World History World War 1
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
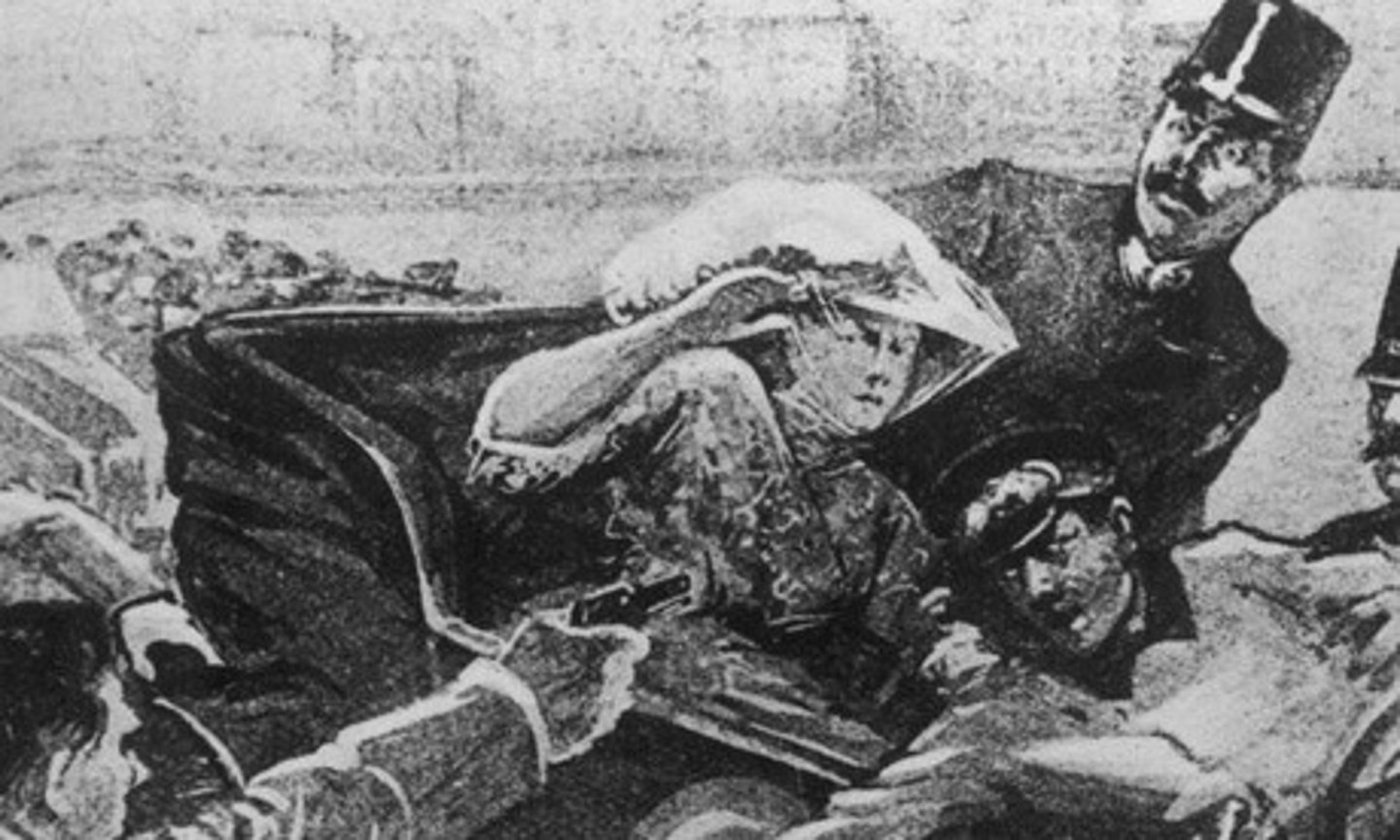
The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand
This was the murder of the heir to the throne of Austria-Hungary. This event was the spark that started World War I.
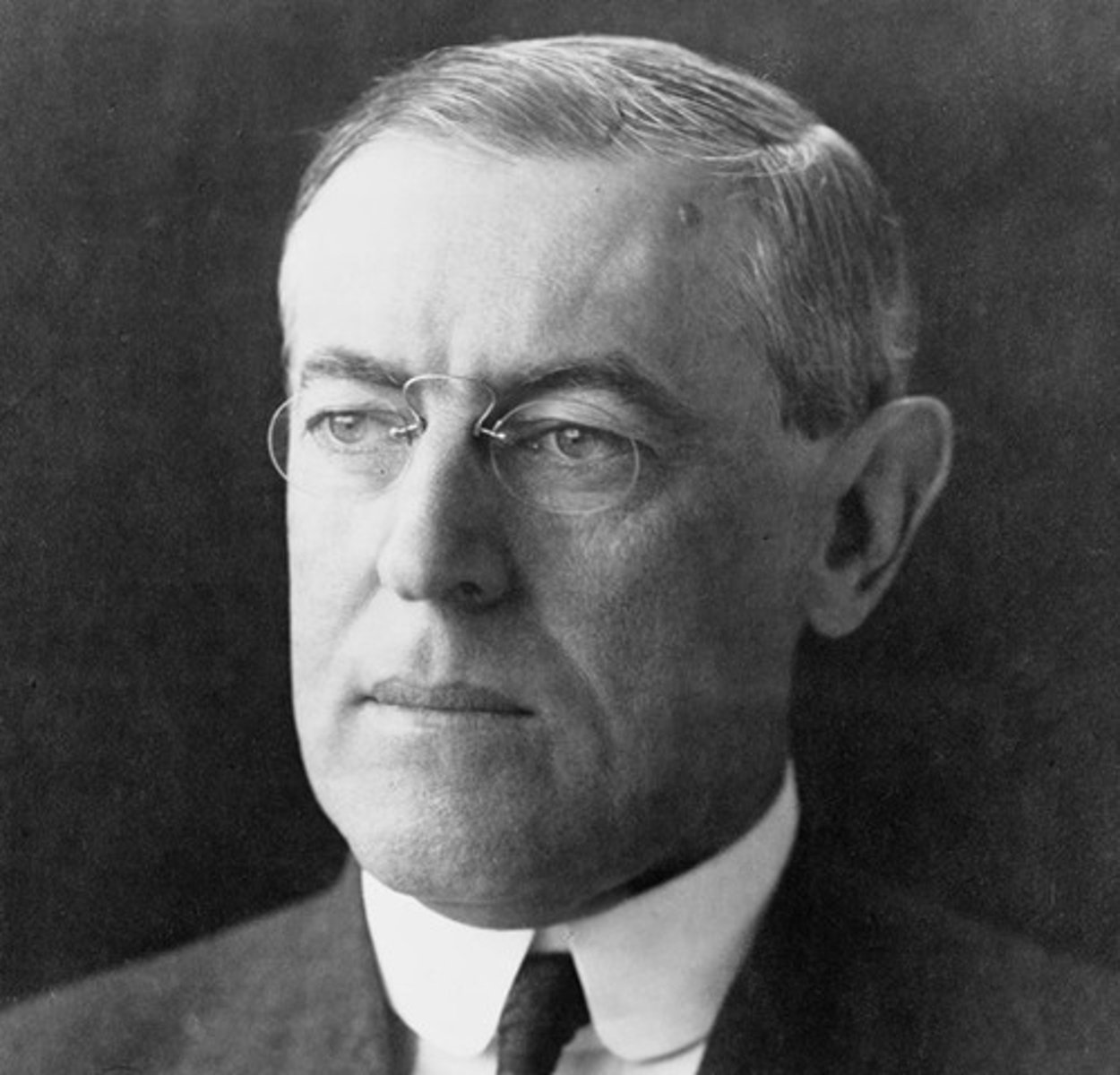
Woodrow Wilson
This was the president who was elected in 1912, and led the US into WWI. Later wrote a plan for post-WWI peace known as the Fourteen Points.

