Biology B2.3- cell specialisation
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
stem cells
unidentified cells that can turn into anything
all cells are switched on, meaning they can make every protein
how stem cells become specialised
turn certain cells off- therefore cant make all proteins
morphogens
single molecules that control cell differentiation
starts switching genes off which causes the cell to specialize
stem cell levels
totipotent
pluripotent
multipotent
unipotent
totipotent level
can differentiate into any type of cell
all stem cells
pluripotent level
can differentiate into many types of cell
multipotent level
can differentiate into a few closely related types of cell
bone marrow
unipotent level
can regenerate but can only differentiate into their associate cell types
liver stem cells can only make liver cells
meristem
in plants
regions of undifferentiated cells
plants only grow at the meristems- can be atypical or typical
found near root and stem tips
emergent properties
the whole is greater than the sum of its parts
each part works better together than by themselves and become more efficient
skeletal muscle
also called striated muscle (has stripes)
how to increase surface area
invagination- folding inwards
microvilli- hairs in the intestine
flatten the cells
other name for red blood cell
erythrocytes
do small or large cells have a big or small surface area:volume ratio
small cells - large ratio
large cells - small ratio
advantages of a small cell
shorter path for diffusion - quicker & more efficient
concentration gradient are easier to measure
disadvantages of small cells
animals loose heat quickly- need to eat constantly
how kidneys increase SA:V ratio
a way of increasing surface area:volume ratio is flattening cells
cells are packed closely together to use space well
tiny microvilli pointing out the cell
lots of mitochondria in the cell
flattens the nephron in the kidneys
proximal convoluted tubule
responsible for absorbing essential substances
secreting waste (ions) from filtered blood
type 2 pneumocytes
capable of mitosis for replacement of both types of alveoli cells
makes it good for diffusion
if cells are damaged they are uncappable of mitosis for replacement
protect and repair alveoli in lungs
box shaped cells
cover about 5% of the surface area
many of them
can divide and replace type 1 and 2 cells after injury
type 1 pheumocytes
flat and thin shape
cover 95% of the alveoli surface
allows gas exchange between alveoli and capillaries
tightly joined together so no fluids can enter
cant divide
3 muscle fibres
cardiac
striated skeletal
smooth
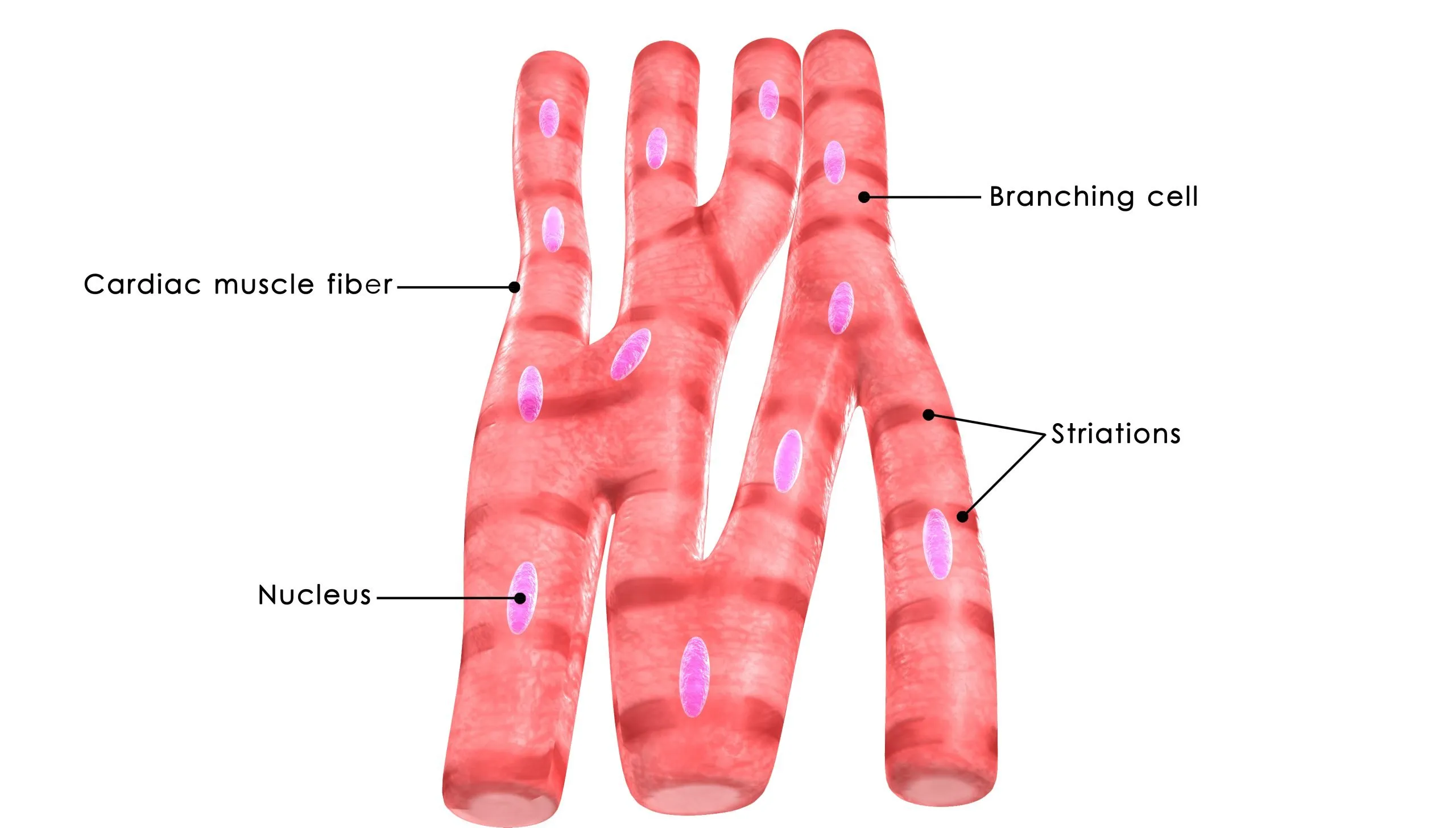
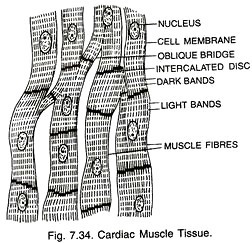
cardiac muscle fibre
in the heart
unique function
contract to pump blood around the body
has branched cells
short due to the branching cells
composed of branched, straited cells
skeletal striated muscle fibre
long cylindrical shape
multiple nuclei
visible bards capable of shortening - produces involuntary movement
generates force and contract to control movement
contract to move body parts
fast contractions
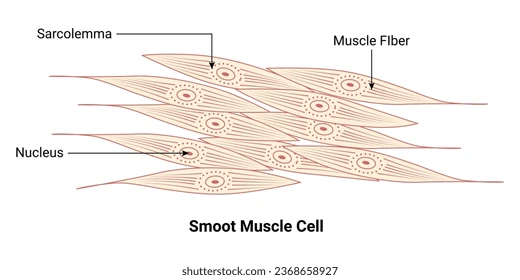
smooth muscle fibre
involuntary
in the walls / organs and blood vessels
moves substances through the organs
spindle shape
non striated cells → they produce voluntary movement