Topic 1C - Key Concepts in Biology: MOVEMENT OF SUBSTANCES IN & AND OUT OF CELLS
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1 Core Practical: Core Practical: Investigate osmosis in potatoes (1.16)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
1.15 What is diffusion?
the movement of molecules form regions of higher concentration to regions of lower concentration
1.15 How do molecules move?
Molecules move down a concentration gradient, as a result of their random movement
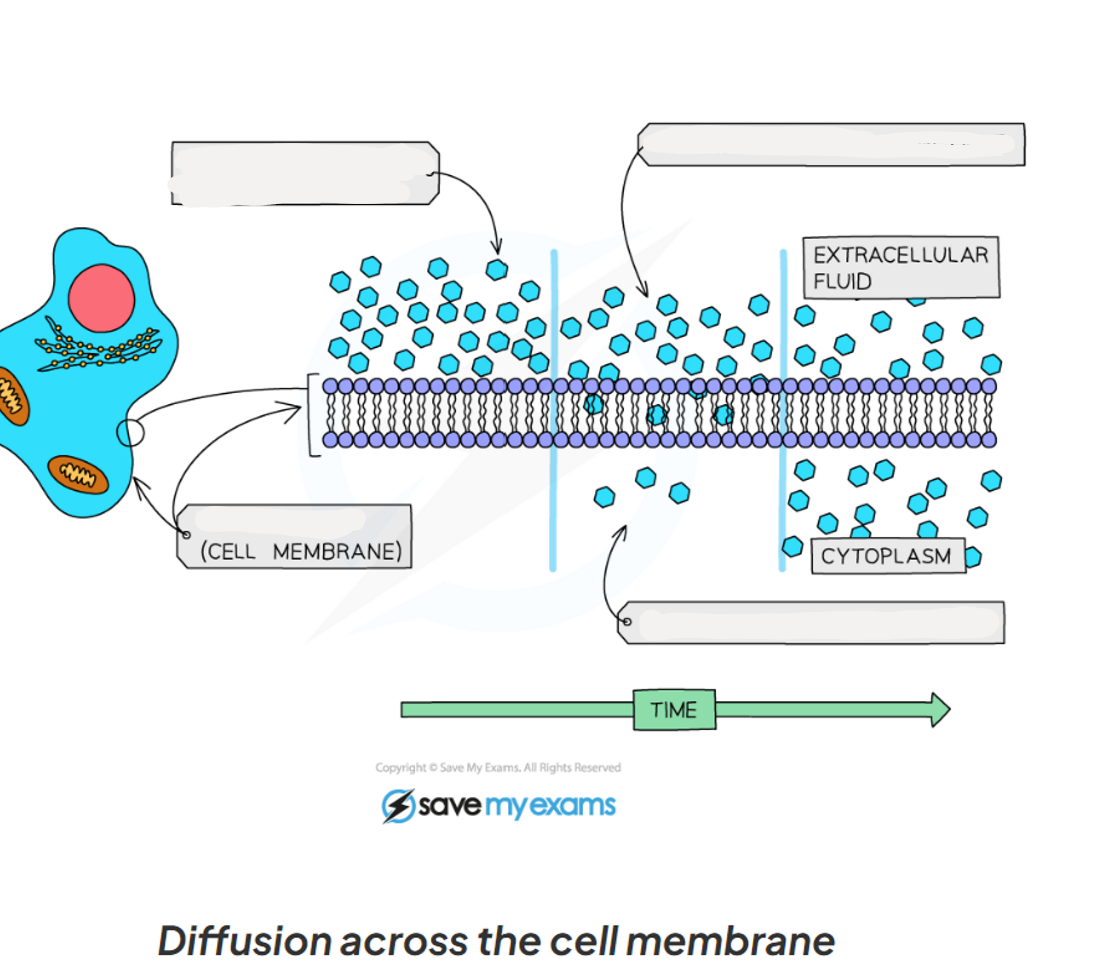
1.15 Label this diagram of molecules moving from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration through a cell membrane
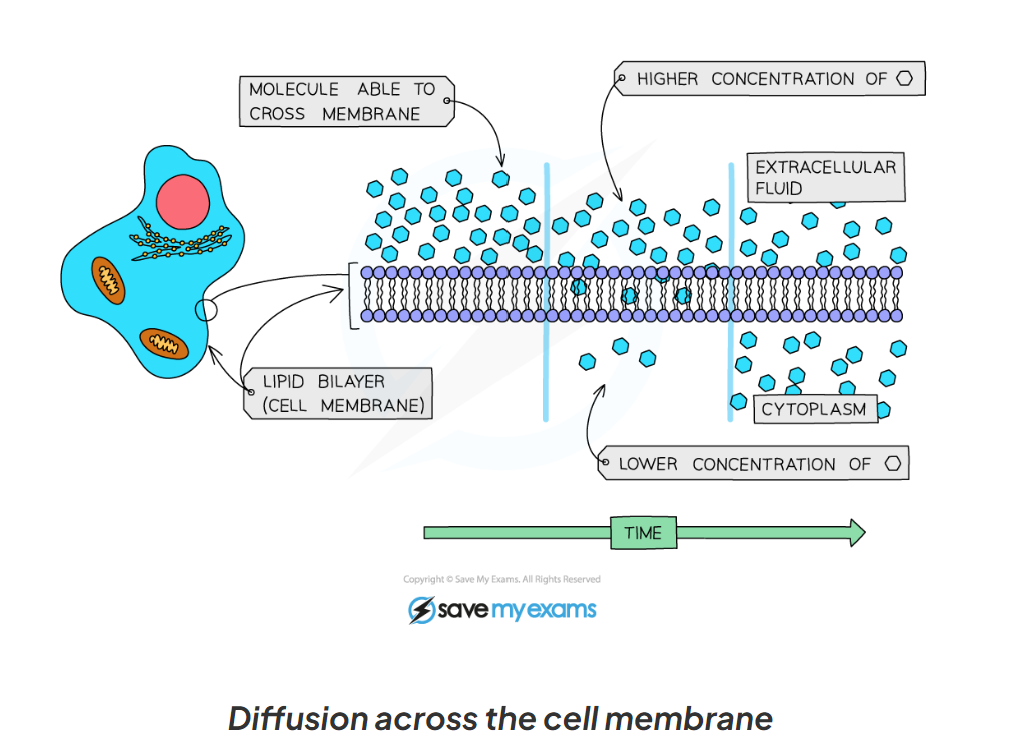
1.15 Explain diffusion in living organisms
-In living organisms the molecules still move down a concentration gradient
-However the cell membrane is a partially permeable membrane - meaning it allows some molecules to cross easily, but other with difficulty or not at all
This is often based on the size of the molecules (smaller molecules can diffuse across whereas larger ones cannot)
1.15 How does diffusion help living organisms?
Helps them to:
-Obtain many of their requirements (nutrients)
-Get rid of many of their waste products
-Carry out gas exchange for respiration
1.15 What diffusion take place in the small intestine?
In the small intestine, digested food molecules such as glucose, amino acids, fatty acids and glycerol diffusion form the lumen to the blood in the small intestine.
1.15 What diffusion takes place in the lungs?
-oxygen diffuses from the alveolar air space to the blood in the capillaries around the alveoli
-carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood in the capillaries around the alveoli to the alveolar air space
1.15 What diffusion take place in the leaves? (Give 3)
