AP Psychology: Unit 2 Part 1: Biological Bases of Behavior (Brain)
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
144 Terms
gentically predisposed
is an increased likelihood of developing a particular disease based on a person's genetic makeup.
Rosenzweig Study
1984 research study showing that rats raised in enriched environments developed thicker cortices than those in impoverished environment.
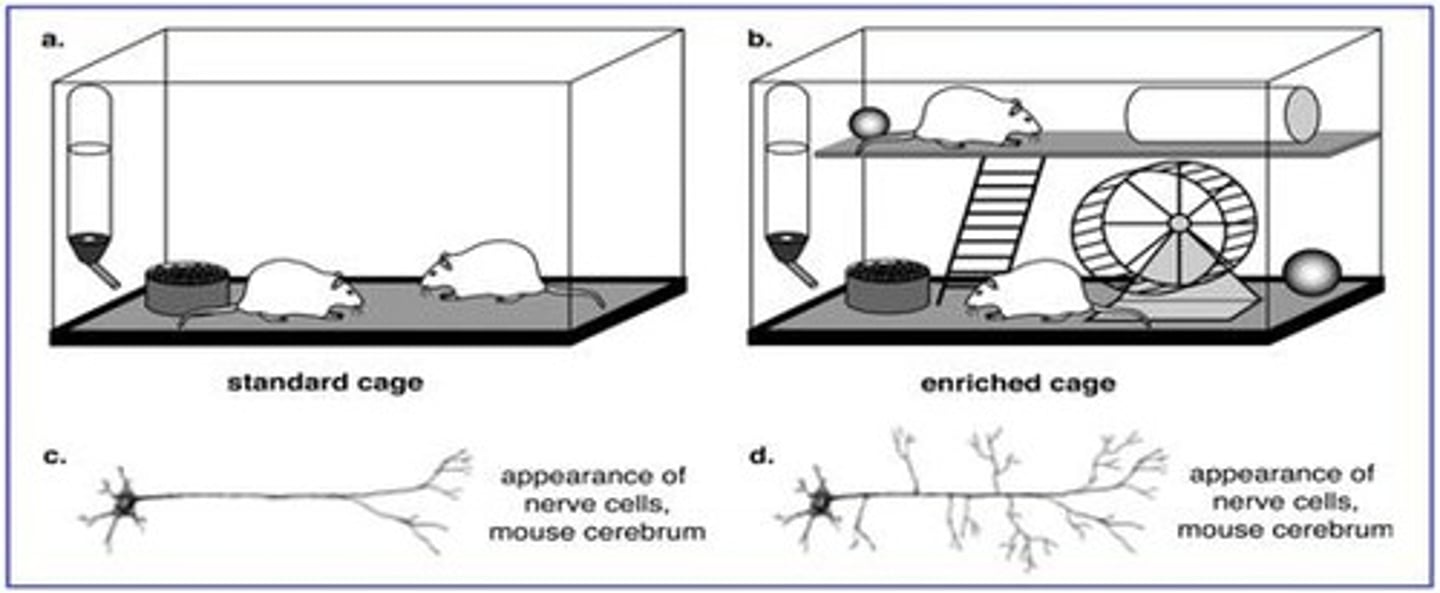
Temperament
refers to a person's stable emotional reactivity and intensity.
Heritability
Variation among people due to differing genes; "differences due to genes; "Group variation in trait explained by genetics
Phrenology
first attempt at localizing functions of brain and giving meaning to "bumps" on the head; considered a pseudo psychology

Nature
referring to ones genes
Nurture
referring to ones environment
James Olds Experiment
Discovered the pleasure center of the brain; He put the rat in a box and stimulated its brain whenever the rat approached a certain corner. Further research showed that stimulation of areas in the limbic system produced pleasure in humans, too; Hypothalamus stimulated and dopamine released.

Right brain hemisphere specialization
Side of the brain responsible for colors, daydreaming, 3D, rhythm, imagination, geometry, distance, sense of direction, faces, emotional expressions
Left brain hemisphere specialization
Side of the brain responsible for words, letters, language, verbal memory, numbers lists, logic, analysis
split-brain patients
A person with corpus callosum severed (often for reasons of eliminating seizures; misfiring in the brain)...in an experiment to show the separation of the hemispheres objects (an apple) presented in the right visual field CAN be named. Objects (a pencil) in the left visual field CANNOT. (Gazzaniga)
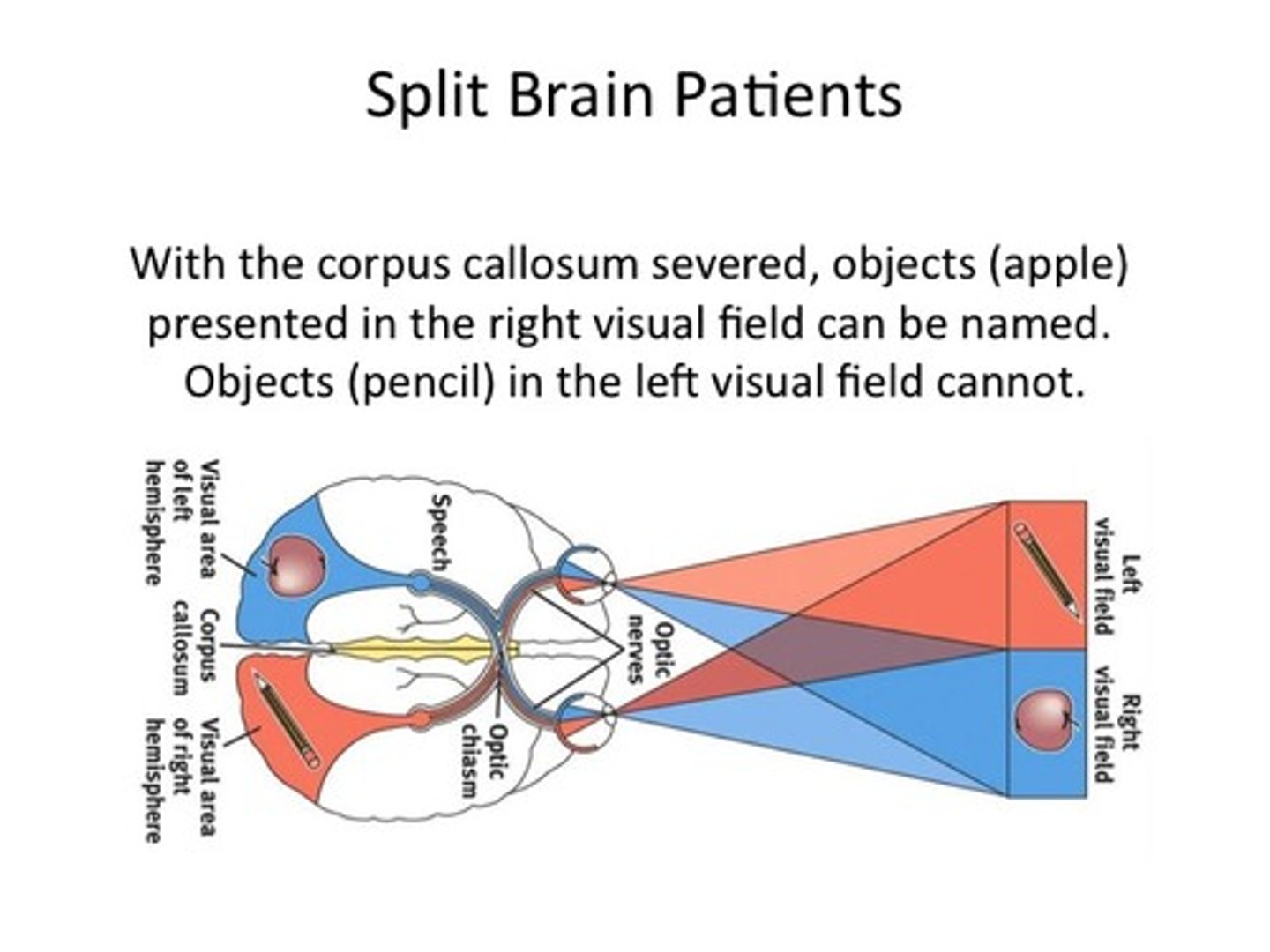
plasticity
the brains ability to taken on functions of missing or damaged areas
thyroid
part of the endocrine system that affects metabolism
parathyroid
part of the endocrine system that regulates the level of calcium in the blood
pancreas
part of the endocrine system that regulates the level of sugar in the blood
gonads
is an endocrine gland that produces the gametes (sex cells) of an organism; testis/male and ovaries/female.
grey matter
in the brain the outer processing layer; it contains numerous cell bodies and relatively few myelinated axons
white matter
in the brain the interconnecting core; it contains relatively very few cell bodies and is composed chiefly of long-range myelinated axon
testis
part of the endocrine system that secretes male sex hormones
ovaries
part of the endocrine system that secretes female sex hormones
homeostasis
A tendency to maintain a balanced or constant internal state; the regulation of any aspect of body chemistry, such as blood glucose, around a particular level
Inhibitory
negative signal sent to the dendrite (-); signal that makes a neuron LESS likely to generate an action potential.
Excitatory
positive signal sent to the dendrite (+); signal that makes a neuron MORE likely to generate an action potential.
Nodes of Ranvier
also known as myelin sheath gaps, are periodic gaps in the insulating myelin sheaths of myelinated axons where the axons membrane is exposed
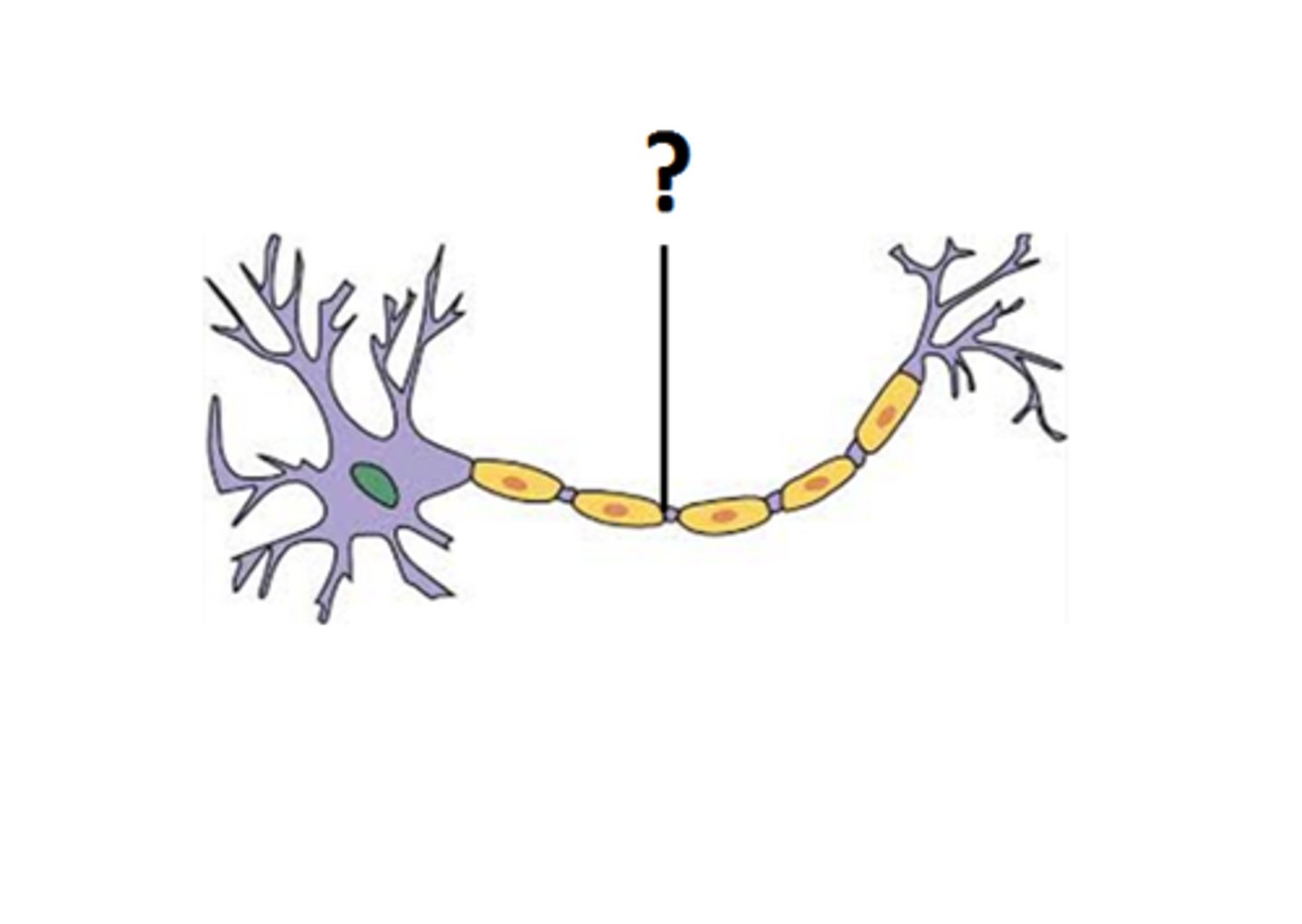
Schwann Cells
any of the cells in the peripheral nervous system that produce the myelin sheath around neuronal axons.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
is a nervous system disease that affects your brain and spinal cord. It damages the myelin sheath, the material that surrounds and protects your nerve cells.
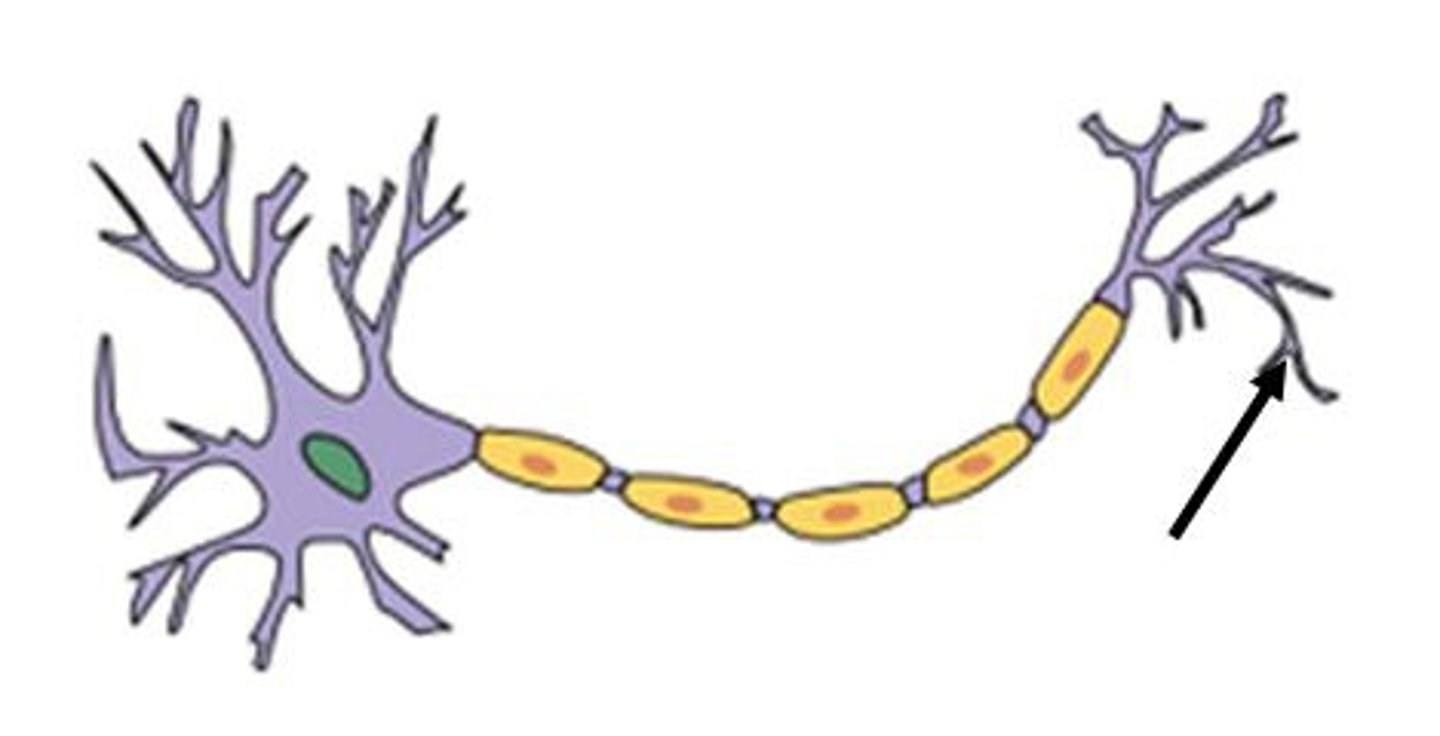
axon terminal
is the very end of a branch of a nerve's axon, a long slender nerve fiber that conducts electrical signals to a nerve synapse
vesicle
fluid filled bubble like structure that's store the neurotransmitters in the axon terminals
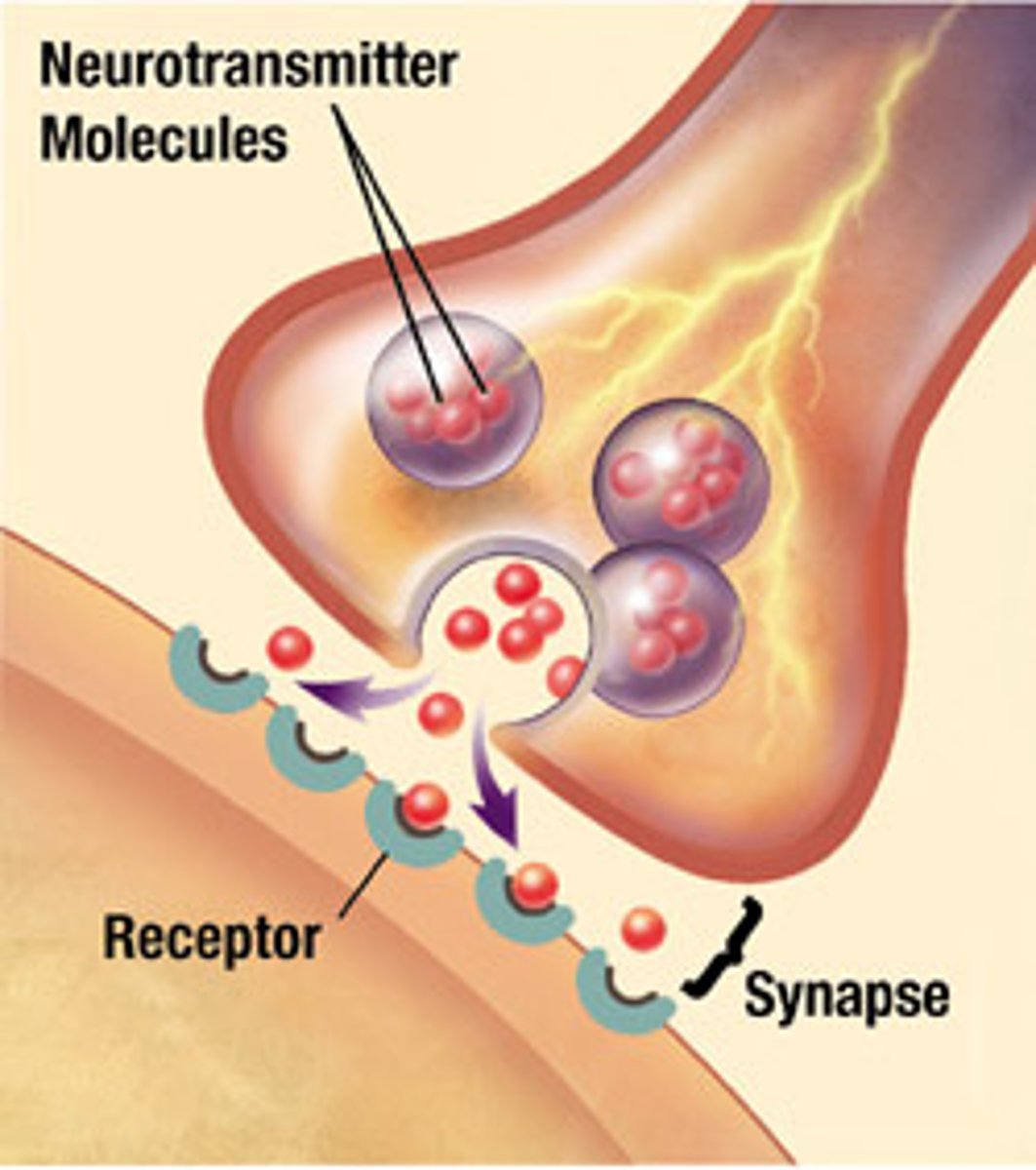
receptor site
lock-key area of the receiving neuron to receive the incoming neurotransmitter
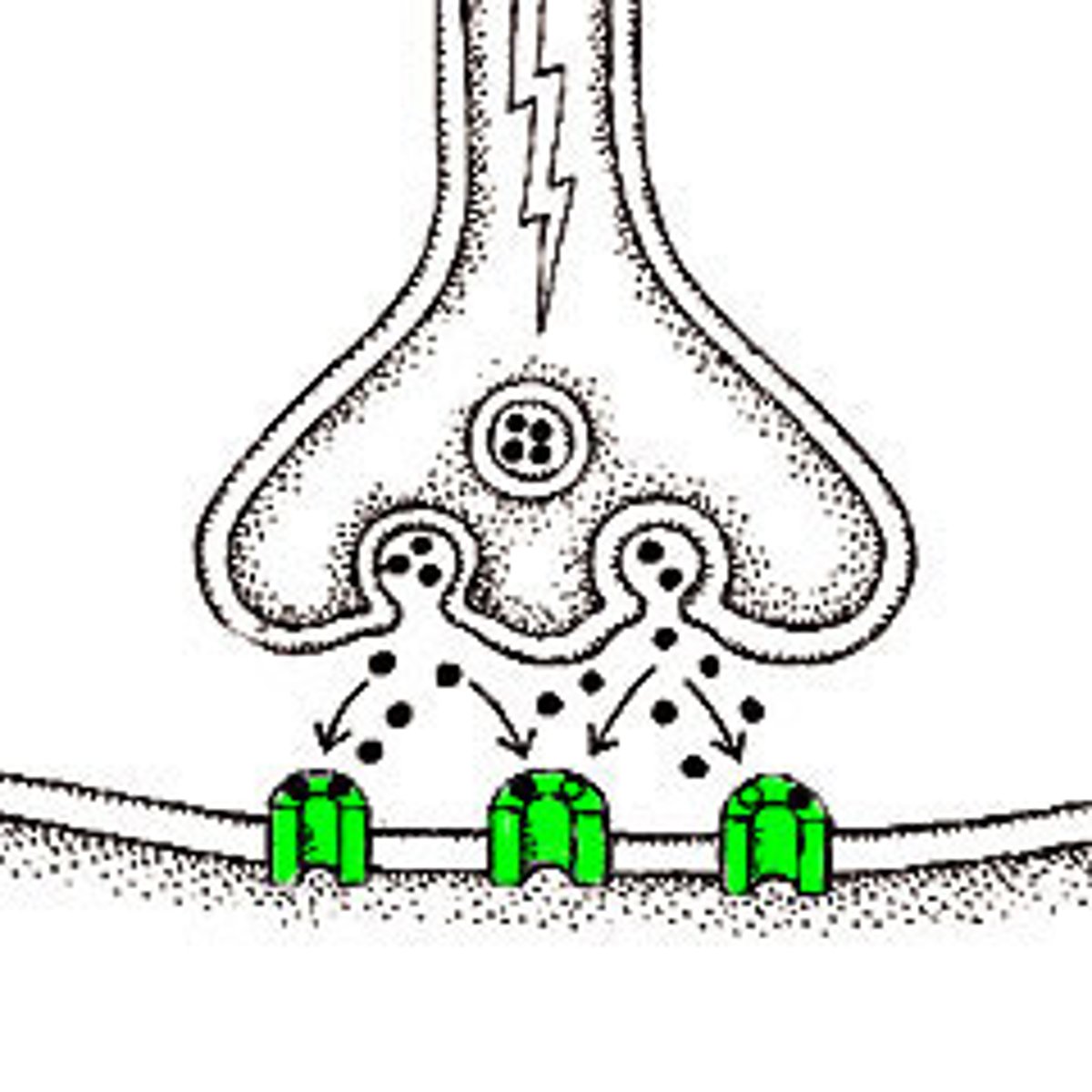
direction of impulse (action potential)
in action potential, action potential will only go this way and not reverse
speed of impulse (action potential)
in action potential, the action potential will always been this speed and say consistent throughout the axon
strength of impulse (action potential)
in action potential the power of the impulse will say consistent throughout the axon
Phineas Gage
1848 railroad worker that was injured by a tamping iron traveling through his brain and separating his frontal lobe from his limbic system; early case of changes in the brain
SNAGGED
Mnemonic device to remember the 7 neurotransmitters we are responsible for.
