Computer Science - OCR - 1.1 Systems Architecture
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Architecture that is used in CPU:
Von Neumann Architecture
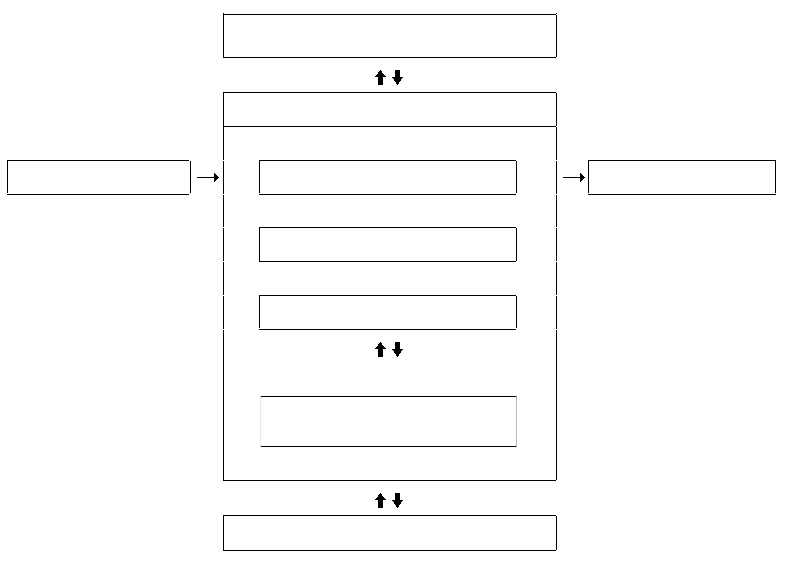
Fill in the blank spaces using the following terms:
Storage, Input, Output, CPU, CU, ALU, Registers, Cache Memory, Main Memory
See image for correct answer:
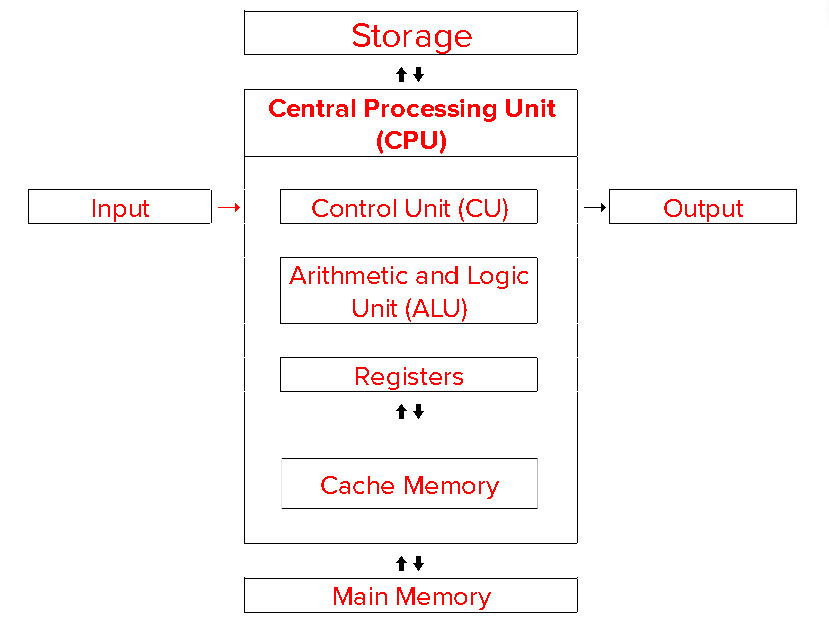
State the function of the CPU:
-FETCH the instructions from memory
-DECODE the instructions
-EXECUTE the instructions
State the function of the ALU:
-Logical Operations - These include AND, OR and NOT
-Shift Operations - the bits in a computer word can be left or right by a certain number of places
-Arithmetic Operations - These include addition, subtraction, multiplication and division
State the function of the CU:
-Controls the execution of instructions in the correct sequence
-Decodes instructions
-Regulates and controls processor timing using regular pulses from the system clock
-Sends and receives control signals to and from other devices within the computer
State the function of the Registers:
-A special very fast memory location within the CPU used in the execution of instructions
Describe, in summary, what happens during the Fetch-Execute Cycle:
The CPU will FETCH the next instruction to be executed from the MEMORY (RAM).
