Orgo Lab Exam 2
1/237
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
238 Terms
What is the importance of working in a chemical fume hood
Protect ourselves from the noxious fumes of the chemicals
Why do we need to clamp glassware?
To prevent the glassware from tipping over
What are some everyday uses of salicylic acid
Acne creams (Facial wash, CereVe and Cetaphil)
Antibacterial agent
Anti-dandruff agent
Precursor to aspirin and Bengay relief cream
Methyl salicylate and salicylic acid are ________ products, meaning they can be found in nature
natural
What is the appearance of methyl salicylate
liquid with minty smell
How is salicylic acid synthesized
Methyl salicylate (l) reaction with NaOH and HCl to replace the ester group on methyl salicylate with a carboxylic acid group to form salicylic acid (s)
Synthesis reaction of salicylic acid
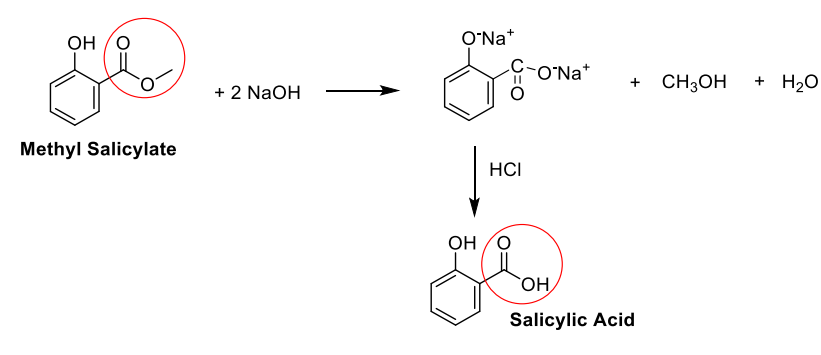
The reaction to form salicylic acid is a __________-promoted reaction
Base promoted
The based (OH-) is a nucleophile that adds to the ester and forms part of the product.
Why is the synthesis of salicylic acid base-promoted and not base-catalyzed?
the base (OH–) is the nucleophile that adds to the ester and forms part of the product. It participates in the reaction and is not regenerated later
Hydrolysis of Triacylglycerols
The three ester groups are cleaved to form glycerol and three long-chain fatty acids
Lipase-catalyzed reaction
Hydrolysis of Triacylglycerols Reaction
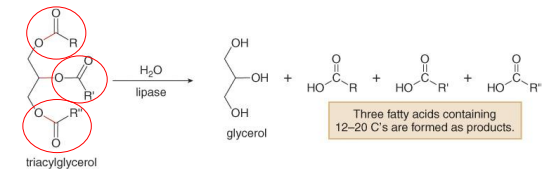
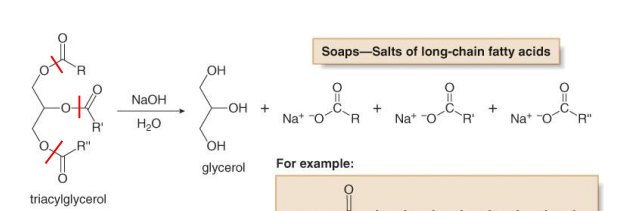
What is Saponification
conversion of ester functional group into carboxylic acid with a base
Experimental details: What glassware and equipment are used in the salicylic acid synthesis lab?
Erlenmeyer flask (Reaction flask)
Ring stand with clamp
Magnetic stir bar
Graduated cylinders
Hot/Stir plate (Heat and stirring will be used)
Pasteur pipettes
What reagents are used in the synthesis of salicylic acid?
methyl salicylate (l), sodium hydroxide/NaOH (l) and Hydrochloric acid/HCl (l)
How do you calculate theoretical yield?
moles of limiting reagent x mol ratio x MW of product = g of product
How do you calculate the theoretical yield of salicylic acid?
mol of methyl salicylate x mol ratio (SA/Methyl salicylate) x MW SA (g/mol) = X g of salicylic acid
What is the limiting reagent in salicylic acid synthesis?
methyl salicylate
How do you calculate precent yield
% Yield = Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield x 100
How to calculate percent yield in mulitstep synthesis
the overall percent yield is determined by multiplying the yield of each step expressed as a decimal then multiply by 100
(% yield 1 x % yield 2 x % yield 3) × 100
What is recrystallization?
