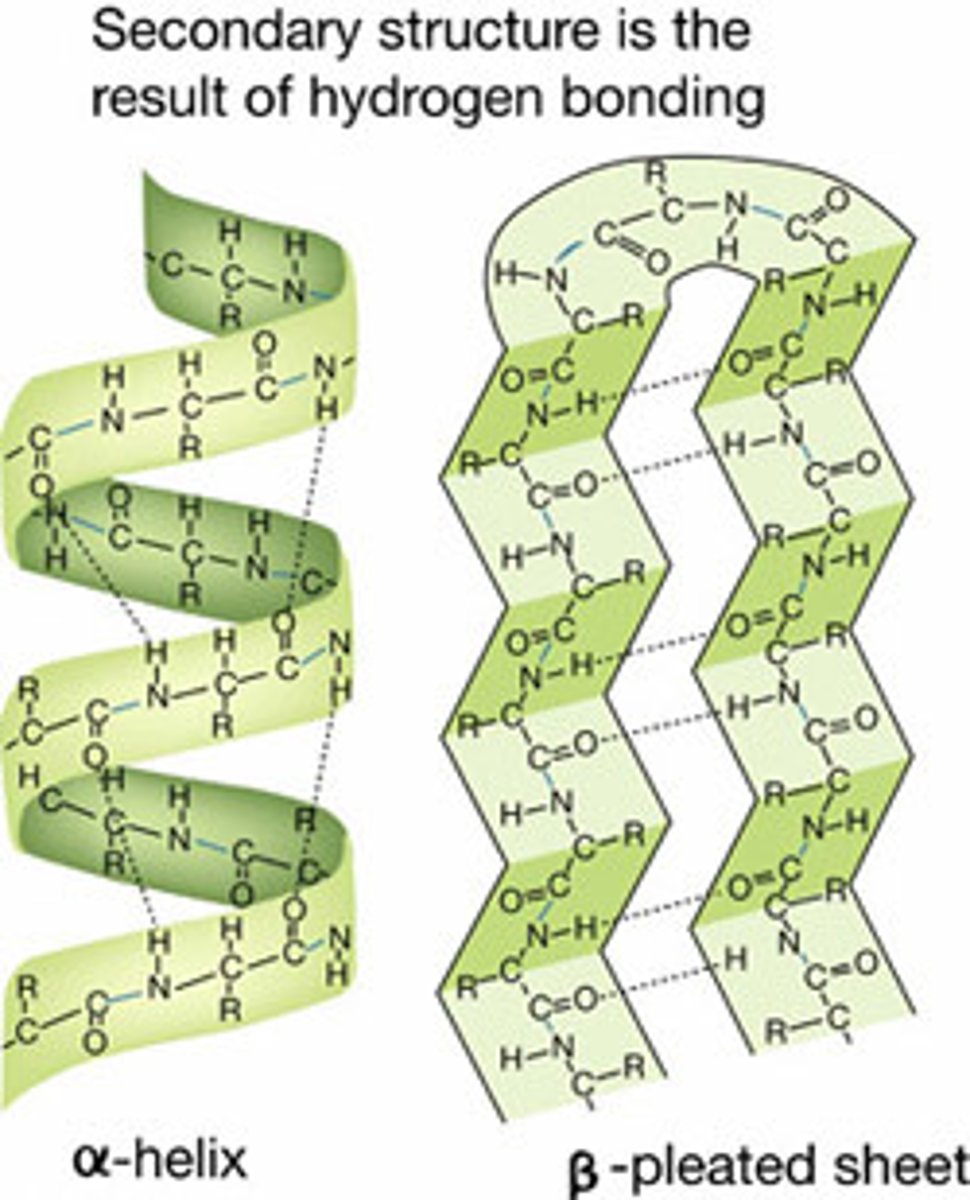
secondary protein structure
occurs when sequince of amino acids linked by hydrogen bonds
tertiary protein structure
occurs when certain attractions are present between alpha helices and pleated sheets
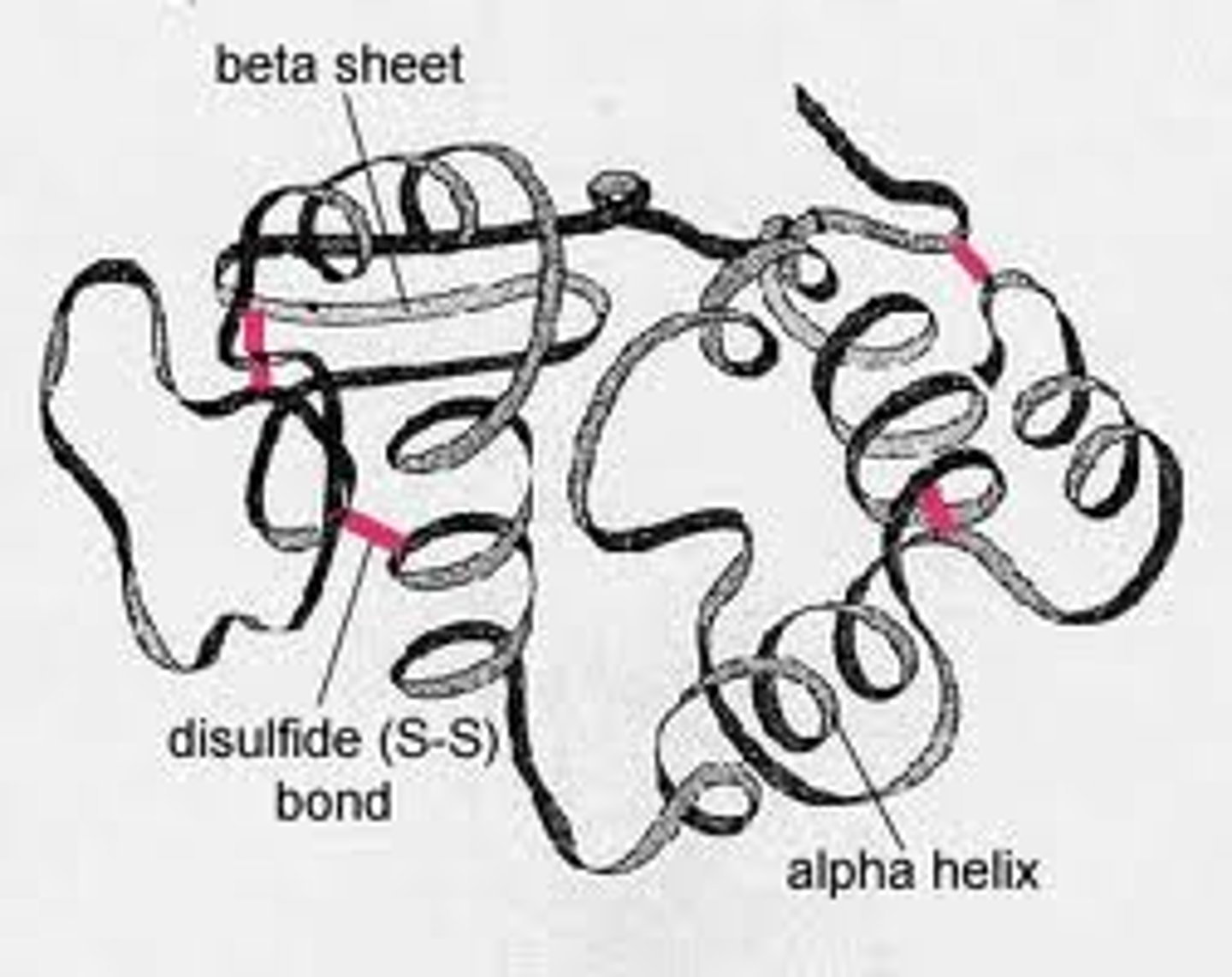
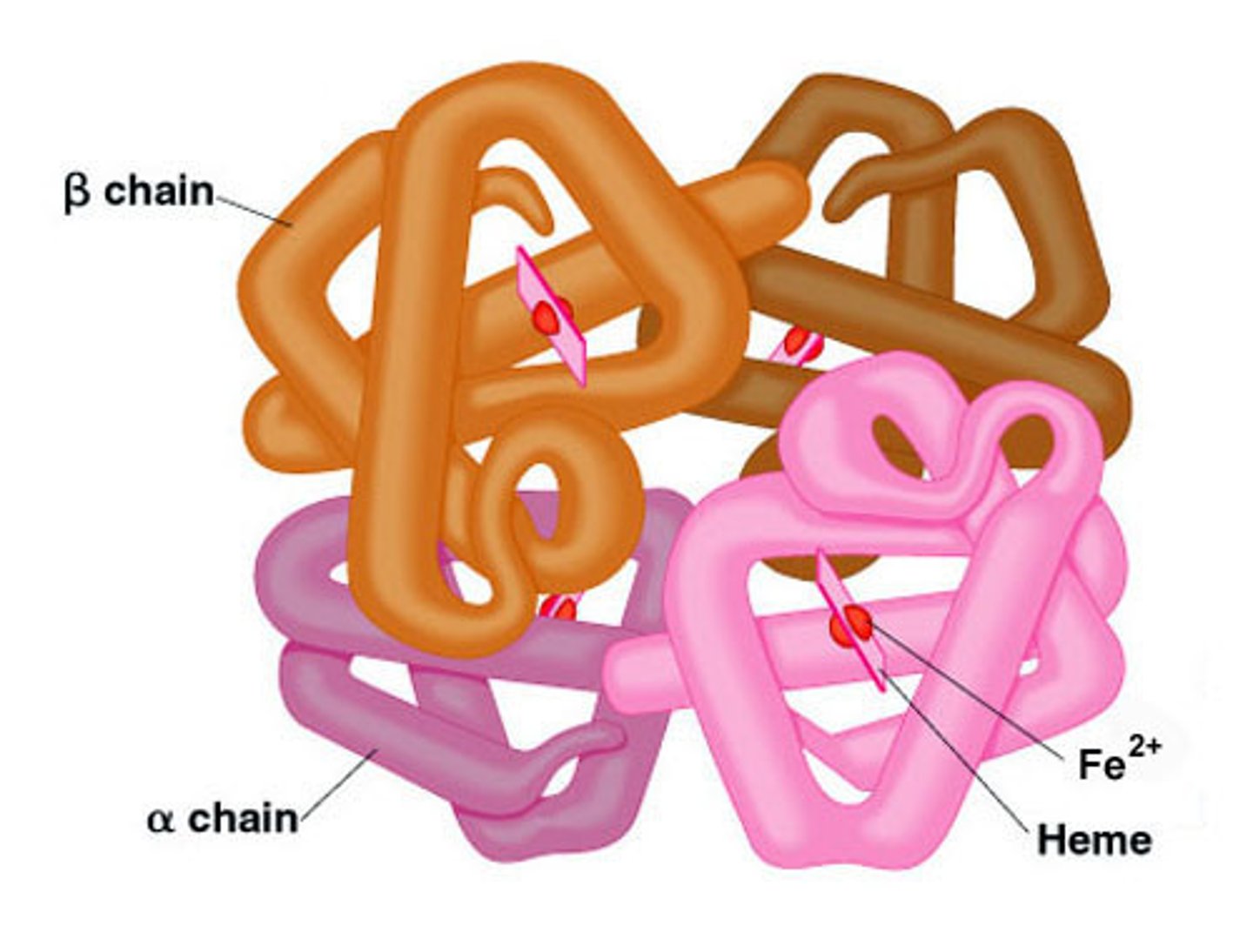
quaternary protein structure
protein consisting of more than one amino acid chain
denaturation of proteins
conformational change in the shape of a molecule, such as a protein, resulting in loss of functio (permanent)
due to:
-HEAT
-EXTREME IN PH
Enzymes
-globular proteins used to catalyse reactions
