MCAT Bio/Biochem 2022
1/340
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
341 Terms
What happens during non competitive binding?
binds at allosteric site
How are peptide bonds formed? Broken?
dehydration synthesis
hydrolysis
What is the tertiary structure of a protein?
3D structure including bending from hydrophilic/hydrophobic interactions R groups
What is the quaternary structure of a protein?
interactions between different polypeptide chains in proteins composed of more than one polypeptide (subunit interaction)
How are carbohydrates broken down into CO2?
oxidation through combustion
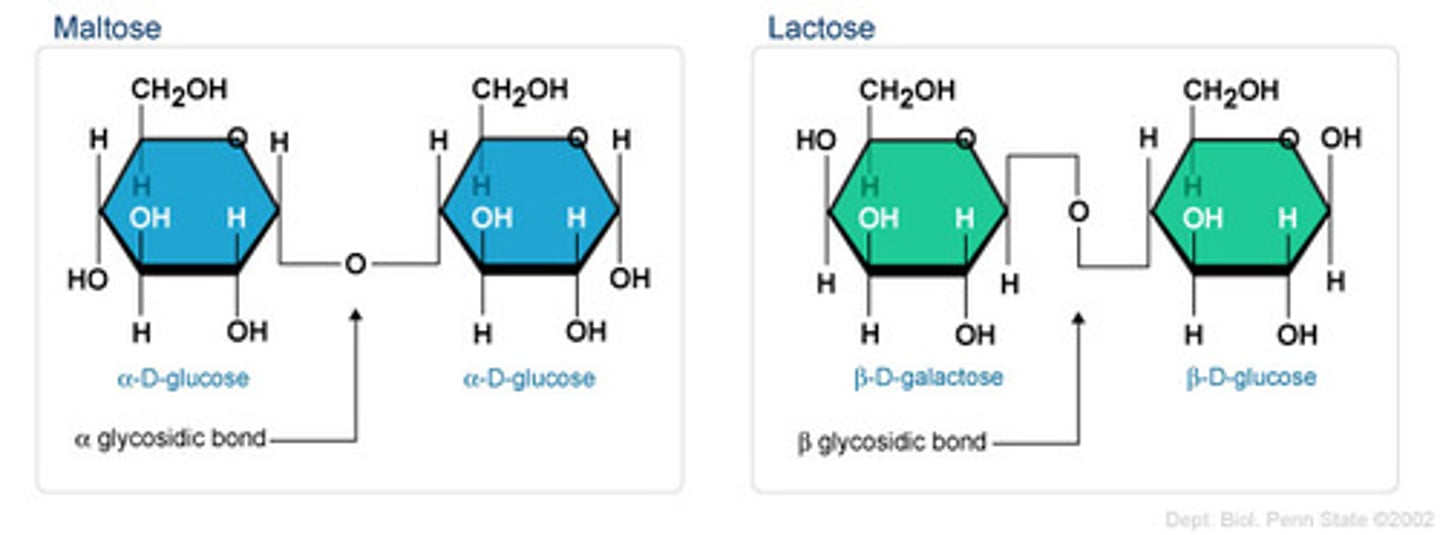
How are carbohydrates linked?
glycosidic linkages through a dehydration reaction
What is sucrose?
glucose + fructose
What is lactose?
glucose + galactose
What is maltose?
glucose + glucose
What is cellulose?
glucose + glucose
What is starch?
storage form of glucose in plants
glycogen
What do alpha linkages look like? Beta?
alpha: H points up, straight bond with O
Beta: H points down, zigzag bond with O
What are triglycerides?
lipids(fat)
stores for fatty acid
3 fatty acids esterified to a glycerol
energy stores
What is another name for lipophilic?
hydrophobic
What is Z? E?
Z: cis
E: trans
What are fatty acid stored as?
fat
What do lipase do?
break down fats into fatty acids and glycerol
Why are fats more efficient energy storage molecules than carbohydrates?
packging: hydrophobicity allows fats to pack together more closely
energy content: more than carbohydrates
Does decreasing lipid tail increase or decrease fluidity?
increase
What doe steroids look like? How are they made?
cholesterol

What is an anhydride linkage?
two phosphates bond together to form pyrophosphate
What is the first law of thermodynamics?
Energy can be transferred and transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed.
What is the second law of thermodynamics?
Every energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy of the universe.
What is the enthalpy equation?
H = E + PV
Is a negative G endergonic or exergonic?
exergonic
What is the Gib's free energy equations?
