Phytochemicals, Nutrition, and Body Weight Management
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
VO2 max
Maximum rate of oxygen consumption during exercise.
Nutrient sensing
Body's ability to detect nutrient levels.
Incretins
Hormones that regulate insulin secretion post-meal.
Functional Food
Foods providing health benefits beyond basic nutrition.
Phytochemicals
Health-promoting compounds found in plant foods.
Zoochemicals
Health-promoting compounds found in animal foods.
Settling Zone
Weight range where body stabilizes genetically.
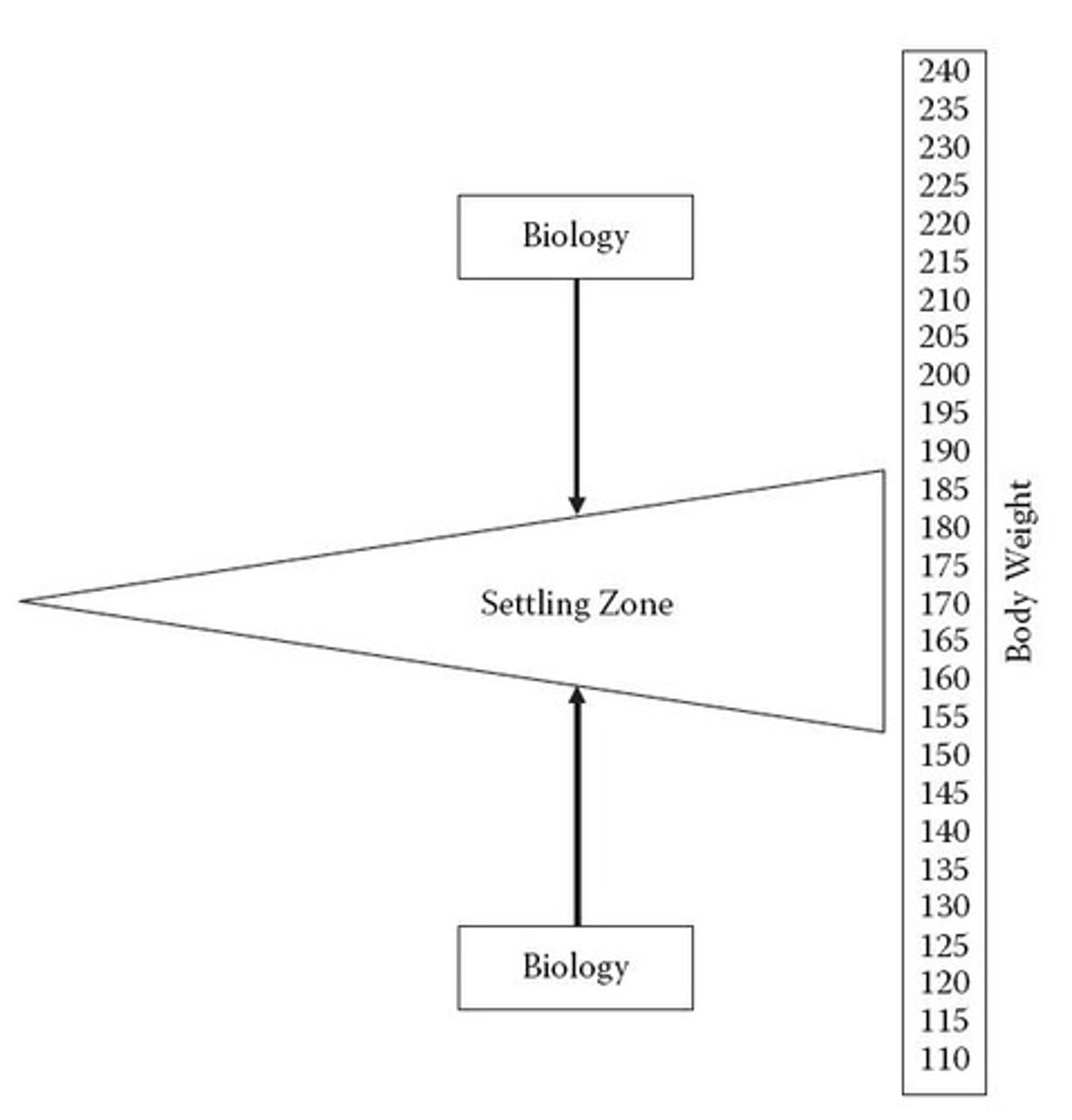
Biological regulatory mechanisms
Processes activated by weight deviations from Settling Zone.