Austria-Hungary
This Central Power declared war on Serbia after Serbia rejected their ultimatum.
Kaiser Wilhelm II of Germany
This German Emperor behaved aggressively through increased militarism. He ended Bismarck's isolation of France by allowing a treaty with Russia to lapse.

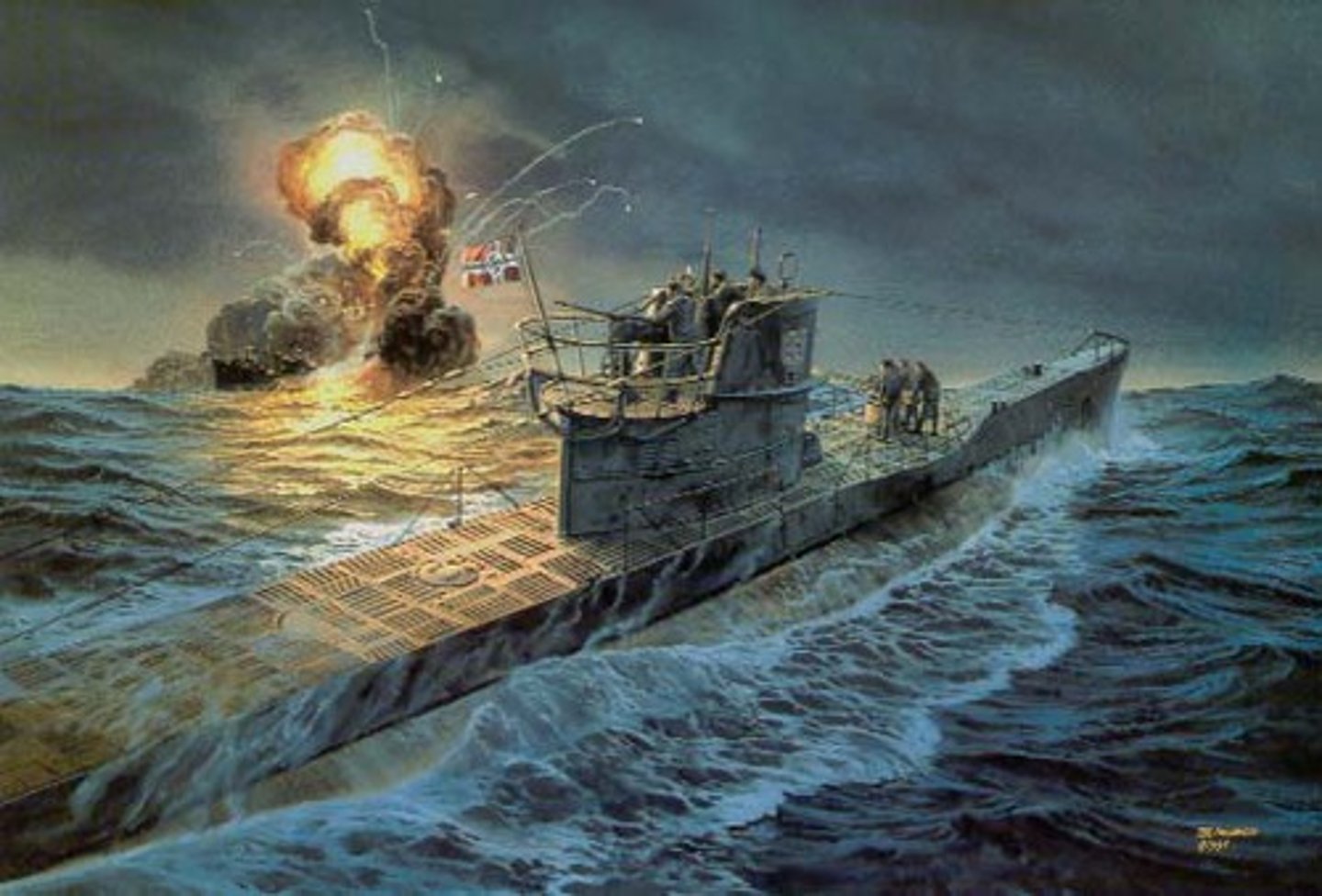
U-boats
Used by the Germans as a means to break Britain's naval blockade. Many British and American ships were attacked in the North Sea and in the Atlantic Ocean.