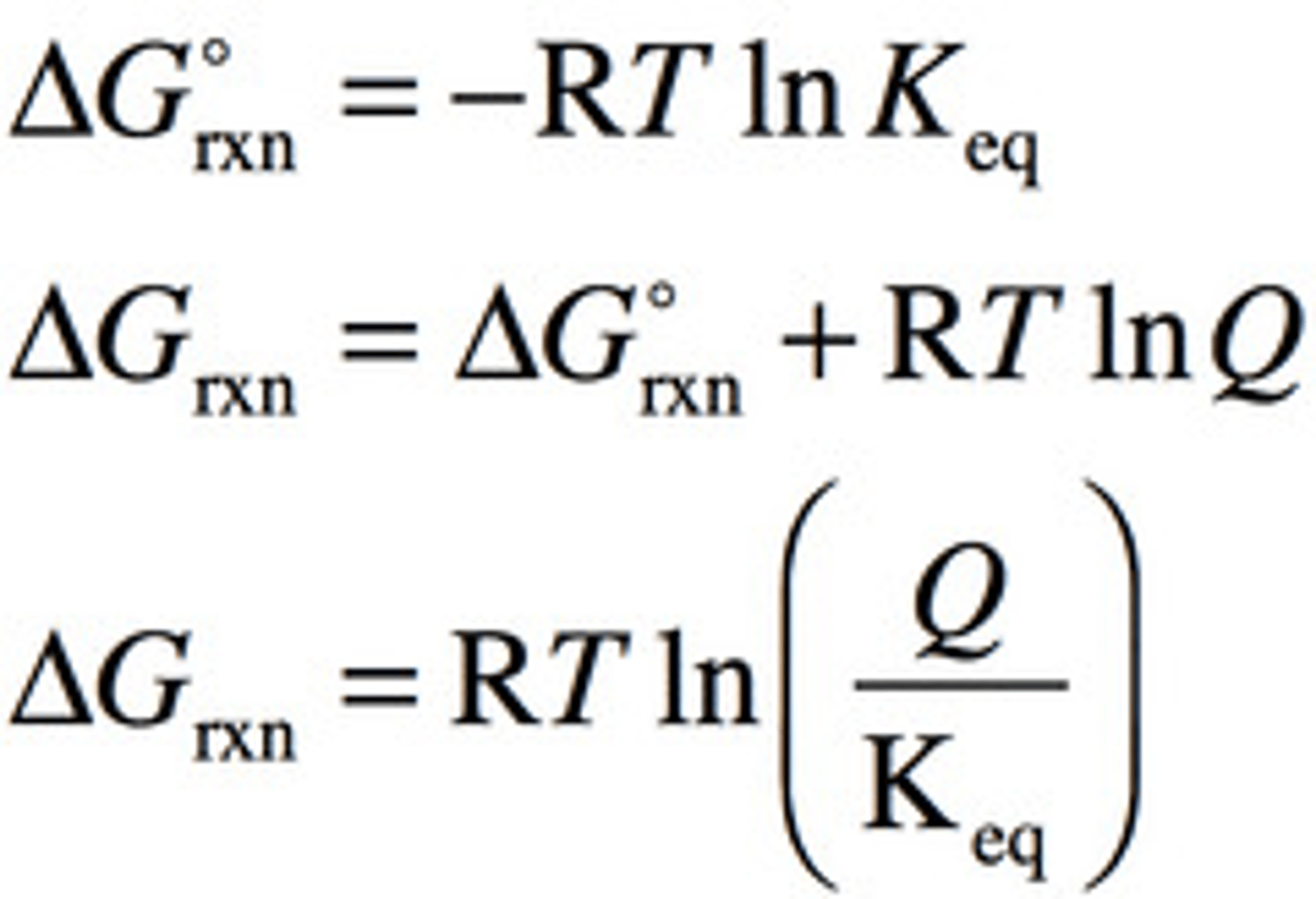
What does a catalyst or enzyme do? Is a catalyst or enzyme used up in a reaction?
lowers activation ennergy, does not change delta G
no its always there
How do we produce glucose?
oxidative catabolism
What is a nucleoside?
base + sugar (no phosphate)
Do purines have one or two rings?
two
Do pyrimidines have one or two rings?
one
How are nucleotides linked?
3'OH-5'P phosphodiester bond
How is the double helix held together?
Weak hydrogen bonds between the pairs of bases
Vaan der Waals
What does DNA gyrase do?
unwinds DNA using ATP
What are kinetochores?
The point on a chromosome by which it is attached to a spindle fiber during division.
What are telomeres?
DNA at the tips of chromosomes
6-8 bp long and guanine rich
What are copy number variants?
genomic loci that are present in some cells or individuals with extra or fewer copies
What are tandem repeats?
repetitive segments of DNA that do not code for proteins
unstable
Where does translation happen?
ribosome
What are the stop codons?
UAA, UAG, UGA
What are the start codons?
AUG (methionine)
What phase does DNA replicate?
S phase of interphase
What is helicase?
Unzips DNA at point of origin
What is topoisomerase?
corrects "overwinding" ahead of replication forks by breaking, swiveling, and rejoining DNA strands
What are single strand binding proteins?
bind to and stabilize single-stranded DNA
What does DNA polymerase require?
template and primer
How are Okazaki fragments joined together?
DNA ligase
What does DNA polymerase I do? II? III? IV? V?
I: removes the RNA primer and replaces it with DNA
II: DNA repair
III:It builds a strand of DNA.
IV & V: Error prone; used to stall other polymerases when DNA repair pathways have been activated.
What is the Hayflick limit?
Cells divide only a certain number of times and then die
What are the types of mutations?
silent: same amino acid
missense: different amino acid
nonsense: stop
frameshift
What are transposons? IS element? Complex? Composite?
segments of DNA that can move from one region of DNA to another
IS: only transposon
Complex transposon: transposon + genes
Composite transposon: transposon + central region + transposon
What do inverted repeats do for transposons?
allow for movement
What is excision repair?
Removal of damaged DNA segments followed by repair synthesis with the correct nucleotide sequence
before replication
What is homologous recombination?
The swapping of chromosome parts between homologous pairs
What is nonhomologous end joining?
brings together 2 ends of DNA fragments to repair double-stranded breaks. no requirement for homology
Are eukaryotes monocistronic or polycistronnic? Prokaryotes?
E: mono
P: poly
What is heterogeneous nuclear RNA?
RNA before processing events (cap and tail or splicing)
What is small nuclear RNA (snRNA)? MicroRNA (miRNA)? PIWI-innteracting RNA (piRNA)? long ncRNA?
snRNA: RNA that deals with splicing in RNA processing
miRNA: act as regulators
piRNA: single stranded, short RNA that prevents transposons from mobilizing
long ncRNA: long RNA that controls transcription by regulating promoter and control splicing and translation. Function in imprinting and X-chromosome inactivation
What is the core enzyme?
