Cardiovascular Exam 3
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
130 Terms
angina pectoris
chest pain or discomfort due to myocardial ischemia
weight or pressure on chest
numbness/tingling in arms
pain
shortness of breath
What are symptoms of angina pectoris
demand angina
chronic stable angina (class or effort as well)
Supply angina
unstable angina and vasospastic angina
women
Are men or women more likely to get vasospastic angina?
stable angina therapeutic objectives
The following therapeutic objectives are for what type of angina?
increase myocardial blood flow by dilating coronary arteries and arterioles (increase oxygen supply)
decrease cardiac load (preload and afterload; decreasing oxygen demand)
decrease heart rate (decrease oxygen demand)
decrease fatty acid metabolism (decrease oxygen demand)
unstable angina therapeutic objectives
The following therapeutic objectives are for what type of angina?
inhibit platelet aggregation and thrombus formation (increase oxygen supply)
decrease cardiac load (preload and afterload; decrease oxygen demand)
vasodilate coronary arteries (increase oxygen supply)
Variant Angina therapeutic objectives
The following therapeutic objectives are for what type of angina?
decrease vasospasm of coronary vessels (CCBs are efficacious in >70% of patients; increase oxygen delivery)
Stable angina - decrease oxygen demand
Variant angina - increase oxygen supply
How does this drug class effect stable and variant angina? nitrates
stable angina - decreases oxygen demand
variant angina - not used
How does this drug class effect stable and variant angina? beta blockers
stable angina - decrease oxygen demand
variant angina - increases oxygen demand
Drugs - verapamil, diltiazem
How does this drug class effect stable and variant angina? Calcium channel blockers. Specifically what drugs?
stable angina - decrease oxygen demand by switching heart from FA metabolism to glucose
variant angina - not used
How does this drug class effect stable and variant angina? partial fatty acid oxidation (pFOx) inhibitors
stable angina - decrease oxygen demand by lowering heart rate
variant angina - not used
How does this drug class effect stable and variant angina? ivabradine
amyl nitrite
This is the only nitrite that can be inhaled
nitroglycerin, isosorbide dinitrate, and isosorbide mononitrate
these are nitrate compounds that are administered via oral, sublingual, topical, transdermal and IV
Decreases preload → decreases oxygen demand
Dilation of veins » arteries
Decrease venous return → decrease in LVEDV and LVEDP
Less strain on the heart
What is the primary effect of nitrites and nitrates?
reduced wall stress (due to decreased preload) → increase in coronary blood flow → increase in oxygen supply
What is the secondary effect of nitrites and nitrates?
Low at 10-20%
High first pass metabolism
The oral availability of Nitroglycerin (NTG) and isosorbide dinitrate (ISDN) is _____. Because of…
mononitrate; 100%
Isosorbate ______nitrate is ____% available after oral administration.
tolerance of nitrites and nitrates
The inactivation of aldehyde dehydrogenase causes…
orthostatic hypotension
reflex tachycardia - due to baroreceptor
severe throbbing headache
What are the major adverse effects of nitro vasodilators (nitrites and nitrates)?
PDE-5 inhibitors for erectile dysfunction
Elevated intracranial pressure
Separate by at least 6 hours.
Nitrites and nitrates are contraindicated in patients that use _______, and patients that have elevated ________ ________.
PDE-5 inhibitors
sildenafil
Vardinafil
MOA: potentiate actions of nitro vasodilators b/c they inhibit breakdown of cGMP
What are specific drugs that interact with nitro vasodilators? What is the MOA that causes the interaction?
pFOX *acts like it only at higher doses
Ranolazine is in what class?
MOA: switches fuel preference of the heart from fatty acids to glucose
Importance: glucose oxidation makes ATP while using LESS oxygen → decreasing Oxygen demand
w/ no hemodynamic changes
What is the MOA of pFOX drugs?
inhibits late Na+ current → limiting Ca2+ entry (Phase 2 of AP) → decreased inotropic effect
What is the primary mechanism of Ranolazine?
positively inotropic drugs
These drugs counteract decreased cardiac output in heart failure.
vasodilators
These drugs counteract increased venous volume and pressure in heart failure
diuretics
These drugs counteract congestion and edema in heart failure.
ACE inhibitors
These drugs counteract renin-angiotension aldosterone system activation in heart failure.
diuretics
these drugs counteract sodium and water retention in heart failure
vasodilators
these drugs counterat increased afterload in heart failure
Beta blockers and ACE inhibitors
These drugs both (two classes) counteract cardiac remodeling in heart failure.
