ORGO M5
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
[CHP 21: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives]
Compounds w/ func group that can be converted » CA via simple acidic/basic hydrolysis
Lactones: cyclic ester
Amide: composite of CA & ammonia/amide
Ammonium salt » amide @ high temp
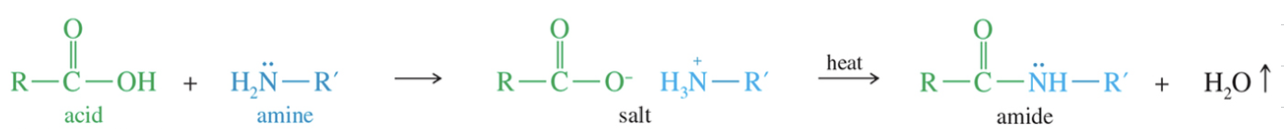
Lactams: cyclic amide
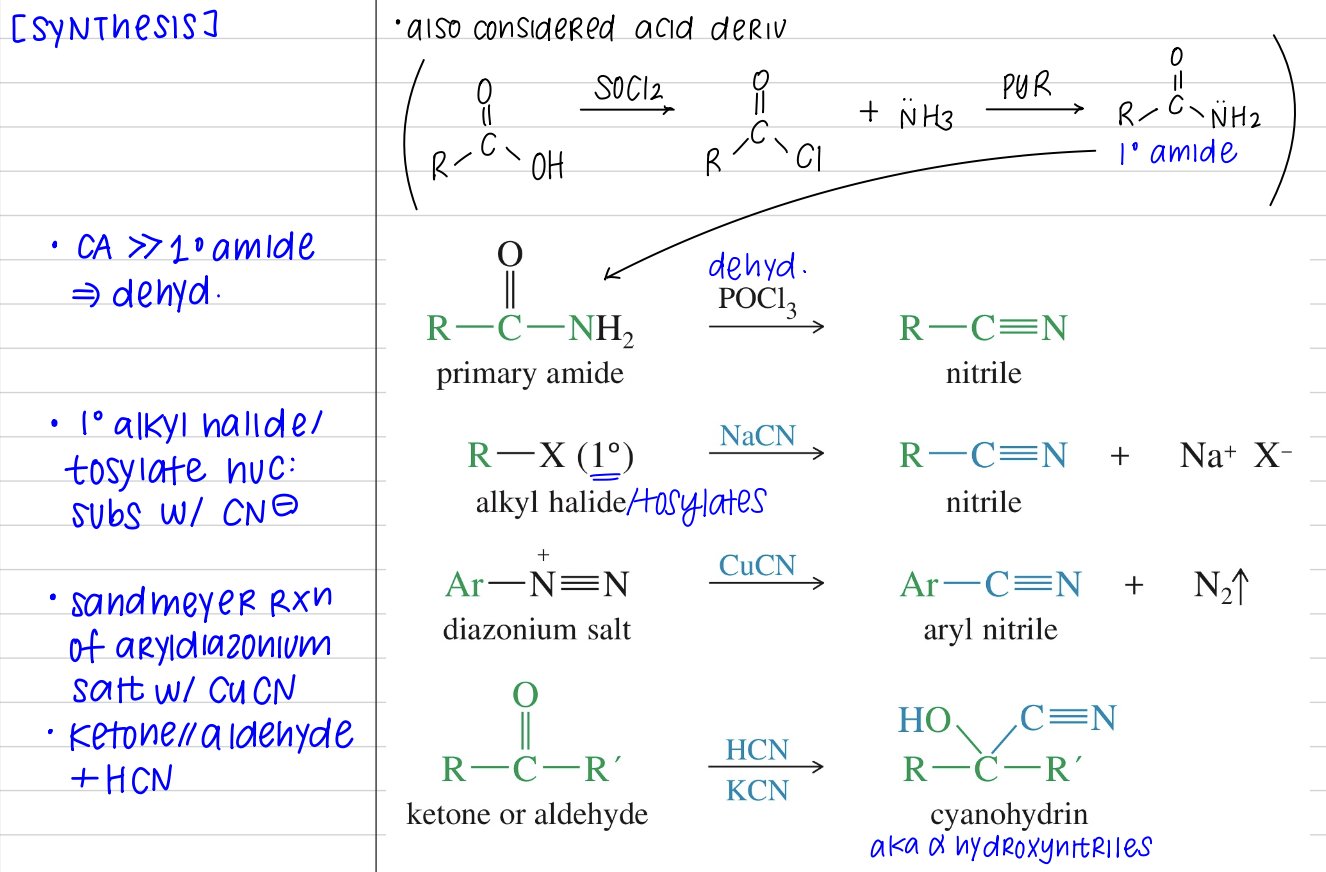
Nitrile: cyano group
a) Hydrolysis » acid
H3O+ excess (nitrile » 1 amide » acid)
b) Synthesis « acid
NH3 + heat (» 1 amide)
POCl3 (» nitrile)
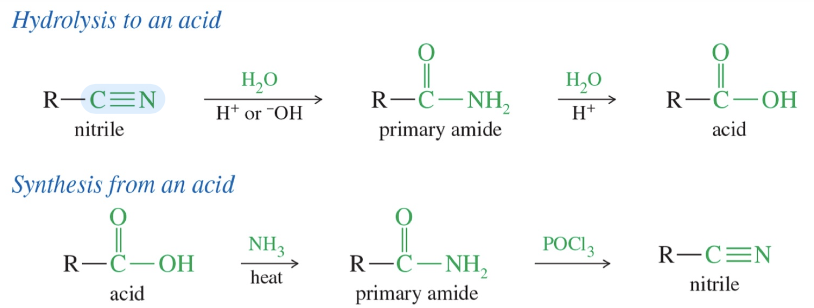
Electronic structure of nitrile
sp hyb w/ 180 bond angle
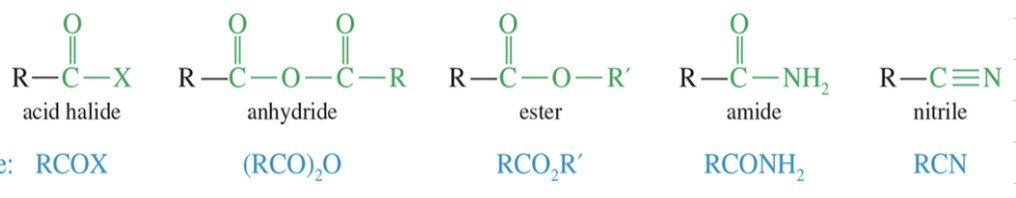
Acid Halide aka acyl halides: activated deriv used in synthesis of other acyl cpd like ester
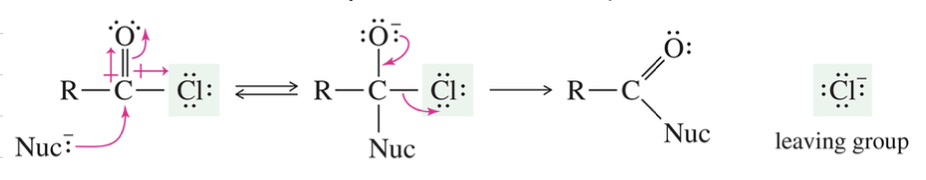
Anhydride: 2 MC of acid w/ H2O loss
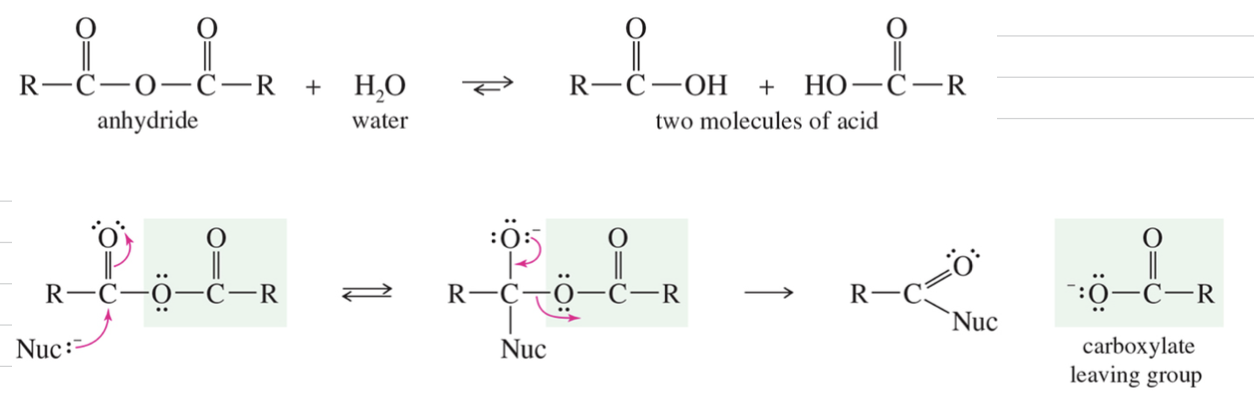
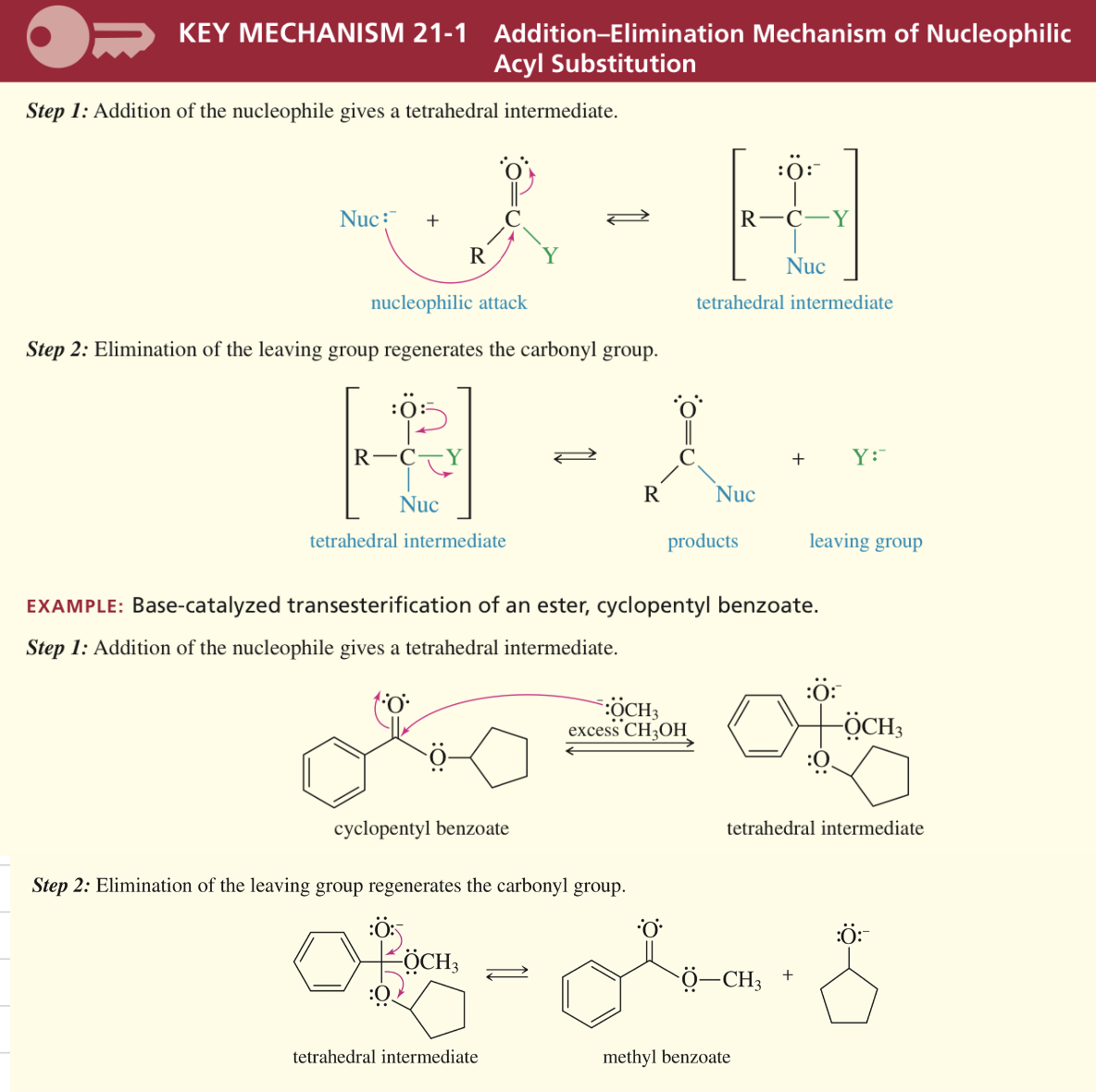
Mech) Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
Interconversion of acid deriv via add/elim mech
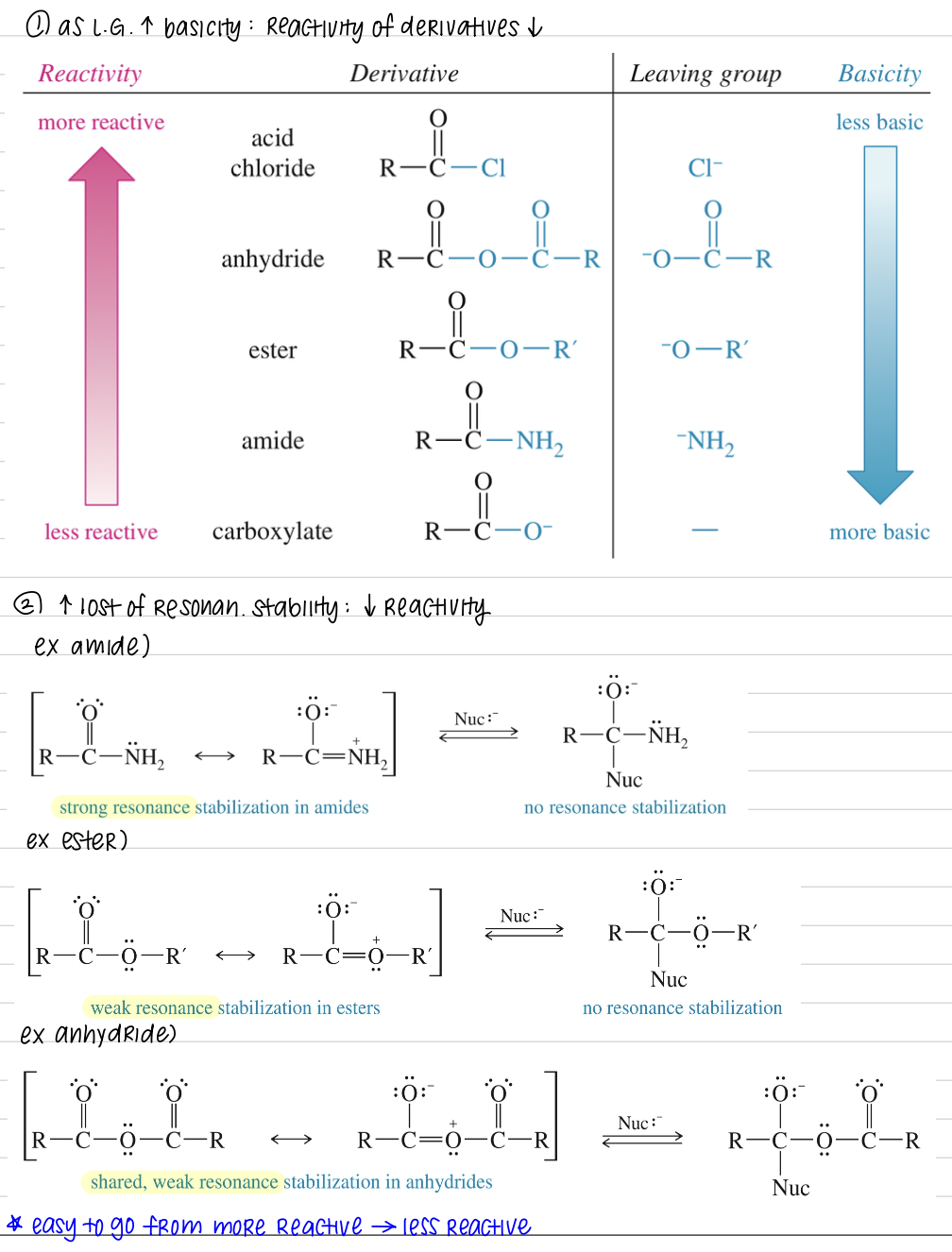
★ Reactivity of acid derivatives
1) Reactivity of acid derivatives ↓ as basicity of L.G. ↑
Bc less basic L.G. means more stable as a L.G. » ↑ reactivity of acid derivatives
2) ↑ loss of resonance stability ↓ reactivity
Amide have strong resonance stabilization followed by weak ester and even weaker anhydride
Tetrahedral intermediate has no resonance stab after nuc attack » amide less reactive
* Easy to go from more reactive » less reactive