Helps to initiate and synthesize RNA. 4 main polypeptides (2 alpha, 1 beta, 1 beta prime) 1 sigma bound only at initiation in prokaryotes
CANNOT ALONE CARRY OUT TRANSCRIPTION
What is a sigma factor or haloenzyme?
a protein needed only for initiation of RNA synthesis that helps find the promoter and increase specific affinity
What is the Pribnow box?
promoter sequence that forms a closed complex when initiated
Do prokaryotes have introns?
nope
What does RNA polymerase I do in prokaryotes? II? III?
I: transcribes rRNA
II: transcribes mRNA
III: transcribes tRNA
Where is the amino acid attached on the tRNA?
3' end
What is the Wobble Hypothesis?
There are fewer tRNAs than codons. It was proposed that the 3' end of the codon allows for a more relaxed bonding with the 5' base of the anticodon. The potential for non-Watson-Crick base pairing at this position allows a single tRNA to pair with several different codons.
What is amino acid activation?
When tRNA attaches to amino acid in cytoplasm (requires ATP)
How big are the prokaryotes ribosome? Eukaryotes?
P: 70S
E: 80S
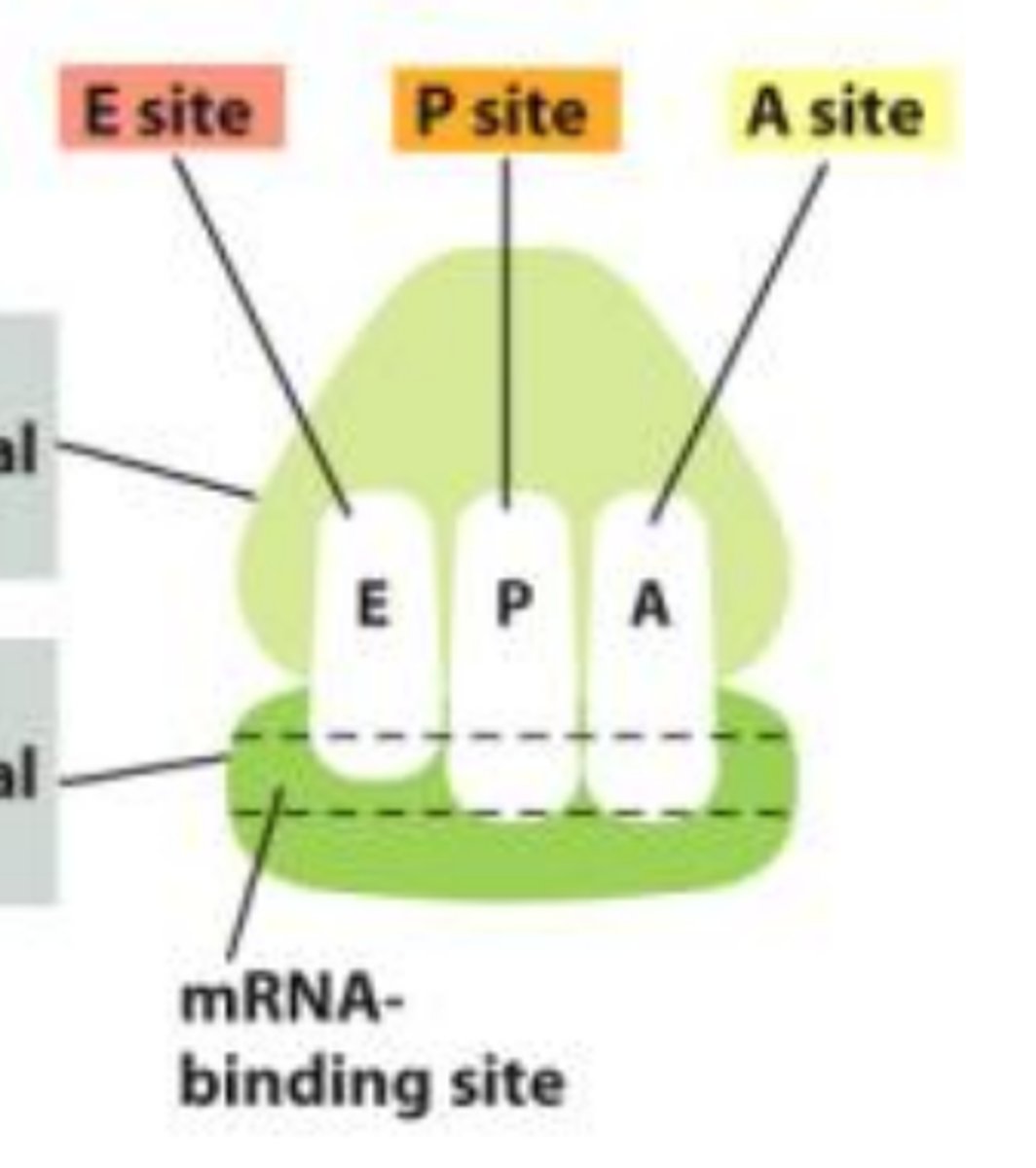
What are the binding sites of ribosomes?
-A site holds tRNA that carries the next amino acid
-P site holds tRNA that carries the growing polypeptide chain
-E site is the exit site where tRNAs leave the ribosome
what is the Shinne-Dalgarno sequence?
prokaryote ribosome binding site that starts transcription
How does initiation start in prokaryotes?
binding IF1 and IF3 to mRNA and then IF2 joins in
What is the lac operon?