-Oxygen diffuses from air spaces between the mesophyll cells to the mitochondria cells
-Carbon dioxide diffuses from air spaces between the mesophyll to the chloroplasts in the mesophyll
-Water vapour diffuses form the stomatal pores to the air outside the stomata
1.15 Give 4 factors which influence the rate of diffusion
1) Surface area to volume ratio
2) Diffusion distance
3) Temperature
4) Concentration gradient
1.15 How does surface area to volume ratio affect the rate of diffusion?
-the bigger a cell or structure is, the smaller its surface area to volume ratio is, slowing down the rate at which substances can move area its surface.
-many cells which are adapted to diffusion have increased surface area in some way - eg root hair cells in plants (which absorb water and mineral ion) and cells lining the ileum in animals (which absorb the products of digestion)
1.15 How do you calculate the surface area to volume rato?
To calculate the:
Surface are (x²): Area of one side multiplied by the number of sides
Volume (x³): height x width x length
Divide the surface area by the volume to find t simplest ratio
1.15 How does the diffusion distance affect the rate of diffusion?
-the smaller the distance the molecules have to travel the faster transport will occur
-this is why blood capillaries and alveoli have walls which are only one cell thick, to ensure that the rate of diffusion across them is as fast as possible
1.15 How does temperature affect the rate of diffusion?
-the higher the temperature, the faster the molecules move as they have more energy.
-this results in more successful collisions against the cell membrane and therefore a faster rate of movement across them (faster rate of diffusion)
1.15 How does the concentration gradient affect the rate of diffusion?
-the greater the difference in concentration on either side of the membrane, the faster movement across it will occur