Micro Lab Exam 2
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
The types of Media are
Enriched, Selective, and Differential
Enriched
contains one or more additives to promote
Selective
contains one or more additives to suppress
Differential
contains an indicator to distinguish between different types of bacteria
What is the selective for Phenylethanol Agar Plate (PEA)
for Gram-positive organisms (phenylethanol)
What is the selective for Mannitol Salt Agar Plate (MSA)
for salt tolerance (Micrococcus and Staphylococcus) (salt tolerance (7.5% NaCl))
What is the Differential for Mannitol Salt Agar Plate (MSA)
for mannitol fermentation – (+) = yellow halo in agar (phenol red indicator)
What is the selective for MacConkey Agar Plate (MAC)
for Gram-negative organisms (crystal violet, bile)
What is the Differential for MacConkey Agar Plate (MAC)
for lactose fermentation – (+) = pink bacteria
(neutral red indicator)
What is the selective for Eosin Methylene Blue Agar Plate (EMB)
for Gram-negative organisms (methylene blue, EosinY)
What is the Differential for Eosin Methylene Blue Agar Plate (EMB)
for lactose fermentation – (+) = shiny green bacteria (methylene blue, EosinY)
What is the Enriched for Blood Agar Plate (BAP)
with 5% sheep RBC
What is the Differential for Blood Agar Plate (BAP)
based on hemolysis (destruction of RBCs)
Types of Hemolysis
β: ?
α: ?
γ: ?
β: complete
α: partial
γ: none
What degrees and how long should you incubate all plates
all plates at 37˚C for 24-48hrs
Phenylethanol Agar (PEA) Serratia marcescens has
no growth (gram negative)
Phenylethanol Agar (PEA) Staphylococcus
epidermidis has
Growth (gram positive)
Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) Escherichia
coli has
no growth (gram negative)
Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) Staphylococcus
aureus has
Growth (gram positive)
Yellow halo = mannitol fermenter
Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) Staphylococcus
epidermidis has
Growth (gram positive)
No yellow halo = not a mannitol fermenter
MacConkey Agar (MAC) Escherichia
coli has
Growth = gram positive
Pink with bile precipitate haze = lactose
fermentation
MacConkey Agar (MAC) Serratia marcescens has
Growth = gram positive
No pink or bile precipitate haze = not a lactose
fermenter
MacConkey Agar (MAC) Staphylococcus epidermidis has
No growth = gram negative
Eosin Methylene Blue Agar (EMB) has Escherichia coli
Growth = gram positive
Green metallic sheen = lactose fermentation
Eosin Methylene Blue Agar (EMB) has Serratia
marcescens
Growth = gram positive
No green metallic sheen = not a lactose fermenter
Eosin Methylene Blue Agar (EMB) has Staphylococcus epidermidis
No growth = gram negative
Blood Agar (BAP) Staphylococcus
aureus has
growth = gram positive
clear halo = β (complete) hemolysis
Blood Agar (BAP) Staphylococcus epidermidis has
growth = gram positive
Red agar/no change = γ (no) hemolysis
Blood Agar (BAP) Streptococcus
viridans has
growth = gram positive
Brownish green = α (partial)hemolysis
What do Biochemical tests do
helps us establish the bacteria’s identity
Phenol Red Broth (PR) tests detect?
The fermentation of sugars
what is the level of phenol Red Broth (PR) pH indicator that is yellow
below pH 6.8 (positive)
Durham tube is used to detect
the formation of gas products
Catalase is produced by what to break down what
Catalase is produced by aerobic and facultative bacteria to break down the hydrogen peroxide
Oxidase Test detects
Detects cytochrome c oxidase
During the Oxidase Procedure positive results will turn the indicator pad what color
dark purple
Citrate Test determine
if sodium citrate is used as a sole carbon source
the pH indicator Bromthymol Blue
Blue – pH 7.6 (positive)
Organisms that can remove the amine group from the amino acid phenylalanine do this by producing an enzyme called
phenylalanase
After incubation, what reagent is added to the agar slant
Ferric chloride
During the phenylalanine Deaminase Test what color forms and is it positive or negative?