inducible operon and contains genes that code for enzymes used in the hydrolysis and metabolism of lactose
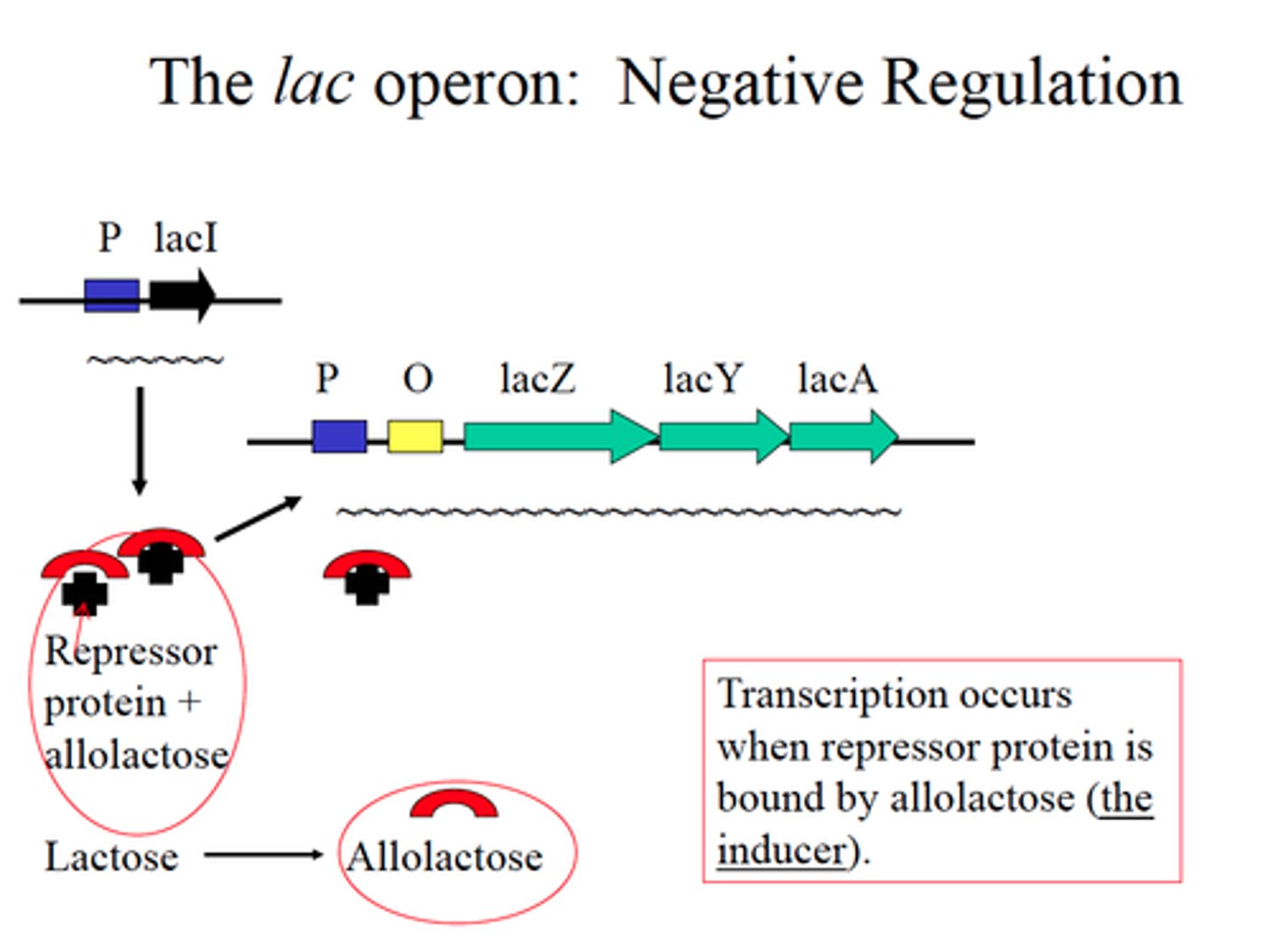
What is the trp operon?
repressible operon
What makes the amino acids acidic?
Negative side chains due to presence of carboxyl group
What makes the amino acids basic?
Positive side chains due to amino groups
What is unique about histidine?
it exists in both a protonated and deprotonated state
What makes the amino acid non polar?
alkyl or aromatic side chain
Which amino acids can be phosphorylated?
serine, threonine, tyrosine
Which amino acids contain sulfur?
cysteine and methionine
What happens when pH is less than the pKa? pH more than?
Less: protonation
More: deprotonation
What happens in tertiary structures?
hydrophobic/hydrophilic interactions
What is the hydrophobic effect?
hydrophobic regions of the protein in its tertiary structure are moved inward and the hydrophilic regions outward
Do enzymes have a thermodynamic or kinetic role?
kinetic only (influencing rate - kinetic - not favorability -thermodynamic)
What does isomerase do?
rearrangement of atoms
What does lyase do?
Cuts C-C bonds w/ ATP
What does oxidoreductase do?
oxidation-reduction reactions
What does polymerase do?
extends DNA chain
What is covalent modification?
phosphorylation by kinases can alter function of proteins
Are allosteric sites covalent or non covalent? Reversible or irreversible?
