Medicinal Chemistry of Pain Agents
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Current agents used for treating pain
• Opioids
• Acetaminophen
• Anti-inflammatories
• Agents used for neuropathic pain
• Agents used to prevent and/or treat headache & migraine
• Topical agents
• Topical analgesics & anesthetics
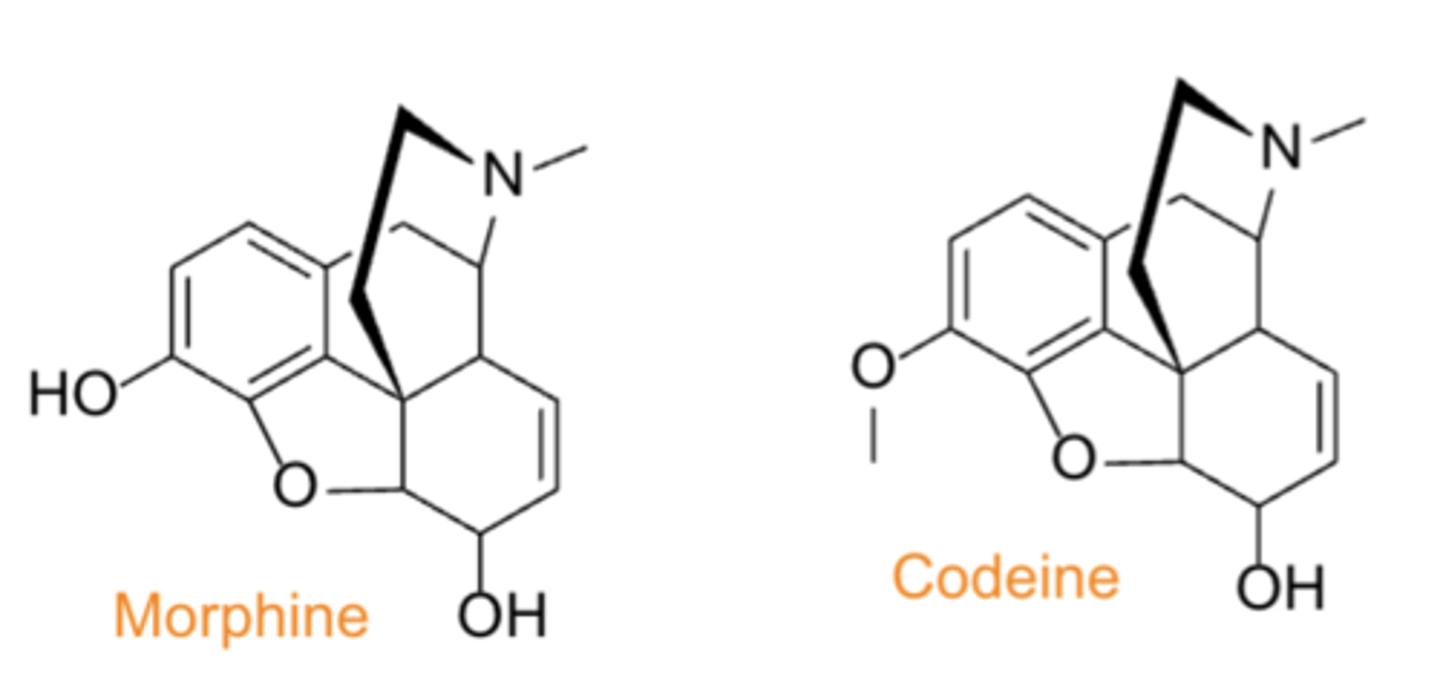
Opium Alkaloids
• Source: opium poppy (Papaver somniferum)
• PC/MOA: agonism at mu opioid receptors in CNS produces analgesia
• Selected compounds: Morphine (MS Contin), Codeine (Tylenol #3®)
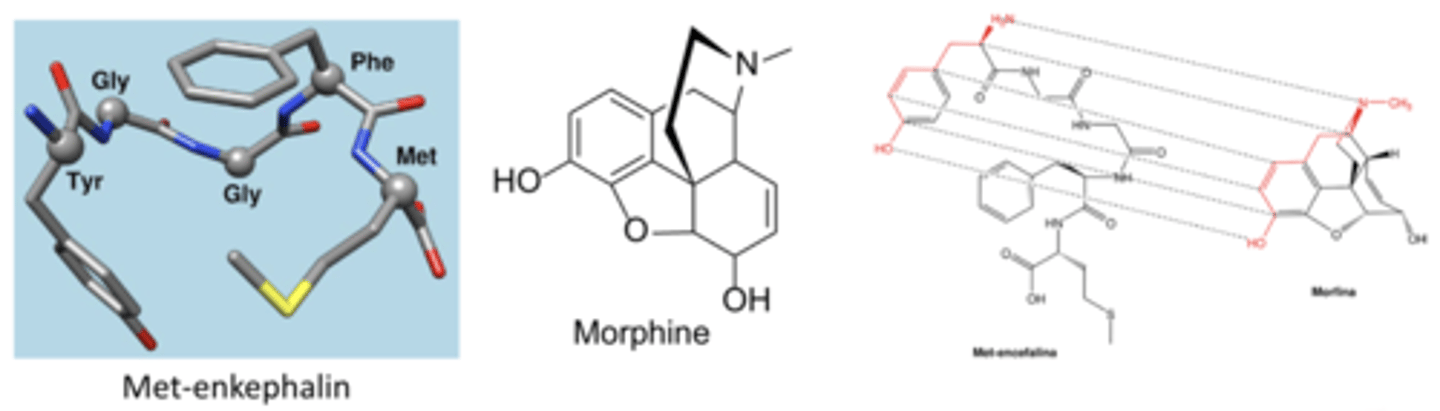
How do opioids act?
Mimic endogenous enkephalins and endorphins
What receptor subtypes do opioids bind to?
- μ
- κ
- δ
What are the risks of opioids?
- tolerance
- dependence
- abuse
- addiction
- overdose
Numbering scheme of opioids
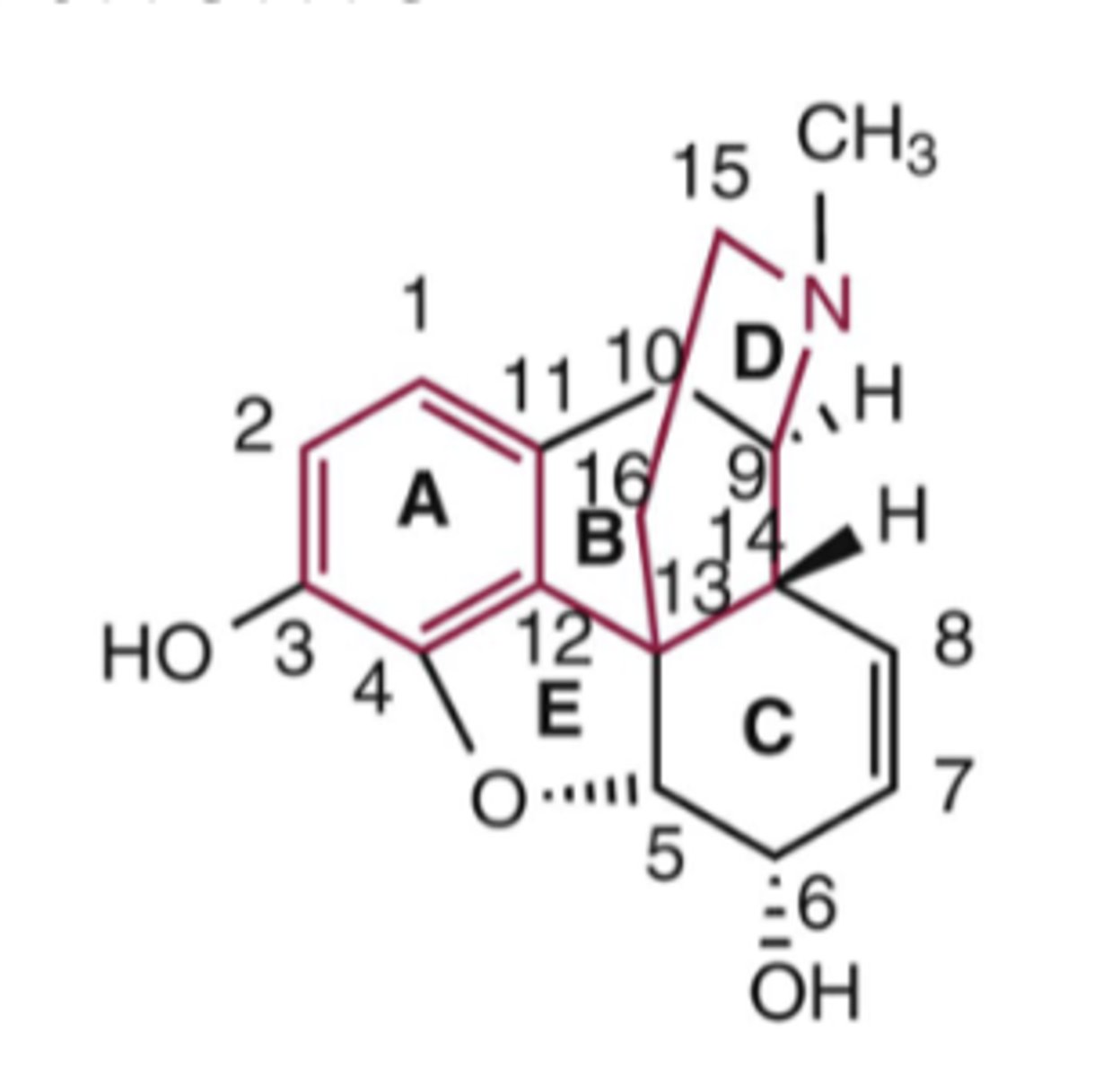
The 2 structural classes of compounds in opioids
- phenanthrenes
- flexible
SAR or opioid agonists: What is the structure of the compound is required for opioid receptor binding*******
Basic (3°) nitrogen required for opioid receptor binding
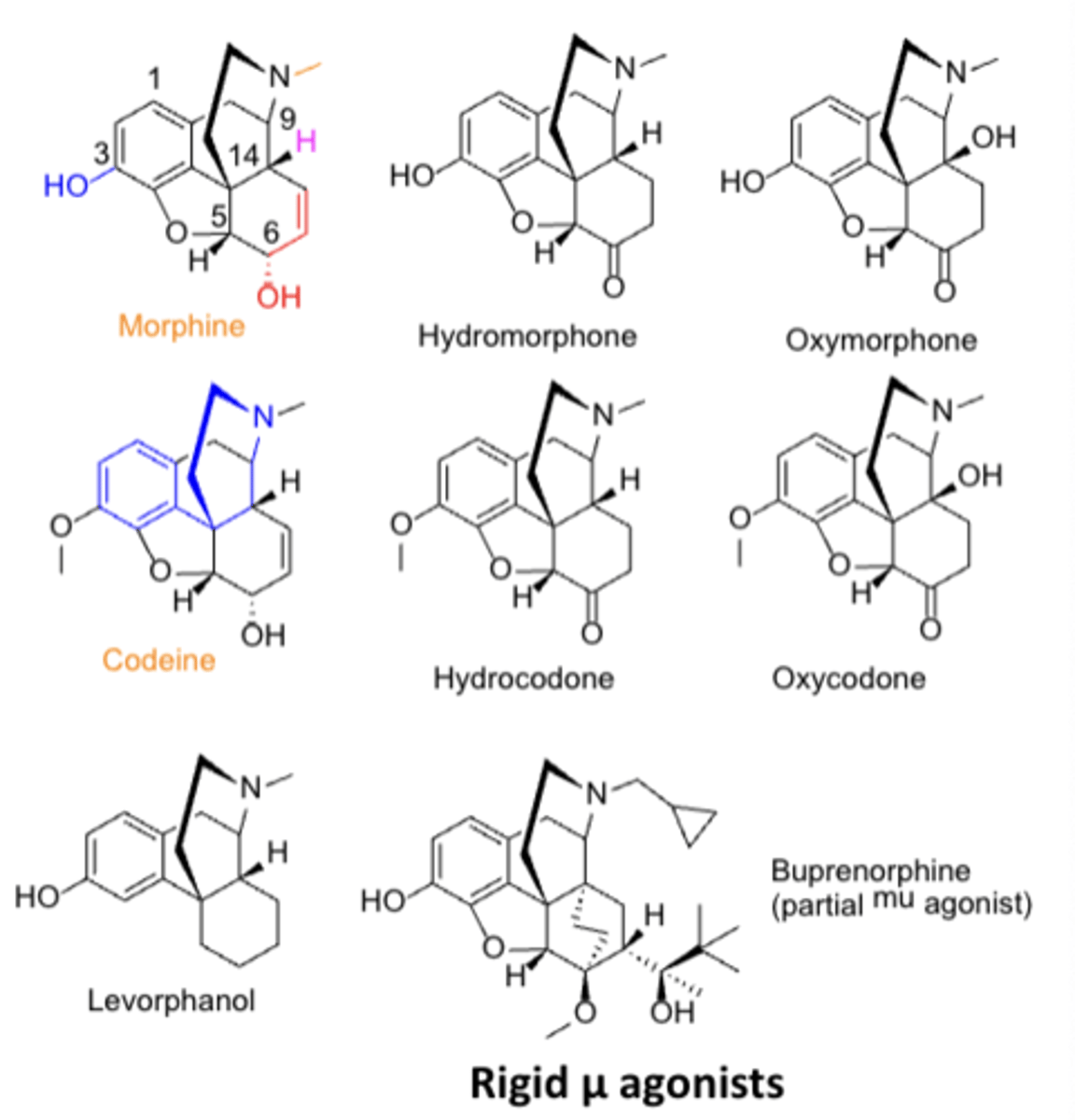
SAR or opioid agonists: Increasing __________ on the ____ atom flips activity from µ __________ to µ _______________*******
Increasing steric bulk on the N atom flips activity from µ agonist to µ antagonist
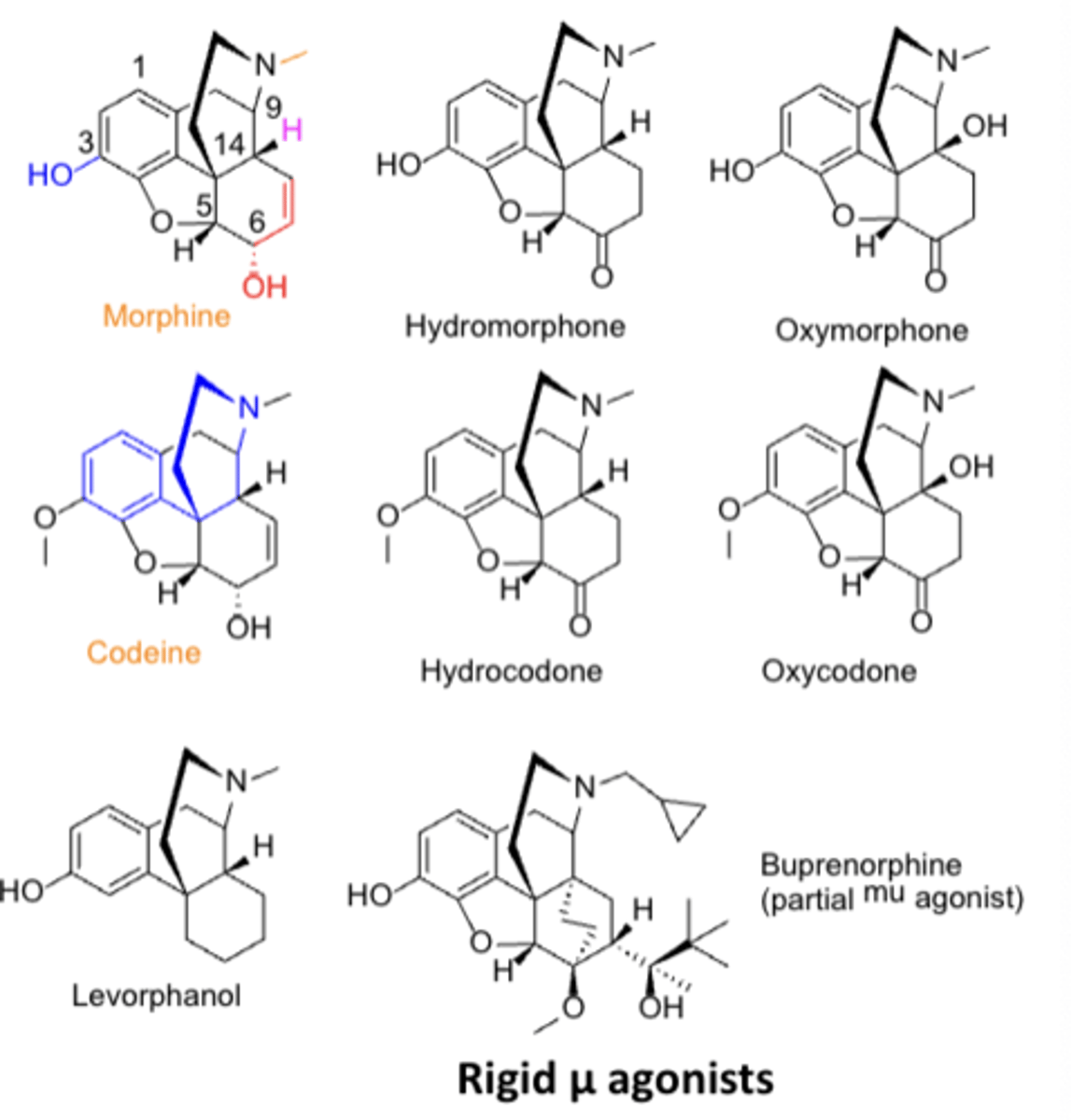
SAR or opioid agonists: All phenanthrene-based agents have a __________ or ___________ at C3*******
