Connective Tissue
1/6
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Provides structure framework for the body. Transports fluids and dissolved materials. Protects organs, stores energy, and defends body against invading microorganisms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
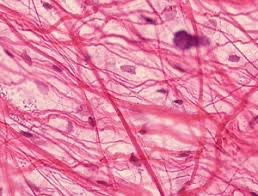
Areolar Tissue - Loose Connective Tissue
Location
Deep dermis of skin, covered by the epithelial lining of the digestive, respiratory, and urinary tracts. Around joints, blood vessels, and nerves.
Function
Cushions organs, provides support, permits independent movement; phagocytic cells provide defense against pathogens.
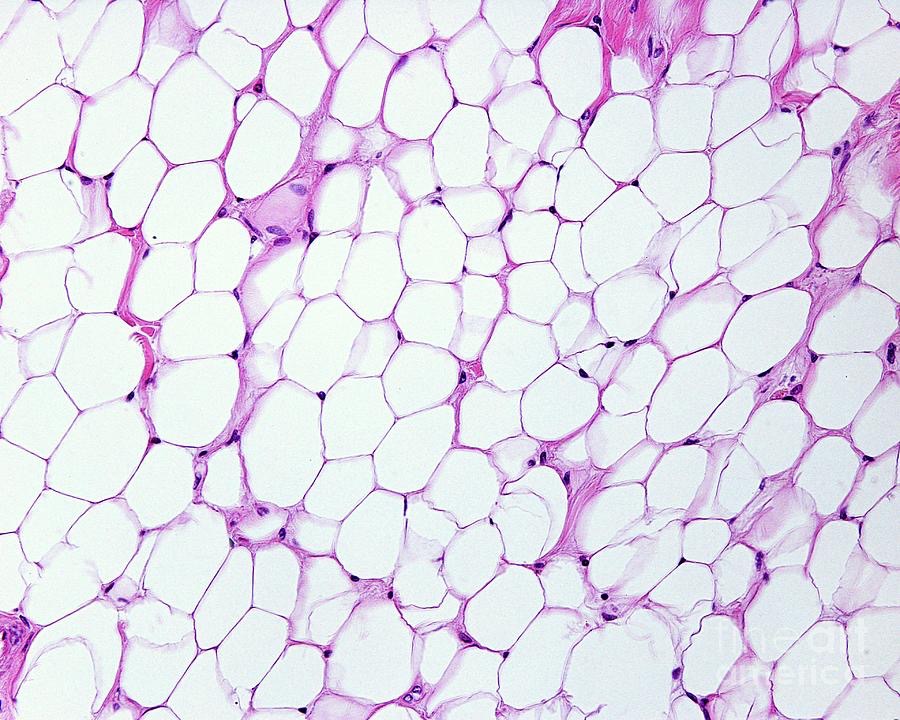
Adipose Tissue (fat) - Loose Connective Tissue
Location
Deep in tissue, especially at sides, buttocks, and breasts; padding around eyes and kidneys.
Function
Provides padding and cushions sock; insulates; and stores energy.

Dense Regular Connective Tissue - Dense Connective Tissue
Location
Between skeletal muscles and skeleton (tendons & aponeuroses; between bones or stabilizing positions of internal organs ligaments); covering skeletal muscles; deep fasciae
Function
Provides firm attachment; conducts pull of muscles; reduces friction between muscles; stabilizes position of bones
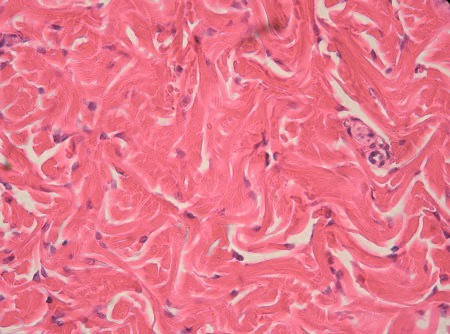
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue - Dense Connective Tissue
Location
Capsules of visceral organs, periostea and perichondria; nerve and muscle sheaths; dermis
Function
Provides strength to resist forces from many directions; helps prevent over expansion of organs, such as the urinary bladder.
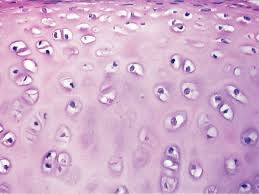
Hyaline Cartilage
Location
Between tips of ribs and bones of sternum; covering bone surfaces at synovial joints; supporting larynx, trachea, and bronchi forming parts of nasal septum.
Function
Provides stiff but flexible support. Reduces friction between bony surfaces.

Osseuos Connective Tissue
Function: Provide Structure, protect vital organs
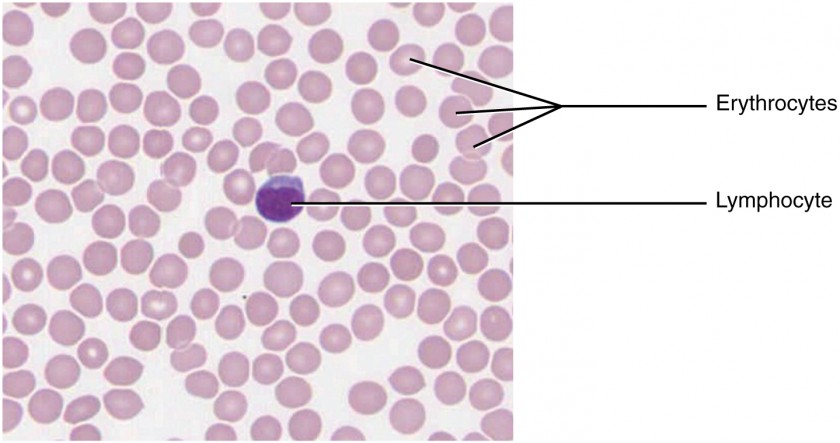
Vascular Connective Tissue
Function: Transport nutrients, oxygen, waste, hormones throughout the body. Contains white blood cells to fight pathogens.