PLTW: Biomedical Science Unit 1 TEST
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
5 steps to a crime scene investigation/how a crime scene is processed
1. Collect evidence
2. Sketch
3. Interview
4. examine
5. photograph
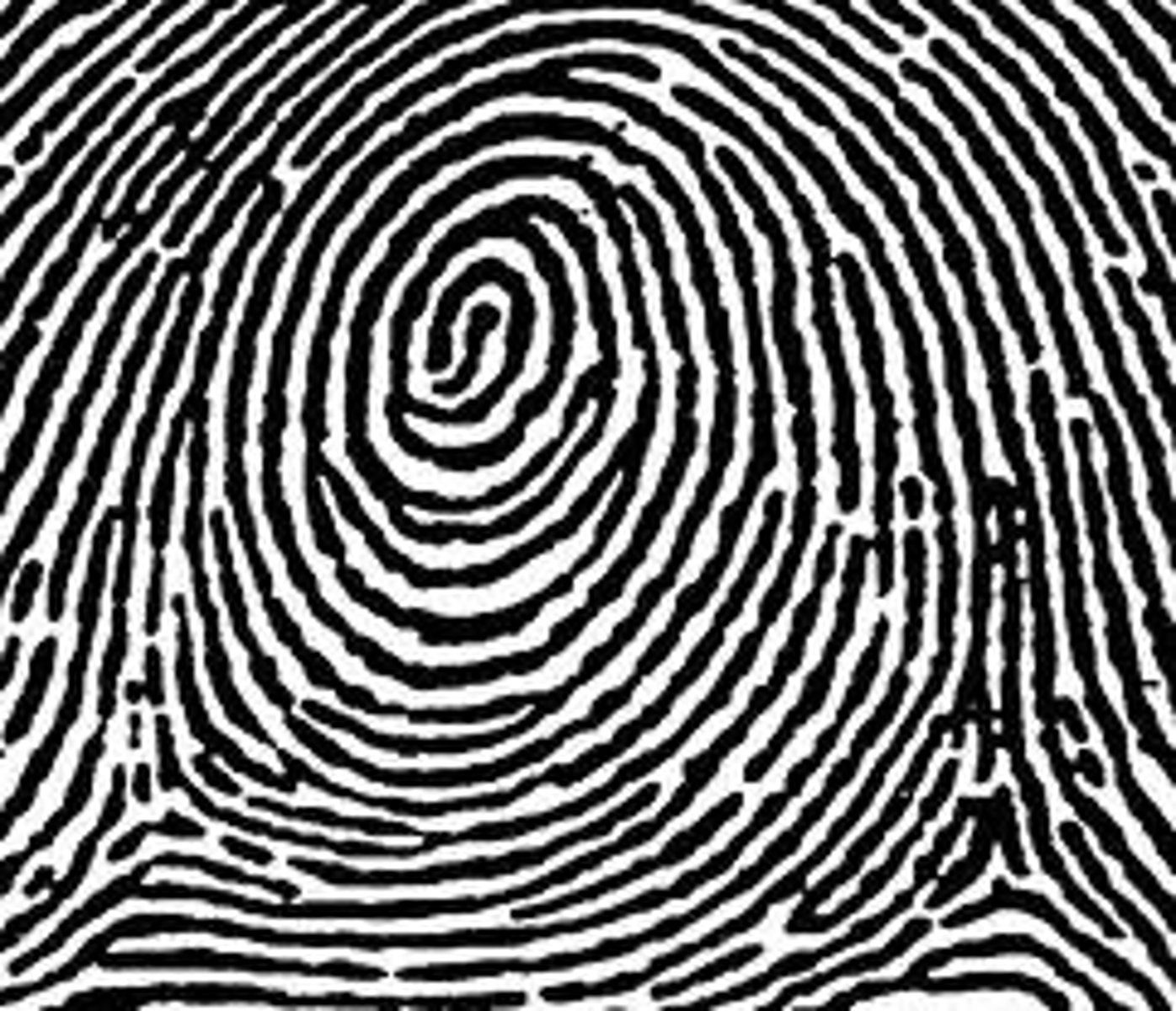
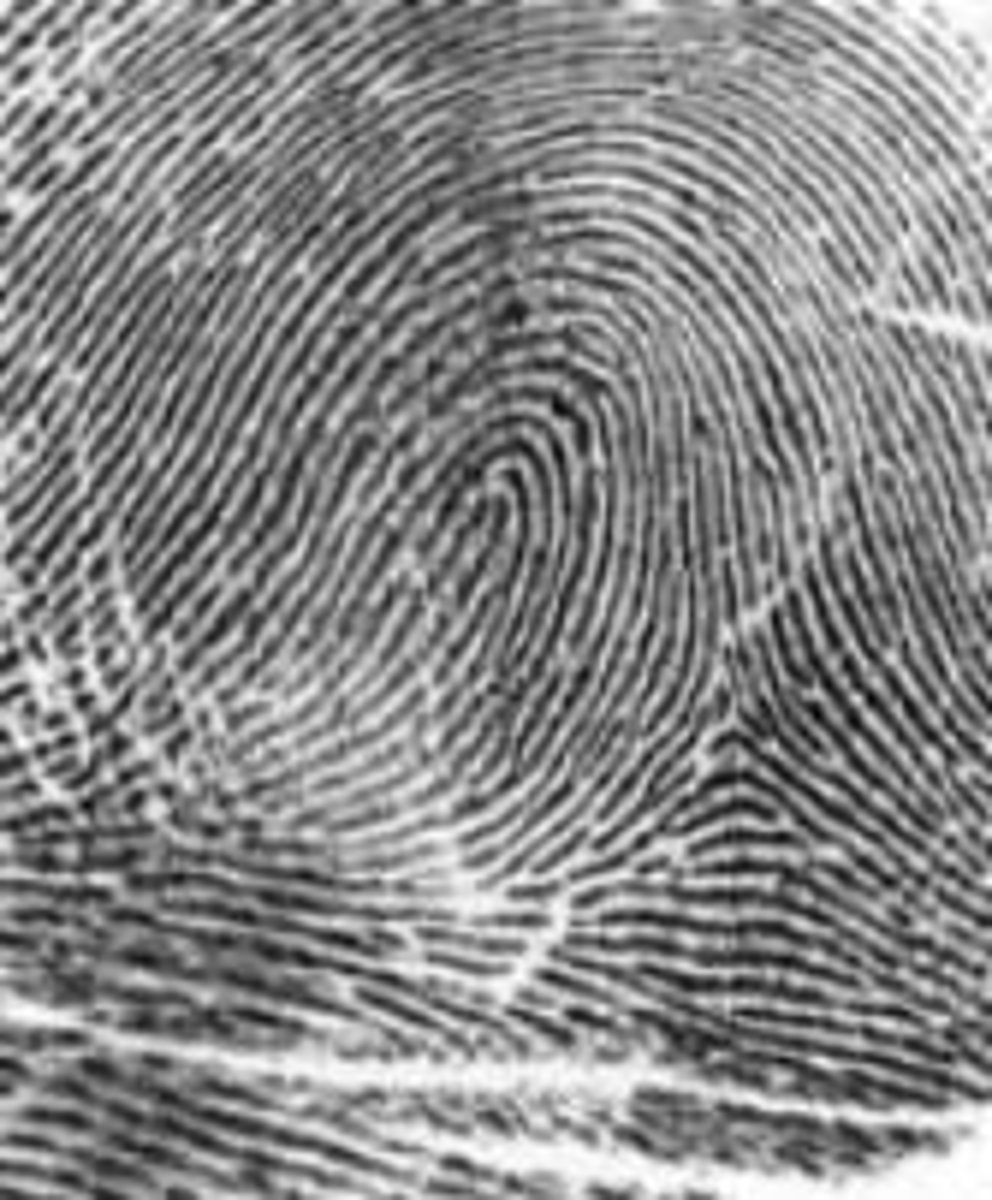
