6.2.4-6.2.6(multiple alleles, sex linkage and codominance)
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
State what is meant multiple alleles
More than 2 alleles, but only 2 are present
Only 2 homologous chromosomes, only 2 gene loci
eg. Blood groups humans
State the 4 blood types
A
B
AB
O
State how blood groups are assigned
They are assigned based on immunoglobin gene, I
State the 3 genes which are assigned by the immunoglobin gene and whether they are recessive or dominant
IA - Dominant
IB - Dominant
Io - Recessive
Give each blood type in their gene forms
A - IA IA
B - IB IB
AB - IA IB
O - Io Io
State the antigens present on red blood cells and the antibodies in the plasma of each blood type
A - Antigen A on red blood cells. Antibody B in plasma
B - Antigen B on red blood cells. Antibody A in plasma
AB - Antigen A and B on red blood cells. No antibodies
O - No antigens on red blood cells. Anti-A and Anti-B antibodies in plasma
State the other type antigen present on red blood cells
Rhesus antigens
State what is meant by a sex linked gene
A gene which is carried on the X or Y chromosomes
State whether the X or Y chromosome is longer
The X chromosome is much longer than the Y
Describe and explain the effects of the X chromosome being longer than the Y
It means that some lengths of the X chromosome have no equivalent homologous portion on the Y chromosome
Characteristics that are controlled by recessive alleles on this non-homologous portion will appear more frequently in the male
This is because there is no portion of the Y chromosome with a dominant allele and so the gene is always expressed
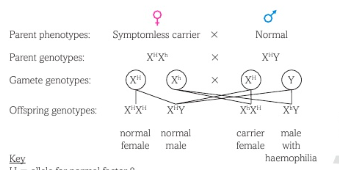
Give an example of sex-linkage of a symptomless carrier female and a normal male showing the Parent genotype, Gamete genotype and the offspring genotypes
Describe what is meant by codominance
It is when alleles are equally dominant and so both are expressed in the phenotype
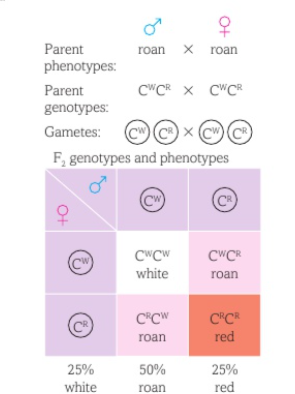
Give an example of Codominance using cow fur colour as an example where both the male and female are heterozygous and the alleles are CR and CW for red colour and white colour. Show the genetic cross, Parent genotypes, offspring genotypes and probability of each phenotype being expressed