non covalent
Reversible
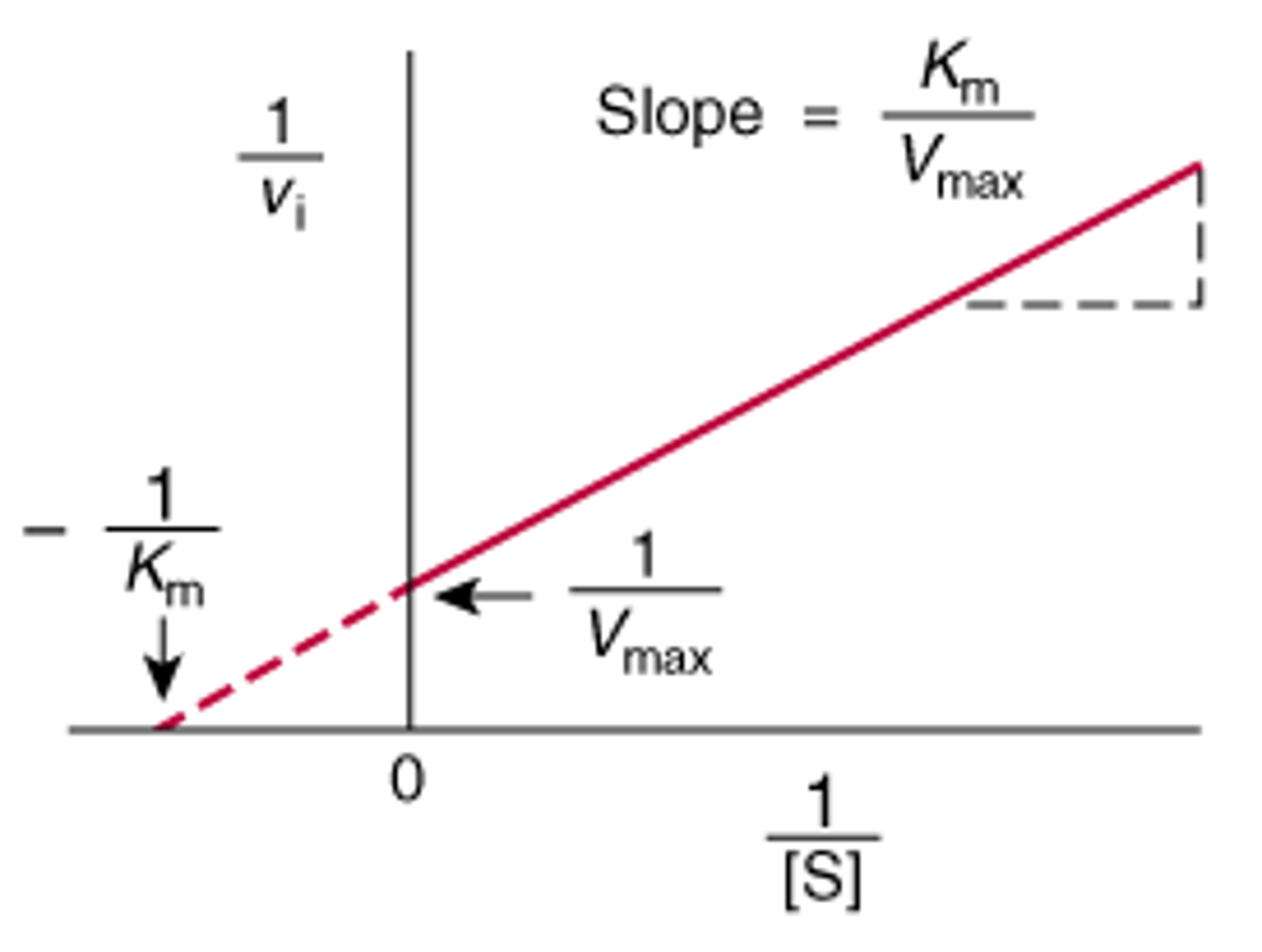
What is Vmax?
the maximum rate of reaction -- when the enzyme is saturated with substrate
What is Km?
Substrate concentration at 1/2 Vmax
What is a low Km?
enzyme has high affinity for substrate
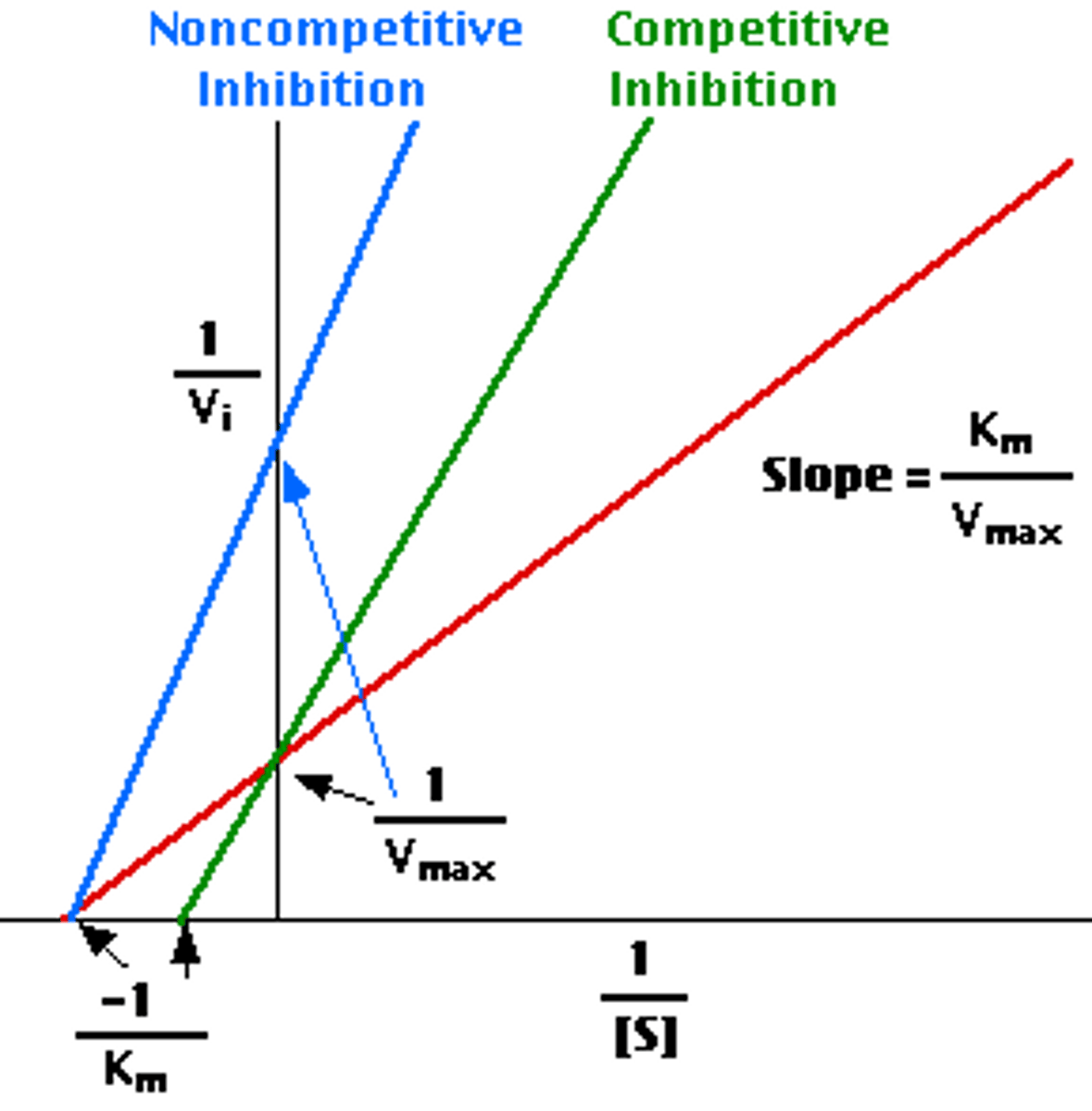
What does is non competitive inhibition [S] vs. [V]?