60-65
A normal ejection fraction is…
Beta blockers
What drug class would you use when your therapeutic objective is decreasing heart rate → decreasing oxygen demand? This drug class unfortunately decreases inotropy as well.
ivabradine
What is the drug can decrease heart rate with not cost to contractility?
visual disturbances
avoid if using: verapamil, diltiazem, or Beta blockers
What are some adverse affects of Ivabradine? If already on WHAT DRUGS you need to avoid.
sympathetic tone declines
urine production increases
renin release declines
What are the 3 major secondary responses from cardiac glycosides?
decrease
decrease
increase
increase
In ischemia:
the decreased oxygen supply causes,
____ ATP availability
____ Na/K ATPase
____ membrane potential
____ arrythmias
positive inotropic effect due to increase in Ca during systole
What is the total net effect in the heart (caused by cardiac glycosides)
Slows AV node conduction velocity = increased PR interval
With cardiac glycosides an increase in vagal tone does what to the AV node conduction velocity?
0.5-2 ng/ml
Ideal is under 1 to decrease mortality
Toxic above 2 ng/ml
What is the ideal therapeutic plasma concentration for digoxin? What is the toxic level?
overloading of intracellular calcium creating oscillations in free calcium
What is the likely cause of spontaneous delayed after polarizations during digoxin use?
decreases - helpful to decrease toxicity
increases
Hyperkalemia ____ digoxin effect (helpful how?)
Hypokalemia ____ digoxin effect
arrhythmia
hypercalemia increase risk of ______ due to calcium overload while using digoxin
Mg DEFICIENCY increases digoxin risk
Mg decreases risk of arrhythmias on digoxin
MONITOR
magnesium interacts with digoxin how?
bolus IV followed by continuous influsion
Half life = 18 minutes
How is nesiritide dosed and what is it’s half life?
Entresto (Sacubitril/Valsartan)
This drug allows the body to use BNP longer, and is a key drug for HFrEF
ventricle and atrium
what are the two types of muscle tissue?
conduct
myococytes _____
calcium current channel
conduction velocity in SA and AV nodes depend on…
sodium channel current
conduction velocity everywhere else (AV bundle, His-Purkinje, and fascicles) depend on…
Fast potentials
Myocytes in atrium and ventricle, bundle of His, and purkinje fibers have _____ (fast/slow) potentials
Slow potentials
the SA and AV nodes have _____ (fast/slow) potentials
Na/K ATPase pump
What is digoxin’s site of action?
Symp/Parasymp tone
What causes arrhythmias?
vagal maneuvers and beta blockers
What can be done to mitigate arrhythmias?
increase in intracellular Ca
Digoxin
late (delayed) afterdepolarizations (DADs) are caused by…
Which drug can cause these?
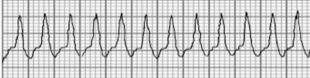
Ventricular Tachycardia
What type of arrhythmia is this?
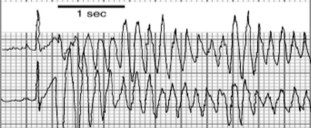
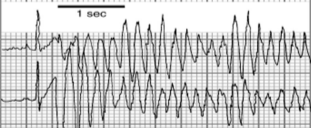
Ventricular tachycardia and torsades de pointes
What type of arrhythmia is this?
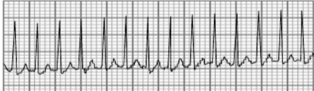
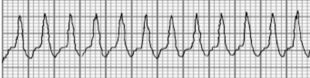
Supraventricular Tachycardia
What type of arrhythmia is this?
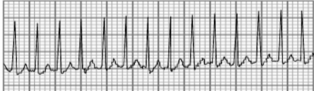
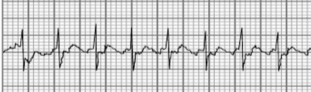
Atrial flutter
Rapid firing out of sink
What type of arrhythmia is this?
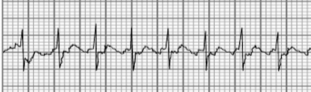
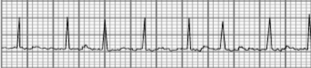
Atrial fibrillation
No effective beating
What type of arrhythmia is this?
antibiotics and antidepressants
What kinds of drugs commonly cause Long QT syndrome?
Class: IA antiarrhymic sodium channel blocker
MOA: local anesthetics acting on nerve and mycardial membranes → slows conduction
Quinidine, Procainamide, Disopyramide: Class and MOA?