Serotonin
neurotransmitter that is in charge of mood, emotional stability, generally inhibitory; referred to as "happiness" drug; symptoms of deficit - mood disorders/depression.
Norepinephrine
neurotransmitter that is in charge physical arousal, energy and can act both as Inhibitory or excitatory; symptoms of deficit - depression; symptoms of surplus - anxiety, stress, nervous tension
Acetylcholine (ACh)
neurotransmitter that is in charge of movement, memory, tells muscles to contract, excitatory; symptoms of deficit - paralysis, Alzheimer 's disease (memory impairment); symptoms of surplus - violent muscle contractions/spasms
Glutamate
neurotransmitter that is in charge of learning, memory, how information moves, all-purpose excitatory and found in many areas of the brain; symptoms of surplus - seizures and migraines...overstimulated
GABA (gamma aminobutryic acid)
neurotransmitter that is in charge of relaxation and sleep, inhibitory; symptoms of deficit - anxiety, seizures, tremors, insomnia; symptoms of surplus - sleep disorders, some eating disorders
Endorphins
neurotransmitter that is in charge of pain relief, positive emotions, generally inhibitory; natural opiate/pain reliever, released during aerobic exercise and linked to positive emotions; "runners high"; symptoms of deficit - body experiences pain; symptoms of surplus - body may not give adequate warning about pain, artificial highs
Dopamaine
neurotransmitter involved in voluntary muscle movements, attention, learning, memory, emotional arousal & rewarding sensations; Symptoms of deficit - Parkinson's Disease; symptoms of surplus, Schizophrenia, Schizophrenia-like symptoms: hallucinations, perceptual disorders and addiction
Mirror Neurons
discovered in the 1990s, play a role in acquisition of new motor skills, the imitation of others and the ability to feel empathy for others. Dysfunctions in this neuron are believe to explain the social deficits seen in autistic disorders.
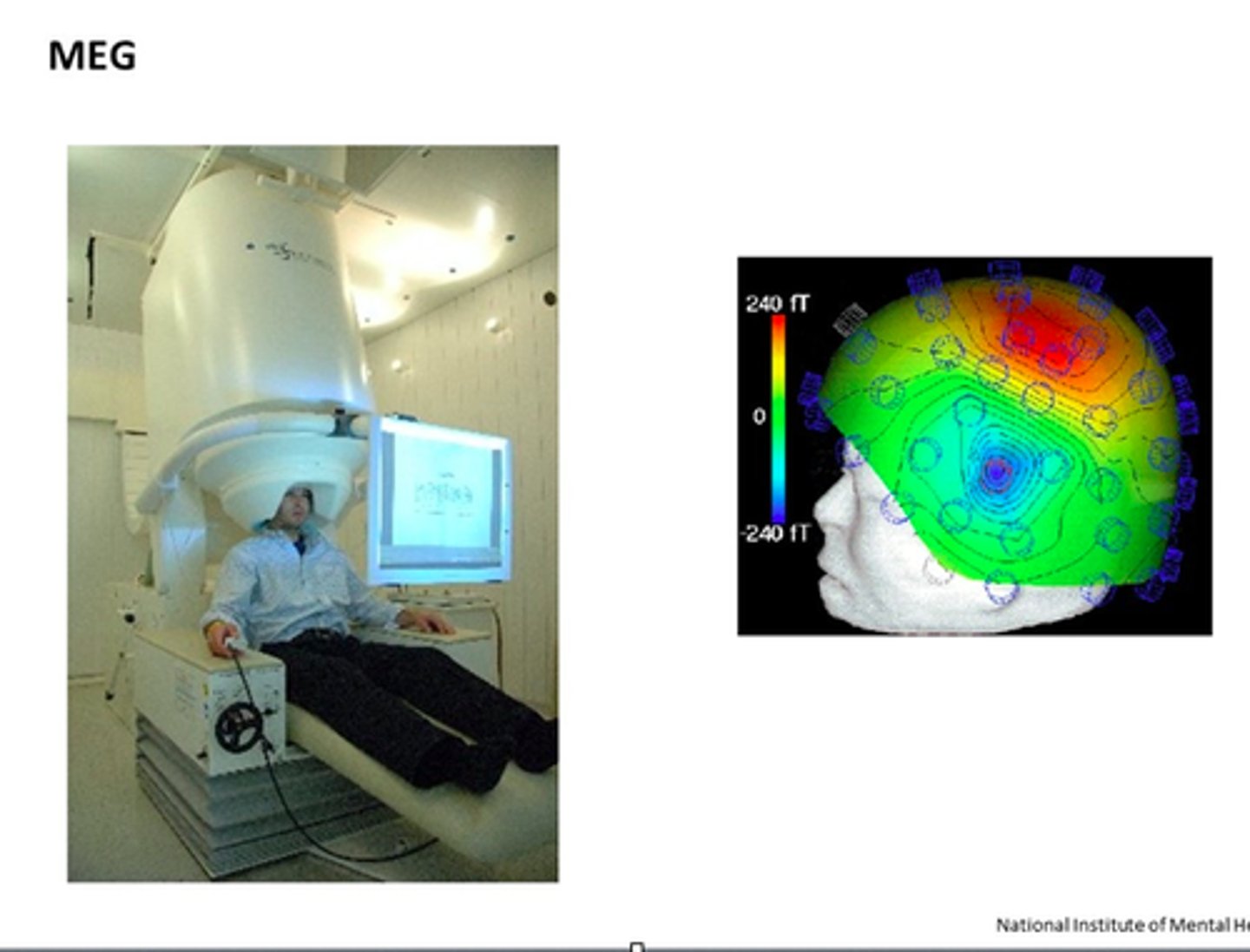
(MEG) Magnetoencephalography
Similar to fMRI-shows what areas light up; Produces at a very fast rate (1/1000 of a second compared to 1-3 seconds for fMRI; Very expensive
biological psychology
the scientific study of the links between biological (genetic, neural, hormonal) and psychological process. Some biological psychologists call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists, behavior geneticists, physiological psychologists, or biopsychologists.)
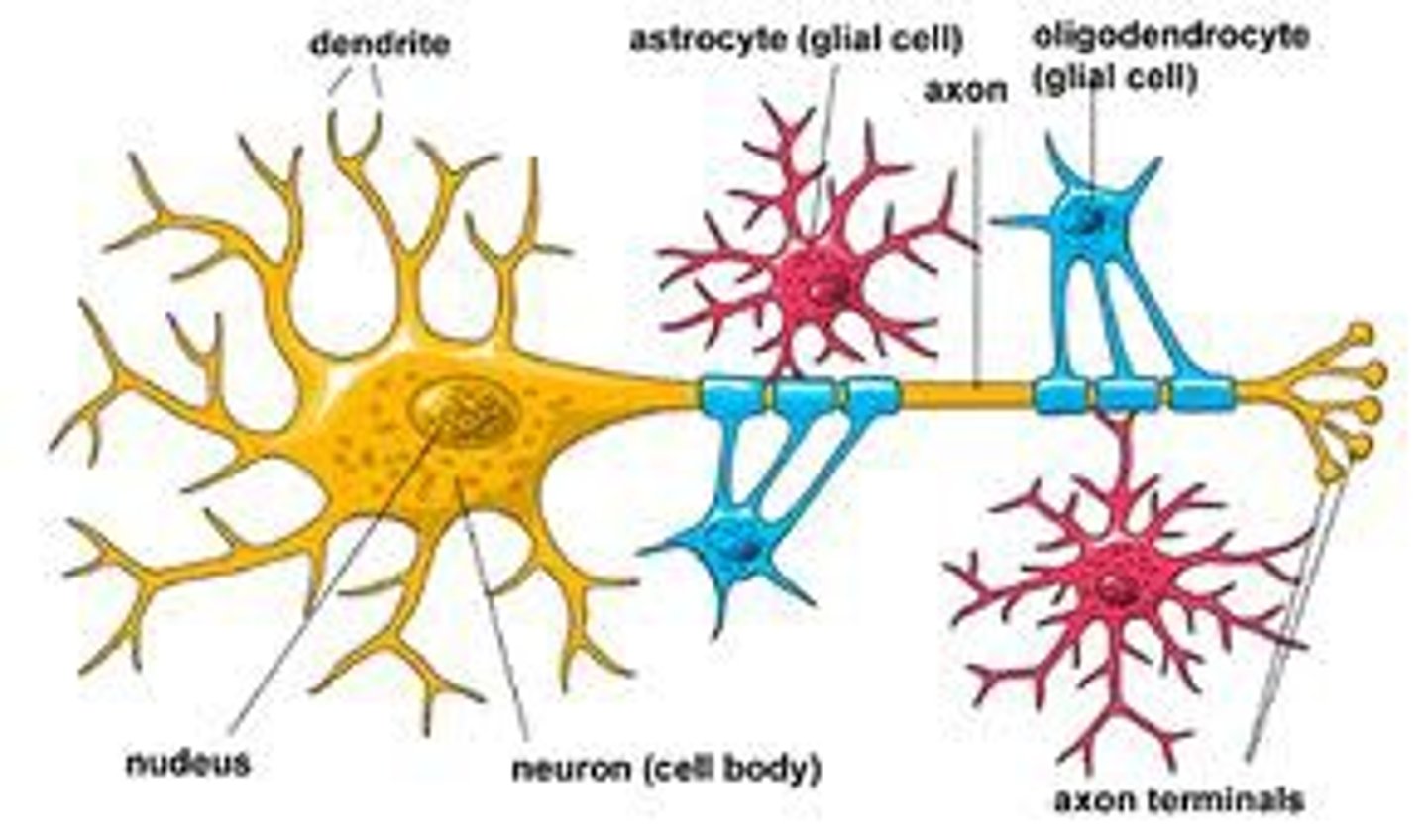
neuron
a nerve cell, the basic building block of the nervous system.
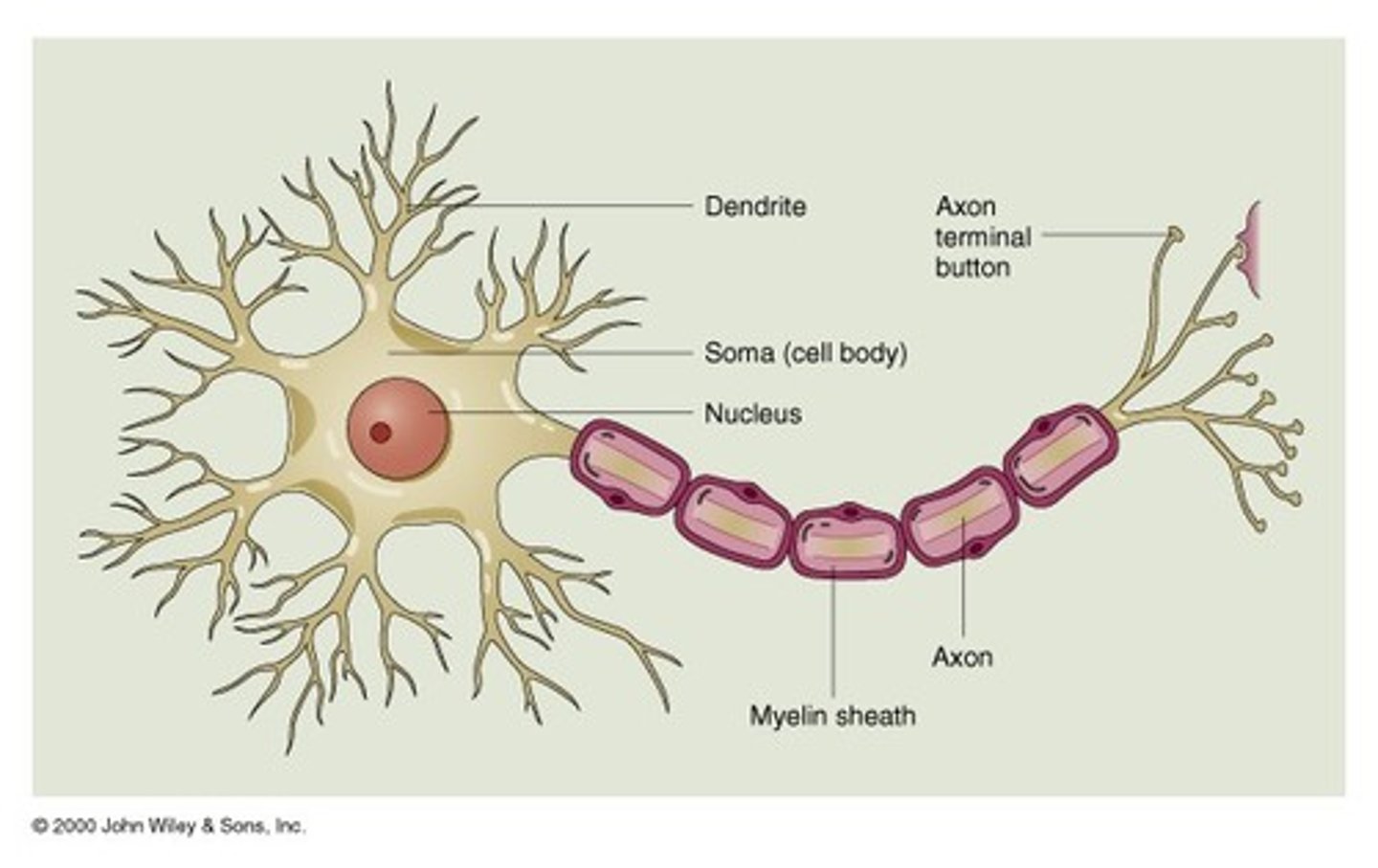
dendrites
a neuron's bushy, branching extensions that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body.
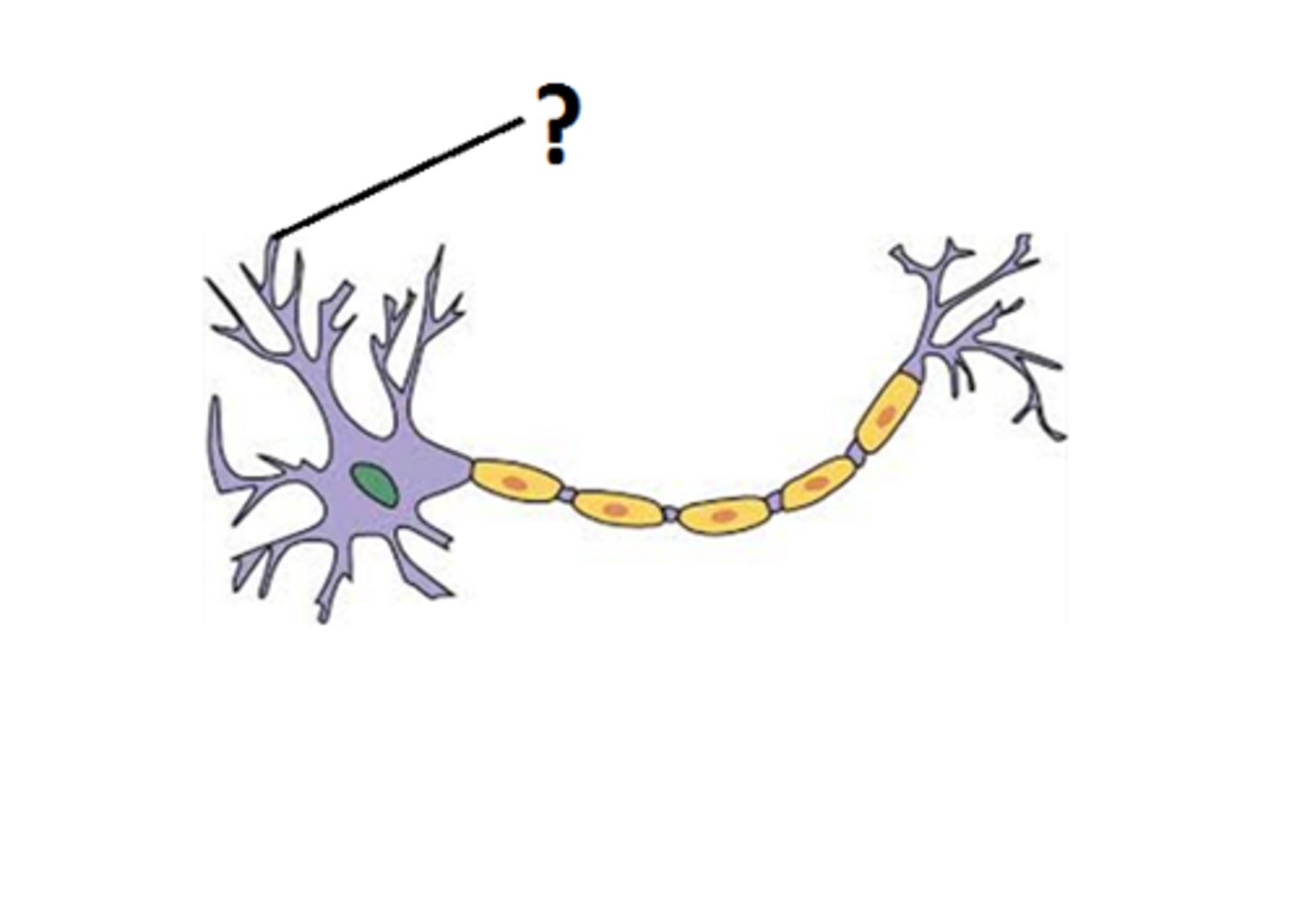
axon
the neuron extension that passes messages through its branches to other neurons or to muscles or glands.