Nationalism
This cause of World War I was based on an intense pride in one's nation. The term also describes the desire of a group to be independent from foreign rule.

Allied Powers
This alliance during WWI included the United States, Great Britain, France, Russia and Italy.
Wilson's Fourteen Points
This is the plan for post-World War I outlined by President Wilson in 1918. The plan provided a framework for lasting peace.

Zimmerman Telegram
This intercepted note offered Mexico land (Texas, Arizona and New Mexico) if Mexico joined the war against the United States.

Lusitania
Germans U-boats sank this British passenger ship in 1915. The event turned American opinion against Germany.

Trench Warfare
This style of warfare was common in WWI, due to the need for protection from the machine gun and heavy artillery.

Armistice, 1918
This was the agreement between the Allies and Central Powers that ended WWI fighting. It began at 11/11/1918 at 11:11 am.

Reparations
This term refers to the payments that Germany was required to make under the treaty of Versailles.

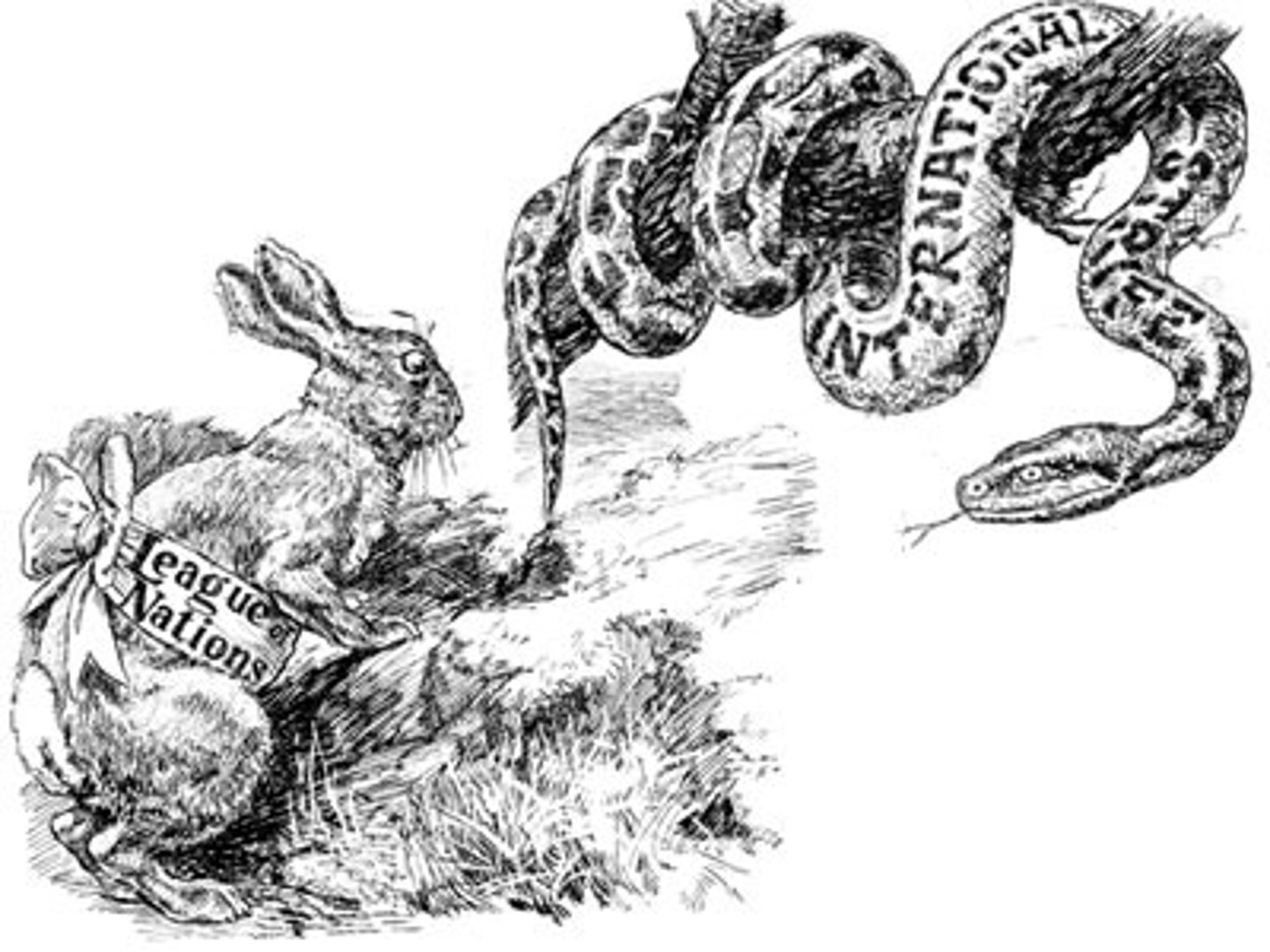
League of Nations
This intergovernmental organization was the only one of Wilson's 14 points to make it into the Treaty of Versailles. It did not work effectively to prevent WWII.

War Guilt Clause
This clause of the Treaty of Versailles placed all blame for WWI with Germany and its allies.

Causes of World War I Imperialism
This cause of World War II resulted from the competition among European nations for colonies in Africa and Asia from 1880-1914. This created tension, especially between Germany and Great Britain.