This instruction is transferred from MEMORY (RAM) into registers within the CPU, by being transferred along the appropriate buses. Instructions are DECODED by the CONTROL UNIT so that they can be executed. The control unit sends SIGNALS to various parts of the CPU, for example the ALU (Arithmetic and Logic Unit)
Describe the FETCH part of the FE cycle in order:
Contents of PC are placed in the MAR
Address is transferred to main memory along address bus
Data (Instruction) is sent back along data bus
Data (Instruction) is received and held in the MDR
The instruction is transferred to the CIR
Instruction is read by the CU for decoding
PC is incremented (points to the next instruction to be executed)
Describe the DECODE part of the FE cycle:
The Data is received by the registers and read by the CU for decoding. The CU decodes to decide what the instruction (Data) means and are ready to execute
Describe the EXECUTE part of the FE cycle:
The Data is then carried out at the requested action.
Define the Processor:
The hardware that executes programs and manages the rest of the hardware
Define the Memory Address Register:
Holds the address (location in memory) of the instruction or piece of data to be fetched or stored
Define the Memory Data Register:
Holds data or a program instruction temporarily when it is fetched from memory or is to be sent to memory
Define the Current Instruction Register
Define the Main Memory:
Used for holding instructions currently being executed and data that is being used
Define the Address Bus:
Carries Memory addresses/locations from the processor (MDR) to Main memory
Define the Data Bus:
Carries data/instructions from main memory back to the processor (MDR) and vice versa
Define the Accumulator:
Memory location in which results of operations carried out in the ALU are temporarily stored
Define the Program Counter:
Holds the memory address of the next instruction to be processed
Describe the Clock Speed and how it impacts performance:
The number of fetch execute cycle instructions per second, measured in hertz (Hz)
A higher clock speed means more FE cycles per second
Describe the role of Cache:
Stores recently or frequently accessed instructions so that the CPU can fetch these from cache instead of the slower RAM
Explain why computers have very low amounts of Cache:
Cache is more expensive and the more added the slower the cache gets
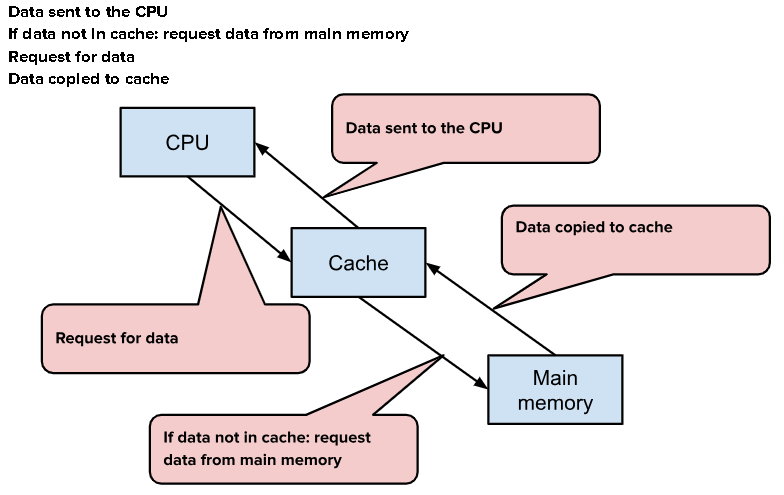
Describe what is happening in the image:
The CPU requests data from the Cache
If the data isn’t in the Cache, the CPU requests data from the Main Memory
The Main Memory copies data to the cache
The data is then sent to the CPU
Describe a quad-core processor:
A processing chip with 4 individual cores that read and operate central processing unit instructions
Give an example of a program that when executed using multiple cores can be executed more quickly than using a single core.
Adding up all the numbers in an array of 1000 values or in a quad core processor adding 50 scores each in a year group of 200 people
Give an example of a program that when executed using multiple cores makes no difference compared to a single core.
Calculating the Fibonacci sequence and listening to music
Describe Parallel Processing:
Parallel processing means that each core can execute different parts of the same process at the same time.
Describe what an embedded term is:
A computer system with its own CPU and memory with a dedicated function within a larger mechanical system
Give an example of an Embedded System:
Washing Machine, Microwave, Oven, Coffee Machine
Describe the main characteristics of an Embedded System:
ROM - The program which controls the machine is stored on ROM and cannot be changed
Interface - Audio Output, Touch screens, Keypads, Digital display, May connect to an external device
Sensors -
Traffic Light → Pressure sensors
Motion sensors → Washing Machine
Temperature sensors
Physical Size - Usually small
Describe the benefits of an Embedded System:
Low cost to produce on mass
As they have a dedicated function they are more reliable
Describe the disadvantages of an Embedded System:
Limited to one specific use
Often written in low level programming languages