★ Interconversion of acid derivatives
Acid chloride > anhydride > ester > amide > carboxylate
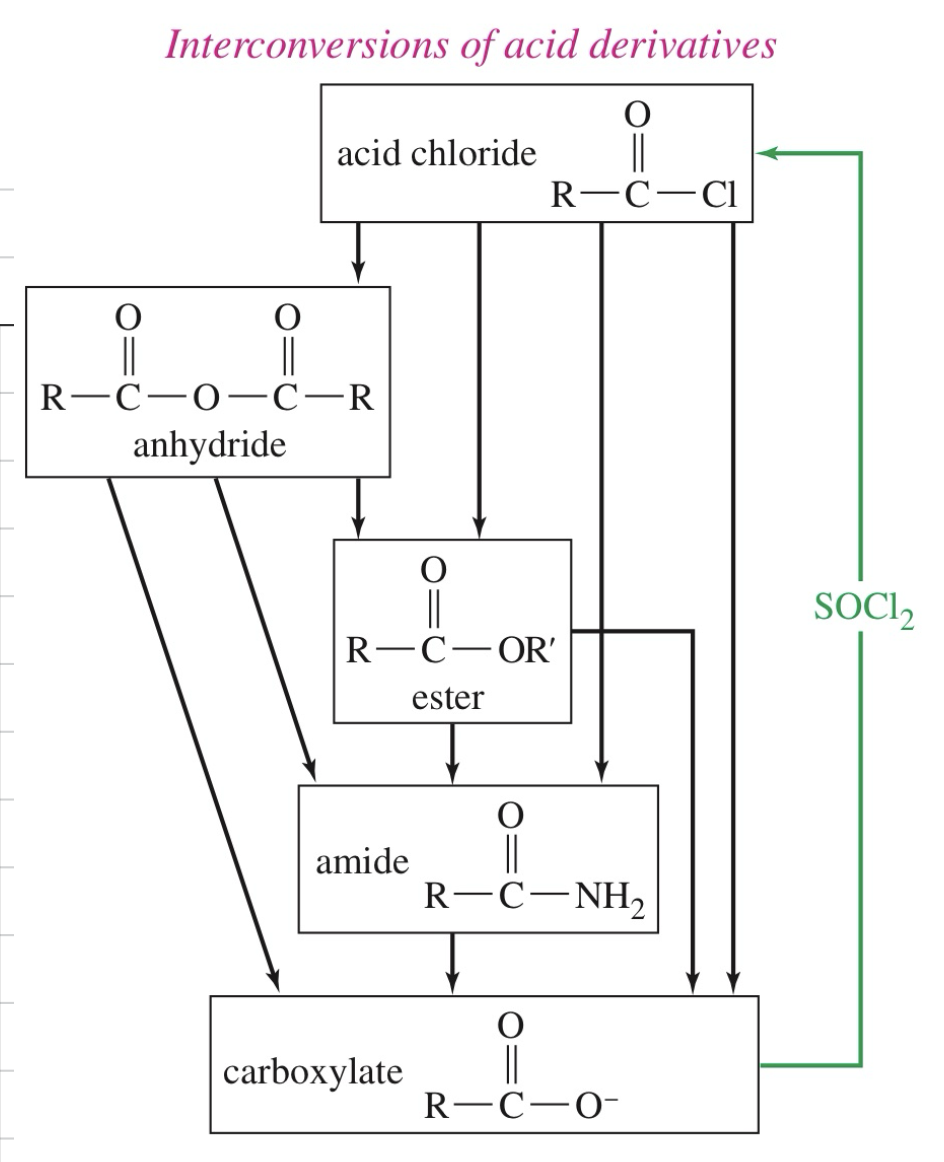
Mech) Acid chloride » anhydride
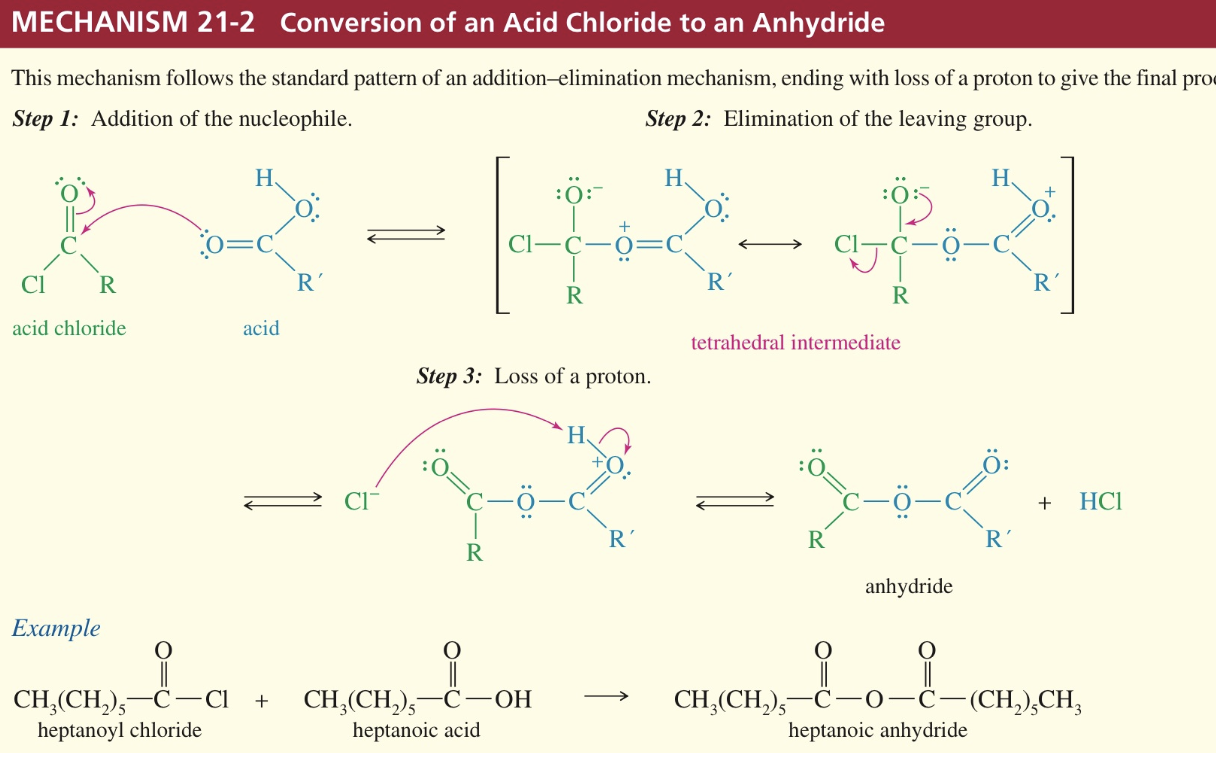
Mech) Acid chloride » ester
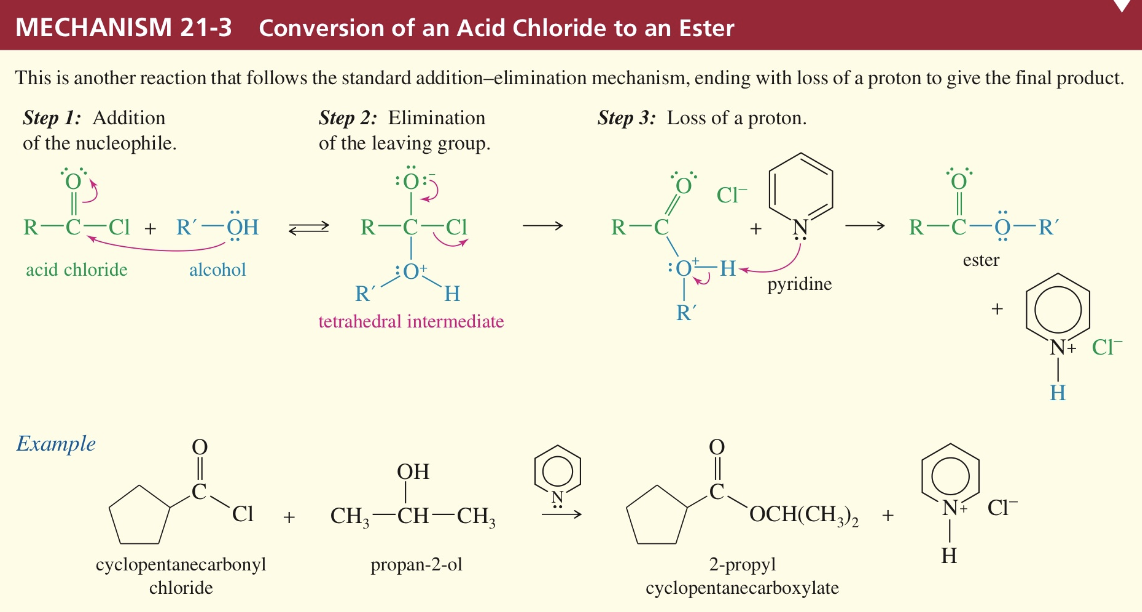
Mech) Acid chloride » amide
+ Ammonia → 1 amide
+ 1 amine → 2 amide
+ 2 amine → 3 amide
Mech) Acid anhydride » ester
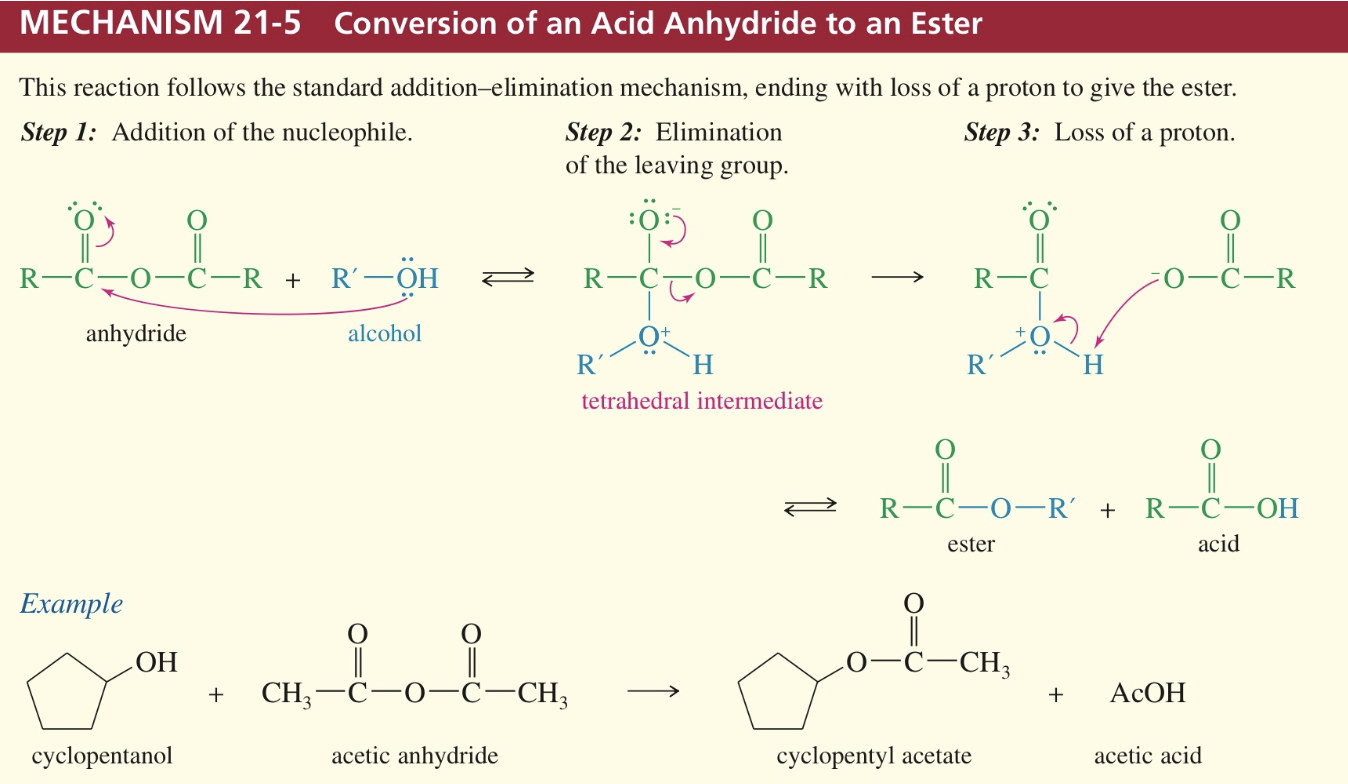
Mech) Acid anhydride » amide
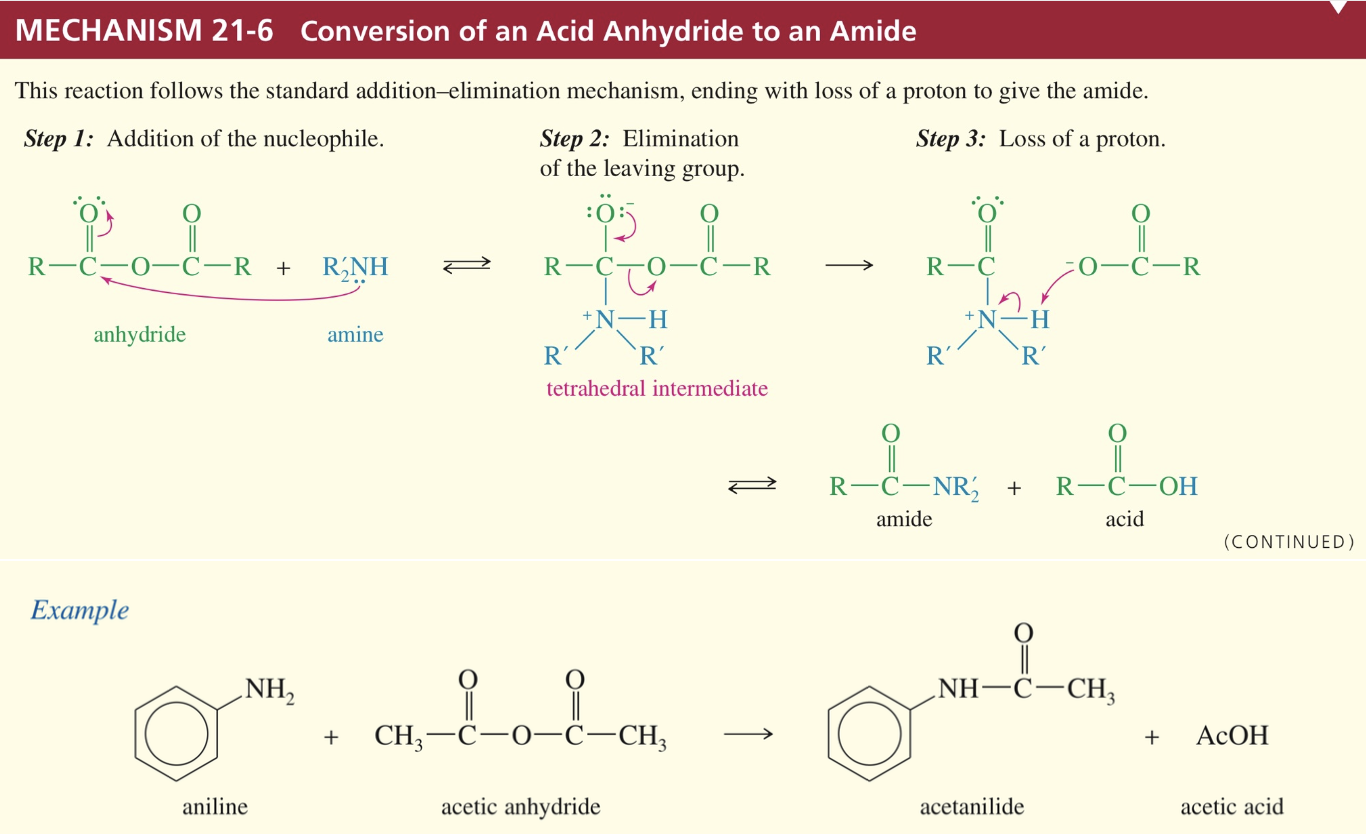
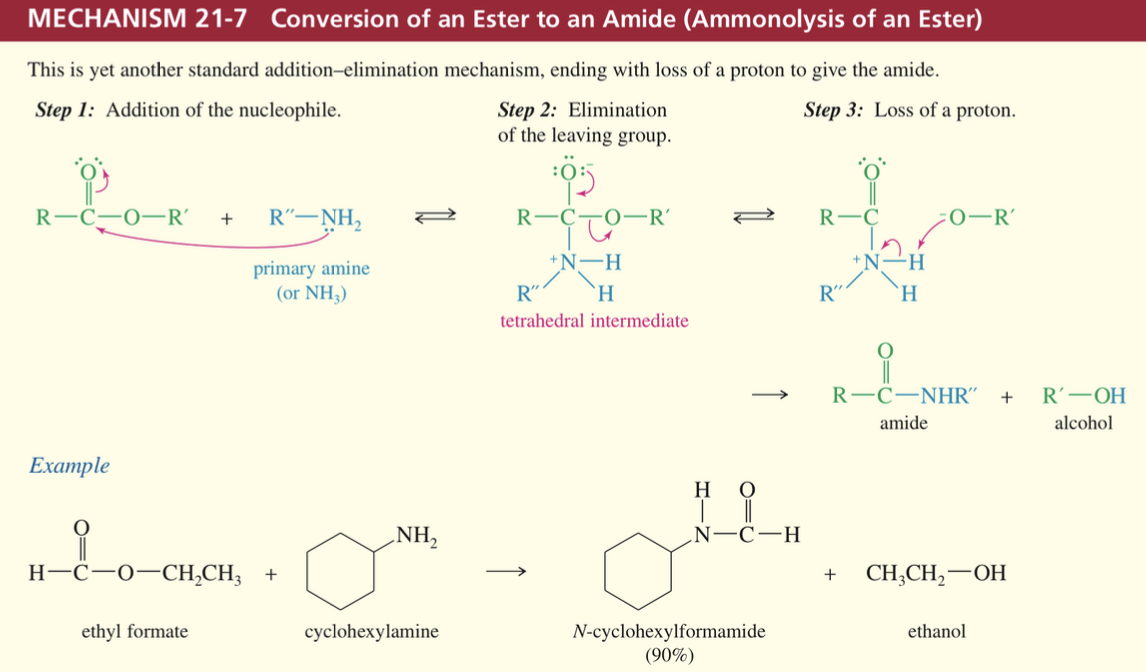
Mech) Ammonolysis of ester » amide
* Nuc needs to be NH3 // 1 amine
* Req. prolonged heat → normally just hydrolyze ester so need to make acid chloride add amine
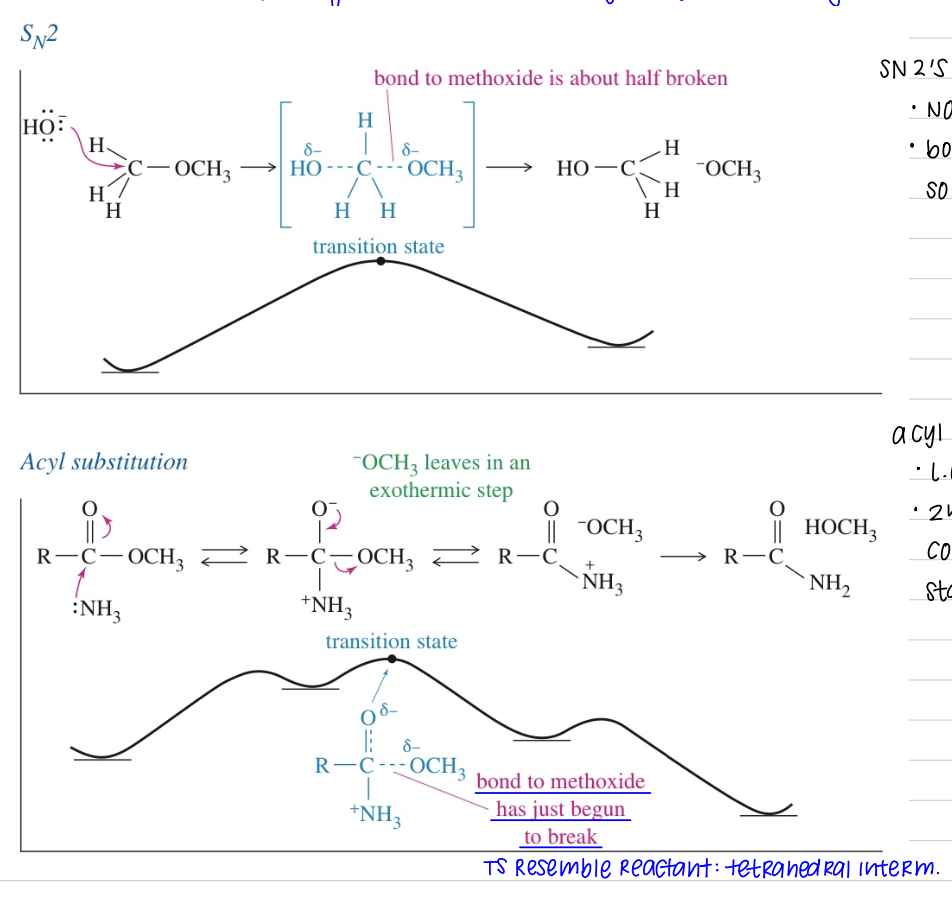
★ L.G. in nuc acyl substitution vs SN2
Diff in mech: SB may serve as L.G. in acyl subs even though it cannot in alkyl subs
SN2’s 1 step mech)
Not strongly endo/exo
Bond of L.G. ½ broken in the TS so rxn is sensitive to nature of L.G.
Acyl Subs)
L.G. leaves in separate 2nd step after tetrahedral interm
2nd step is highly exo: converting tetra int. → more stable MC
bond to methoxide just begun to break
Mech) Acid anhydride
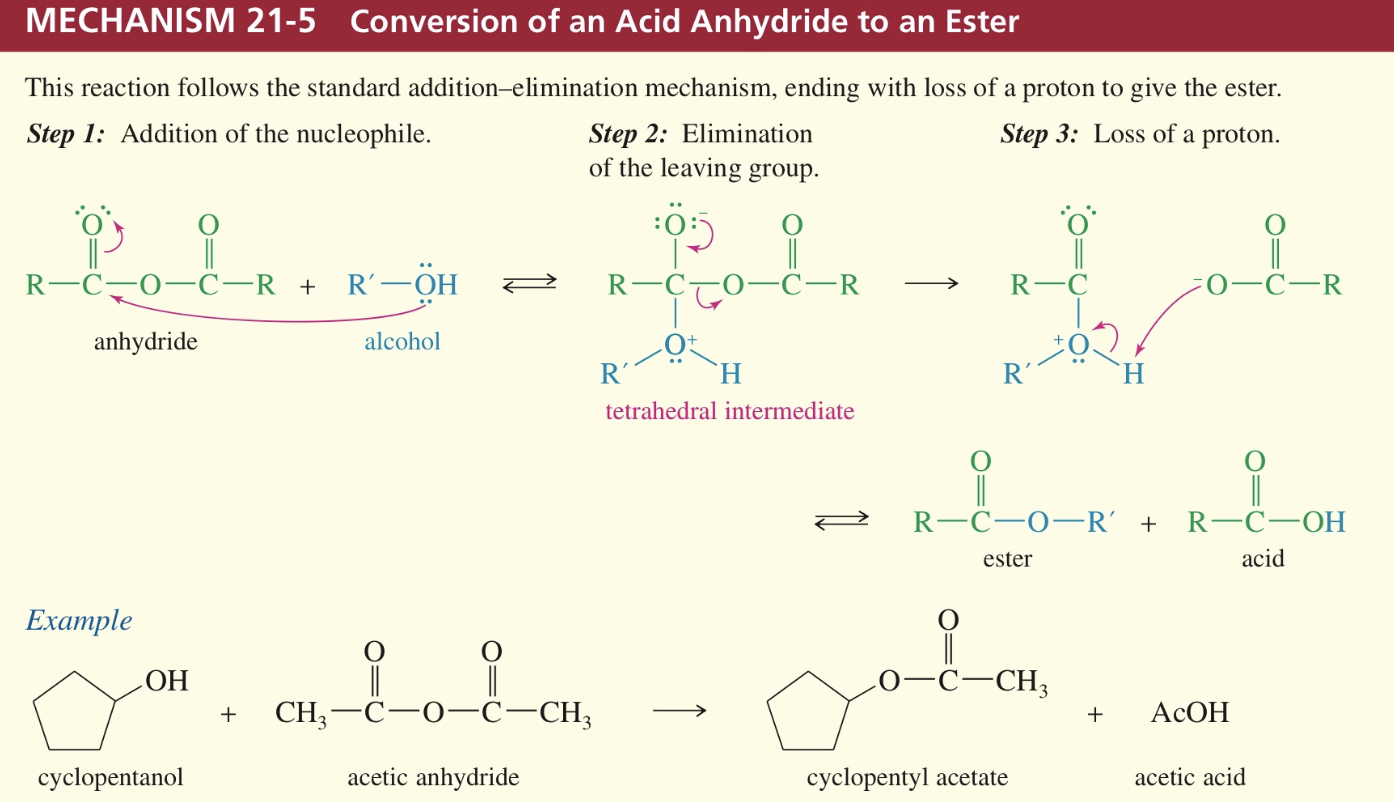
Transesterfication
One alkoxy group can be replaced by another w/ acid/base catalyst
w/ large excess of desired alcohol
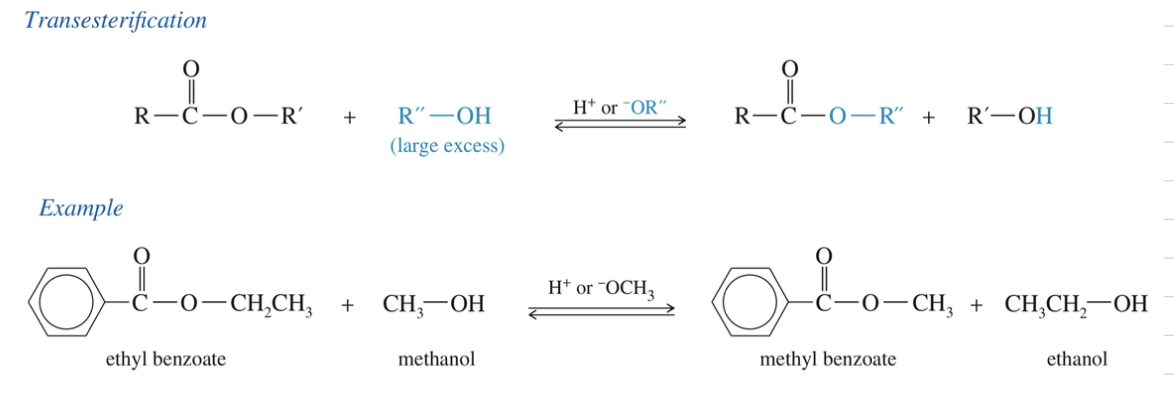
Mech) Transesterfication (base cat vs acid cat)
Hydrolysis of CA Derivatives
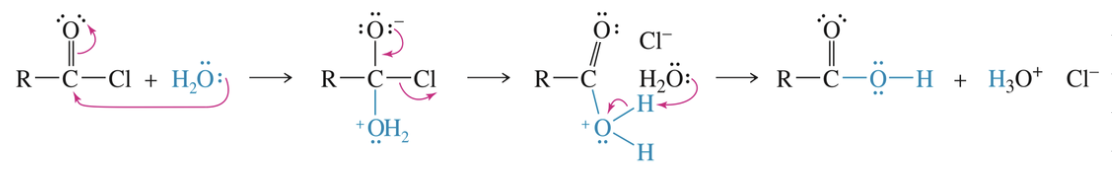
a) Hydrolysis of acid halide & anhydride
Occur quickly even under neutral condition