3 primary fingerprint ridge patterns
arch, whorl, loop
arch
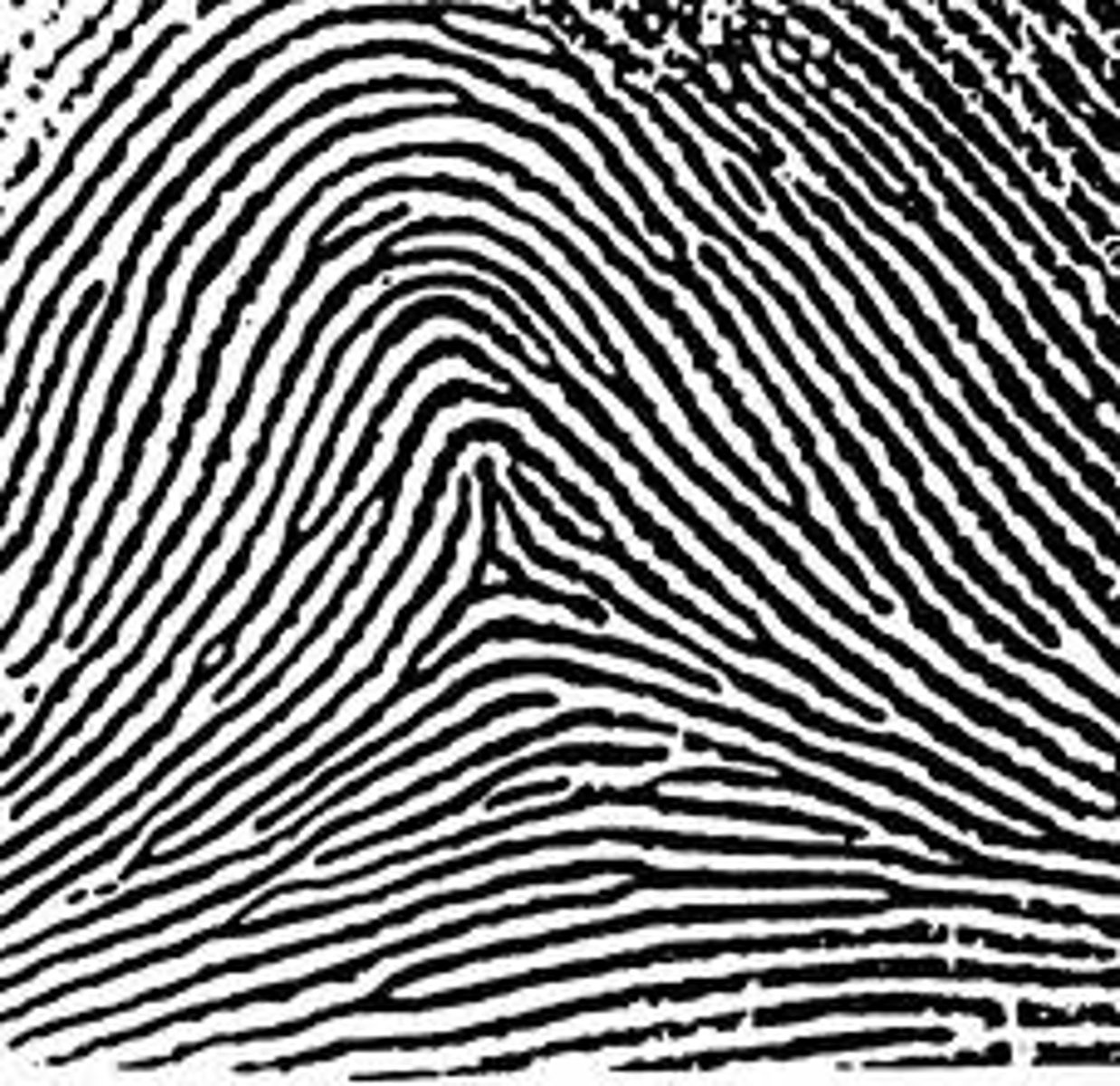

whorl

loop

Independent variable
manipulated by the researcher.
