MP322 Master Set
1/446
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
447 Terms
What does MIT stand for (thyroid)?
monoiodotyrosine
What does DIT stand for (thyroid)?
diiodotyrosine
How is T4 → T3 conversion done?
via deiodination
What are examples of antithyroid drugs?
carbimazole and propylthiouracil
How do antithyroid drugs work?
they work by inhibiting the enzyme thyorid peroxidase which converts tyrosine into MIT and DIT (through addition of iodine)
this prevents the synthesis of T3 and T4
What is active form of carbimazole?
methimazole
What are the adrenal glands made up of?
adrenal cortex and adrenal medulla
What are mineral corticosteroids?
Where are these produced?
e.g aldosterone
involved in sodium resorption and potassium excretion in kidneys
the adrenal cortex
What are glucorticorticosteroids?
Where made?
e.g. cortisol
regulates body’s response to stress
adrenal cortex
What does the adrenal medulla make?
80% adrenaline
20% noradrenaline
What are cellular actions of cortisol?
increases blood glucose levels
maintains the responsiveness of blood vessels to vasoconstrictive stimuli
has effects on immune system, nervous system and kidneys
anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressant
How is cortisol secreted?
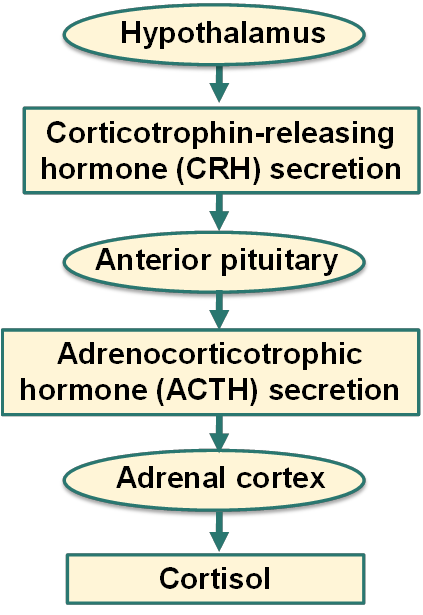

What causes Addison’s disease?
When does onset of disease occur?
due to dysfunction/ destruction of adrenal cortex
when 90%+ of both adrenal cortices are destroyed
What are symptoms of Addison’s disease?
hyperpigmentation
extreme fatigue
weight loss
decreased appetite
low BP causing light headedness and dizziness
GI disturbance
salt cravings
low blood glucose
What causes Addison’s disease?
autoimmune destruction of the adrenal gland
infections
invasion
haemorrhage
What is treatment for Addison’s disease?
hydrocortisone (Glucocorticosteroids)
fludrocortisone (mineral corticosteroid)
treatment is lifelong
What is adrenal crisis?
sudden severe pain in lower back, abdomen or legs
severe vomiting and diarrhoea
dehydration
low BP
loss of consciousness
can result in death
What is Cushing’s syndrome?
hypersecretion of cortisol
What are signs and symptoms of Cushing’s syndrome?
moon face
thin skin, legs and arms
fat pads
high BP
poor wound healing
red striation
bruisability
What are causes of Cushing’s syndrome?
pituitary tumour leading to increased secretion of ACTH (most common)
adrenocortical tumours
tumours near hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal gland pathway
What is ACTH dependent Cushing’s?
body makes too much ACTH because of tumour
What is ACTH independent Cushing’s?
ACTH level is low
adrenal glands are making too much cortisol due to adrenal tumour
What is a thyroid follicle?
What is colloid?
specialised cell located in thyroid that is circular
located in lumen of follicle and is where thyroid precursors are stored and then synthesised and released from
What are key elements of thyroid synthesis?
iodine and tyrosine
How does thyroid synthesis occur?