Convenient way to purify a solid organic compound by using a suitable solvent.
What is the rule for selecting a good solvent for recrystallization?
The solid you are trying to purify should be soluble in the hot solvent and insoluble in a cold or room temperature solvent.
Vacuuum Filtration Schematic
In drawing of schematic include:
Buchner funnel
Adapter
Clamp on neck of vacuum flask
Ring stand
Rubber tubing
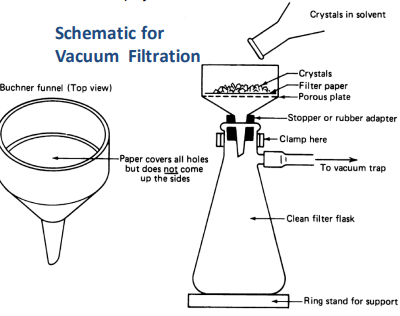
Vacuum filtration: why do we use a rubber adapter?
To ensure a tight seal between Buchner funnel and vacuum flask
Vacuum filtration: why do we use heavy-walled rubber tubing?
to prevent the tubing from collapsing from atmospheric pressure on the outside when the vacuum is applied
What is melting point range?
The temperature range with a compound changes from solid to liquid phase and loses order of crystalline lattice
Presence of impurities (purple above) will ________the observed MP range of a compound
Decrease
They disrupt the crystalline lattice of the product (salicylic acid/aspirin)
Digital MeltTemp: How to read melting point range
First reading of the range: temperature at which the solid block first begins to liquefy
Second reading of the range: temperature at which the solid is completely melted
Digital MeltTemp: Why does the sample have to be heated slowly?
Thermometer Lag – occurs when the sample melts before the thermometer has a chance to reach that temperature – leading to a depressed MP range
Broad range – is observed when melting too quickly.
Digital MeltTemp: Sample for testing MPR are placed in a _________ tube
capillary
Synthesis of Salicylic Acid: Waste Disposal Procedure
Collect filtrate in a 250 ml Beaker labelled “waste acidic filtrate” and neutralize it at the Neutralizing hood with NaHO3
Stir beaker and check pH
When pH is neutral (green) dispose of the neutralized solution in the sink with lots of water
Methyl salicylate is treated with ______ ______ in water to convert the methyl ester group to carboxylic acid
sodium hydroxide
Why is an Erlenmeyer flask used in the synthesis of salicylic acid lab
The sloping sides help reduce the amount of solvent the evaporates and splashing
Hazard: Sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid are _________
corrosive
In recrystallization, why does the solution need to cool slowly?
So the impurities will remain in the filtrate
What is another name for the filtrate or bulk solution of a reaction
mother liquor
At what approximate temperature will the reaction mixture containing methyl salicylate and 30 mL of an aqueous solution of 4M sodium hydroxide boil?
100 ºC (BP of water)
Why is it important to clamp your vacuum filter flask, even though it has a flat bottom?
Salicylic acid has some solubility in water. What would happen if you washed your crystals with too much water, during vacuum filtration?
The product salicylic acid crystals will be lost
What happens with HCl is added to solution of methyl salicylate and NaOH?
A white precipitate (salicylic acid) will form
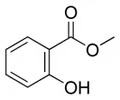
Methyl salicylate Structure
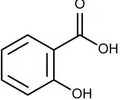
Salicylic Acid structure
How to find mass solution using density and volume
Density x volume= mass
Why is it necessary to empty out the the filtrate from the vacuum filter flask, before pulling air over the crystals being dried inside the Buchner funnel?
The filtrate must be emptied from the flash so it does not decrease the pressure in the vacuum system when the salicylic crystals are drying
Are large crystals more likely to form when solutions are cooled quickly or slowly? and Why?
Large crystals are more likely to form when the solution is cooled slowly because all the impurities will have enough time to return to the solution
How is aspirin synthesized from salicylic acid?