Dependent variable
Measurable effect, outcome, or response in which the research is interested. results vary based on the independent variable.
Control Group/variable
The group in an experiment that serves as a comparison against the experimental group where the independent variable is applied.
Forensic Science
The application of scientific knowledge to questions of civil and criminal law.
Hypothesis
Clear prediction of the anticipated results of an experiment.
Negative Control
Control group where we don't know the outcome.
Positive Control
Group expected to have a positve result, allowing the researcher to show that the experiment set up was capable of producing results.
Types of Blood in ABO system
Type A, Type B, Type AB, Type O
Clumping with a serum that is Anti-A indicates
(same with Anti-B)
that the blood type has "B" in it
cuticle
What is the outermost layer of the hair?
cortex
Home to pigment containing granules - gives hair color.
medula
the base of the brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing
Adenine
A component of the nucleic acids, energy-carrying molecules such as ATP, and certain conenzymes. Chemically, it is a purine base.
Chromosome
Any of the usually linear bodies in the cell nucleus that contain the genetic material.
Cytosine
A component of nucleic acids that carry hereditary information in DNA and RNA in cells. Chemically, it is a pyrimidine base.
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
A double-stranded, helical nucleic acid molecule capable of replicating and determining the inherited structure of a cell's proteins.
Gel Electrophoresis
The separation of nucleic acids or proteins, on the basis of their size and electrical charge, by measuring their rate of movement through an electical field in a gel.
Gene
A discrete unit of hereditary information consisting of a specific nucleotide sequence in DNA (or RNA, in some viruses).
Guanine
A component of nucleic acids that carry hereditary information in DNA and RNA in cells. Chemically, it is a purine base.
Double helix
DNA's form
Nucleotide
A building block of DNA, consisting of a five-carbon sugar covalently bonded to a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group.
How is alcohol used to extract DNA?
DNA is insoluble in alcohol, so it forces DNA out
Restriction Enzyme/restriction endonucleases
an enzyme that recognizes specific nucleotide sequences and cuts up DNA.
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs)
A section of DNA that is cut into different pieces by the same restriction enzyme due to differences in the nucleotide sequence (the different sections in a DNA strand vut by restriction enzymes)
Thymine
A component of nucleic acids that carry hereditary information in DNA and RNA in cells. Chemically, it is a pyrimidine base.
What medical profession performs autopsies?
forensic pathologist (medical examiner)
What are the base pairs?
A - T, G - C
What is the difference between the purines and the pryimidines?
Purines have two carbon-nitrogen rings and four nitrogen atoms. Pryimidines have one carbon-nitrogen ring and two nitrogen atoms.
What two base pairs are purines?
Adenine and guanine
What two base pairs are pyrimidines?
Cytosine and guanine
Why do purines bond with pryimidines in the DNA ladder?
They are opposite poles and have the same number of hydrogen bonds.
Explain the role that restriction enzymes and gel electrophoresis play in DNA profiling.
Restriction enzymes cut the DNA at specific nucleotide sequences and gel electrophoresis seperates nucleic acids or proteins by size.
What would happen if the gel was placed with the DNA starting closest to the positive electrode? Explain.
The process wouldn't work because the DNA would run backwards.
True/False: Chromosomes are composed of genes and chromosomes make up DNA.
True
If someobody has blood type A what anti-bodies would they have?
Anti-A antibodies
why do people have different blood types?
Your DNA codes for certain antigens on your red blood cells; those antigens determine your blood type.
Which blood type would give no response to both A and B anti-bodies?
O
What is the relatioship between antibodies and antigens?