-unchanged by reaction
-specific to substrate
-can be reused for next substrate
-made active by high temps
-work best at particular temp and pH (pH affects formation of ionic bonds of amino acid amine groups)
-biological catalysts
-specific
-can be denatured at high temps and pH changes
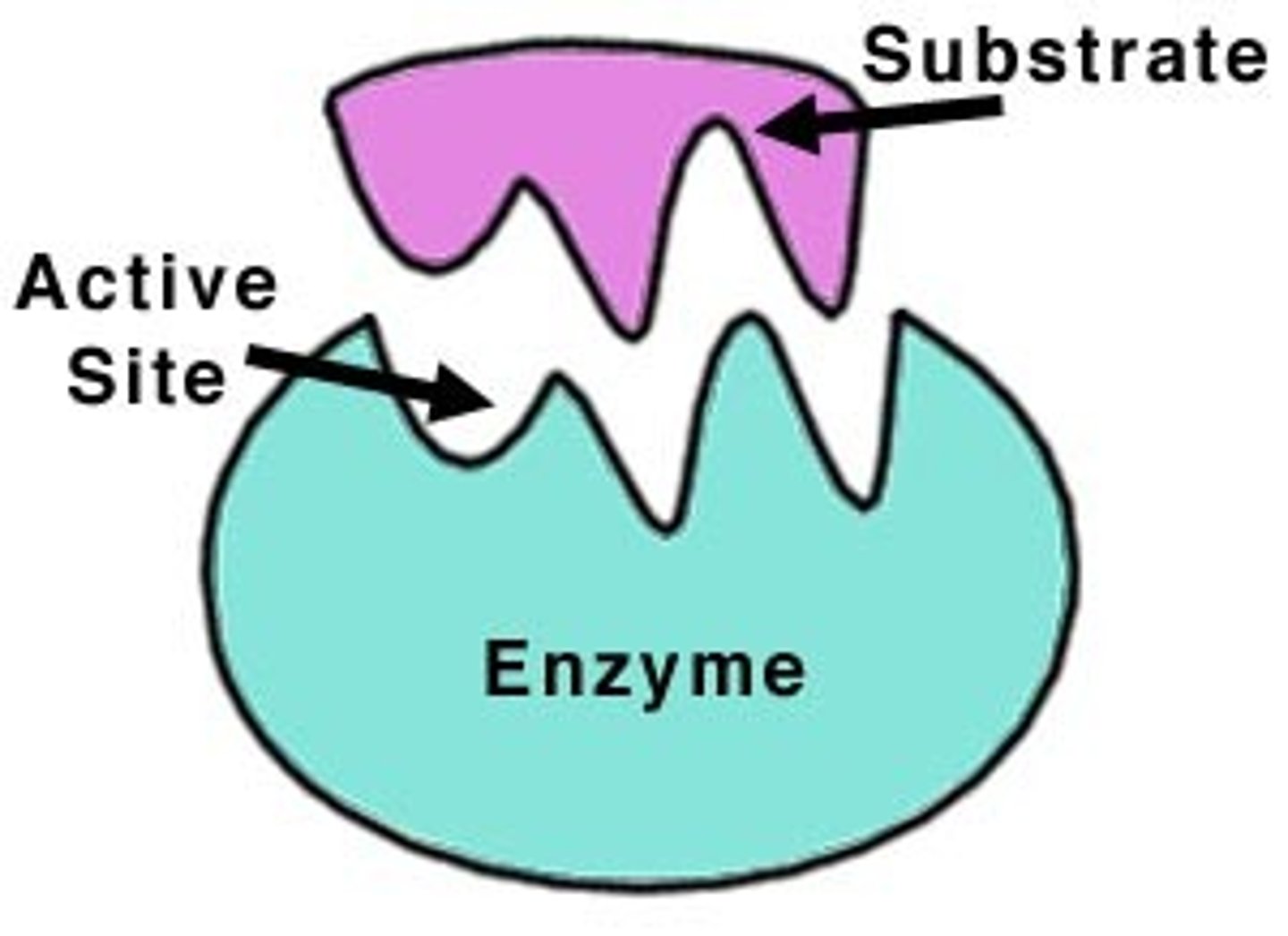
Active site
The part of an enzyme or antibody where the chemical reaction occurs. / binding site/position on surface of enzyme
-affected by temp and pH
enzyme catalysis
-collision
-most enzyme reaction occur when substrate dissolve in water
-all molecule dissolved in water r inrandom motion (move seperate)