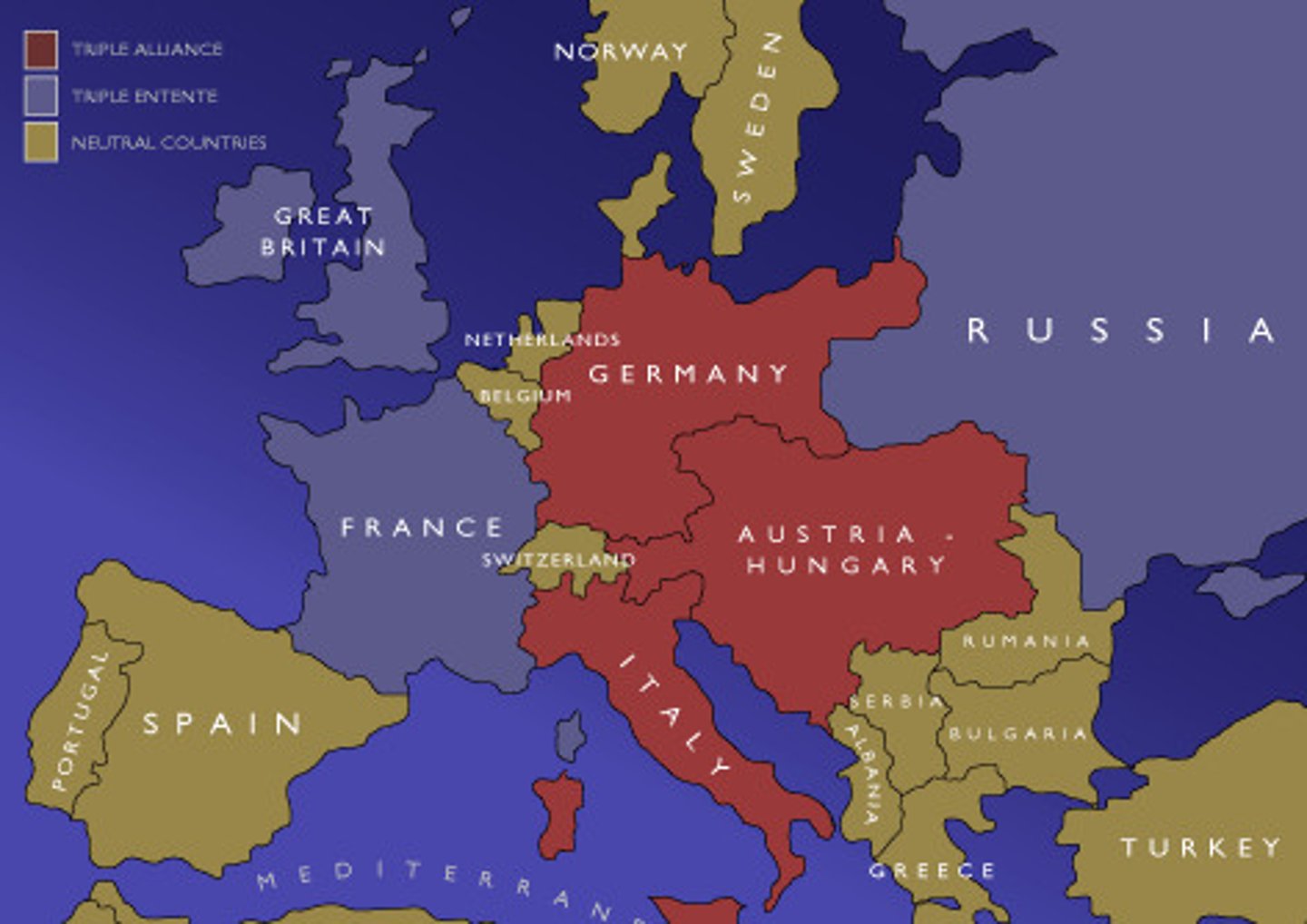
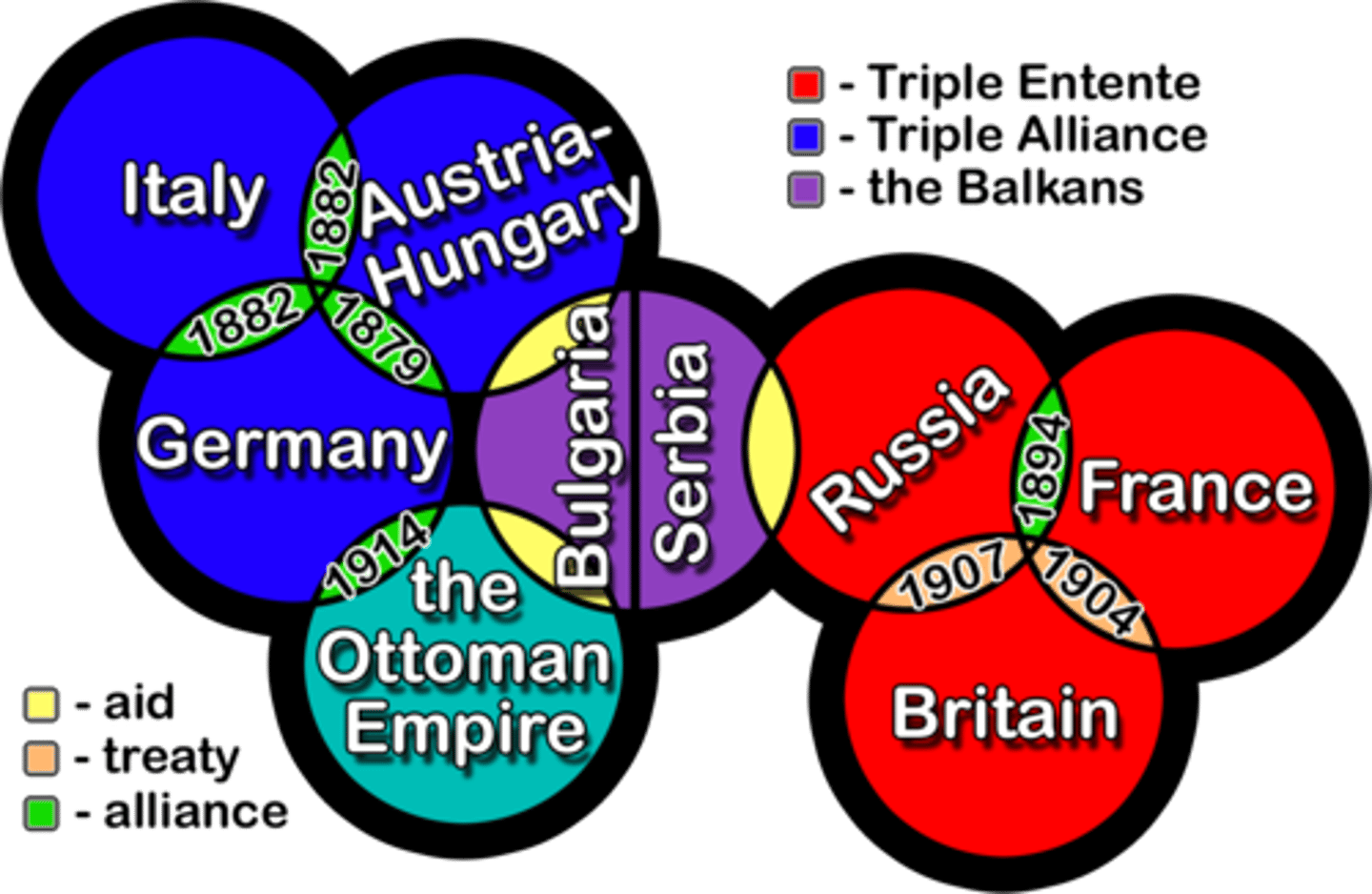
Causes of World War I Alliances
This was a major cause of WWI. Two major alliances formed the Triple Alliance (Germany, Austria, Italy) and the Triple Entente (France, England, Russia). This alliance system made world war likely, by drawing all countries into a small war.
