biol 201: lab exam
1/94
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
(L1) eyepieces/ ocular lenses
(L1) where you look into the microscope, magnified by 10x
(L1) head
holds eyepieces
(L1) nosepiece
holds objective lens
(L1) objective lenses
(L1) lenses that magnify the image and increase resolution
(L1) coaxial coarse and fine adjustment knob
(L1) moves the stage up and down to adjust focus
(L1) stage
(L1) platform for slide
(L1) coaxial stage motion knob
(L1) moves the stage in the 4 directions
(L1) condenser
(L1) focuses light onto slide
(L1) aperture iris diaphragm
(L1) controls the angle of light from lamp, adjusts contrast
(L1) field iris diaphragm
controls width of light reaching the condenser, adjusts contrast
(L2) brownian movement
(L2) continuous random movement of particles [in water]
(L2) diffusion
(L2) net movement of particles from a higher-concentrated area to a lower-concentrated area
(L2) rate of diffusion depends on
(L2) factors like size, shape, mass of particles, and temperature [higher temp, larger size, smaller particles= faster rate]
(L2) osmosis
(L2) diffusion of water in and out of cell through carrier proteins called aquaporins
(L2) isotonic
(L2) concentration of a solute is equal to the concentration of the solution [“the cell is isotonic to its environment”]
(L2) hypertonic
(L2) concentration of solute is higher than the reference solution [if the solution is hypertonic to the cytoplasm, water will move out of the cell]
(L2) hypotonic
(L2) concentration of solute is lower than the reference solution [if the solution is hypotonic to the cytoplasm, water will move into the cell]
(L2) cyclosis
(L2) cycling of the cytoplasm in the cell
(L1) resolution vs magnification
(L1) resolution: distinguishing two object from another; magnification: making small object appear larger
(L3) prokaryotes reproduce by
(L3) binary fission
(L3) eukaryotes reproduce by
(L3) mitotic cell division (PPMAT!)
(L3) the cell cycle’s longest phase
(L3) interphase
(L3) interphase’s periods and jobs
(L3) G1 (Gap 1): cell builds proteins and grows larger
S (Synthesis): growing and copying nuclear DNA
G2 (Gap 2): growing and prepares for cell division
(L3) mitotic phases
(L3) mitosis: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
cytokinesis: division of cytoplasm
(L3) prophase
(L3) chromosomes condense and are visible, nucleolus disappears, spindle begins to form
(L3) prometaphase
(L3) nuclear envelope breaks up, spindle attaches to centromeres and begins to pull on chromosomes
(L3) metaphase
