bio unit 2 chap 7
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
lipids, proteins
what are the staple ingredients of a membrane
amphipathic
a molecule that has both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions
fluid mosaic model
the membrane is a mosaic of protein molecules drifting laterally in a fluid bilayer of phospholipids
no (groups of proteins are associated in long lasting, specialized patches, where they carry out common functions)
are proteins randomly distributed in the membrane?
hydrophobic interactions
a weak chemical interaction caused when molecules that do not mix with water come together to exclude water
hydrophobic interactions
what are membranes mainly held together by?
yes
can some of the phospholipids and proteins shift around and change places within the membrane?
yes
can a membrane solidify?
type of lipids it’s made of
what does the temperature the membrane solidifies at depend on?
unsaturated (the kinks in their tails caused by double bonds makes it harder for them to pack close together to make solids, therefore enhancing membrane fluidity)
what kind of tails do phospholipids that stay liquid at lower temperatures have?
saturated (tails have no double bonds and are straighter, allowing them to pack closer together and solidify easier)
what kind of tails do phospholipids that solidify at higher temperatures have?
yes
do unsaturated lipids have double bonds?
no
do saturated lipids have double bonds?
between phospholipids in membranes
where is cholesterol located?
cholesterol (at high temperatures, it restrains the movement of phospholipids, making them less fluid, however it also hinders the close packing of phospholipids, making them less prone to solidify)
this steroid helps the membrane resist changes in fluidity with changes in temperature
fluidity
this affects the permeability of the membrane and the ability for membrane proteins to move where they are needed to function
proteins (different kinds of cells contain different kinds of membrane proteins)
what determines the membrane’s function?
integral proteins
transmembrane proteins that penetrate and often span the hydrophobic portion of a membrane. They have both hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions
transmembrane proteins
a protein that spans the entire membrane
hydrophilic channels
channels in some proteins that allow hydrophilic substances to pass through hydrophobic areas (cell membrane)
peripheral proteins
proteins loosely bound to the surface of a membrane or to an integral protein. NOT embedded in the lipid bilayer
transport, enzymatic activity, transferring signals, cell recognition, intercellular joining, attachment to cytoskeleton or ECM
what are the six functions of membrane proteins
glycolipid
carb attached to a lipid
selective permeability
allowing some substances to cross the plasma membrane easier than others
nonpolar
which molecules have a easier time passing through the cell membrane? non polar or polar/ions?
transport proteins
proteins that span the membrane that help polar/ionic/hydrophilic substances pass through the cell membrane
aquaporins
a type of transport/channel protein that facilitates osmosis- or the diffusion of free water across the membrane
channel proteins
proteins that have hydrophilic channels that functions as tunnels so hydrophilic molecules can pass thru the hydrophobic interior of the cell membrane
carrier proteins
transport proteins that change shape around the hydrophilic molecules to bring them inside/outside the cell
diffusion
the movement of particles so they spread out into a space- in this case the movement of a substance from a region where it is more concentrated to a region where it is less concentrated
passive transport
the diffusion of a substance across a membrane that uses NO ENERGY- it moves WITH the concentration gradient (high conc to low conc)
osmosis
the diffusion of free water across a selectively permeable membrane- high to low
hypotonic
more solvent, less solute
lysed
the cell bursts in bio terms, when animal cells are in a hypotonic environment
hypertonic
more solute, less solvent
tonicity
the ability for a surrounding solution to cause a cell to gain or lose water
isotonic
equal concentrations of solute and solvent
turgid
optimum state for plant cells, plant cells are in a hypotonic environment, meaning water will flow into the cell and create pressure
hypertonic
in what environment do both plant and animal cells shrivel up/plasmolyze?
hypotonic
what environment should plant cells be in?
isotonic
what environment should animal cells be in?
facilitated diffusion
a type of passive diffusion with the assist of transport proteins (to move ions and etc.)