All phenanthrene-based agents have a phenolic hydroxyl or methoxy ether at C3
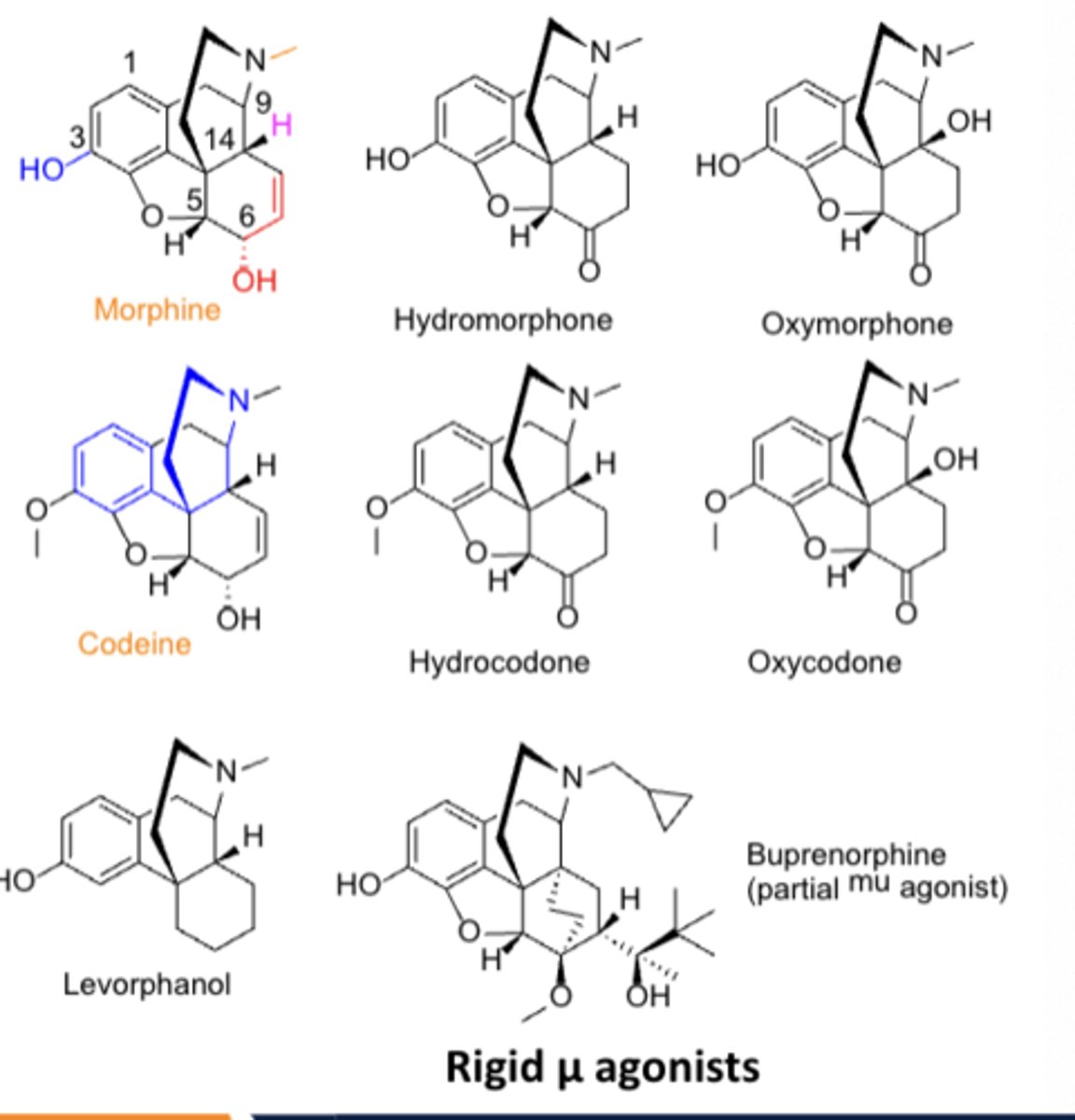
SAR or opioid agonists: Converting from a __________ to a ___________ at C6 increases potency*******
Converting from a hydroxyl to a ketone at C6 increases potency
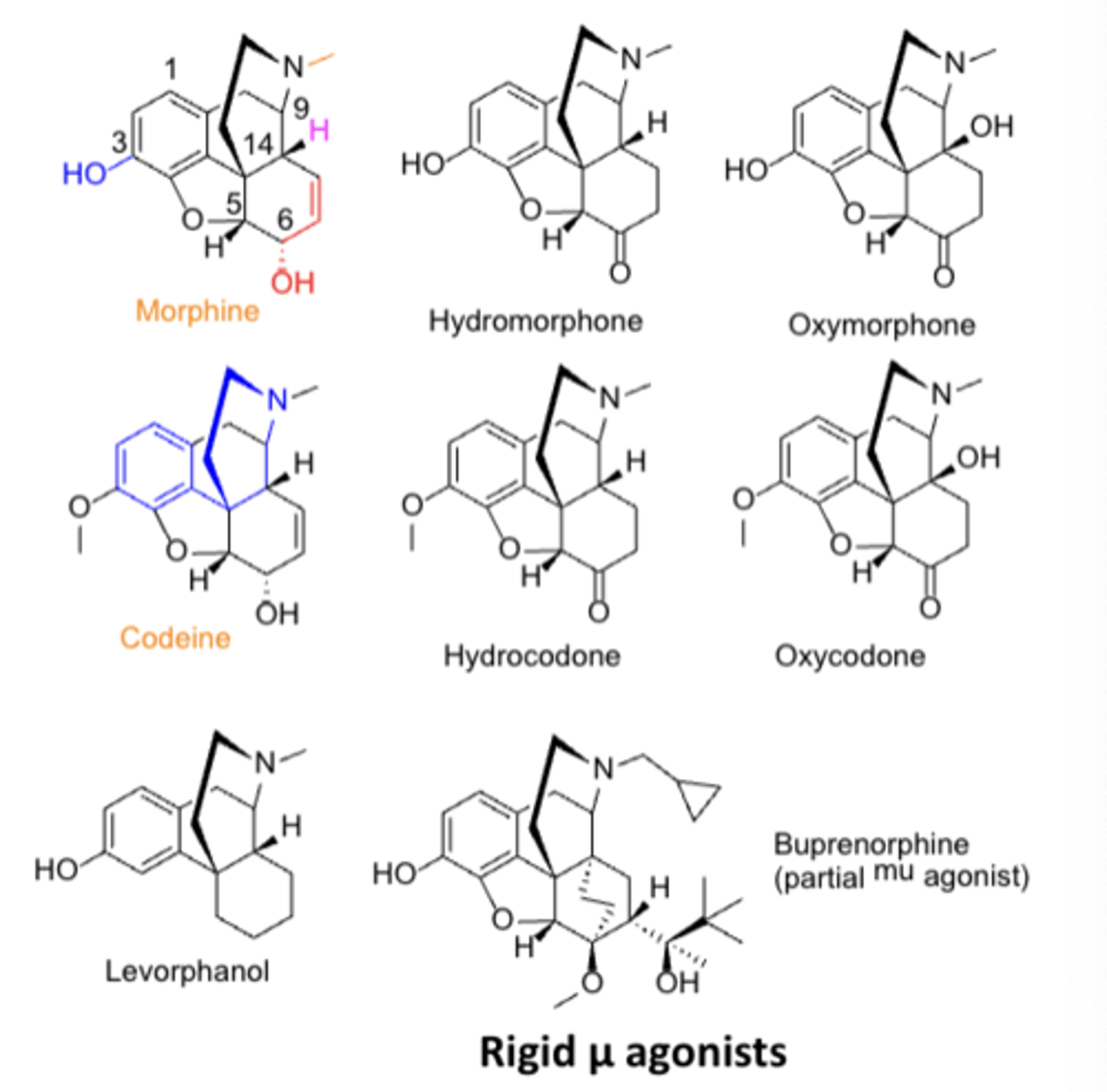
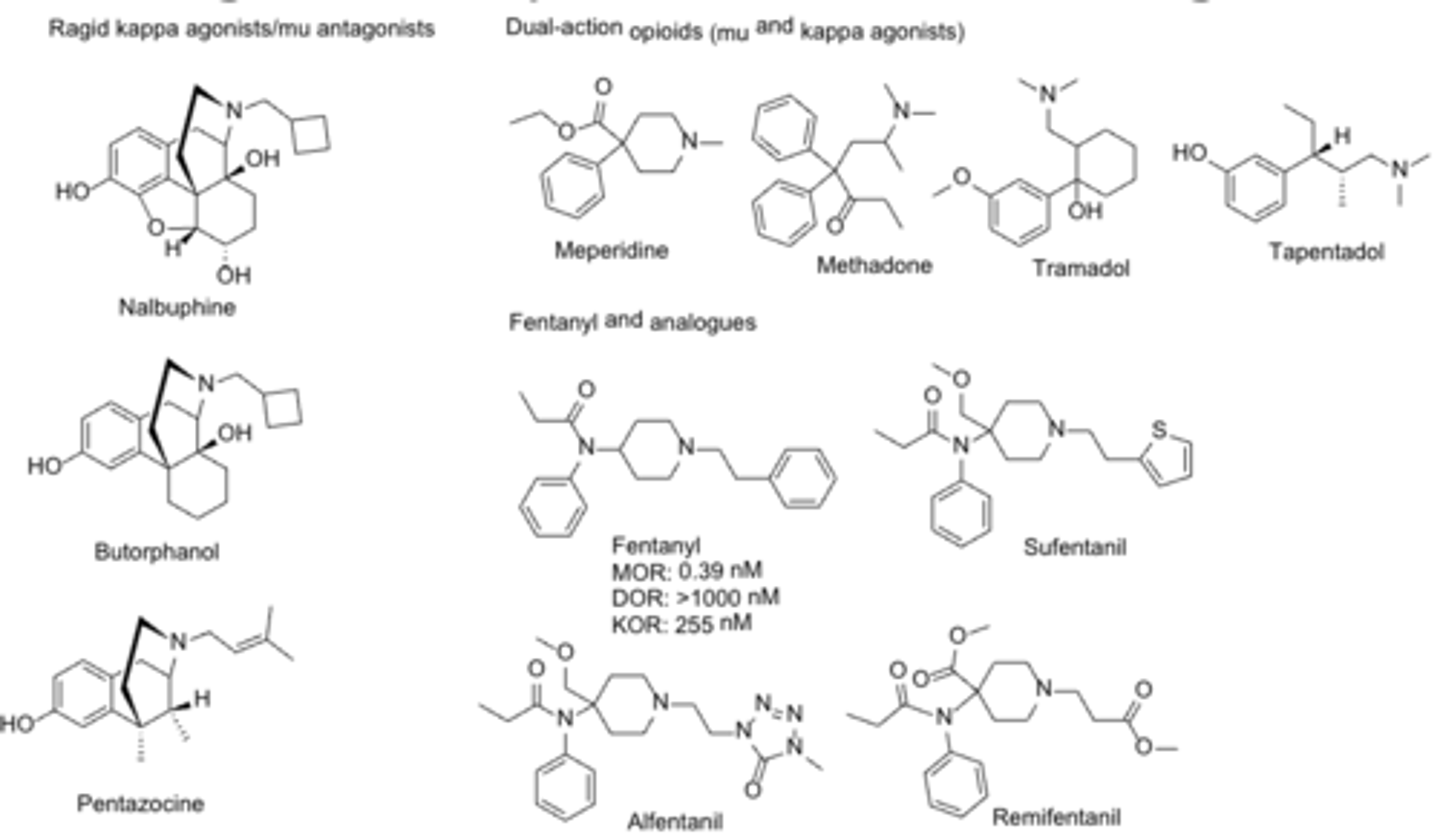
Opioid: conversion from one group to others by eliminating groups
1. nalbuphine-we dont need furan
2. butorphanol- dont need ring
3. meperidine- dont need other ring
Distribution of opioids
Well-distributed throughout the body, including breast milk
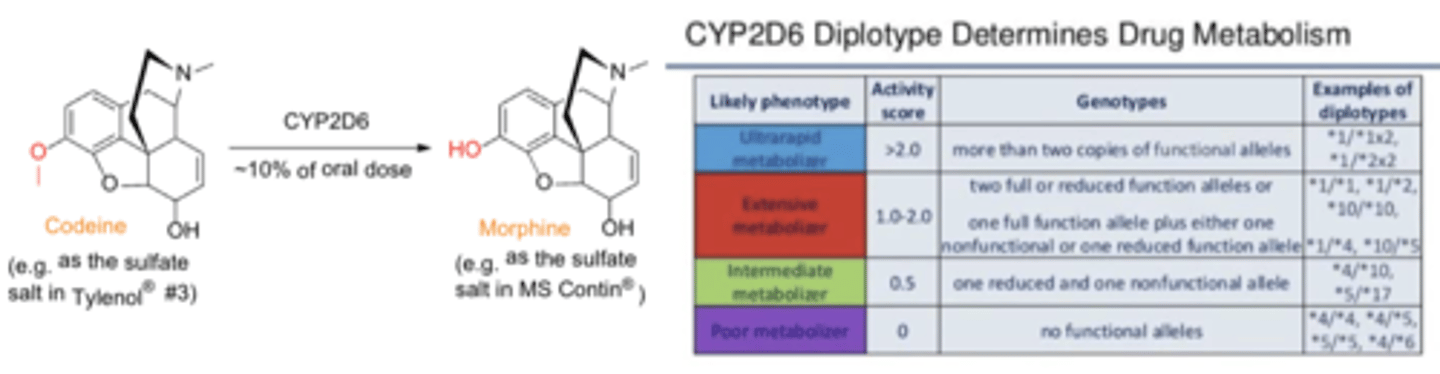
Role of pharmacogenetics in the metabolism of opioids*******
CYP2D6
Toxicity issues associated with opioids*******
• Hypersensitivity
• Opioid-induced constipation (OIC)
• Sedation
• Physical & psychological dependence (opioids) & abuse potential (opioids, dextromethorphan)
Morphine (MS Contin)
TC:
PC/MOA:
CC:
TC: analgesic agent
PC/MOA: mu opioid receptor agonist
CC: phenanthrene
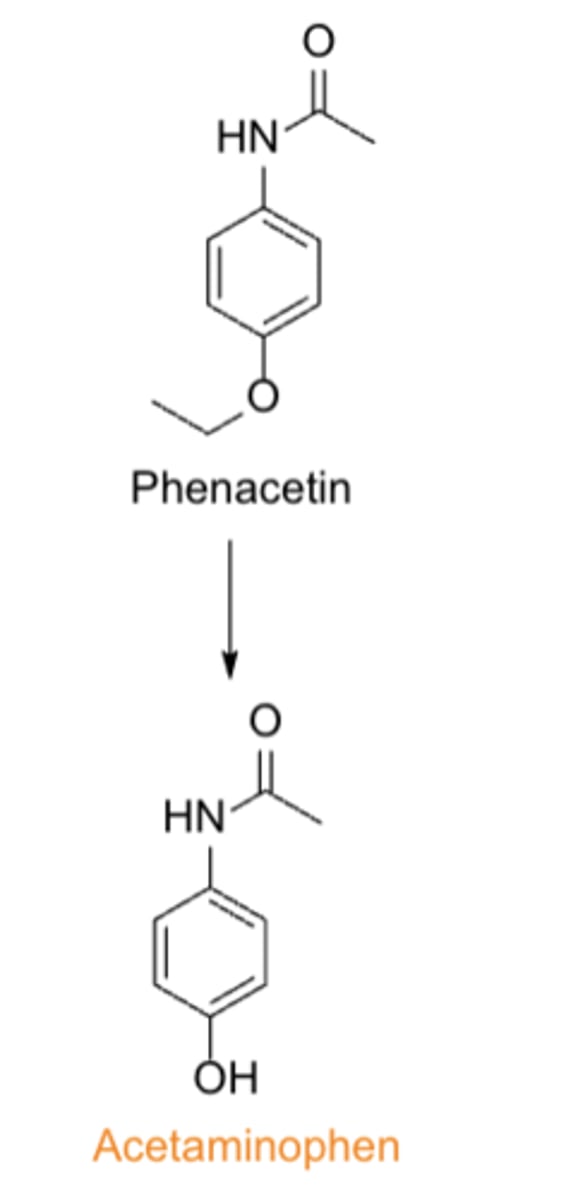
Acetaminophen was first marketed as...
- phenacetin in 1955
- withdrawn by FDA in 1983 due to its carcinogenic and kidney-damaging properties
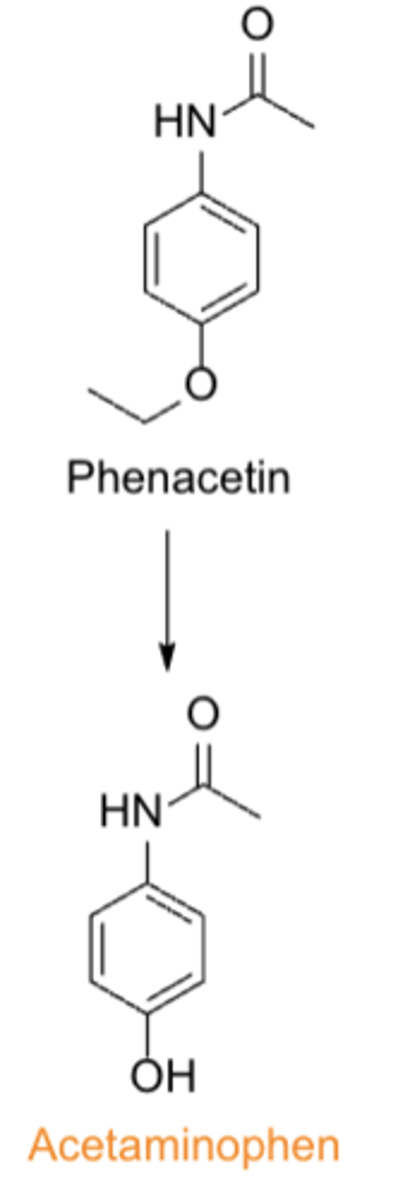
SAR of acetaminophen: Aminophenols, including acetaminophen, are less toxic than the corresponding ___________________ derivatives
aniline (non-OH) derivatives
MOA of acetaminophen
- not fully understood