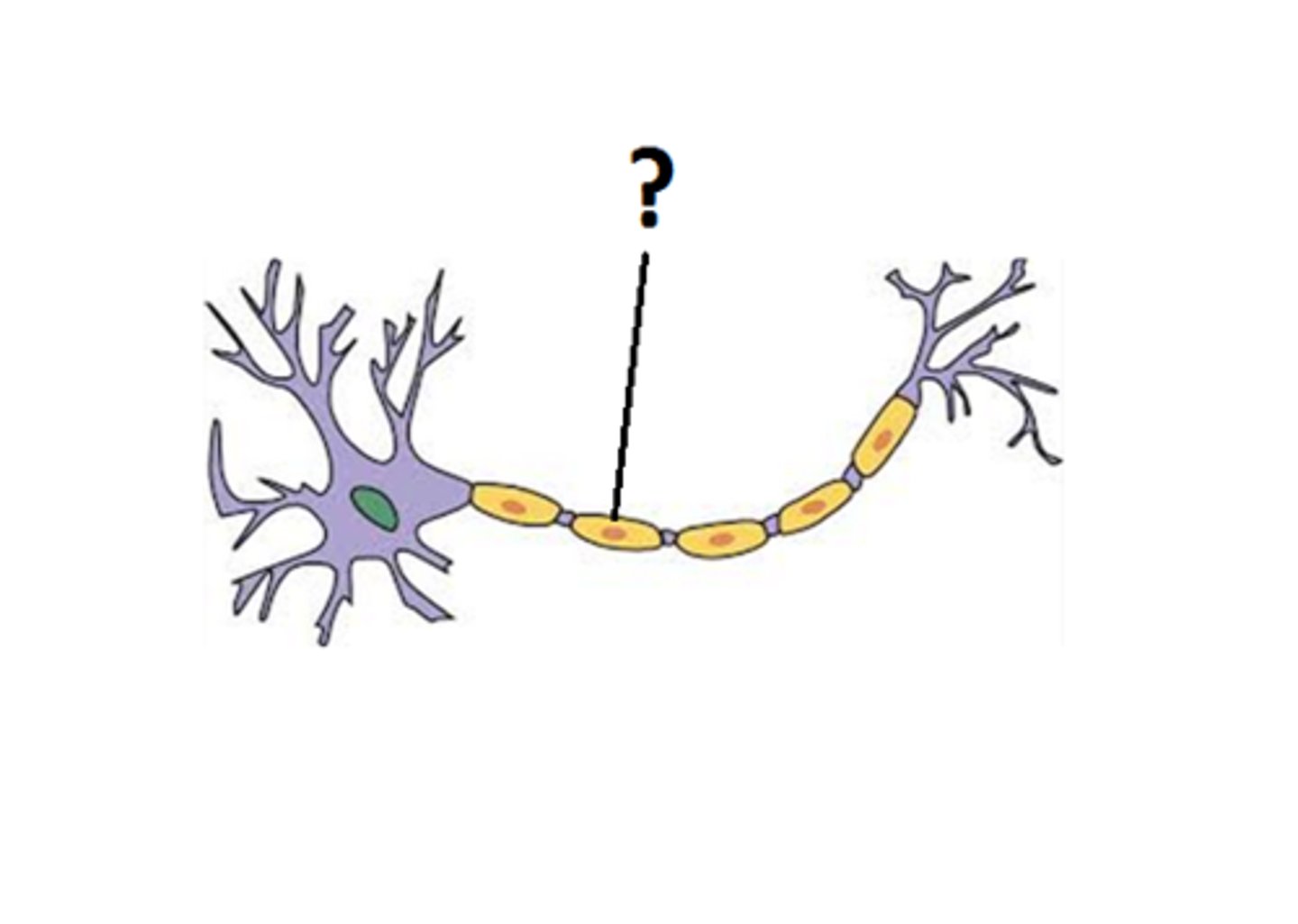
myelin sheath
a fatty tissue layer segmentally encasing the axons of some neurons; enables vastly greater transmission speed as neural impulses hope from one sausage-like node to the next.
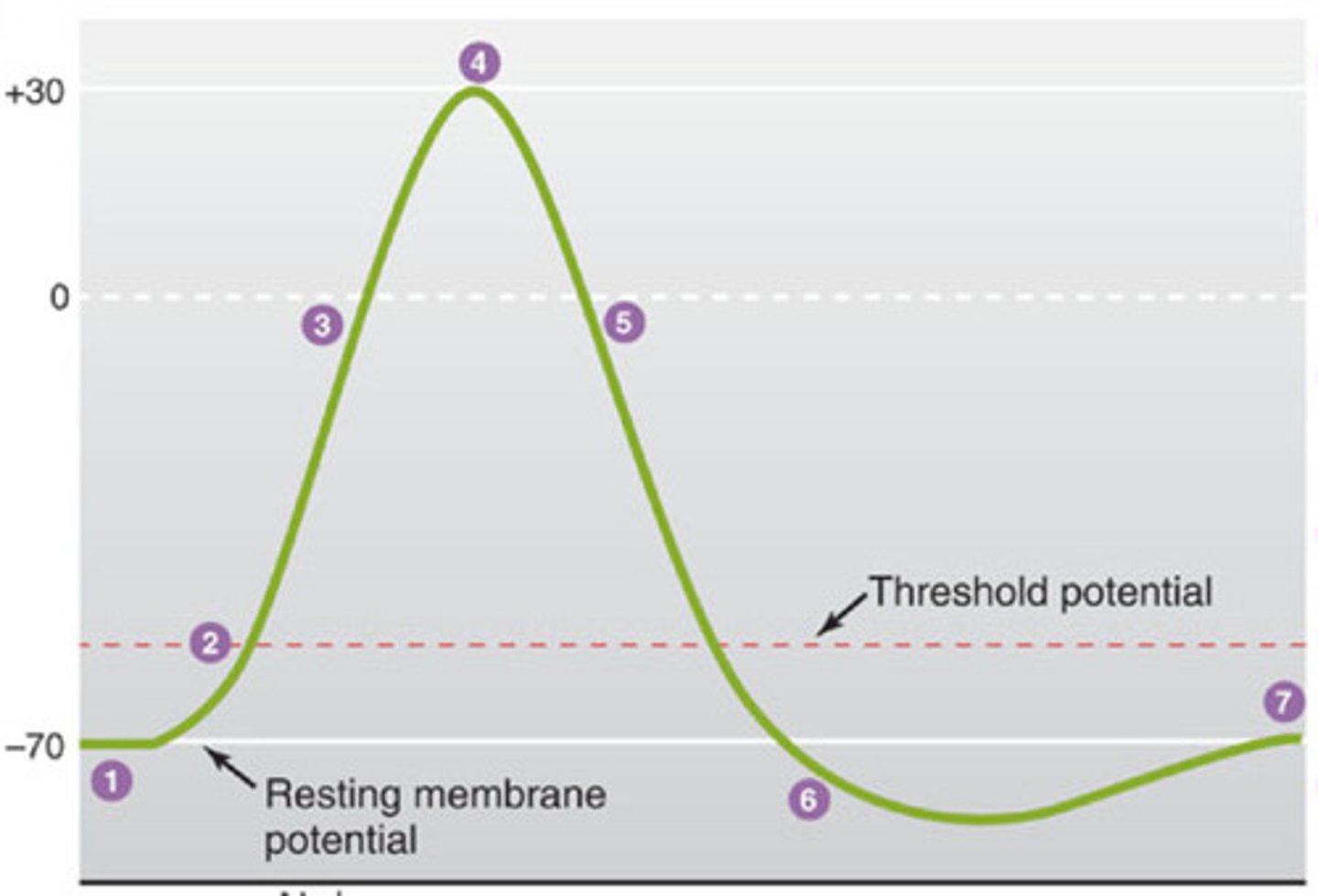
action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon.
resting potential
neurons normal state; polarized neuron; positive on the outside of the axon and negative in the inside
depolarization
as action potential is occurring the axon is having positive ions flood the axon and channels open in axon to send message
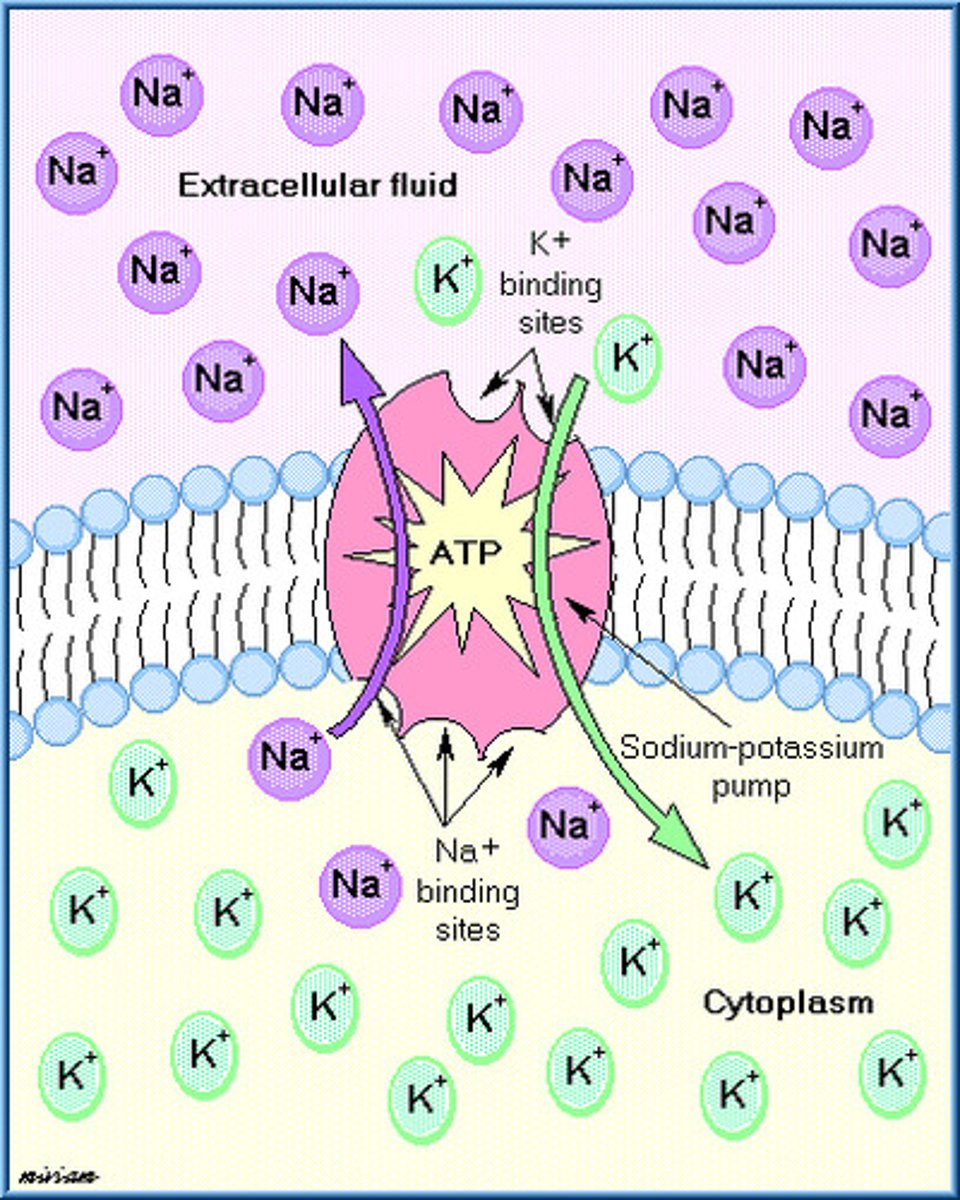
sodium-potassium pumps
a gate/pump that is selectively permeable gates on the axon; they allows Sodium (Na++) ions to pass through permeable axon wall and allows Potassium (K+) ions out of axon
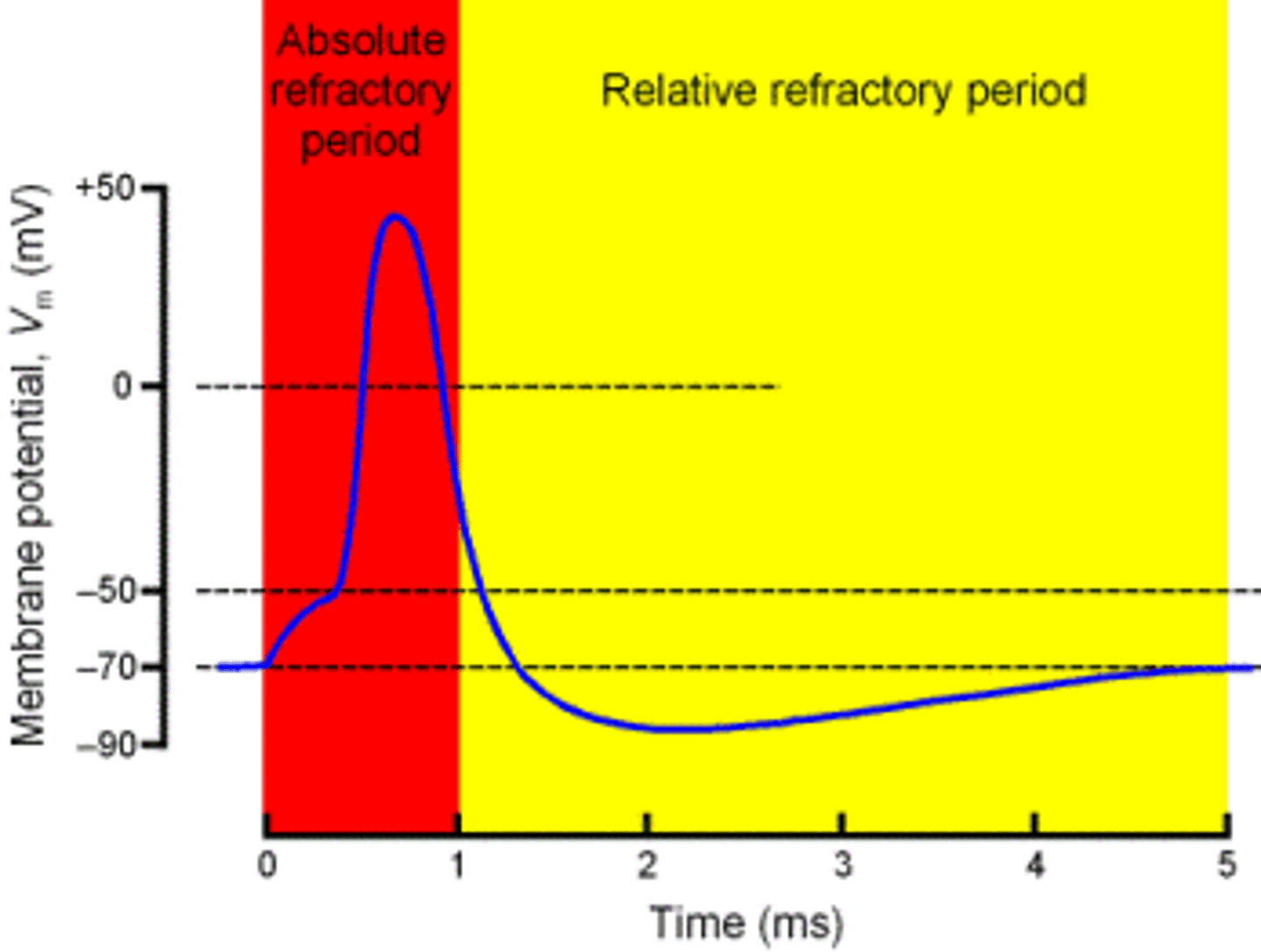
refractory period
a period of inactivity after a neuron has fired.
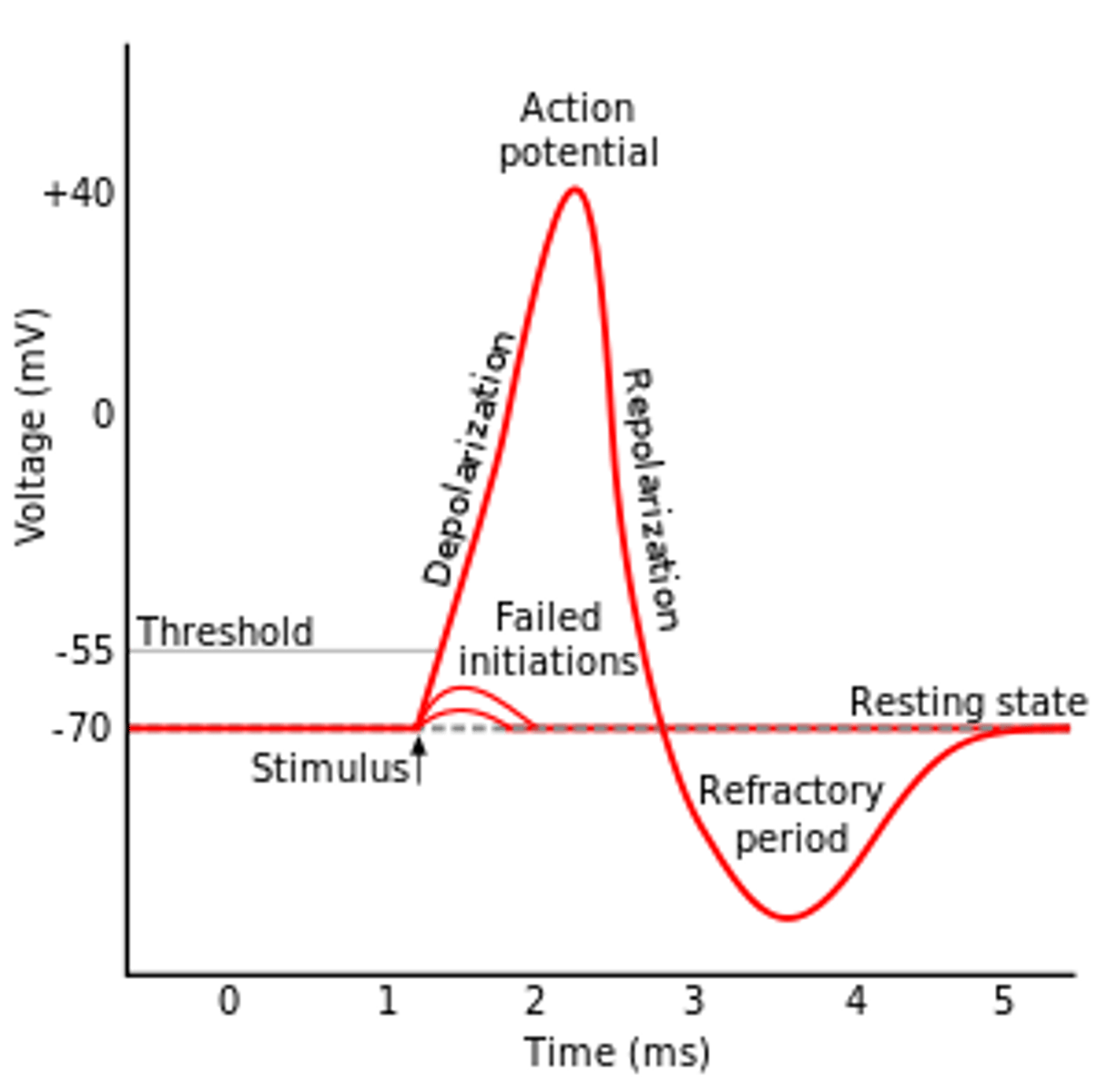
re-polarization
after neuron is fired it must get back to resting potential by this process
threshold
the level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse; excitatory signals minus the inhibitory signals exceed a minimum intensity the neuron fires an action potential

all-or-none response
a neuron's reaction of either firing (with a full-strength response) or not.