iodine is transported through the blood using sodium
diffuses into follicle cell
iodine is then transported to the colloid where it is attached to rings of tyrosine in thyroglobulin
iodine is either added to MIT or DIT
the iodine rings then join together (MIT + DIT or DIT + DIT)
forms T4 or T3
the T3/T4 is then endocytosed back into the blood
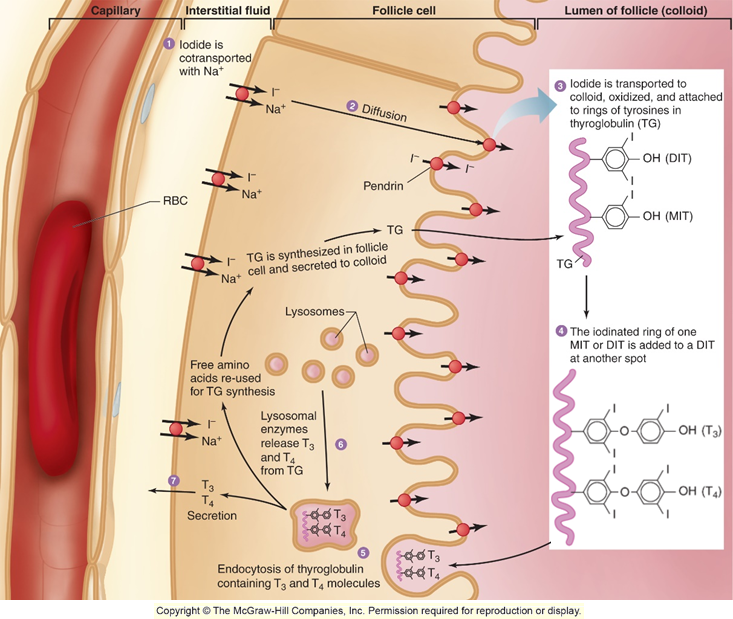

What is the active form of thyroxine?
T3
How is T4 converted to T3?
Via deiodination
How do T3/T4 travel in the blood?
using plasma proteins TBG and TTR
How is thyroid hormone secreted (hint: hypothalamus)?
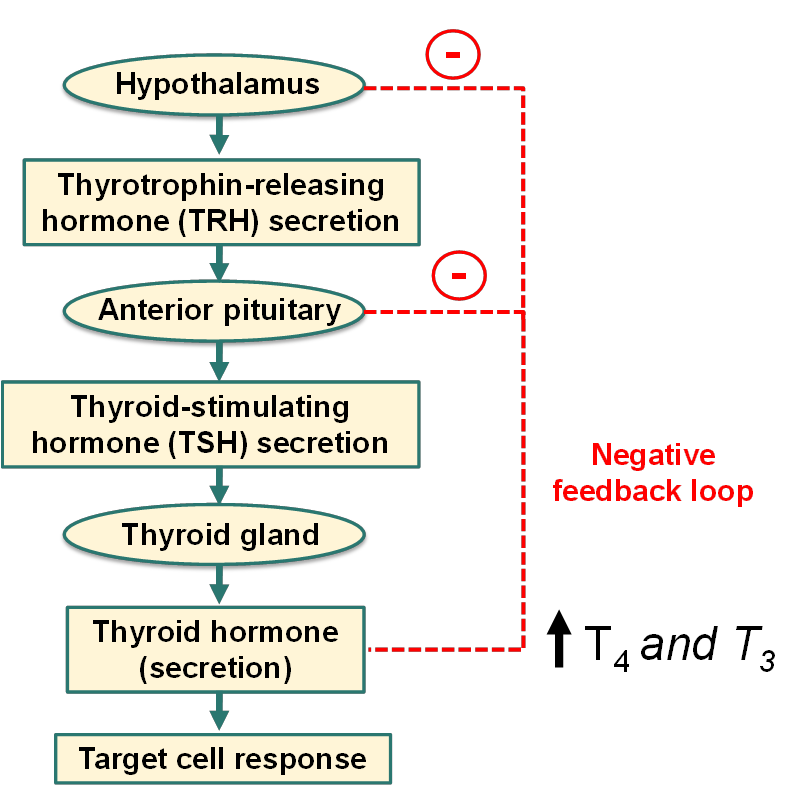

What is euthyroid, hypothyroid and hyperthyroid?
euthyroid = normal secretion of thyroid hormones
hypothyroid = subnormal secretion
hyperthyroid = excessive secretion
What does thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) do?
stimulates production of T3 and T4
also increases DNA replication, cell division and follicular cell protein synthesis
What happens when TSH conc is excessive?
leads to rapid cell division of thyroid cells → enlargement of thyroid gland (goitre)
What do T3 and T4 do?
increase basal metabolic rate and maintain it
increase in heat production
increase response to sympathetic output
permits normal growth and development
What is cretinism?
