Unit 1 Biology (From Lectures!!)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This is the complete list of vocab from the end of each slideshow presented in lectures.
Last updated 5:29 AM on 1/31/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
1
New cards
1000 Genome Project
* Frequently Displayed on Maps
* Launched to establish a deep catalogue of human genetic variation
* Launched to establish a deep catalogue of human genetic variation
2
New cards
Pie Graphs
* The pie graphs represent the frequency of something in different populations
* Each circle is a pie chart showing the frequency of something
* Each circle is a pie chart showing the frequency of something
3
New cards
Scatterplot

4
New cards
Line of Best Fit

5
New cards
Autotroph
An organism that can produce its own food from raw materials and energy
6
New cards
Ways to obtain Vitamin D
1. via Photosynthetic Reaction
2. diet (Dairy, Fish)
7
New cards
Eukaryote
* Multi-cellular
* possesses a defined nucleus
* possesses a defined nucleus
8
New cards
Prokaryote
* Uni-cellular
* lacks a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
* lacks a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
9
New cards
Phenotype
Anything that results in a outward or observable manifestation on/in the organism
10
New cards
Examples of Phenotypic Traits
* Shape of protein
* Efficiency of Enzyme
* Amount of Enzyme Produced
* Shape of Cell
* Function of tissue
* Susceptibility to a disease
* Efficiency of Enzyme
* Amount of Enzyme Produced
* Shape of Cell
* Function of tissue
* Susceptibility to a disease
11
New cards
Genotype
Anything at the DNA level
12
New cards
Examples of genotypes
* Sequence of DNA that codes for a protein
* Sequence of DNA that doesn't code for a protein
* Presence / Absence of a mutation
* Length of a gene
* Number of copies of a gene
* Number of copies of a chromosome
* Sequence of DNA that doesn't code for a protein
* Presence / Absence of a mutation
* Length of a gene
* Number of copies of a gene
* Number of copies of a chromosome
13
New cards
When did the “genomic era” of biology begin?
2001
14
New cards
What does “GWAS” stand for?
Genome-Wide Association Studies
15
New cards
What does GWAS allow you to identify?
* The sequence of DNA in an organism
* Connections between genotypes and phenotypes
* The size of an organism’s genome
* Connections between genotypes and phenotypes
* The size of an organism’s genome
16
New cards
SNP
Single nucleotide polymorphism
17
New cards
Exon
coding sequence of eukaryotic genes
18
New cards
Intron
non-coding sequence of eukaryotic genes
19
New cards
DNA is a unique molecule with a relationship between
structure & function
20
New cards
DNA structure includes its
* chemistry
* subunits
* polarity
* stoichiometry
* 1D,2D,3D appearance
* subunits
* polarity
* stoichiometry
* 1D,2D,3D appearance
21
New cards
DNA function
* Store information
* Maintain information
* Express information
* Transmit information
* Be configured/rewritten
* Maintain information
* Express information
* Transmit information
* Be configured/rewritten
22
New cards
dNTP
deoxynucleoside triphosphate
23
New cards
DNA subunits
* nitrogenous base(A,G,T,C)
* five-carbon sugar
* phosphate group
* five-carbon sugar
* phosphate group
24
New cards
DNA micromolecule
nucleotide
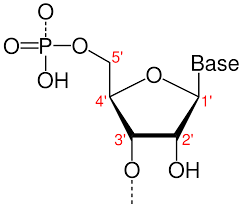
25
New cards
DNA polymer
* two long polymers of nucleotides
* runs anti-parallel
* forms double-helix
* runs anti-parallel
* forms double-helix
26
New cards
Purine
* double-ringed structure
* nitrogenous base
* A and G
* nitrogenous base
* A and G
27
New cards
Pyrimadine
* single-ringed structure
* nitrogenous base
* T, C, and U(RNA)
* nitrogenous base
* T, C, and U(RNA)
28
New cards
Who Discovered DNA is a double helix
* Watson
* Crick
* Franklin
* Crick
* Franklin
29
New cards
van der Waals forces
* The weak attraction between two atoms (electron cloud of one atom interact with the nucleus of the other)
30
New cards
Covalent bond
* strong chemical bond based on the sharing of electrons between 2 atoms
31
New cards
How can nucleotides be broken?