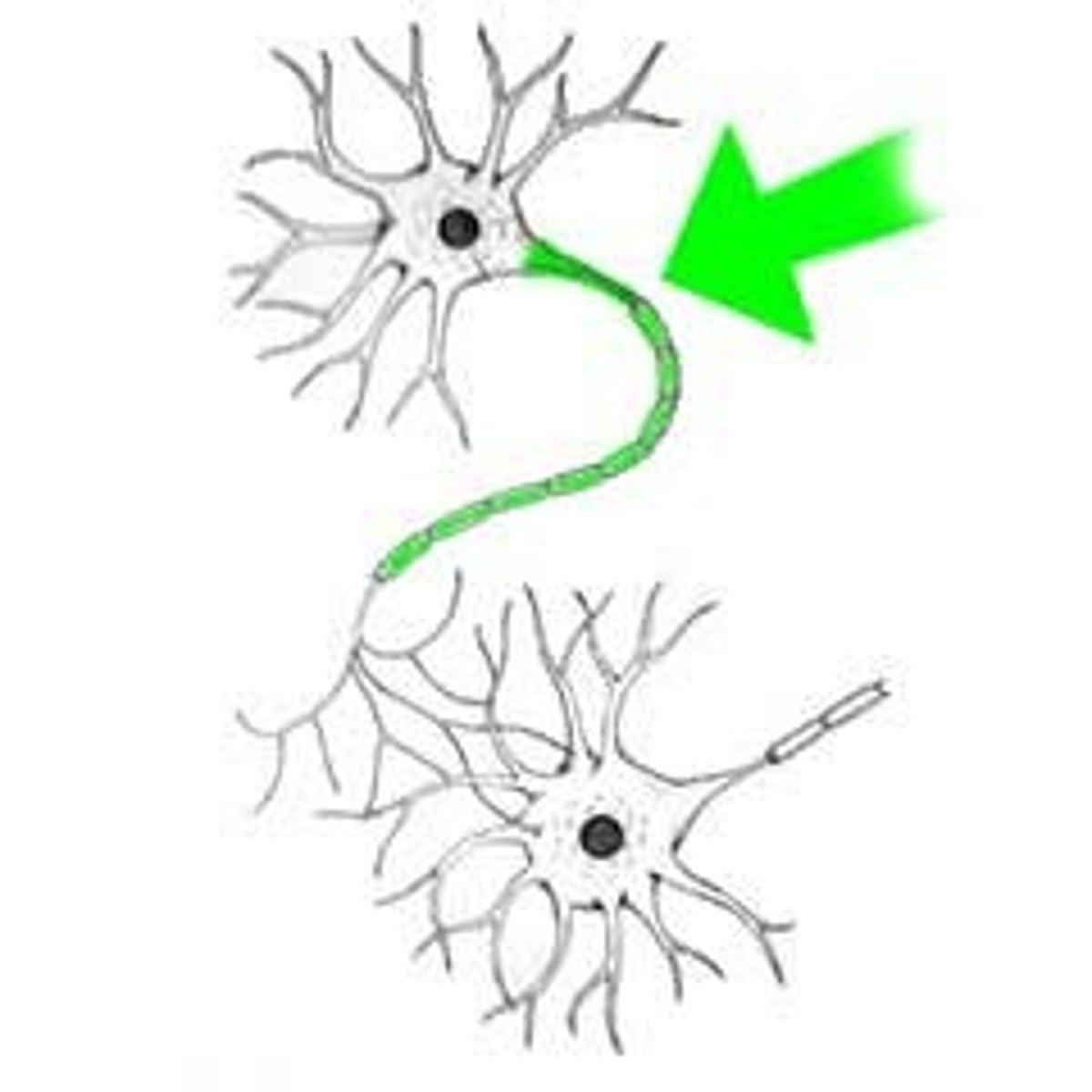
synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron. The tiny gap at this junction is called the synaptic gap or synaptic cleft
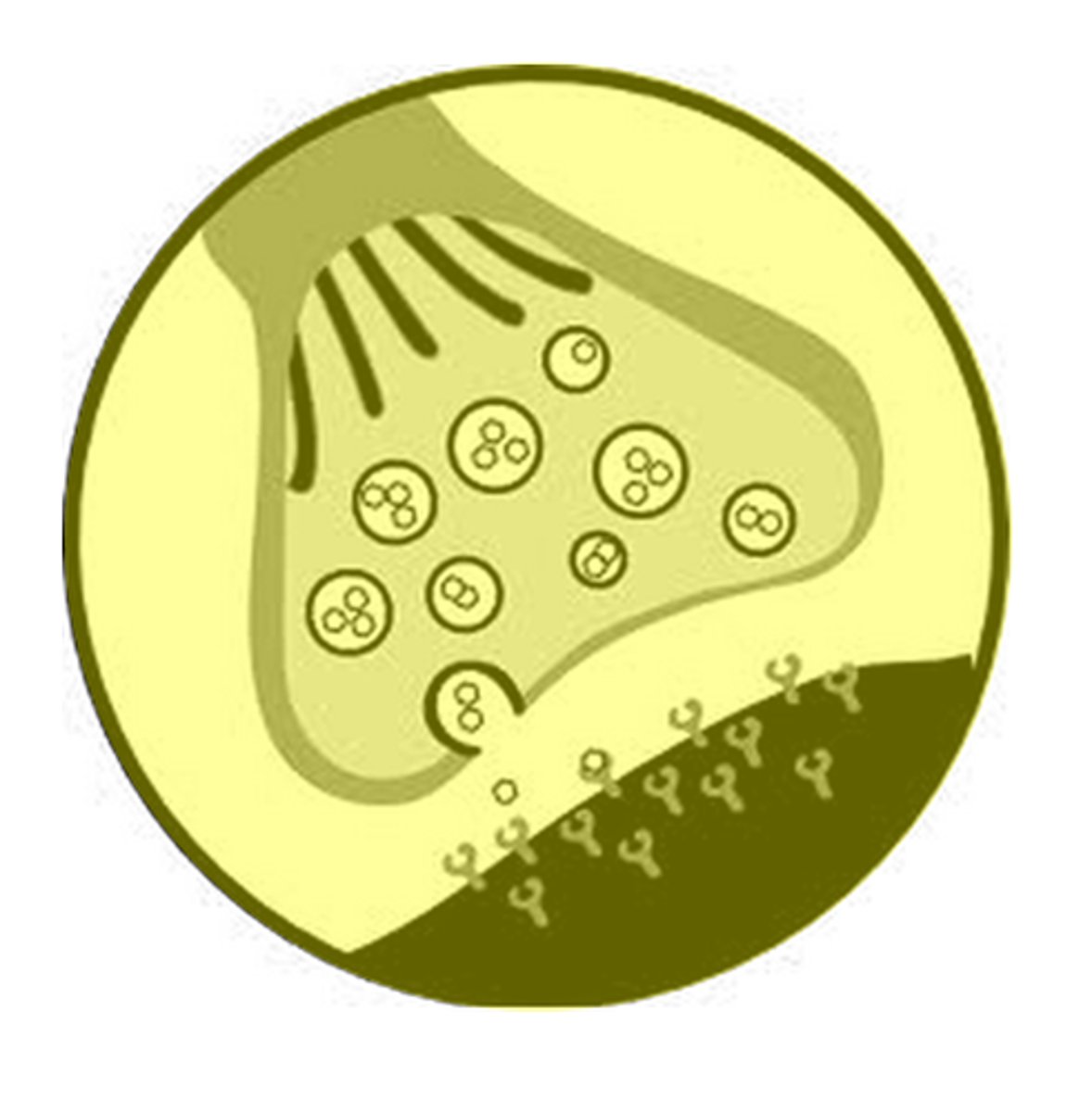
neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons when released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing whether that neuron will generate a neural impulse.
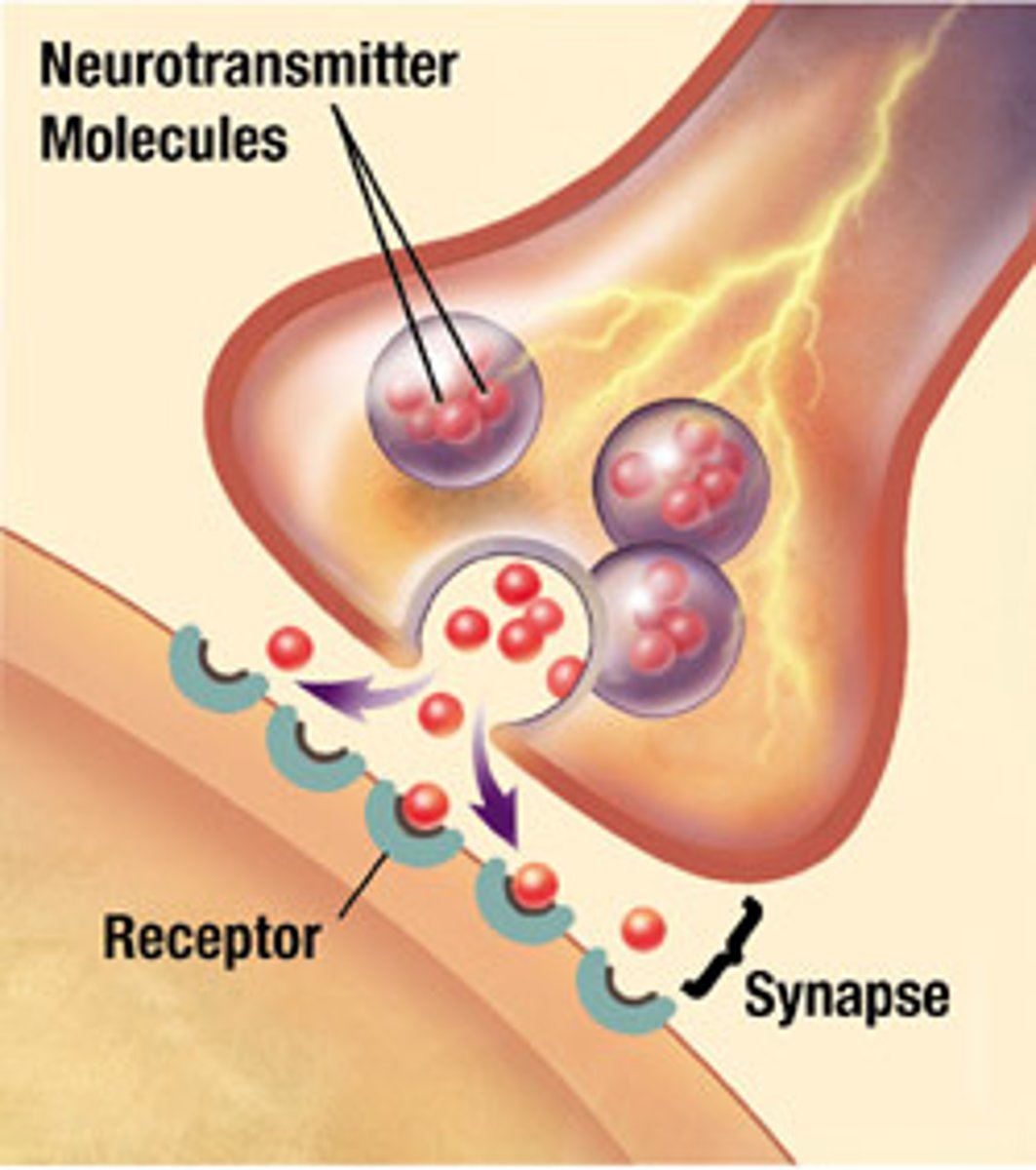
reuptake
a neurotransmitter's reabsorption by the sending neuron; applies the brakes on the neurotransmitters action

agonist
a molecule that, by binding to a receptor sit, stimulates a response; mimics neurotransmitter
antagonist
a molecule that, by binding to a receptor site, inhibits or blocks a response; blocks neurotransmitter from working
nervous system
the body's speedy, electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells of the peripheral and central systems.
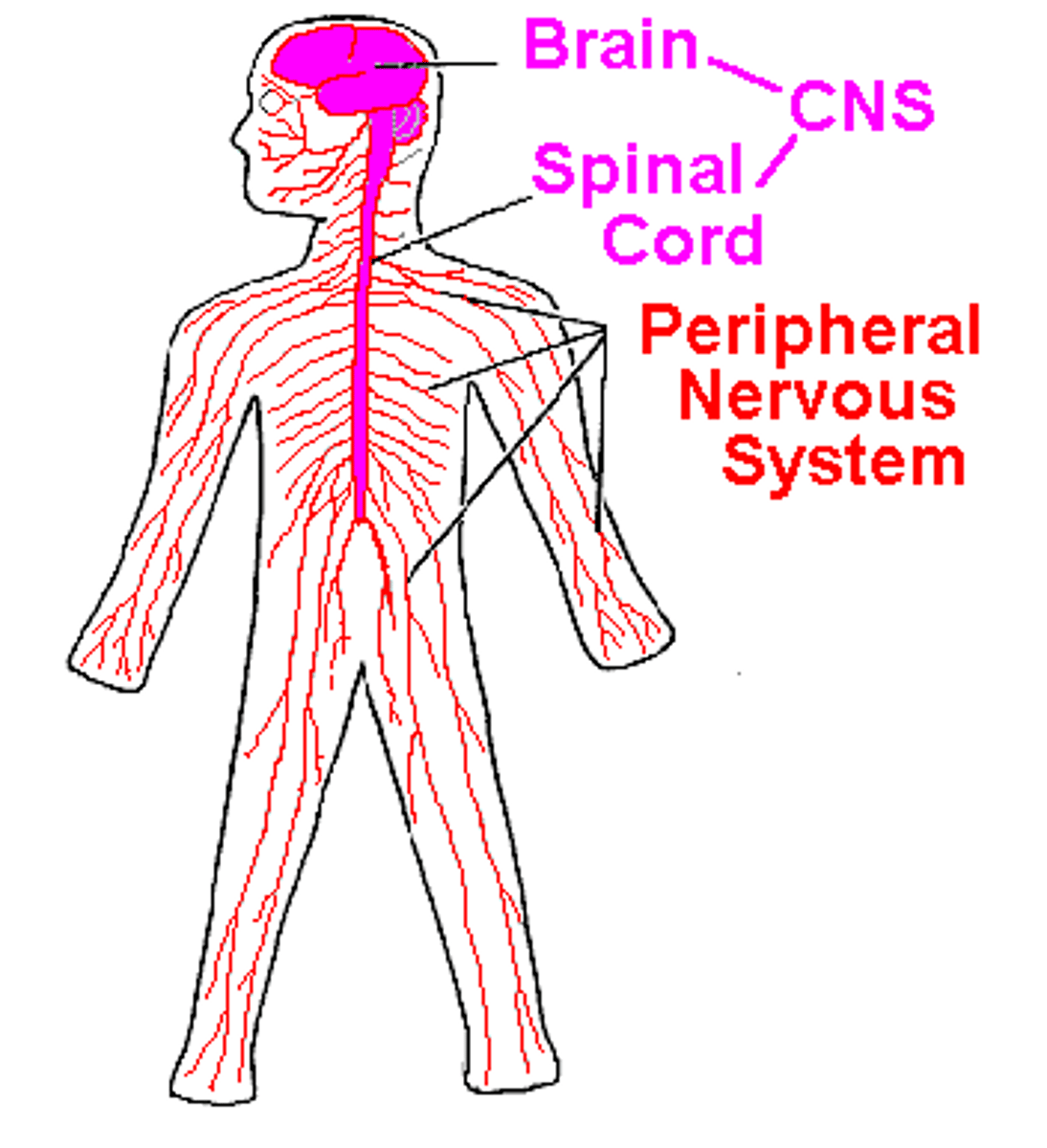
Peripheral nervous system
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body.
nerves
bundled axons that form neural "cables" connecting the central nervous system with muscles, glands, and sense organs.
sensory (afferent) neurons
neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord.
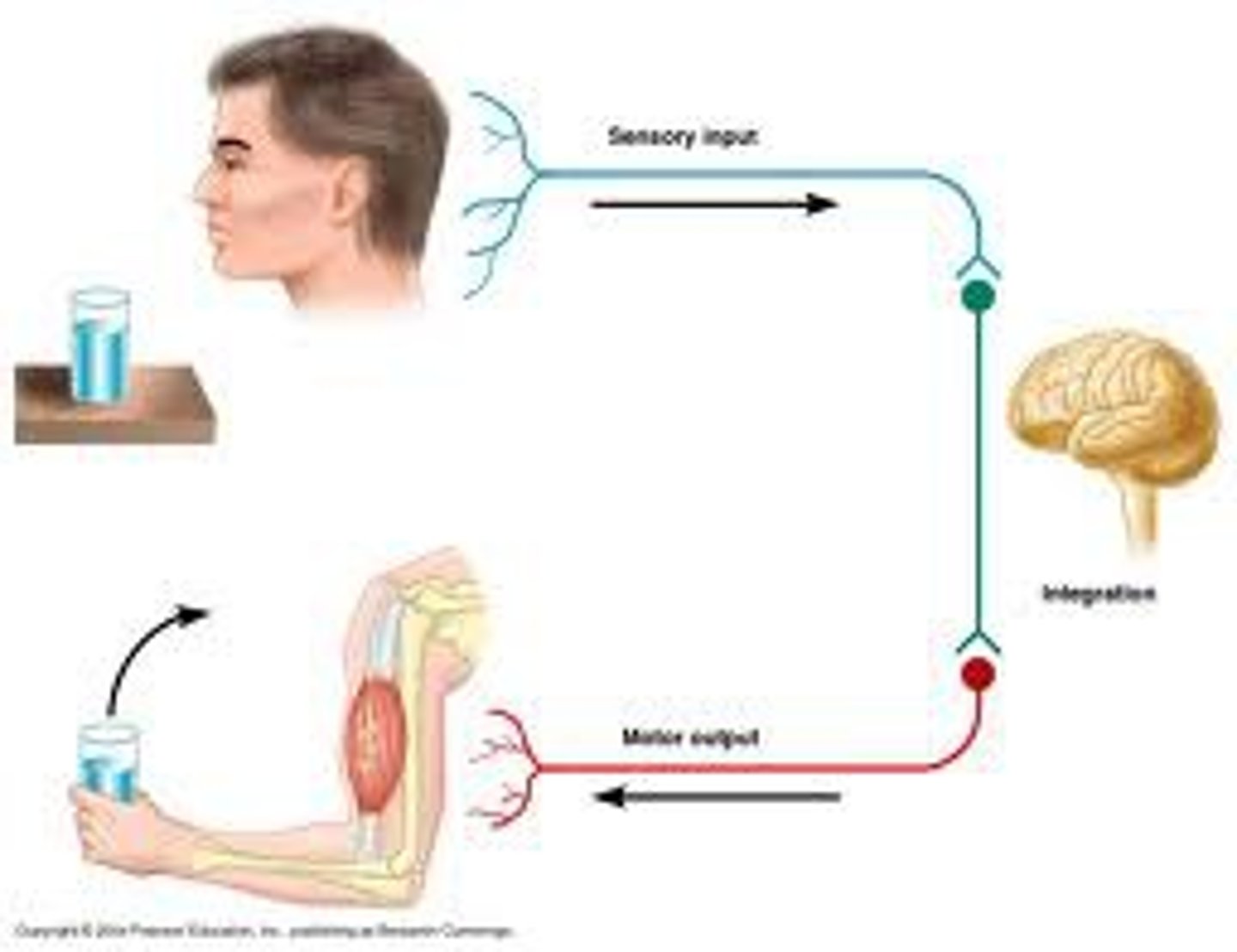
motor (efferent) neurons
neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands.
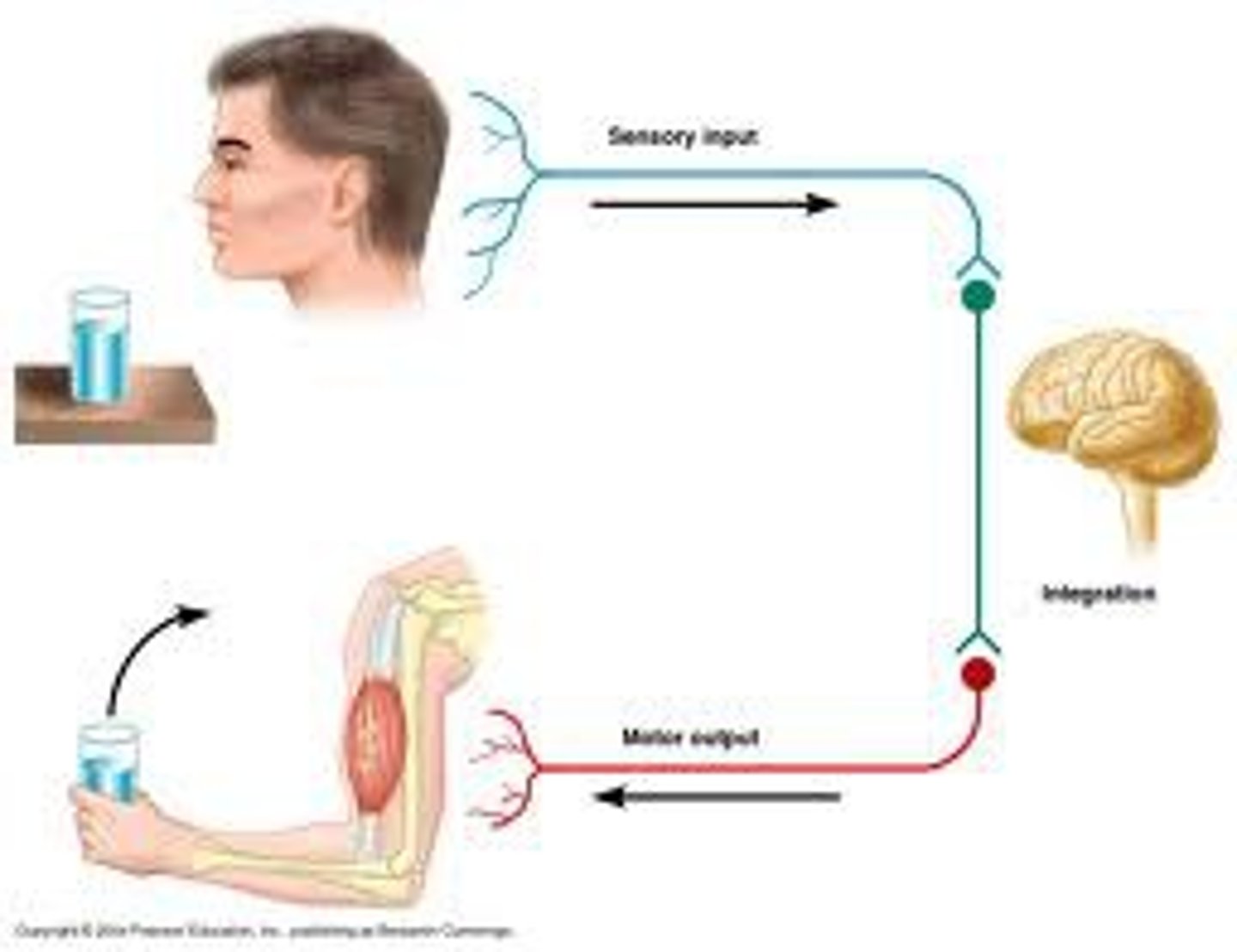
interneurons
neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs.
somatic nervous system
nervous system the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls voluntary movement of the body's skeletal muscles; so....my choice!