Formation of a green color = positive
Starch Hydrolysis Test determines
if the microbe of interest produces the enzyme
amylase
if starch is broken down in a Starch Hydrolysis Test what happens
the iodine cannot combine with it, and no
purple/black color will be formed = positive for amylase production
Urea can be hydrolyzed using what enzyme
urease
Urea Hydrolysis Test pH level
pink – above pH7.4 (positive)
What does SIM stand for?
Hydrogen Sulfide, Indole, and Motility Test
(H2S)
Hydrogen Sulfide
SIM Medium
Positive = blackening of the media
Indole
by-product that is produced when the bacteria
hydrolyze tryptophan utilizing the enzyme tryptophanase
Presence of indole can be determined
by adding what reagent
Kovac’s after incubation
Positive = pink
Motility
Diffuse growth through the media (hazy) = positive for motility
Phenol red:
yellow – below pH6.8 (positive)
Phenol Red Broth Durham tube:
bubble = positive for gas
Catalase Test Bubbles
positive
Catalase Test Oxidase Test Dark Purple
positive
Citrate Test blue
pH7.6 (positive)
What do you have to add one dropper full of Ferric Chloride
to each tube
Phenylalanine Deaminase
Phenylalanine Deaminase Formation of a green color
positive
What type of plate do you have to ass enough Iodine Reagent to cover the plate
Starch Hydrolysis
Starch Hydrolysis Clear zone in agar around growth
positive
Urease Test
pink – above pH7.4 (positive)
What test do you have to add 5 drops of Kovac’s Reagent to
Indole SIM test
SIM Test
Indole: pink Kovac’s reagent =
positive
SIM test
Sulfur reduction: black =
positive
SIM test
Motility: diffuse (hazy) growth away from stab line =
positive
The Staphylococci
Gram positive
Grow in clusters
Staphylococcus aureus
30% of population is a S. aureus carrier – normal flora
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Normal flora of everyone’s skin
The Enterobacteriaceae
Gram-negative
ADD PICURE SLIDE 11 chapt 11 the Enterobacteriaceae grow as
single bacilli
Pathogenesis
major source of food poisoning and water contamination
Shigella
Cause of food poisoning and water contamination
Pathogenesis cont. Escherichia
Most common cause of water contamination