(L3) spindle pulling on centromeres causes chromosomes to line up along the metaphase plate
(L3) anaphase
(L3) chromatids break free of each other and are pulled to either end the the cell by spindle
(L3) telophase
(L3) spindle begins to disappear, chromosomes disperse, nucleoli begins to form, nuclear envelope begins to develop
(L3) end of telophase: plants vs animals
(L3) plants: cell wall begins to form- cell plate
animals: cell pinches- cleavage furrow
(L3) spermatogenesis
(L3) primary spermatocyte (2n), secondary spermatocytes (n), spermatids (n), spermatozoa
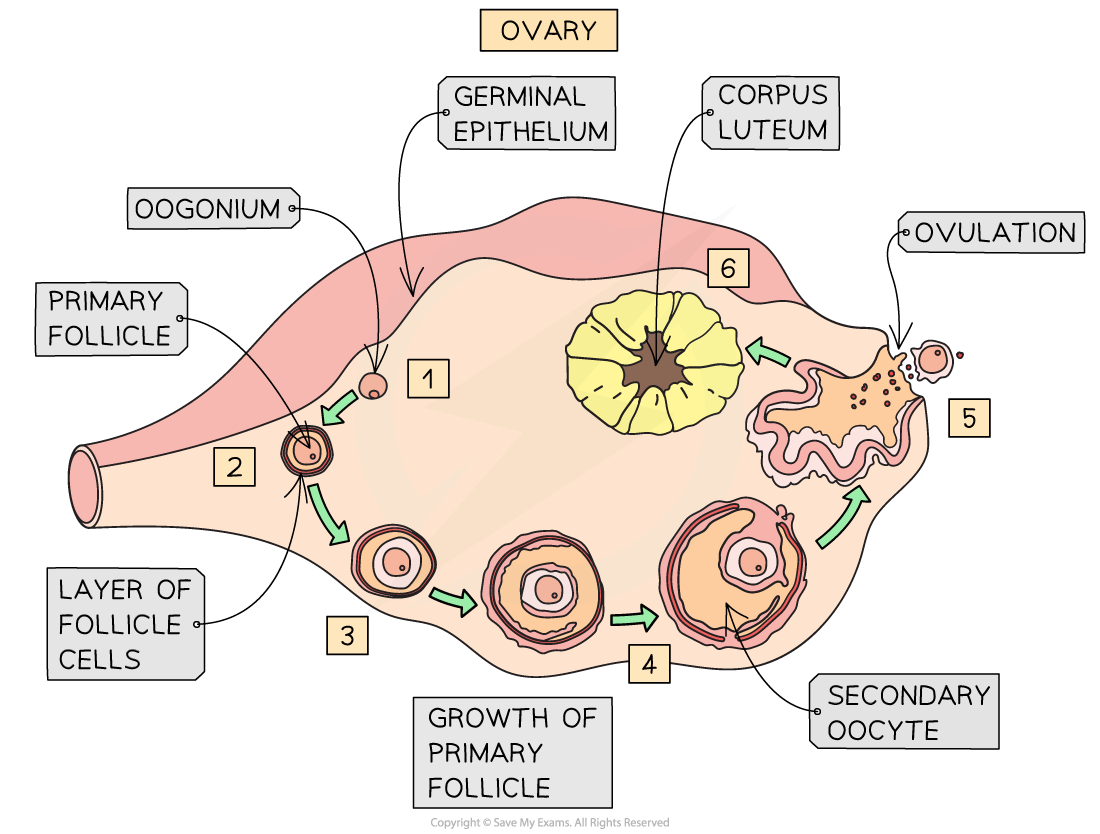
(L3) oogensis
(L3) primary oocyte (2n), secondary oocyte (n), ootid (n), ovum (n)
(L3) in the seminiferous tubule
(L3) large sertoli- nurse cells
outside → in: spermatogonia, primary spermatocytes, secondary spermatocytes, spermatids, spermatozoa (with flagella)
(L4) are gametes 2n or n
(L4) n (haploid)
(L4) genetic drift vs natural selection
(L4) change in allele frequency due to chance; greater average reproductive rate as the result of a particular genetic trait
(L4) heterozygote
(L4) a diploid cell with both the dominant and recessive allele at a locus
(L5) transcription
(L5) enzyme RNA polymerase binds to DNA at promoter, building RNA from 3’ to 5’ until terminator sequence
(L5) translation
(L5) ribosome travels from codon to codon, from 5’ to 3’, until the stop codon
(L5) DNA bases
(L5) guanine, cytosine, adenine, thymine
(L5) RNA bases
(L5) guanine, cytosine, adenine, uracil
(L6) classification order
(L6) domain, kingdom, phyla, classes, order, family, genus, species
(L6) main domains
(L6) eukarya, archaea, bacteria
(L6) D Bacteria
(L6) prokaryotes, generally chemoheterotrophic, unicellular
(L6) bacteria’s three shapes
(L6) bacillus (rod), coccus (sphere), spirillum (spiral)
(L6) ex: cyanobacteria
(L6) green algae: all photoautotrophs, long filaments
(L6) D Eukarya
(L6) main difference: have membrane-bound nucleus
(L6) eukarya’s kingdoms
(L6) about 12, three main: plantae, animalia, fungi
(L6) ex: diatoms
(L6) kingdom protista, unicellular, photoautotrophs, many different shapes
(L6) multicellular organisms ex
brown algae, red algae, mushrooms, some green algae…
(L6) photo and chemotrophs
(L6) obtain energy from sunlight vs from chemicals
(L6) auto and heterotrophs
(L6) obtain nutrients from themselves vs from others
(L6) fungi kingdom
(L6) mostly multicellular, chemoheterotrophs, long filaments called hyphae organized into a mat called mycelium, large pores between cells
(L7) plants!