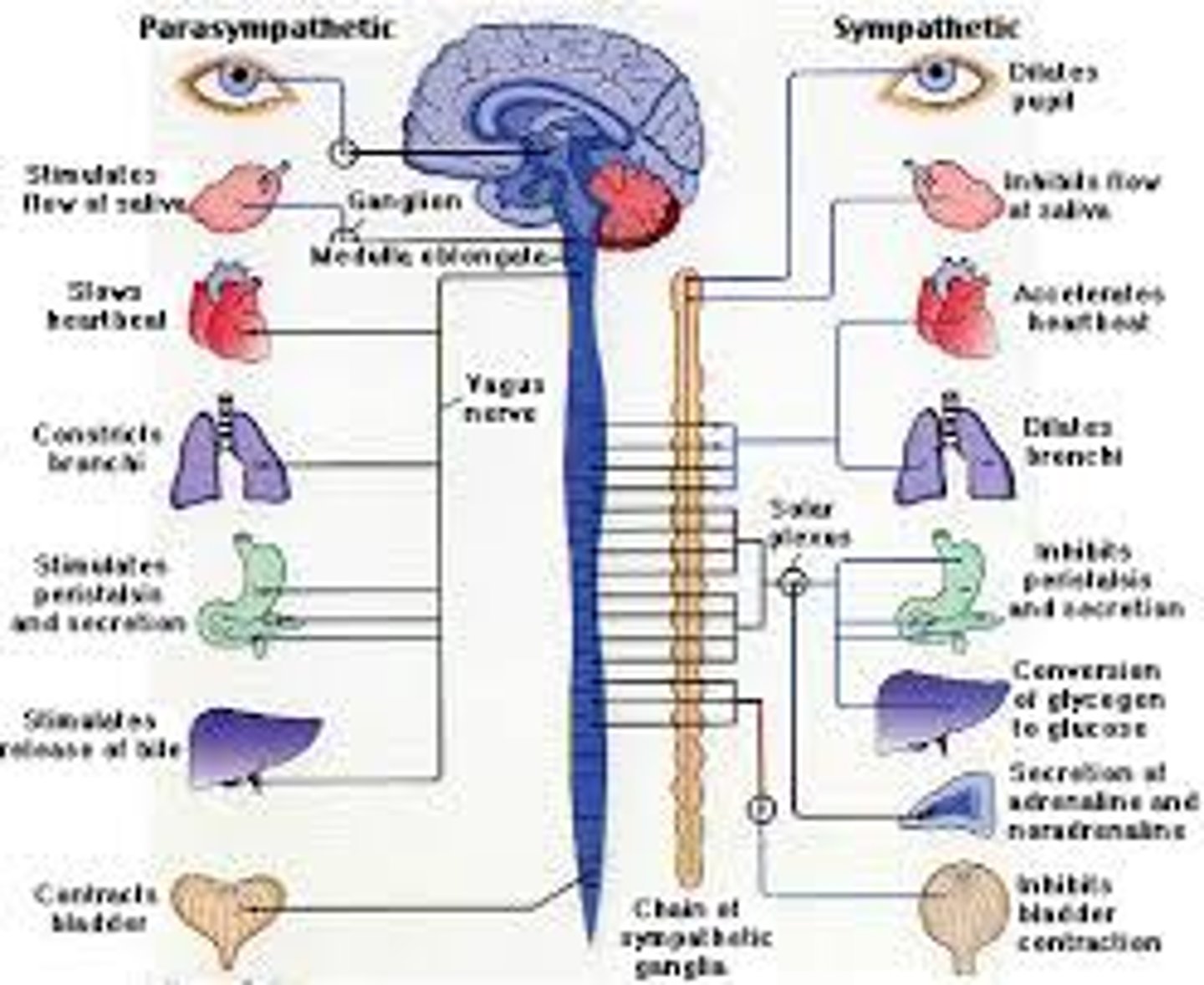
autonomic nervous system
the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart). Its parasympathetic division calms. (automatic...heartbeat, breathing, etc.,)

sympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations. (fight or flight)
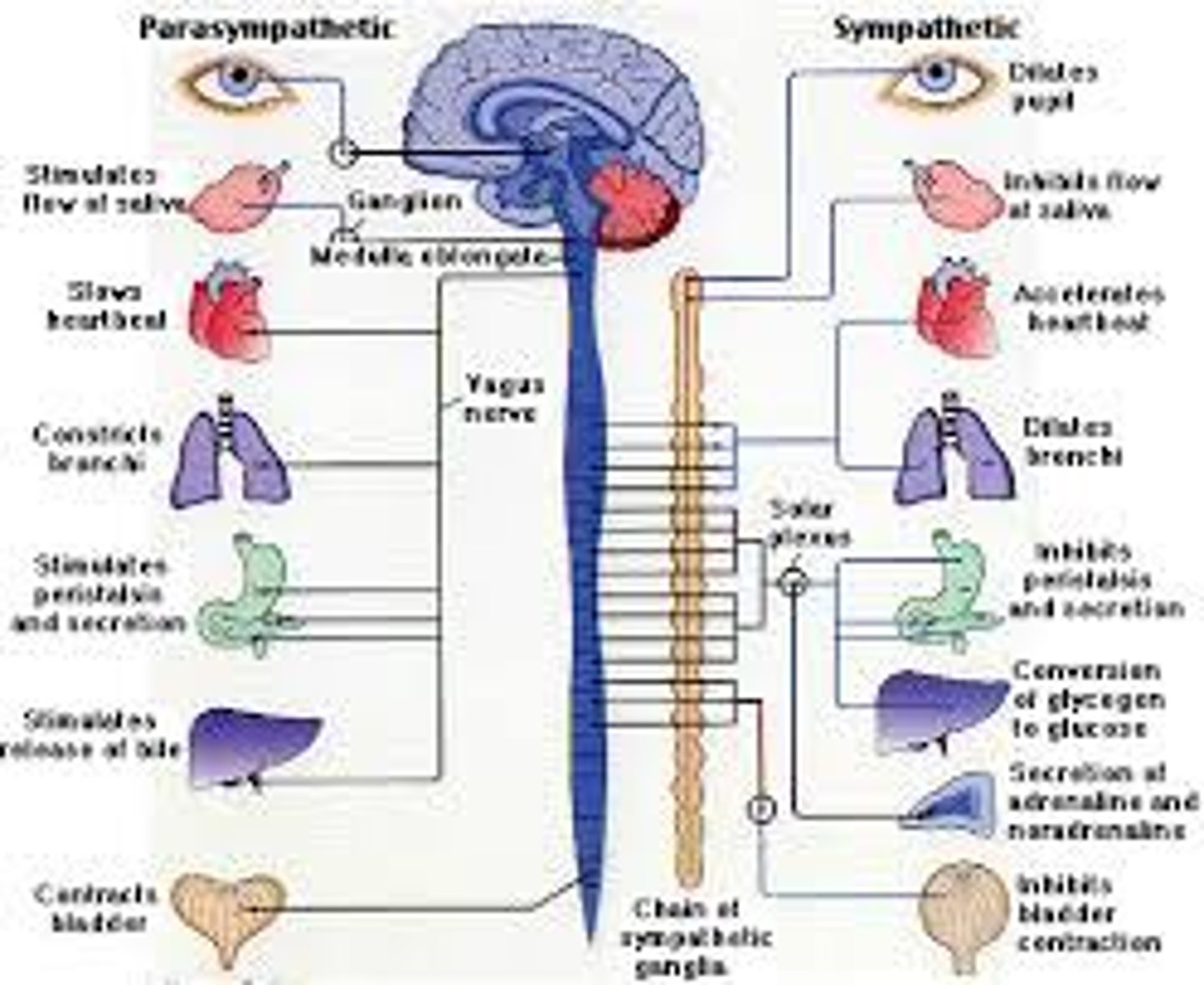
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous that calms the body, conserving its energy. (calming, paramedics are meant to calm at the scene of an accident)
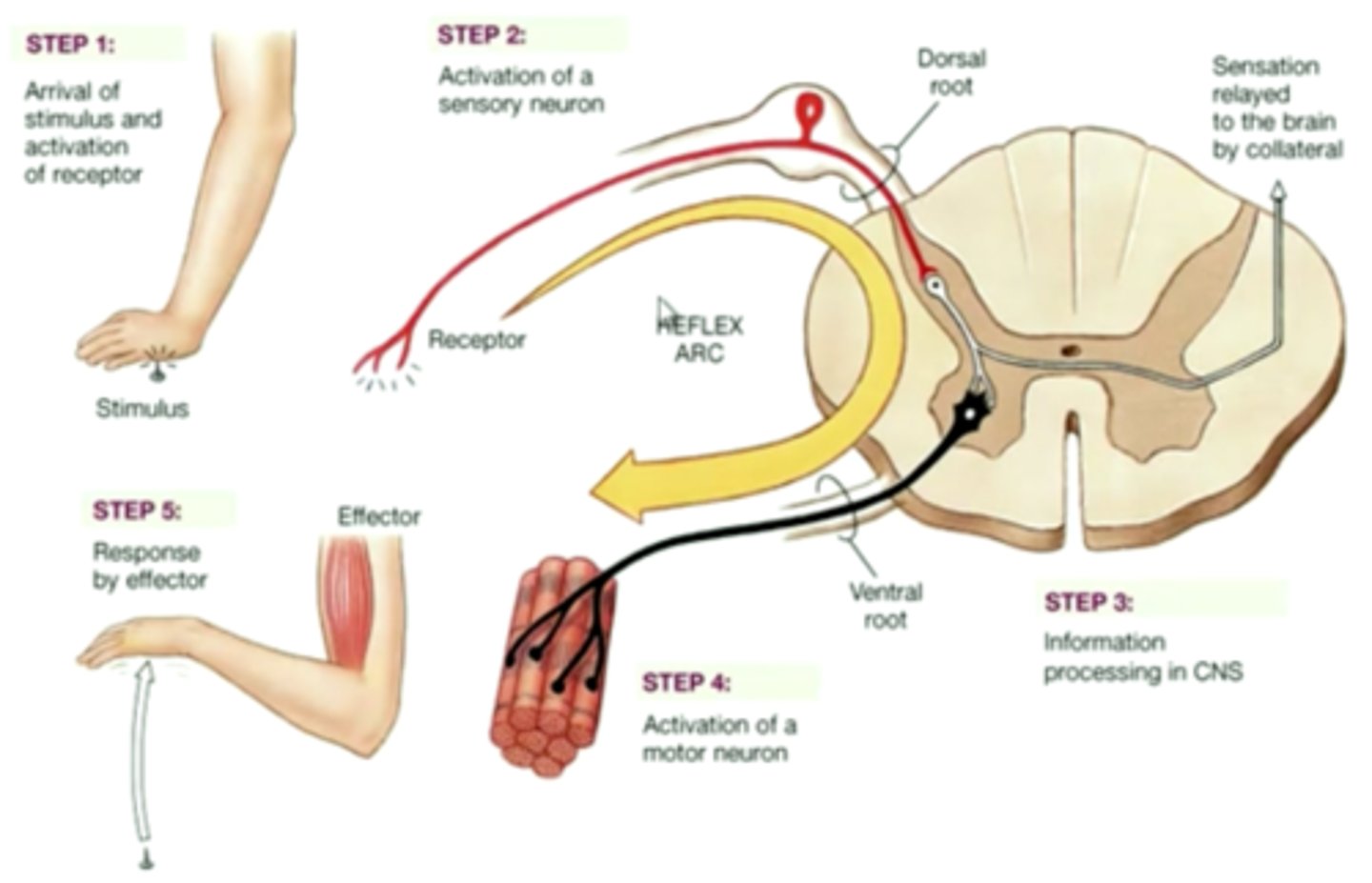
reflex
a simple, automatic response to a sensory stimulus, such as the knee-jerk response.
endocrine system
the body's "slow" chemical communication system; a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream
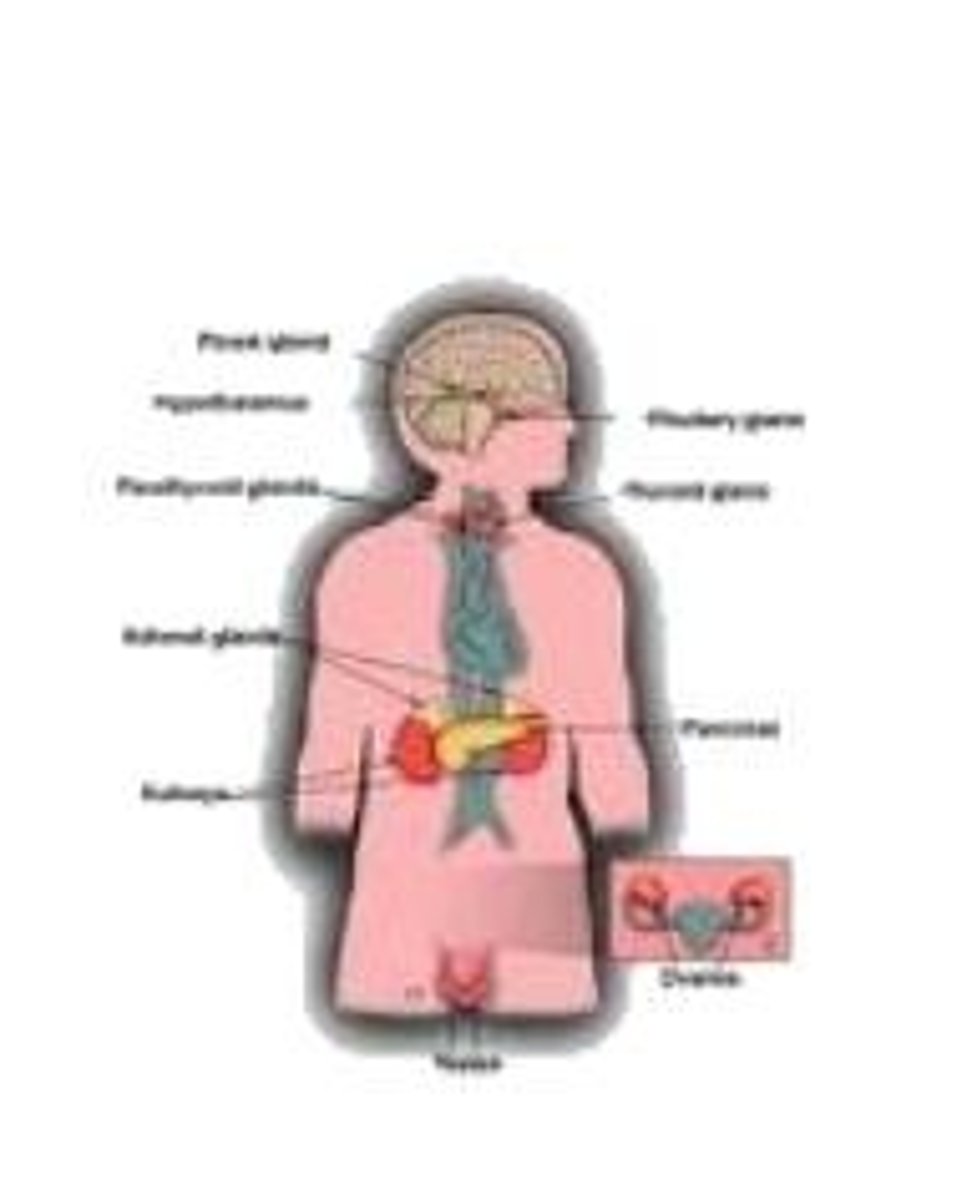
hormones
chemical messengers that are manufactured by the endocrine glands travel through the bloodstream and affect other tissues.
adrenal glands
a pair of endocrine glands that sit just above the kidneys and secret hormones (epinephrine) that help arouse the body in times of stress
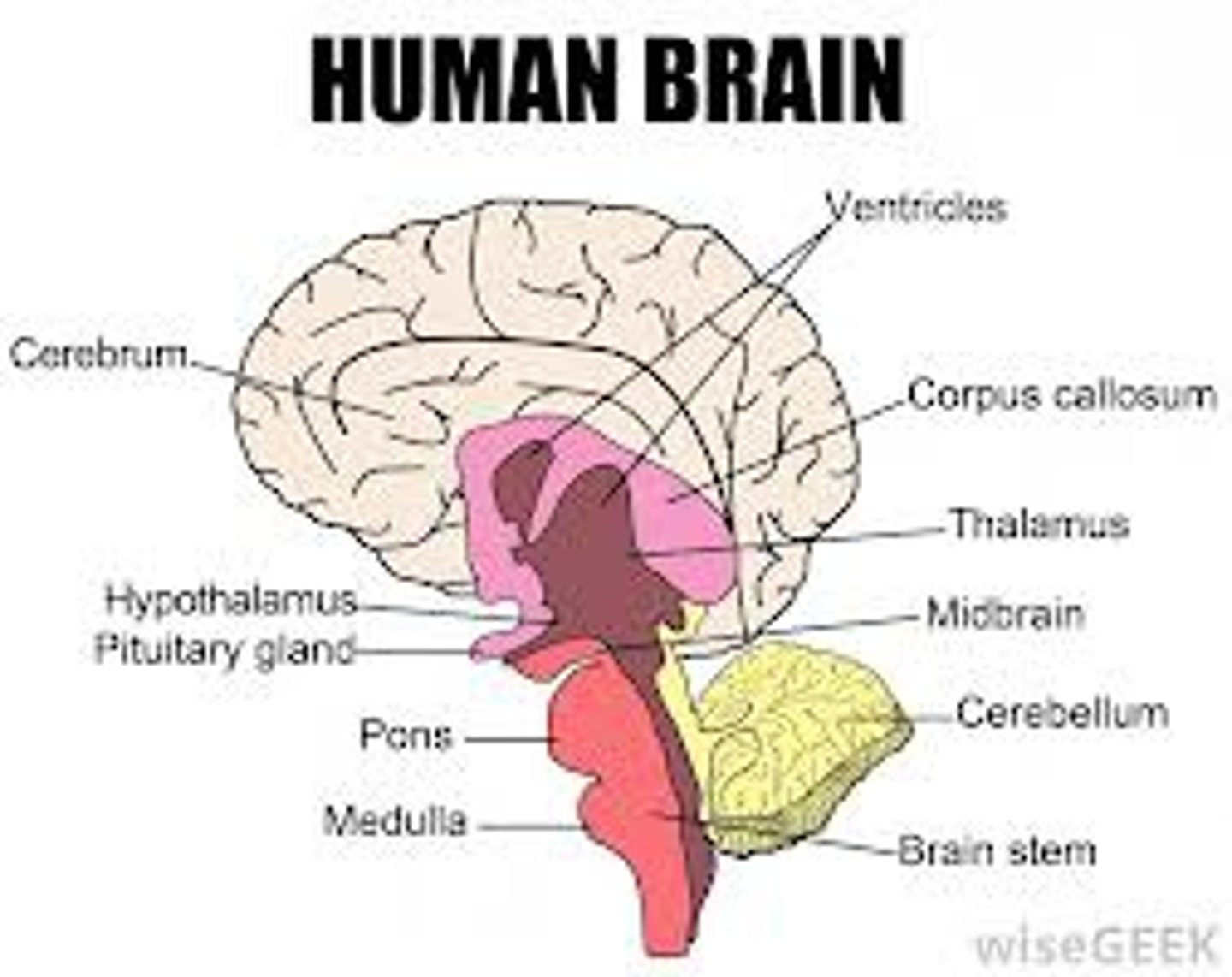
pituitary gland
"master gland;" the endocrine system's most influential gland. Under the influence of the hypothalamus, this regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands.
lesion
tissue destruction. This is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue.
(EEG) electroencephalogram
an amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity sweeping across the brain's surface. These waves are measured by electrodes placed on the scalp.