Antibodies are proteins that attach to foreign antigens and cause agglutination.
presumptive test
test that presumes the presence of the questioned substanced, looks for hemoglobin protein which contains iron
confirmatory test
test that confirms the presence of blood, looks for certain antigens
how many antigens are in type AB blood?
2
what does a CSI NOT do at a crime scene?ta
pronounce the victim dead at the scene
a microsopic sample of hair can provide us with sex, race, and age but not
identity
if a substance is blood it will have ___ results for each test:
positive - luminol
pink - presumptive
ALWAYS crystals - confirmatory
if a substance is not blood it will have ___ results for each test:
negative: luminol
clear: presumptive
no crystals: confirmatory
the faster the blood droplet falllingthrough air, the (more or less) circular the blood drop will be?
less
as height increases, the diameter of the blood _____
increases
what makes you different in DNA than your friends?
different sequence of nitrogenous bases
our genome is composed of ___
chromosomes
chromosomes are made up of
genes
what does detergent do to help extract DNA?
detergent breaks down the lipids in nuclear/cell membrane which llows DAN to be extracted
if adenine has 30% and cytosine has 20%, what % does guanine have?
20%
is thymine has 15%, what % does adenine have?
30%
if guanine has 40%, what % does thymine have?
10%
what is DNA?
deoxyribonucleic acid, nucleic acid
what is DNA's monomer?
nucleotide
what does meat tenderizer do as a buffer
breaks down the proteins in the bilayer
what arethe parts of DNA?
phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar, and nitrogenous bases
what is the 2nd strand of TTGCACGG?
AACGTGCC
DNA can be found in
blood, semen, urine, sweat, bone, hair, saliva, and clothing
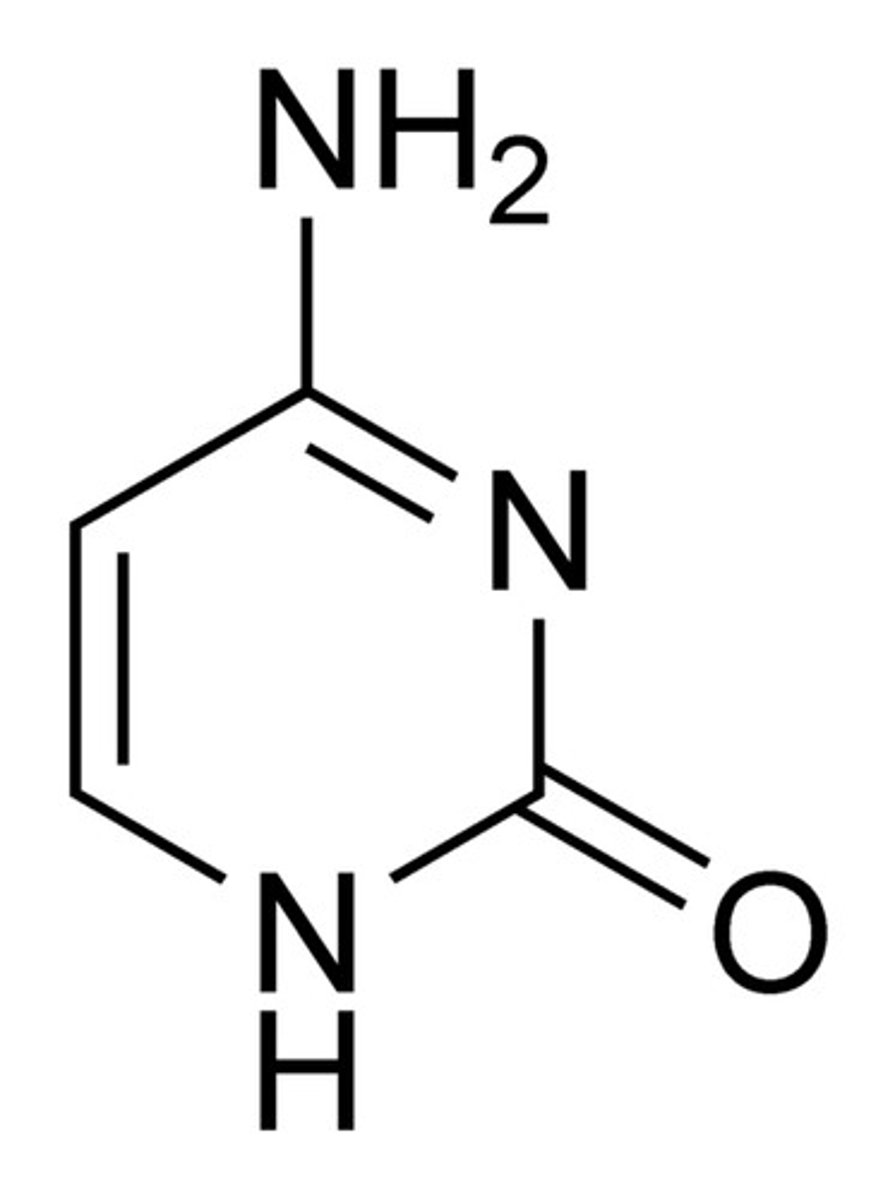
pyrimidine base
thymine and cytosine
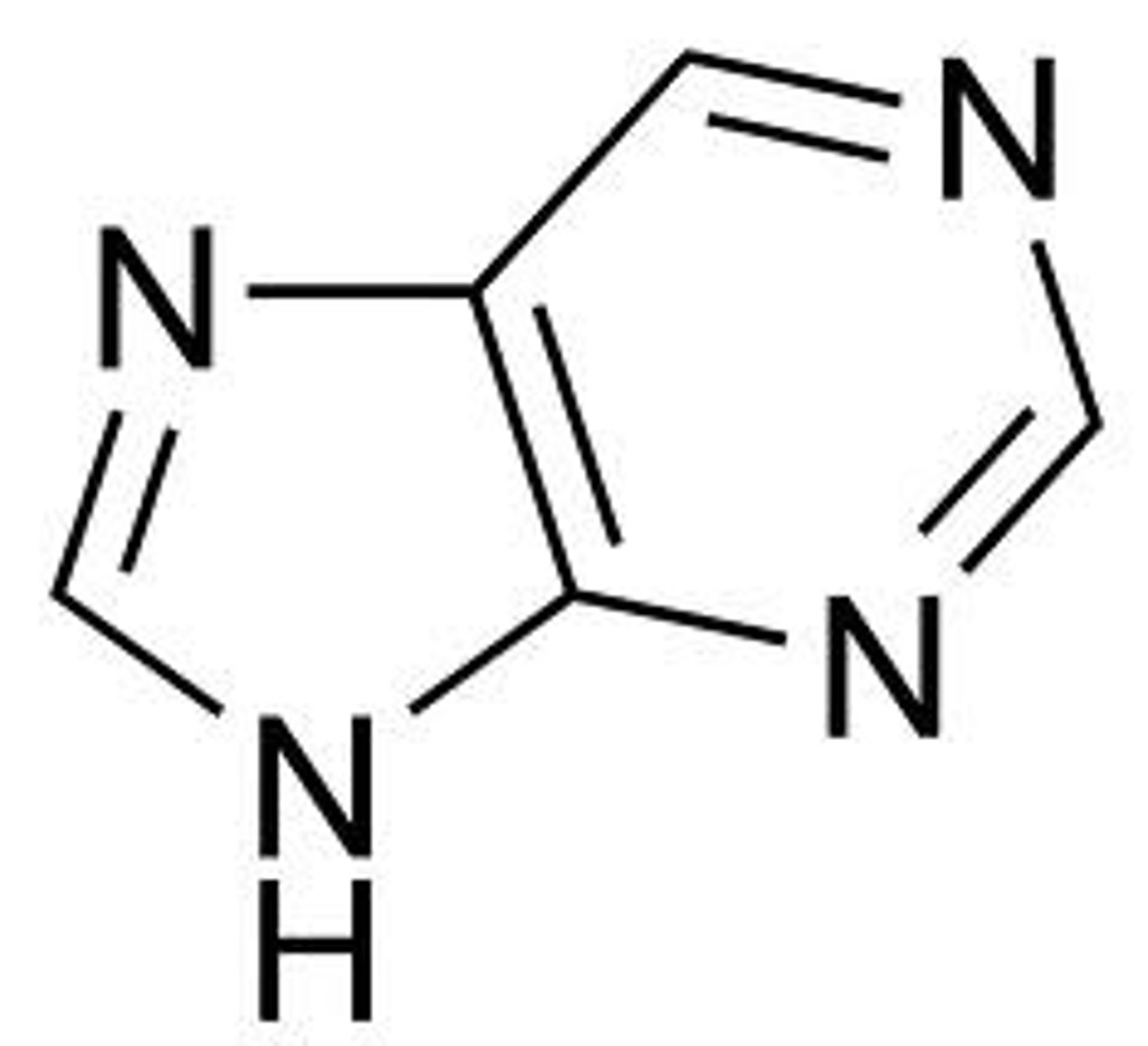
purine base
Adenine and Guanine
what does a 911 disbatcher do
recieves the emergency calls
what does a CSI do?
observe, take photos, # the evidence, estimate time of death
what do police do at a crime scene?
arrests the perpetrator if the scenen is "hot", pronounce the scene safe, calls, ambulance, secures the scene
what do EMTs do at aa crime scene?
give immediate medical care, prounounce people dead
what do prosecutors do at a crime scene?
present evidence to the judge to try to prove someone as guilty or innocent
how do mistakes in a criminal investigationcompromise the case?
mistakes can build up on top of each other sending detectives down the wrong paths, etc.
7 steps to experimental design
1. Identify the problem or question
2. Predict a solution to the problem or an answer to the question
3. Design an experiment to test your hypothesis
4. Carry out the experiment
5. Analyze the data and observations
6. State the conclusion
7. Complete a summary paragraph
subjective data
things a person tells you, beliefs, cannot be proven
objective data
information perceptible to the senses; can be proved
vital signs
heart rate/pulse, respiratory rate, etc.
trace evidence
hairs, fibers, glass, small things/evidences that help us figure out where people were
pulse and respiration rate are connected because,