(L7) multicellular, photoautotrophic, evolved about 500 million years ago; mostly angiosperms
(L7) seeds
(L7) cotyledon: food storage (monocots have 1, dicots have 2), endosperm: food, radicle: embryonic root, plumule: embryonic leaf
(L7) plant tissues
(L7) meristem (embryonic), dermal (outer surface), ground (photosynthesis, food, support), vascular (xylem and phloem)
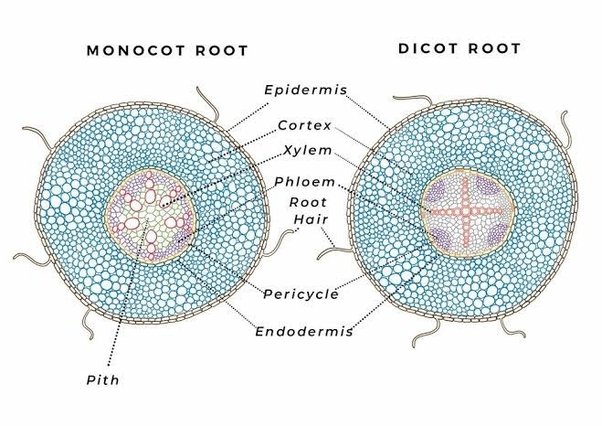
(L7) monocot vs dicot roots
(L7) monocot root: xylem form a circle, pith in center, phloem around xylem, no cambium
dicot root: xylem in condensed center, has cambium, no pith
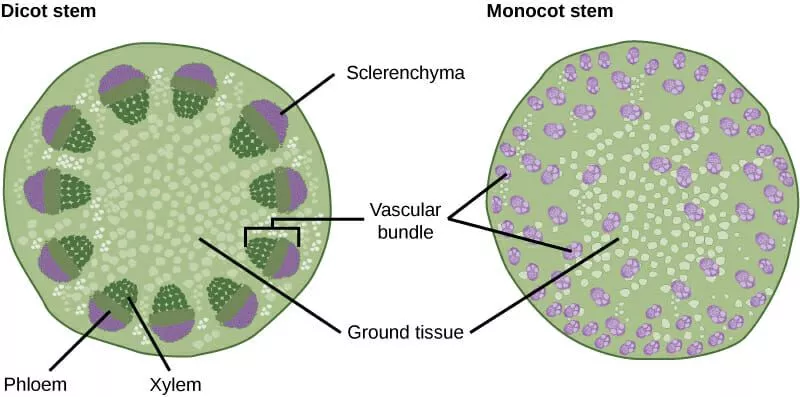
(L7) monocot vs dicot stems
(L7) monocot stem: scattered vascular bundles, no pith, no cambium
dicot stem: vascular bundle in cambium circle, pith in center
(L7) monocot vs dicot leaves
(L7) monocot leaf: parallel veins
dicot leaf: branching veins, petiole- stalk
(L7) monocot vs dicot flowers
(L7) monocot flowers: in 3s and multiples of 3s
dicot flowers: 4s and 5s and multiples of 4s and 5s
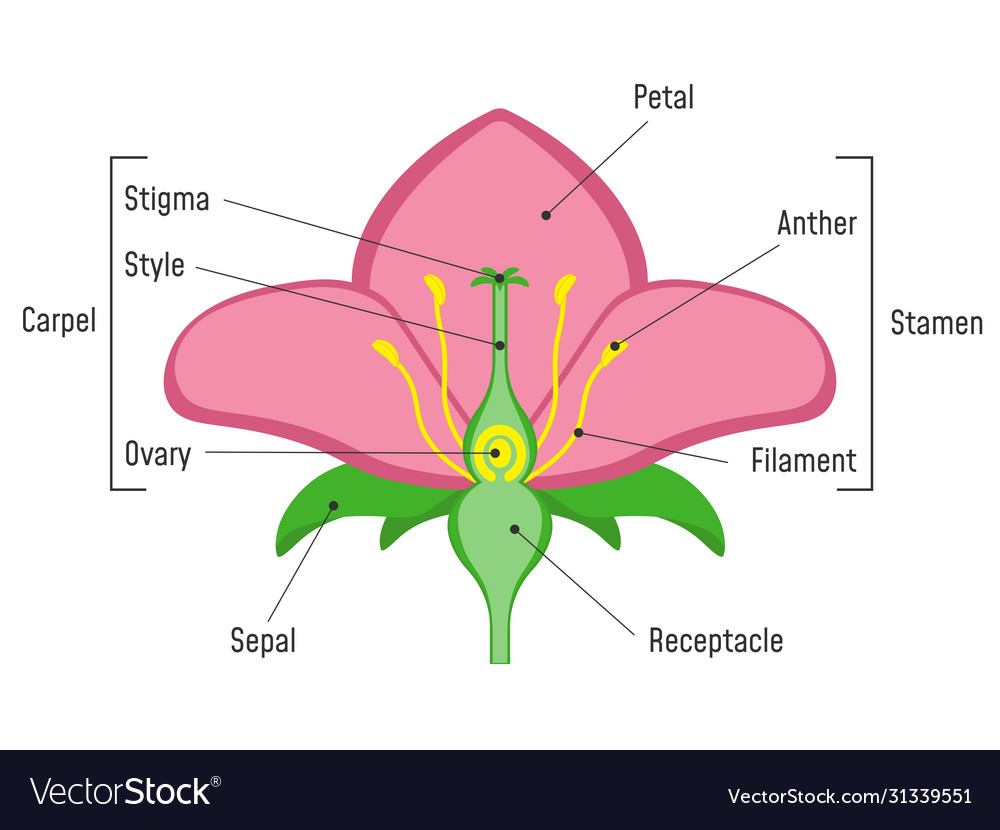
(L7) flower parts
(L7) carpel: stigma at top, style, ovary at base, ovules inside
stamen: filament, anther- made of 2 pollen sacks
sepals and petals
receptacle: base of flower
(L8) basic animal tissues
(L8) epithelial (surface), connective, muscle (contractile), nervous
