Muscle tissue
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
function
allows the body to move
allows movement of individual structures within the body
e.g. causes heart to beat
allows lungs to relax and expand
moves food through the digestive system
muscle
a specialised tissue containing cells capable of contraction
myogenesis
process of developing muscle tissue
occurs during embryonic development
muscle fibres form from the fusion of myoblasts into multi-nucleated fibres called myotubes
embryonic —> myoblasts —> myotubes —> myofibres
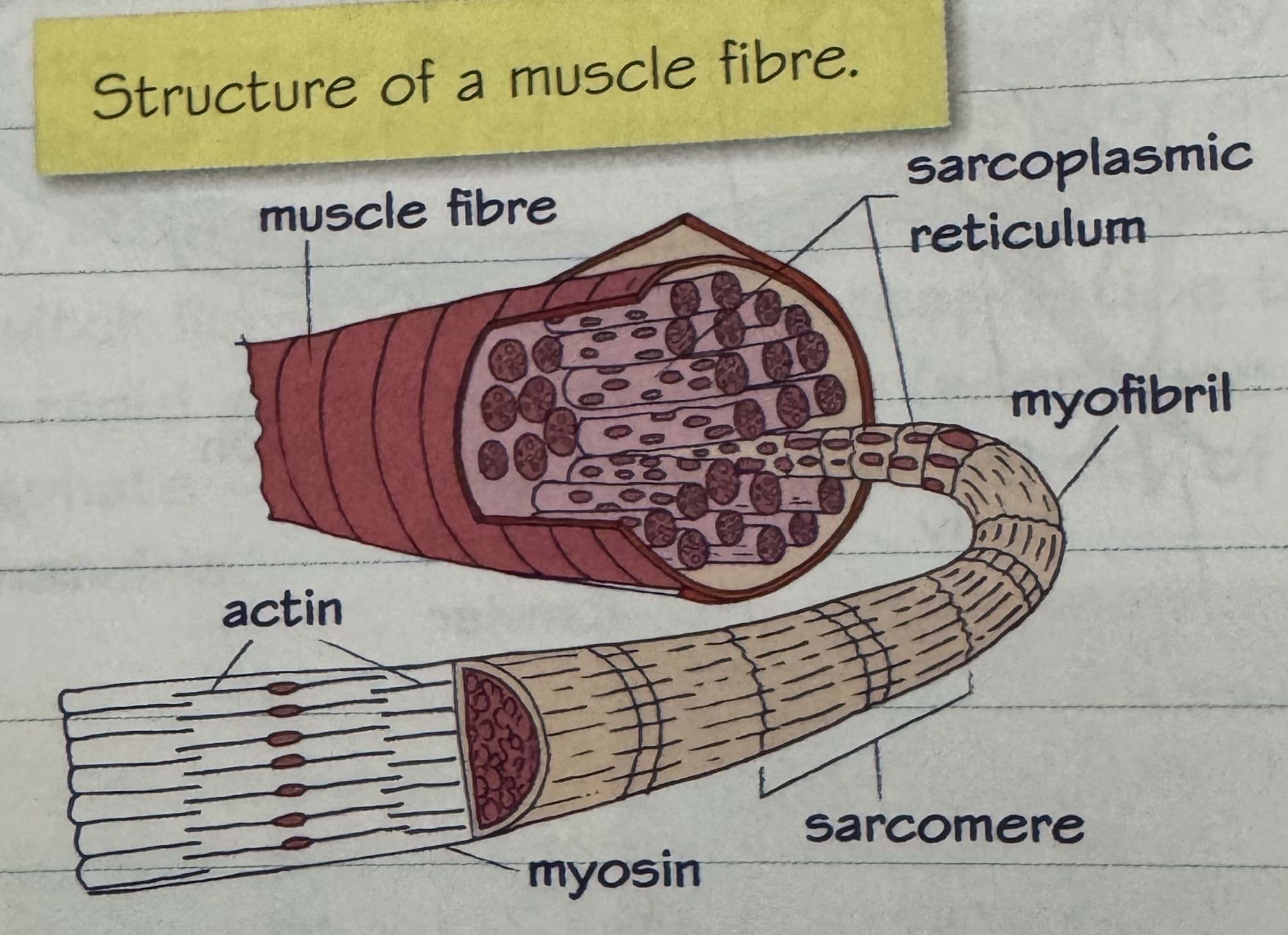
myofibrils
cylindrical strands of contractile proteins that make up muscle fibres
what can myofibrils be broken down into?
sarcomeres
sarcomeres
segments of myofibrils that contain bundles of parallel actin and myosin filaments
what is enabled when the actin and myosin filaments slide in between each other?
muscle contraction
shortening of the sarcomere
structure of muscle fibre diagram
types of muscle
skeletal, cardiac, smooth
is skeletal muscle voluntary or involuntary?
voluntary
is cardiac muscle voluntary or involuntary?
involuntary
is smooth muscle voluntary or involuntary?
involuntary
why is cardiac muscle involuntary?
it is myogenic - it can contract without nervous input
voluntary muscle
used consciously
involuntary muscle
controlled by the autonomic nervous system
where is skeletal muscle located?