- may involve activity at TRPV1 receptors or inhibition of the reuptake of endogenous cannabinoids in the CNS
Indications of acetaminophen
Relief of fever and/or pain, particularly in individuals who are sensitive to salicylates
T/F: Antipyretic effects of acetaminophen require CNS/BBB penetration
TRUE
ADMET of acetaminophen
A: oral BA is 88 ± 15%
D: well-distributed throughout body, <20% plasma protein bound
E: via metabolites in urine
T: contraindications: hepatic disease, DDI: alcohol, warfarin
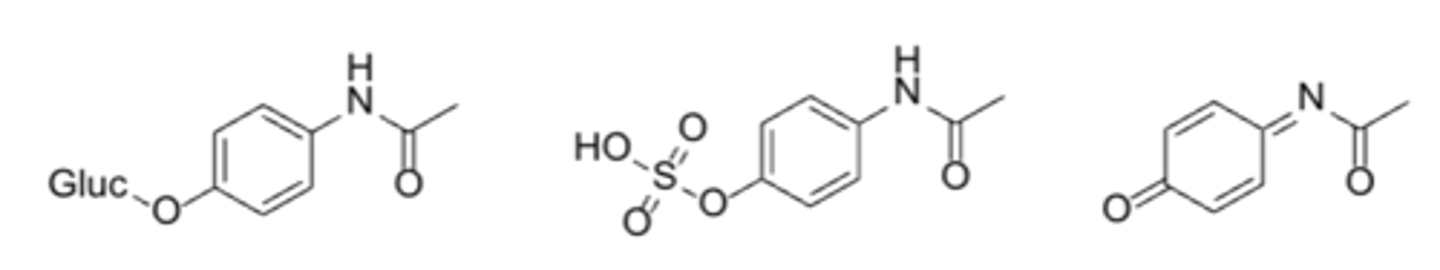
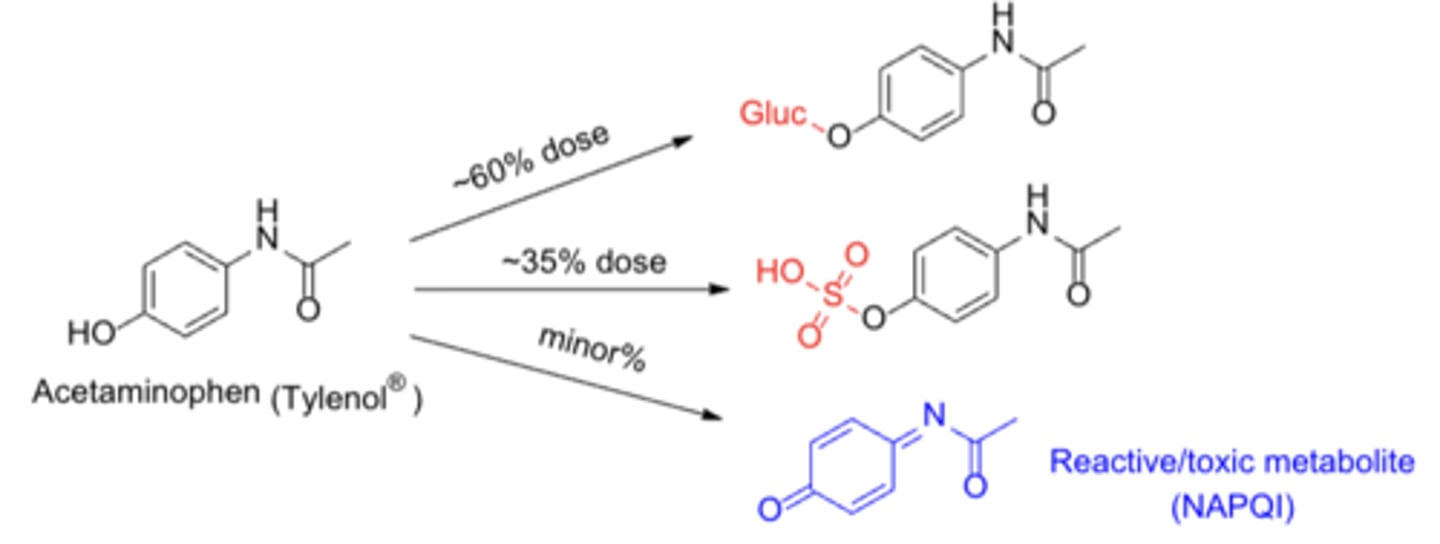
Metabolism of acetaminophen*****
- Major pathways: O-Glucuronidation/sulfation
- Minor toxic pathway: CYP1A2, CYP2E1, CYP3A4-mediated catalysis
- N-Acetyl-para-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI): the reactive benzoquinonemetabolite responsible for acetaminophen's hepatotoxicity
Acetaminophen
- TC:
- PC/MOA:
- CC:
- TC: analgesic & antipyretic
- PC/MOA: unclear, may involve actions at TRPV1 vanilloid & cannabinoid receptors
- CC: substituted phenol
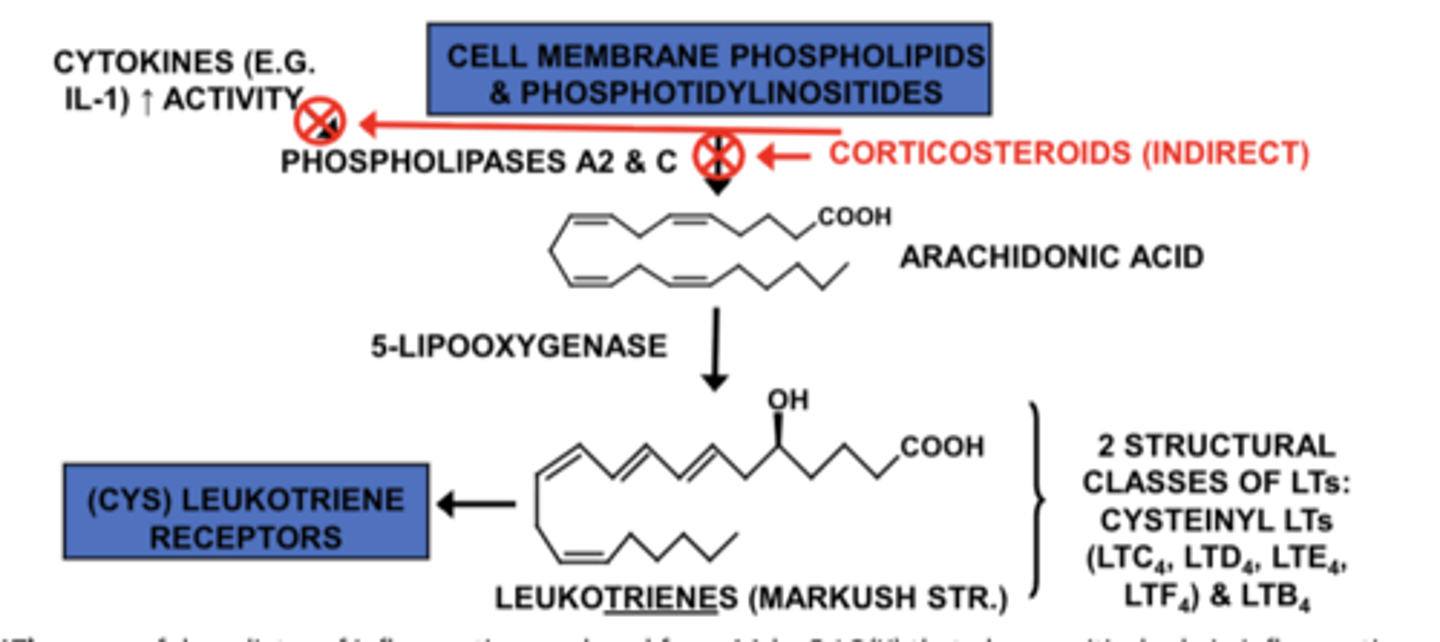
What path of the arachidonic acid cascade do corticosteroids indirectly affect?
Corticosteroids indirectly inhibit phospholipases A2 & C, so arachidonic acid is not released, blocking both COX and LOX pathways. This is why they are anti-inflammatory
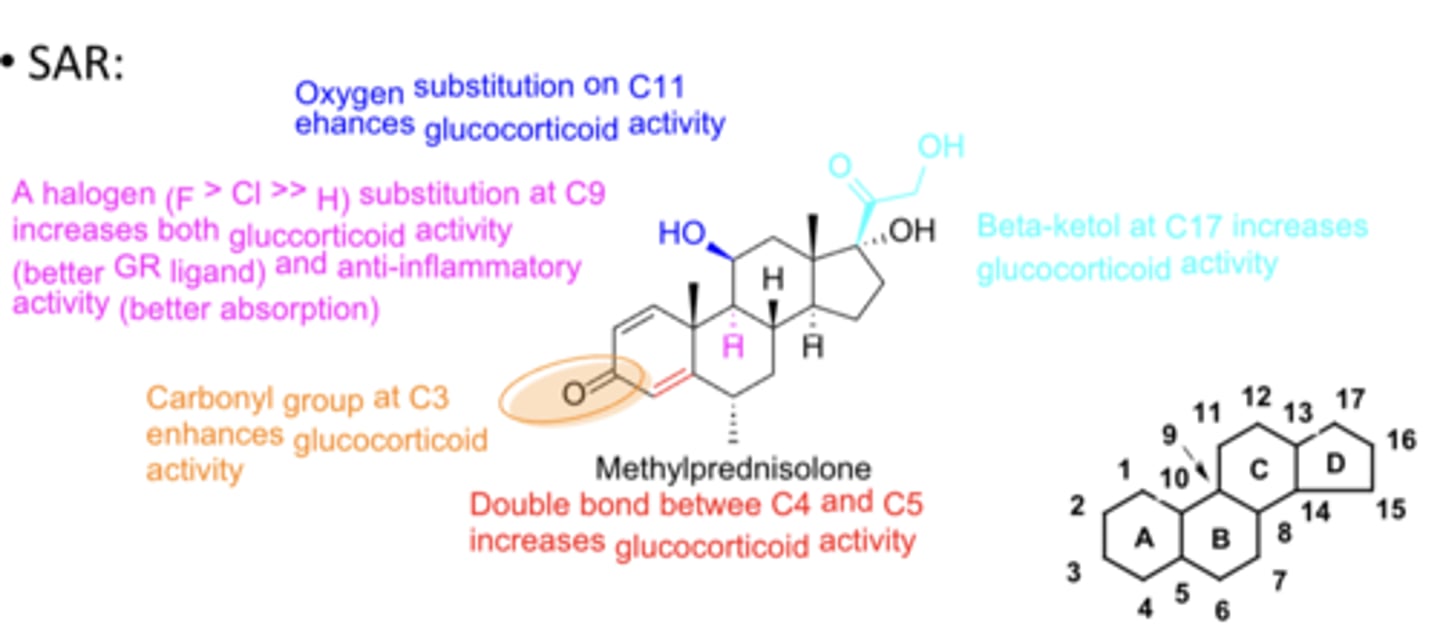
Corticosteroid special structures on carbons*******
- Carbonyl group at C3 enhances glucocorticoid activity
- Double bond between C4 and C5 increases glucocorticoid activity