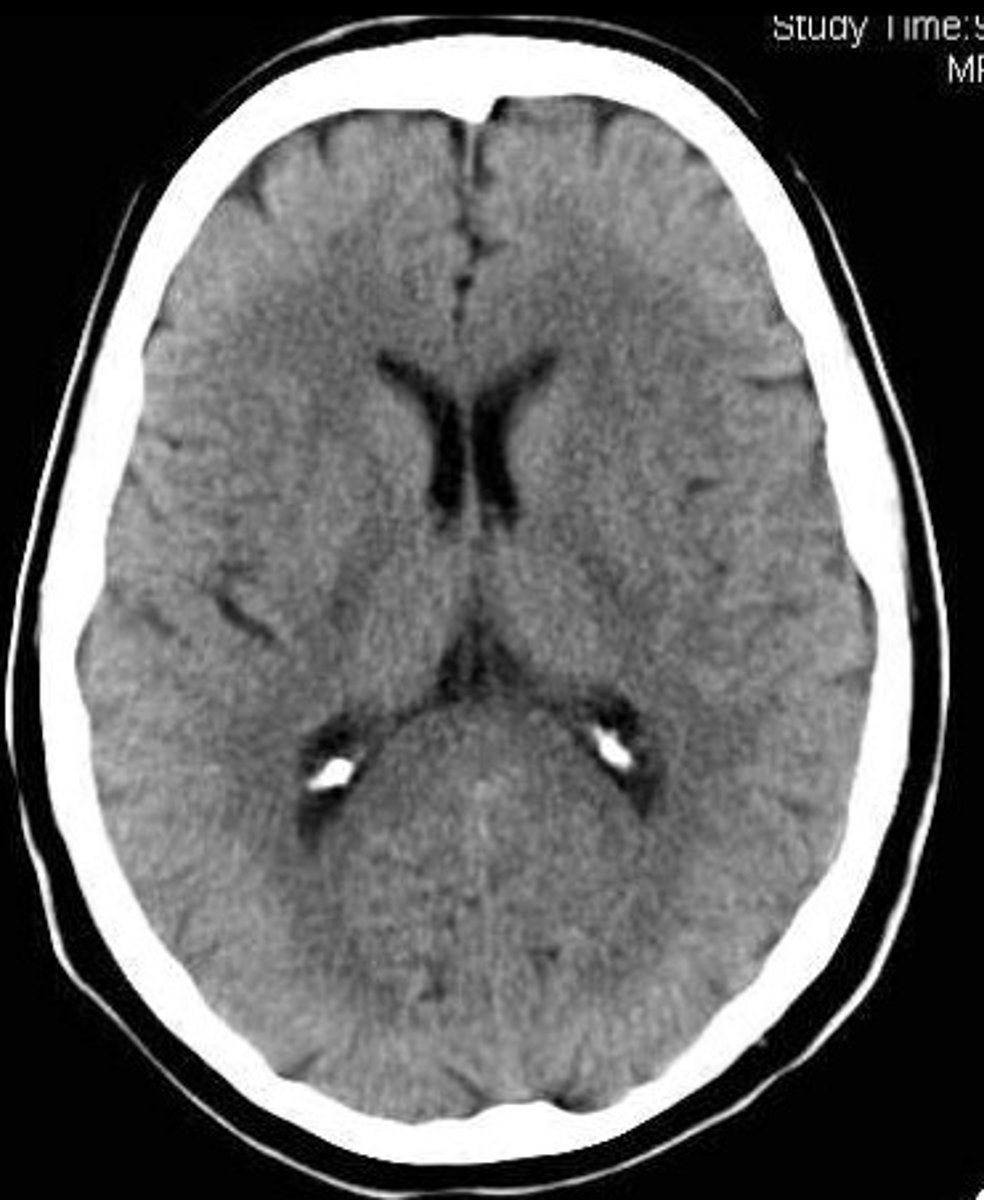
(CT) computed tomography scan
a series of X-ray photographs taken from different angles and combined by computer into a composite representation of a slice of the brain's structure
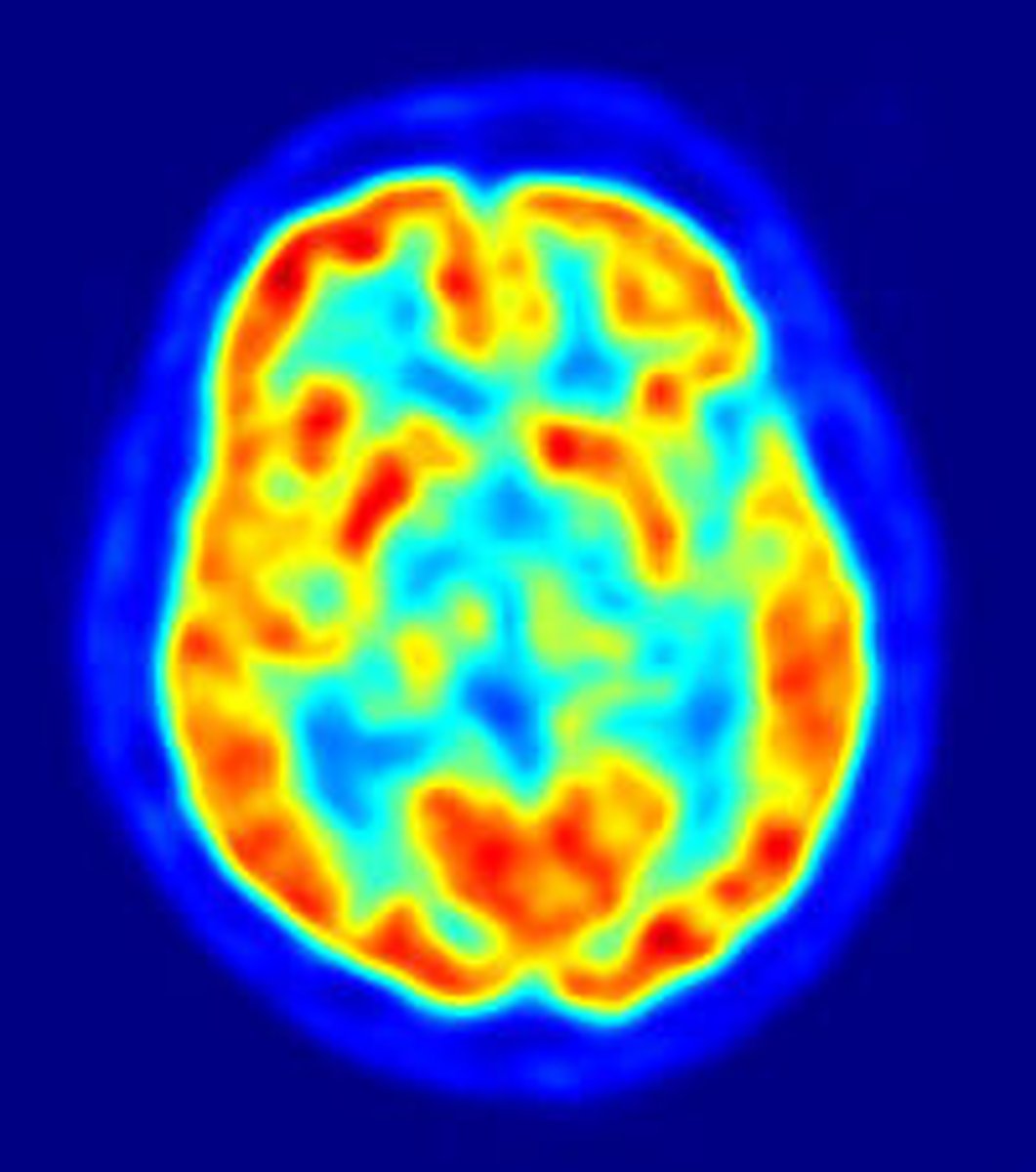
(PET) positron emission tomography scan
a visual display of brain activity that detects where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain performs a given task
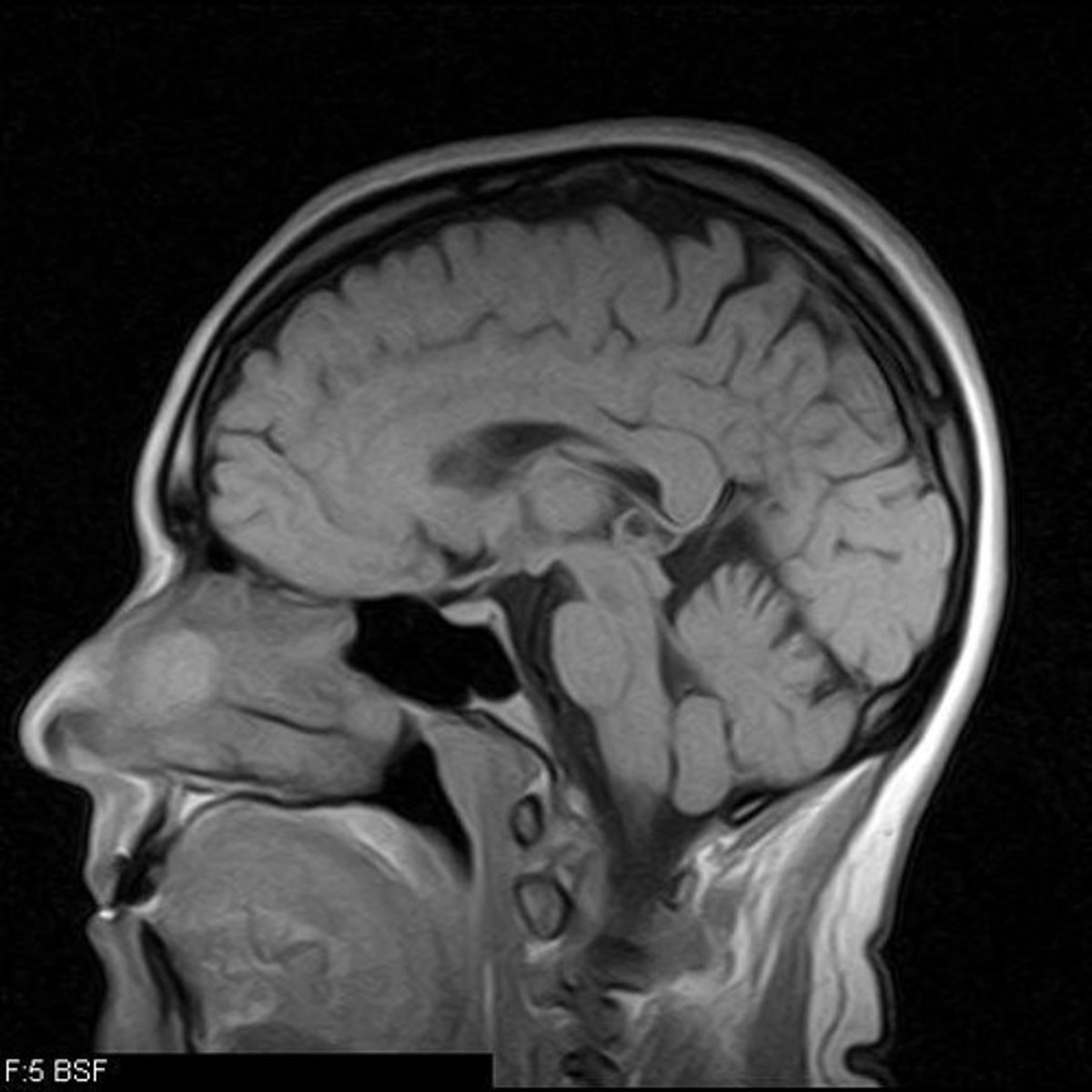
(MRI) magnetic resonance imaging
a technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated image of soft tissue. The images show brain anatomy.
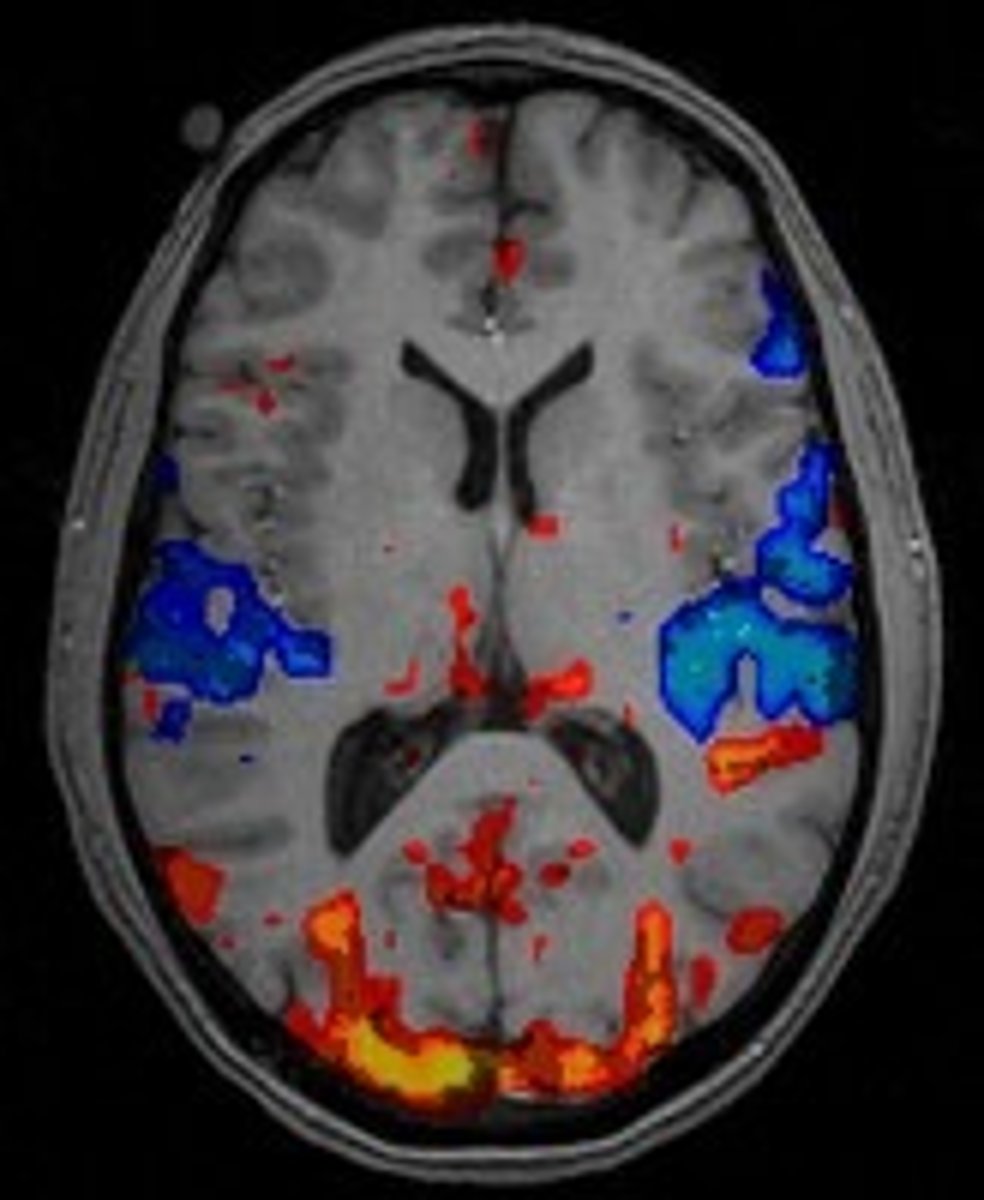
(fMRI) Functional MRI
technique for revealing blood flow and, therefore, brain activity by comparing successive MRI scans. These scans show brain functions as well as its structure.
Cerebrum
"the whole brain;" The largest division of the brain. It is divided into two hemispheres, each of which is divided into four lobes.
brainstem
the oldest part and central core of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull; this is responsible for automatic survival functions; hindbrain
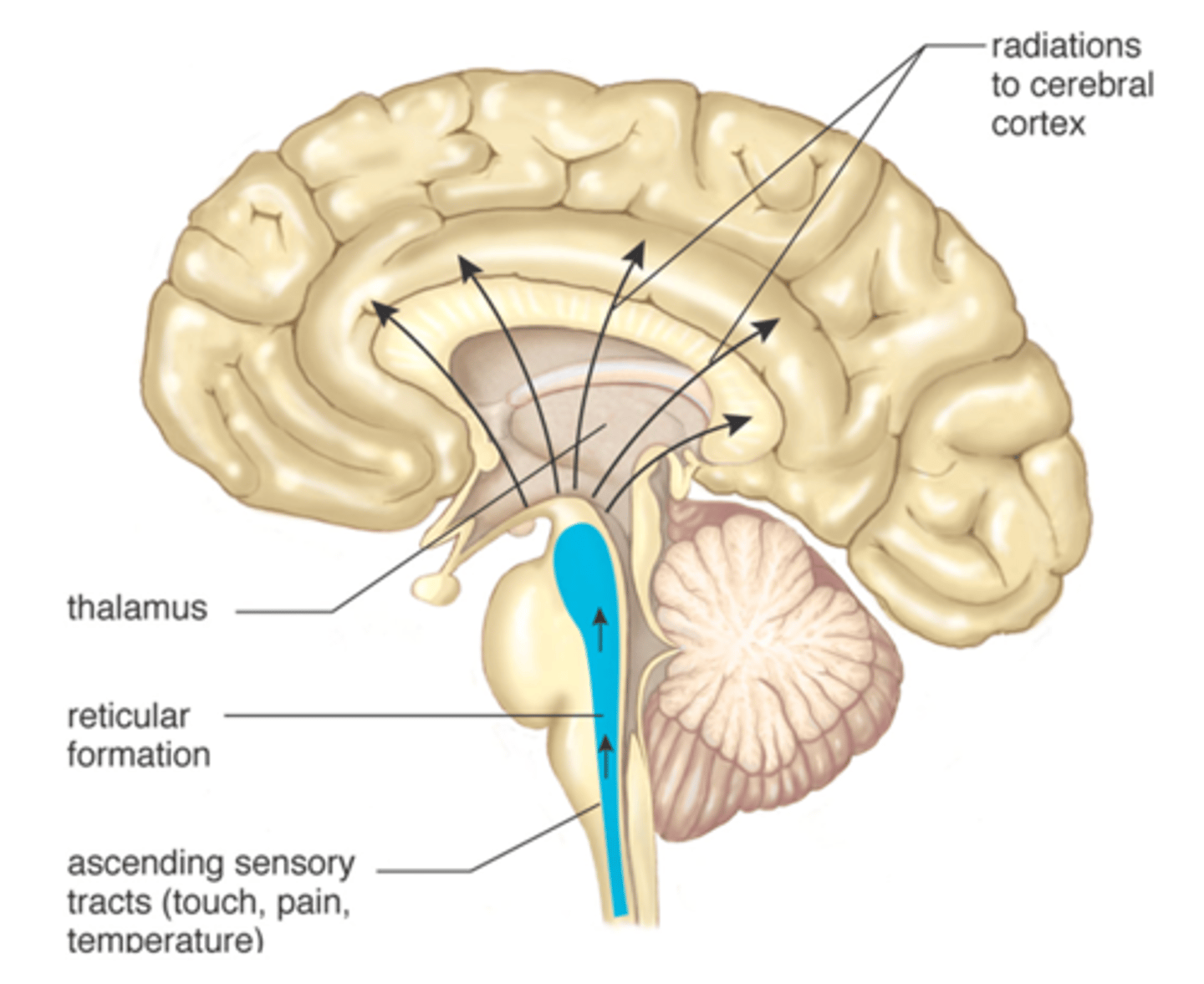
reticular formation
found in the brainstem, carries sleep and arousal messages through the brainstem; States of Consciousness
