VI : Cytokines
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
• Innate immunity
• Adaptive response to infection
Cytokines are small Soluble Proteins That Regulate
• Bacterial lipopolysaccharides
• Flagellin
• Other bacterial products
• Ligation of cell-adhesion molecules
Cytokines are Induced In Response To Specific Stimuli
• Synergy
• Pleiotropy
• Redundancy
• Antagonism
Different Ways Cytokines Act
Synergy
Different Ways Cytokines Act
– cytokines act together.
Pleiotropy
Different Ways Cytokines Act
– 1 cytokine has many actions.
Redundancy
Different Ways Cytokines Act
– different cytokines have the same function.
Antagonism
Different Ways Cytokines Act
– cytokines counteract each other.
• Regulation of Growth
• Differentiation
• Gene Expression
In Vivo Effects of Cytokine Expression on Leukocytes & Other Cells
• Autocrine Stimulation
• Paracrine Stimulation
• Systemic/Endocrine Activities
Cytokines Exert Effects Through
T
Cytokines have Multiple Actions Due To:
• Widespread distribution of receptors on many cell types. (t/f)
T
Cytokines have Multiple Actions Due To:
• Ability to alter expression of numerous genes. (t/f)
F
Cytokines may share properties & receptors.
Cytokines may not share properties & receptors. (t/f)
T
Cytokines can determine whether the host will be able to mound an effective defense. (t/f)
T
Cytokines can determine whether the host will be able to mound an effective defense. (t/f)
• Tumor Necrosis Factors (TNFs)
• Interferons (IFNs)
• Chemokines
• Transforming Growth Factors (TGFs)
• Colony-Stimulating Factors (CSFs)
Cytokines Major Families
• Interleukin – 1 (IL – 1)
• Tumor Necrosis Factors (TNFs) – alpha
• Interleukin – 6 (IL – 6)
• Chemokines
• Transforming Growth Factor – BETA
• Interferons Alpha & Beta
Cytokines Involved in Triggering Recruitment of Effector Cells
Interleukin – 1 (IL-1)
- Acts as an endogenous pyrogen.
Interleukin – 1 (IL-1)
- Induces fever in the acute-phase response through its actions on the hypothalamus.
• Vascular cell-adhesion molecules
• Chemokines
• IL– 6
Interleukin -1 (IL-1) Induces the production of:
IL – 1a
IL – 1b
IL – 1RA
Interleukin – 1 (IL-1) induces :
• Monocytes
• Macrophages
• Dendritic Cells
DMM
IL – 1a & IL – 1b Are Proinflammatory Cytokines Produced By:
• Fever
• Activation of Phagocytosis
• Production of acute-phase proteins
IL – 1b is Responsible for most of the systemic activity attributed to IL – 1:
ILRA
It acts as an antagonist IL – 1 by blocking the IL – 1 receptor & limiting the availability of the receptor for IL – 1.
Tumor Necrosis Factors (TNFs) – alpha
- Most prominent of TNF family
Tumor Necrosis Factors (TNFs) – alpha
- Exists in membrane-bound & soluble forms.
Tumor Necrosis Factors (TNFs) – alpha
- Causes vasodilation & ↑ vasopermeability.
Tumor Necrosis Factors (TNFs) – alpha
- Is triggered by presence of lipopolysaccharide (found in gram – bacteria).
Tumor Necrosis Factors (TNFs) – alpha
- Is secreted by activated monocytes & macrophages.
Tumor Necrosis Factors (TNFs) – alpha
- Can activate T cells through its ability to induce expression of MHC class II molecules, vascular adhesion molecules, & chemokines, in a similar manner to IL – 1.
Chemokines
- Enhance motility & promote migration of many types of WBC toward the source of the chemokine (chemotaxis).
• Alpha (CXC)
• Beta (CC)
• C
• CX3C
Chemokines are classified into 4 families based on the position of N-terminal cysteine residues:
Chemokines
- Are involved in the initiation & development of inflammatory responses in numerous dx process.
Chemokines
- Combined into the tx in areas of inflammation
Type I Interferons (IFN– Alpha & IFN–Beta)
- Interfere with viral replication.
Type I Interferons (IFN– Alpha & IFN–Beta)
- Are produced by dendritic cells.
Type I Interferons (IFN– Alpha & IFN–Beta)
- Induce production of proteins & pathways that interfere with viral replication & cell division.
Type I Interferons (IFN– Alpha & IFN–Beta)
- Activate natural killer cells.
Type I Interferons (IFN– Alpha & IFN–Beta)
- Enhance the expression of MHC Class I proteins
Type I Interferons (IFN– Alpha & IFN–Beta)
- Are active against certain malignancies & other inflammatory processes.
Cytokines in Adaptive Immune Response
- Are mainly secreted by T cells, especially T helper cells.
Cytokines in Adaptive Immune Response
- Affect T & B cells functions more directly than cytokines involved in the innate & immune response.