What does it result in?
extreme iodine deficiency
mental retardation
stunted growth
deaf-mutism
What is salt now fortified with?
salt
What do results with thyroid function test coincide with?
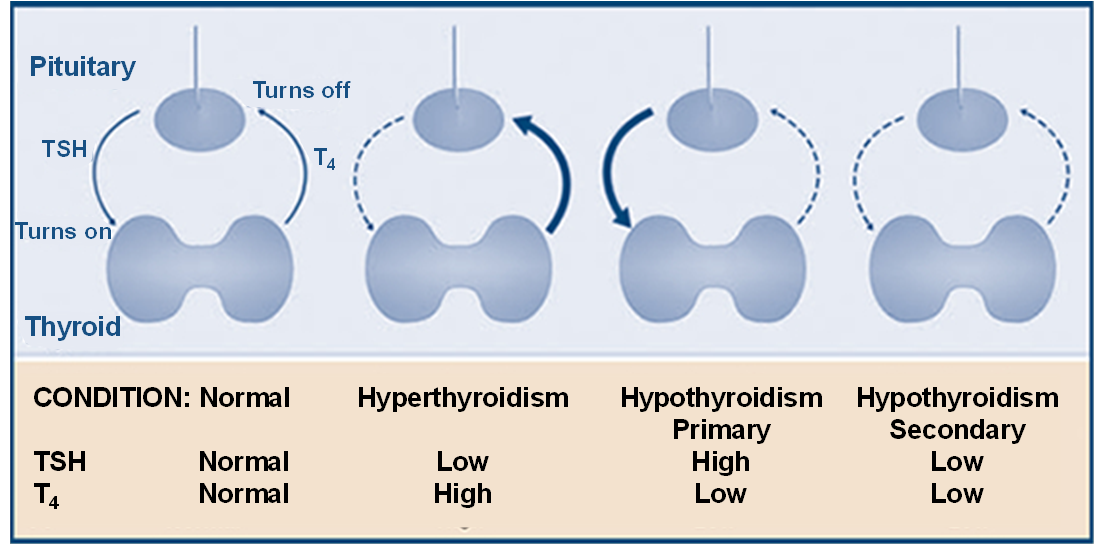

What is the most common cause of primary hypothyroidism?
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
autoimmune disorder where body produces antibodies against thyroid peroxidase
more prevalent in women
T4 decreases and TSH increases
can result in goitre
What are adverse effects of levothyroxine?
hair loss first months of treatment
headaches
insomnia
nervousness
fever
hot flashes
sweating
pounding heart beat
appetite changes
weight changes
What is secondary hypothyroidism?
problem with anterior pituitary or hypothalamus not producing enough TSH or TRH so low levels of TSH and T4
Why are TSH levels low in hyperthyroidism and T4 levels are high?
T4 high causes -ve feedback loop on TSH so low levels of TSH
What is myxoedema coma?
What are symptoms?
end result of untreated hypothyroidism
hypothermia
progressive weakness → loss of consciousness
seizures and respiratory depression
can lead to death if untreated quickly
What drugs affect thyroid function?
corticosteroids
can decrease basal production of TRH and TSH → less T4 and T3
lithium
inhibits release of T4 and T3 and interferes with peripheral deiodination
amiodarone
can cause hypo and hyperthyroidism
cholestyramine
reduces the absorption of T3
What are signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism?
heat intolerance
palpitations
weight loss even when appetite is increased
restlessness
nervousness
fatigue
increased sweating
frequent bowel movements
goitre
What is most common cause of hyperthyroidism?
How does this disease come about?
Grave’s disease
autoimmune disease caused by TSI (thyroid stimulating immunoglobulins)
TSI activates TSH receptors on thyroid follicular cells causing an increase in secretion of T4 and T3
What are treatments for hyperthyroidism?
surgery
radioactive iodine (emits radiation that acts on cells responsible for causing hyperthyroidism)
thioamides
carbimazole and propylthiouracil
How do thioamides work?
carbimazole and propylthiouracil
inhibits thyroid peroxidase (enzyme responsible for iodination of tyrosine) and prevents T4 and T3 synthesis
slow onset (4-6 weeks)
generally safe but may cause agranulocytosis (reduction in neutrophils) so increases risk of infection
What is one potential problem of thioamides?
may cause agranulocytosis which is the reduction in neutrophils which increases risk of infection
What does thyroid peroxidase do?
is the enzyme responsible for iodination of tyrosine (MIT and DIT)
What is metformin MOA?
reduces hepatic gluconeogenesis
What are S/E to metformin?