Body weight
Total mass of bone, muscle, fat, and fluids.
Healthy body weight
Weight promoting good health and activity levels.
Obesity
Excess body fat linked to health risks.
Body composition
Proportions of fat and lean mass in body.
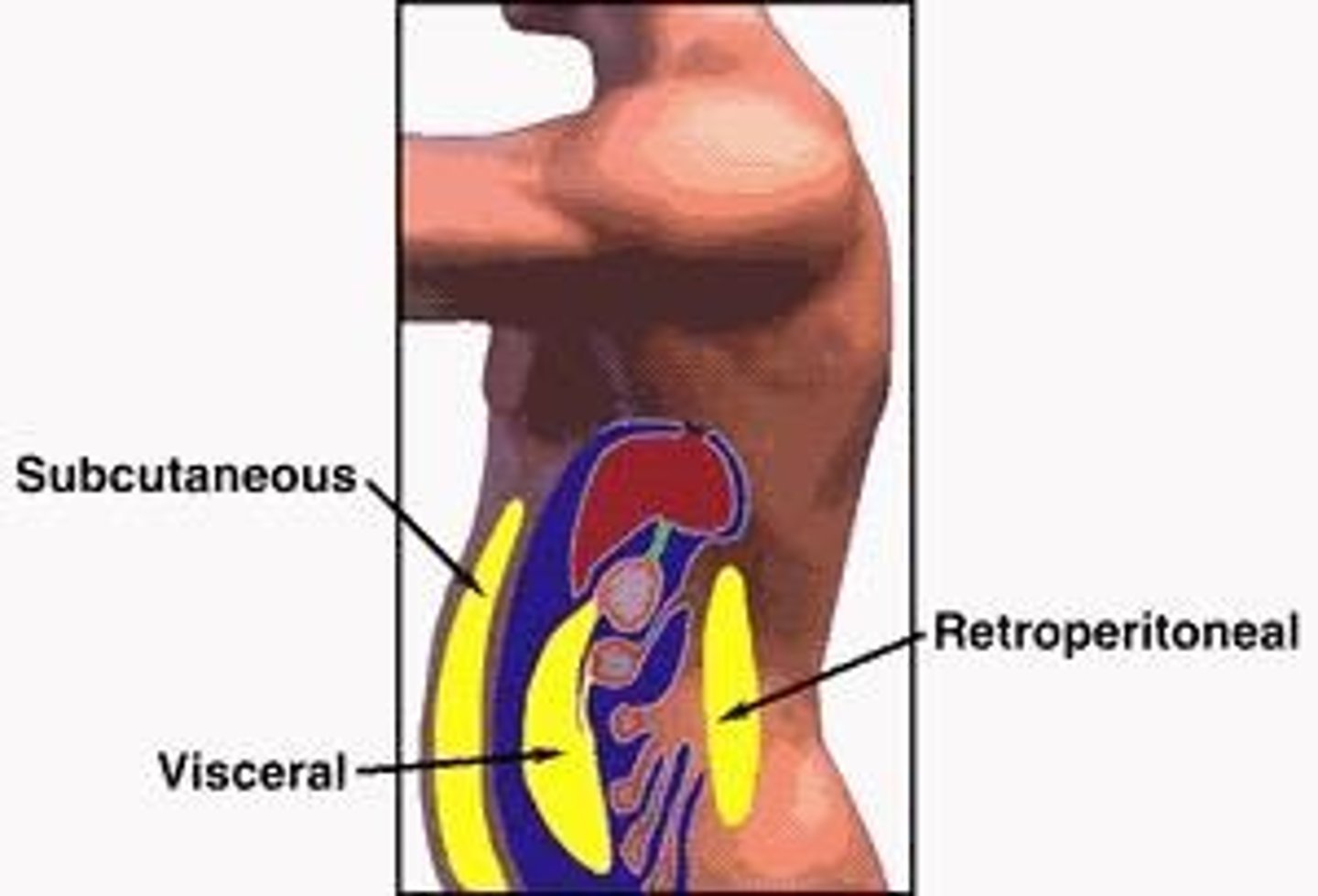
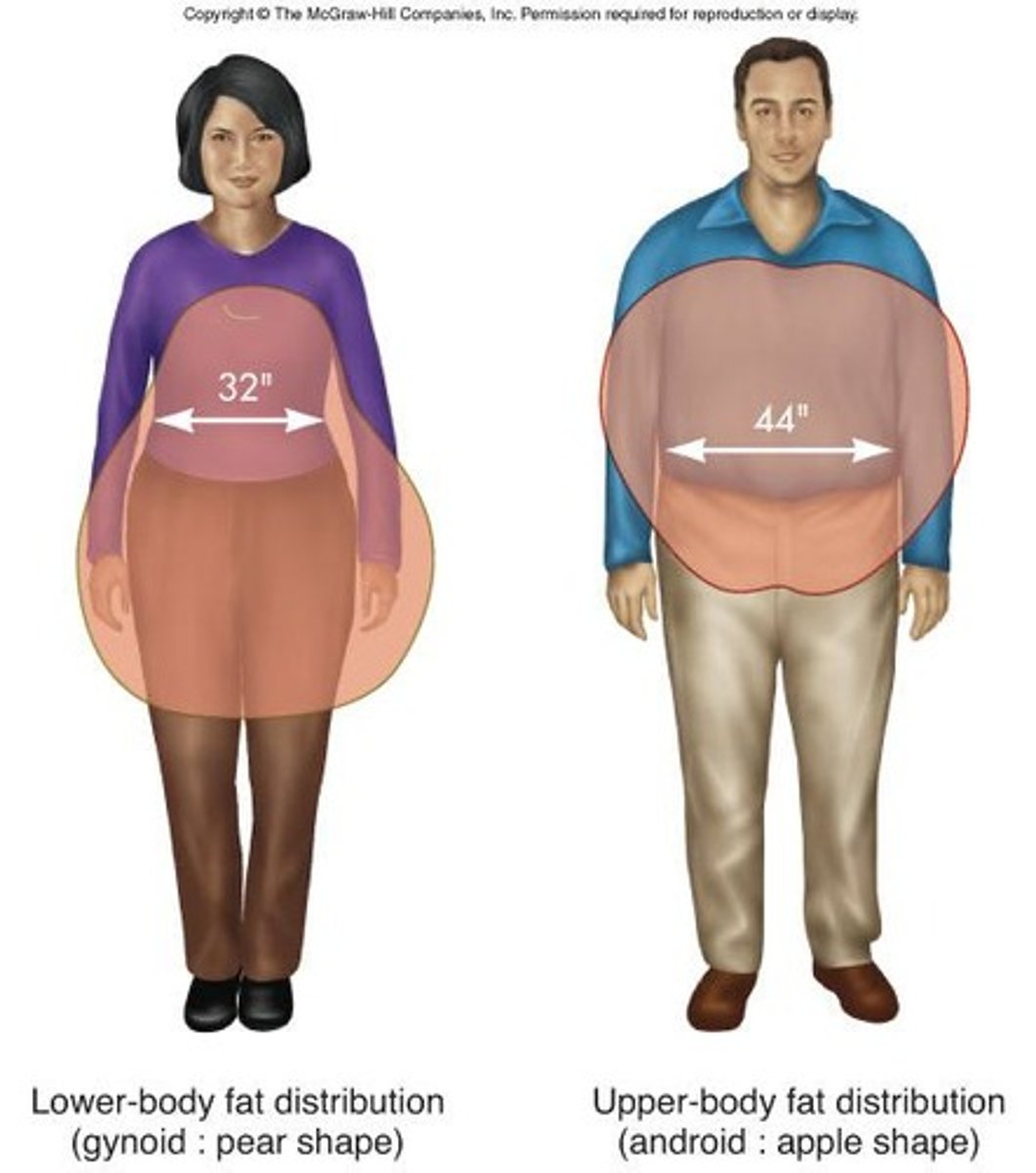
Body fat distribution
Pattern of fat storage in the body.
Visceral fat
Fat surrounding organs, increasing disease risk.