M.A.I.N.
These are the four long-term causes of World War I. Militarism, Alliances, Imperialism, Nationalism.
Triple Alliance
This alliance was made Germany, Austria-Hungary and Italy in the years before WWI. IN RED ABOVE
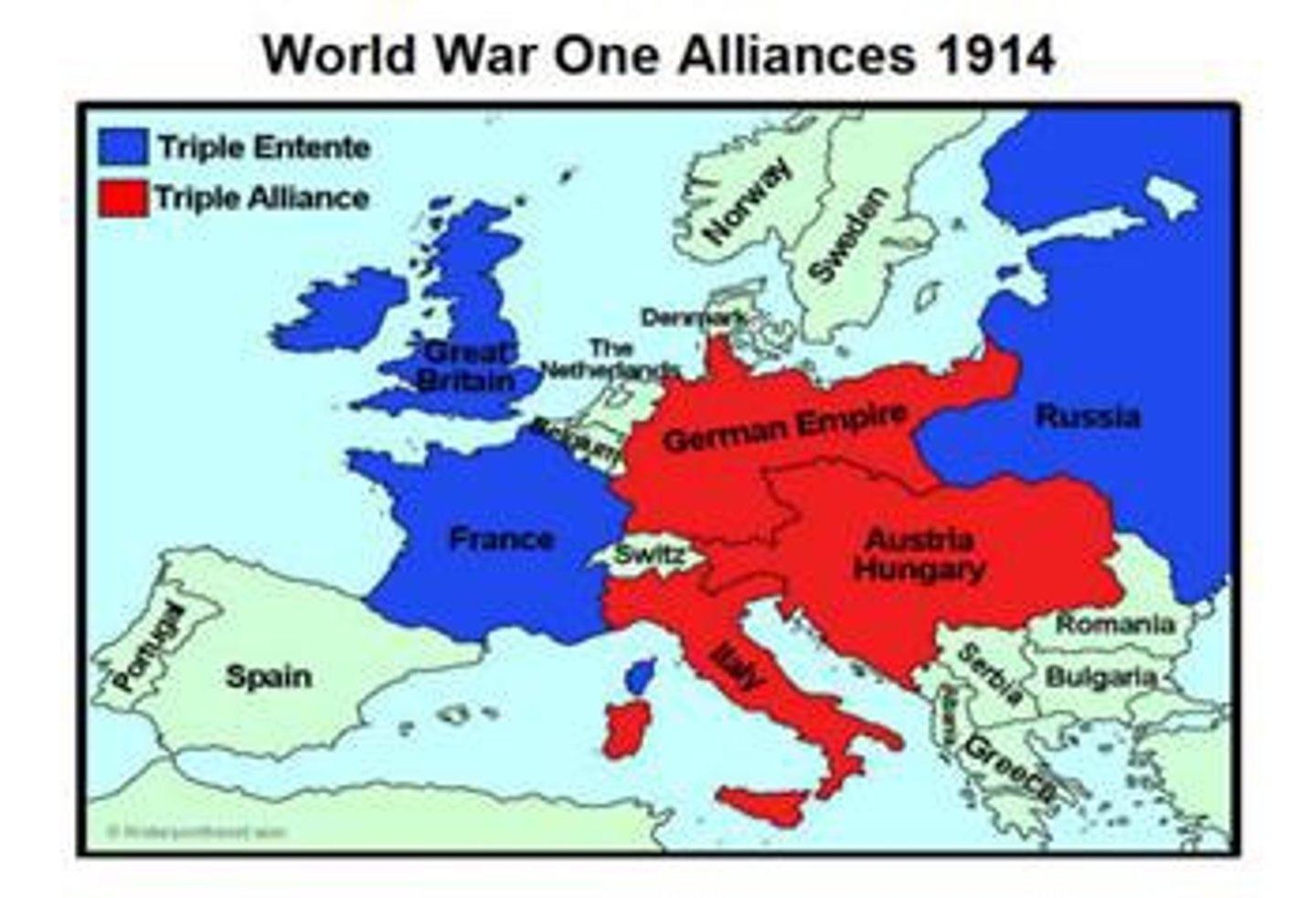
Triple Entente
This alliance was made between Great Britain, France and Russia in the years before WWI. IN BLUE ABOVE
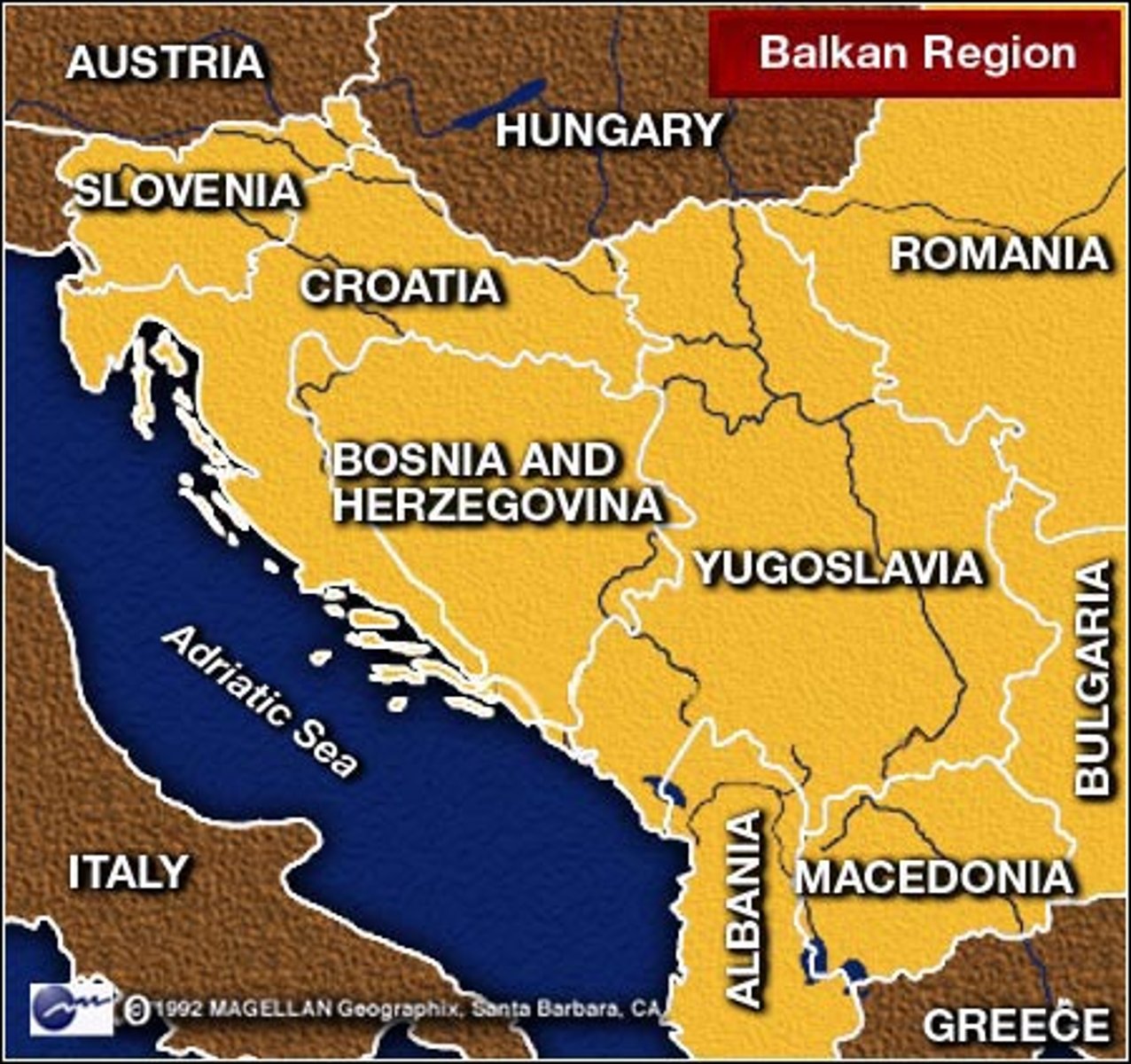
Balkan Region