the more your blood pumps, the more oxygen needed for your blood
polygraph tests
record vitals to check when you might be lying vs telling the truth
digital forensic scientist
they track where poeple have gone and what people have posted online, tracking their digital footprint
minutiae
tiny details in a fingerprint, lines, shapes, size, etc.
red blood cells (erythrocytes)
carry oxygen from lungs to body cells, bring up carbon dioxide to be exhaled
white blood cells (leukocytes)
defend our body from disease by fighting the diease and creating antibodies against diseases
Platelets (thrombocytes)
create blood clotting
antigens
Foreign material that invades the body/disease
antibodies
Specialized proteins that aid in destroying infectious agents
aggulation
clumping of red blood cells, like when testing for blood type
blood spatter
Can be analyzed to determine patterns that give investigators clues to how a crime might have happened
blood transfers
when blood is transfered onto other objects
0 blood type
universal donor, no aggulation
AB blood type
universal recipient, A & B aggulation
A blood type
A aggulation
B blood type
B aggulation
hemoglobin
Oxygen carrying pigment in red blood cells
blood spatter analyst
Career responsible for reconstructing a scene based on blood evidence, trying to figure out what happened in the crime due to the certain blood spatter (direction, force, etc)
genome
all of an organism's genetic material
protein
chromosome codes for proteins which codes for a trait
eukaryotes
has nucleus, DNA in nucleus
prokaryotes
no nucleus, DNA in cytoplasm