attached to, support and move the skeleton
where is cardiac muscle located?
specialised muscles found in the heart
where is smooth muscle located?
digestive system, reproductive tracts, the vascular system, bladder and bowels
appearance of skeletal muscle
cylindrical shape with multiple nuclei arranged around the outside
striated appearance due to the arrangement of the fibres
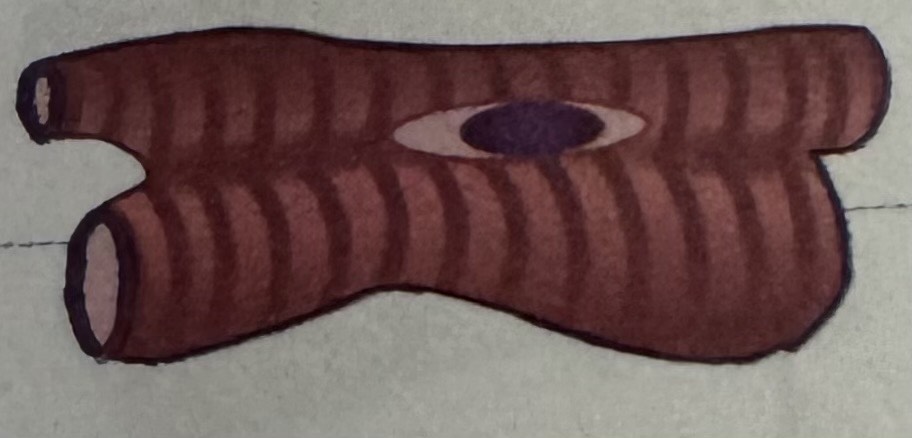
appearance of cardiac muscle
elongated, branching cells
one or two nuclei per cell
striations characterised by dark and light bands
found with excitatory and conductive muscle fibres, which conduct electrical impulses and control the heartbeat
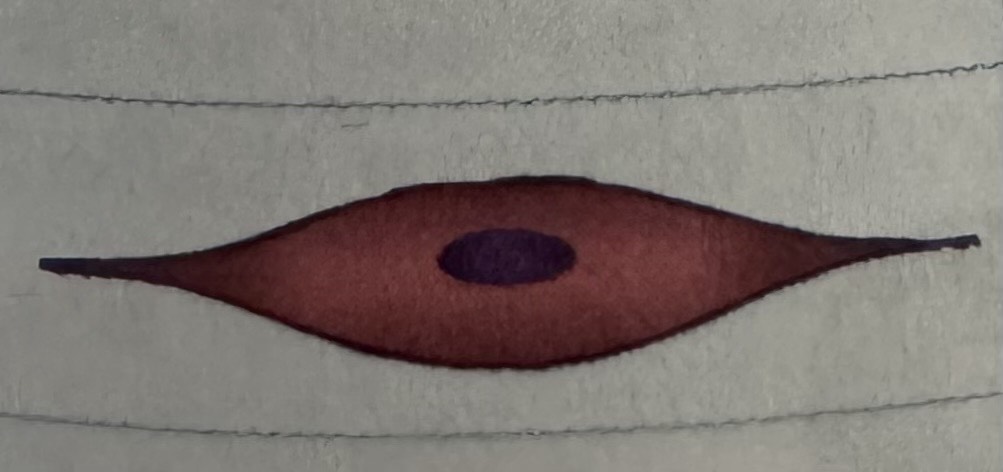
appearance of smooth muscle
spindle-shaped cells with one nucleus
function of skeletal muscle
movement of the skeleton at joints
work in antagonistic pairs
function of cardiac muscle
contraction of the heart tissue
function of smooth muscle
allows hollow organs to contract
skeletal muscle diagram
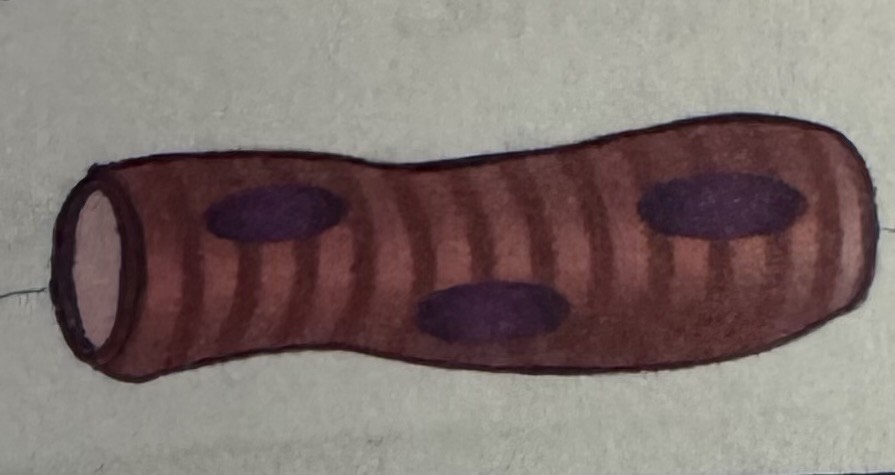

cardiac muscle diagram
smooth muscle diagram