gated channels
channels that open/close in response to a stimulus
active transport
the movement of a substance across the cell membrane AGAINST its concentration gradient, expends energy (ATP) and is mediated by specific transport proteins
sodium potassium pump
a transport protein that actively transports sodium out of the cell and potassium in, also the main pump for animals
membrane potential (also usually the inside of the cell is negative to the outside of the cell, so cations (positive ions) are attracted in and anions (negative ions) are pushed out)
the difference in electrical charge across a cell’s plasma membrane due to the differential distribution of ions. It affects the activity of all excitable cells and the transmembrane movement of all charged substances
electrochemical gradient
the combination of chemical (concentration diff) and electrical forces (membrane potential/charge diff) acting on an ion
electrogenic pump
a transport protein that generates voltage across a membrane
proton pump (H+ ions)
what is the main electrogenic pump for bacteria/plants/fungi?
cotransport
the coupling of the downhill diffusion of one substance to the uphill transport of another against its own concentration gradient
FOR EXAMPLE… sucrose can enter the cell but ONLY ON H+ ions, so, sucrose and H+ diffuse TOGETHER INTO THE CELL WITH THEIR CONCENTRATION GRADIENTS, then after H+ has performed its duty, it gets pumped back out
vesicles
what do large molecules enter and leave the cell on??
exocytosis
the secretion of molecules by the cell by the fusion of vesicles containing them with the plasma membrane
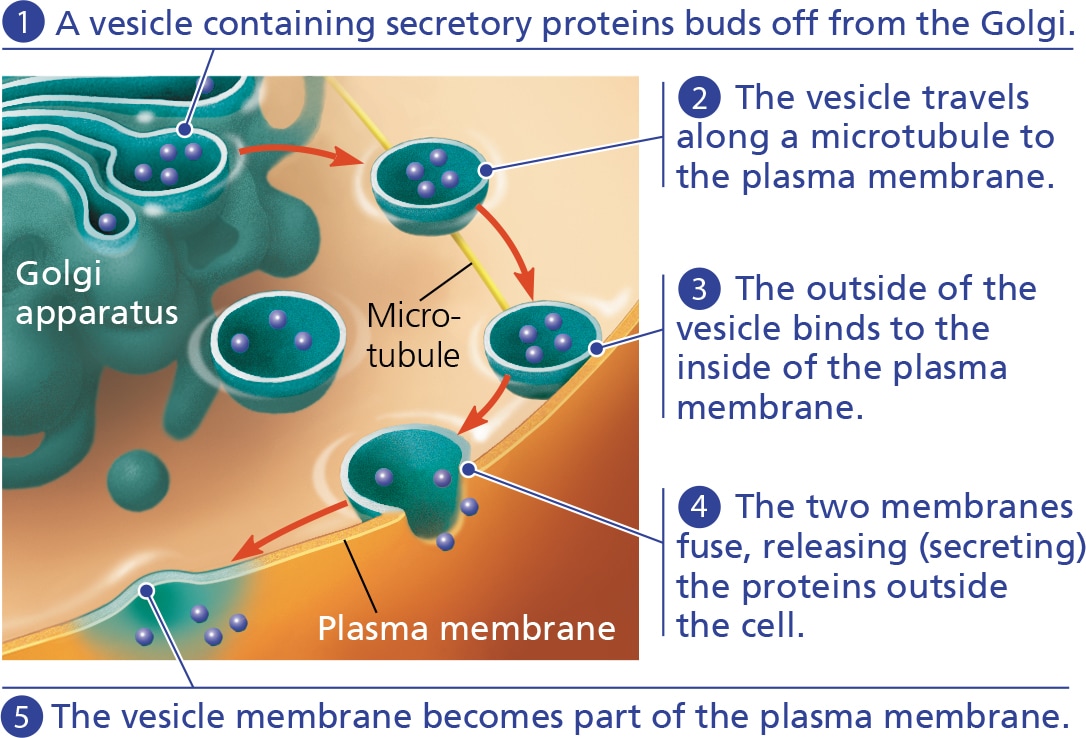
endocytosis
the cell takes in molecules via formation of vesicles form the plasma membrane
pinocytosis, phagocytosis, receptor mediated
what are the three types of endocytosis
phagocytosis
LARGE particles are taken up by endocytosis (cellular eating)
pinocytosis
cell ingests extracellular fluid and its dissolved solutes (cellular drinking)
receptor mediated endocytosis
a type of endocytosis/pinocytosis that takes in specific substances in the extracellular fluid, even if those substances aren’t particularly abundant. Works by having receptors in the vesicle that is forming that attracts specific substances.