• Th1
• Th2
• T regulatory Cells (Tregs)
Cytokines in Adaptive Immune Response
- 3 Main Subclasses of Cd4+ T Cells:
Cytokines in Adaptive Immune Response
- When the T-cell receptor (TCR) on a CD4+ T helper cell capture antigen, clonal expansion of the T cell occurs.
Cytokines in Adaptive Immune Response
- Differentiation into Th1, Th2, o Tregs cell lineages is influenced by the spectrum of cytokine expressed in the initial response
Interferon gamma
Interleukin-2 / T-cell Growth Factor
Th1 Cytokines
Interleukin–4 (IL–4)
Interleukin–10 (IL–10)
Th2 Cytokines
T regulatory Cell (Tregs)
- Are CD4+ & CD25+ T cells.
T regulatory Cell (Tregs)
- Helps establish peripheral tolerance to various self-antigens, allergens, tumor antigens, transplant antigens, & infectious agents.
T regulatory Cell (Tregs)
- Produce TGF–B that suppresses other T cells.
T regulatory Cell (Tregs)
- Induce IL–10 & TGF–B expression in adaptive Tr1 cells in the peripheral circulation.
• Il–10 inhibition of proinflammatory cytokines
• Inhibition of costimulatory molecule expression on APCs.
T regulatory Cell (Tregs)
- T–cell suppression occurs through:
T regulatory Cell (Tregs)
- The immune response is down-regulated, & chronic inflammation is prevented.
Th17
Cytokines in Both Innate & Adaptive Immunity
Th17
- Have a role in host defense against bacterial & fungal infections at mucosal surfaces.
Th17
- Involves Th17 cell secreting IL-17 family of cytokines to promote continuous recruitment of neutrophils.
Th17
- Promote release of antimicrobial peptides.
Th17
- When dysregulated, have been implicated in pathogenesis of multiple inflammatory diseases & several autoimmune conditions.
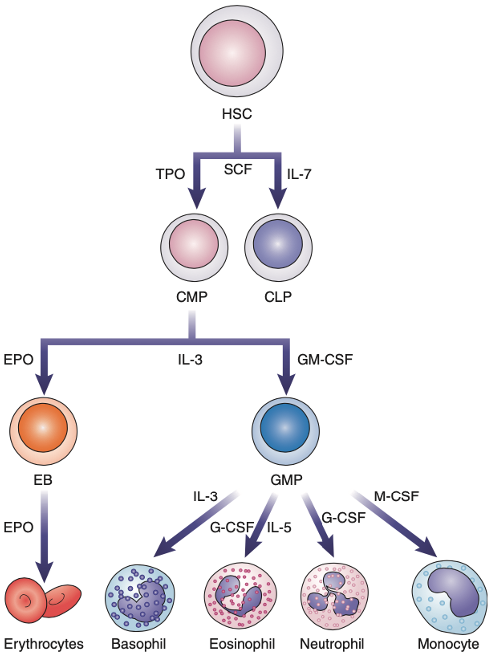
• Interleukin–3 (IL–3)
• Erythropoietin (EPO)
• Granulocytes (G–CSF)
• Macrophage (M–CSF)
• Granulocyte–Macrophages (GM–CSF)
Colony–Stimulating Factors (CSFs)
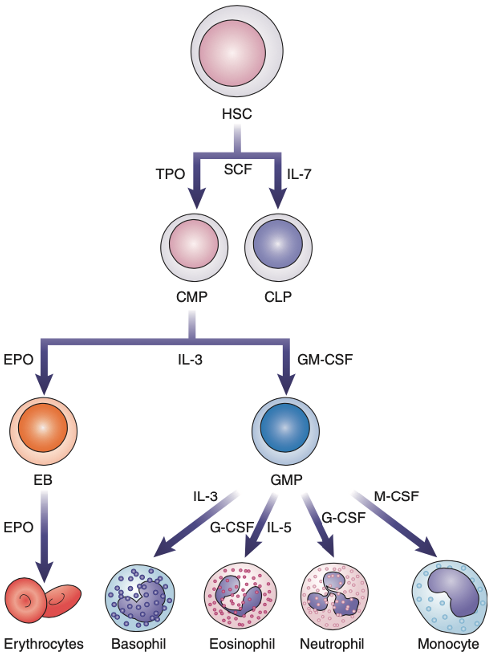
Colony–Stimulating Factors (CSFs
Stimulate growth of hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow in response to inflammatory cytokines such as IL–1.
Erythropoietin (EPO)
- Is primarily produced in the kidneys.
Erythropoietin (EPO)
- Regulates RBC production in the bone marrow.
F
- RBC proliferation induced by EPO improves oxygenation of the tissues & eventually switches off EPO production.
Erythropoietin (EPO) (t/f)
- RBC proliferation induced by EPO improves oxygenation of the tissues & eventually switches on EPO production.
T
Cytokines & Anticytokine Therapies (t/f)
• Disrupt the interaction between cytokines (e.g. inflixmab)
F
• Some use monoclonal antibodies that function as cytokine agonists.