-if not immobilized enzyme moved too (slower cause big)
-collision result of random movements in substrate n enzyme
-substrate may be at any angle to active site for collision
-successfull collisions when binding take place
collision
coming together of substrate molecule and active site
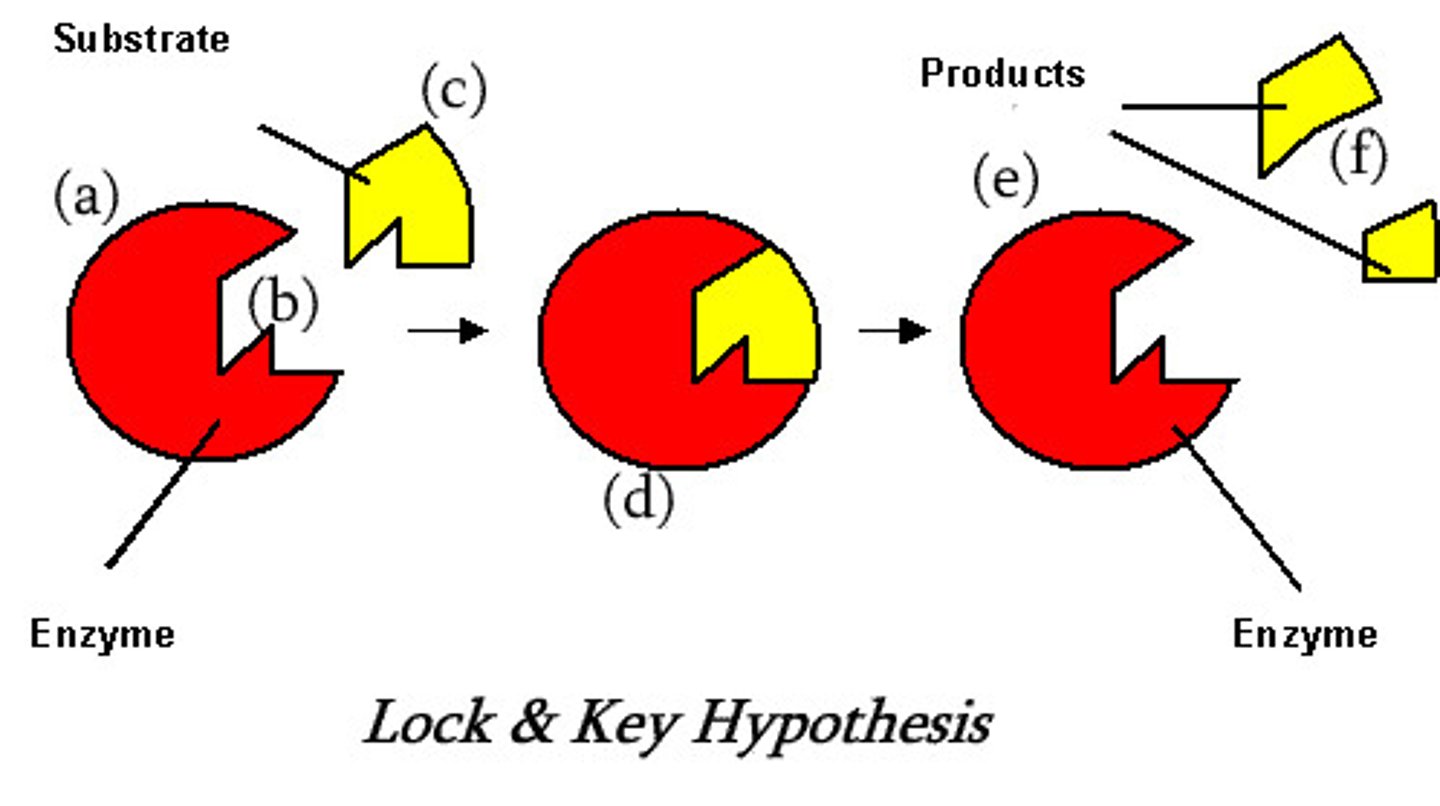
Enzyme lock and key model
-active site for enzyme is very specific in shape, w/ very precise chem properties
-active sites match shapes of their substrates - enzyme therefore substrate specific
-enzyme is 'locl', substrate is 'key'
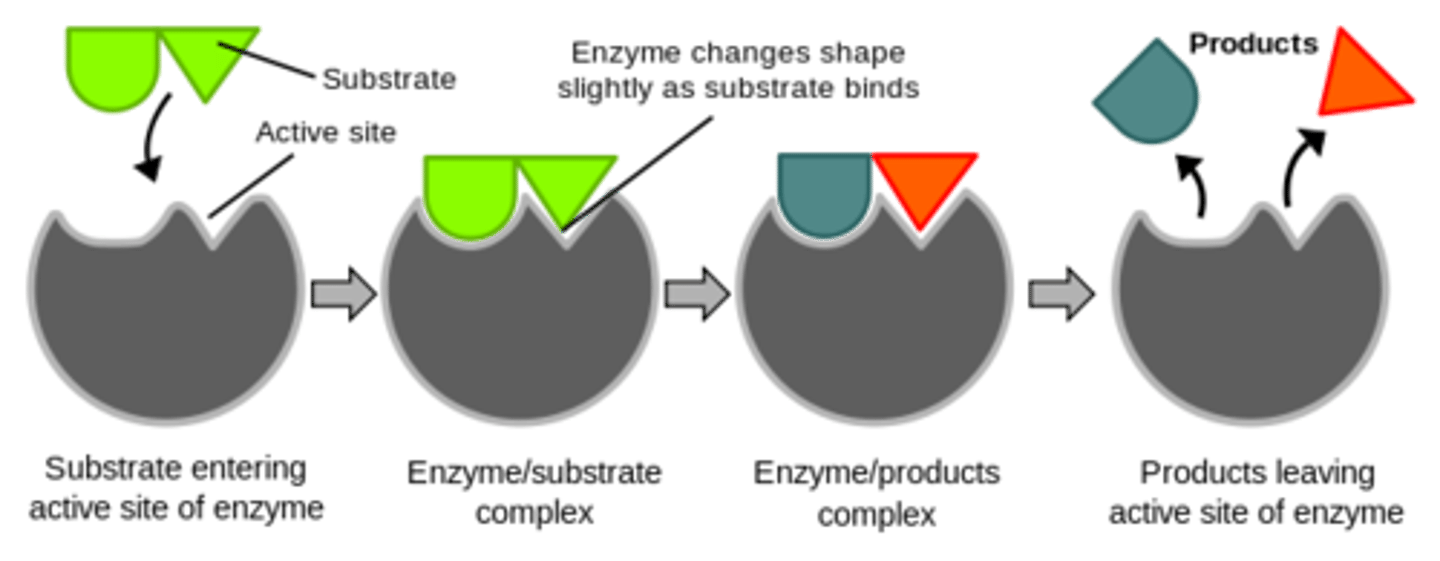
