respiratory system 🫁
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
1
New cards
what is the respiratory system involved in?
the exchange of CO2 and O2 between air and the blood
2
New cards
where do..
a) CO2
b) O2
move from and to
a) CO2
b) O2
move from and to
a) blood to lungs
b) air inhaled into the lungs to blood
b) air inhaled into the lungs to blood
3
New cards
between which two structures does gas exchange occur?
(the air in) the alveoli and (the blood in) pulmonary capillaries
4
New cards
1. is oxygen concentration high or low in:
a) air in the alveoli
b) blood in the pulmonary capillaries
2. what does this tell us?
1. \
a) high
b) low
2. that oxygen diffuses from the alveoli to the pulmonary capillaries
5
New cards
1. is CO2 concentration high or low in:
a) air in the alveoli
b) blood in the pulmonary capillaries
2. what does this tell us?
1. \
a) low
b) high
2. that CO2 diffuses from the pulmomary capillaries to the alveoli
6
New cards
define breathing
the process of moving air in and out of the lungs
7
New cards
what happens if a person stops breathing?
concentration of O2 in the alveoli drops as the oxygen moves to the pulmonary capillaries. when the O2 levels are equal between the two, O2 stops diffusing
8
New cards
what are the 2 phases of breathing?
inhalation and exhalation
9
New cards
do the lungs contain muscle?
no
10
New cards
what is the diaphragm and what does it do?
a skeletal muscle separating the chest and abdominal cavities. when it contracts, we inhale
11
New cards
which organs are in the thoracic cavity? (2)
which organs are in the abdominal cavity? (3)
which organs are in the abdominal cavity? (3)
thoracic- heart and lungs
abdominal- stomach, liver, intestines (+)
abdominal- stomach, liver, intestines (+)
12
New cards
what are the steps of inhalation (4)
1. diaphragm contracts and moves down
2. the thoracic cavity increases in volume
3. air pressure in the alveoli decreases
4. air from outside the body rushes into the lungs
13
New cards
does the diaphragm move up or down when contracting?
down
14
New cards
what are the steps of exhalation (4)
1. the diaphragm relaxes and moves up
2. the thoracic cavity decreases in volume
3. air pressure in the alveoli increases
4. air is squeezed out of the lungs
15
New cards
how does the respiratory system clean itself? (2)
1) sticky mucus traps tiny particles
2) cilia lining the trachea beat, moving the mucus containing trapped particles up and out of the trachea
2) cilia lining the trachea beat, moving the mucus containing trapped particles up and out of the trachea
16
New cards
where in the respiratory system are mucus-secreting goblet cells found? (3)
lining the trachea, bronchi and bronchioles
17
New cards
what is internal respiration?
the process by which gases are exchanged between the blood and cells in the body
18
New cards
what is external respiration?
the process by which gases are exchanged between the air in the alveoli and the blood in pulmonary cap.
19
New cards
during internal respiration…
1. O2 diffuses from __ to __
2. CO2 diffuses from __ to __
1. O2 diffuses from __ to __
2. CO2 diffuses from __ to __
1. blood, body cells
2. body cells, blood
20
New cards
during external respiration…
1. O2 diffuses from __ to __
2. CO2 diffuses from __ to __
1. O2 diffuses from __ to __
2. CO2 diffuses from __ to __
1. air in alveoli, blood
2. blood, air in alveoli
21
New cards
what is the pleura?
a two layer membrane covering each lung and lining the thoracic cavity
22
New cards
what is the pathway of air in the respiratory system? (8)
nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronci, bronchial tubes, bronchioles and alveoli
23
New cards
what are hollow spaces in the nose?
nasal passages
24
New cards
what are 3 functions of the nasal passages?
to warm, moisten and filter air before it reaches the lungs
25
New cards
how do humans make sounds?
by controlling vibrations of the vocal cords
26
New cards
what is the larynx? what are the vocal cords?
larynx- voice box
vocal cords- two pairs of membranes stretched across the inside of the larynx
vocal cords- two pairs of membranes stretched across the inside of the larynx
27
New cards
what keeps the trachea open?
rings of cartilage in its walls
28
New cards
how does smoking affect cilia?
smoking stops the motion of cilia for a short period of time
29
New cards
name the…
a) number of cell layers in alveoli
b) number of alveoli in the lungs
c) total surface area of the alveoli
\
a) number of cell layers in alveoli
b) number of alveoli in the lungs
c) total surface area of the alveoli
\
a) 1
b) 300 million
c) 70 square meters
b) 300 million
c) 70 square meters
30
New cards
what is emphysema
scarlike tissue forms in the alveoli, reducing surface area and the elasticity of the lungs and causes shortness of breath
31
New cards
what are the four stages of gas exchange?
breathing, external respiration, internal respiration, oxygen and carbon dioxide transport
32
New cards
how many times does one breathe per minute?