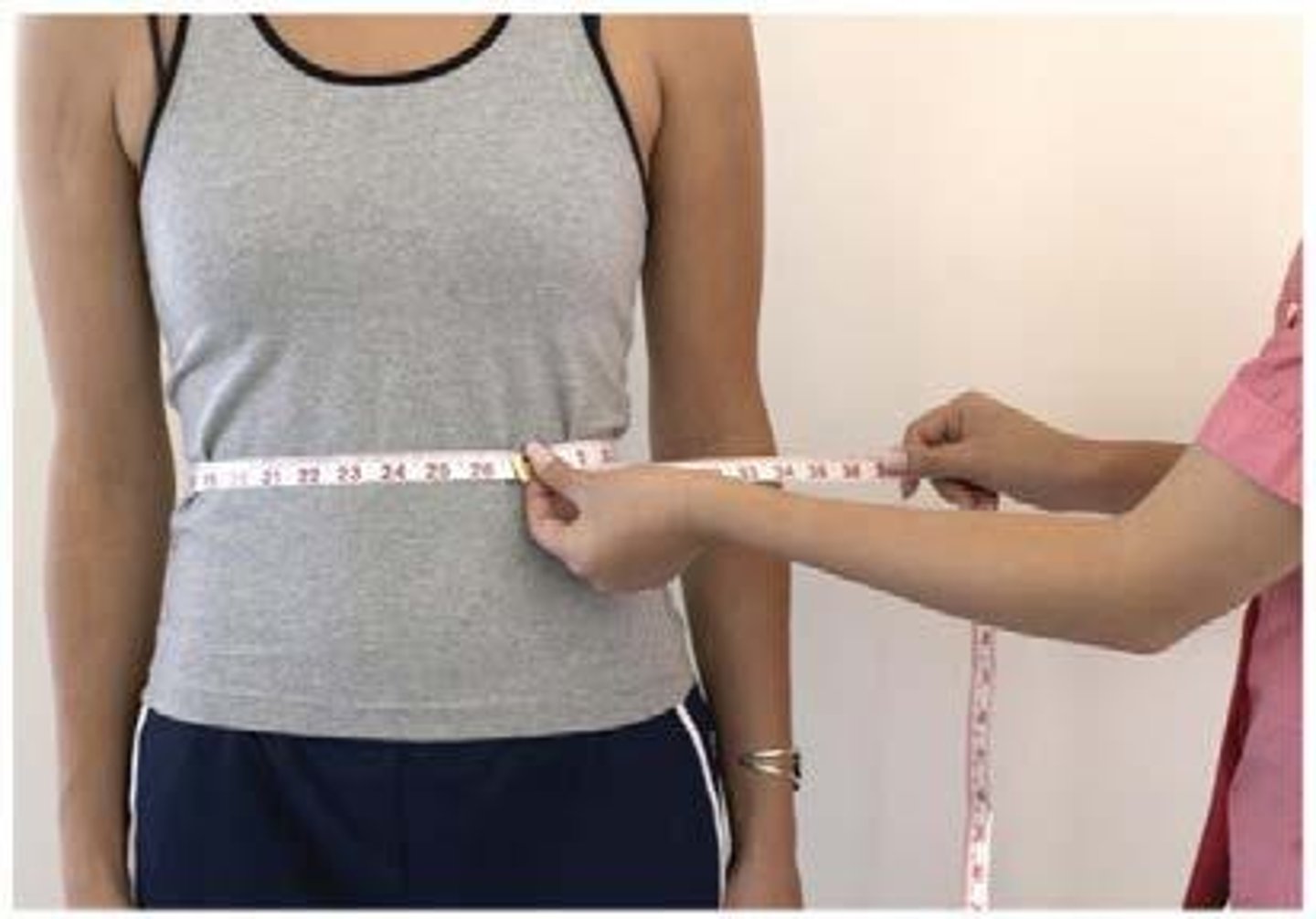
Waist-to-hip ratio
Measure of fat distribution; men > 0.90.
Waist circumference
Measurement indicating fat distribution; men > 40 in.
Fitness
Body's capacity to perform aerobic work.
Health at every size
Acceptance of body diversity regardless of weight.
Normalized eating
Eating in response to hunger and fullness cues.