GI upset (why patients start with a lower dose to try and avoid)
vit B12 deficiency
What is MOA for sulfonylreas?
stimulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells
glucose = ATP:ADP ratio increase = ATP sensitive K+ channels close = depolarisation = voltage gated calcium ion channels open = influx of intracellular calcium = insulin secretion
What is SGLT2 MOA?
act by inhibiting glucose transporter SGLT2 which mediates glucose reabsorption
What are examples of incretins?
What do incretins do?
GLP-1 and GIP
incretins are hormones that are released after eating that increase release of insulin from pancreatic beta cells, and suppress glucagon release in alpha cells
incretins slow digestion by increasing the time it takes for food to leave the body and gives a feeling of being full
How do DDP4 gliptins work?
inhibit DDP4 enzyme which is an enzyme that degrades incretins (GLP and GIP)
this causes incretins to remain active allowing for insulin release and glucagon suppression
Does metformin follow Lipinski Rule of 5 ?
no, but is still orally available
What is the difference between T1D and T2D?
type 1 = loss of insulin production
type 2 = receptors are resistant to insulin or insufficient secretion of insulin
Where is insulin produced?
Where is glucagon produced?
insulin = pancreatic beta cells
glucagon = pancreatic alpha cells
What are causes of hyperglycaemia?
loss insulin-stimulated glucose uptake (so build-up of glucose in blood)
loss of insulin repression of gluconeogenesis
loss of insulin repression of glycogen breakdown
How does insulin repress gluconeogenesis and glycogen breakdown?
acts as a off switch for these processes
What percentage of diabetes are type 1?
5-10%
Why do T1D produces no/little insulin?
due to pancreatic beta cells being destroyed by immune system = autoimmune disorder
How do T2D cells respond to insulin?
cells are in an insulin-resistant state
How do beta cells try to compensate for insulin resistance in T2D?
What are drawbacks?
produce more insulin
once beta cells can no longer produce enough insulin to combat the resistance = T2D
What are factors that increase likelihood of developing T2D?
obesity
lack of exercise
diet
genetic factors (increase likelihood of parent, sibling or child has T2D)
When are T1D symptoms made apparent?
rapid onset of symptoms
typically severe e.g. ketoacidosis which requires hospitalisation for treatment
What percentage of women develop gestational diabetes?
When does it typically develop?
When does it disappear?
25% women
during 2nd trimester
after birth of child (so temporary condition)
What are tests used to diagnose diabetes?
fasting glucose test
no food or drink (except water) for 8-10 hrs then test blood glucose
random glucose test
glucose tolerance test
HBA1c test
How is a glucose tolerance test conducted?
patient fasts for at least 8 hrs
blood glucose measured immediately before and after drinking 75g of glucose dissolved in water
What are the values for fasting/ random glucose test?
normal = 3.9-5.9mmol/L
prediabetes = 5.5 - 6.9 mmol/L
diabetic = >7mmol/L
What are the values for the glucose tolerance test?
11.1 mmol/L indicates diabetes
7.9-11.1 indicates impaired glucose tolerance
What is HBA1c?
What does this help to measure?
What does it help to diagnose?
glycated blood that is the binding of haemoglobin A and glucose
measures the average blood glucose levels over the last 3 months (average RBC life span)
T2D, T1D develops quickly (normally quicker than 3 months so might not catch in a HBA1c test)
What are values for HBA1c test?
>48mmol/mol indicates diabetes
42-48mmol/mol indicates risk of developing diabetes
What is BP goal for diabetics?
What is HBA1c goal for diabetics?
What is total cholesterol level goal for diabetics?