Lowe Vmax
no change Km
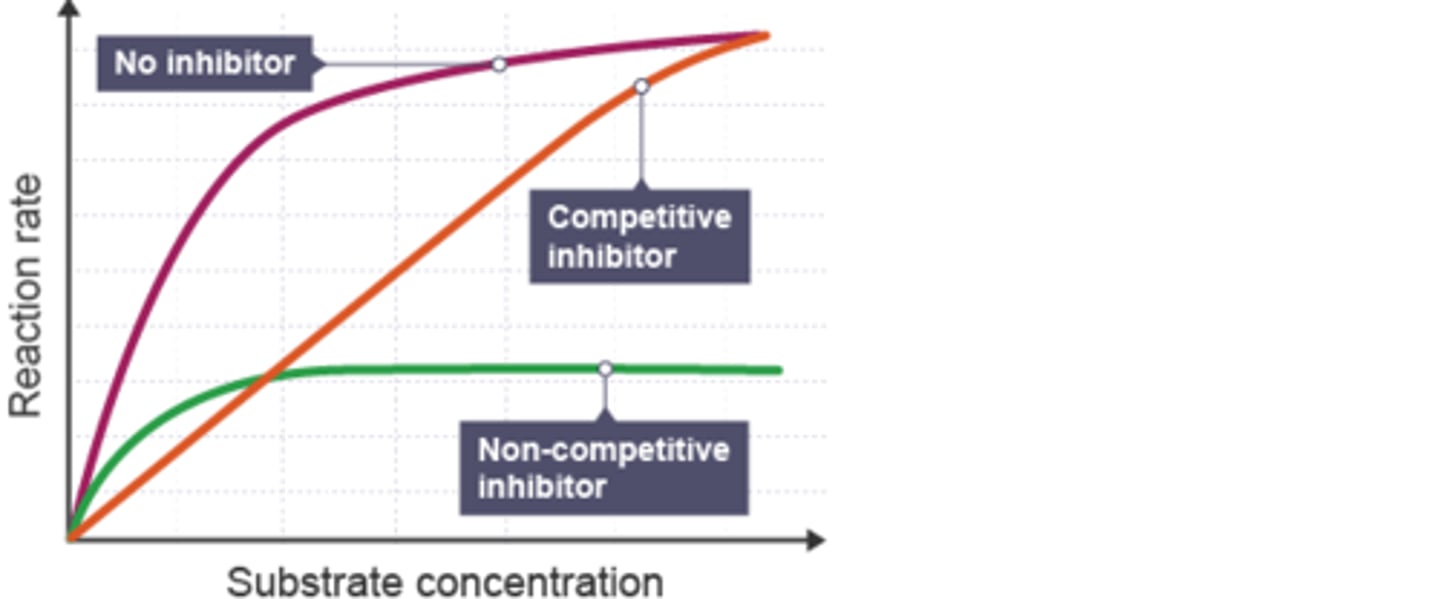
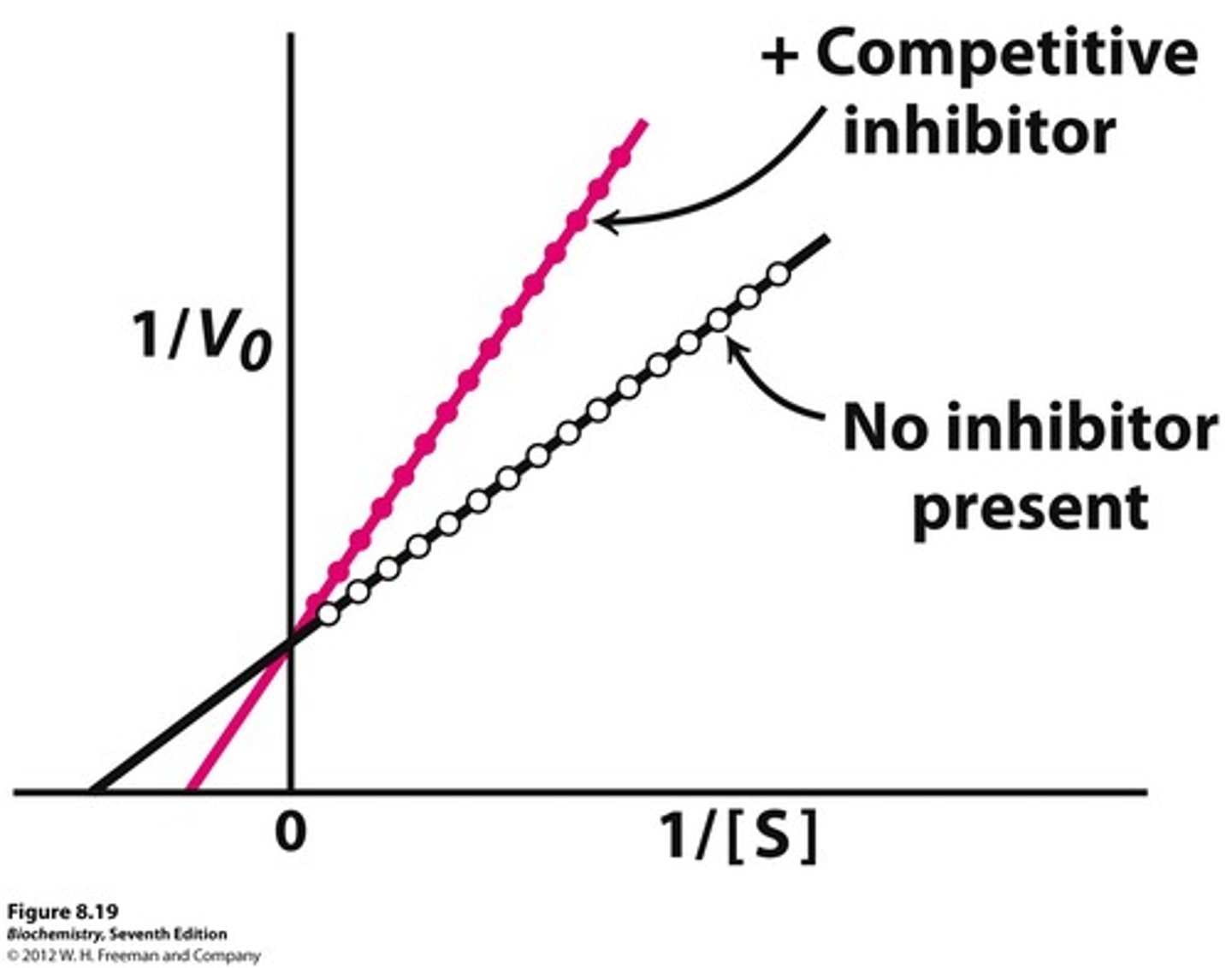
What does is competitive