Slavic Region of intense nationalism and imperial domination in mountains of south/eastern Europe - spark to set off powder keg of Europe.
Central Powers
This was a major alliance at the 'center' of Europe during World War I, made up of Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and Ottoman Empire.
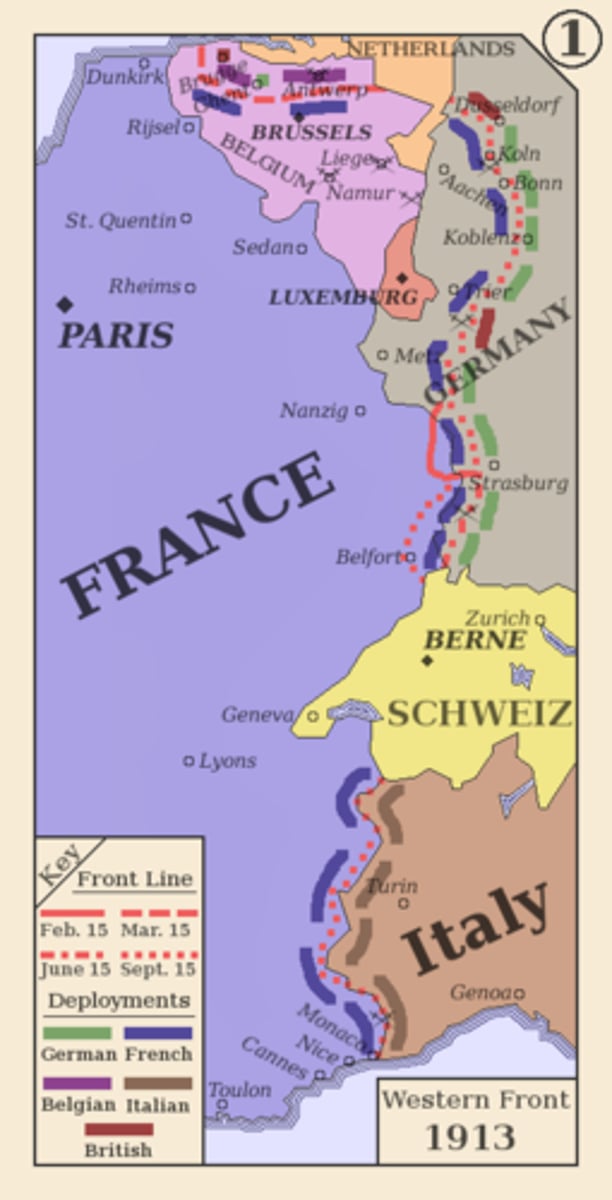
Western Front
This was a major front in World War I. A line of trenches and fortifications in World War I that stretched without a break from Switzerland to the North Sea.