- Halogen substitution (F>Cl>>H) at C9 increases both glucocorticoid activity (better GR ligand) and anti-inflammatory activity (better absorption)
- Oxygen substitution on C11 enhances glucocorticoid activity
- Beta-ketol at C17 increases GC activity & increases topical/inhaled absorption
Glucocorticoid steroids
- TC:
- PC/MOA:
- CC:
- TC: anti-inflammatories
- PC/MOA: GR agonists
- CC: steroids
Relatively non-selective NSAID chemical classes (4)
• Salicylates
• Fenamates (fenamic acids)
• Acetic acids
• Propionic acid
NSAIDs more selective for COX2...
- Oxicams (enolic acids)
COX2 selective NSAIDs
- coxibs
- pyrazolones
What are the risks of NSAIDs*******
- may cause an increased risk of serious CV thrombotic events, MI, stroke
- risk may increase with duration of use
- pts with CV disease or risk factors for CV disease may be at greater risk
What does the FDA require the drug label for all NSAIDs to describe?*******
- risk of kidney problems in unborn babies that result in low amniotic fluid
- recommended to avoid NSAIDs in pregnant women at 20 weeks or later in pregnancy
SAR trends for COX1/nonselective inhibition
- acidic group (typically COOH) required for activity
- aromatic/heteroaromatic ring next to acidic group
- A separate, additional lipophilic group increases affinity for COX enzymes
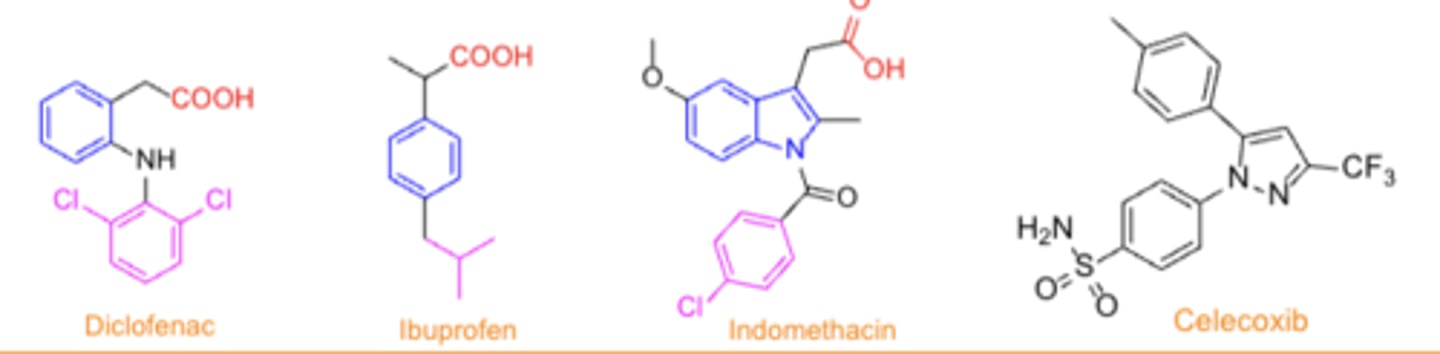
Most selective COX2 inhibitors (Coxibs) follow a different...
("3-ring") pattern
What agents are more COX1 selective?