inhibition [S] vs. [V]?
No change Vmax
raise Km
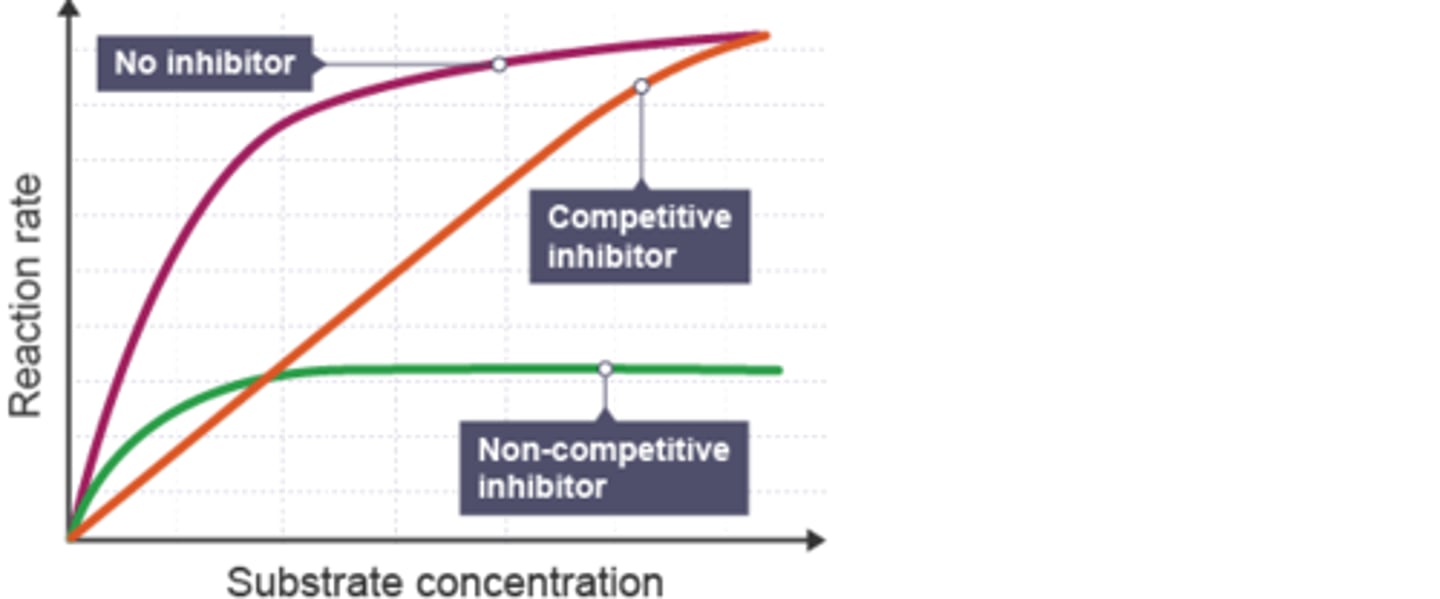
What happens during uncompetitive binding?