the phenol group of salicylic acid is transformed into a ester group
Appearance of salicylic acid
White needle-like crystals
What are the medicinal effects of aspirin
analgesic (pain reliever)
Antipyretic (fever reducer)
Anti-inflammatory
What is the chemical name of aspirin
Acetylsalicylic acid
The synthesis of aspirin from salicylic acid is a __________ reaction
esterfication
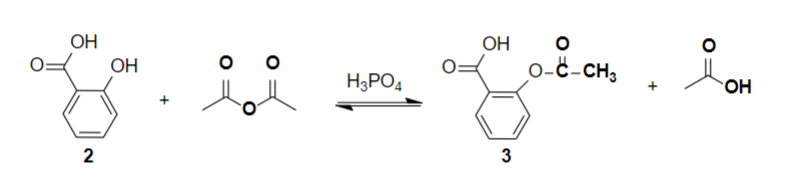
Synthesis reaction of aspirin
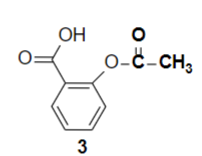
Structure of Aspirin
The Synthesis of Aspirin, why is acetic anhydride in excess?
it is required to drive the reaction towards completion
In the synthesis of aspirin, acetic anhydride serves as the _________
solvent
Structure of acetic anhydride
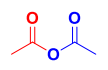
The synthesis of aspirin is a _____-step reaction
2
What acid catalyst is required in the synthesis of aspirin?
Phosphoric acid (H3PO4)
To favor the formation of aspirin, _____ equivalents of acetic anhydride are used to every 1 equivalent of salicylic acid
3
What is the limiting reagent in the synthesis of aspirin?
salicylic acid
What is an equivalent?
The experimental mol ratio of the limiting reactant to another reactant
How do you calculate the theoretical yield of aspirin?
X g SA x 1 mol Aspirin/1 mol SA x MW Aspirin = X g Aspirin
How do you calculate the overall yield of aspirin synthesis (Lab A and B)
[(% yield from Lab A) x (% yield from Lab B) x 100
Which solvent is best for the recrystallization of aspirin? Water or ethanol?
Water because aspirin does not dissolve in water at room temperature/ cold
Aspirin purity check with Iron chloride (FeCl3): What function group reacts with FeCl3
Phenols react with FeCl3 to produce a deep purple solution, meaning there are traces of salicylic acid in aspirin product
Phosphoric acid is a _________ chemical
corrosive
Acetic anhydride is a _________ chemical and nasal ____________
corrosive and irritant
What is halogenated waste?
Chemical waste containing halogens (Cl, F, I, Br)
Aspirin synthesis: ethanol should be disposed of in _________
the non-halogenated waste container
Aspirin synthesis: solution from aqueous FeCl3 should be disposed of in _________
The FeCl3 waste container
What are the six classification of chemical hazards?
1) Flammable- Easily ignitable material with low flash point temp
2) Corrosive- Attack and destroy exposed body tissues (chemical burns)
3) Lachrymator- Causes watering in eyes
4) Carcinogen- Causes cancer
5) Teratogen- interfere with fetal development
6) Reactive- Explode (BOOM)
What are some examples of flammable chemicals?
Diethyl ether, acetone and tert-butyl methyl ether
What are some examples of corrosive chemicals?
Most are strong oxidizers, strong bases and acids
Ex: H2SO4, NaOH, HNO3, Ca(OH)2, Br2
What are some examples of lachrymator chemicals?
Thionyl chloride, Acrolein, Methacryloyl chloride
What are some examples of teratogenic chemicals?
Phenol, Benzene, Dinitrotoluene, Dioxane
What are some examples of reactive chemicals?
Na metal, sodium hydride, calcium carbide
What are some examples of carcinogenic chemicals?
Benzene, Arsenic, Methylene chloride (or Dichloromethane/DCM)
National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) Ratings
Blue: Health Hazard
Red: Fire Hazard
White: Specific Hazard
Yellow: Reactivity Hazard

Merck Index: Where can you find the density of a compound?
In the properties labeled as d25, d20 or D15
Merck Index: What does nD stand for?
The refractive index (NOT density)
What is the melting point range of salicylic acid?
158-160 C
What is the melting point range of aspirin?
134-136 C
What is the boiling point range of acetic anhydride?
138-140 C
What is miscibility?
The forming a homogenous mix between tow chemicals
Why are miscible liquids not suitable for extraction?
Two liquids are in a homogenous mixture so they cannot be separation
You must have two (miscible or immiscible) liquids for liquid-liquid extraction
immiscible
What is the physical appearance of aspirin?
