Endocrine System
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Endocrine system
A system of glands that secrete hormones into the blood to target cellular receptors
slower and longer-lasting than nervous system
Endocrine
refers to glands/ tissues that make or release hormones that travel in the bloodstream to control the actions of other cells or organs
Hormone
chemical messenger secreted into the blood/ extracellular fluid by one cell and have an effect on the functioning of other cells in other parts of the body
does NOT include local hormones: have an effect locally not globally around body
List the main glands in the endocrine system
hypothalamus
pineal gland
pituitary gland
thyroid gland
parathyroid gland
thymus
adrenal glands
pancreas
ovaries/ testes
Hypothalamus
secrete ‘Releasing’ hormones (TRH, CRH, GnRH)
controls pituitary gland
regulates hunger, thirst, temperature, circadian rhythm
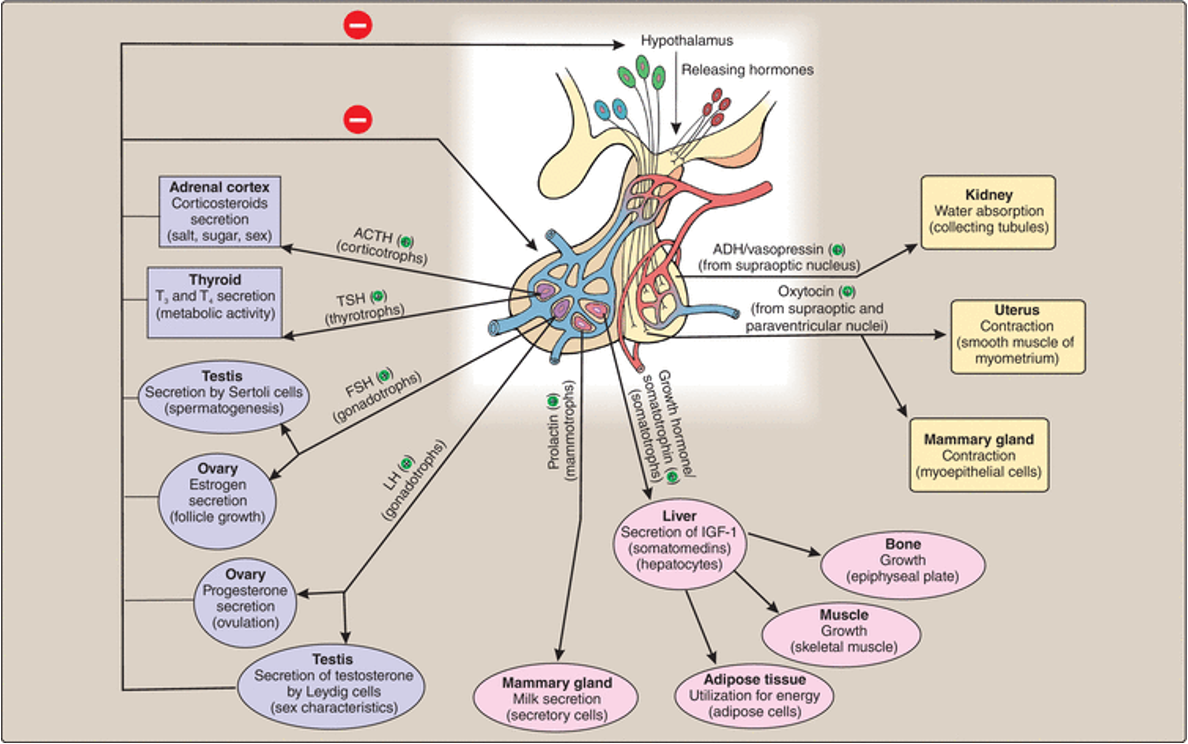
Pituitary gland
Anterior pituitary hormones:
GH (growth hormone: promotes growth of bone, muscle, adipose tissue)
Prolactin (stimulates lactation/ maternal behaviours)
Stimulating/ tropic hormones:
TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone)
FSH (follicular stimulating hormone) - spermatogenesis/ ovary follicle growth
LH (luteinising hormone) - sex hormone
ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) - steroid hormone stimulates release of cortisol
Posterior pituitary hormones:
oxytocin (expression of milk and uterine contraction)
ADH (aka vasopressin) (water reabsorption in kidney, promotes vasoconstriction
why trigger vasoconstriction when blood plasma is hypertonic?