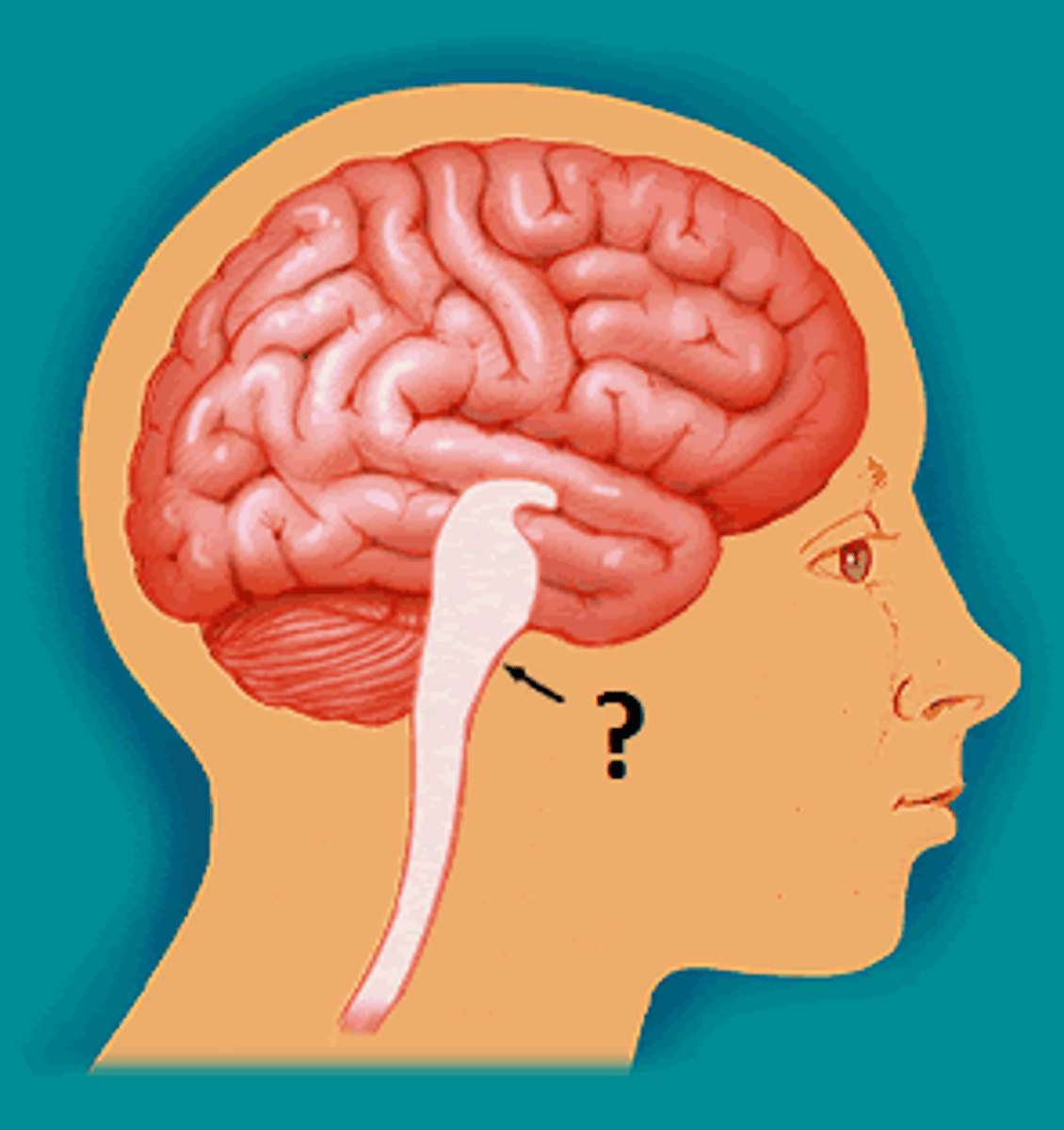
medulla
the base of the brainstem; regulates unconscious functions; breathing, circulation, heart rate
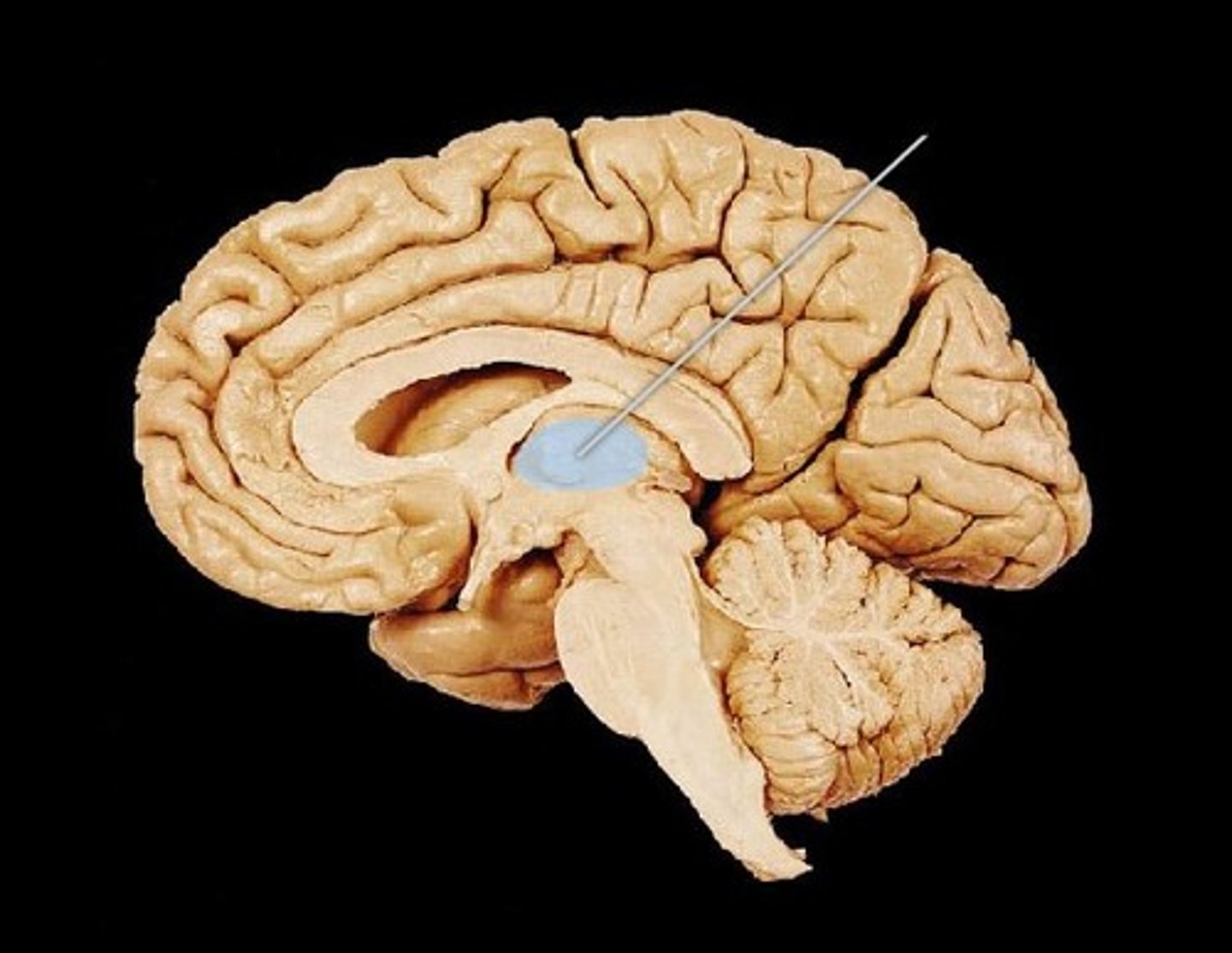
thalamus
the brain's sensory control center, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla; handles all sense except smell
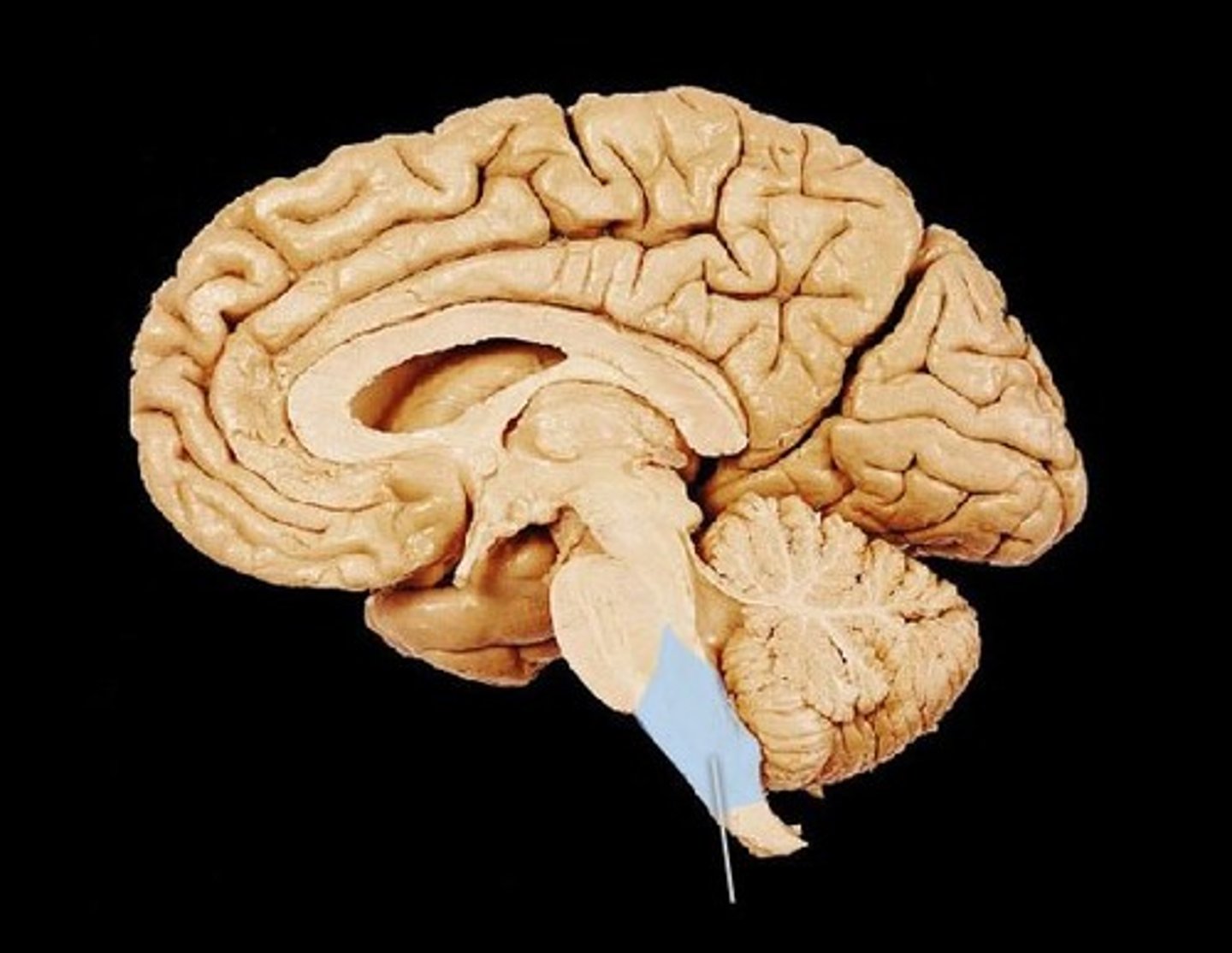
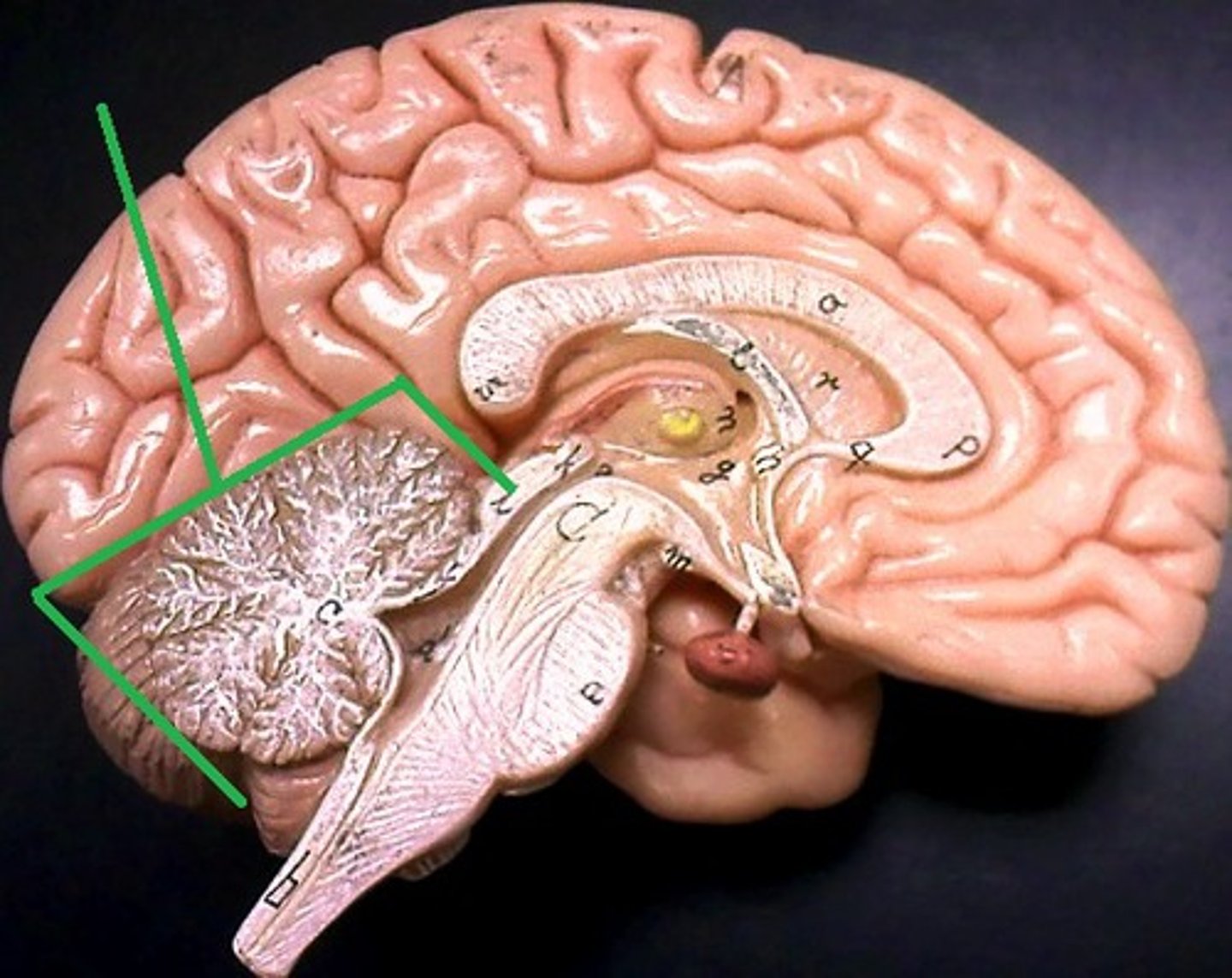
cerebellum
the "little brain" at the rear of the brainstem; functions include processing sensory input, coordinating muscle movement output and balance, and enabling nonverbal learning and memory.
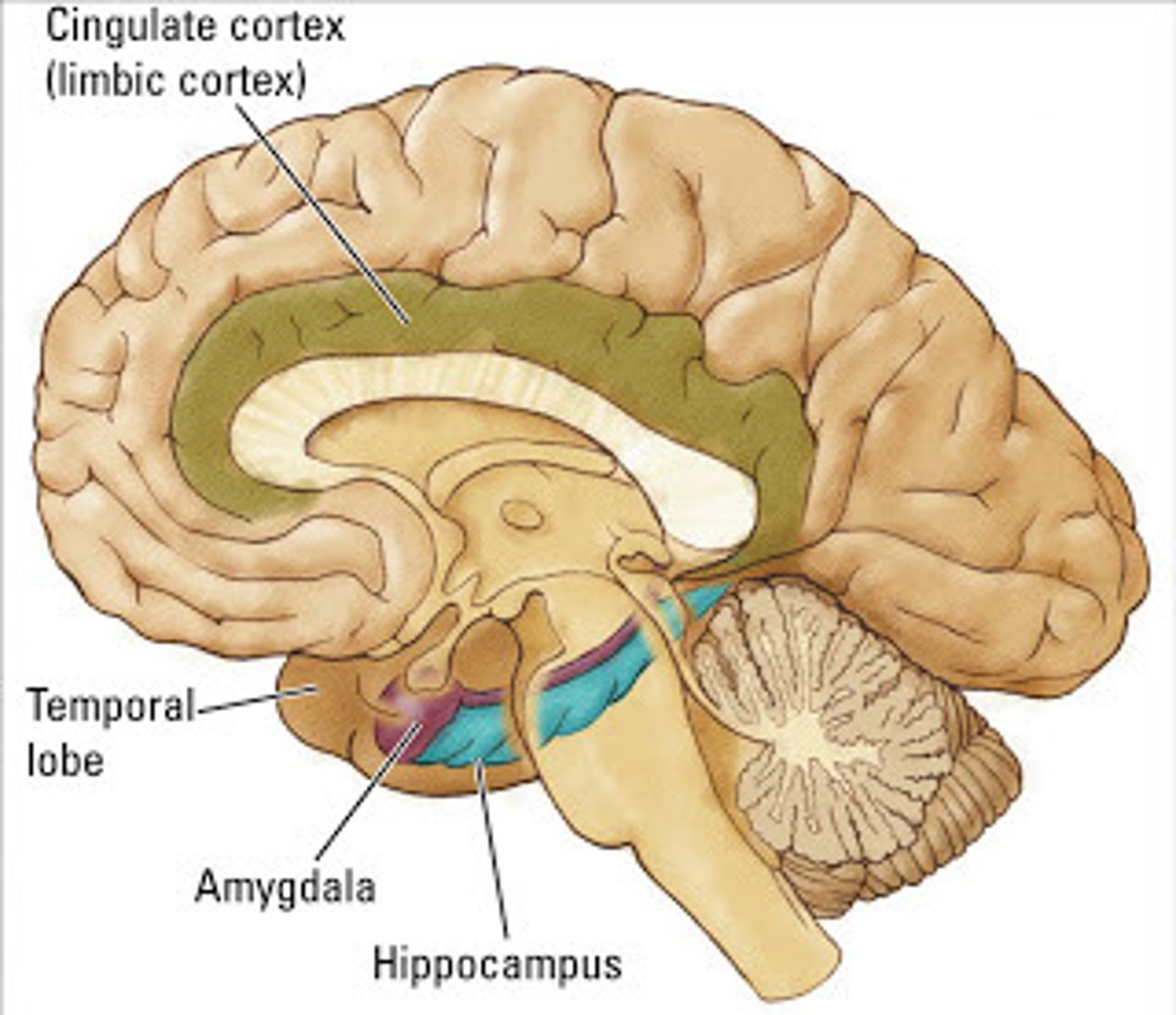
limbic system
doughnut-shaped system of neural structures at the border of the brainstem and cerebrum; including the hippocampus, amygdala, and hypothalamus; located below the cerebral hemispheres; associated with emotions and drives.
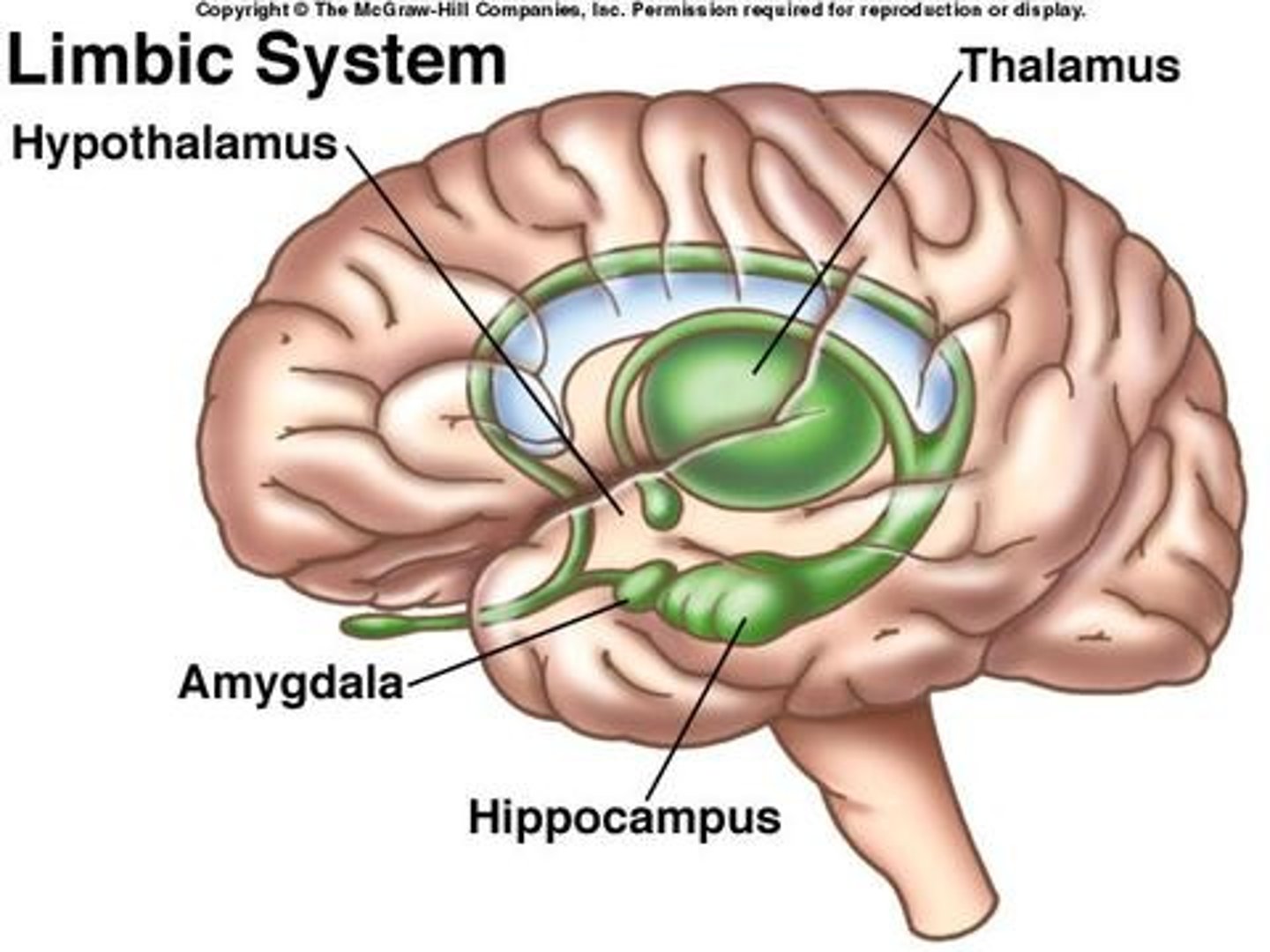
amygdala
found in the Limbic System; Controls aggression & emotional impulses/fear & anger (consists of two lima bean-sized neural clusters )
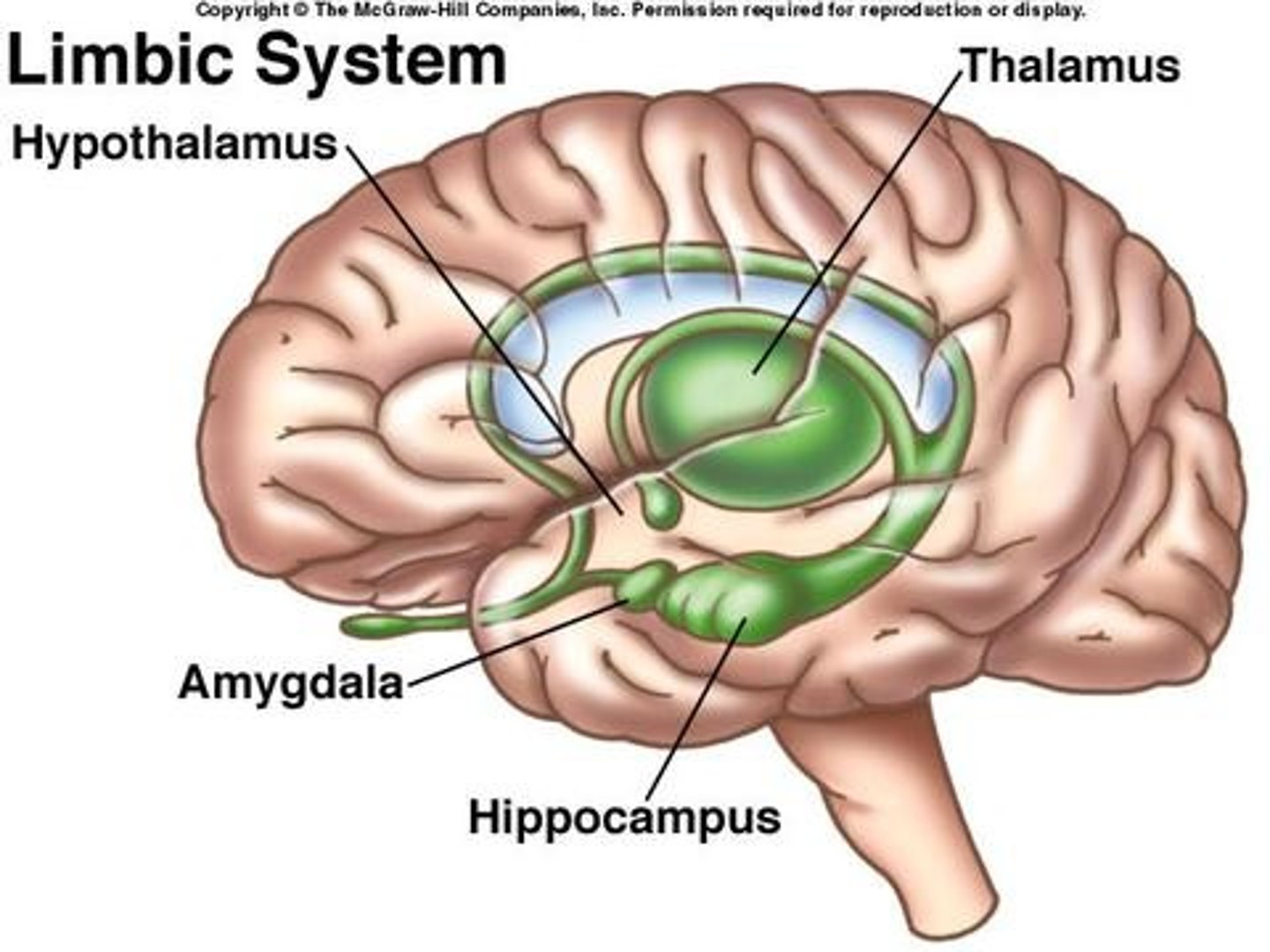
hypothalamus
a neural structure lying below (hypo) the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating drinking body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward.