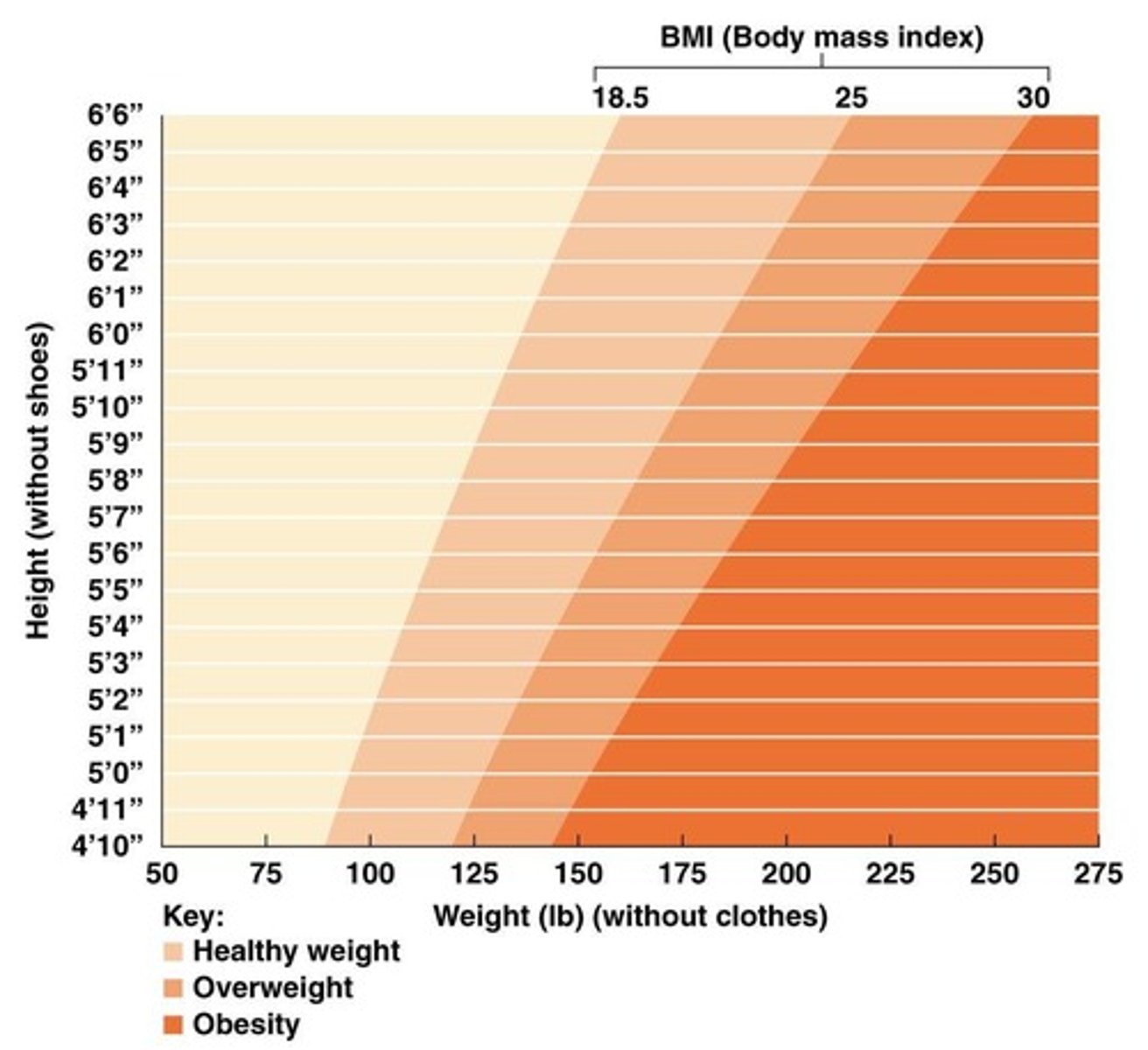
Body mass index (BMI)
Weight (kg) divided by height (m) squared.