b) Hydrolysis of ester aka base catalyzed Saponification
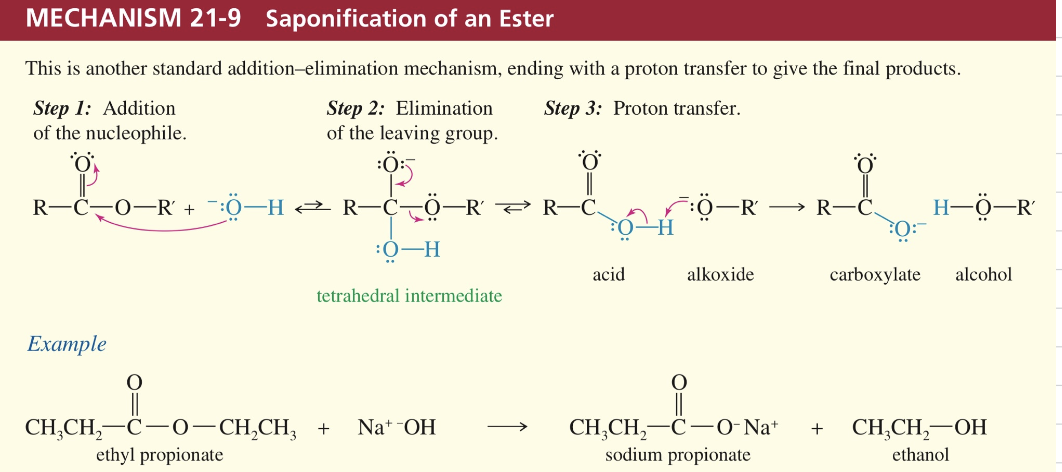
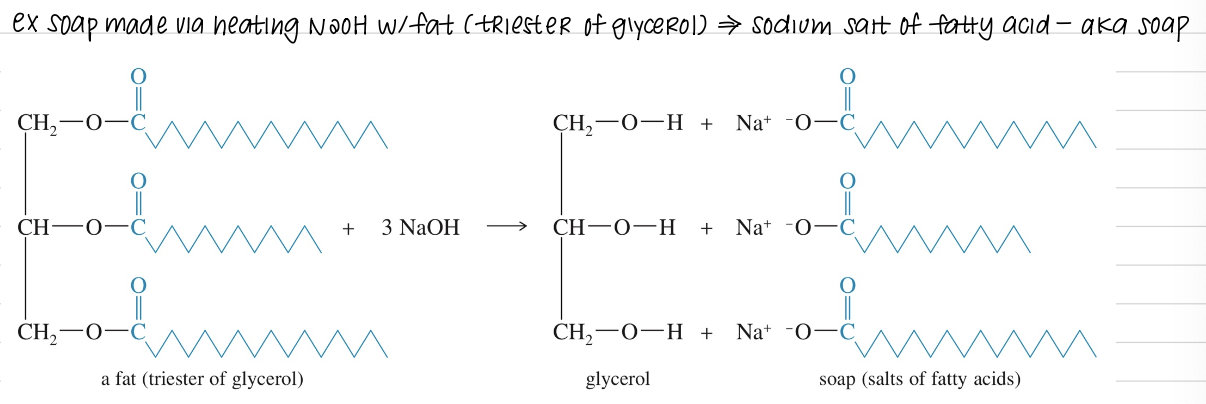
ex) saponification
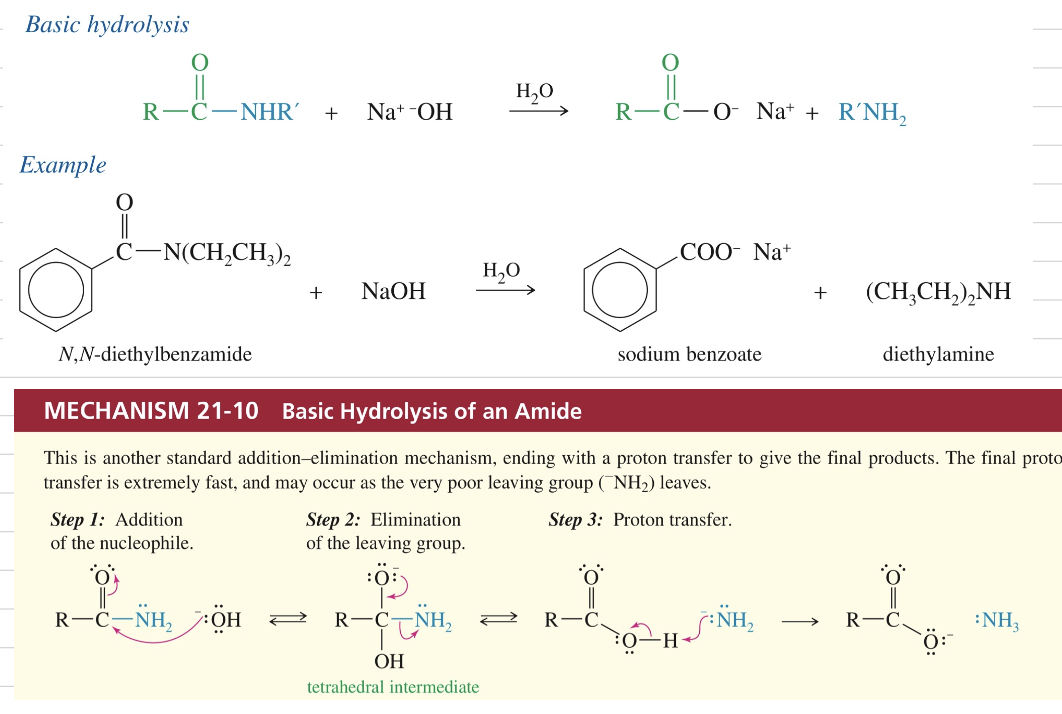
c.b) Hydrolysis of amides (basic)
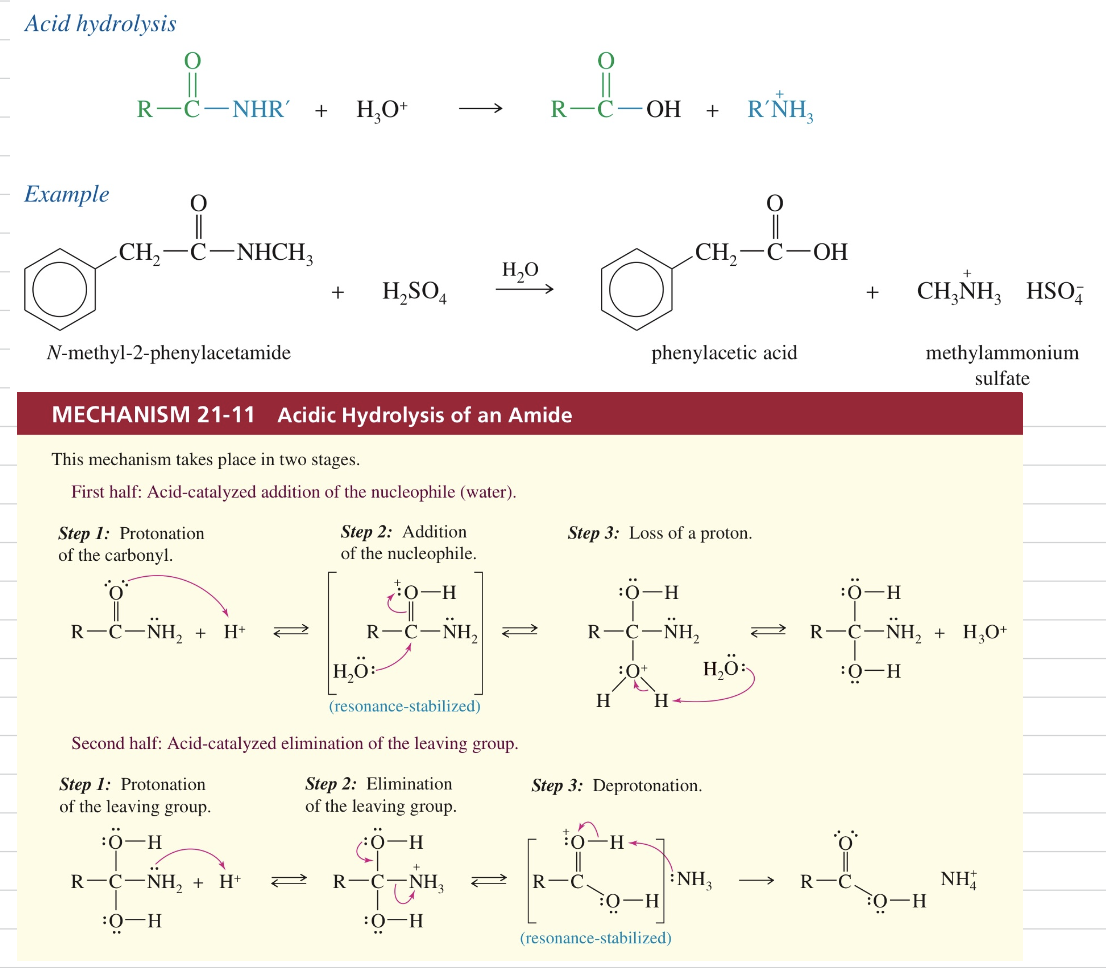
c.a) Hydrolysis of amides (acidic)
d.b) Hydrolysis of nitriles (basic)
HEAT w/ H2O/EtOH
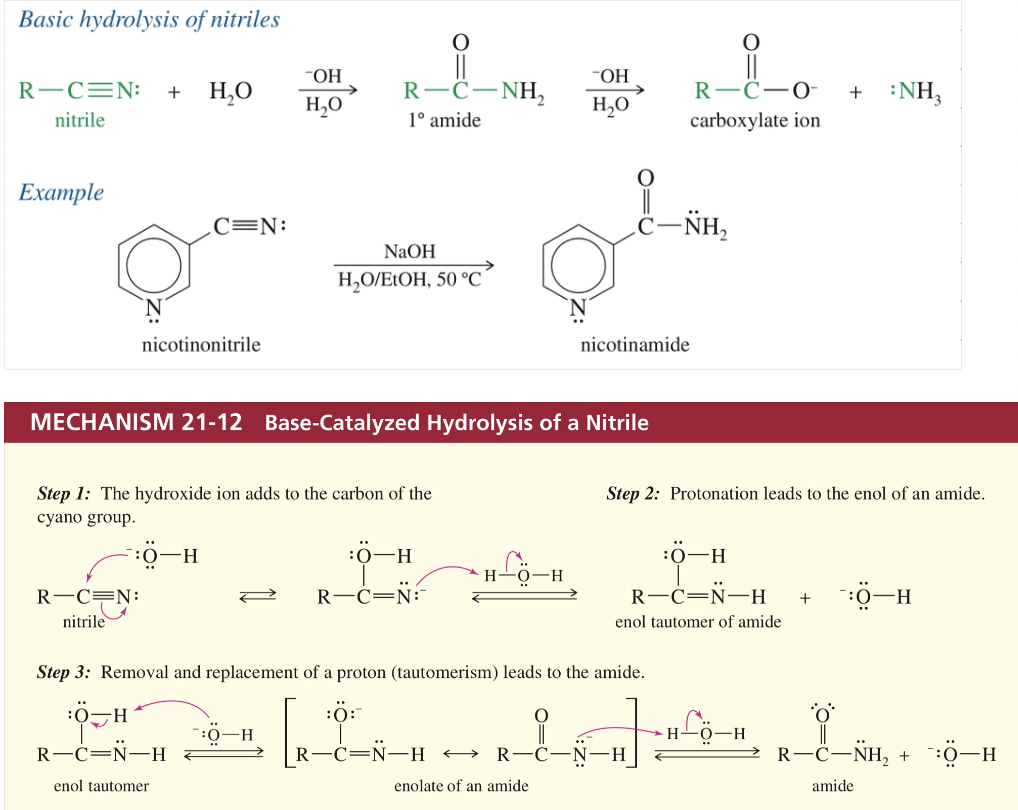
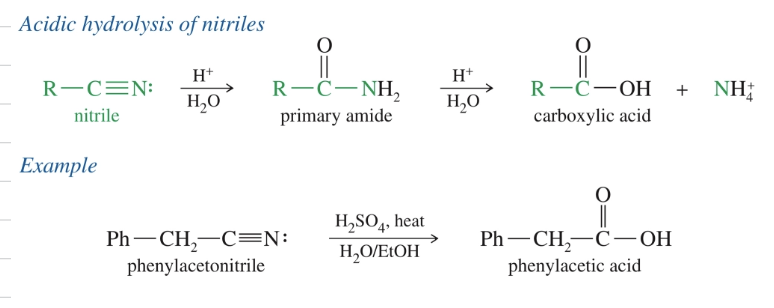
d.a) Hydrolysis of nitriles (acidic)
HEAT w/ H2O/EtOH
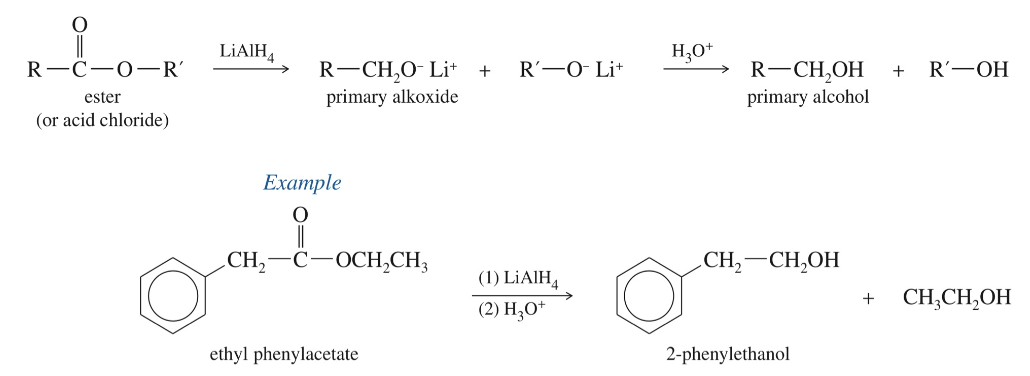
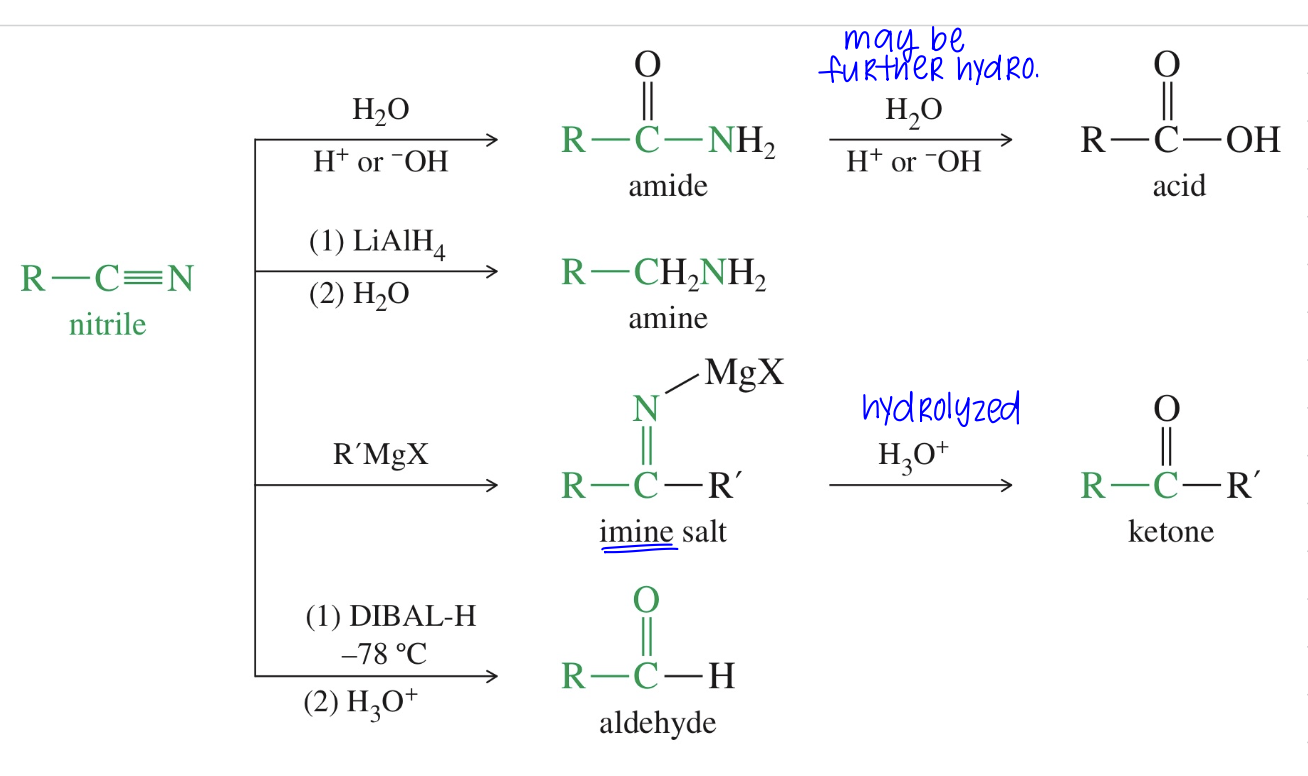
Reduction of acid derivatives w/ hydrides
a) Hydride reduction to alcohol
LiAlH4 & H3O+ reduce » 1 alcohol
Acid chloride
Anhydride
ester
NaBH4 reduce acid chloride » 1 alcohol
acid chloride more reactive than other deriv
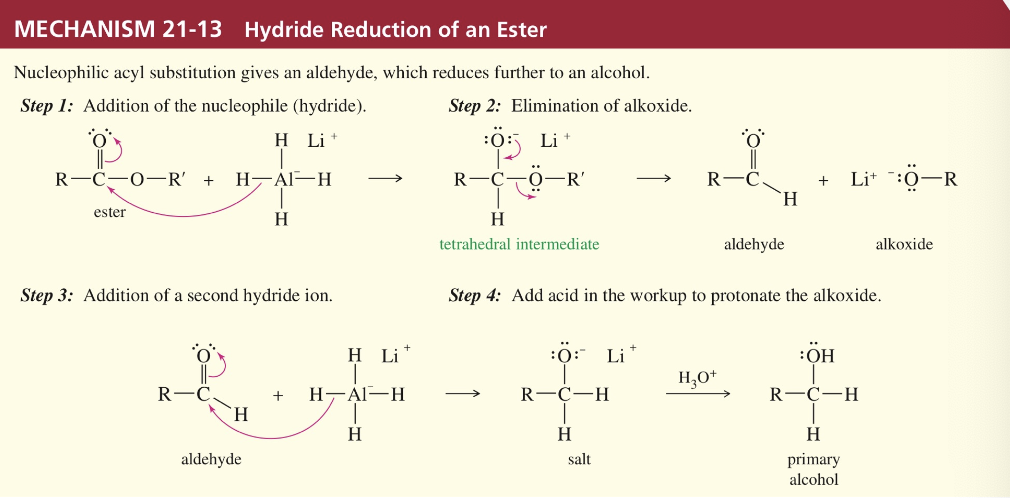
Mech) Hydride reduction to alcohol
b) Reduction to aldehyde from acid chloride // nitrile // ester
Acid chloride)
LiAlH(O-t-Bu)3 DIBAL-H
Ester
(i-Bu)2AlH
H2O

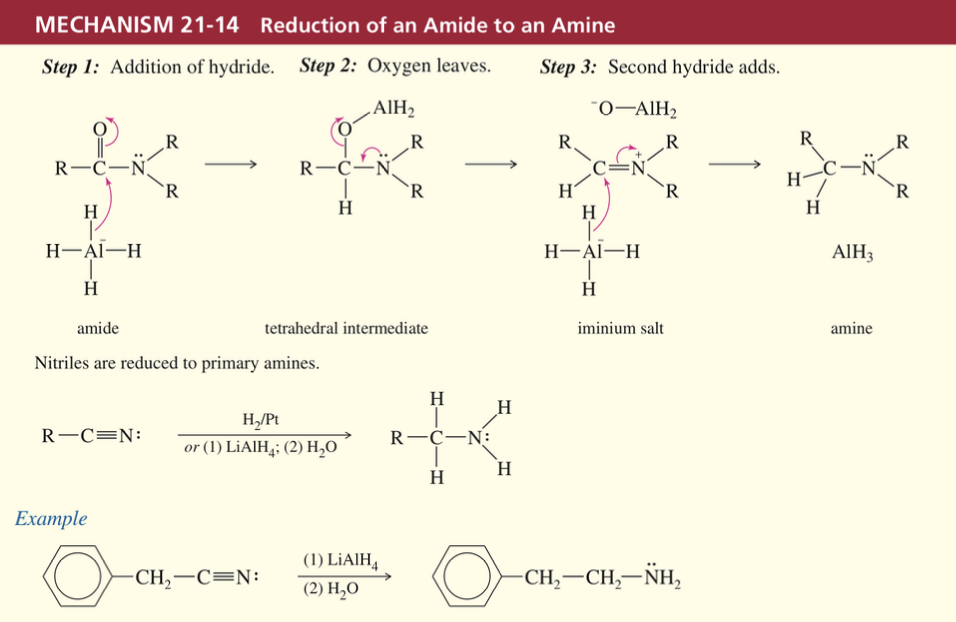
c) Reduction to amines from amide // nitrile
LiAlH4
H2O
(For nitrile H2/Pt)
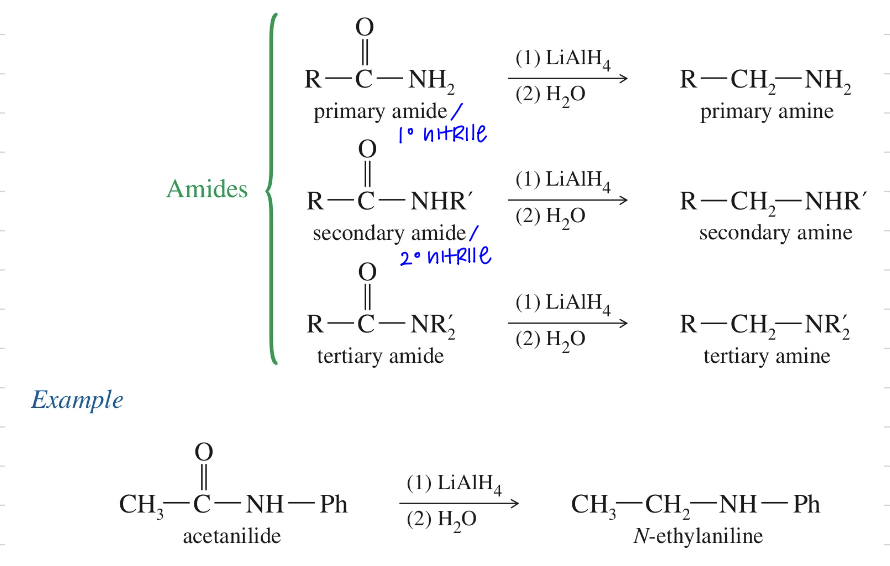
Mech) Hydride reduction of amide » 1 amine
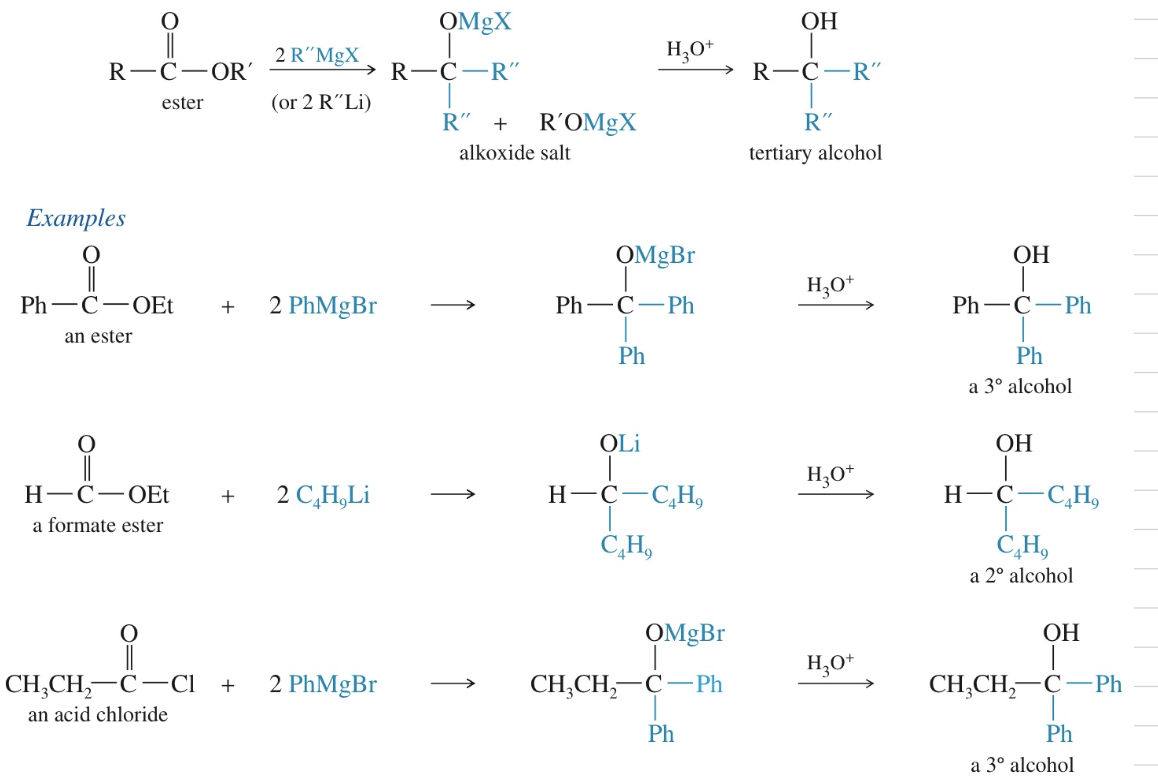
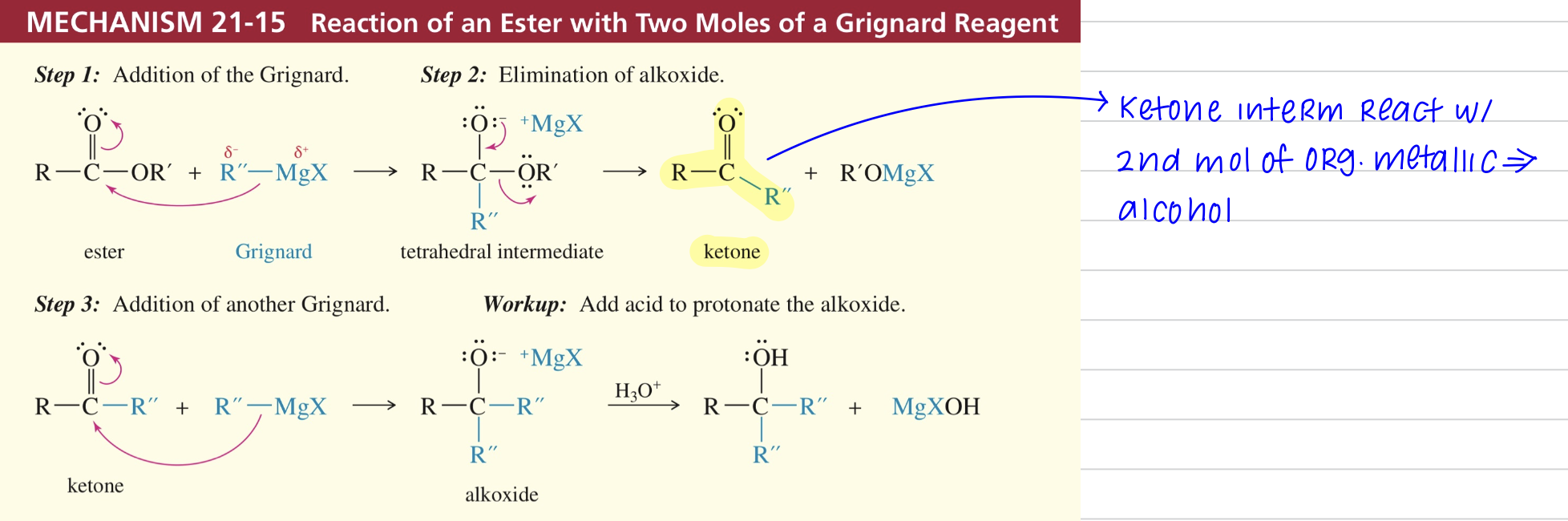
Reduction of acid derivatives w/ Organometalic Reagents
a) acid chloride // ester » alcohol via GR adding twice
a)
2 RMgBr
H3O+
b)
2 RLi
H3O+
Mech) Rxn of ester w/ 2 moles of GR
b) Acid chloride react once w/ dialkylcuprate Reagent » ketone
R2CuLi