Hippocampus
found in the Limbic System; handles learning and memory; specially the formation of NEW memories
cerebral cortex
the intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells covering the cerebral hemispheres; the body's ultimate control and information-processing center.

glial cells
cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons; they also play a role in learning and thinking.
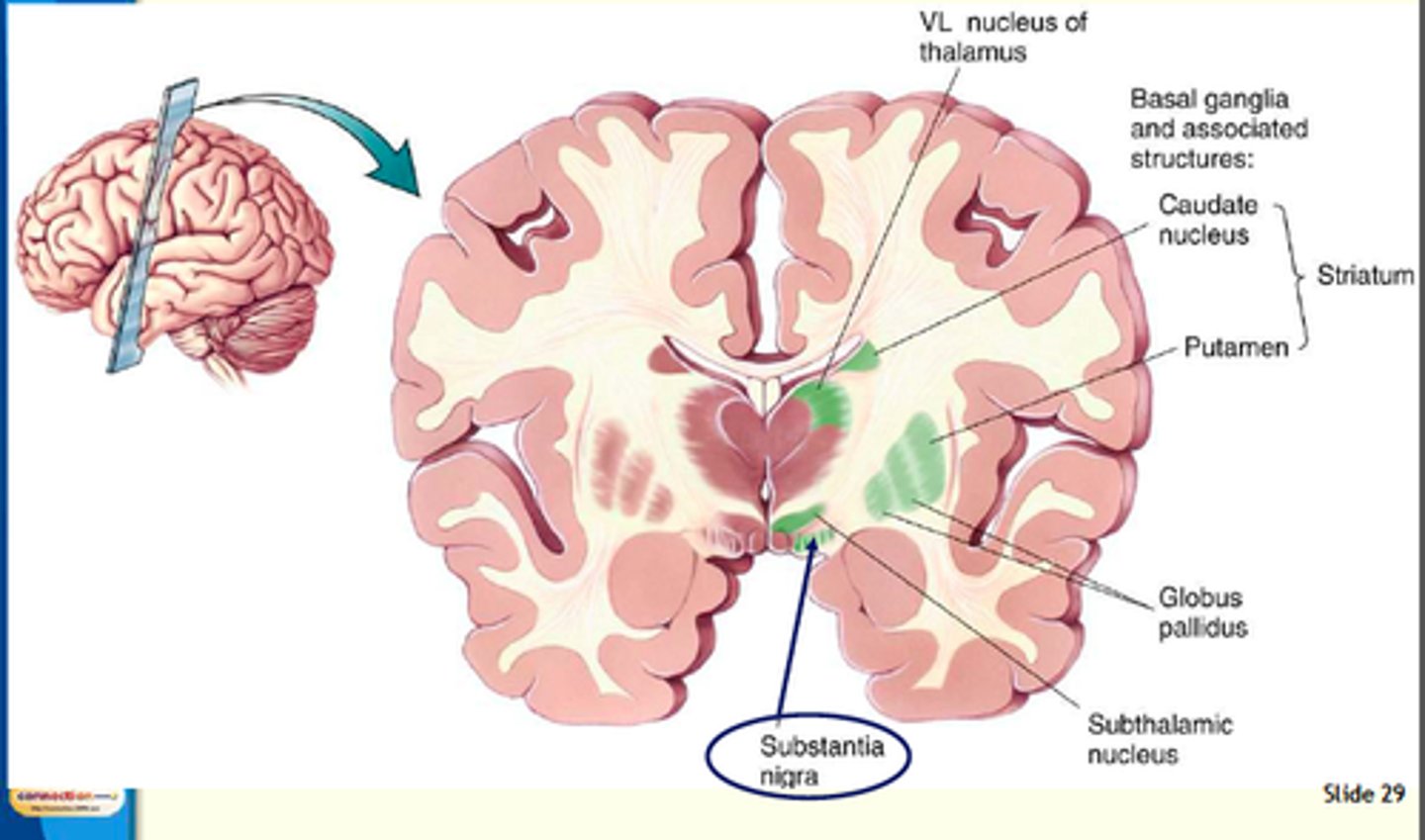
basal ganglia
inner structure of the brain handling fine motor & voluntary movements (not part of limbic system)
frontal lobes
portion of the cerebral cortex lying just behind the forehead; involved in speaking and muscle movements and in making plans and judgments.
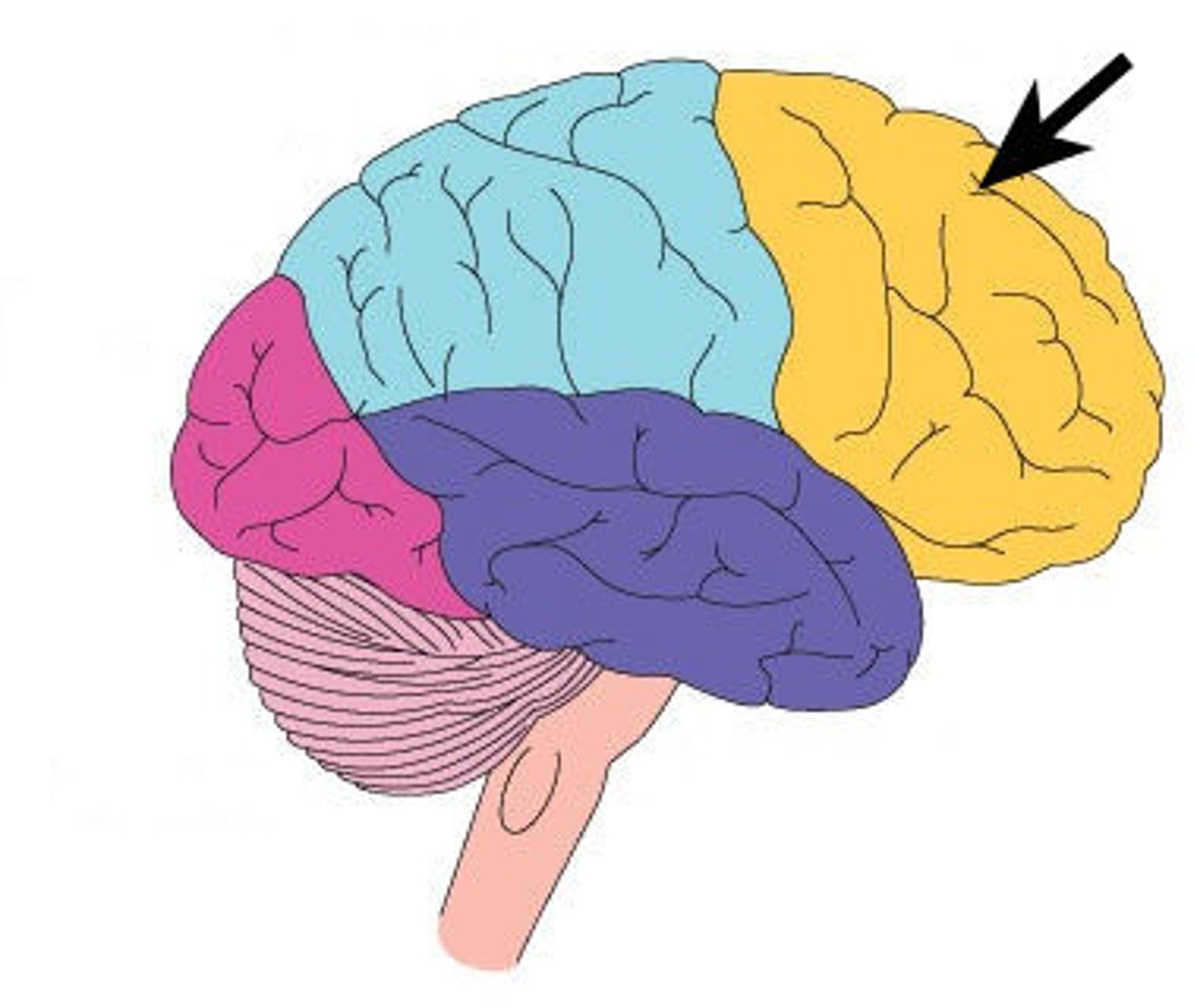
parietal lobes
portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch and body position.
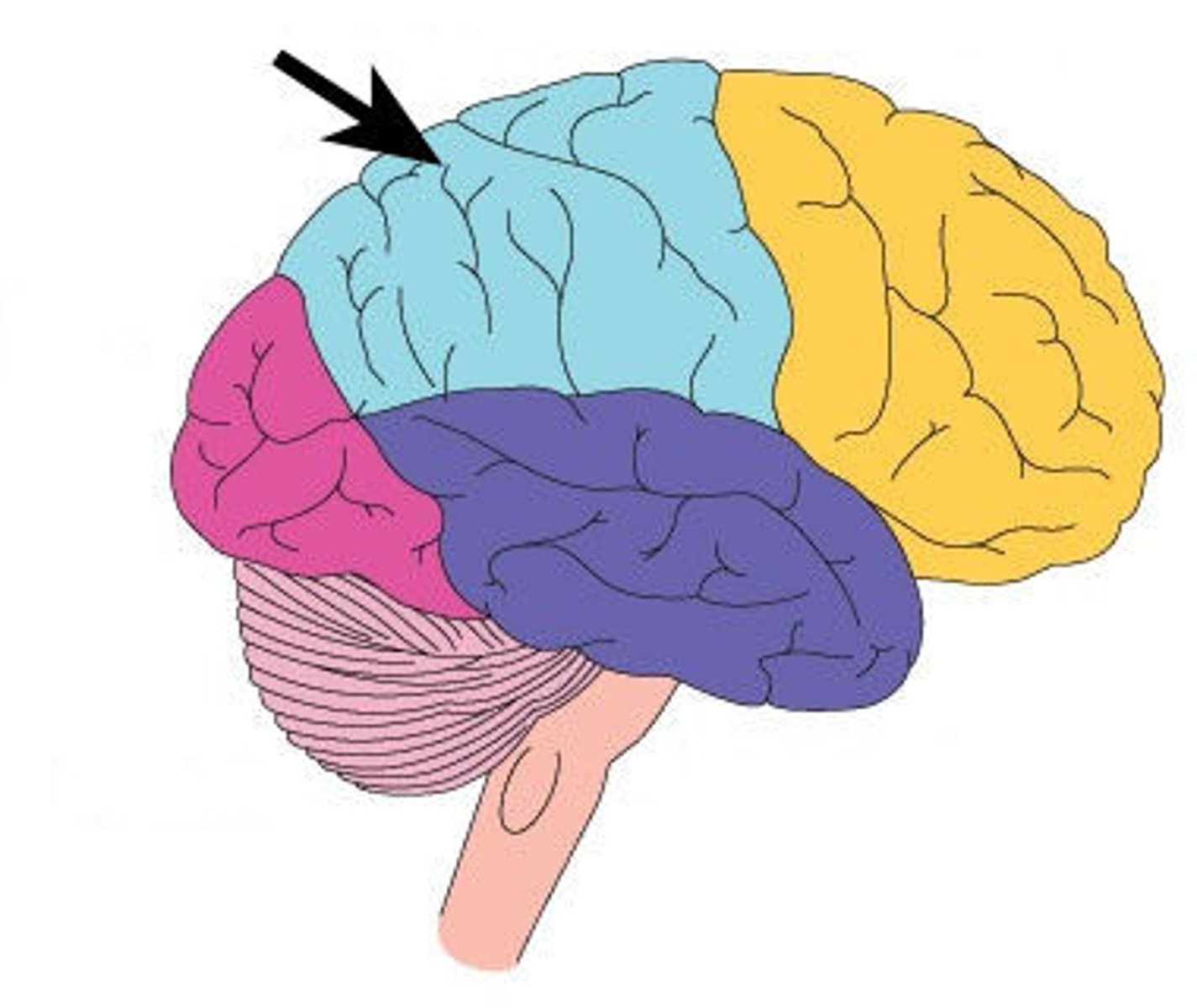
pre-frontal cortex
is the cerebral cortex which covers the front part of the frontal lobe; primary spot for decision making
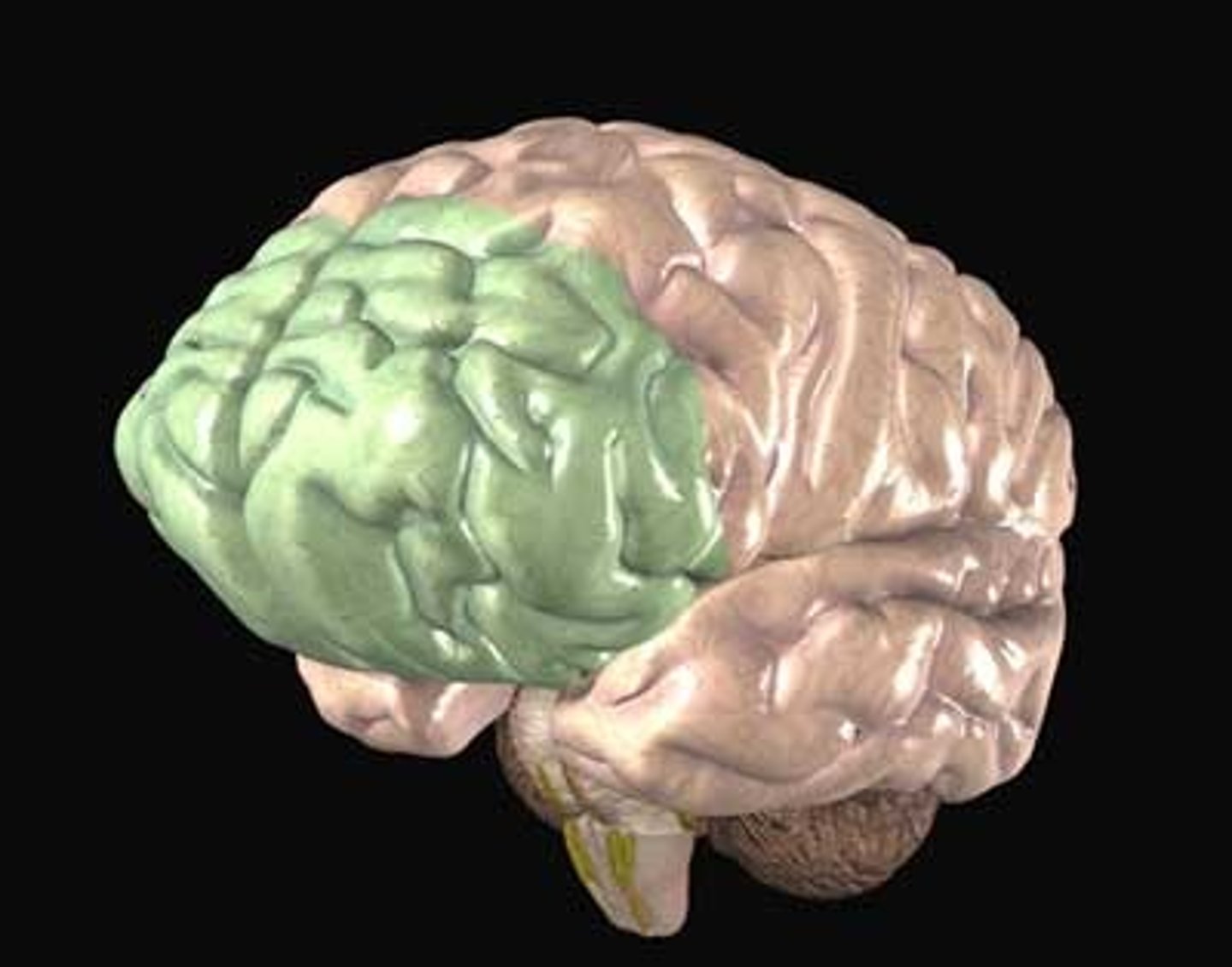
Broca's Area
found in the left frontal lobe that is in charge of speech production
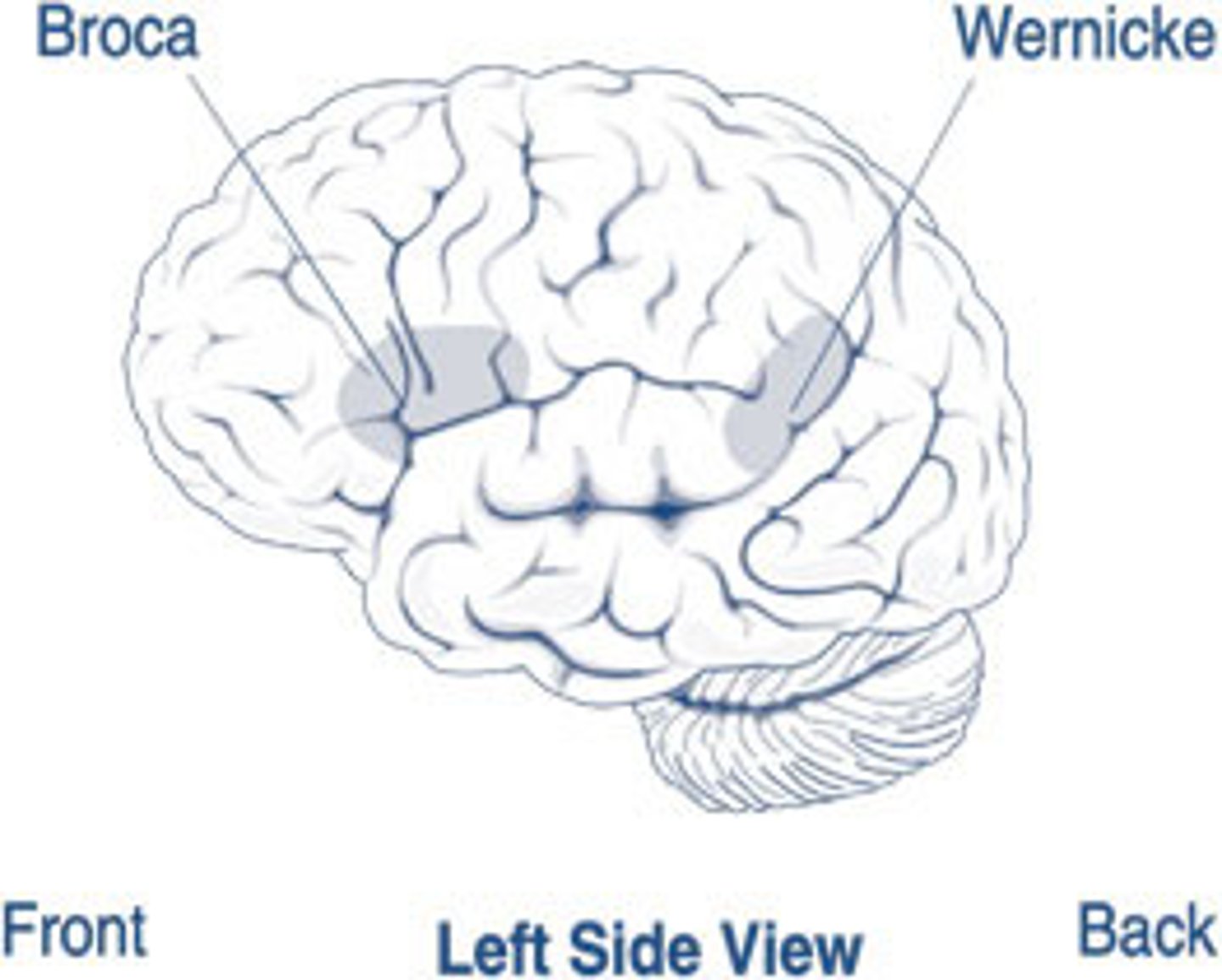
Broca's Aphasia
damage to this area of the left frontal lobe someone can't speak correctly directly or can only say one word for all words (tono!)