- naproxen
- ibuprofen
- indomethacin
agents that are more COX2 selective
- acetaminophen
- meloxicam
- celecoxib
- diclofenac
NSAIDs: Salicylates
- MOA: non-selective inhibition of COX enzymes (main difference is the level of selectivity)
- Many are OTC
- oral, topical
cautions: GI, renal, blood side-effects (Similar side-effects for all classes of NSAIDs due to MOA)
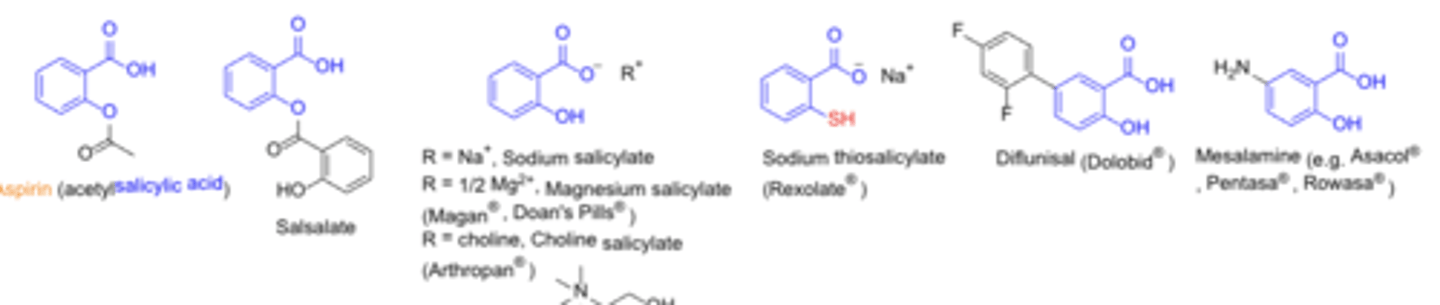
Acetylated salicylates (non-selective)*******
covalent, irreversible inhibition of COX enzymes (other classes are NOT covalent and irreversible)
Non-acetylated salicylates*******
noncovalent, reversible COX inhibition
Side-effects and therapeutic effects are associated with the presence of....
carboxylic acid group
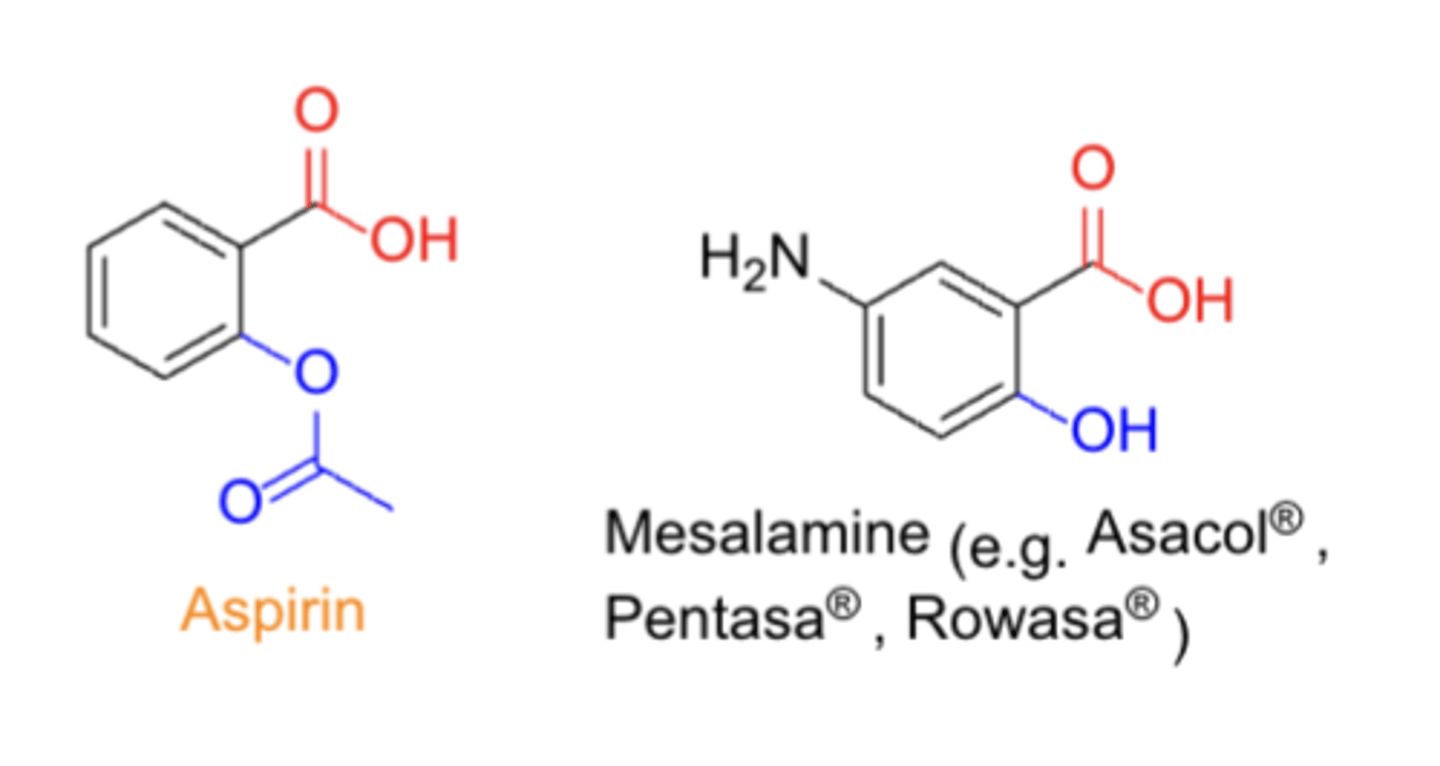
What is required for therapeutic activity
- ortho-hydroxyl
- ortho-ester group
Aspirin:
TC:
PC/MOA:
CC:
- TC: analgesics & anti-inflammatory
- PC/MOA: COX inhibitor (non-selective)
- CC: salicylate (salt or ester of o-hydroxybenzoic acid)
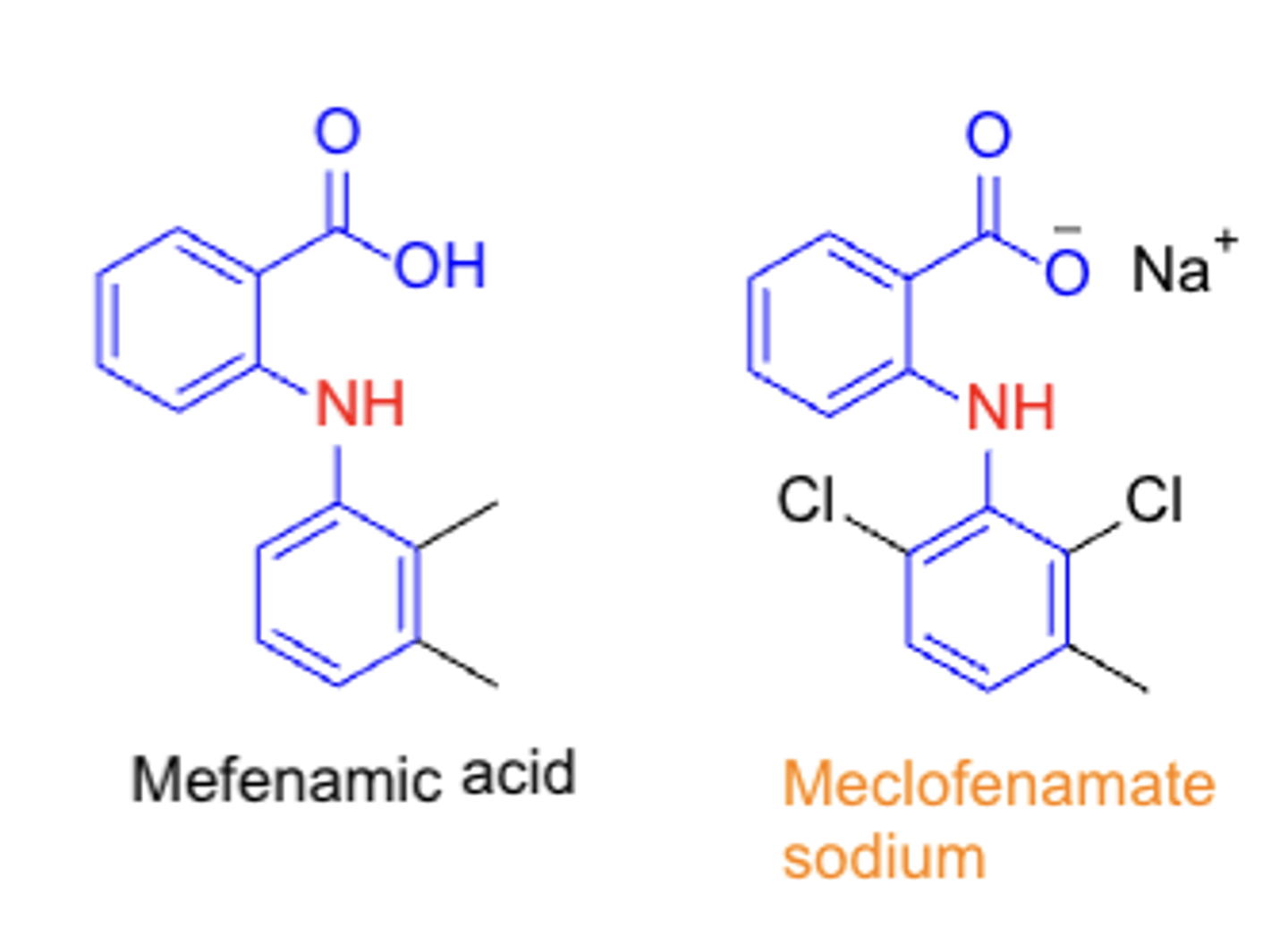
Fenamates/fenamic acids (N-arylanthanilic acids)
TC:
PC/MOA:
CC:
- TC: analgesic & anti-inflammatory