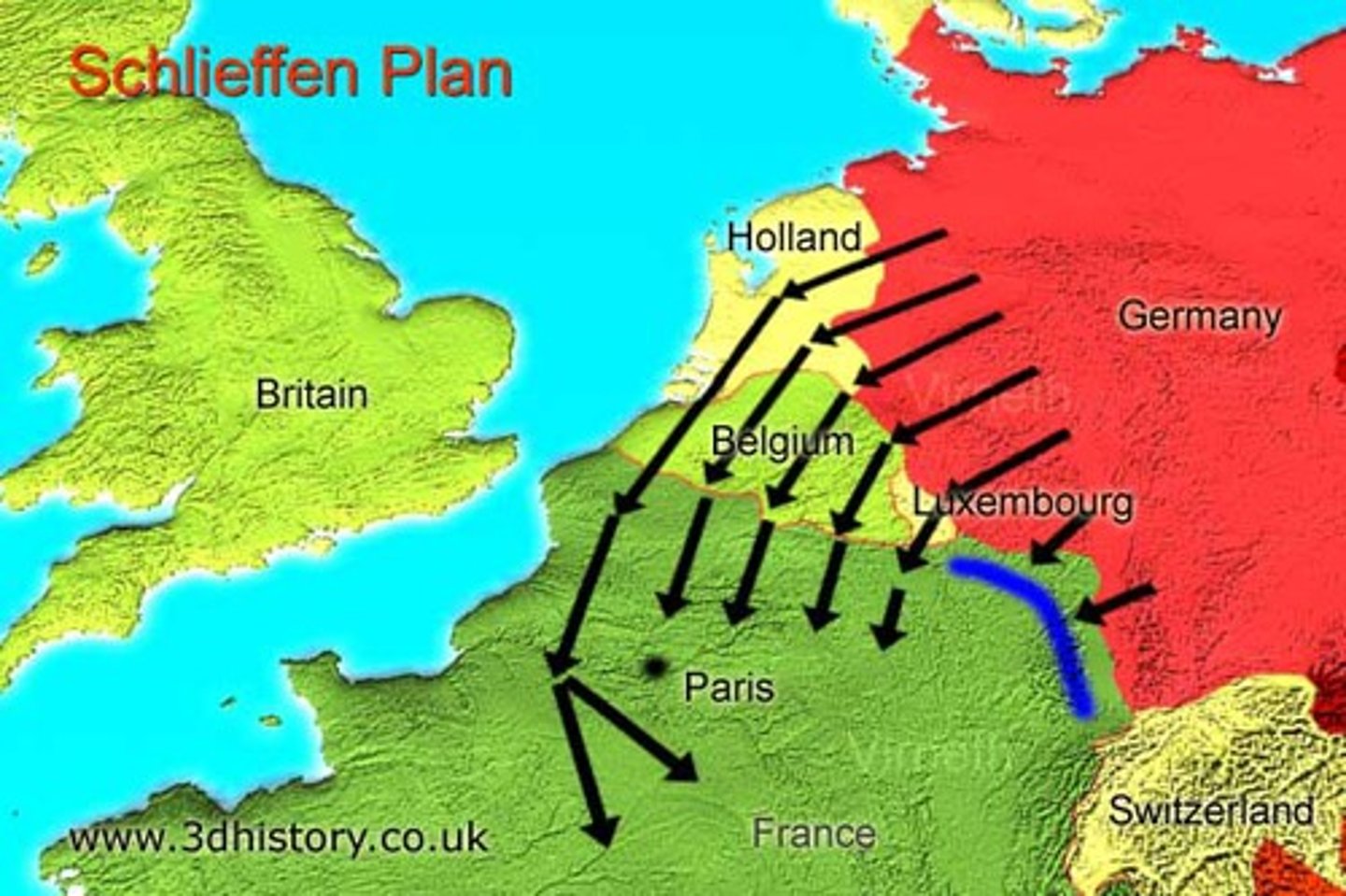
Schlieffen Plan
This was Germany's military plan at the outbreak of WWl to avoid a 2-front war. The plan called for an invasion of France through neutral Belgium. A small force would be sent east to Russia.
Eastern Front
This was a front in WWI. The region of fighting happened along the German-Russian Border where Russians and Serbs battled Germans, Austrians, and Turks.
How did the overseas colonies contribute to the Allied victory in World War I?
Colonies provided troops and labor.
United States
This country entered the war in 1917. Its entrance was the greatest factor in ending the stalemate and achieving Allied victory.
Unrestricted Submarine Warfare
A policy that the Germans announced on January 1917 which stated that their submarines would sink any ship in the British waters. Resulted in entry of the US into World War I.
Militarism
This cause of World War I was a policy of building up strong armed forces to prepare for war.
Treaty of Versailles
Treaty which ended World War I.