Hypertonic: conc of water in blood plasma decreased
maintains blood pressure
Thyroid
produces:
thyroxine (T4) and T3 (regulates metabolism, growth, heart function, etc)
Calcitonin (regulates calcium levels)
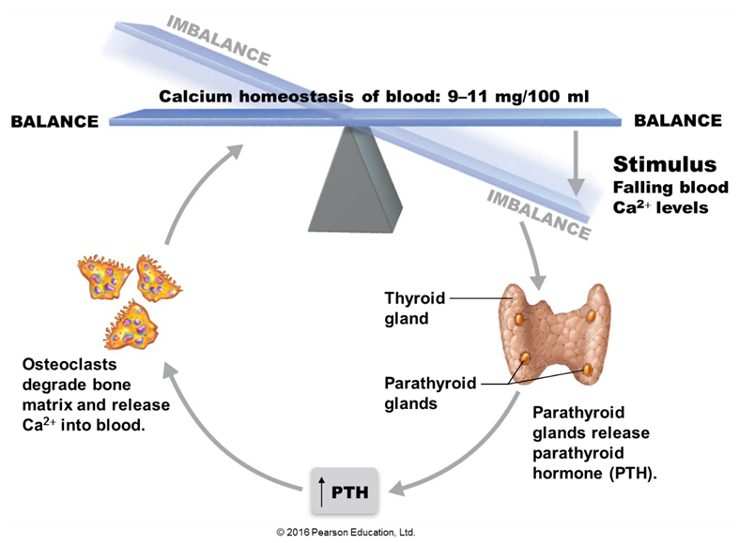
Parathyroid
produces parathyroid hormone (PTH) (increases blood calcium levels)
Adrenal gland
produces:
cortisol
aldosterone
adrenaline
noradrenaline
All involved in stress response, metabolism, blood pressure regulation
Thymus
Produces:
Thymosin
Thymopoietin
Thymulin
(Maturation of T-cells, helps establish immune competence in early life)
Pineal gland
Produces melatonin (regulates sleep-wake cycle)
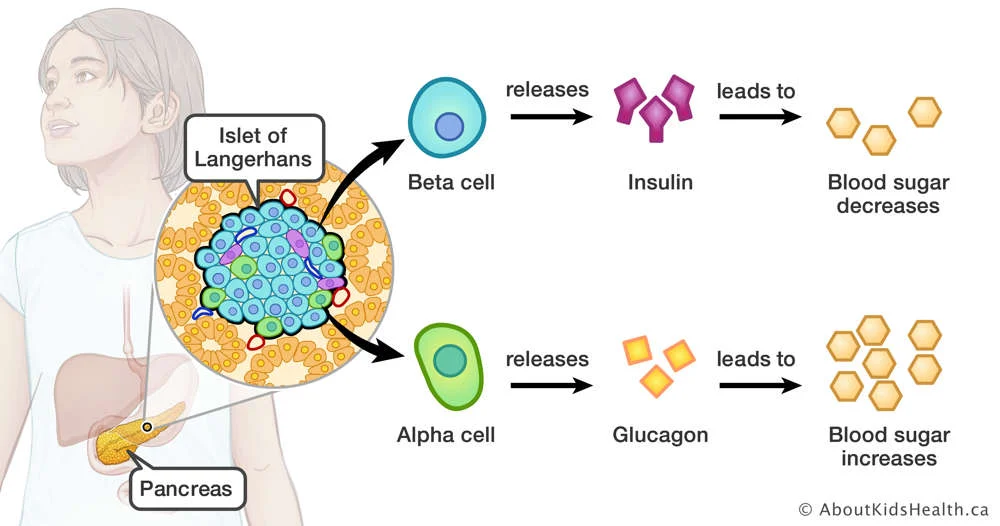
Pancreas
Islets of Langerhans contain:
alpha cells which secrete glucagon (increase blood glucose)
beta cells which secrete insulin (decrease blood glucose)
Delta cells which secrete somatostatin
Ovaries
Produce estrogen and progesterone (female reproductive functions, menstrual cycle)
Testes
Produce testosterone (male reproductive functions, sperm production)
Explain how lipophilic hormones interact with intracelular receptors
dissolve into the mb, move across mb
targets are usually intracellular receptors
Explain how lipophobic hormones interact with cell surface receptors