- PC/MOA: COX inhibitor (non-selective)
- CC: fenamic acid (N-arylanthranilic acids)
NSAIDs: Acetic acid agents*****
- diclofenac
- indomethacin
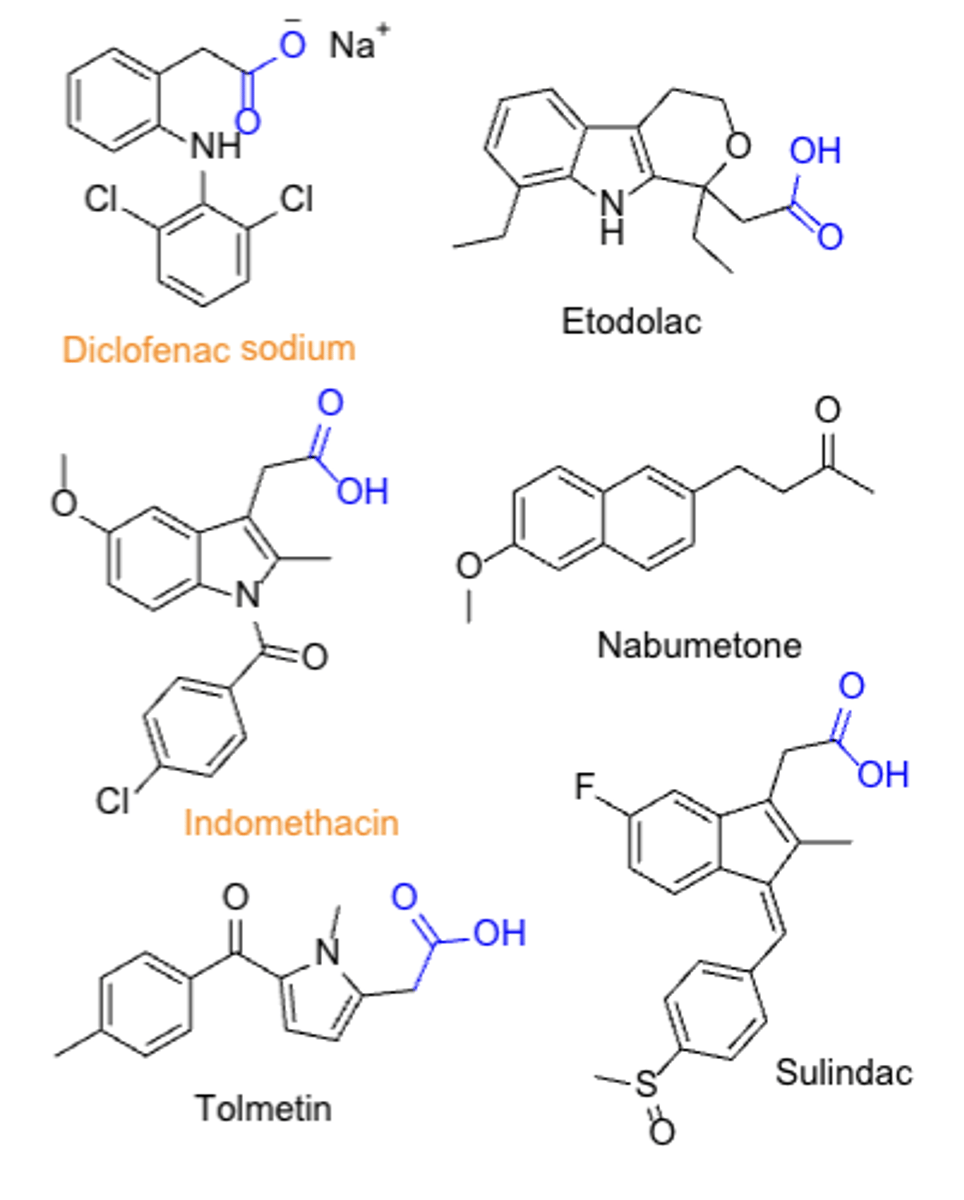
Metabolic activation of the acetic acid prodrugs
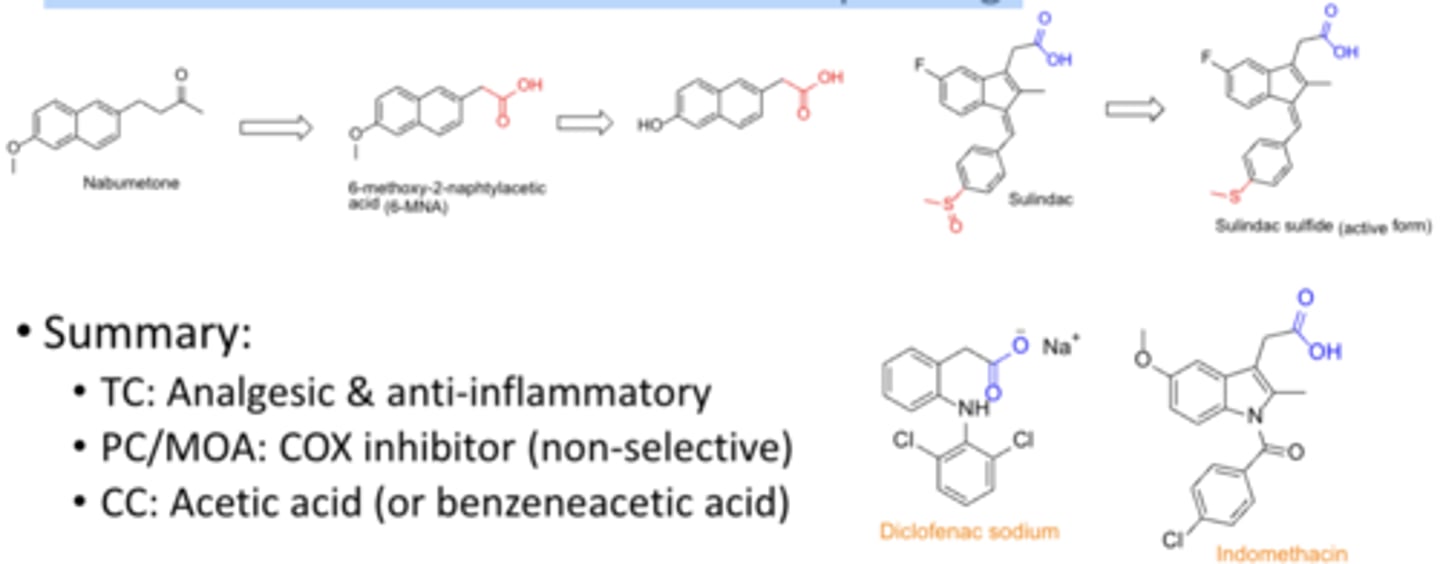
NSAID: Acetic acid
TC:
PC/MOA:
CC:
TC: analgesic & anti-inflammatory
PC/MOA: COX inhibitor (non-selective)
CC: acetic acid (or benzeneacetic acid)
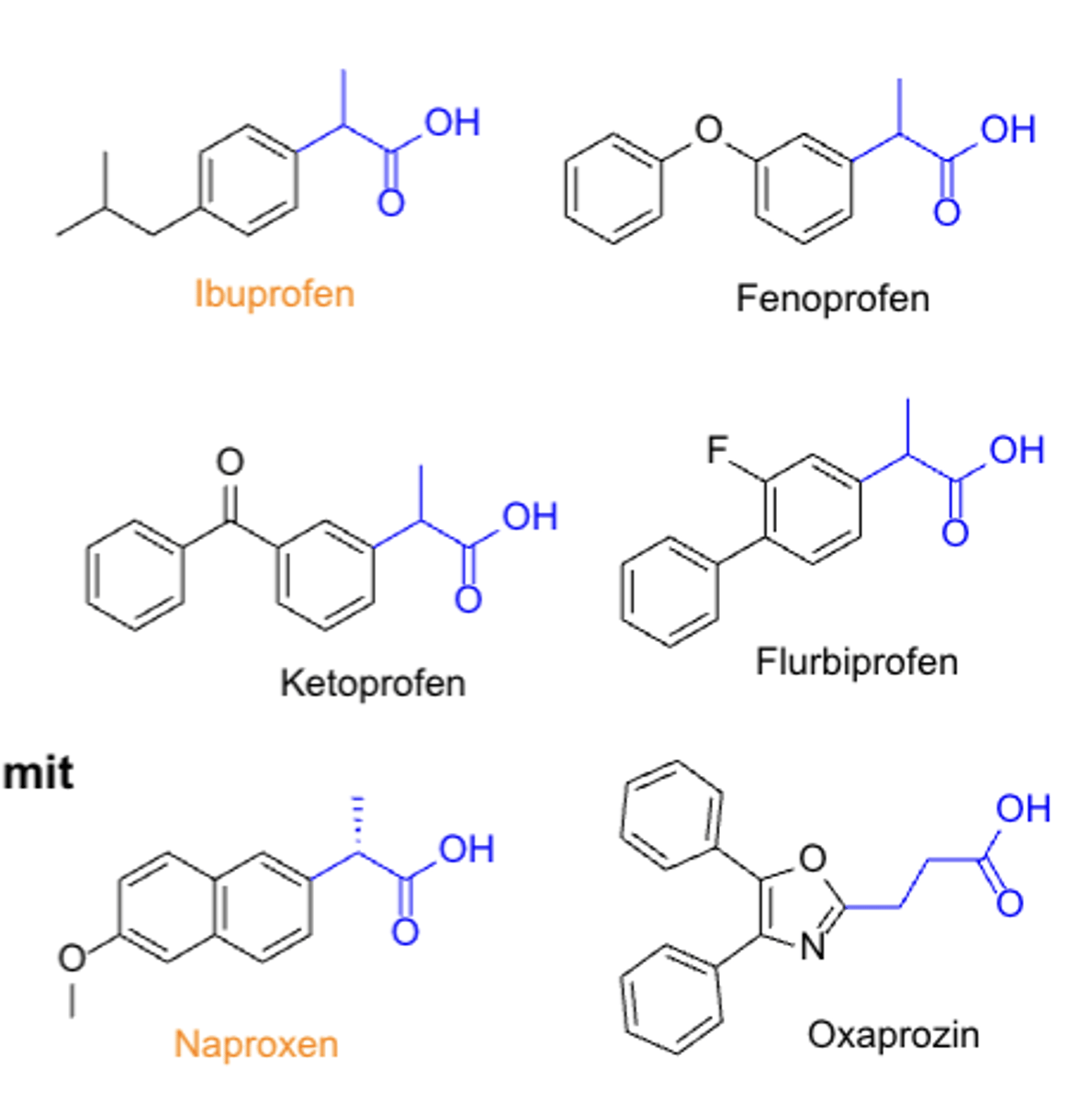
NSAIDs: propionic acid*****
- largest group of NSAIDs
- S is more potent than R, but we use the racemate because they are interchangeable in body
- ibuprofen, naproxen
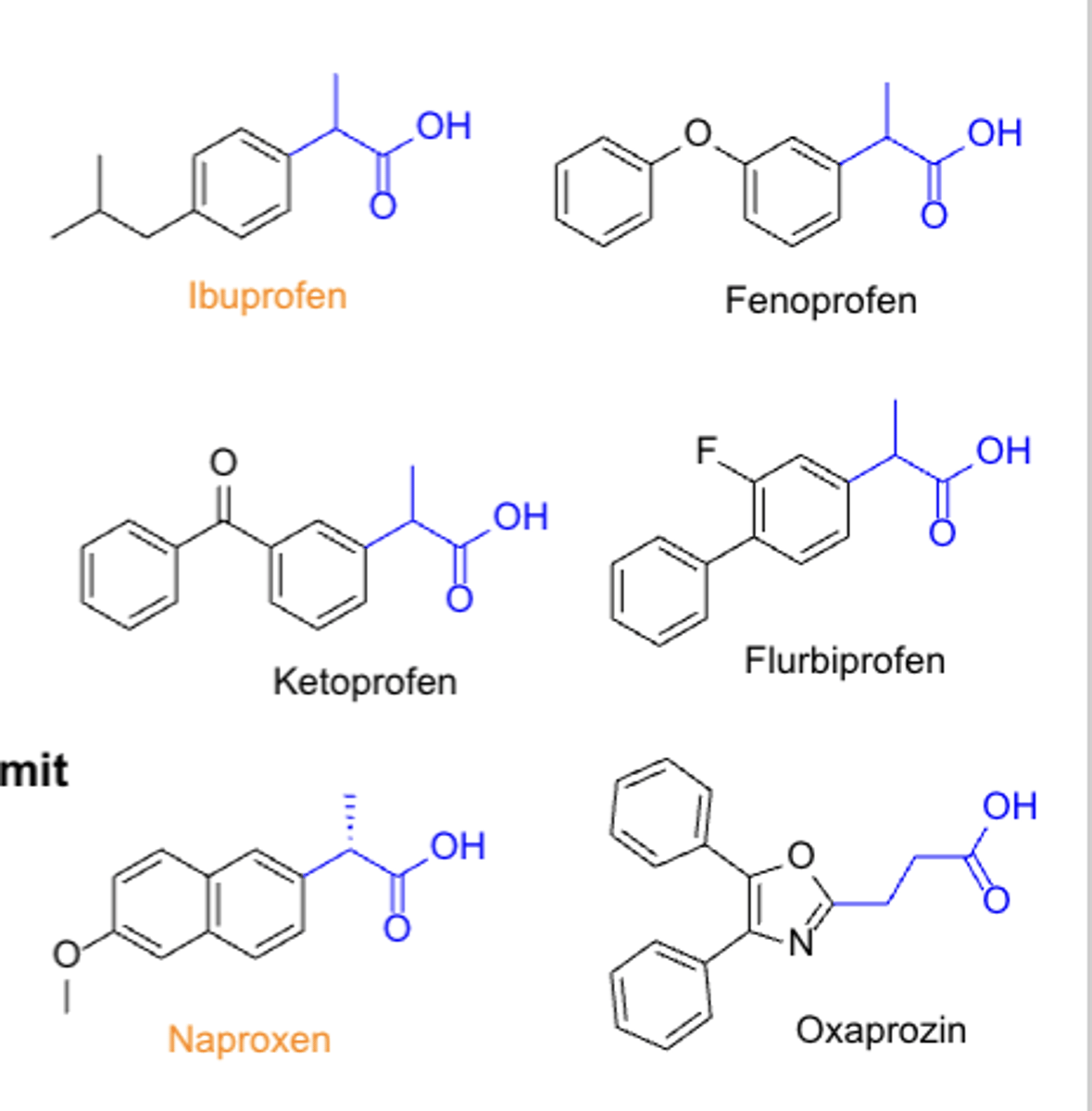
Propionic acid
TC:
PC/MOA:
CC:
- TC: analgesic & anti-inflammatory (antipyretic)
- PC/MOA: COX inhibitor non-selective
- CC: propionic acid
NSAIDs: Oxicams (enolic acids) MOA
- inhibit COX enzymes
- also inhibit the migration of leukocytes to inflamed areas & the release of lysosomal enzymes from these cells
- meloxicam
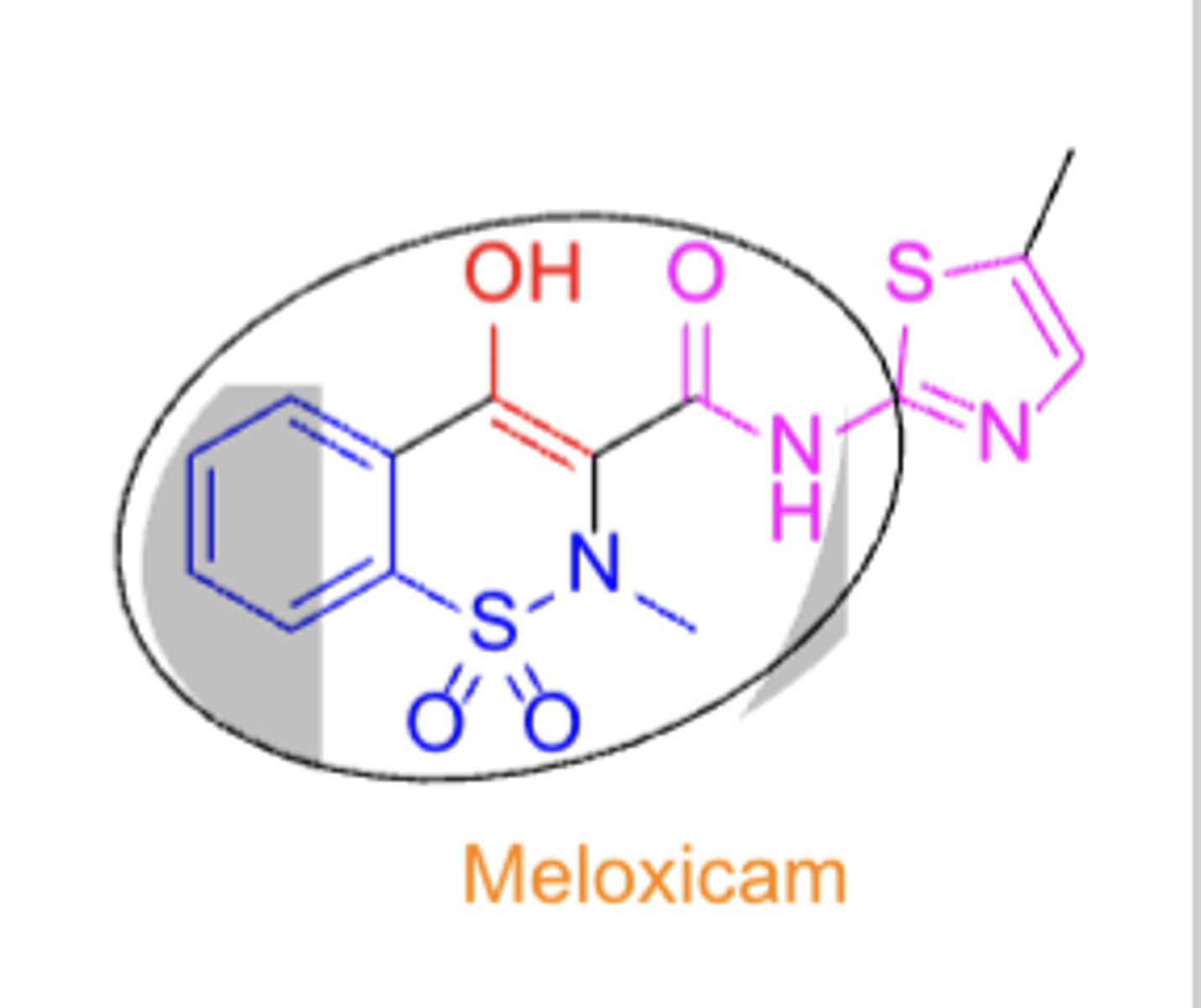
SAR of oxicams
- tautomeric enol
- ring N-methyl group
- N-heteroaryl carboxamide
Oxicams
TC:
PC/MOA:
CC:
- TC: analgesic & anti-inflammatory