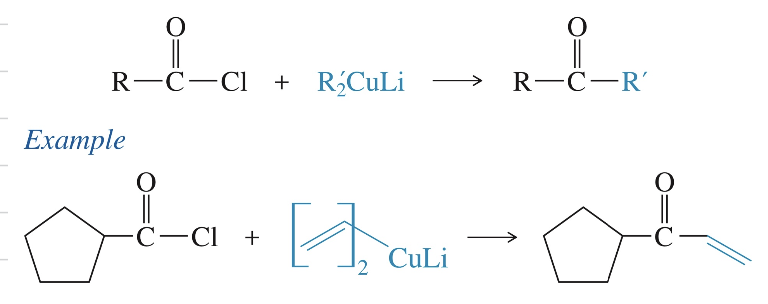
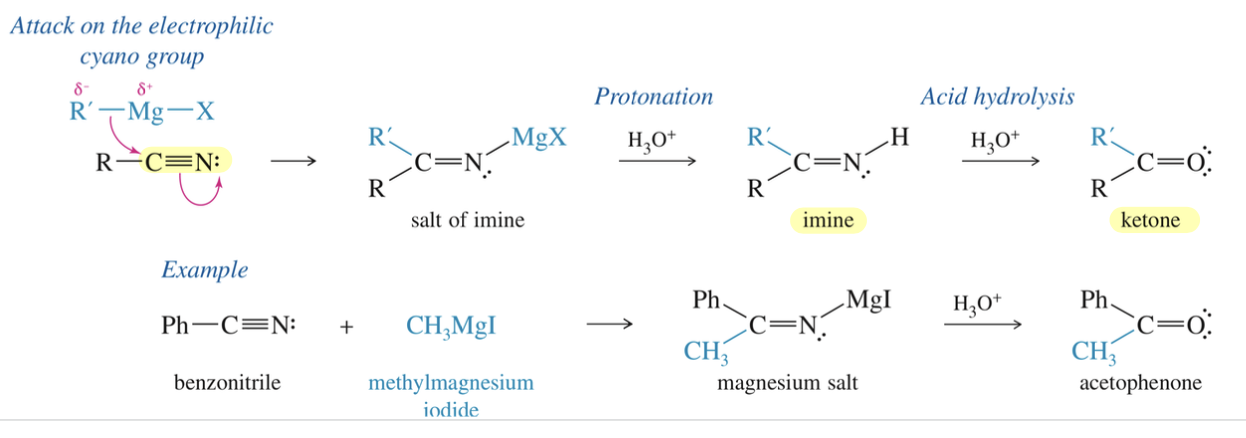
c) Nitrile » imine » ketone via GR
2 RMgBr
H3O+
[Summary of Acid Chloride Chemistry]
Bc so reactive, not found in nature
Synthesis: COOH » COCl
SOCl2 // COCl2
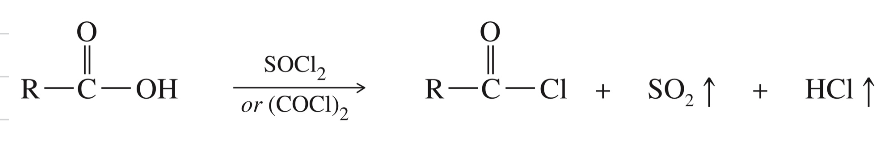
Acid chloride » other acid derivatives
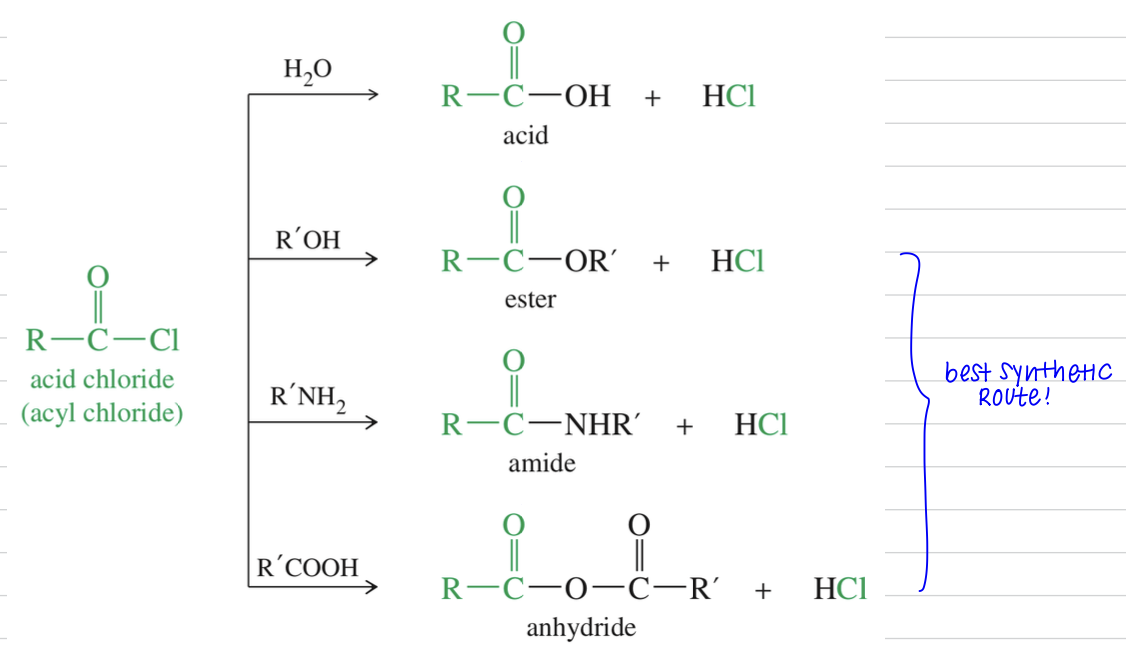
Rxn of acid chloride
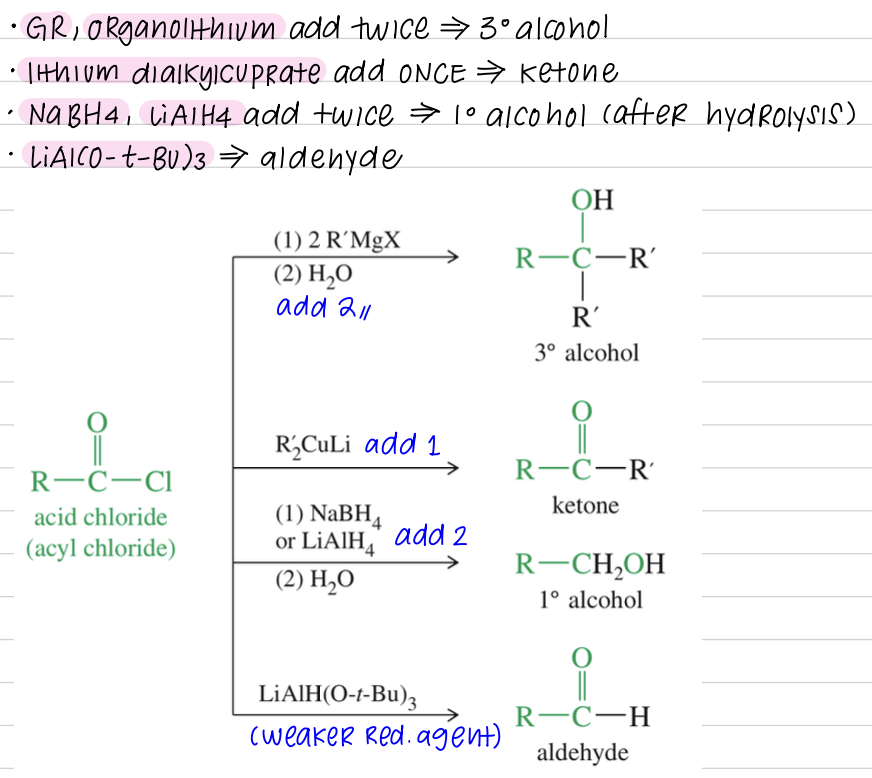
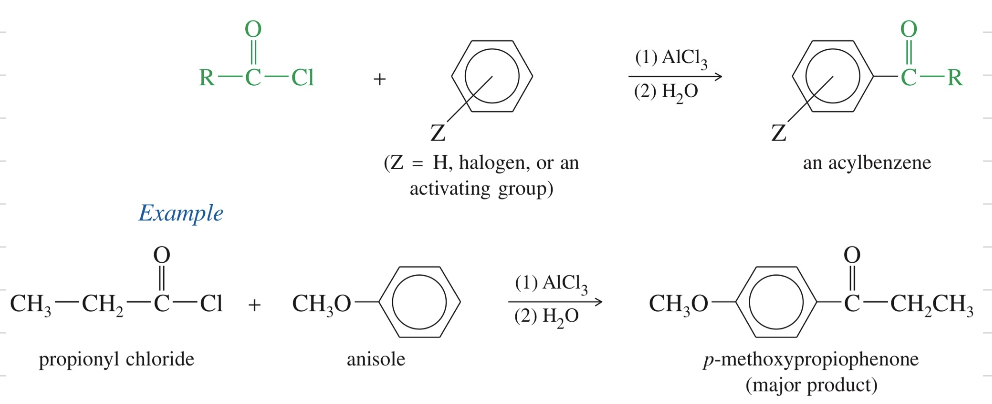
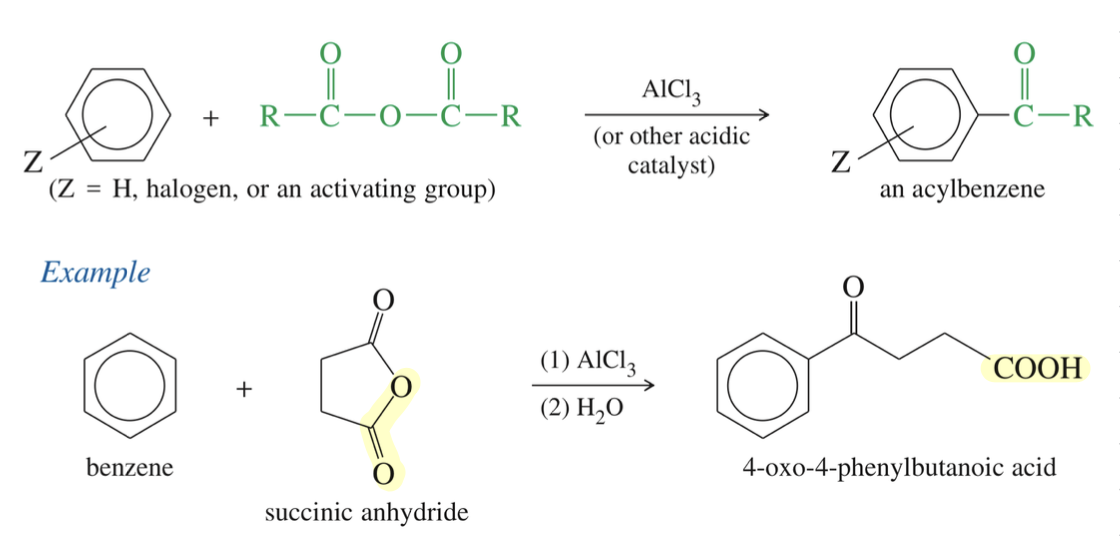
Friedel Craft Acylation of Aro Ring
[Summary of Anhydride Chemistry]
Synthesis: Acid Chloride + CA (& pyr) // Carboxylate Salt
Chloride + CA + pyr
// Chloride + Carboxylate Salt
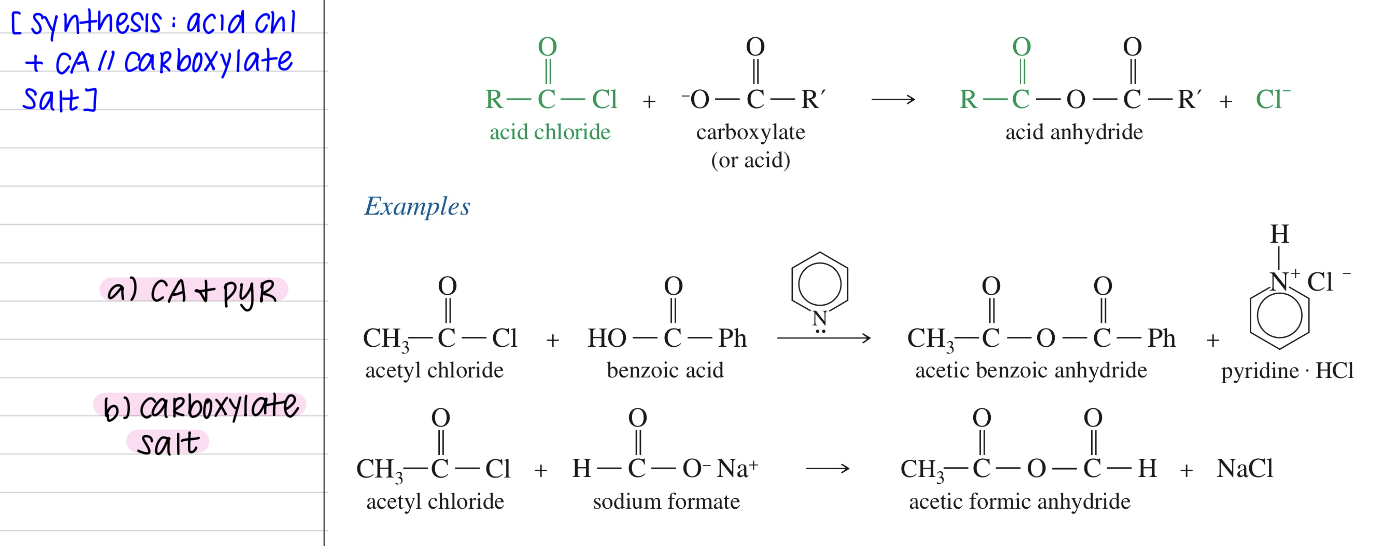
Rxn of Anhydride
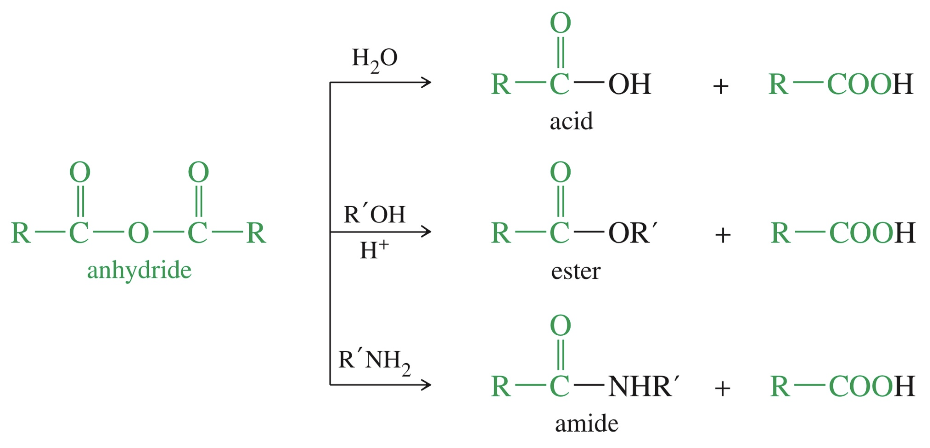
★ Acetic formic anhydride react @ formyl group → more electrophilic & less hindered
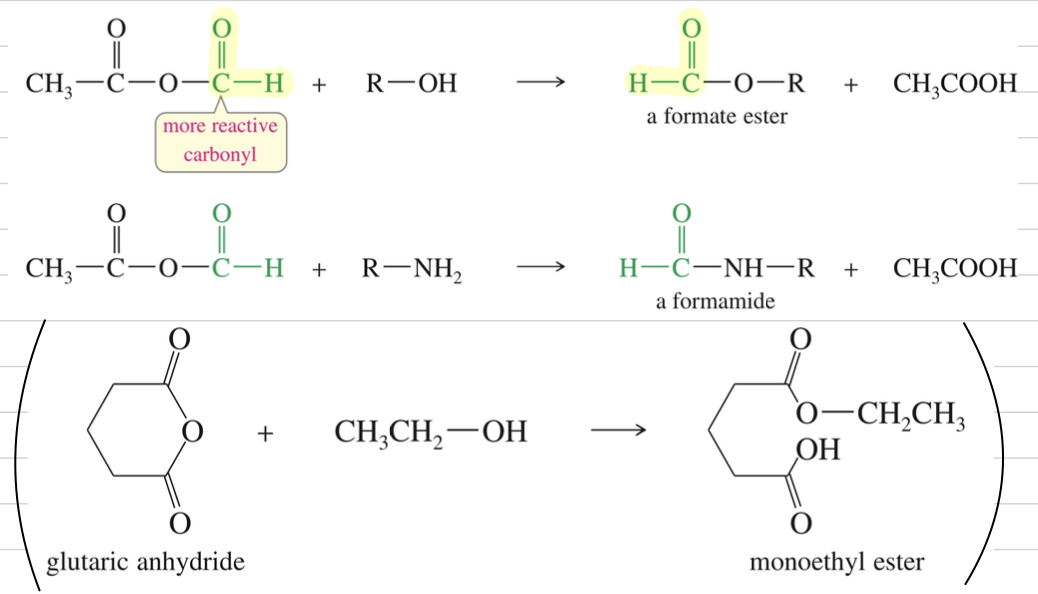
Friedel Craft Acylation
★ FC to cyclic anhydride » only 1 acid react » 2nd acid free to undergo further rxn
[Summary of Ester Chemistry]
Synthesis
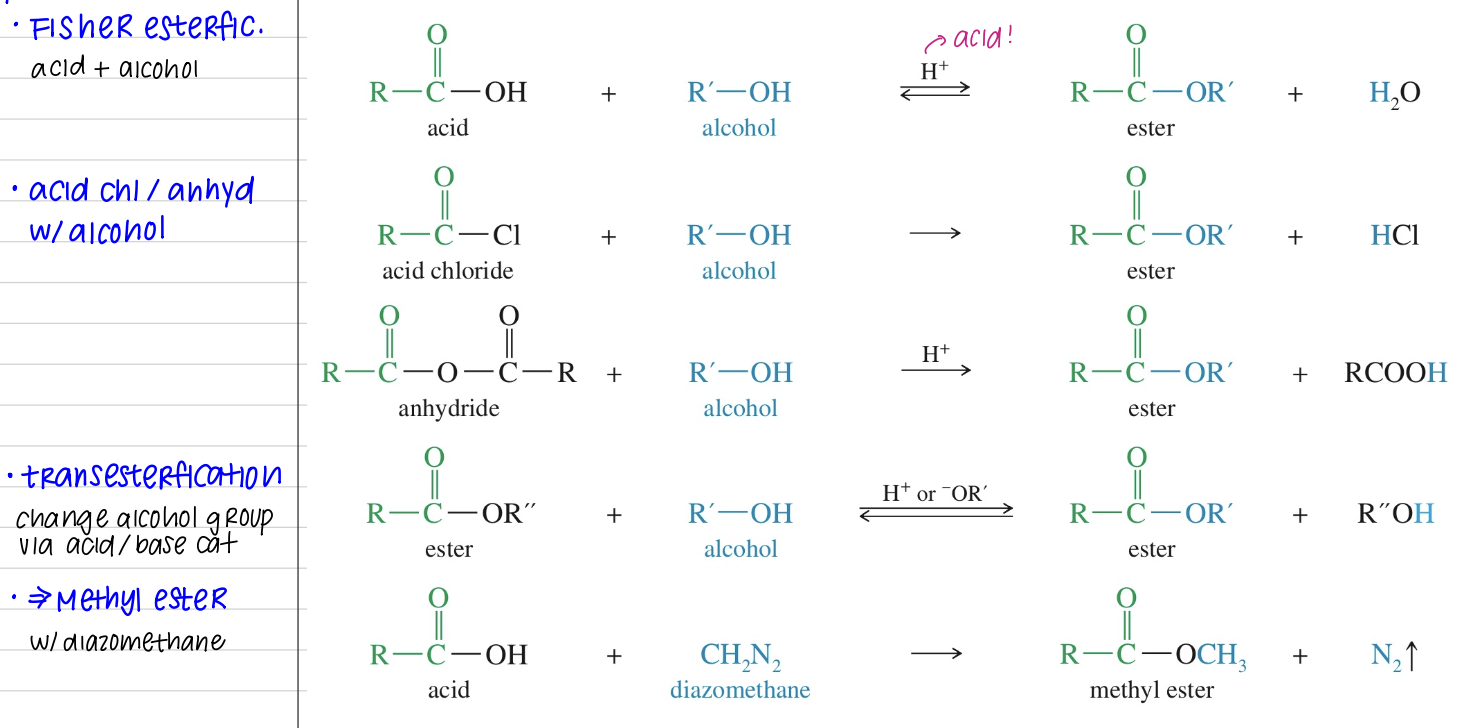
Reaction
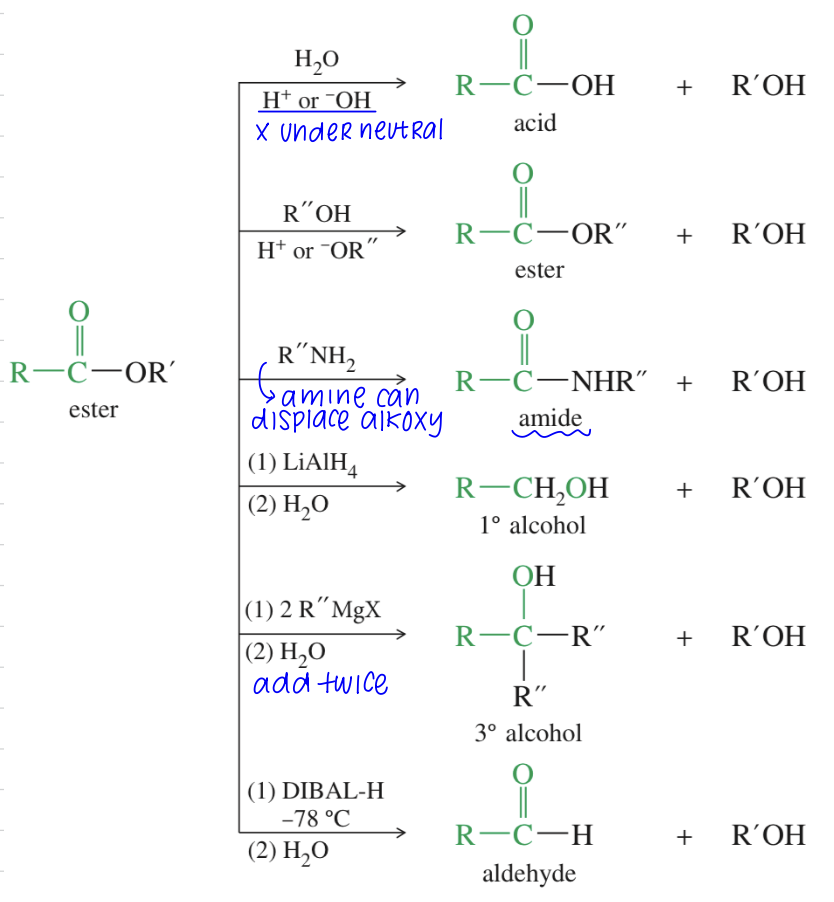
Formation of Lactones via spontaneous fischer esterfication of stable 5-6 mem ring
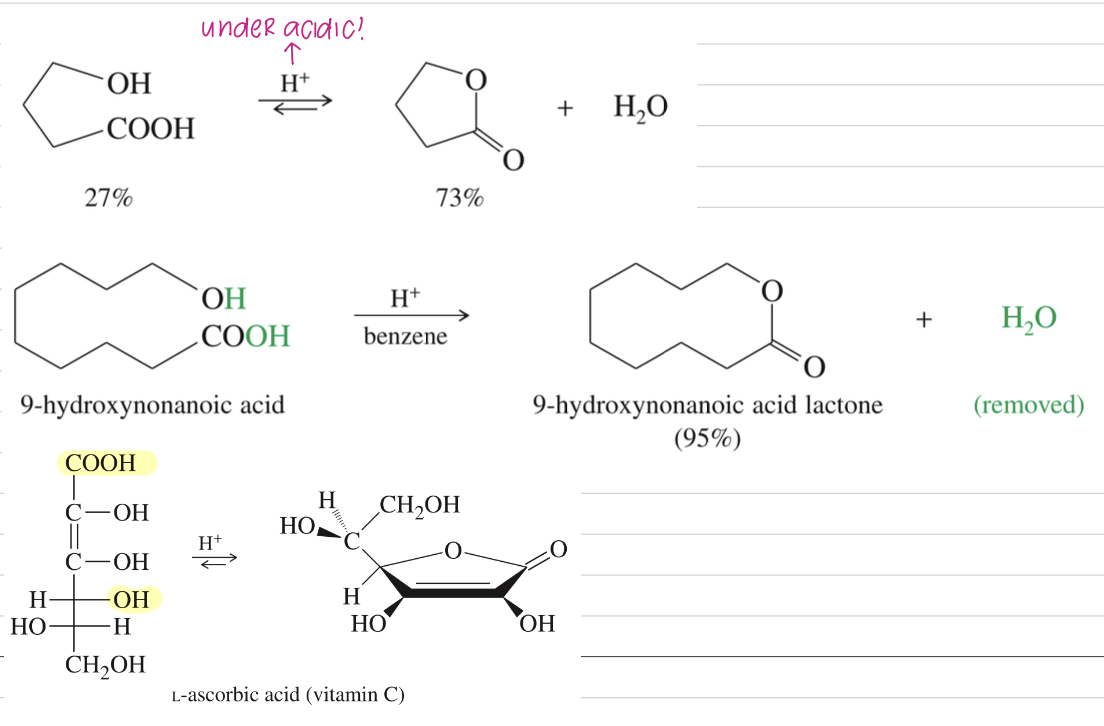
[Summary of Amide Chemistry]
Unlike amine NOT BASIC or NUC
can only be protonated w/ SA
Synthesis
Bc amide is least reactive » made from any others
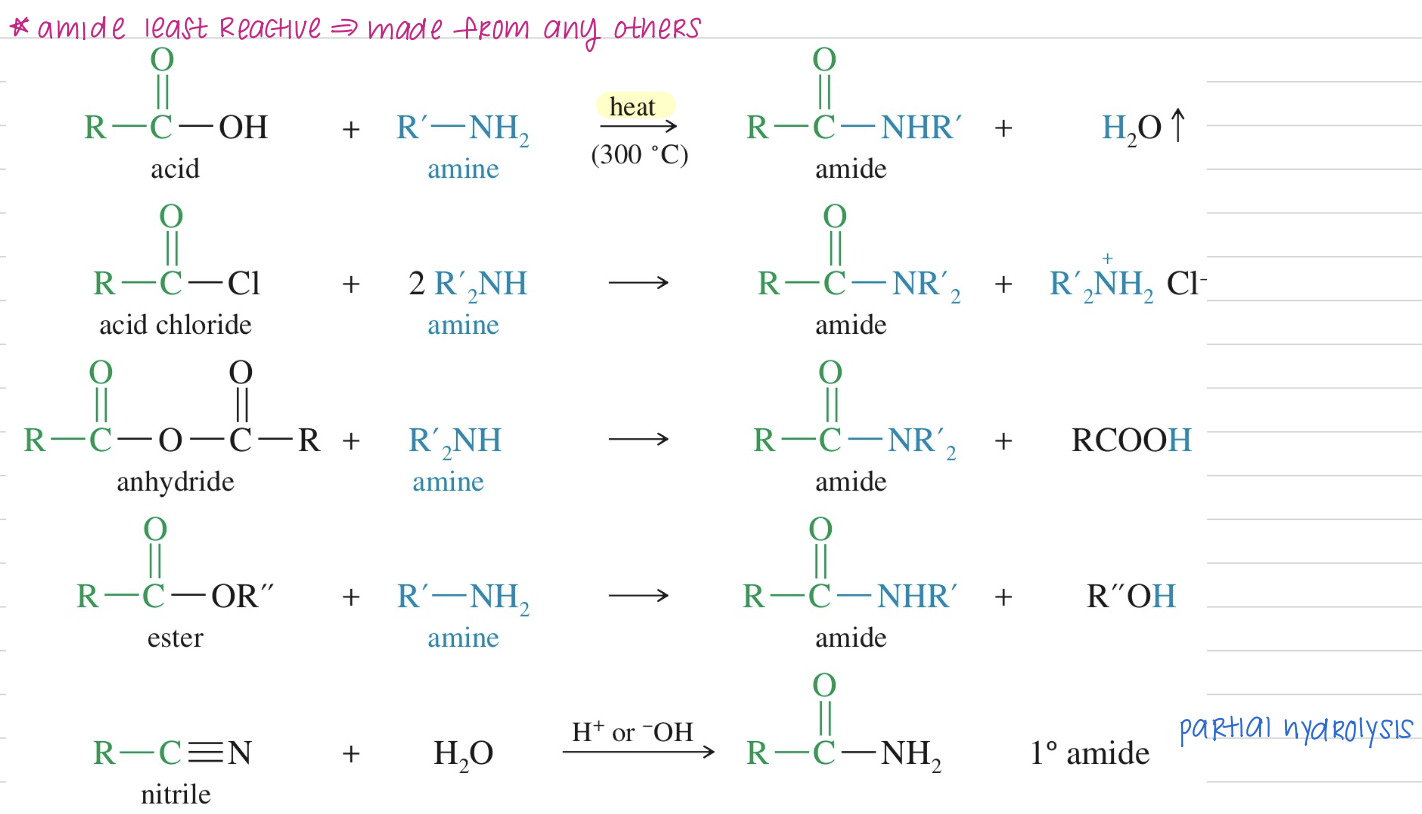
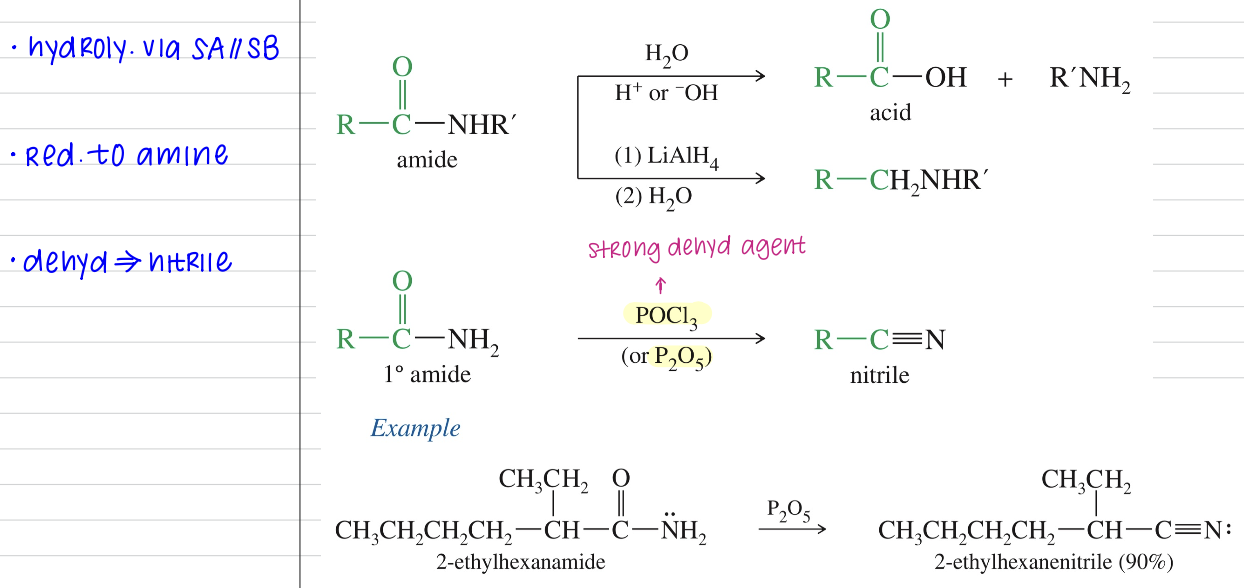
Reaction
Not easily convert to other deriv w/ nuc aryl subs!