(L8) morphology
(L8) layer and shape of cells
simple: one layer vs stratified: more than one layer
squamous: flat vs cuboidal: box vs columnar: long boxes
(L8) loose connective tissue vs fibrous connective tissue
(L8) loose: matrix is liquid, fibroblasts: irregular shaped cells
fibrous: strong parallel fibers with fibroblasts between them- tendons/ ligaments
(L8) adipose tissue
(L8) matrix with adipose cells with large droplets of fat in them
(L8) blood
(L8) plasma and cellular elements: erythrocytes (red blood cells), leukocytes (white blood cells), thrombocytes (platelets)
(L8) types of muscle tissue
(L8) skeletal/ striated muscle tissue (long, ribbed fibers), smooth muscle tissue (long and tapered), cardiac muscle tissue (short)
(L8) nerve tissue
(L8) neurons, glia cells- help neurons function
(L9) porifera
(L9) sponges
no symmetry, hermaphrodites, internal fertilization, no systems

(L9) cnidaria
(L9) coral, jelly fish
radial symmetry, usually hermaphrodites, fertilization usually external, nerve net, incomplete digestive system, no other systems

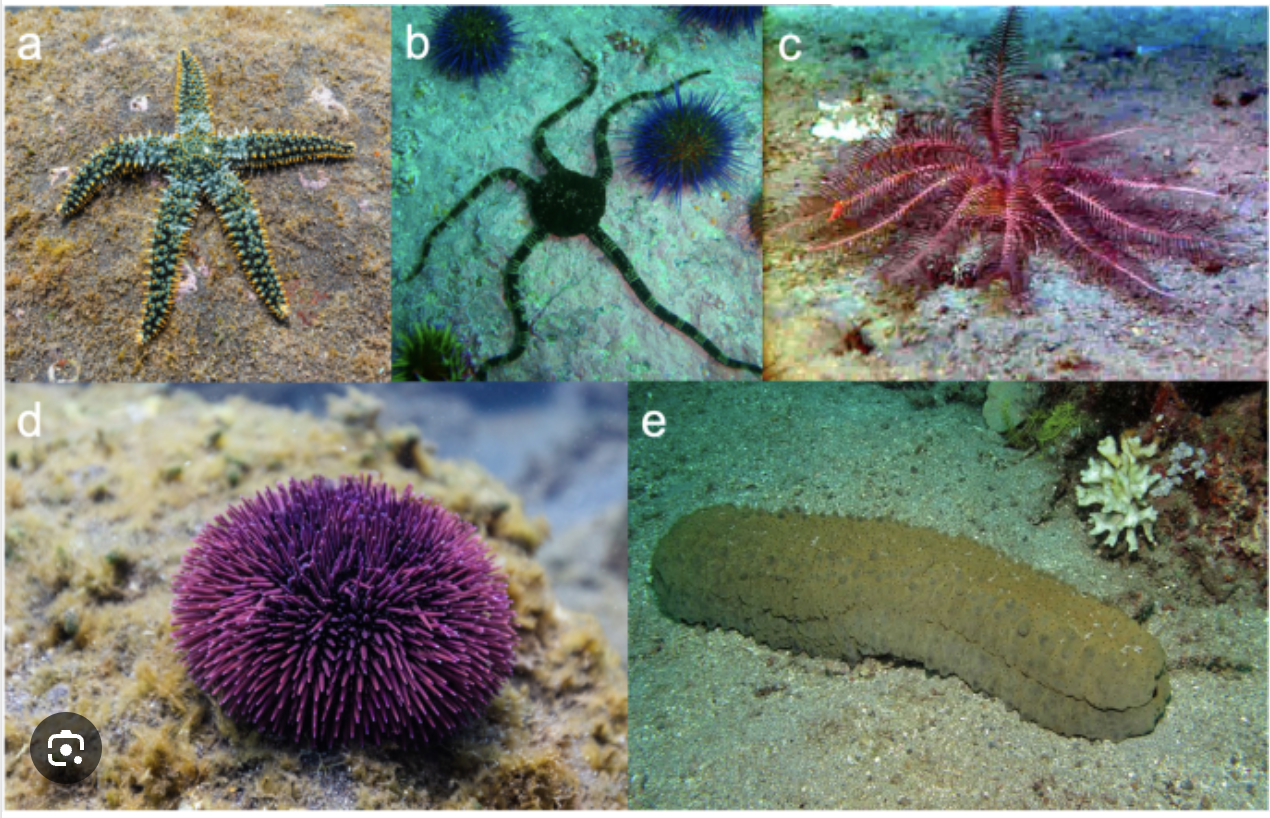
(L9) echinodermata
(L9) starfish
symmetrical, usually seperate sexes, external fertilization, nerve ring, complete digestive system, open 1-chambered heart, gills

(L9) chordata
(L9) lab 10!