- PC/MOA: COX inhibitor (non-selective)
- CC: oxicam
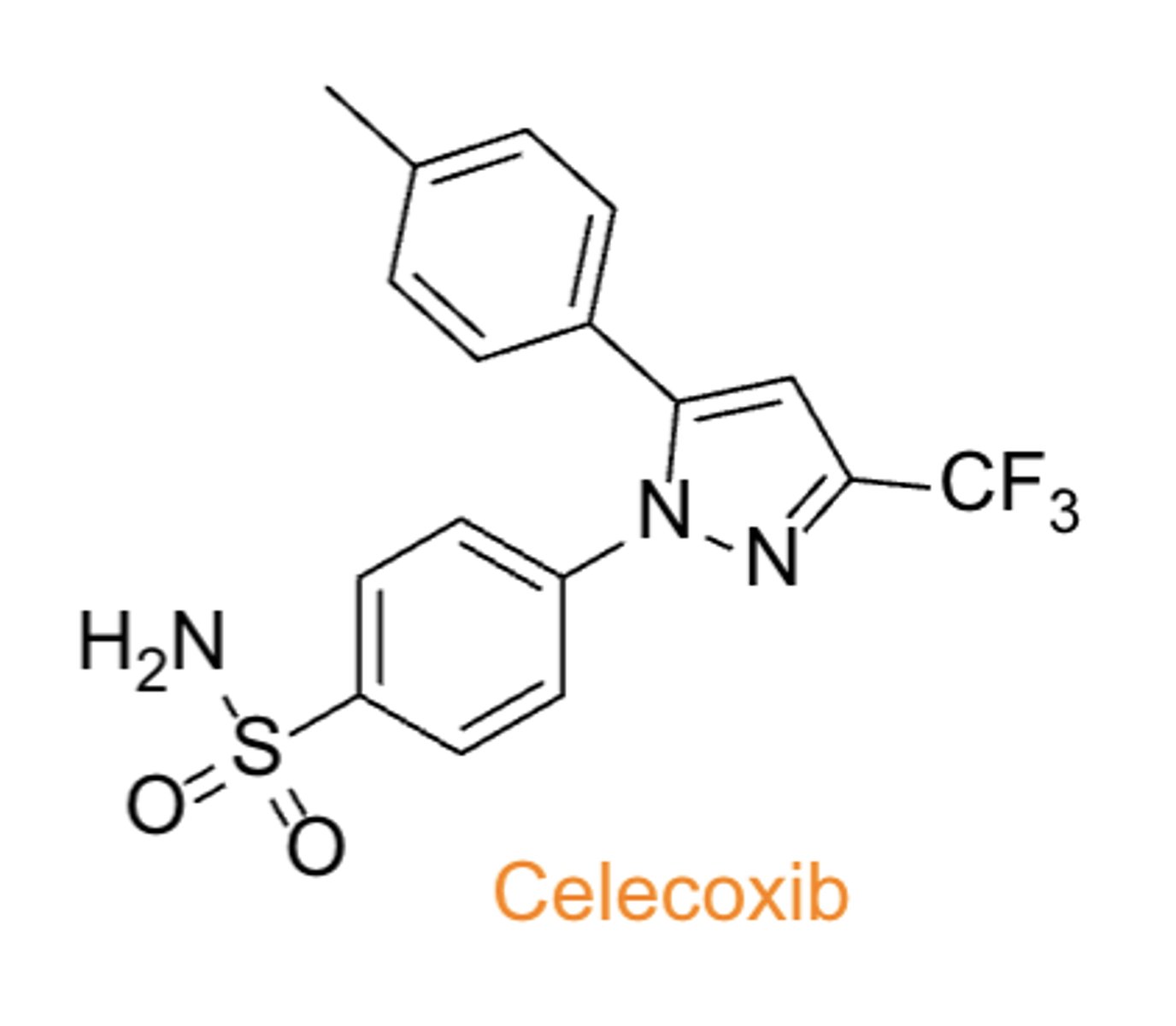
NSAIDs: Coxibs*****
- selective for inhibition of COX2
- celecoxib (first COX2 selective inhibitor)
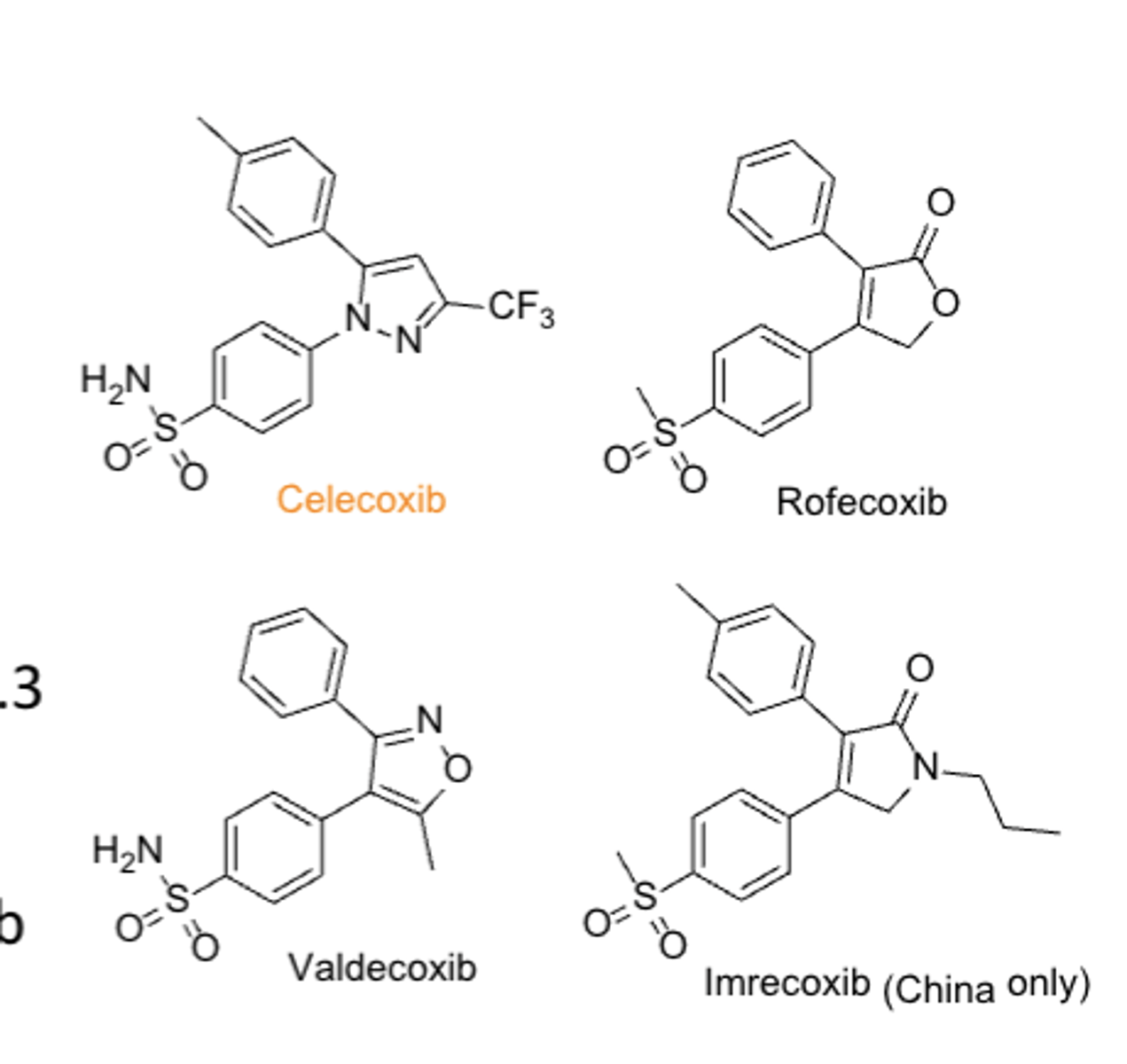
Why were rofecoxib and valdecoxib withdrawn from the market?*****
high risks of serious CV events
Coxibs
TC:
PC/MOA:
CC:
- TC: analgesic & anti-inflammatory
- PC/MOA: COX2 inhibitor
- CC: diaryl-substituted pyrazole
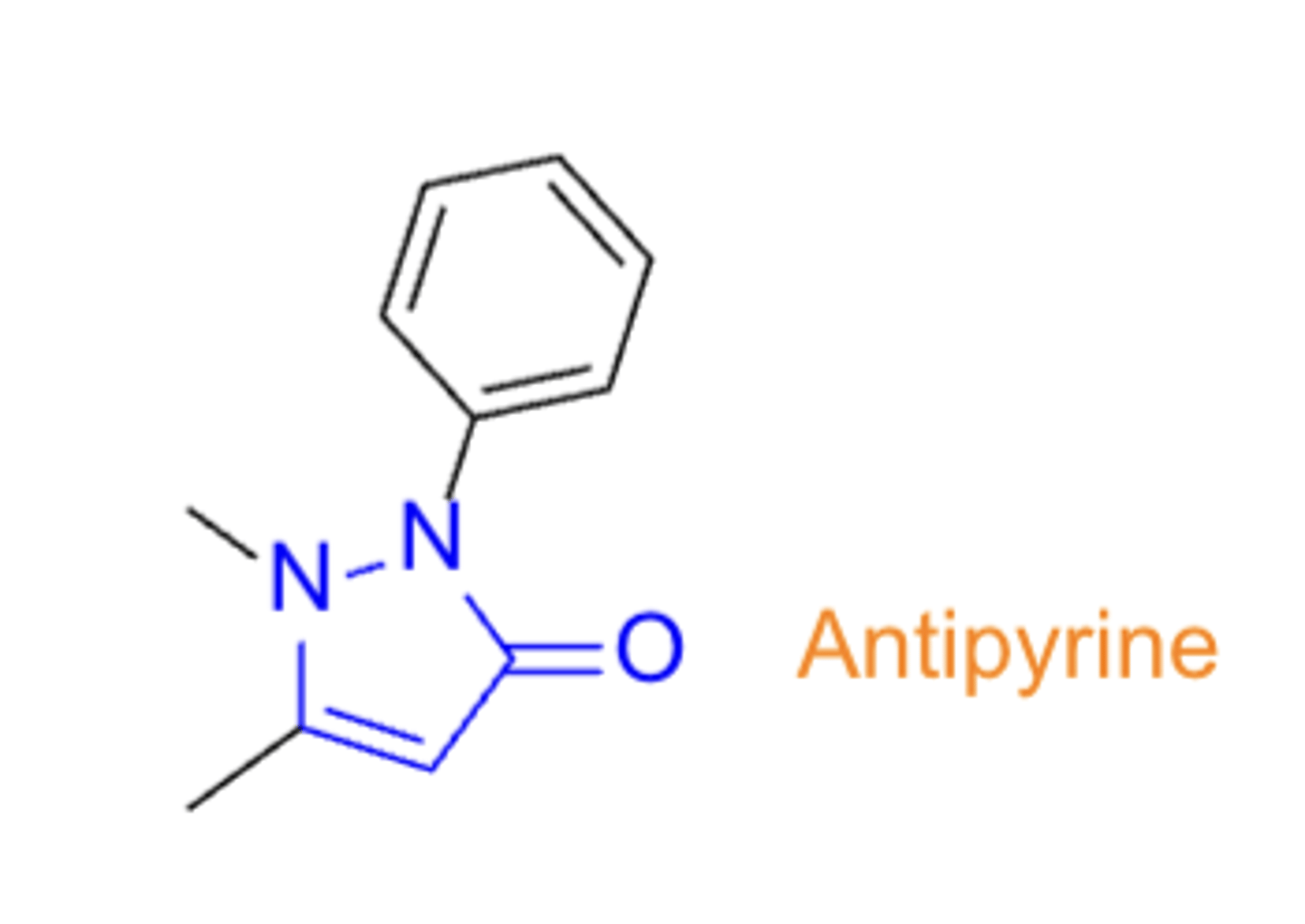
NSAIDs: Pyrazolones
- antipyrine
- not widely used
- no COOH group present, unlike other NSAIDs
- relatively selective to COX3
Agents used for neuropathic pain
- SNRIs
- TCAs
- Calcium channel inhibitors
- Sodium channel inhibitors
- Opioids
- NMDA receptor antagonists
Agents that are Calcium channel inhibitors
- gabapentin (Neurontin),
-pregabalin (Lyrica)
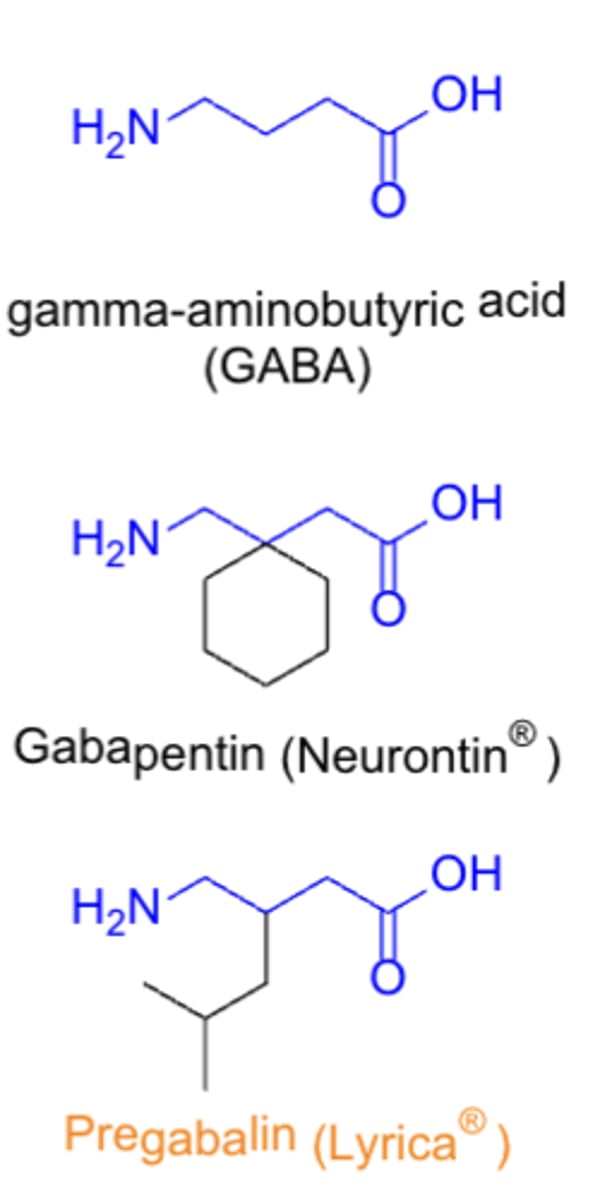
ADMET of pregabalin
A: well-absorbed orally
E: primarily renally
T: dizziness, somnolence, dry mouth & edema are among the most common SEs/ADRs
CCIs
TC:
PC/MOA:
CC:
TC: analgesic (and anti-epileptic)
PC/MOA: alpha2-delta ligand
CC: GABA analog
Agents used for headache & migraine