binds at enzyme-substrate complex
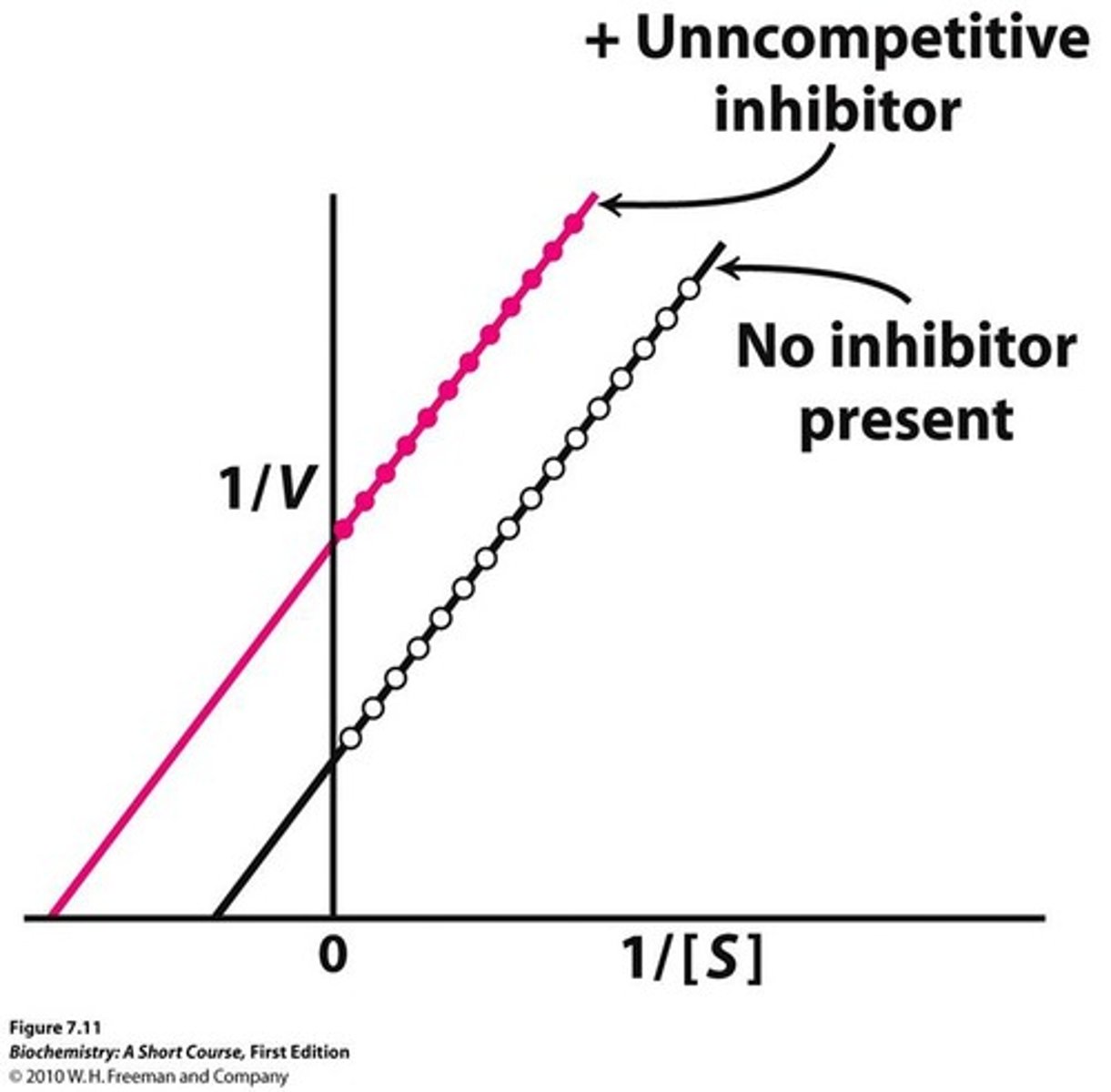
What does is uncompetitive inhibition [S] vs. [V]?
lower Km and Vmax
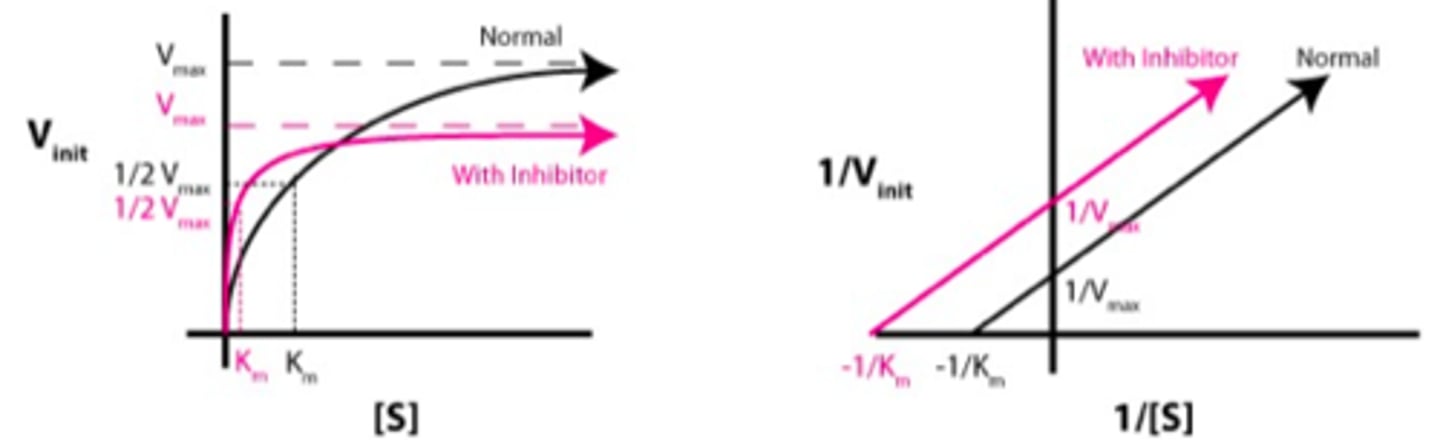
What happens during mixed type inhibition binding?
lower Vmax
Km varies
In a line weaver burk plot, what is the slope? Y intercept? X intercept?
What is a competitive line weaver burk plot?
What is a noncompetitive line weaver burk plot?
What is a uncompetitive line weaver burk plot?