Dehydration using POCl3 // P2O5
Formation of 5 // 6 mem Lactam via heat // Dehyd. agent
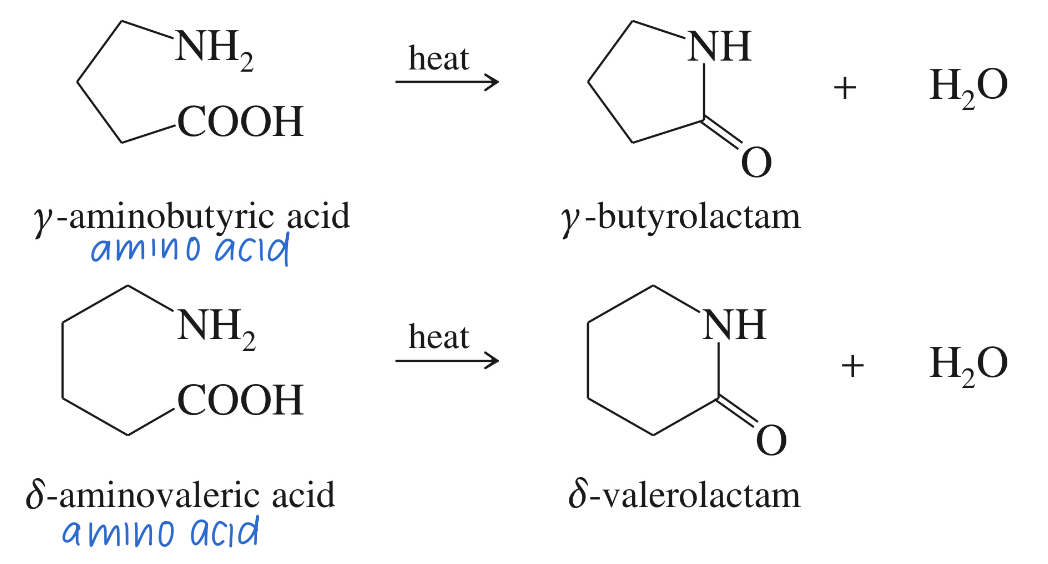
Reactivity of Lactam ★ B Lactam unusually reactive due to the 4 ring strain » acylate variety of nuc!
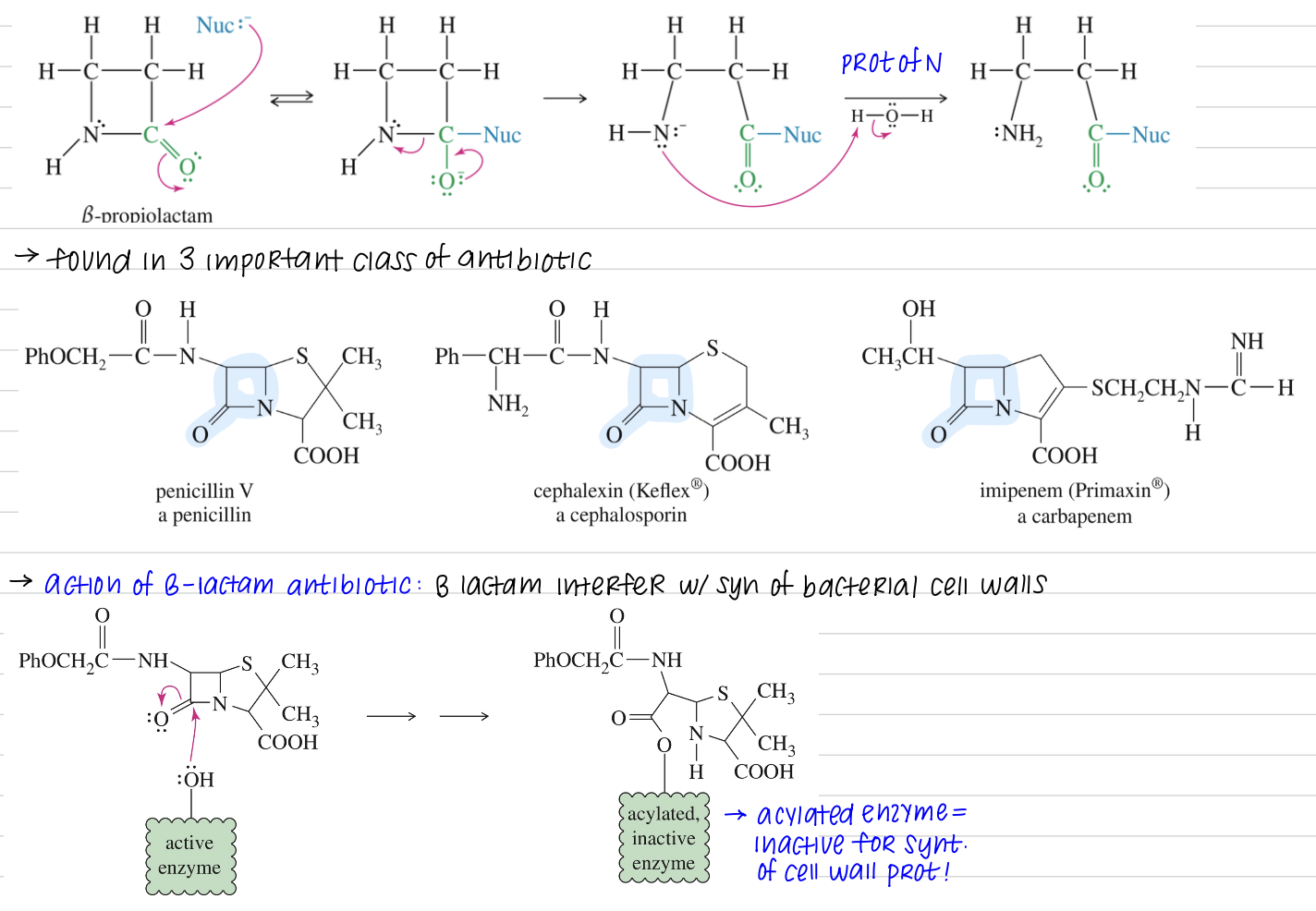
[Summary of Nitriles Chemistry]
Synthesis of nitriles
Reaction of Nitriles
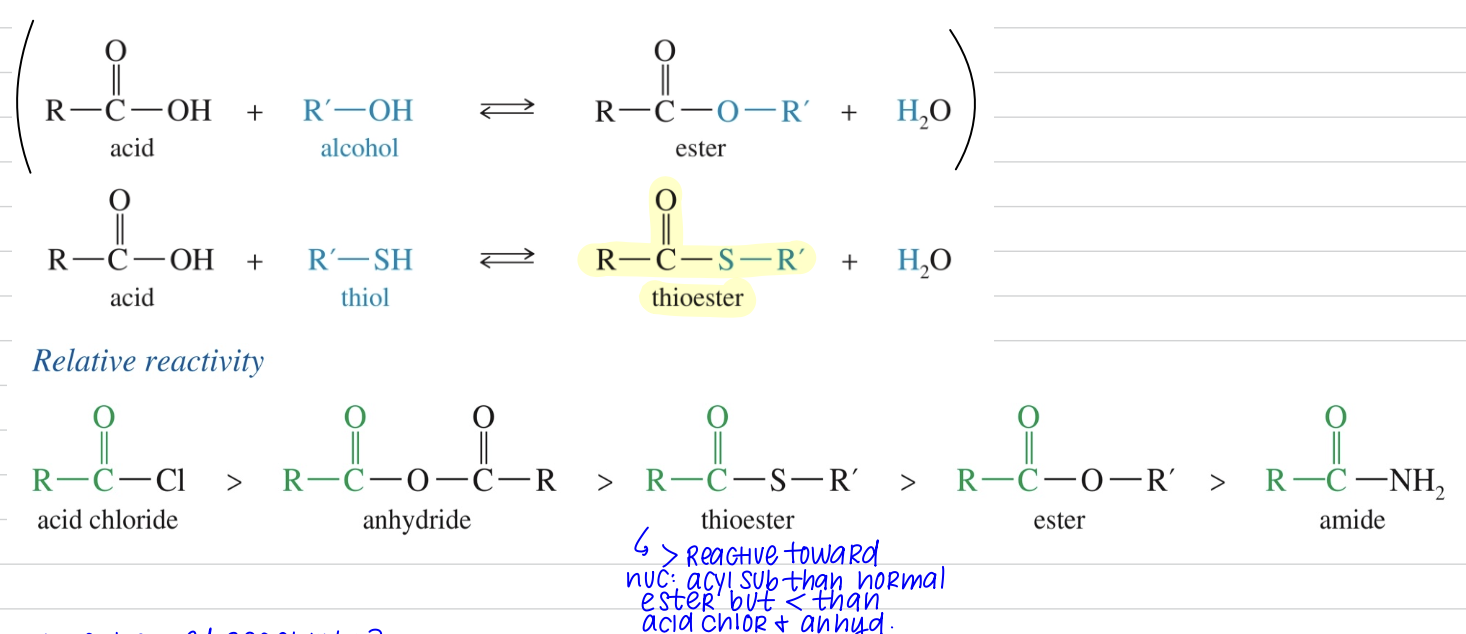
Thioester
> reactive toward NAS than ester but < reactive than acid chloride, anhydride
★ Enhanced reactivity of thioester
< Resonance stabilization of thioester
2p orb C & 3p orb S diff size, distance from nuc
Weak overlap of p orb » weaker C-S bond vs C-O
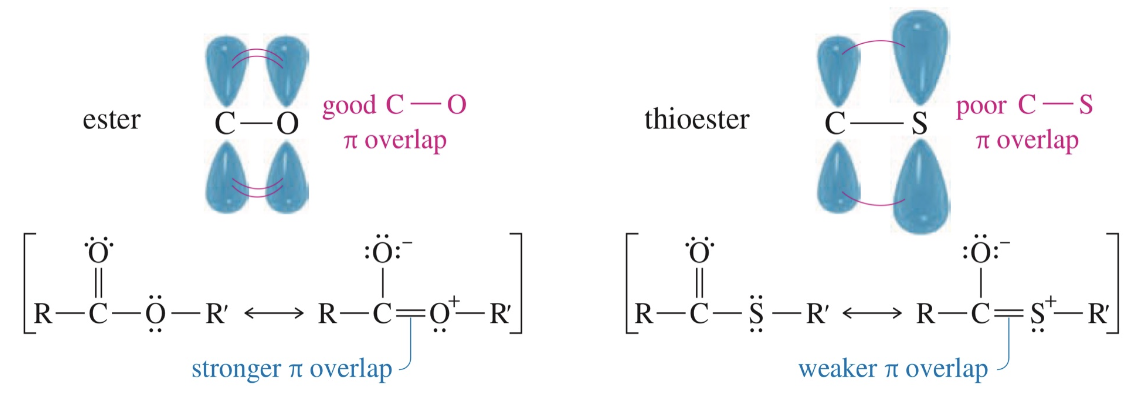
- SR better L.G. vs - OR
Sulfide less basic & larger so (-) charge spread over > volume
S more polarizable vs O so more bonding as leave
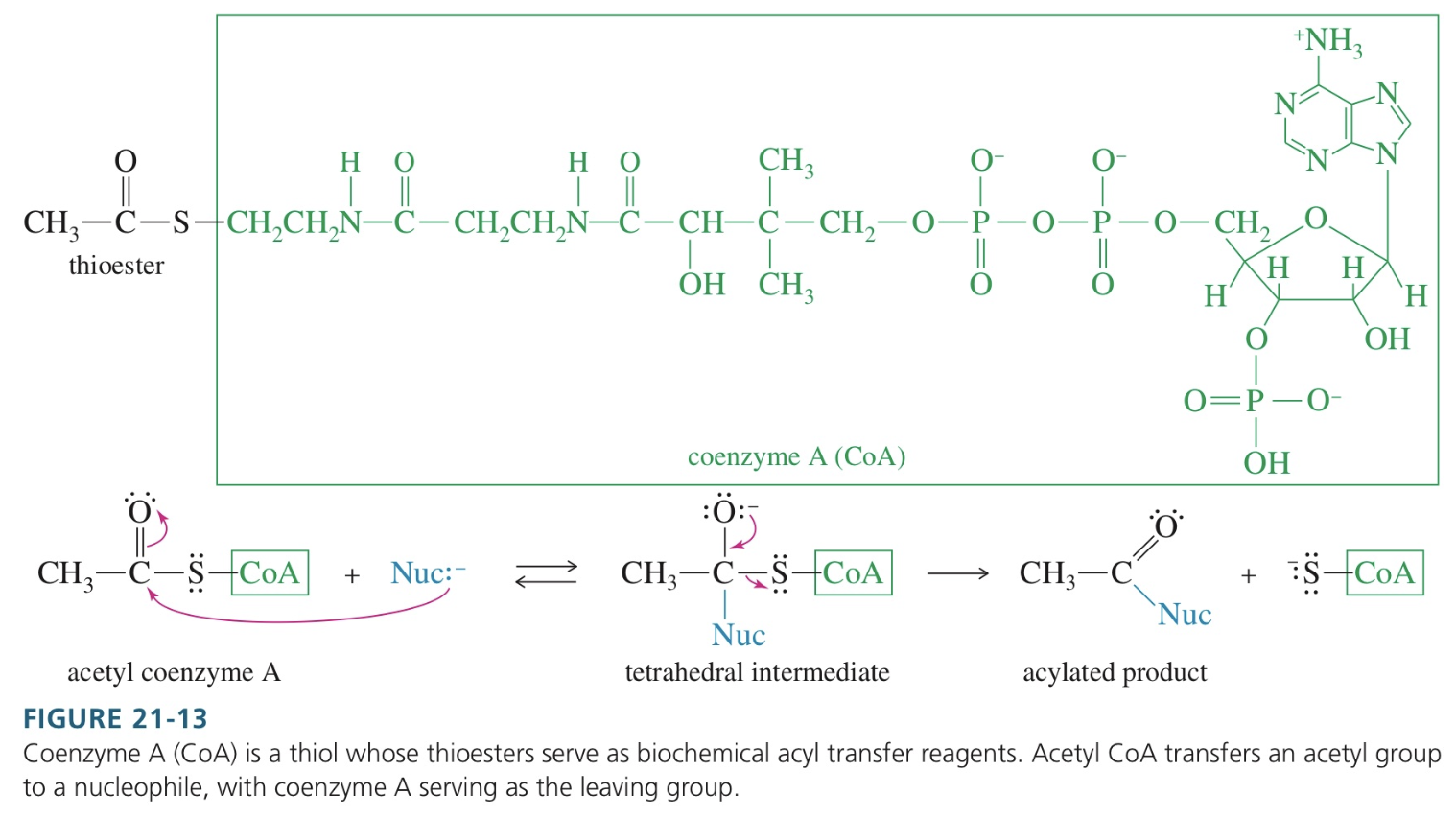
Structure of Coenzyme A
Biochemical acyl transfer reagent
Thioester not prone to hydrolysis yet good selective acylation → common acylating agent in living system
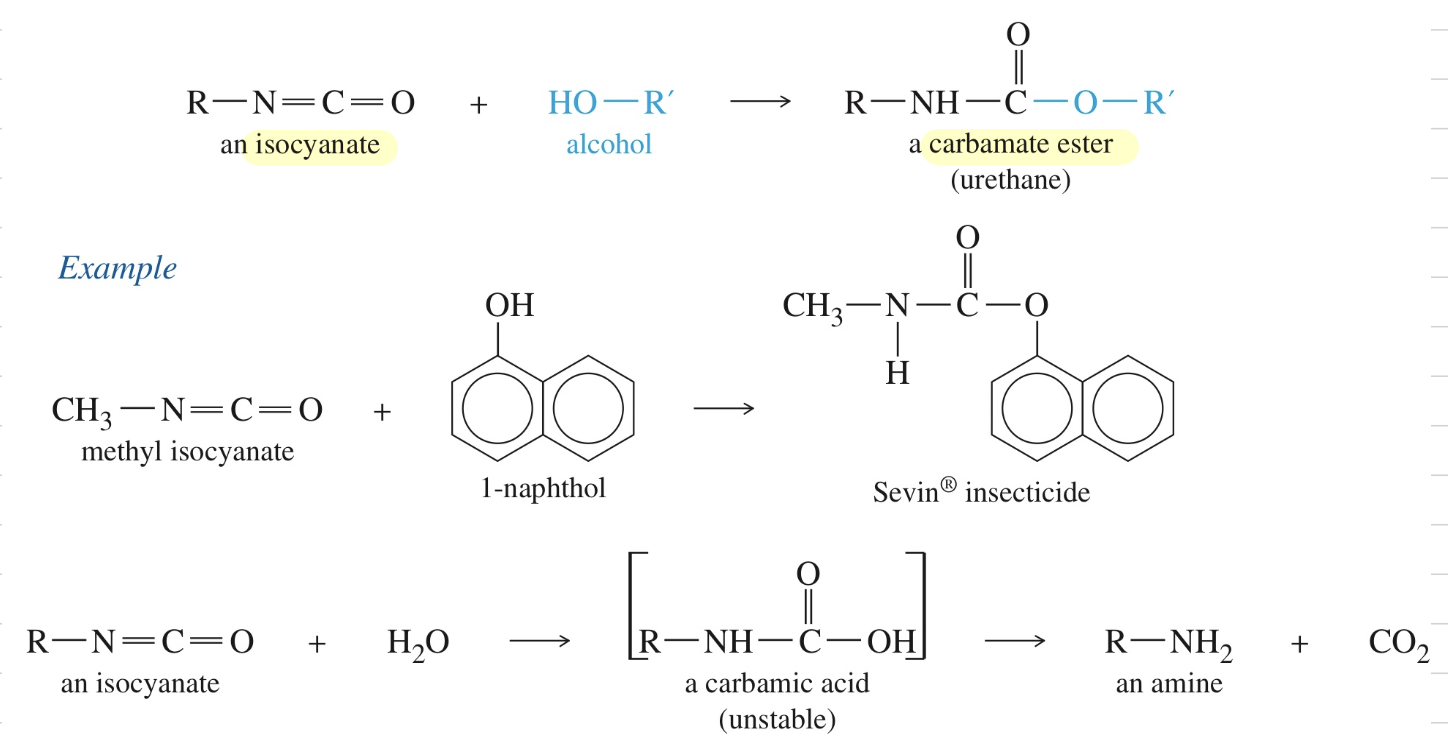
Synthesis of Carbamate Ester
R-NCO (isocyanate) + HO-R (alcohol)
[CHP 22: Condensation & Alpha Subs of Carbonyl Cpd]
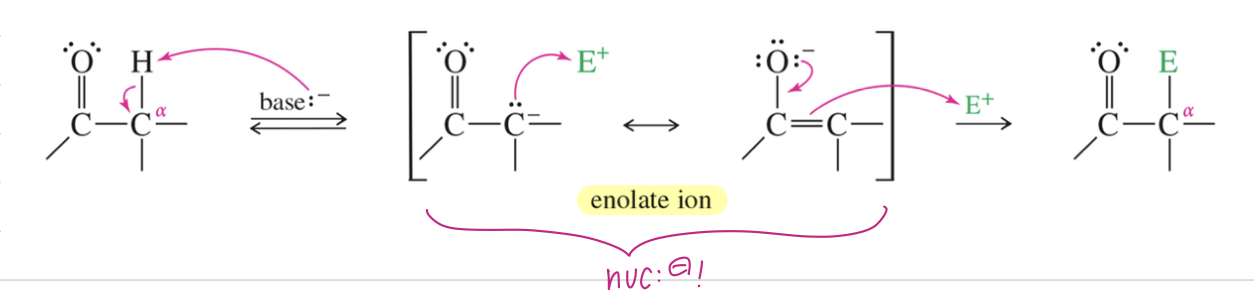
Alpha Substitution
Subs of 1 H attached to α C w/ Elec
** Enolate ion interm
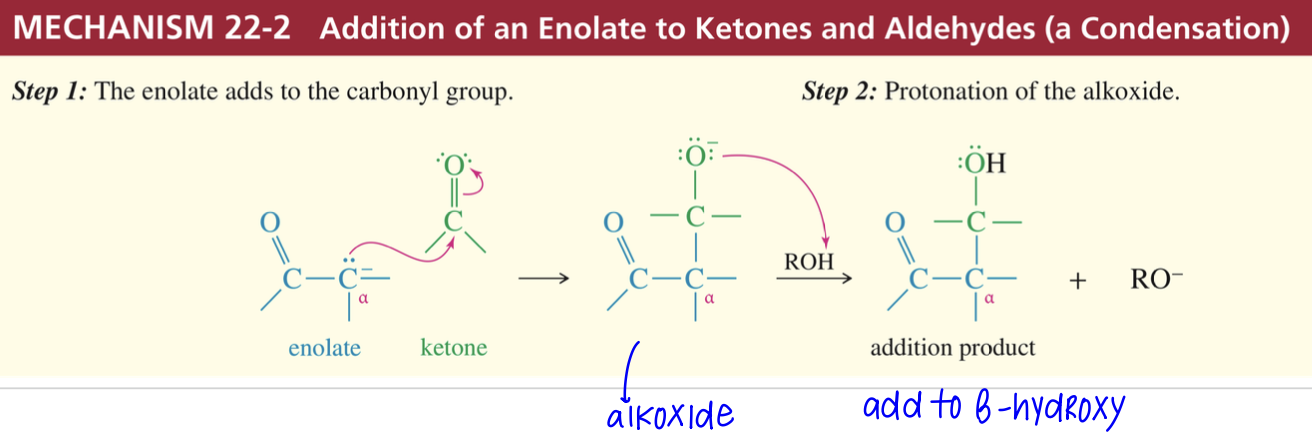
Condensation of enolate w/ aldehyde // ketone
Ketone // aldehyde
ROH
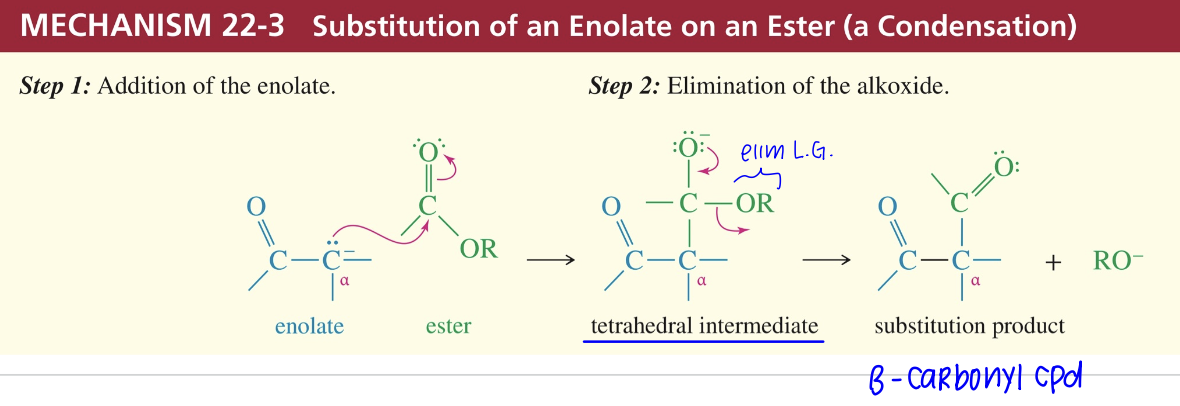
Condensation of enolate w/ ester
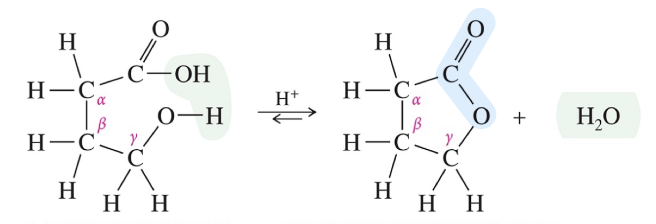
Keto-Enol Tautomerism
Interconv of isomer via migration of (1) proton & (2) double bond =
Not resonance
Keto form is favored » stronger C=O stable
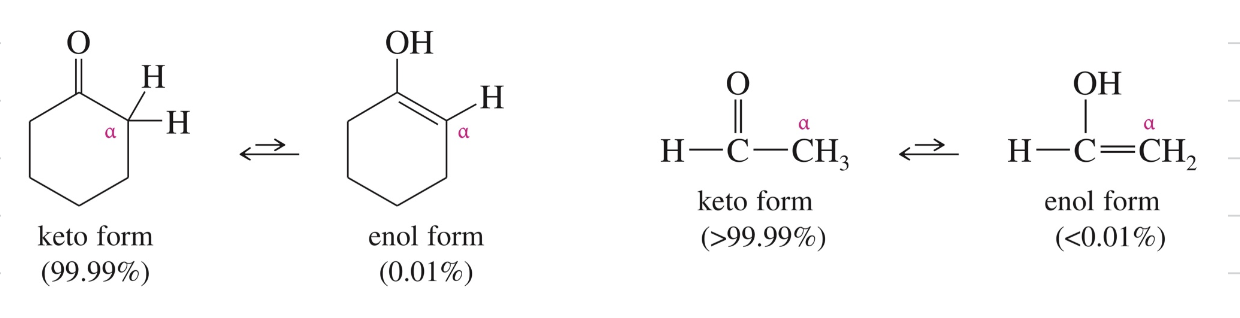
a) Base-Cat (α H abstracted first by base)
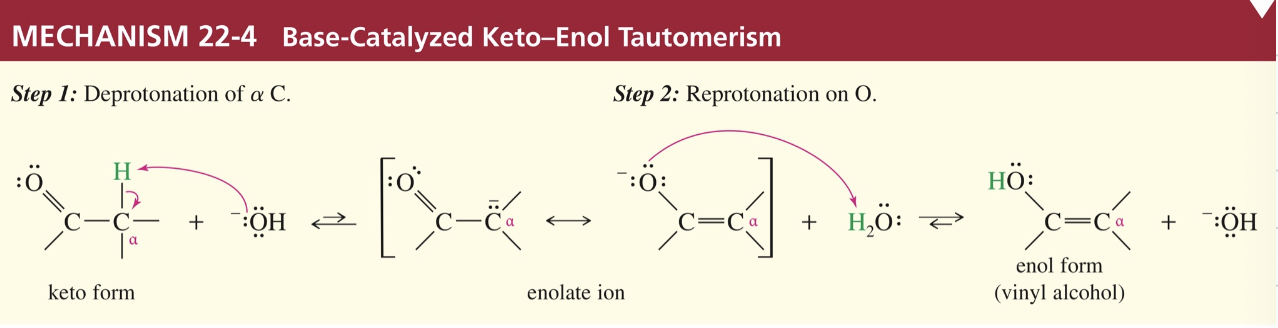
b) Acid- Cat (O of carbonyl abstracts H from acid & then H on α abstracted)
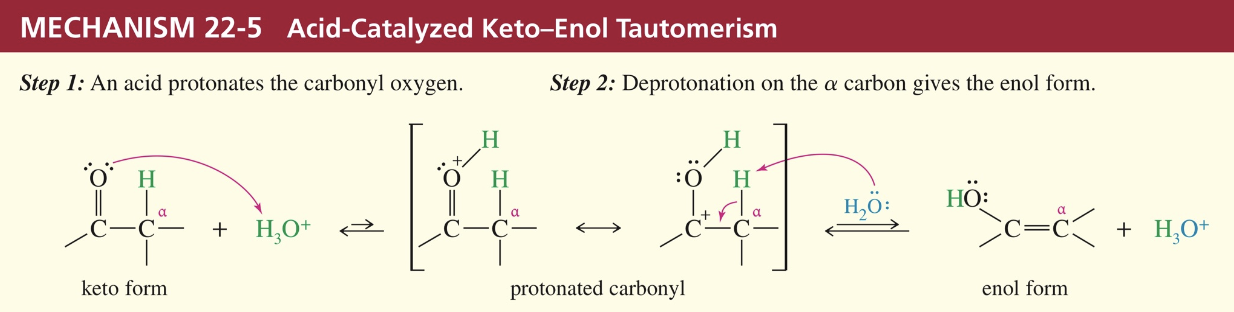
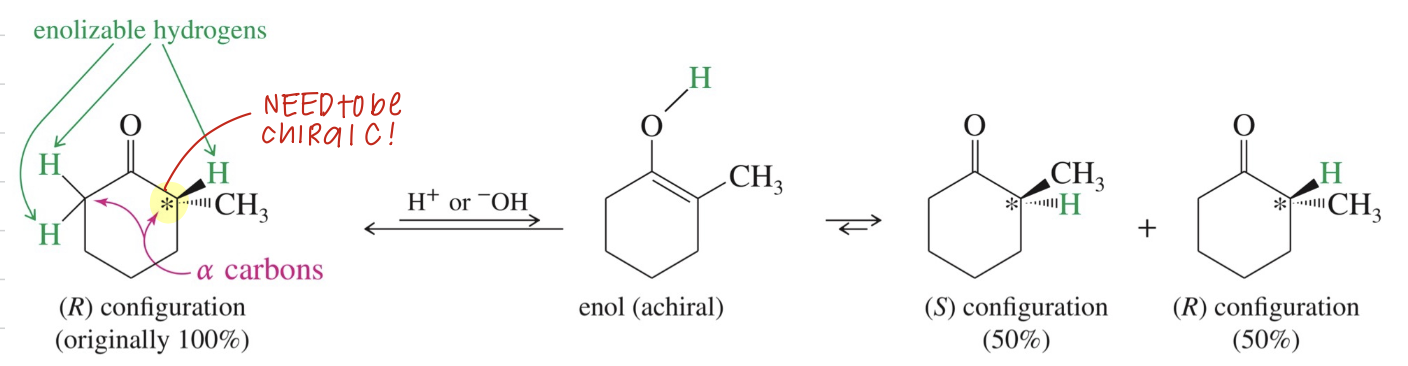
★ Racemization
If α C that is chiral has enolizable H atom, acid // base allow α C to invert configuration w/ enol being intermediate » racemization
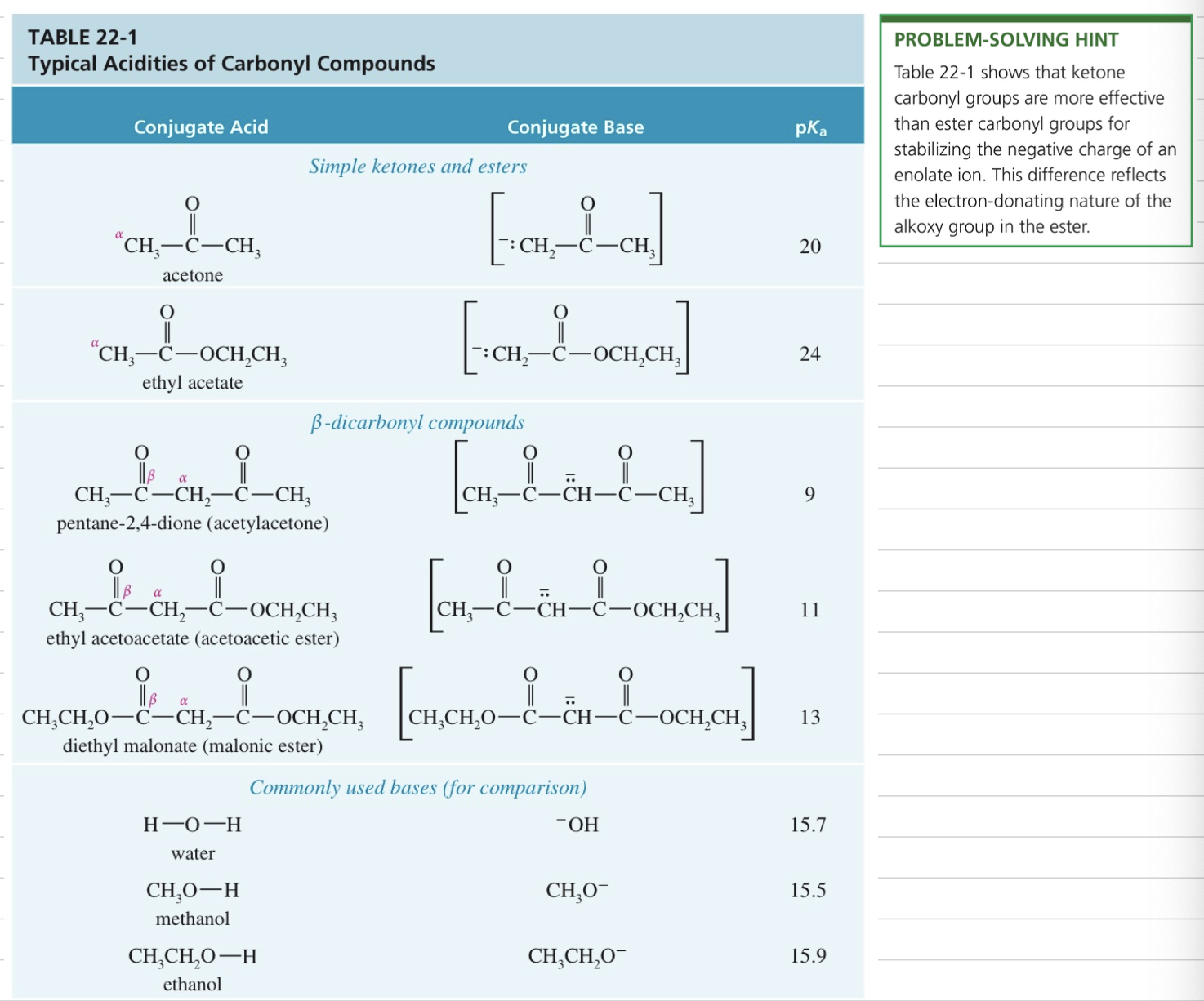
Acidity of α H (pka ~20)
> acidic than alkane or alkene (pka > 40) or alkyne (pka = 25)
< acidic than water (pka = 15.7) // alcohol (pKa = 16-19)