bilateral symmetry, usually seperate sexs, brain and ganglia and sense organs, complete digestive system, closed heart with 2 or more chambers, lungs or gills, excretory system

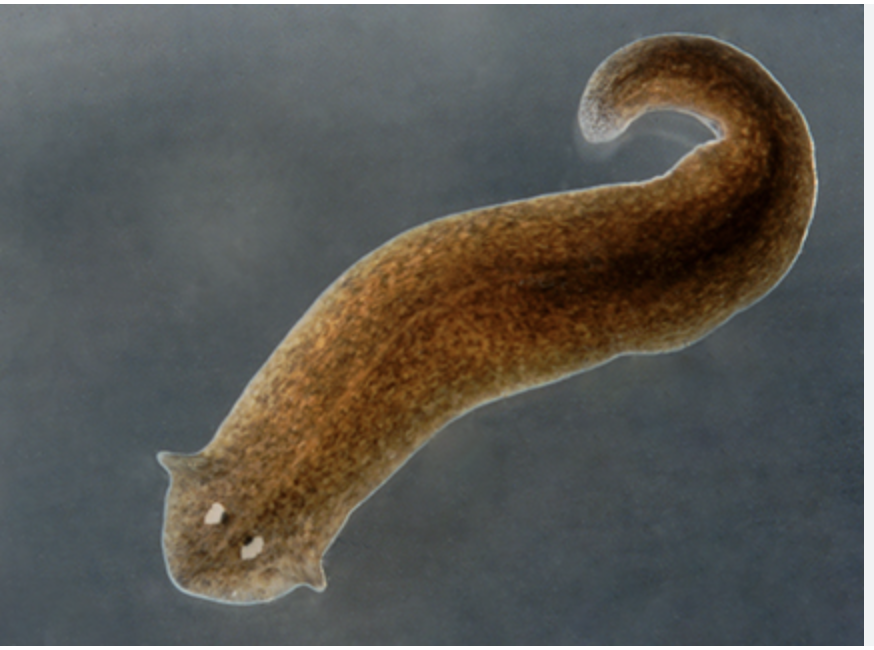
(L9) platyhelpminthes
(L9) flatworms
bilateral symmetry, internal fertilization, simple brain, incomplete digestive system
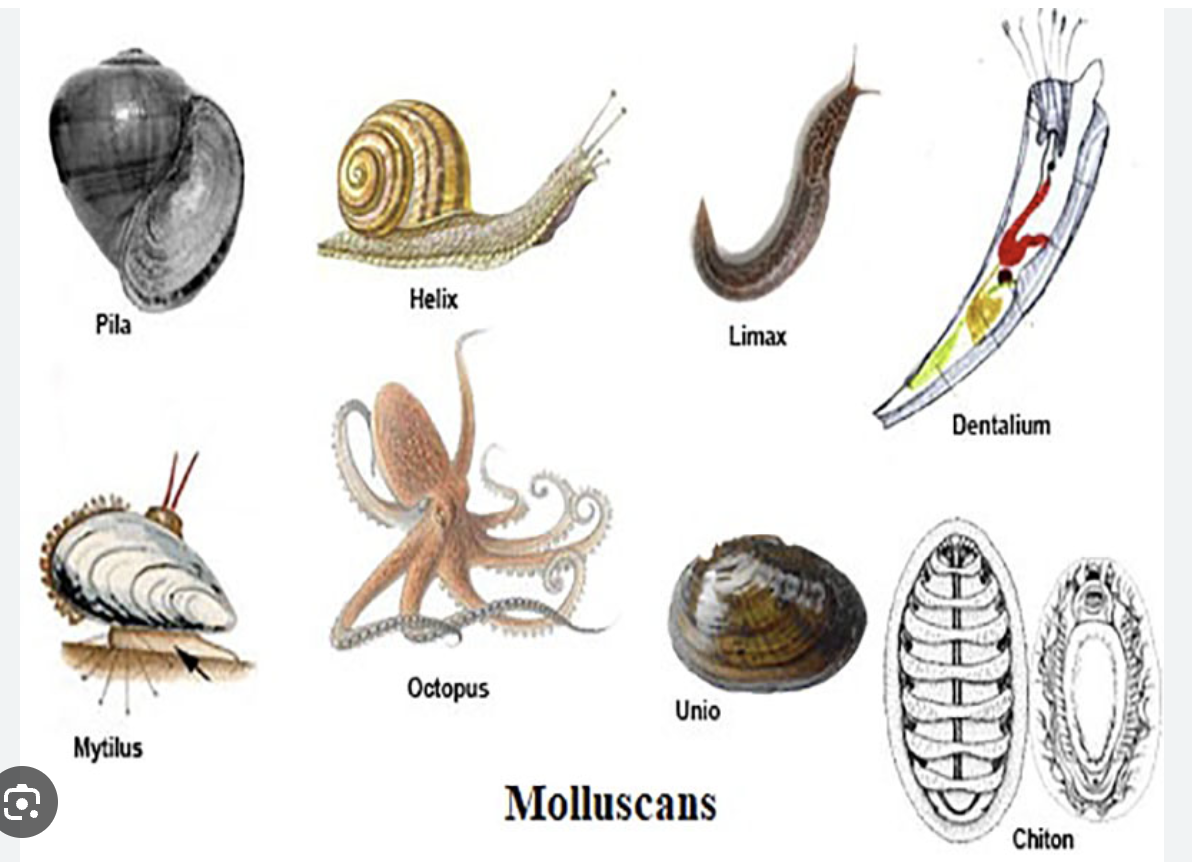
(L9) mollusca
(L9) snails, squids…
some symmetrical, usually seperate sexes, usually external fertilization, nerve ring, complete digestive system, mostly open heart with 3 chambers, gills, single muscular foot
(L9) annelida
(L9) segmented worms
bilateral symmetry, usually hermaphrodites, nerve ring, complete digestive system, several closed one chamber heart

(L9) nematoda
(L9) round worms
bilateral symmetry, usually seperate sexes, internal fertilization, nerve ring, complete digestive system

(L9) arthropoda
(L9) spiders…
jointed legs, bilateral symmetry, seperate sexes, internal fertilization, brain, complete digestive system, open one chamber heart, trachea or lungs or gills, exoskeleton
(L9) which phylum have parasites