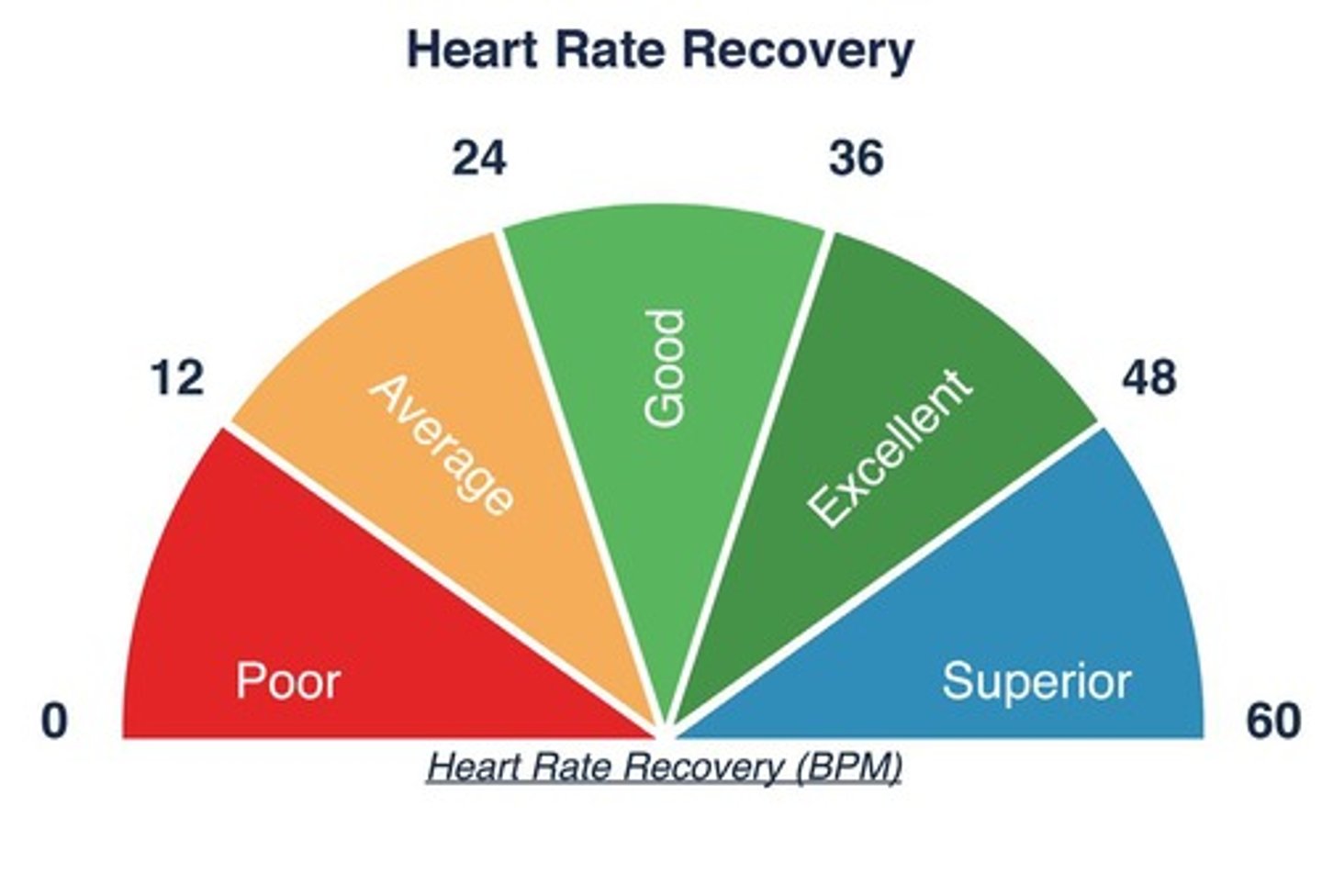
Heart rate drop
Rate of heart rate decrease per minute post-exercise.
Maximal oxygen uptake
Best measure of cardiovascular fitness.
Training effects on VO2 max
Training can double VO2 max in some individuals.
Phytochemicals
Plant substances with health-promoting properties.
Glucagon
Hormone that raises blood glucose levels.
Insulin
Hormone that lowers blood glucose levels.
Incretins
Peptide hormones enhancing insulin secretion post-meal.
GIP
Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, an incretin hormone.
GLP-1
Glucagon-like peptide-1, an incretin hormone.
Nutrient Sensing
Cells detect and respond to nutrient availability.
Neurolymphocrine System
System integrating neural and hormonal responses to nutrients.
Zoochemical
Animal-derived compounds with health benefits.
Superfoods
Foods rich in nutrients and beneficial compounds.
Avocado Nutritional Value
150g provides 40% fiber, 25% vitamin C.
Kale Nutritional Value
100g contains 200% vitamin A, 134% vitamin C.
Açaí Juice Nutritional Value
Provides 6% daily vitamin A per glass.