<130/80mmHg
48
no greater than 5
What are symptoms of diabetes (more acute)?
dehydration
frequent urination
fatigue
nausea and vomiting
polyphagia (increased hunger)
weight loss (T1D)
UTI and thrush (glucose in urine)
poor wound healing
blurry vision
How does Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) occur?
due to glucose being unavailable body uses fat as an energy source
free fatty acids are converted to ketones by the liver → energy source
ketones cause blood to become more acidic
life threatening
When should T1D ketone levels be checked?
at time of diagnosis
during an illness (when patient is ill)
during a growth spurt
when insulin is taken incorrectly
What are symptoms of DKA?
extreme thirst
frequent urination
nausea
vomiting
confusion
irritability
loss of consciousness → coma → death
What indicates DKA?
ketones present in urine
high blood glucose levels
fruity smelling breath
What is treatment for DKA?
fluid replacement, insulin and mineral replacement
What are chronic complications of Diabetes?
vascular damage
high BP
neuropathy
nephropathy
retinopathy
increased risk of CV risk
What are regular checks diabetics should do?
regular eye, kidney, BP, foot checks
When should a diabetic be put on a primary prevention statin?
if >40 y/old or been diagnosed for 10+ years
How does diabetic foot occur?
due to either nerve damage leading to sensation loss in peripherals or due to poor blood flow to feet
patient cant feel cuts so go unnoticed - infection
no blood flowing - area cant heal
If a mother has poorly controlled diabetes, what are risks in pregnancy?
increased risk of miscarriage, stillbirth and birth defects
How are blood glucose levels regulated?
regulated by insulin secretion
> glucose in blood = greater insulin secretion
How is insulin secreted (process)?
increase in glucose in beta cells leads to an increase in ATP:ADP ratio
this increase in ratio leads to ATP-sensitive K+ channels to close and membrane depolarisation occurs
depolarisation causes voltage gated Ca2+ ion channels to open
increase in intracellular calcium promotes the secretion of insulin
insulin secreted via a vesicle that exits cell through exocytosis
What is the insulin signalling pathway?
IR binds to insulin causing autophosphorylation of the receptor
the phosphorylates residues on IR act as binding sites for IRS
IR phosphorylates 4 tyrosine residues on IRS
phosphoinositide-3-kinase binds to the phosphorylated tyrosines, converting PIP2 → PIP3
PIP3 activates PDK1 which phosphorylates and activates PKB
activated protein kinase B then diffuses through the cell and activates processes such as glucose transport and glycogen synthesis
How does glucose uptake into adipocytes and muscles occur?
GLUT4 transporter protein contained inside the cell
protein AS160 holds the GLUT4 inside the cell
PKB phosphorylates AS160 deactivating it
this allows GLUT4 to fuse with cell membrane causing increased glucose uptake into muscle and adipocytes
What is Fox01?
What does Fox01 do?
a transcription factor
regulates gene expression that mediates gluconeogenesis
What does insulin do to Fox01?
How does insulin go about doing this?
prevents Fox01 moving to the nucleus (stopping gene expression, which prevent gluconeogenesis)
insulin signalling pathway occurs, resulting in PKB
PKB phosphorylates Fox01 stopping it from entering the nucleus → no longer can regulate gene expression and mediate gluconeogenesis
What autoantibodies being present increase risk of developing T1D?
autoantibodies against these proteins;
GAD-65
Insulin
IA-2
ZnT8
What is treatment of T1D?
subcutaneous injections of insulin that are required lifelong
How often should T1D monitor blood glucose levels?
before meals, before bed, before driving, before and after exercise, when ill etc.
When a T1D is about to drive what must their blood glucose level be minimum?
What should they do if blood glucose is not at the correct level?
5 to drive (or at risk of hypo on the road)
15g of fast acting cards, wait 15 mins and then re-check blood glucose levels
What inhibits insulin signalling pathway?
PTP1B (protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B)
phosphorylation of serine residues by PKC
How does PTP1B inhibit insulin signalling pathway?
Why does obesity increase PTP1B expression?
dephosphorylates IR, means IRS an no longer bind = inhibits pathway
causes pro-inflammatory cytokine e.g TNFalpha, these express PTP1B
How does phosphorylation of serine cause inhibition of insulin signalling pathway?
serine being phosphorylated by PKC results in inhibition as tyrosine on IRS can no longer be phosphorylated
How does obesity and excess fat affect insulin signalling pathway?
fatty acids produce 2 intermediates (DAG and ceramide)
DAG produces PKC = serine phosphorylation instead of tyrosine phosphorylation (inhibition)
Ceramide causes PKB inhibition
What is adiponectin and what does it do?
secreted from adipocytes and promotes insulin sensitivity in cells
When is less adiponectin secreted?
in obesity, less adiponectin is secreted = insulin resistance