(L9) annelida (leeches), platyhelminthes (tapeworms), nematoda (pinworms), chordata (lamprey)
(L10) oviparous vs viviparous vs ovoviviparous
(L10) layed egg with nutrition in egg (ie chicken) vs nutrition inside mother with live birth (ie humans) vs egg with nutrition inside mother and live birth (ie whale shark, seahorse…)
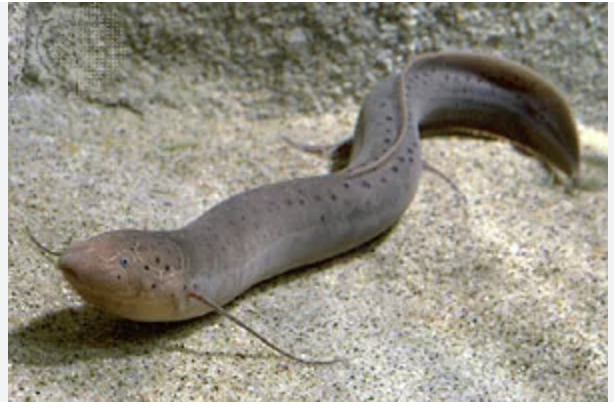
(L10) lampreys
(L10) eel-like fish, no jaws
slimy and smooth skin, notochord and simple cartilage skeleton, no jaw has teeth and toothed tongue, 2 chambered heart, 7 pair gill slits, fertilization external and oviparous, brain with small cerebrum, poikilotherm

(L10) cartilaginous fish
(L10) sharks…
slimy scaled skin, notochord and cartilage skeleton, movable jaw and teeth, 2 chambered heart, 5 pair gill slits, internal fertilization and oviparous, brain with small cerebrum, poikilotherm

(L10) ray-finned fish
(L10) seahorse
slimy skin with scales, vertebrae, movable jaw and teeth (but seahorses don’t have teeth), 2 chambered heart, 5 gill slits, external fertilization (usually oviparous but seahorses are ovoviviparous), brain with small cerebrum, swim bladder, poikilotherm

(L10) lungfish
(L10) lungfish!