Rhubarb Toxicity
Rhubarb leaves are poisonous; stems are safe.
Common Food Toxins
Toxins in plants that can be harmful.
Glycoalkaloids
Toxic compounds found in potatoes and cassava.
Trypsin Inhibitors
Proteins that inhibit digestion in soy and peas.
Food Synergy
Combined effects of foods enhancing health benefits.
Dietary Patterns
Overall eating habits influencing health outcomes.
Whole Grains
Grains containing bran, germ, and endosperm.
Functional Foods
Foods providing health benefits beyond basic nutrition.
Epigenetic Imprinting
Long-term changes in gene expression from environment.
Avidin
Protein that binds biotin tightly.
Biotin
Vitamin B7, essential for metabolism.
Lectins
Carbohydrate-binding proteins with sugar specificity.
Cooking
Reduces lectin activity in foods.
Salicin
Compound not showing aspirin-like anticlotting effects.
White Willow
Source of salicin, used for pain relief.
Carotenoids
Plant pigments with antioxidant properties.
Lycopene
Carotenoid giving tomatoes their red color.
β-Carotene
Carotenoid providing significant vitamin A activity.
Flavonoids
Plant compounds proposed to reduce inflammation.
Uric Acid
Waste product from purine metabolism.
Antioxidant Activity
Ability to neutralize free radicals.
Phenolic Compounds
Plant metabolites with health benefits.
Glycyrrhiza glabra
Plant source of licorice compounds.
Phytoestrogens
Plant-derived compounds mimicking estrogen.
Soy Isoflavones
Phytoestrogens found in soy products.
Indoles
Compounds found in cruciferous vegetables.
Allium Vegetables
Includes garlic and onions, rich in sulfur.
Nitrates
Compounds that can convert to nitric oxide.
Nitrosamines
Potentially harmful compounds from nitrites.
Ginger Phytochemicals
Compounds with anti-inflammatory and nausea effects.
Caffeine
Stimulant that inhibits cAMP breakdown.
Flavonoids
Plant compounds that may reduce inflammation and disease.
Phytoestrogens
Plant-derived compounds mimicking estrogen effects.
Nitrate
Compound found in vegetables, beneficial for blood flow.
Antioxidants
Substances preventing oxidative damage in cells.
Alcohol
Organic compound affecting metabolism and health.
Undernutrition
Deficiency in essential nutrients affecting health.
Sarcopenia
Age-related loss of muscle mass and strength.
Lectins
Carbohydrate-binding proteins affecting nutrient absorption.
Glycoalkaloids
Toxic compounds found in certain uncooked plants.
Trypsin Inhibitors
Proteins that inhibit digestive enzyme activity.
Carotenoids
Pigments in plants with antioxidant properties.
β-Carotene
Carotenoid providing vitamin A activity.
Indoles
Compounds in cruciferous vegetables with health benefits.
Isothiocyanates
Compounds in cruciferous vegetables aiding cancer protection.
Alliums
Vegetables like garlic and onions with health benefits.
Phenolic Compounds
Plant compounds with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
Antioxidant Activity
Ability to inhibit oxidative stress in cells.
Oxyradical-Scavenging Capacity
Measure of antioxidant effectiveness in foods.
Prudent Diet
Dietary pattern emphasizing whole foods and balance.
Western Diet
Diet characterized by high processed food intake.
Solidago virgaurea
Goldenrod, used for anti-inflammatory and diuretic effects.
Vanilla planifolia
Vanilla, utilized in food and perfumery.
Viburnum prunifolium
Black haw, known for antispasmodic properties.
Beets
Rich in nitrates, beneficial for health.
Nitric oxide
Vasodilator formed from nitrites.
Red meat cooking
High temperatures can form genotoxic nitrosamines.
Ginger phytochemicals
Compounds like 6-gingerol, beneficial for inflammation.
Ethanol
Two-carbon alcohol, soluble in water and lipids.
Alcohol dehydrogenase
Main enzyme for ethanol metabolism.
Microsomal ethanol oxidizing system
Second major pathway for ethanol metabolism.
Fatty acid ethyl ester synthase
Catalyzes non-oxidative ethanol metabolism.
Lipogenesis
Conversion of carbohydrates to fatty acids.
Cirrhosis
Irreversible liver condition with scar tissue.