12-25 times per minute
33
New cards
which structure controls breathing?
the respiratory center
34
New cards
what are chemoreceptors?
\-structures found in large arteries that sense the amount of O2 and CO2 in the blood
\-stimulates the respiratory center to increase breathing rate when CO2 increases
\-stimulates the respiratory center to increase breathing rate when CO2 increases
35
New cards
what is oxyhemoglobin?
oxygen and hemoglobin that combine in the lungs
36
New cards
which three ways is CO2 carried to the lungs?
1) combines with water and forms carbonic acid, then breaks down into hydrogen and bicarbonate ions -70%
2) combines with hemoglobin to make carboxyhemoglobin -20%
3) dissolves in plasma -10%
2) combines with hemoglobin to make carboxyhemoglobin -20%
3) dissolves in plasma -10%
37
New cards
what is…
a) asthma
b) bronchitis
a) asthma
b) bronchitis
a) allergic reaction causing a range of difficulty breathing. bronchioles spasm, squeezing air passages
b) bronchial tube lining becomes irritated/swollen, causing alveoli to swell and clog with mucus and coughing
b) bronchial tube lining becomes irritated/swollen, causing alveoli to swell and clog with mucus and coughing
38
New cards
what is…?
a) pneumonia
b) lung cancer
a) pneumonia
b) lung cancer
a) alveoli fill with fluid, preventing gas exchange
b) tumours form in the lungs as a result of uncontrollable cell growth
b) tumours form in the lungs as a result of uncontrollable cell growth
39
New cards
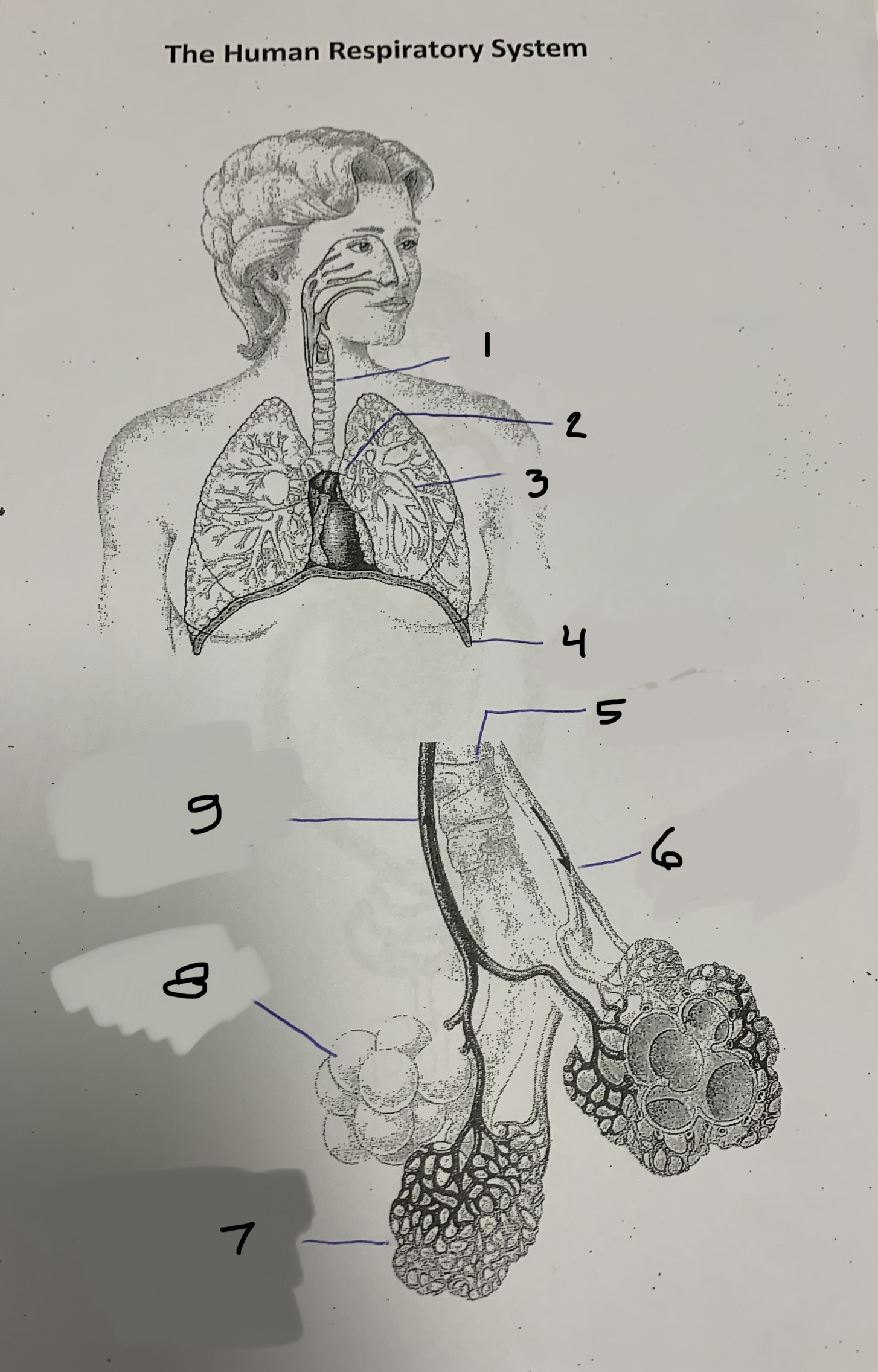
label
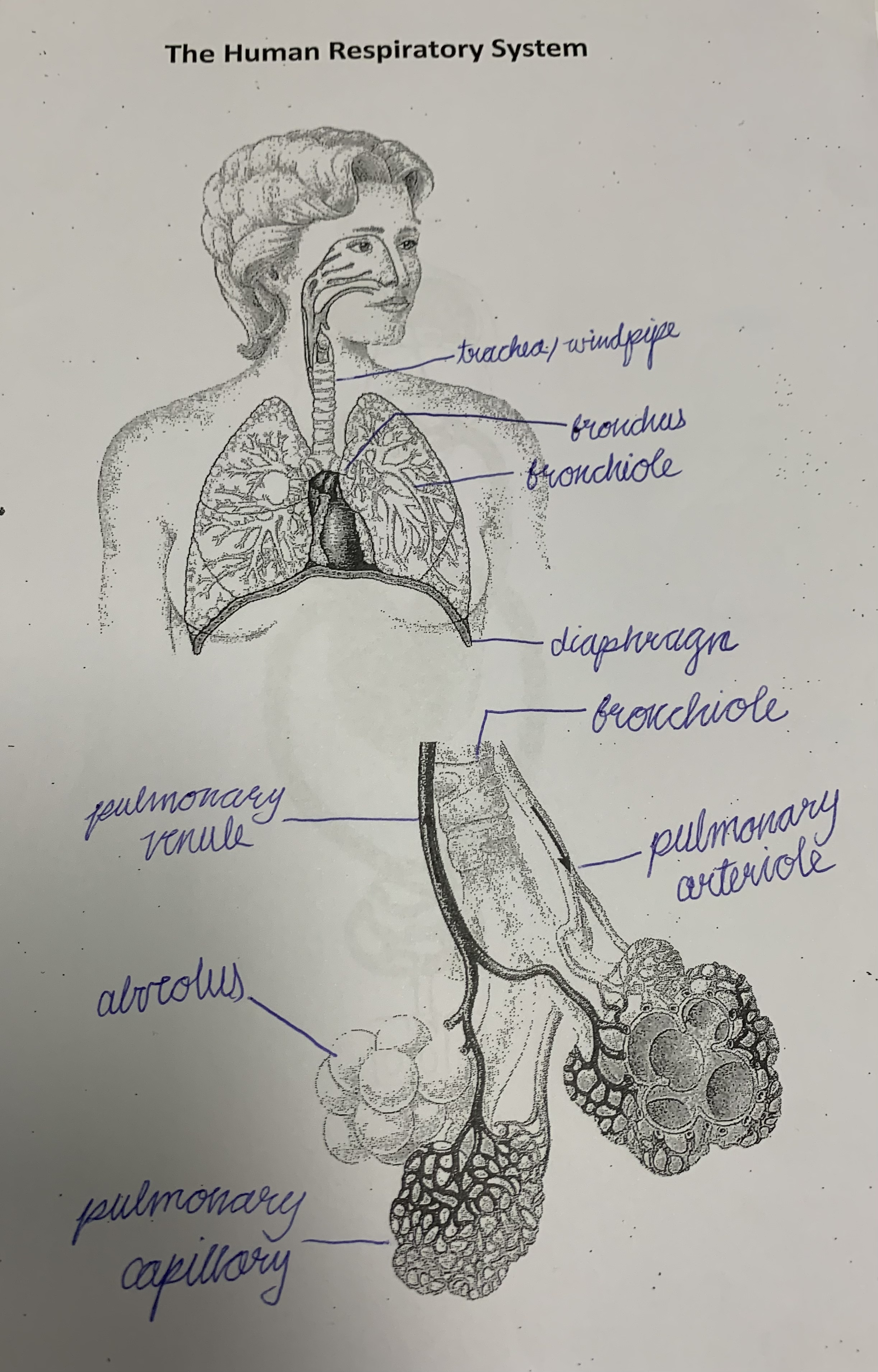
40
New cards
what is..?
1) HbO2
2) H2CO3
3) HCO3
4) HbCO2
1) HbO2
2) H2CO3
3) HCO3
4) HbCO2
1) oxyhemoglobin
2) carbonic acid
3) bicarbonate ions
4) carboxyhemoglobin
2) carbonic acid
3) bicarbonate ions
4) carboxyhemoglobin