bone skeleton, slimy skin with scales, movable jaw and teeth, 2.5 chambered heart, 5 gill slits and simple lungs, external fertilization and oviparous, brain with small cerebrum, poikilotherm

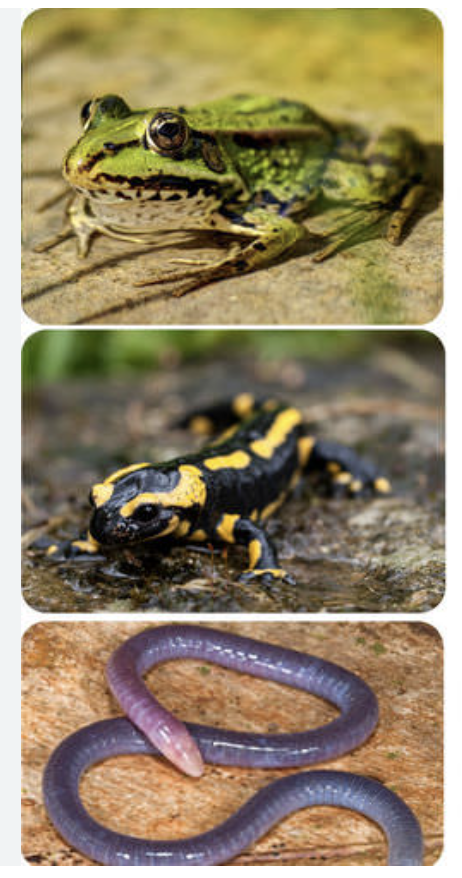
(L10) amphibians
(L10) frogs, toads, caecilians…
slimy and smooth skin (toads rough), bone skeleton, movable jaw with teeth (except toads no teeth), 3 chambered heart, simple lungs, external fertilization and oviparous, brain with moderate cerebrum, webbed hands, poikilotherm

(L10) mammals
(L10) moose, platypus, baleen whale
skin with hair, bone skeleton, movable jaw with specialized teeth (baleen whale no teeth), 4 chambered heart, lung pair, internal fertilization and viviparous, brain with large cerebrum, homeotherm

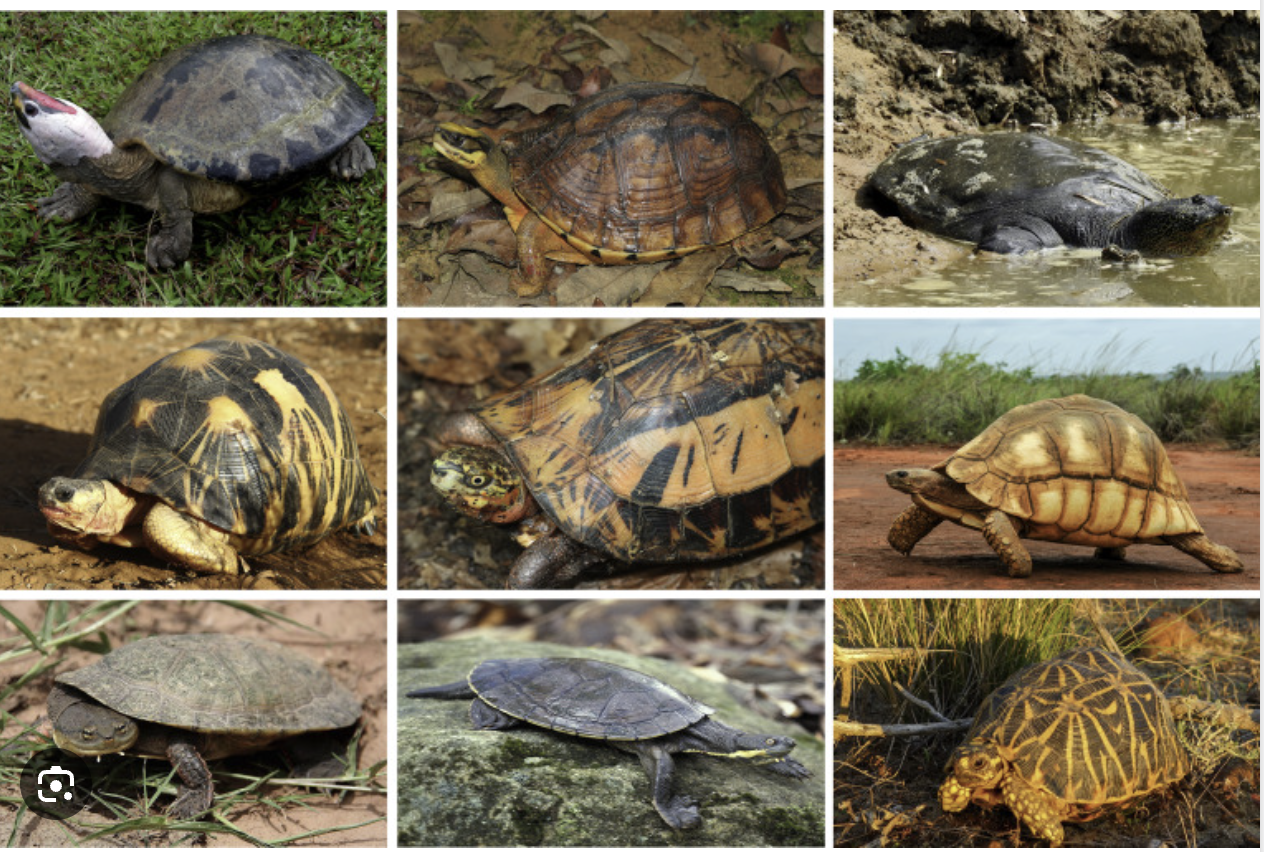
(L10) turtles and tortoises
(L10) turts <3
bony shell, dry skin with scales, bone skeleton, movable jaw with teeth and a horny beak, 3.5 chambered heart, pair of lungs, internal fertilization and oviparous, brain with moderate cerebrum, webbed hands, poikilotherm

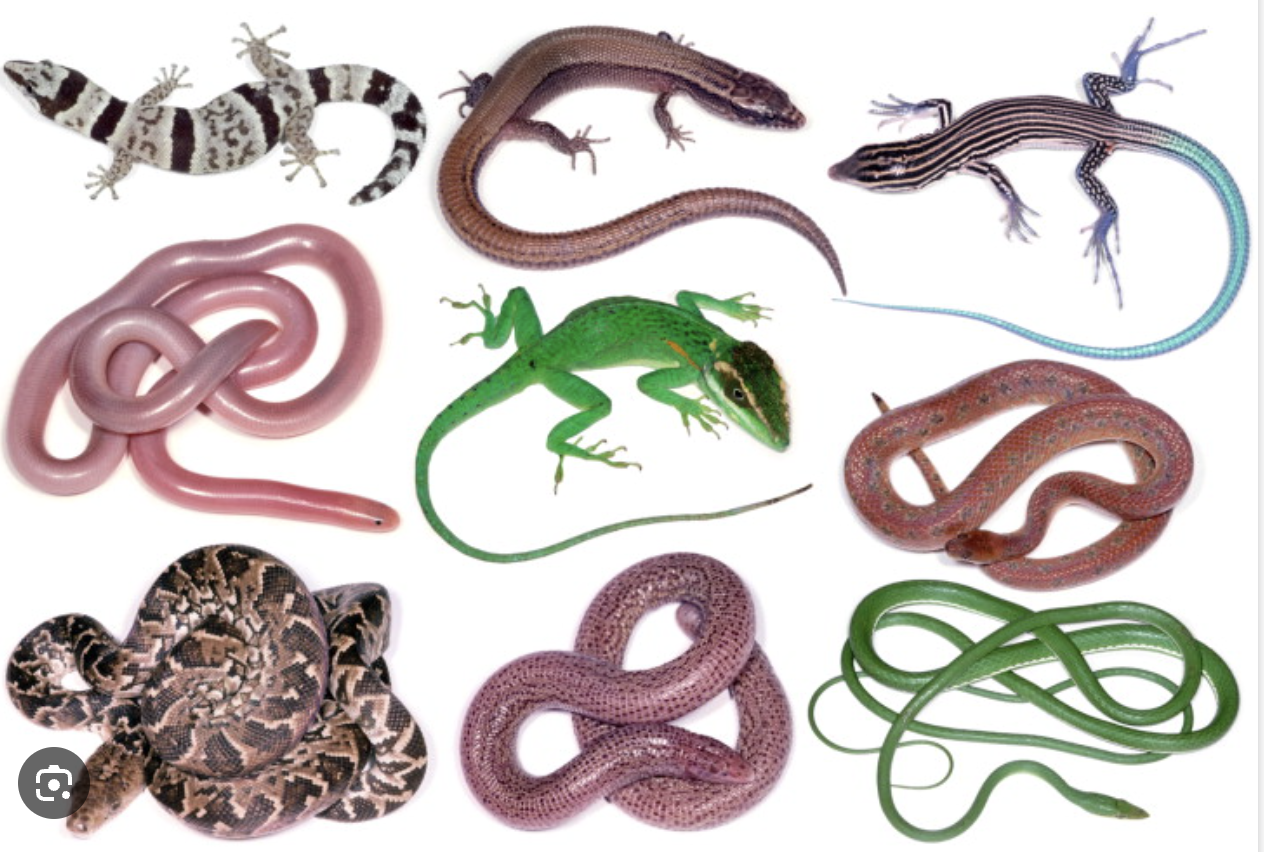
(L10) lizards and snakes
(L10) garter snake, flying lizard