Indication: supraventricular arrhythmias, supraventricular tachycardia
Adverse effects: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, dizziness, anti-cholinergic effects
Quinidine
Indication
Adverse effects
Indication: similar to quinidine, good for patients that are unresponsive to quinidine
Adverse effects: lupus syndrome
Administration: Oral
Procainamide
Indication
Adverse effects
Administration
Indication: certain ventricular and atrial arrhythmias
Adverse effects: anti-cholinergic effects
Administration: oral
Disopyramide
Indication
Adverse Effects
Administration
Class: IB antiarrhythmic sodium channel blockers
Lidocaine, Tocainide, Mexiletine, Phenytoin
Class?
Indication: DOC emergency treatment of ventricular arrhythmias, prevention of ventricular arrhythmias
Adverse effects: CNS, heart, dizziness, paresthesia, seizures
Admin: IV injection
Lidocaine
Indication
Adverse effects
Administration
Indication - treatment and prevention of ventricular arrhythmias
Adverse effects - GI, CNS effects
Admin - oral
Tocainide
Indication
Adverse effects
Administration
Indication - ventricular arrhythmias
Adverse - GI, CNS, dizziness
Admin - oral
Mexiletine
indication - atrial and ventricular arrhythmias DUE TO DIGITALIS TOX
Adverse/Contra - agents that liberate phenytoin can cause toxicity
Admin - Oral and IV
Phenytoin
1C Antiarrhythmic Sodium channel blockers
Flecainide and encainide what class?
Indication - ventricular arrhythmias
Adverse - aggrevate existing arrhythmias, blurred vision, headache, nausea, abdominal pain
Admin - oral
Flecanide
Indication
Adverse
Admin
Encainide has a less negative inotropic effect
What is the difference between Flecainide and encainide?
Quinidine
What is the prototype drug for class 1 sodium channel blockers?
Class II antiarrhythmic drugs, beta-adrenergic receptor blockers
Propranolol, what class?
MOA - decrease sympathetic activity in heart → reduce cAMP levels → reduces Ca influx → decrease conduction through AV node
Prototype - propranolol
What is the MOA and prototype drug of Class II antiarrhythmics?
Indication - supraventricular arrhythmias, digitalis induced ventricular arrhythmias
What is the indication of class II antiarrhythmics
Too much positive inotropic effect
What does it mean when an arrhythmia is digitalis-induced?
Potassium channel blockers
Class III antiarrhythmic drugs are also called ____ channel blockers.
Class II antiarrhythmic drugs, potassium channel blockers
Class?
Bretylium Tosylate, Amiodarone
Indication - management of ventricular tachycardia and fibrilation due to other first line treatments (defibrillation or lidocaine)
Adverse - hypotension (orthostatic hypotension)
Admin - injection used in hospital settings
Bretylium Tosylate
Indication
Adverse effects
Administration
Indication - only ventricular arrhythmias
Adverse - nausea, constipation, liver problems, heart arrhythmias, vision, death, NOT FOR PREGNANCY
Admin - idk
Amiodarone
Indication
Adverse effects
Calcium channel blockers
Class IV antiarrhythmics are also called ____ channel blockers.
Verapamil
What is the prototype drug for Class IV antiarrhythmic drugs?
Indication - treatment of supraventricular arrhythmias
Adverse - (IV) hypotension, bradycardia, asystole w/ atrioventricular blocks
Admin - oral and IV
Verapamil
Indication
Adverse effects
Admin
Hypertension
Ischemia (loss of muscle)
valvular regurgitation (volume overload)
What are some factors that indicate development of heart failure?
<40%
HFrEF LVEF?
>50%
Evidence of LV filling pressures
HFpEF LVEF? Other indications?
Fatigue
Orthopnea
Dyspnea
cough
edema
Symptoms of CHF
Echocardiogram
What is the gold standard test for diagnostic tests?
More severe the disease = increase in BNP
What does the BNP tell you?
Stage A
What stage of HF:
no symptoms
At risk - heart disease, cardiac biomarkers, family history
Stage B
What stage of HF:
no symptoms
reduced function, elevating filling pressures suggested
Stage C - Symptomatic HF
What stage of HF:
symptoms
structural heart disease
Stage D - Advanced HF
What stage of HF:
symptoms that interfere with daily life
ARNI, ACEi or ARB
Beta blocker
MRA
SGLT2i
Diuretics as needed
What are the pillars of treating HFrEF?
Diuretics and SGLT2i
What are the go to drug(s) for HFpEF?