Only small amount of enolate at EQ (key nucleophile)
Formation & Stability of Enolate Ion
Even though keto-enol tautomerism EQ favor keto form addition of elec shift EQ to formation of more enol (bc enol attack elec)
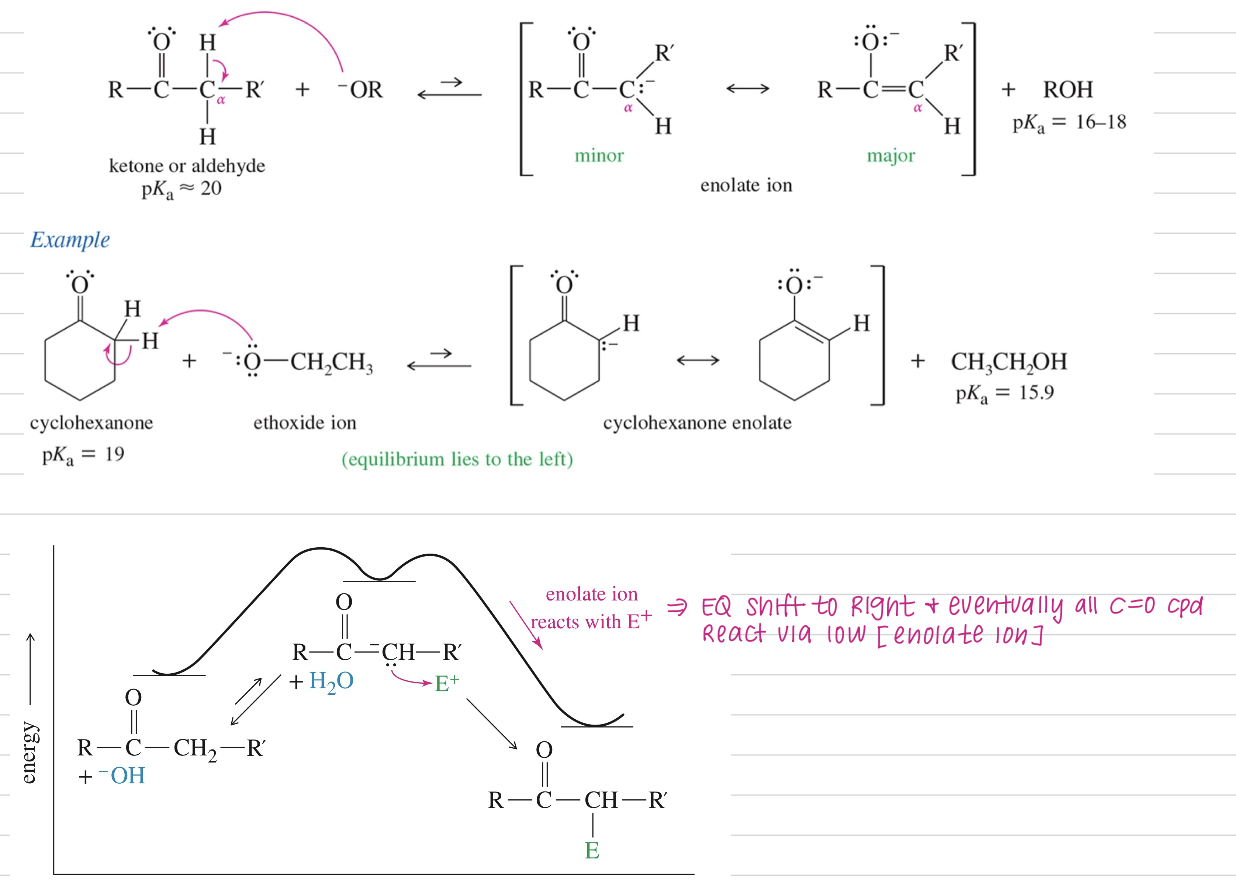
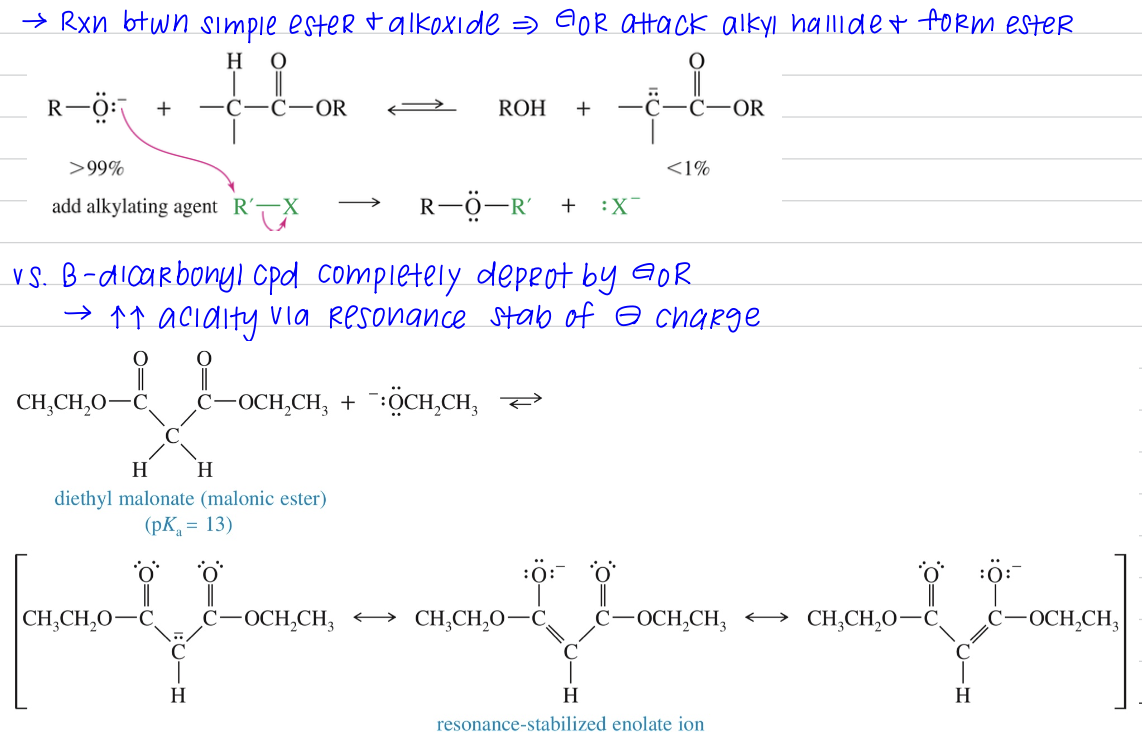
However… EQ mis of enolate & base not work sometimes bc base react w/ elec faster than enolate
Soln: Use Lithium Diisopropylamide LDA
LDA Synthesis) akyllithium reagent to deprot diisopropylamine
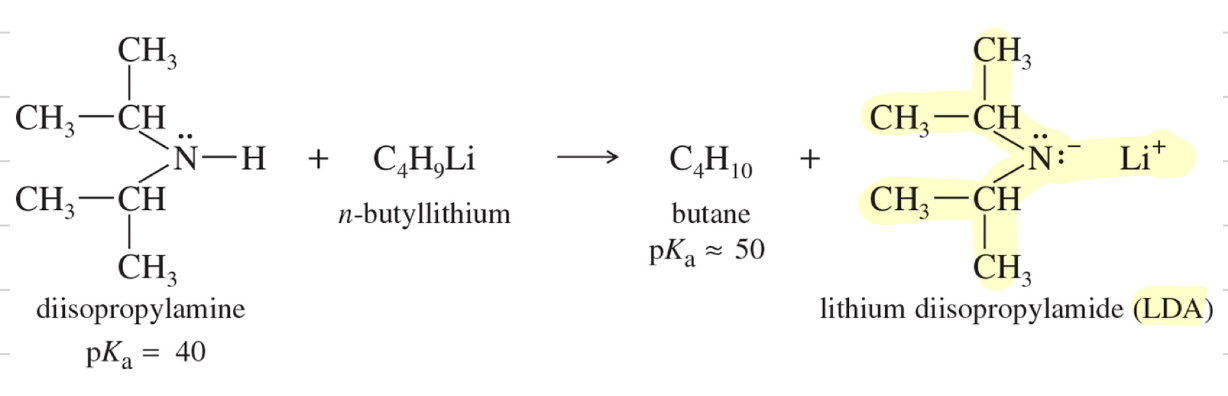
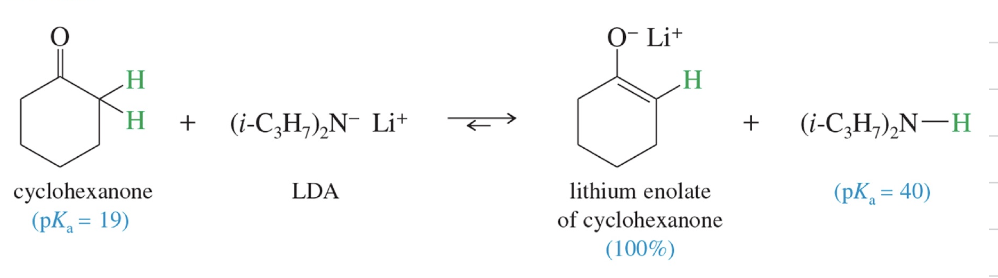
** LDA convert carbonyl cpd » completely to enolate
ex) Enolate of cyclohexanone
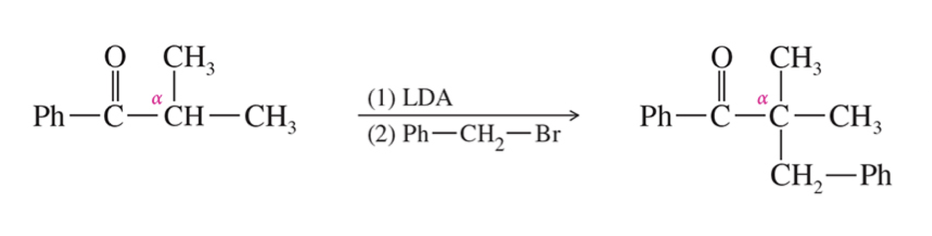
Alkylation of Enolate Ion
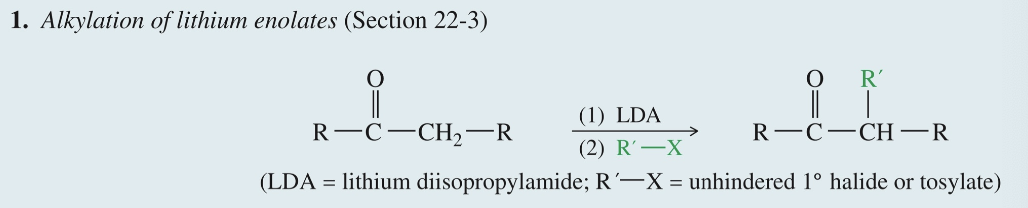
LDA
R-X
Rxn usually take place @ α C forming new C-C bond
LDA forms enolate » act as nuc & displace halide
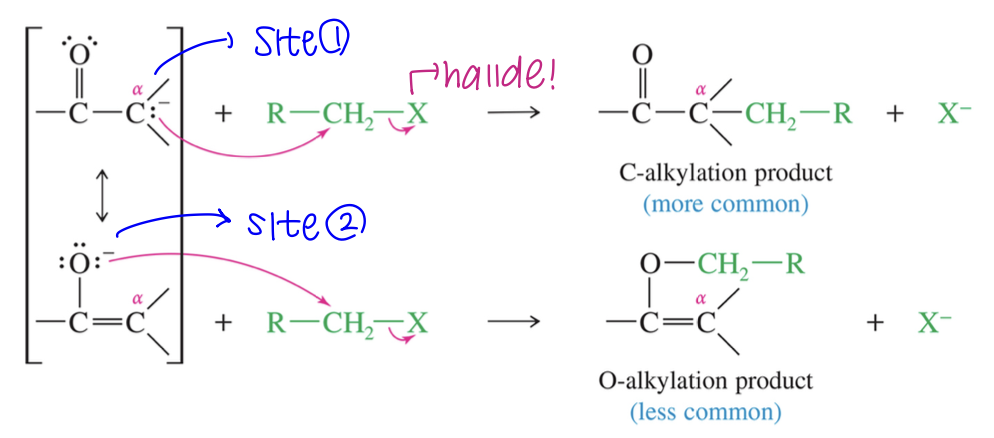
Enolate has 2 nuc sites (oxygen & α C) & can react w/ either of these sites
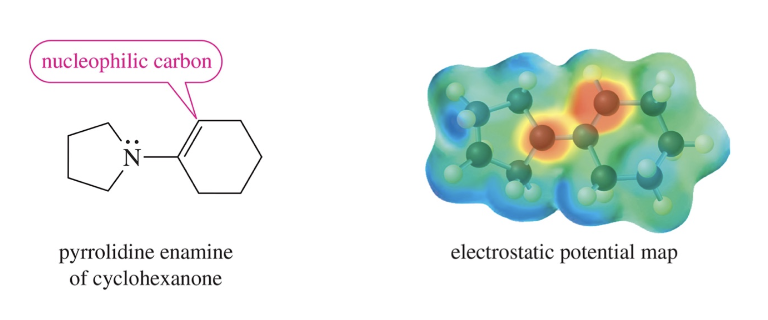
Enamine Formation
Ketone // aldehyde react w/ 2° amine to form enamine
Enamine has nuc α C » used to attack electrophiles
Electrostatic potential map)
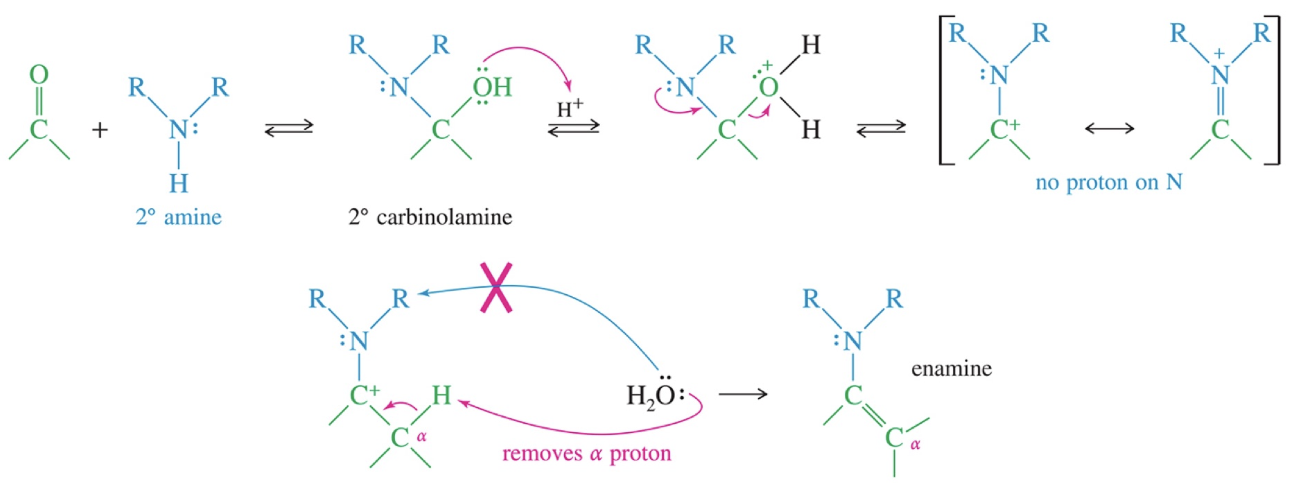
Mech of Enamine Formation
Ketone // aldehyde
2° amine
H3O+
★ Enamine > reactive vs enol but < than enolate
» Iminium ion unreactive
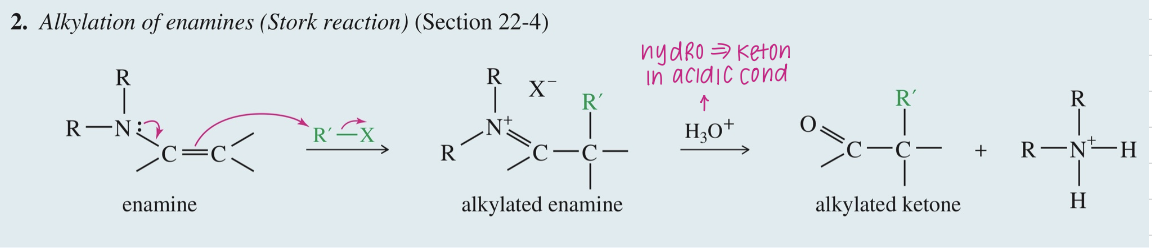
Alkylation of Enamine aka Stork Rxn

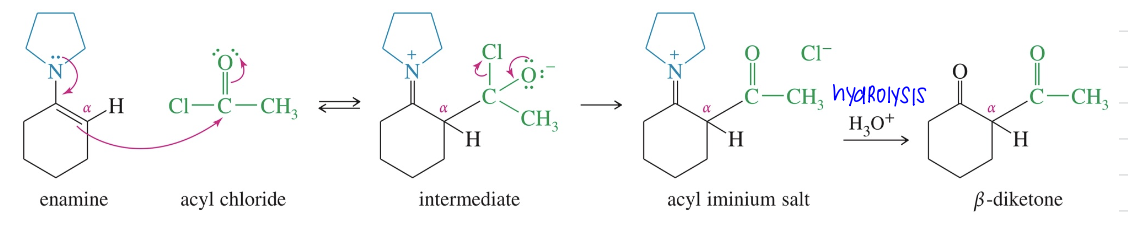
Acylation of Enamine aka Stork Rxn
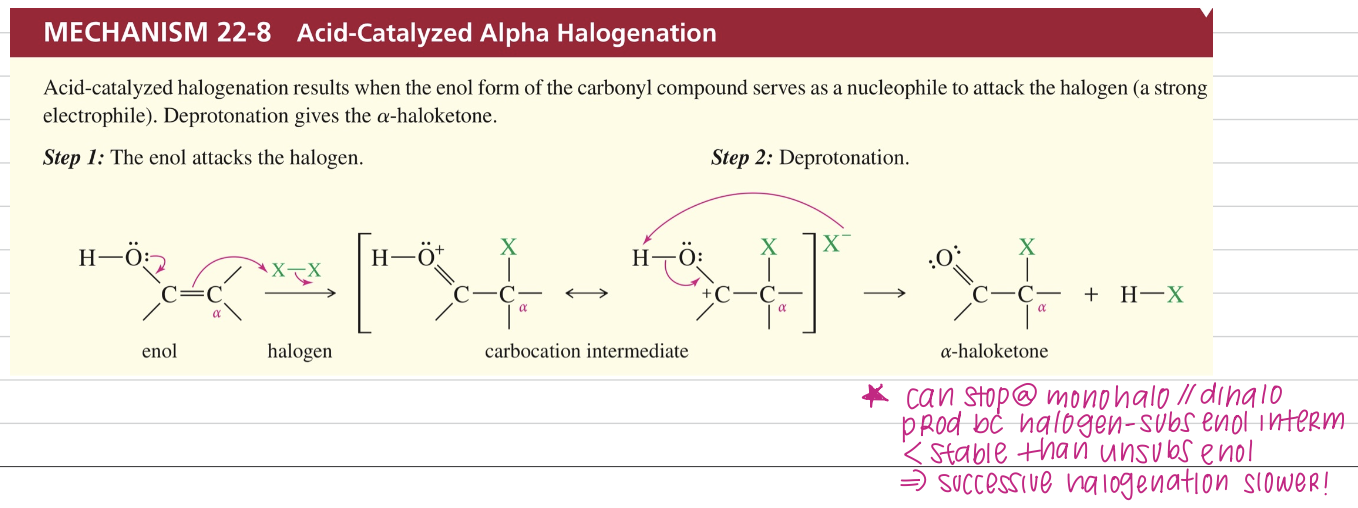
α-Halogenation of Ketone
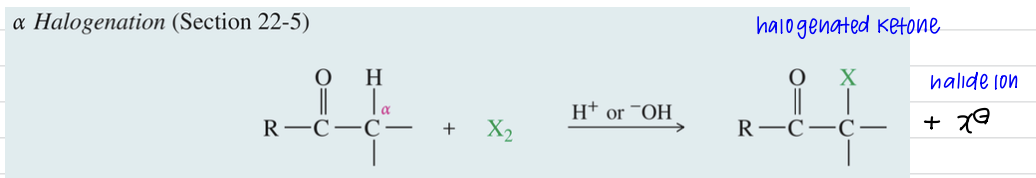
a) Base promoted α halogenation ★ base promoted MULTIPLE halogenation
X2 (halogen)
Base
Base promoted and not catalyzed bc full equiv of base consumed in rxn
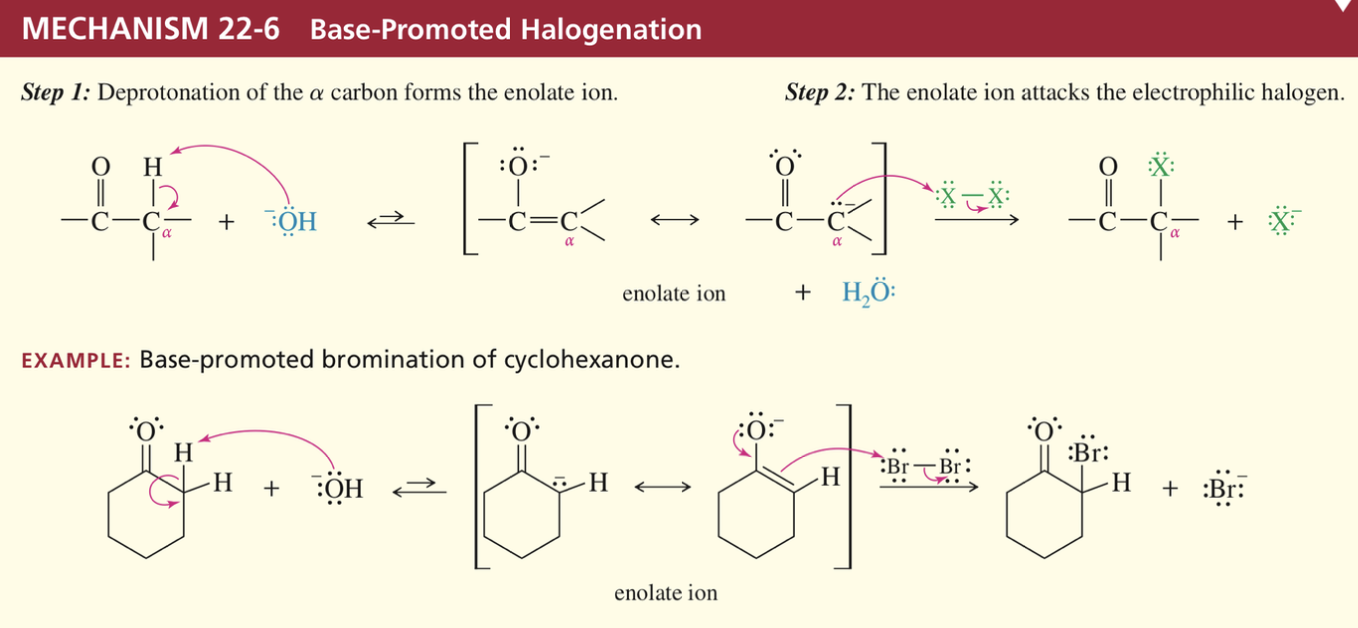
α haloketone produced is > reactive than ketone bc enolate stab via EWG halogen
2nd halogenation faster than 1st
Not useful in producing mono-halogenated ketones
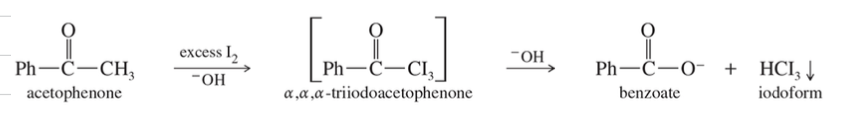
Haloform Rxn
Methyl Ketone react w/
H2
NaOH (under strongly basic condition)
» carboxylate ion & haloform
** Trihalomethyl ketone interm (not isolated)
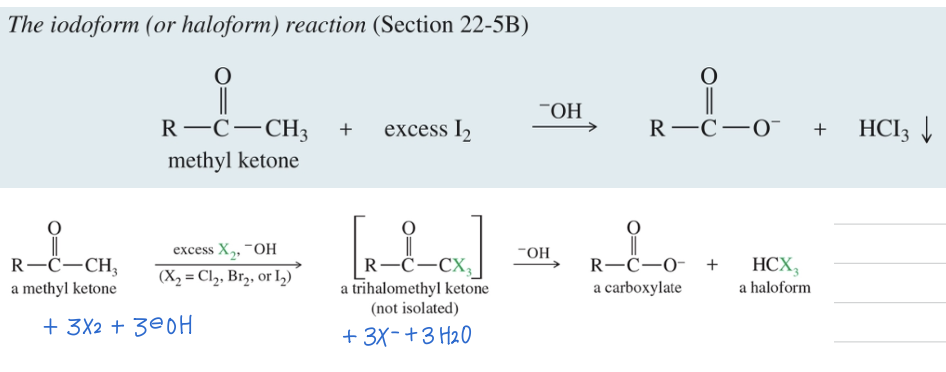
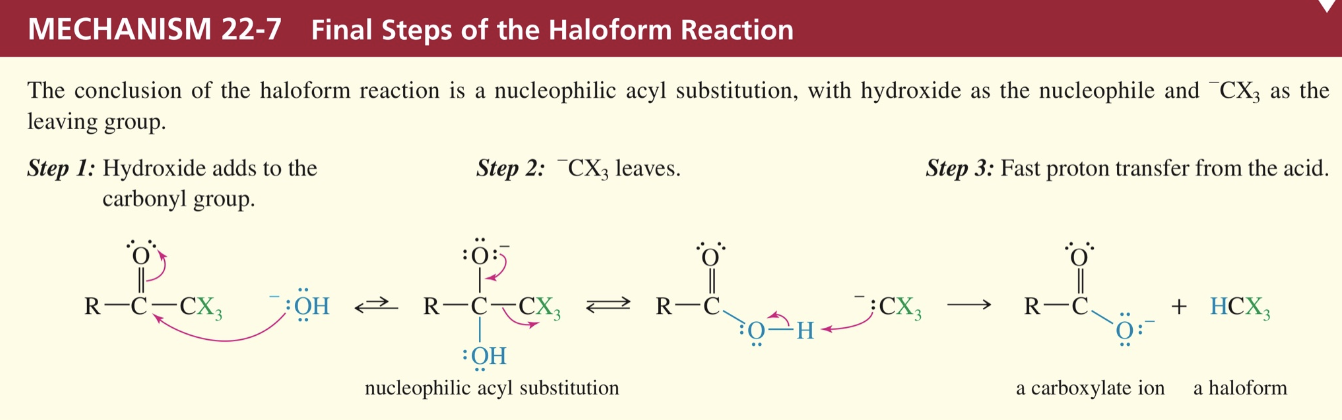
NAS where -OH is nuc, -CX3 is L.G.