To ensure water is safe for consumption…
it is screened for E. coli, which is referred to in this instance as a coliform.
Unknown Project includes
two different organisms
MSA isolates
Staphylococcus organism
MAC isolates
Enterobacteriaceae organism
Members of the Enterobacteriaceae family,
such as coliforms (E. coli), are
gram-negative
Bottled spring water =
generally potable because it’s regulated
Water straight from a natural spring =
not guaranteed safe unless tested
Mannitol fermentation
MSA - Staphylococci
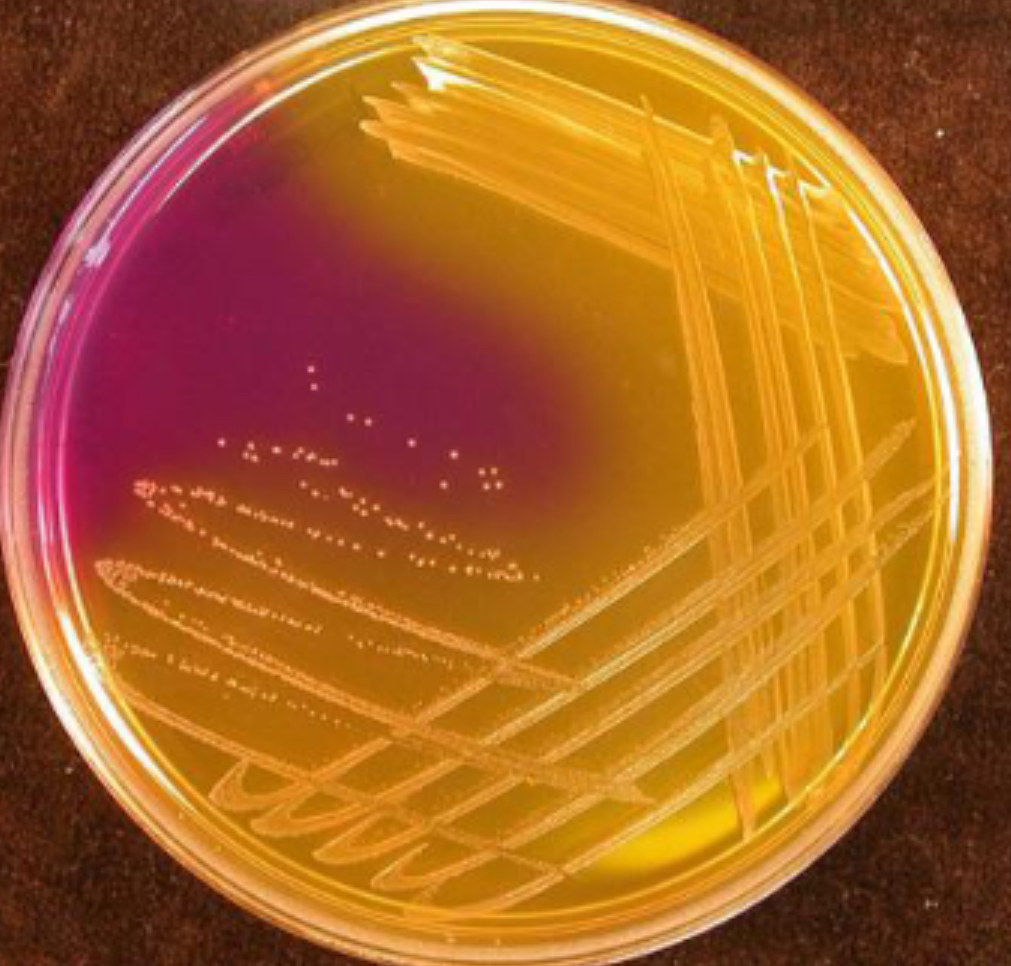
Lactose fermentation
MAC - Enterobacteriaceae
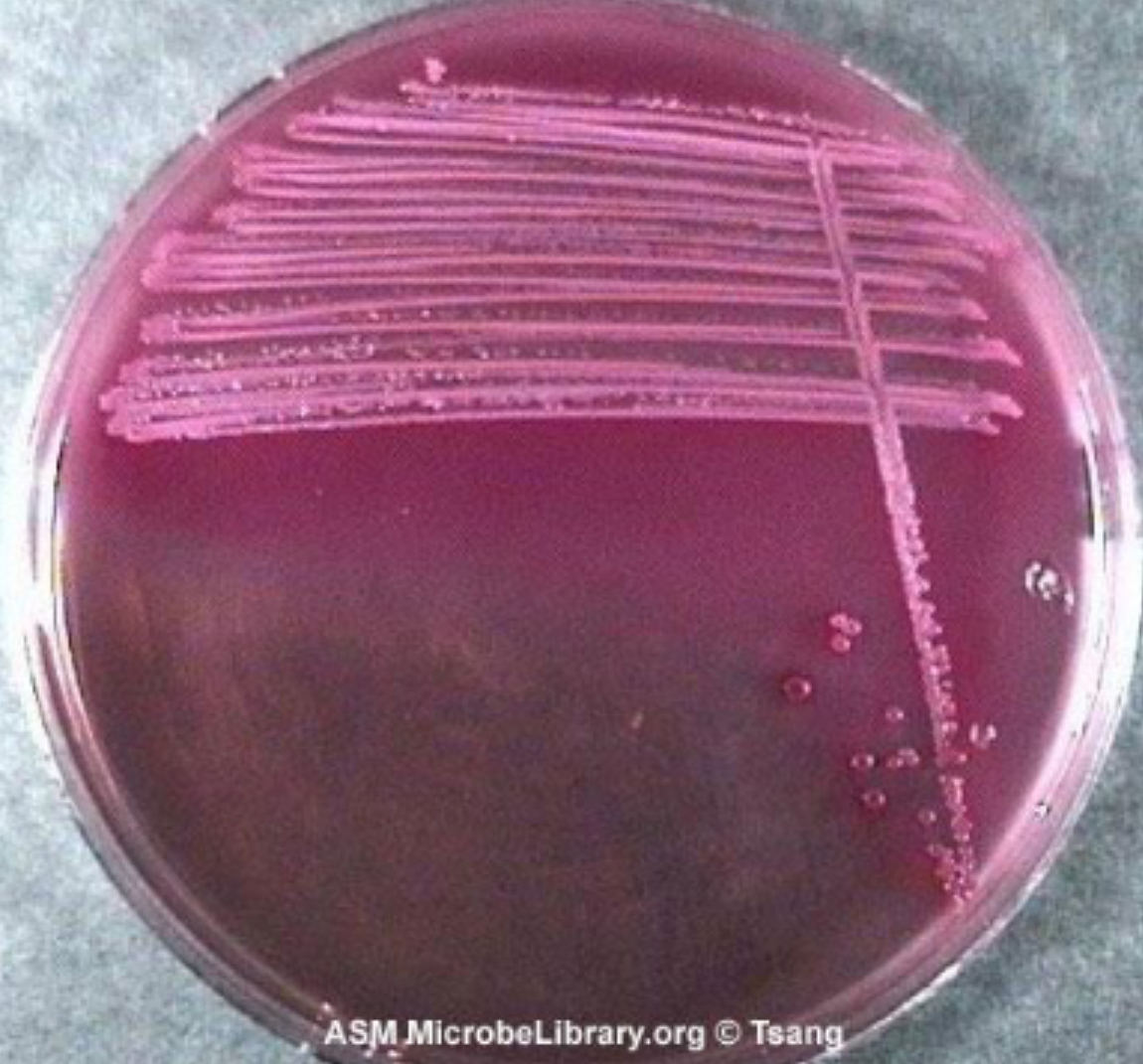

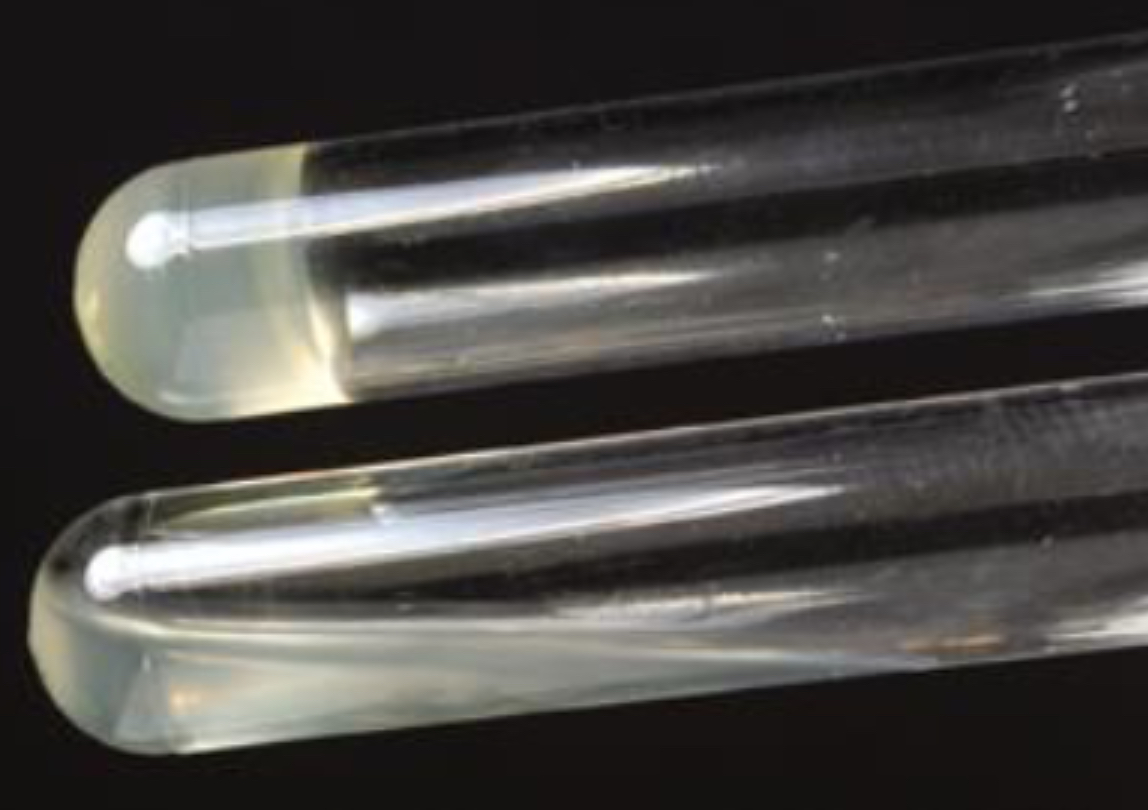
MSA – Staphylococci Tests
BAP/Novobiocin Susceptibility Test
what do you use in BAP/Novobiocin Susceptibility Test
1 Novobiocin antibiotic disk

MSA – Staphylococci Tests
Coagulase

MAC – Enterobacteriaceae Tests
Citrate Utilization
With Citrate Utilization what do you have to do
Cap tube loosely to ensure bacteria have enough oxygen
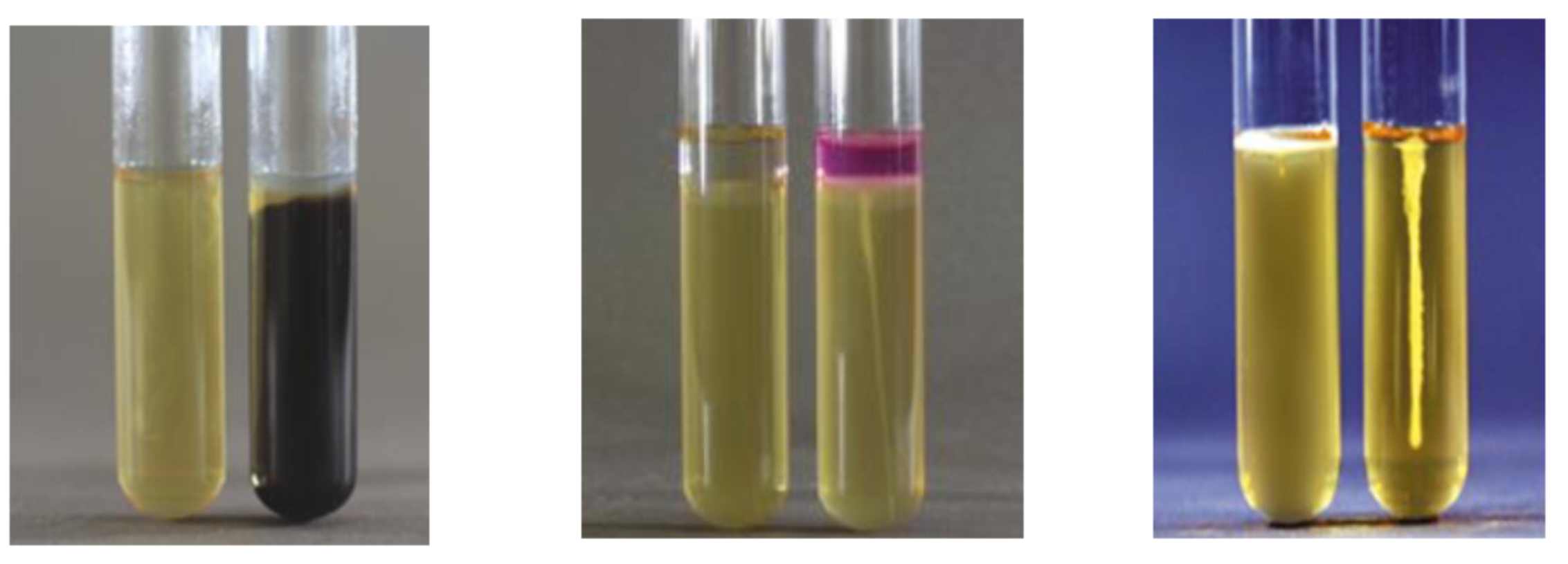

MAC – Enterobacteriaceae Tests
SIM Test
The Streptococci
Gram positive, chains of catalase negative cocci
Streptococci species are divided into
groups
Epidemiology
the study of the causes, occurrence, transmission, distribution, and prevention of disease in the population
Common modes of transmission:
Inhalation, Direct skin contact, Ingestion, etc
Index Case:
the first person that is infected with a disease
Prevalence Rate:
the total number of cases of a disease occurring at a specific time point in a defined population
Calculation of Prevalence Rate formula
(Total Number of Cases)/(Number of People in the population) = (make sure to convert to percent)
This is the initiation of the epidemic –
the index case will be infected” if they have the one candy that is covered in a powder that glows under ____ (fomite)
blacklight
How does disease spreads
through shaking hands (direct skin contact)
Expected Results Mannitol Fermentation yellow =
positive
Expected Results BAP Clearing of blood agar =
complete (β) hemolysis
Expected Results BAP Brownish green blood agar =
partial (α) hemolysis