unable to cross cell mb so bind to cell surface receptors which triggers intracellular cascade of response
Briefly describe the role of the hypothalamus in the endocrine system
part of limbic system
key in homeostasis
central regulator of autonomic nervous system
central regulator of endocrine system
controls function of pituitary gland (posterior pituitary via neural connections, anterior pituitary via vascular connections) - hypothalamic-pituitary axis)

Briefly describe the role of the pituitary gland in the endocrine system
releases ‘coordinating’ hormones
controls hormone levels produced in other glands and tissues
Outline which hormones are produced by the anterior and posterior pituitary gland
Anterior:
Growth hormones (of bone, muscle, adipose tissue)
Prolactin (stimulates lactation/ maternal behaviour)
Stimulating (tropic) hormones: Thyroid STimulating hormones (TSH), Follicular Stimulating Hormone (FSH), Luteinising Hormone (LH), Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Posterior:
Oxytocin: expression of milk, uterus contraction
Vaspressin (aka antidiuretic hormone): promotes kidney reabsorption of water, promotes vasoconstriction (increase peripheral resistance)
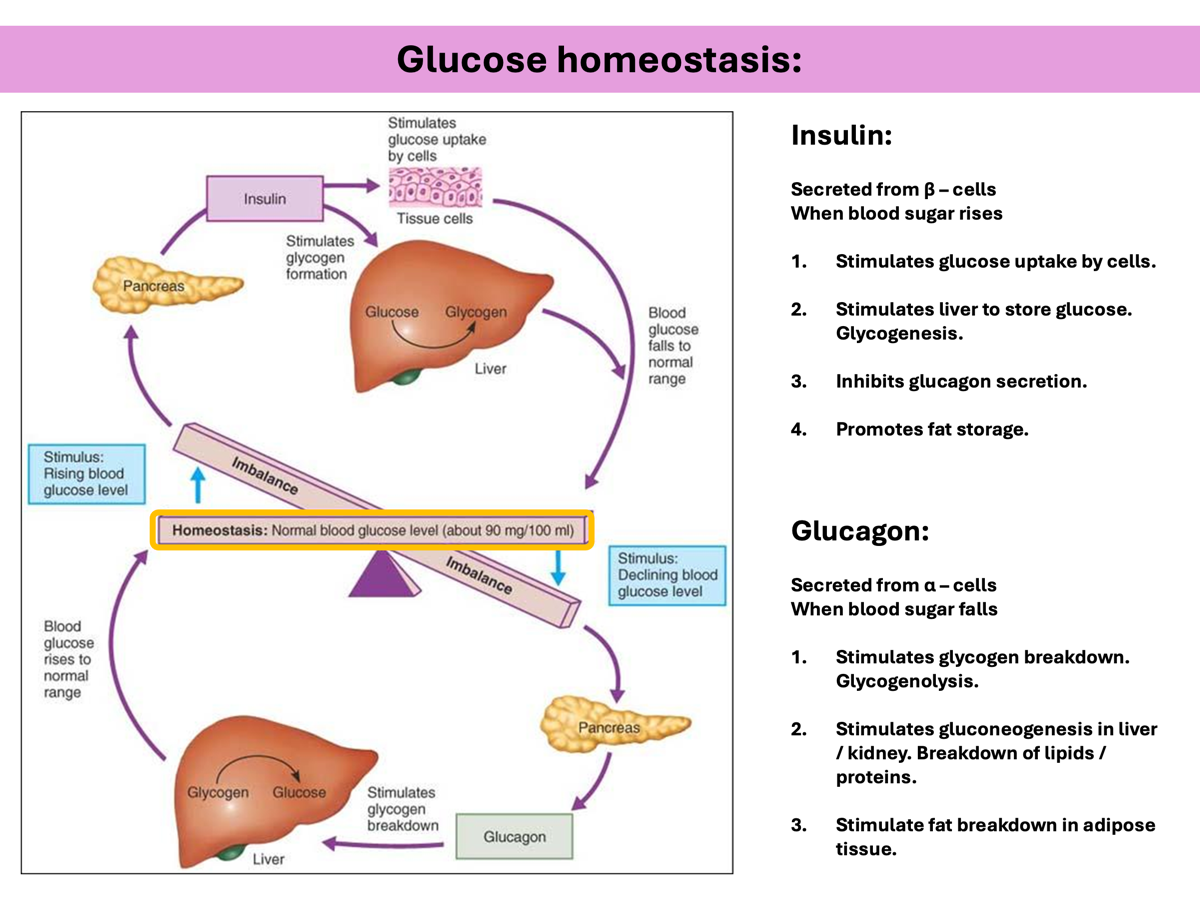
Describe the role of pancreatic hormones insulin and glucagon in glucose homeostasis.