+ Iodoform (CHI3) Test used to identify Methyl Ketone
Alcohol can give + iodoform test
Iodoform (CHI3) is yellow solid that ppt out of soln
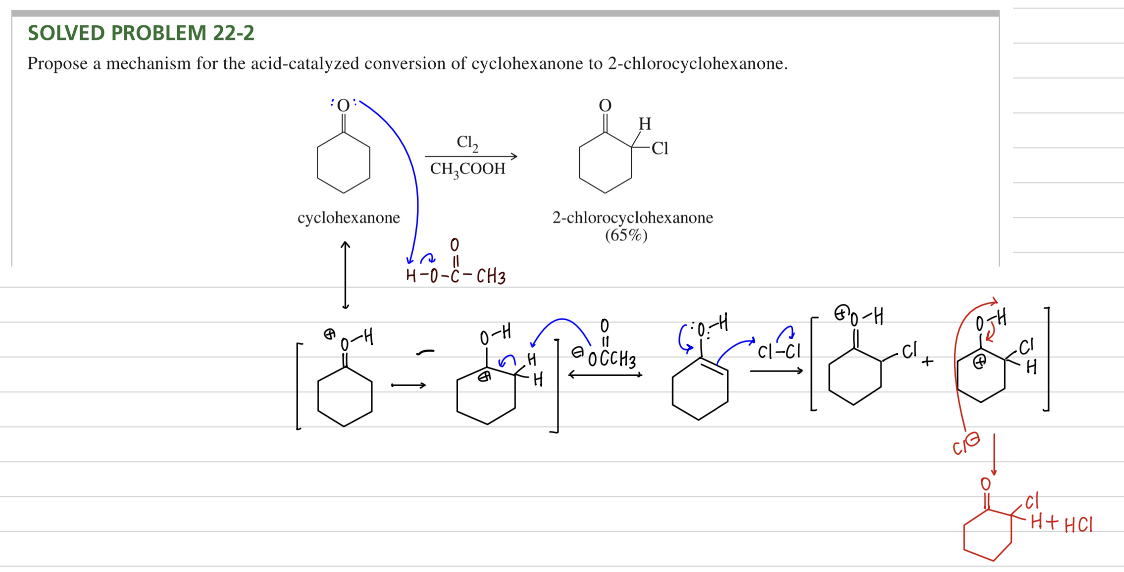
a) Acid catalyzed α halogenation ★ More control on multiple halogenation
X2 (halogen)
CH3COOH
Acidic halogenation may replace one or more α H depending on amount of X2 (halogen) used
Bc halogen subs enol interm is stable
★ Unlike ketones… aldehydes are easily oxidized & X2 (halognes) are strong oxidizing agent
Attempt to halogenate aldehydes » oxidation of carboxylic acids
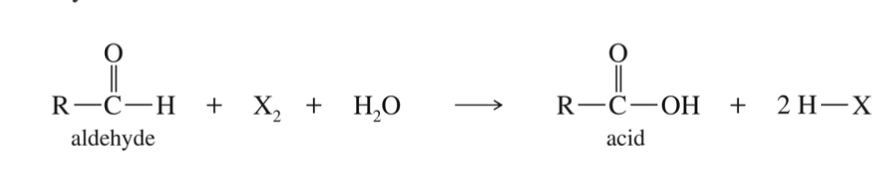
α-Bromination of Acid: Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky (HVZ) Rxn
Carboxylic acid
1) Br2 & PBr3
» α bromo acyl bromide
2) H2O
» α bromo acid ★ Commonly used to convert to α amino acid via acess NH3
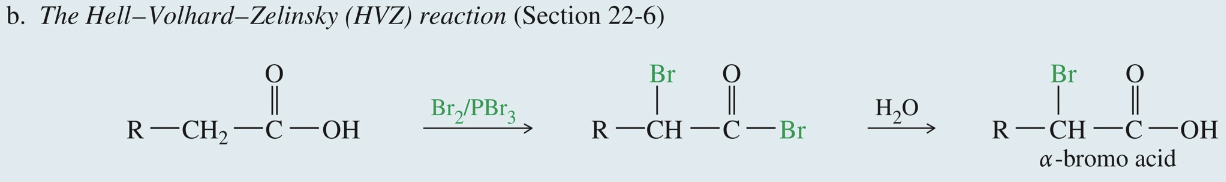
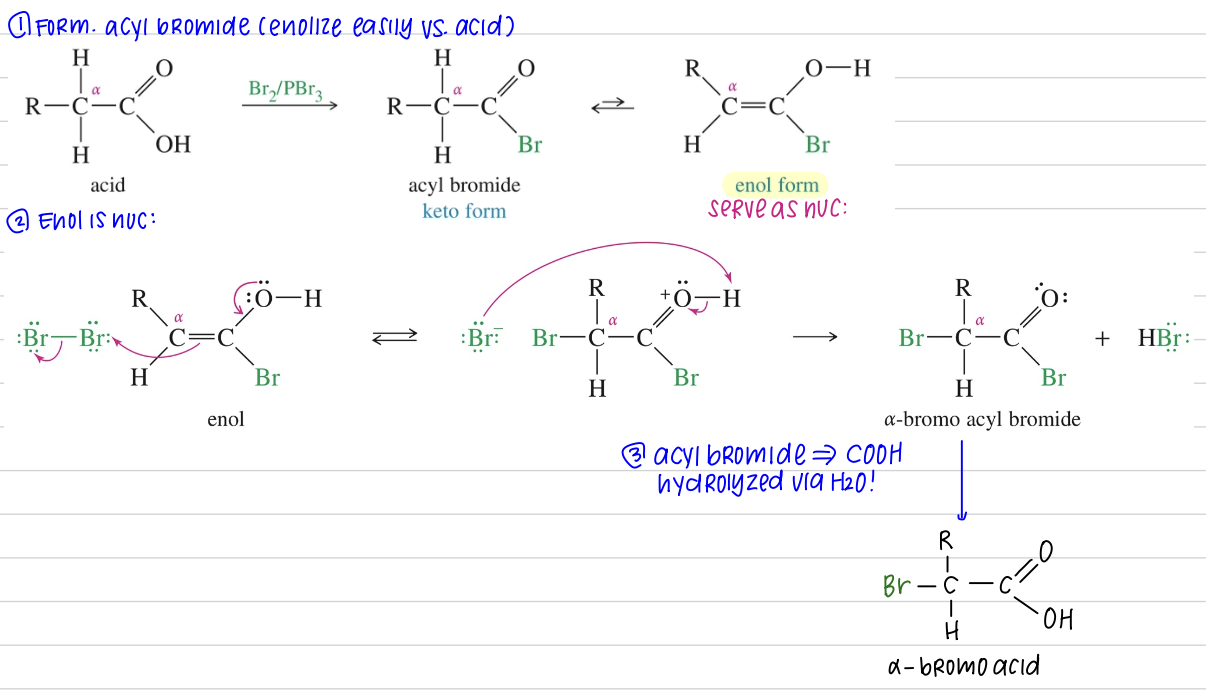
α bromo acid » α amino acid
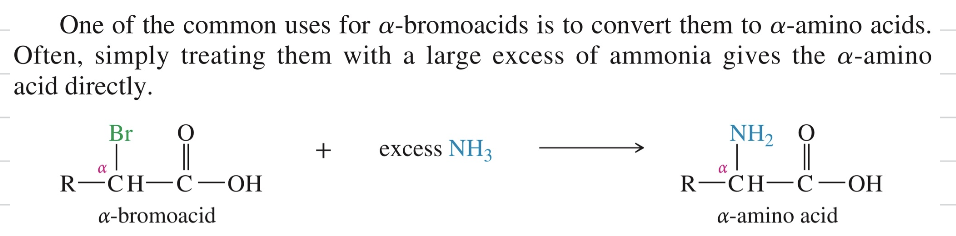
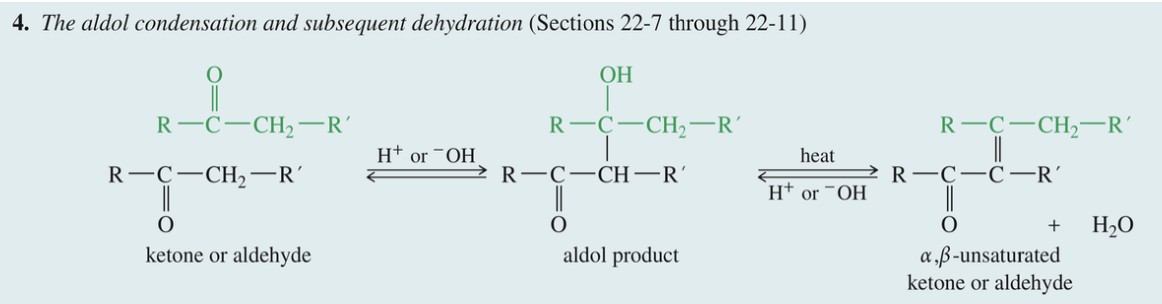
Aldol Condensation
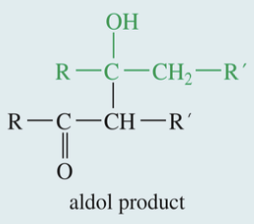
& Subs Dehydration
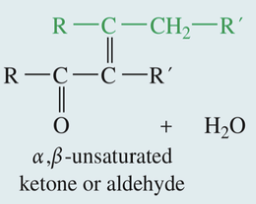
Ketone // aldehyde
1) H+ // -OH
» aldol product
2) Heat & H+ // -OH
» α, b- unsaturated ketone // aldehyde
Dehydration of aldol product)
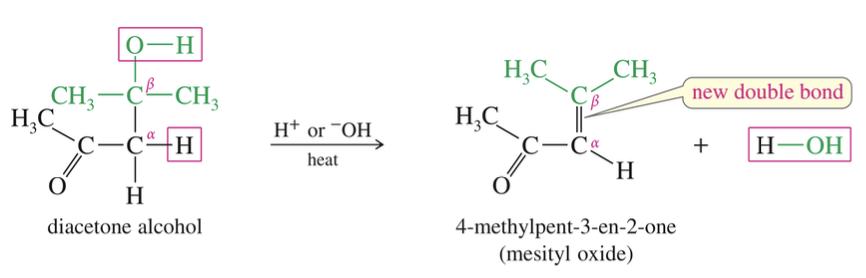
Produce α, b- unsaturated conjugated aldehyde // ketone
a) Base Cat Aldol Condensation
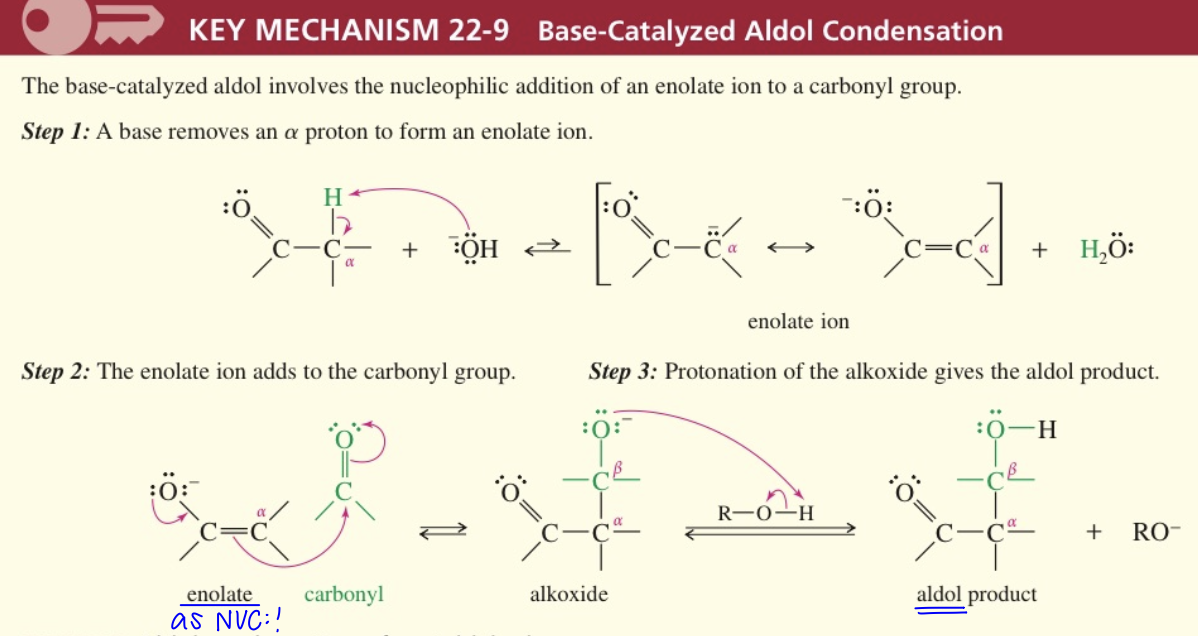
NUC addition of enolate ion to another carbonyl group
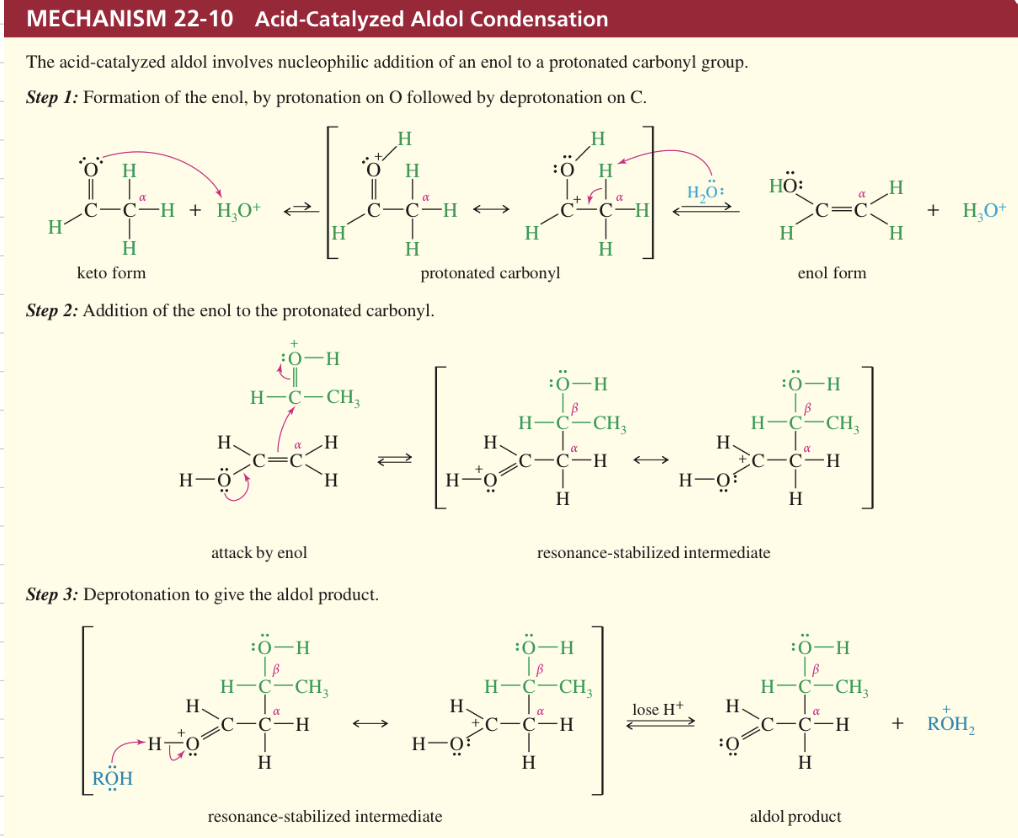
a) Acid Cat Aldol Condensation