* Heat
* Enzymes
* Enzymes
32
New cards
Phosphate attached to
5’ end
33
New cards
Sugar attached to
3’ end
34
New cards
Condensation Reaction
Covalent bonding between C3 and the phosphate of a nucleotide
35
New cards
Transmission Genetics
The study of how phenotypic traits are passed between generations
36
New cards
Central Dogma of Biology
Genetic information flows in only one direction. DNA, RNA, protein
37
New cards
Origin of Replication
* The location of a specific DNA sequence where DNA replication begins.
* Eukaryotes can have multiple
* Prokaryotes only have one
\
* Eukaryotes can have multiple
* Prokaryotes only have one
\
38
New cards
Helicase
* An enzyme that unwinds the DNA double helix (requires energy)
* Binds to ssDNA within the replication bubble
* Binds to ssDNA within the replication bubble
39
New cards
Leading Strand
* continuously replicating strand
* 3’ - 5’ direction
* 3’ - 5’ direction
40
New cards
Lagging Strand
* discontinuous replication strands
* 5’ - 3’ direction
* 5’ - 3’ direction
41
New cards
RNA Primer
* A short nucleic acid sequence that initiates DNA synthesis
42
New cards
Molecular Genetics
The study of molecular bases of:
* genetic information
* hereditary transmission
* conversion to phenotypes(expression)
* genetic information
* hereditary transmission
* conversion to phenotypes(expression)
43
New cards
Primase
An enzyme that synthesizes short RNA sequences called primers
44
New cards
DNA polymerase
An enzyme that is responsible for forming new copies of DNA
45
New cards
Topoisomerase
An enzyme responsible for reducing supercoils in DNA by breaking and rejoining DNA fragments
46
New cards
Single Stranded Binding Proteins(SSBPS)
stabilize unwound strands
47
New cards
Blue Pie Graph
25%
48
New cards
Green Pie Graph
2\.5%
49
New cards
Red Pie Graph
.25%
50
New cards
Somatic mutations
* A permanent genetic change in a somatic cell
* These mutations affect only the individual; not passed onto offspring
* These mutations affect only the individual; not passed onto offspring
51
New cards
Germ line mutations
* A mutation in a cell that produces gametes
* A gamete with the mutation passes it on to a new organism at fertilization
* A gamete with the mutation passes it on to a new organism at fertilization
52
New cards
Loss of function mutation
* A mutation that results in the loss of a functional protein
* May cause a gene to not be expressed at all
* May cause a gene to not be expressed at all
53
New cards
Gain of function mutation
* A mutation that results in a protein with a new function
* Alters function of protein
* Alters function of protein
54
New cards
Point mutation
* A mutation that results from the gain, loss, or substitution of a single nucleotide (base pair)
55
New cards
Transition
* purine nucleotide replaced by another purine
* pyrimidine nucleotide replaced by another pyrimidine
* pyrimidine nucleotide replaced by another pyrimidine
56
New cards
Transversion
* purine nucleotide replaced by pyrimidine
* pyrimidine nucleotide replaced by purine
* pyrimidine nucleotide replaced by purine
57
New cards
Silent mutation
A change in a gene’s sequence that has no effect on the amino acid. Does not change the amino acid that correlates with the codon
58
New cards
Missense
A change in a gene’s sequence that changes the amino acid at that site in the encoded protein
59
New cards
Nonsense mutation
Base pair mutation causing mRNA sense codon to become a stop codon
60
New cards
Loss of stop mutation
Base pair mutation cause mRNA stop codon to become a sense codon
61
New cards
Frame shift mutation
the addition or deletion of a single or two adjacent nucleotides in a gene sequence(non-functional protein)
62
New cards
Chromosomal rearrangements
large changes in the sequence of DNA caused by breakage and rejoining of DNA molecules
63
New cards
Deletion
Mutation resulting from loss of continuous segment of gene/chromosome
64
New cards
Duplication
Mutation in which segment of a chromosome is duplicated
65
New cards
Inversion
Rare 180 degree reversal of DNA sequence within a segment of a gene or chromosome
66
New cards
Translocation
Rare mutational event that moves a portion of a chromosome to a new location
67
New cards
Spontaneous mutations
permanent changes in the genetic material without any outside influence
68
New cards
Induced mutation
permanent change in the genetic material with a mutagen (outside agent)