mol bio exam 3
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
what is a glycosidic bond
bond between sugar and base
how is a dinucleotide formed
sugar’s 3’OH group attacks phosphate group in an atp catalyzed fashion
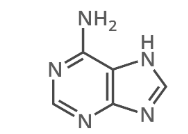
what is this?
adenonine
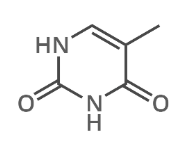
what is this?
thymine
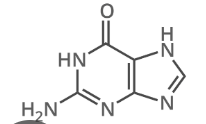
what is this
guanine
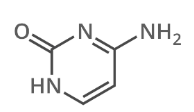
what is this
cytosine
steps of dna replication (general)
initiation at multiple ori; helicase opens bubble; primase (pol alpha) makes primer; dna poly extends 3’ end; topoisomerase prevents supercoiling; rna primers removed and replaced by dna polymerase; ligase seals gaps
leading strand replication
pcna clamp holds dna pol epsilon synthesizes leading strand
moves toward helicase
lagging strand synthesis
moves away from helicase incrementally; ssBP bind ssdna to prevent degradation; pol delta synthesizes lagging strand; ligase ligates nicks in okazaki frags
bacterial replication
signle oriC; dna mediated distortion opens + unwinds DNA; helicase moves 5’ to 3’ on lagging strand (euk go 3’-5’); primase and pol III are recruited; 2nd pol III recruited for lagging strand
bacterial replication termination
only one ter site —> pol III replisomes collide nad dissociate —> topoisomerase and dna gyrase unlink the products
antibiotic target
dna gyrase bc diff enough from topoisomerase
req for antibiotic resistance
mutation changes structure of antibiotic target (making it less fit)
genetic change must occur
change must be inherited
selective pressure req
how do mutations prevent antibiotic use
change the target site
change uptake into the cell (ex: efflux pumps)
- easy to make changes to genetic code bc of operons + easy uptake of genetic material between bacterial cells
what happens if rna primers remain
lagging strand and maybe leading strand will get degraded
how does proofreading work
dNTPs enter DNA pol active site
recognizes correct BP via minor groove interaction via H bond formation
wrong BP unbinds active —> editing site and is cut by exonuclease
Challenge: tautomers resemble other bases and lead to nonstandard BP
role of M2+ in active site of dna pol
to allow negative charges of phosphate groups to come tg
topoisomerase 1
cuts ssDNAt
topoisomerase 2
cuts dsDNA
how are histone mod patterns preserved
g1/s phase —> synthesize histones
make histone modifications before fork is made (dna pol wont be affected and wave of euchr before fork)
h3/h4 tetramers stau associated while h2a/h2b unbind and rebind (w random strand)
chromatin remodeling complexes aid w histone displacement
how does telomerase work
binds 3’ end
adds dNTPs w bound RNA template (repeats many times for long extension)
primer is added near 3’ end
dna poly and ligase
homologous recomb steps
spo11 cuts
strand invasion via rad11
additional dna synth
cleavage
BER summary
glycosylase flips out base and cuts glycosidic bonds
AP endonuc and phosphodiesterase remove sugar phosphate
dna poly and ligase (may replace a flap)
NER steps
excision nuc cuts strands
helicase separates them
cut piece is released
poly and ligase
transcription coupled NER
rna pol II pauses at damage
backs up
repair mechanism
MMR
MSH binds to mismatch site
MLH cuts backbone of newly synth (nascent strand)
strand removal
dna pol + ligase
HDR steps
dsDNA break —> overhang creation
rad51 facilitates invasion
dna pol extends using template
uninvasion + ligation
MMR as needed
NHEJ
Ku heterodimers bind broken ends
nt removed during processing —> overhangs
join endsin
innate immunity
aggresssive and broadly reactive
immediate detection of intruders
adaptive immunity
intelligent and specific
tailored response
aggressive or suppressive
rag complex
made of rag1 + rag2 binding to rss motifs
catalyze ds breaks between rss and gene segment
proper alignment may req looping
mechanism of vdj recombination
rag complex binds to rss motifs + catalyzes dsDNA breaks
creates hairpins at coding ends
endonuc, artemis are recruited and activated by dna pKcs —> cleaves hairpin loop and generates overhangs
Tdt randomly adds non templated nucleotides
NHEJ using Ku proteins and ligase —> RSS ends turn into signal joint
what are piRNAs
silence transposable elements and help maintain genomic stability
longer than mirRNAs
bound by piwi proteins
transcribed by uni/ bidirectional transposons
function of pirnas
allow transposon rna degradation (ex: post-transcriptional silencing)
can direct dna methylation of transposon/ repetitive elements
relevance
important in germline + stem cells
affect fertility
implicated in cancer
pirna vs mirna
mirna req dicer
pirna can act pre/ post transcriptionally
transposition
transposase —> loop + ds break to remove transposon in donor chromosome
ds break repaired via nhej
new loc is cut and transposon added