insulin: reduces blood glucose concentration
glucagon: increases blood glucose concentration
Action of Insulin
Secreted from β – cells when blood sugar rises
1.Stimulates glucose uptake by cells.
2.Stimulates liver to store glucose. Glycogenesis.
3.Inhibits glucagon secretion.
4.Promotes fat storage.
Action of glucagon
Secreted from α – cells when blood sugar falls
1.Stimulates glycogen breakdown. Glycogenolysis.
2.Stimulates gluconeogenesis in liver / kidney. Breakdown of lipids / proteins.
3.Stimulate fat breakdown in adipose tissue.
Describe the role of the thyroxine produced in the thyroid gland.
Thyroid gland produces thyroxine (T4) Note: T3 is a faster acting form of T4.
Highly lipid soluble (lipophilic) so enters cells.
Binds to cytoplasmic receptors and transported to nucleus to regulate gene activation.
Increased metabolism.
Burn more energy at rest.
Enhances carbohydrate consumption.
Increases mitochondrial function.
Promotes growth in children.
Increases mental activity.
Radioactive Iodine
Risk factor for cancer
Treatment option for thyroid cancer
What is T3?
T3 is more potent faster acting form of T4.
Describe the role of the parathyroid gland, parathyroid hormone.
Parathyroid glands: four glands embedded in the thyroid.
Produce parathyroid hormone involved in blood calcium homeostasis. (break down bone)
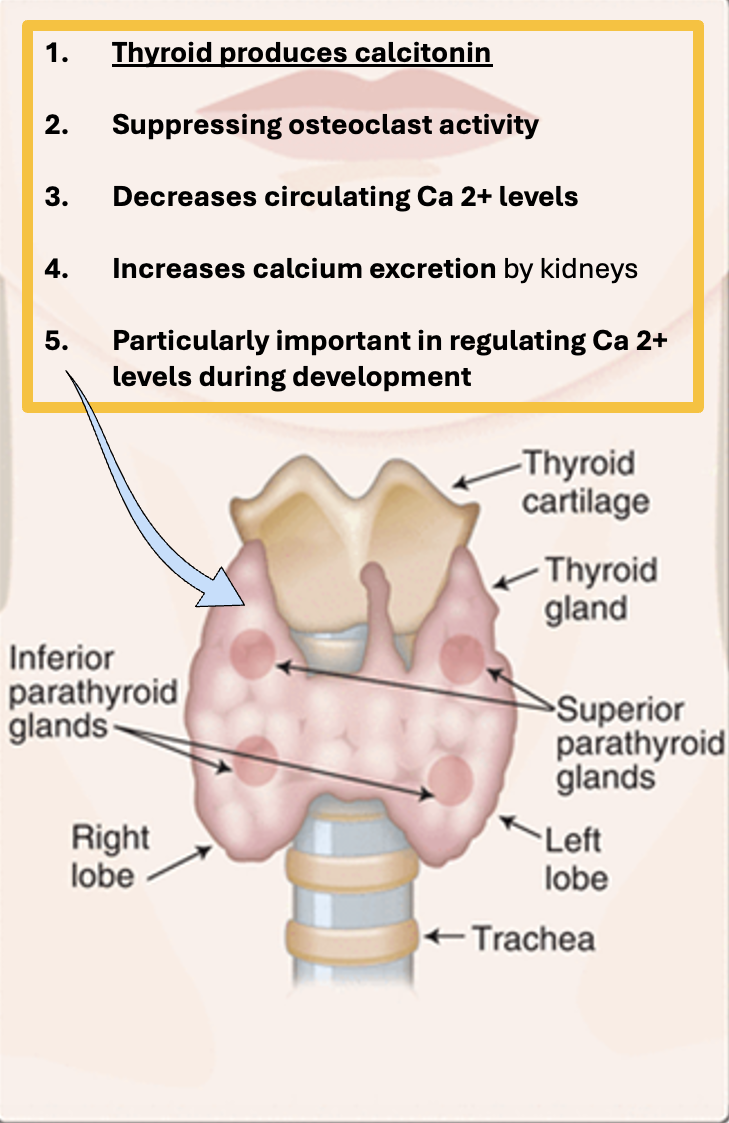
Describe the role of calcitonin produced in the thyroid gland.
