PSYC102: CH9 - Motivation & Emotion
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Emotion
Motivated mental state or feeling associated with our our evaluation of our experiences
Discrete Emotions Theory
Theory that humans experience a small number of distinct emotions that are rooted in our biology
Primary Emotions
Small number (perhaps 7) of emotions believed by some theorists to be cross-culturally universal
Display Rules
Cross-cultural “guidelines” for how and when to express emotions
Cognitive Theories of Emotion
Propose emotions are products of thinking
James-Lange Theory of Emotion
Emotions result from our interpretations of our bodily reactions to stimuli
Somatic Marker Theory
Theory proposing that we use our “gut reactions” to help us determine how we should act
Cannon-Bard Theory
An emotion provoking event leads simultaneously to an emotion and to bodily reactions
Two-Factor Theory
Emotions are produced by an undifferentiated state of arousal along with an attribution (explanation) of that arousal
Motivation
Drives that propel us in a specific direction, used for achieving goals
Goals
Physiological, Hedonic, Gain, Social, Cognitive
Drives
Internal states caused by lack of equilibrium in an organism’s physiological needs
Drive Reduction Theory
Certain drives motivate us to act in ways that minimize aversive states
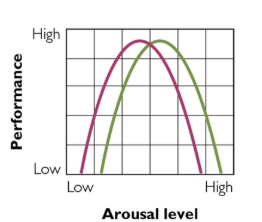
Yerkes-Dodson Law
A non-linear relationship between arousal and performance
Approach Drives
Motivated toward something desirable or rewarding
Studying to get a scholarship
Eating a dessert
Avoidance Drive
Motivated away from something unpleasant, harmful, or threatening
Not touching a hot stove
Avoiding an argument
Incentive Theories
We are motivated to pursue goals by positive outcomes
Extrinsic Motivation
People are motivated by external goals
Doing chores to get an allowance
Studying to get a good grade
Intrinsic Motivation
People are motivated by internal goals
Studying because a topic is interesting
Running because it feels good
Glucostatic Theory
When our blood glucose levels drop, hunger creates a drive to eat to restore the proper level of glucose
Priming
Exposed to information that “activate” hunger and eating related information
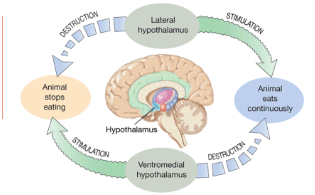
Hypothalamus
Lateral Hypothalamus: Key role in initiating eating
Ventromedial Hypothalamus: Let us know when to stop eating