★ Driving Aldol Conden » Completion
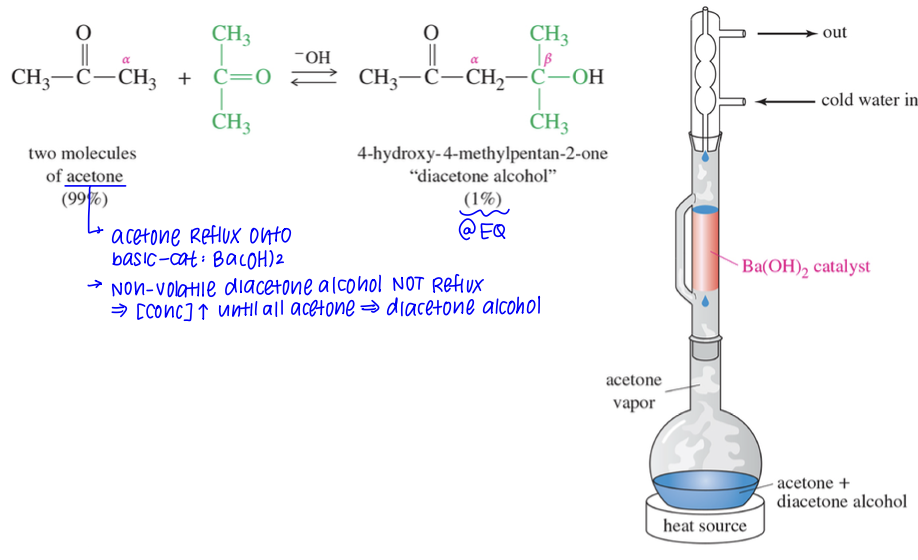
Reflux acetone using Ba(OH)2 while non volatile diacetone alcohol product not reflux
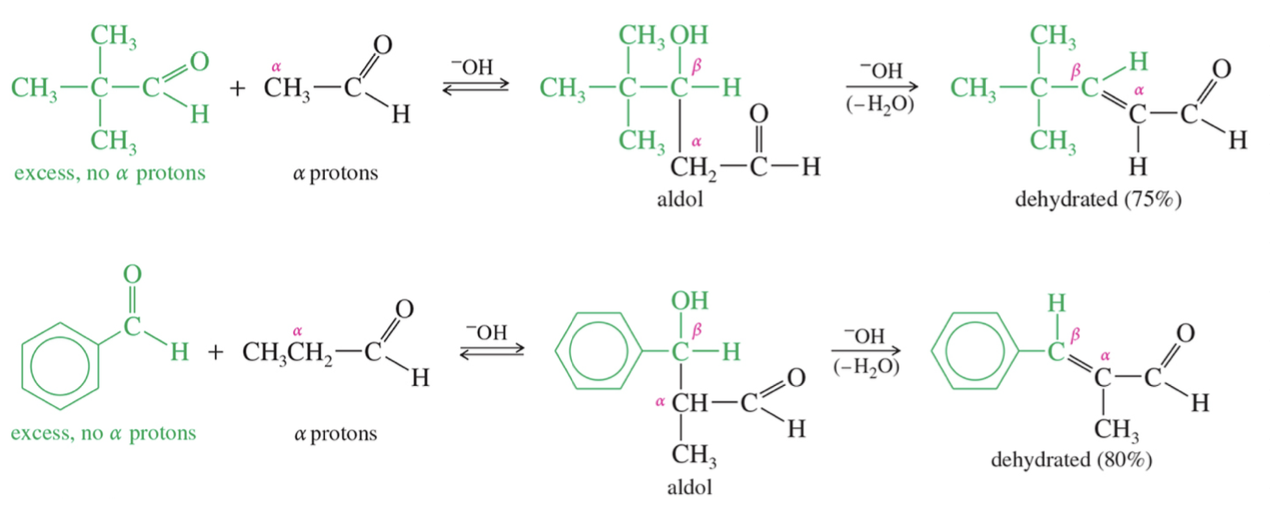
★ Crossed Aldol Condensation
When enolate of one aldehyde // ketone adds to carbonyl group of diff aldehyde // ketone » crossed aldol condensation
Use LDA to just make desired enolate ion » add cpd we want as electrophile (control which enolate add to which carbonyl group)
★ Problem Solving Strategy
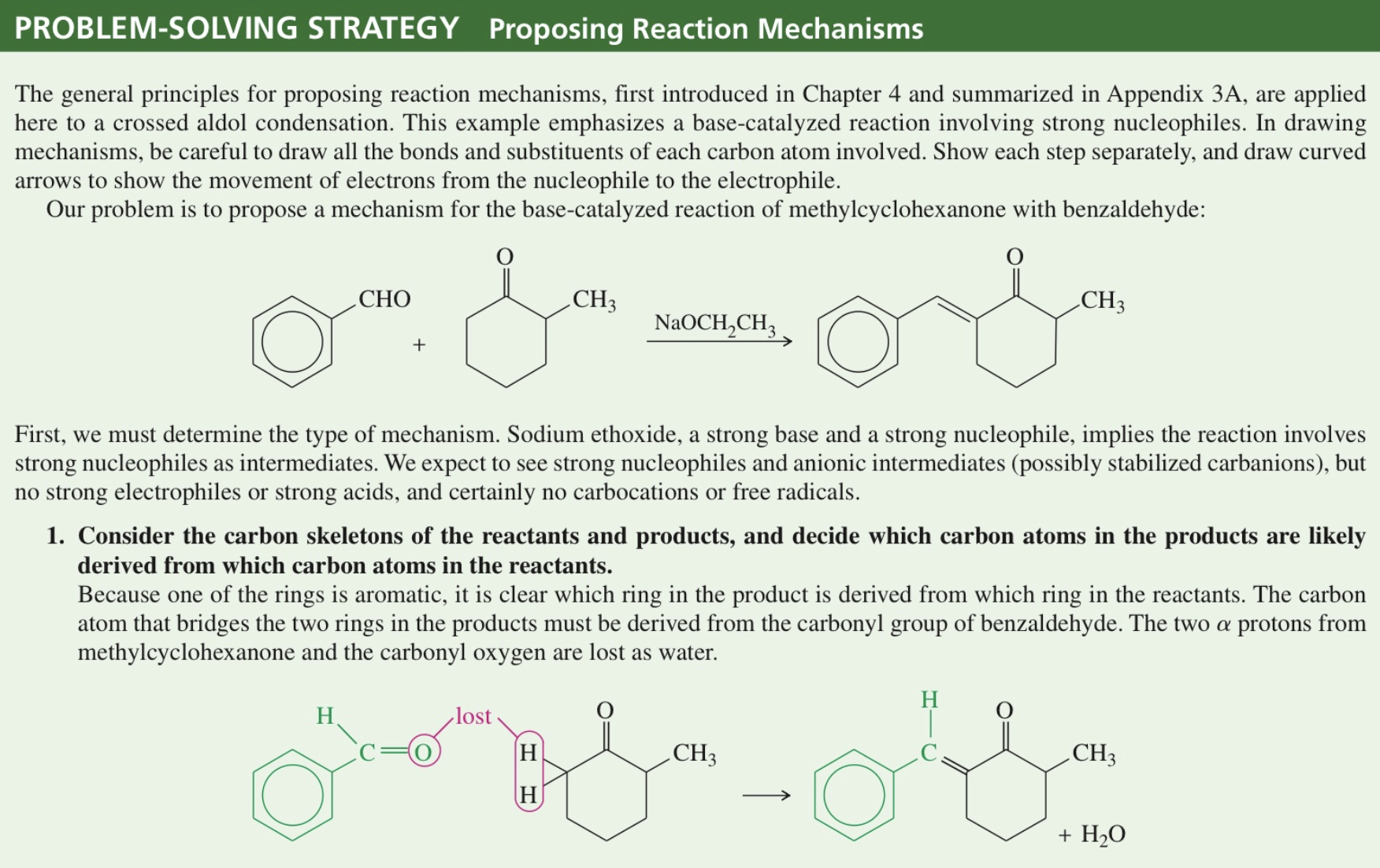
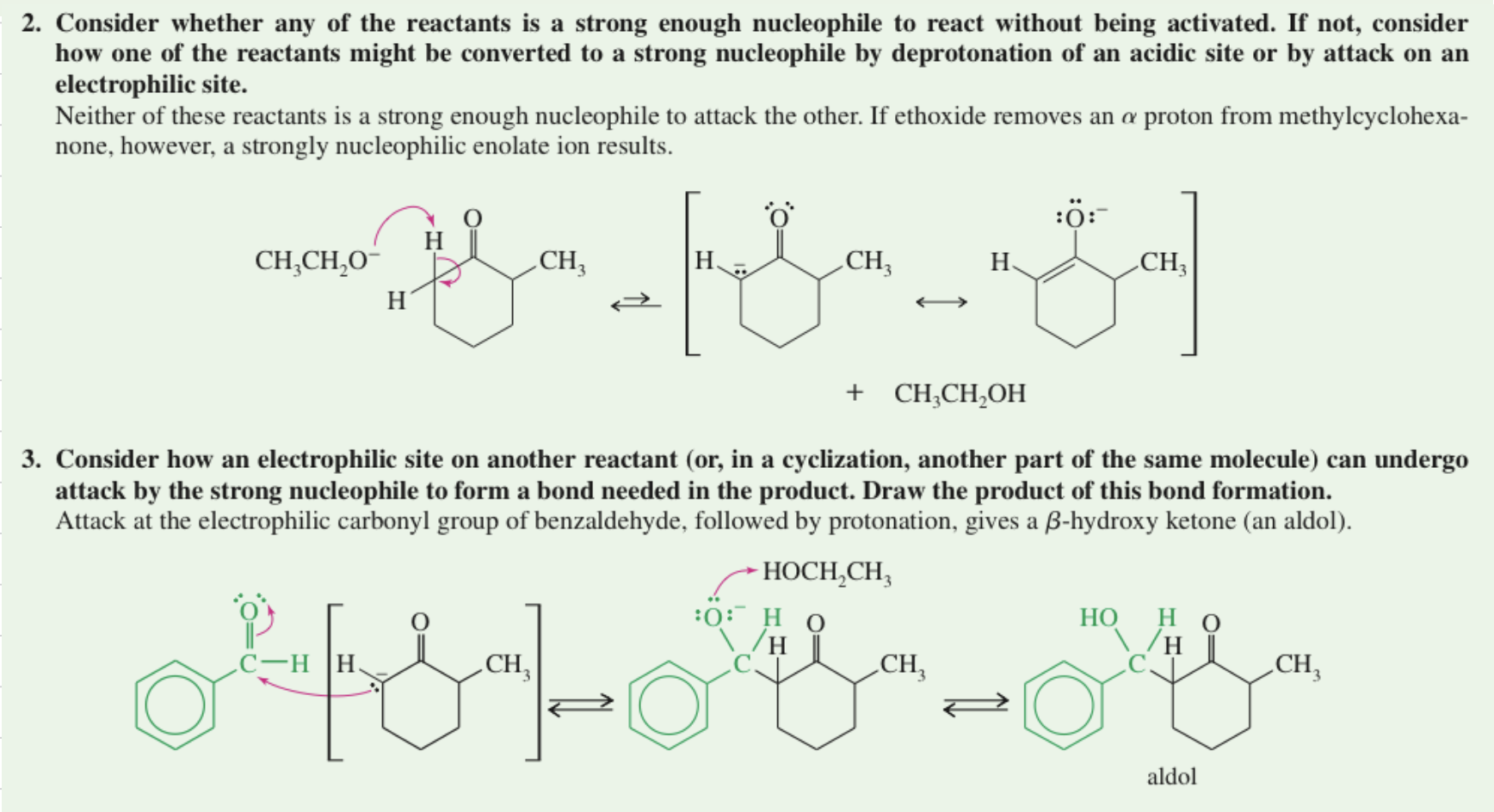
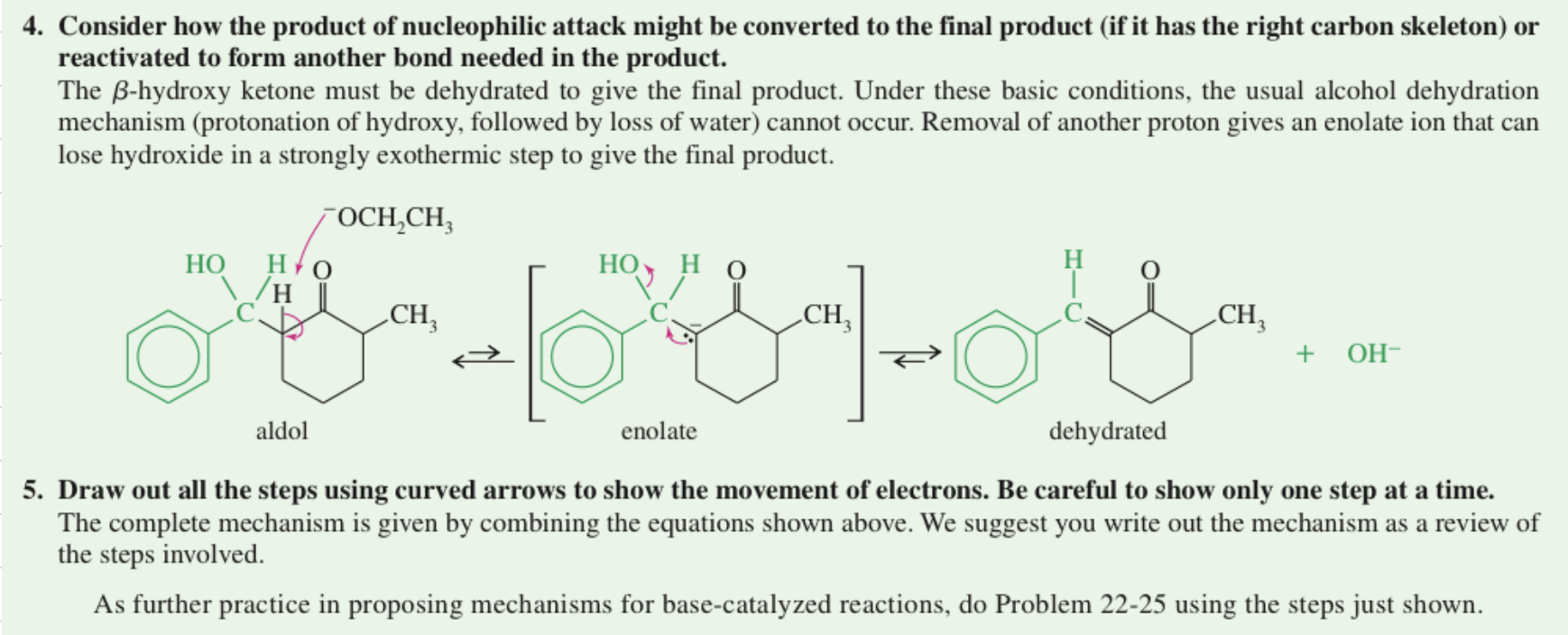
Aldol Cyclization intra MC aldol rxn
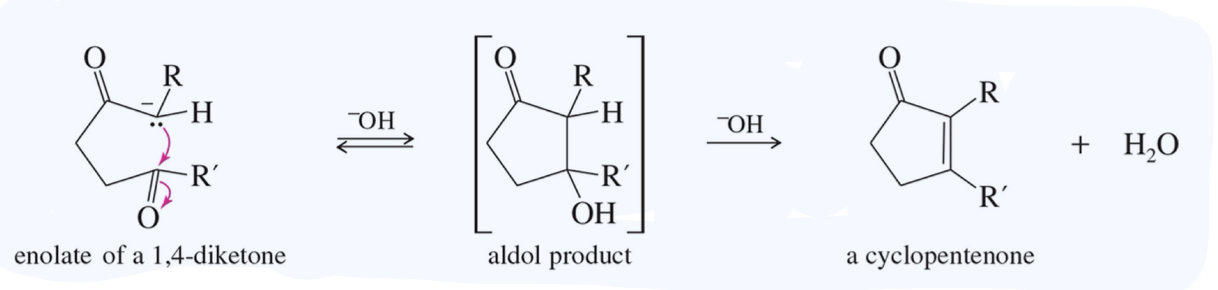
ex)
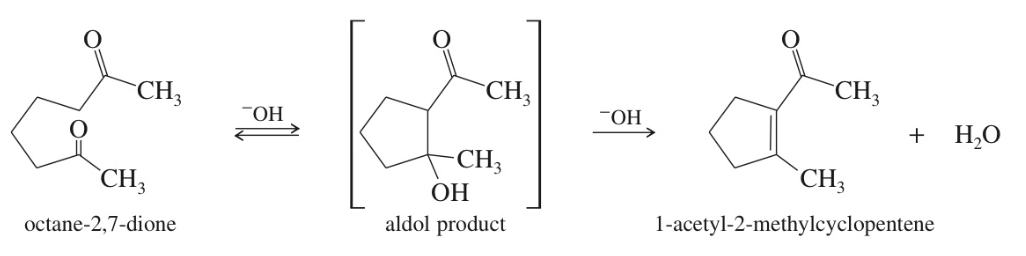
+ Planning synthesis using aldol condensation
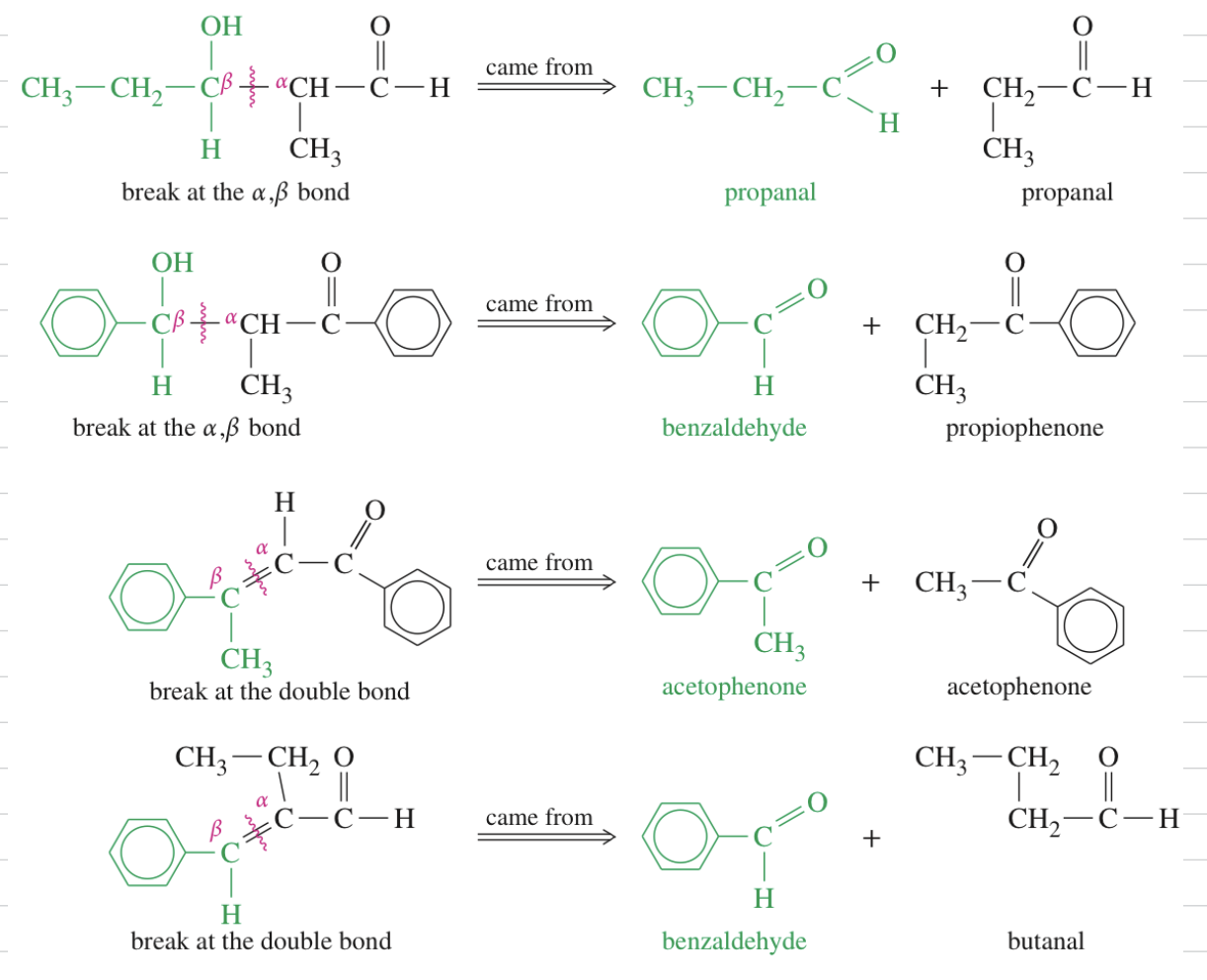
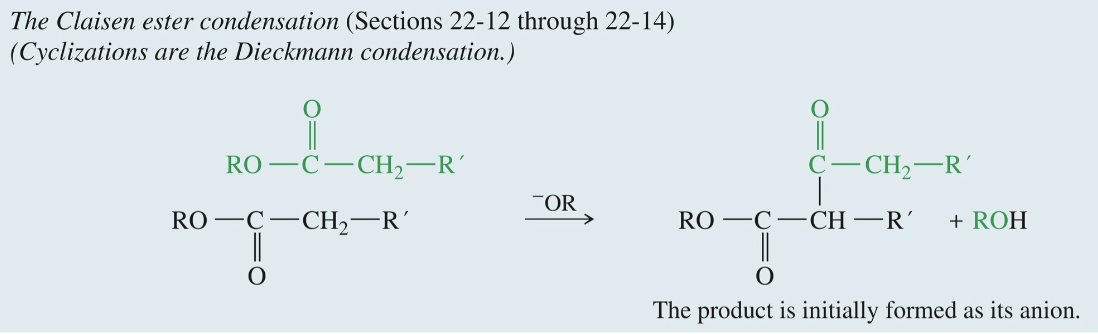
Claisen Ester Condensation
2 Esters
1) -OR
2) H3O+
α H is weakly acidic
< acidic vs ketone & aldehyde bc C=O stab via reasonance w. other O » less capable of stab (-) charge of enolate ion
Ester MC undergo NAS via enolate
Mech)
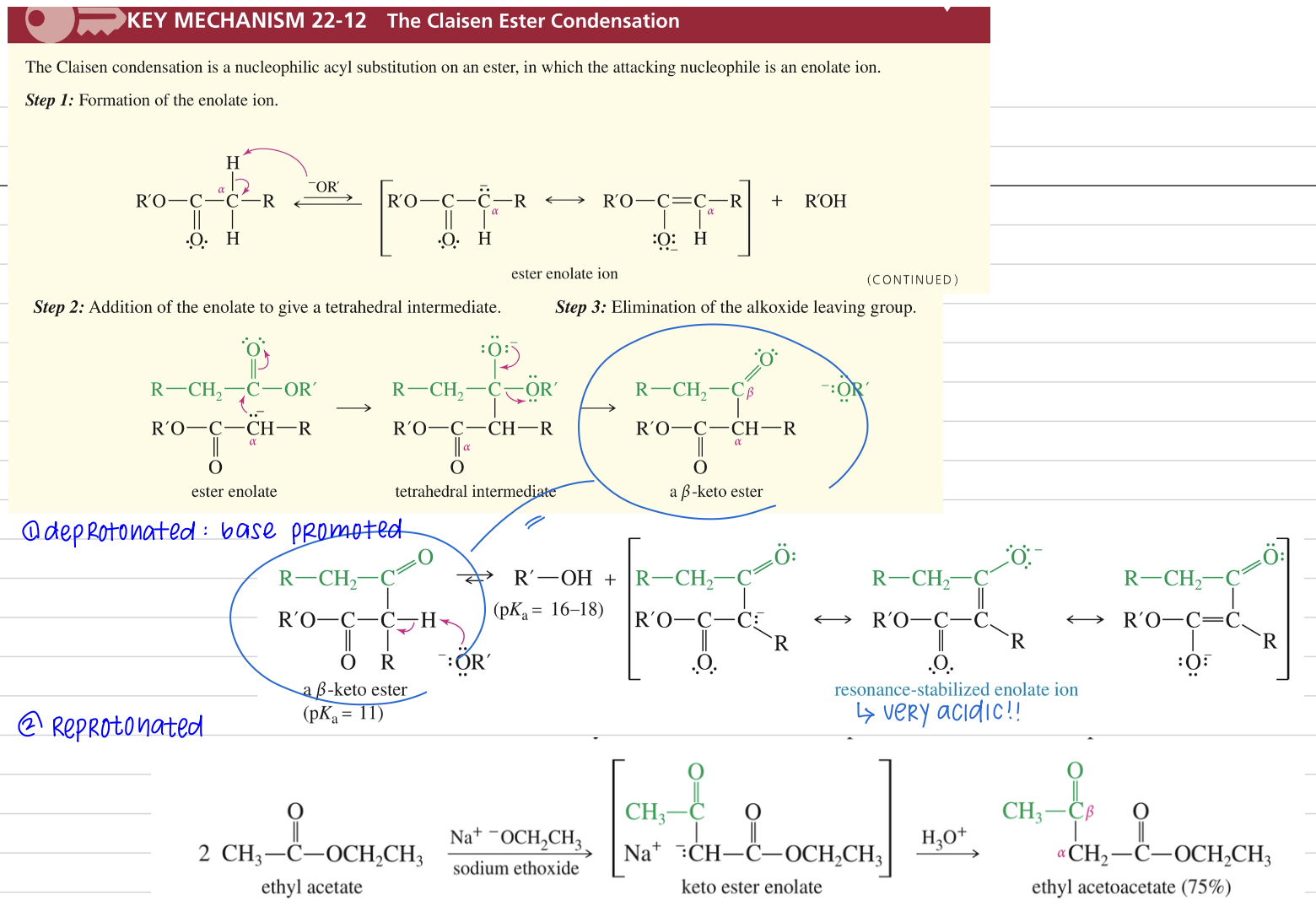
★ Good choice if one ester w/ α H and other w/out
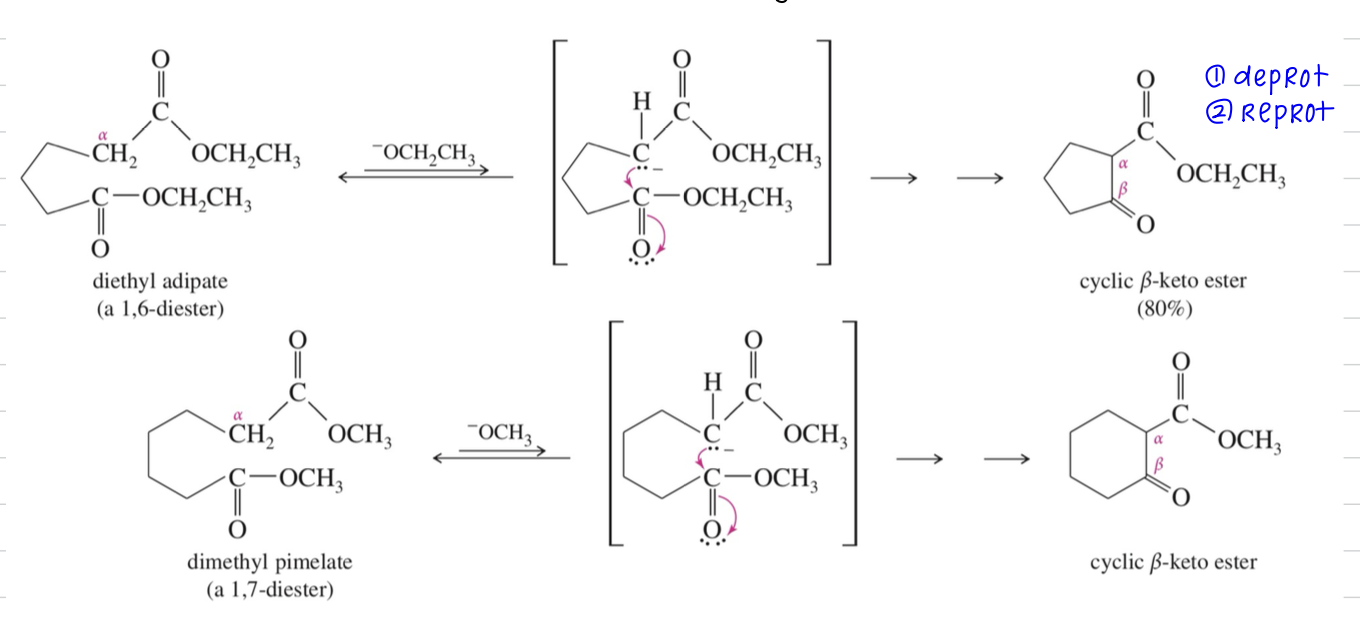
Dieckmann Condensation aka Claisen cyclization »5-6 mem ring
★ If condensation btwn ketone // aldehyde & ester, ketone // aldehyde becomes enolate first bc > acidic & attack ester
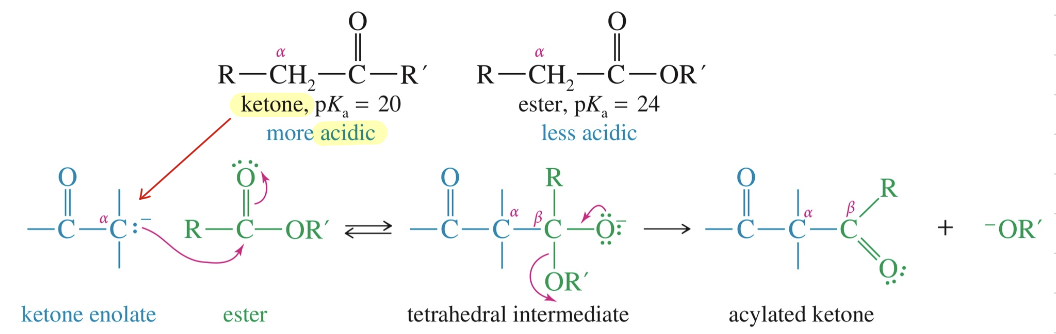
Acidity of Carbonyl Cpd: capacity to stab (-) charge » which enolate nuc and which elec