1.Thyroid produces calcitonin
2.Suppressing osteoclast activity
3.Decreases circulating Ca 2+ levels
4.Increases calcium excretion by kidneys
5.Particularly important in regulating Ca 2+ levels during development
Explain where melatonin is produced and what effect it has on the sleep cycle.
Pineal gland secretes melatonin (regulation of sleep cycles)
sunlight detected by receptors, decreases melatonin production by pineal gland, melatonin concentration decreases
no light = melatonin production increases = circulating melatonin concentration increases prompting sleep
Briefly outline the role of the hormones produced by the thymus.
Thymus produces:
• Thymosin
• Thymopoietin and Thymulin
Primary Function:
Facilitates the maturation of T-cells (adaptive immunity).
Helps establish immunocompetence in early life.
Activity Over Time:
Most active during childhood and adolescence.
After puberty – gradually shrinks and endocrine activity decreases.
Some residual function persists in adulthood.
Thymosin
A group of peptides that promote the development and differentiation of T-lymphocytes (T-cells).
Thymopoietin and Thymulin
Involved in T-cell maturation and immune regulation.
Describe the location and general anatomy of the adrenal glands.
Adrenal Cortex: produces steroid hormones (glucocorticois and mineralcorticoids)
Adrenal Medulla: produces catecholamines (‘sympathetic’ hormones of adrenaline and noradrenaline)
Outline the role of androgens, cortisone and aldosterone as hormones produced by the adrenal cortex.
Cortex produces:
zona glomerulosa: aldosterone (regulates blood pressure via the regulation of fluid and electrolyte balance)
zona fasciculata: cortisone (stress response)
zona reticularis: androgens - women and men (production and maintenance of sex hormones)
List the three stages of the stress response.
The alarm reaction:
Resistance or adaptation:
Exhaustion
Stage 1 of stress response: Alarm reaction
Sympathetic activation
Release of norepinephrine to activate fight or flight response
Release of epinephrine from adrenal medulla
Stage 2 of stress response: Resistance or adaptation:
a.corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)
b.Stimulates anterior pituitary releasing ACTH
c.This causes adrenal cortex to release cortisol
d.Cortisol can maintain long term alert with continued triggers of stress
increased blood glucose
lipolysis
glycogenolysis in liver
suppression of immune system
suppression of inflamatory response
Stage 3 of stress response: exhaustion
Chronic stress leads to hypertension, depression, anxiety, heart disease, diabetes
Explain the role of cortisol in maintaining the response to long term stress.