Enzyme induced fit model
BETTER EXPLAINS ENZYME ACTIVITY THEN THAT SILLY LOCK AND KEY
-as substrate approaches enzyme, it induces conformational change in active site - changes shape to fit substrate
-this stresses substrate, reducing activation energy of reaction
Nucleotide
Single unit of a nucleic acid
-very large molecules contructed by linking together nucleotides to form a polymer
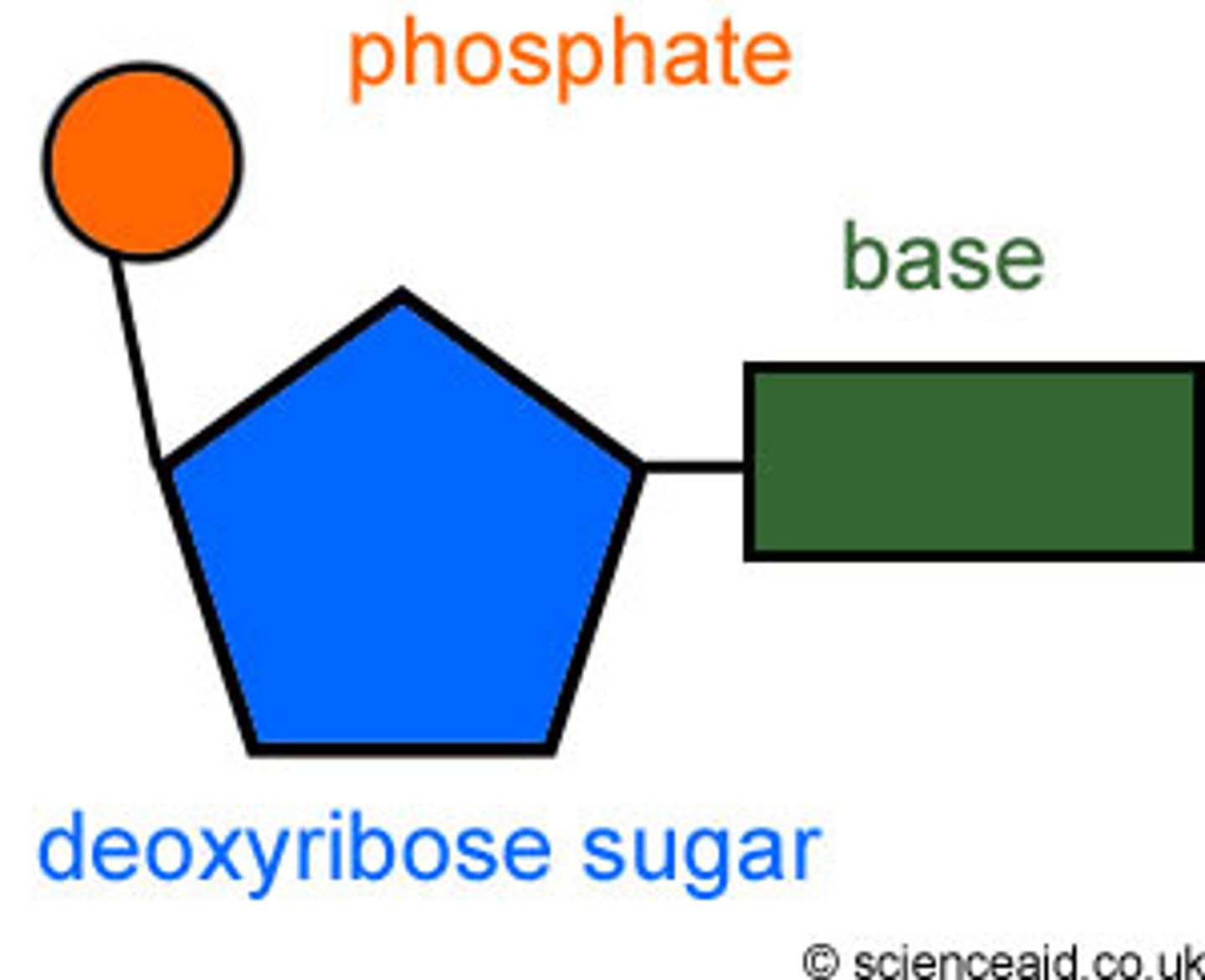
the 4 Nitrogenous Bases
Adenine
Guanine
Thymine (in RNA its Uracil)
Cytosine
AT
GC
Compare DNA and RNA
Bases:
RNA - Uracil
DNA - Thymine
sugars:
RNA - ribose
DNA - deoxyribose