Cytokines & Anticytokine Therapies (t/f)
• Some do not use monoclonal antibodies that function as cytokine agonists.
T
Cytokines & Anticytokine Therapies (t/f)
• Some use hybrid proteins containing cytokine receptor binding sites attached to immunoglpbulin constant regions to block cytokine activity (e.g. etanercept)
F
• Some block IL-17 function (e.g. ixekizumab)
Cytokines & Anticytokine Therapies (t/f)
• Some block IL-7 function (e.g. ixekizumab)
• ELISpot Assay
• Multiplexed ELISAs
• Microbead Assays –
Clinical Assays for Cytokines
Multiplexed ELISAs
Clinical Assays for Cytokines
– can detect 12 to 25 pro & anti-inflammatory cytokines in one reaction.
ELISpot Assay
Clinical Assays for Cytokines
– employs the ELISA technique on vitro activated peripheral WBCs.
Microbead Assays
Clinical Assays for Cytokines
– allow the simultaneous detection of multiple cytokines in a single tube.
b. pleiotropy.
The ability of a single cytokine to alter the expression of several genes is called
a. redundancy.
b. pleiotropy.
c. autocrine stimulation.
d. endocrine effect.
a. Mediation of the innate immune response
Which of the following effects can be attributed to IL-1?
a. Mediation of the innate immune response
b. Differentiation of stem cells
c. Halted growth of virally infected cells
d. Stimulation of mast cells
d. All of the above
Which of the following precursors are target cells for IL-3?
a. Myeloid precursors
b. Lymphoid precursors
c. Erythroid precursors
d. All of the above
d. Decreased eosinophil count
A lack of IL-4 may result in which of the following effects?
a. Inability to fight off viral infections
b. Increased risk of tumors
c. Lack of IgM
d. Decreased eosinophil count
c. IL-2
Which of the following cytokines is also known as the T-cell growth factor?
a. IFN-γ
b. IL-12
c. IL-2
d. IL-10
a. Increased IL-2 receptor expression by the Th cell producing it
Which of the following represents an autocrine effect of IL-2?
a. Increased IL-2 receptor expression by the Th cell producing it
b. Macrophages signaled to the area of antigen stimulation
c. Proliferation of antigen-stimulated B cells
d. Increased synthesis of acute-phase proteins
throughout the body
d. IFN-α and IFN-β inhibit cell proliferation, whereas IFN-gamma stimulates antigen presentation by class II MHC molecules.
IFN-α and IFN-β differ in which way from IFN-gamma?
a. IFN-α and IFN-β are called immune interferons, and IFN-gamma is not.
b. IFN-α and IFN-β primarily activate macrophages, whereas IFN-gamma halts viral activity.
c. IFN-α and IFN-β are made primarily by activated T cells, whereas IFN-gamma is made by fibroblasts.
d. IFN-α and IFN-β inhibit cell proliferation, whereas IFN-gamma stimulates antigen presentation by class II MHC molecules.
b. TNF
A patient in septic shock caused by a gram-negative bacterial infection exhibits the following symptoms: high fever, very low blood pressure, and disseminated intravascular coagulation. Which cytokine is the most likely contributor to these symptoms?
a. IL-2
b. TNF
c. IL-12
d. IL-7
c. IFN-gamma
IL-10 acts as an antagonist to what cytokine?
a. IL-4
b. TNF-α
c. IFN-gamma
d. TGF-β
d. ELISA testing
Which would be the best assay to measure a specific cytokine?
a. Blast formation
b. T-cell proliferation
c. Measurement of leukocyte chemotaxis
d. ELISA testing
b. Decrease in IL-2
Selective destruction of Th cells by the human immunodeficiency virus contributes to immune suppression by which means?
a. Decrease in IL-1
b. Decrease in IL-2
c. Decrease in IL-8
d. Decrease in IL-10
b. Increase production of certain types of leukocytes
Why might a colony stimulating factor be given to a cancer patient?
a. Stimulate activity of NK cells
b. Increase production of certain types of leukocytes
c. Decrease the production of TNF
d. Increase production of mast cells
a. Decreased ability to fight gram-negative bacterial infections
Which of the following would result from a lack of TNF?
a. Decreased ability to fight gram-negative bacterial infections
b. Increased expression of class II MHC molecules
c. Decreased survival of cancer cells
d. Increased risk of septic shock
c. IL-12
Which cytokine acts to promote differentiation of T cells to the Th1 subclass?
a. IL-4
b. IFN-α
c. IL-12
d. IL-10
b. Suppression of the immune response by inducing IL-10
What is the major function of T regulatory cells?
a. Suppression of the immune response by producing TNF
b. Suppression of the immune response by inducing IL-10
c. Proliferation of the immune response by producing IL-2
d. Proliferation of the immune response by inducing IL-4
d. TNF-α and IL-6
Th17 cells affect the innate immune response by inducing production of which cytokines?
a. IFN-γ and IL-2
b. IL-4 and IL-10
c. IL-2 and IL-4
d. TNF-α and IL-6