Cortisol can maintain long term alert with continued triggers of stress
Increased blood glucose (via pancreatic hormones)
Lipolysis
Glycogenolysis in liver
Suppression of immune system
Suppression of inflammatory response
Describe the return to rest after the stress response
Negative feedback reduces activation of HPA axis
(Time dependent)
Gradual return to former ‘rest’ state

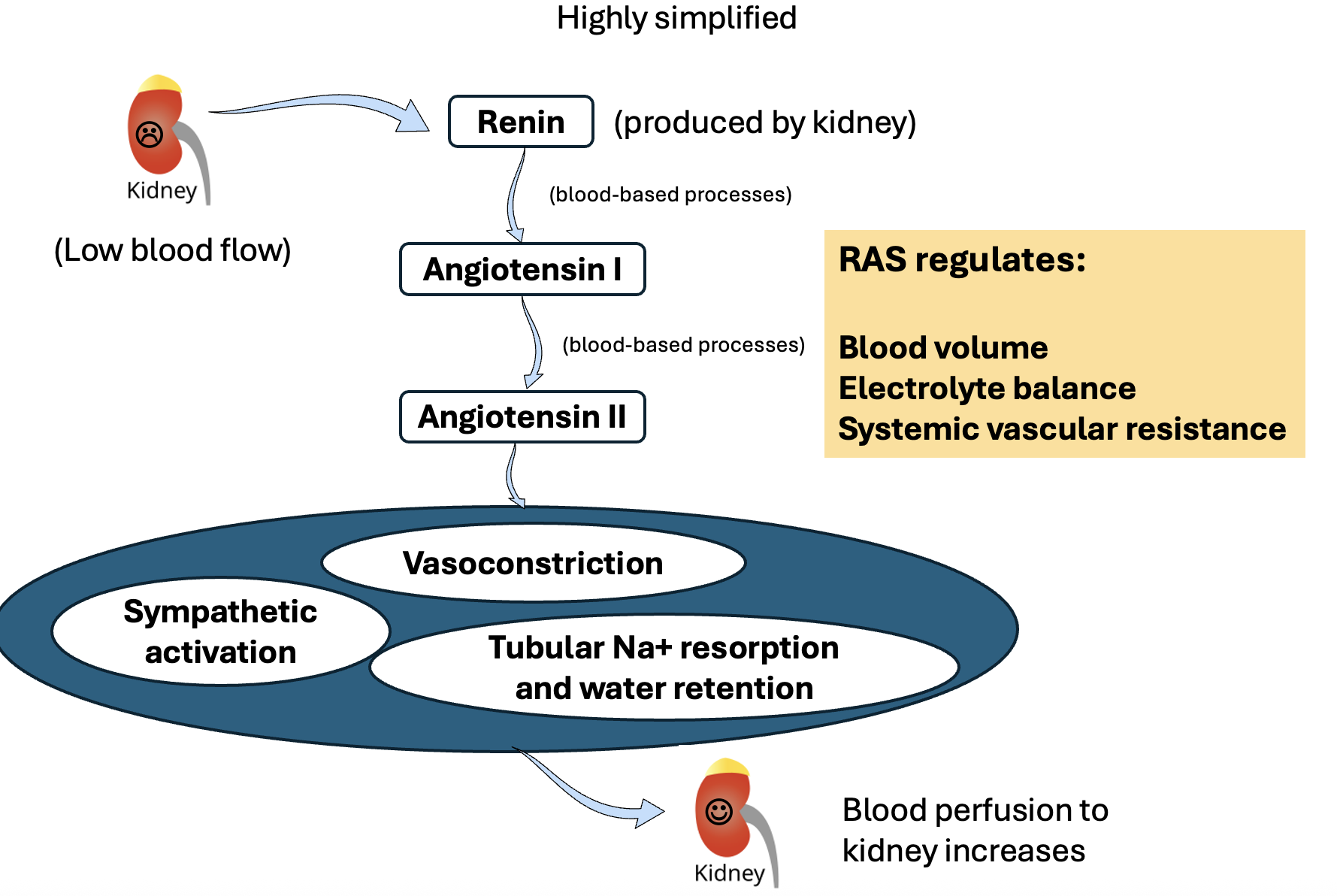
Briefly describe how the renin angiotensin system regulates blood volume, electrolyte balance and systemic vascular resistance.
low blood flow through glomerulus
low perfusion triggers renin to be produced
renin converts angioteninogen into angiotenin 1
Angiotensin 1 converted into Angiotenin 2
Angiotensin 2 responsible for vasoconstriction, sympathetic activation, tubular Na+ resorption and water retention
blood perfusion to kidney increases
RAS also regulates:
blood volume
electrolyte balance
systemic vascular resistance
Why trigger vasoconstriction when blood plasma is hypertonic?
Hormone secreted to maintain blood pressure