White shiny crystals
Schematic for liquid extraction
Include: Ring stand, stopcock, Erlenmeyer flask, stem, sep funnel and glass stopper and short/long stem funnel
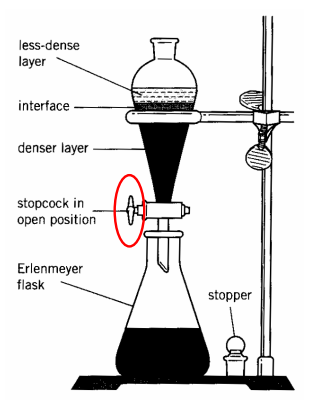
In a separatory funnel, the layers settle based on……
densities and miscibility
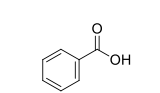
Structure of benzoic acid
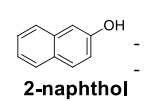
Structure of 2-naphthol
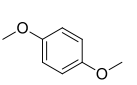
Structure of 1,4-dimethoxy benzene
In the separatory funnel, the more dense layer is the ______ layer
bottom
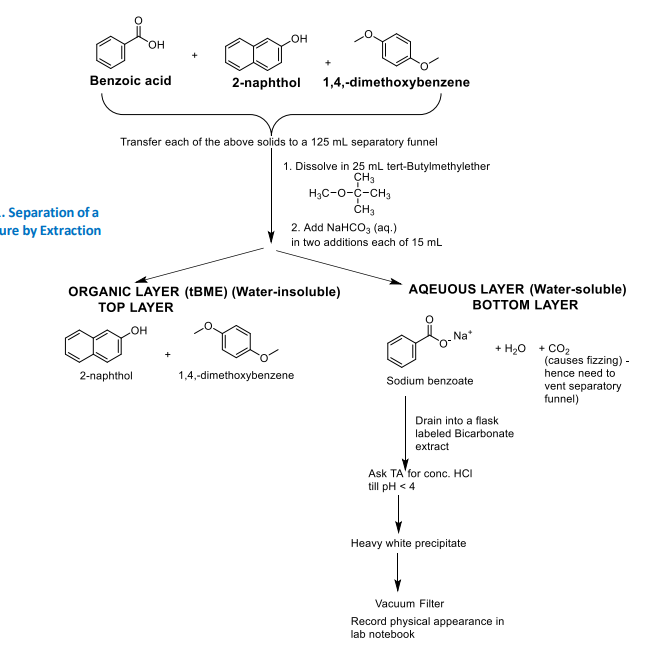
Flow chart of ternary mix by extraction
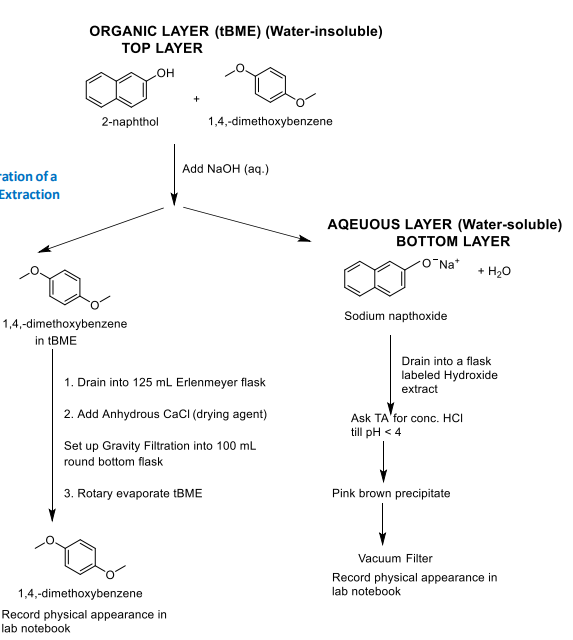
Flow chart of ternary mix by extraction part 2
What are the forces that control Solubility?
Van der Waals forces
Dipole-Dipole Forces
Hydrogen Bonding
Theory of Extraction
It is always better to several smaller extraction than one big extraction because it increases the theoretical recovery of the product
How to calculate the partition or distribution coefficient K

Aqueous solution are immiscible with __________ solvents such as ether, hexane and methylene chloride
organic
What are drying agents?
Anhydrous salts that will bond with water mixed in product and retains it as a water of crystallization
Removed from product using gravity filtration
When a drying agent is added, first it clumps together, it becomes _________ when enough is added
free floating
Gravity filtration vs Vacuum filtration
Gravity filtration is used when a solute is mixed with a low-boiling solvent whereas vacuum filtration is used when it is mixed with a high-boiling organic
Gravity filtration to remove from product