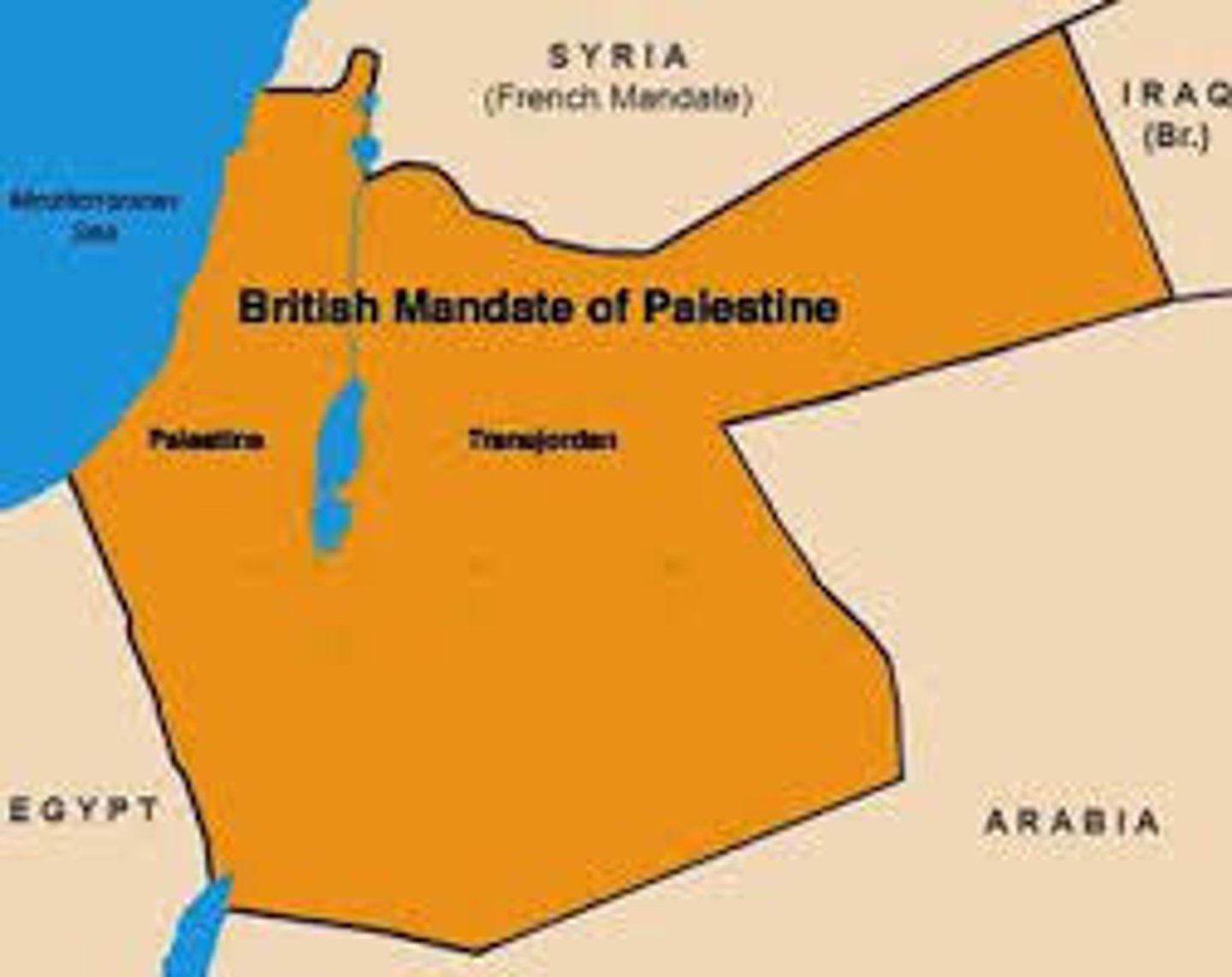
Mandate system
System by which Great Britain and France were given control over lands of the former Ottoman Empire to help them ultimately achieve independence. Included lands which eventually became Iraq, Transjordan, Palestine, Syria, and Lebanon.
Battle of the Marne, 1914
Initial battle of the war that stopped the German advance toward Paris. Taxi cabs brought additional troops to battle.
German invasion of Belgium
This event brought Britain into the war.
Austrian ultimatum to Serbia
Austria's response to the assassination of archduke Franz Ferdinand.
Weapons used during WWI
machine gun, tank, airplane, poison gas, long-range artillery
machine gun
Weapon responsible for many of the deaths during WWI; Led to the stalemate on the Western Front and the creation of trenches.
blockade
Britain's naval strategy to starve Germany of needed supplies
Italy
This country switched sides, abandoning their pre-war alliance and joining the other side.
Russia
This country dropped out of the war in 1917 to have a communist revolution; Had a large, poorly trained army that ran short of supplies during WWI; Forced Germany into a two-front war by diverting troops from the Western Front.
Battles at Verdun and Somme
These 1916 battles along the Western Front resulted in tremendous loss of life with little territorial gain.
Battle of Tannenberg
The Russians were defeated by the Germans at this battle on the Eastern Front, even though the Russians outnumbered the Germans 4 to 1. Russian general committed suicide due to humiliation from defeat.
Armenians
Victims of genocide that took place during WWI
Countries created from land that belonged to Russia
Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland
Countries created from land that once belonged to Austria-Hungary
Czechoslovakia, Austria, Hungary, Yugoslavia, Poland
Big Four at Paris Peace Conference
U.S., France, Britain, Italy
Black Hand
Organization that was responsible for the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand
No Man's Land
Area located between enemy trenches
Battle of Gallipoli
Battle where Ottoman Turks stopped the Allies from seizing the Dardanelles. Troops from Australia and New Zealand aided Allied forces.
UN definition of genocide
Planned, systematic "Intent to destroy" .
mustard gas
Weapon that caused blindness and possibly a slow death over a period of weeks.
Gavrilo Princip
The assassin of Archduke Francis Ferdinand of Austria. He was a member of the Black Hand.
Lawrence of Arabia
British officer who urged Arab nationalists to revolt against Ottoman control.
1914-1918
Years of WWI
Experiences of trench warfare
Boredom, lice, rats, poison gas, artillery bombardment, machine gun fire, trench foot.
Japan
This country seized German territory in China during WWI.
Ways Germany punished by Treaty of Versailles
War guilt, military reduction, reparations, loss of colonies, loss of German territory.
war of attrition
A war based on wearing the other side down by constant attacks and heavy losses
total war
A conflict in which the participating countries devote all their resources to the war effort
rationing
Restricting the amount of food and other goods people may buy during wartime to assure adequate supplies for the military
propaganda
information, especially of a biased or misleading nature, used to promote or publicize a particular political cause or point of view; used to gain support for the war
women's role in WWI
large numbers of women were recruited into jobs vacated by men who had gone to fight in the war. New jobs were also created as part of the war effort, for example in munitions factories.