dry skin with scales, bone skeleton, movable jaw with teeth, 3.5 chambered heart, lungs but snakes have 1 lung, internal fertilization and oviparous, brain with moderate cerebrum, poikilotherms

(L10) crocodilians
(L10) crocs, alligators
aquatic but breathes air, dry skin with scales, bone skeleton, movable jaw with teeth, 4 chambered heart, pair of lungs, internal fertilization and oviparous, brain with moderate cerebrum, partial webbing, poikilotherms
(L10) birds
(L10) chickens, ducks…
skin with feathers and scales, bone skeleton, movable jaw with no teeth and beak, 4 chambered heart, 2 lungs, internal fertilization and oviparous, brain with large cerebrum, wings, homeotherms
(L10) this class has 7 pairs of gill slits
(L10) lampreys
(L10) this class has 5 pairs of gill slits
(L10) lungfish, amphibians (yellow perch), cartilaginous fish (hammerhead shark)
(L10) this class has 2 chambered hearts
(L10) ray finned fish (yellow perch), cartilaginous fish (sting ray), lamprey
(L10) this class has 2.5 chambered hearts
(L10) lungfish
(L10) this class has a 3 chambered heart
(L10) amphibians (newt)
(L10) this class has 3.5 chambered hearts
(L10) lizards and snakes (garter snake), turtles and tortoises (sea turtle)
(L10) this class has a 4 chambered heart
(L10) mammals (beaver), birds (chicken), crocodilians (crocodile)