number of strands:
RNA - single stranded (and not always linear sometimes)
DNA - 2 parallel complementary strandes form double helix
DNA Replication
production of new strands of DNA with base sequences identical to existing strands
-dna of organisim contains instructions for that organism
purpose of DNA replication
-reproduction -new daughter cells
-growth in multicellular organisms (new cells = larger)
-tissue replacement in multicellular organisms
When DNA replication occurs
INTERPHASE (Synsthesis/S)
-exact copies of chromosones are made
gives sister chromatids - chromosones and their copies which will be seperated in mitosis
-therefore each sister has full set of DNA
semi conservative
DNA replication is semi-conservative
-as 1 double strand of DNA replicates, each new double stranch of DNA that's produced contains 1 strand of OG DNA and 1 strand of newly synthesised DNA
-each OG strand of DNA molecule acts as template for new strand to build from
-ensures new strands are exact copies of original
Complementary base rule
Adenine (A) + Thymine (T)
Cytosine (C) + Guanine (G)
SINGLE OR MULTIPLE PRIMERS
Leading strand in DNA replication only requires single primer
Lagging strand equired primers placed at regular intervals
Free nucleotides
deoxynucleoside triphosphates
-extra phosphate groups carry energy which is used for formation of covalent bonds
DNA replication enzymes in Eukaryotes
-DNA polymerase attatches to RNA primer and replicates DNA in a 5' to 3' direction
-when reaches another RNA primer, it detatches and 'leapfrogs' to next primer following the helicase
DNA Polymerase3
attatches to RNA primer and replicates DNA in a 5' to 3' direction
-assembles the new strands of DNA by placing free nucleotides in correct sequence according to base sequence of template strand and complementary base pairing rule