- adrenergics (BB), propranolol
- GABAergics, barbiturates (butalbital)
- serotonergics, triptans (sumatriptan)
- CGRP inhibitors, MABs, small molecules (ubrogepant)
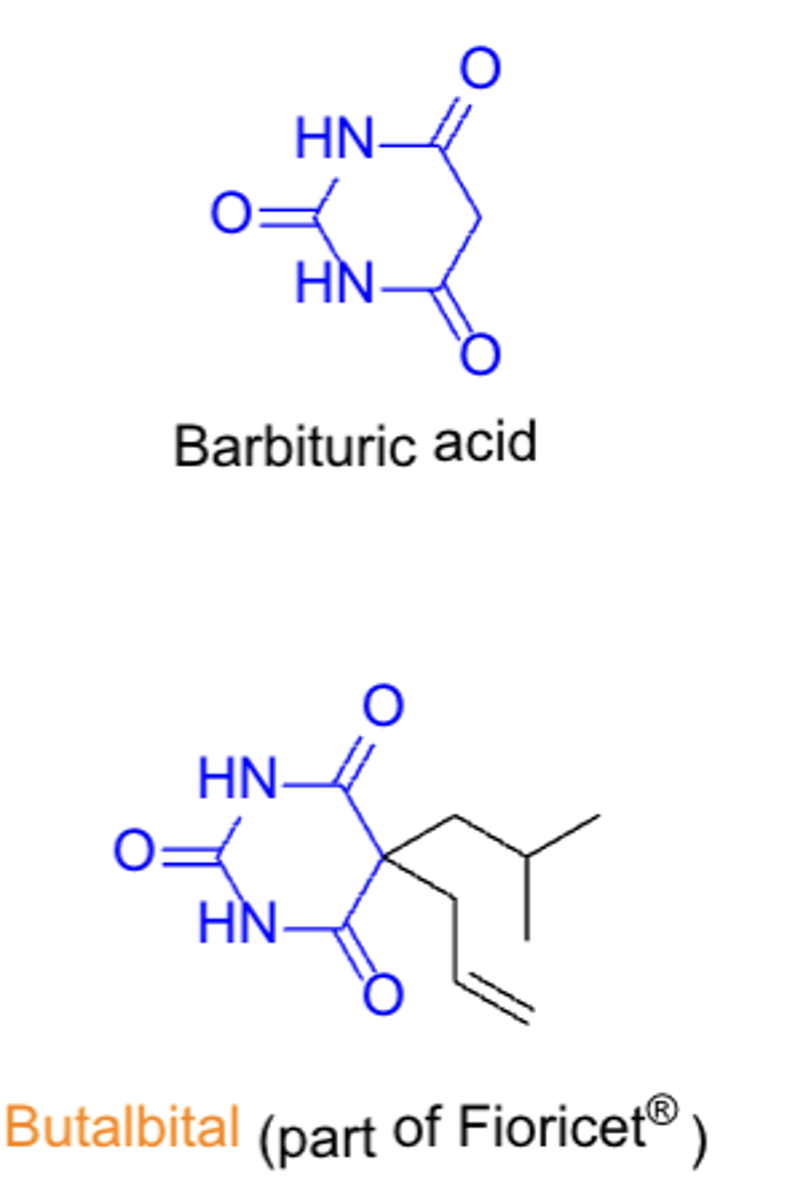
GABAergics: agents, MOA, and ADMET
- butalbital
- GABAergic (positive allosteric modulator that enhances GABA activity)
- CNS effects (sedation), potential for addiction
Serotonergics: Triptans
- family of tryptamine-based drugs for treating migraines and cluster headaches
- agents: sumatriptan
- SAR: similar to serotonin, N-substituents
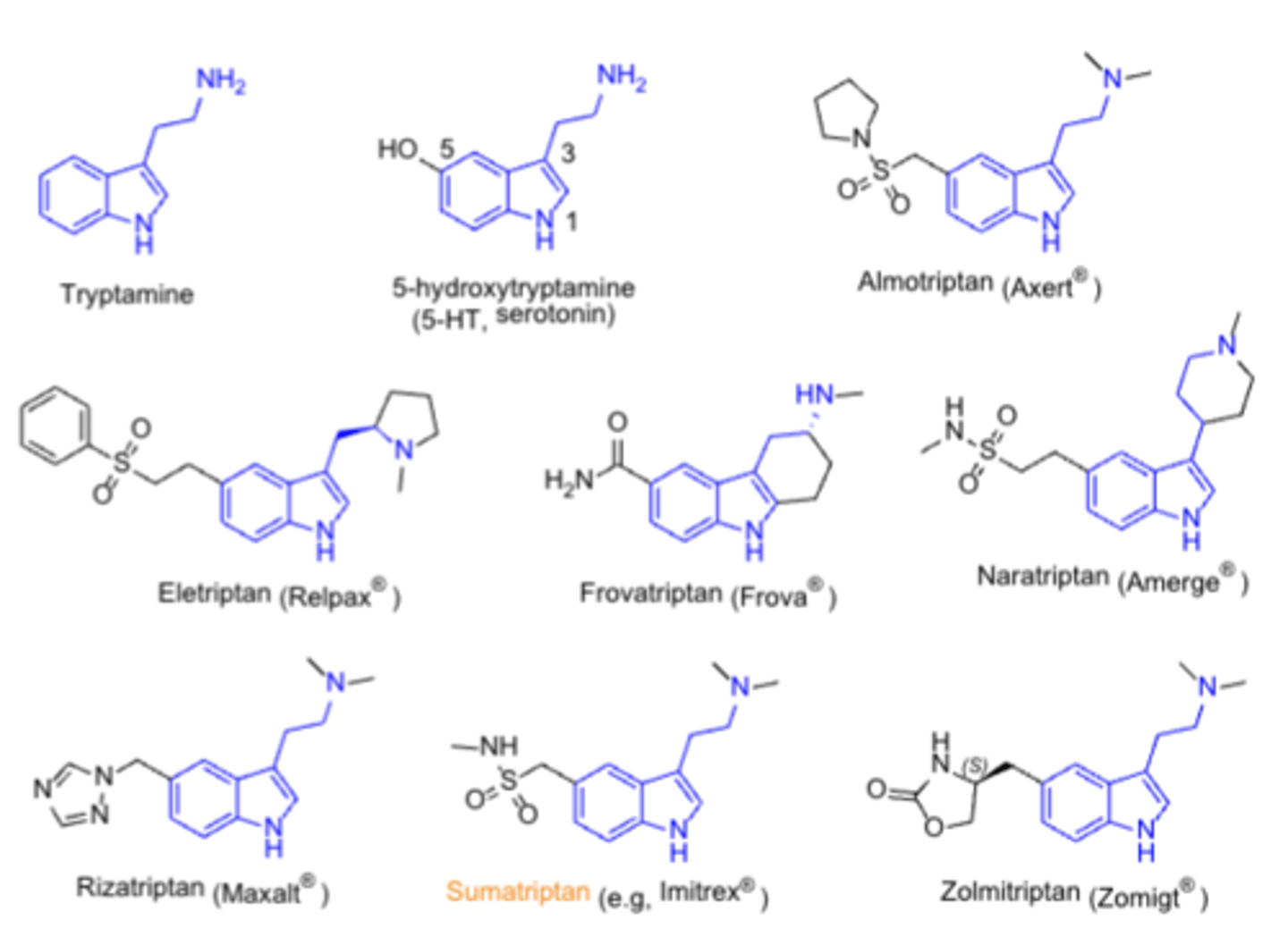
Serotonergics ADMET
A: more lipophilic agents (eletriptan) have better CNS penetration, but more CNS effects
M: several have active metabolites
T: contraindicated in several CV diseases; risk of serotonin syndrome if not used with other serotonergic agents
Serotonergics
TC:
PC/MOA:
CC:
TC: antimigraine agent
PC/MOA: 5-HT1B/5-HT1D receptor agonists
CC: indoethylamines
Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) inhibitors
- signaline system that plays a key role in migraine pathophys
- MABs
- ubrogepant
- cost/insurance coverage is a limiting factor
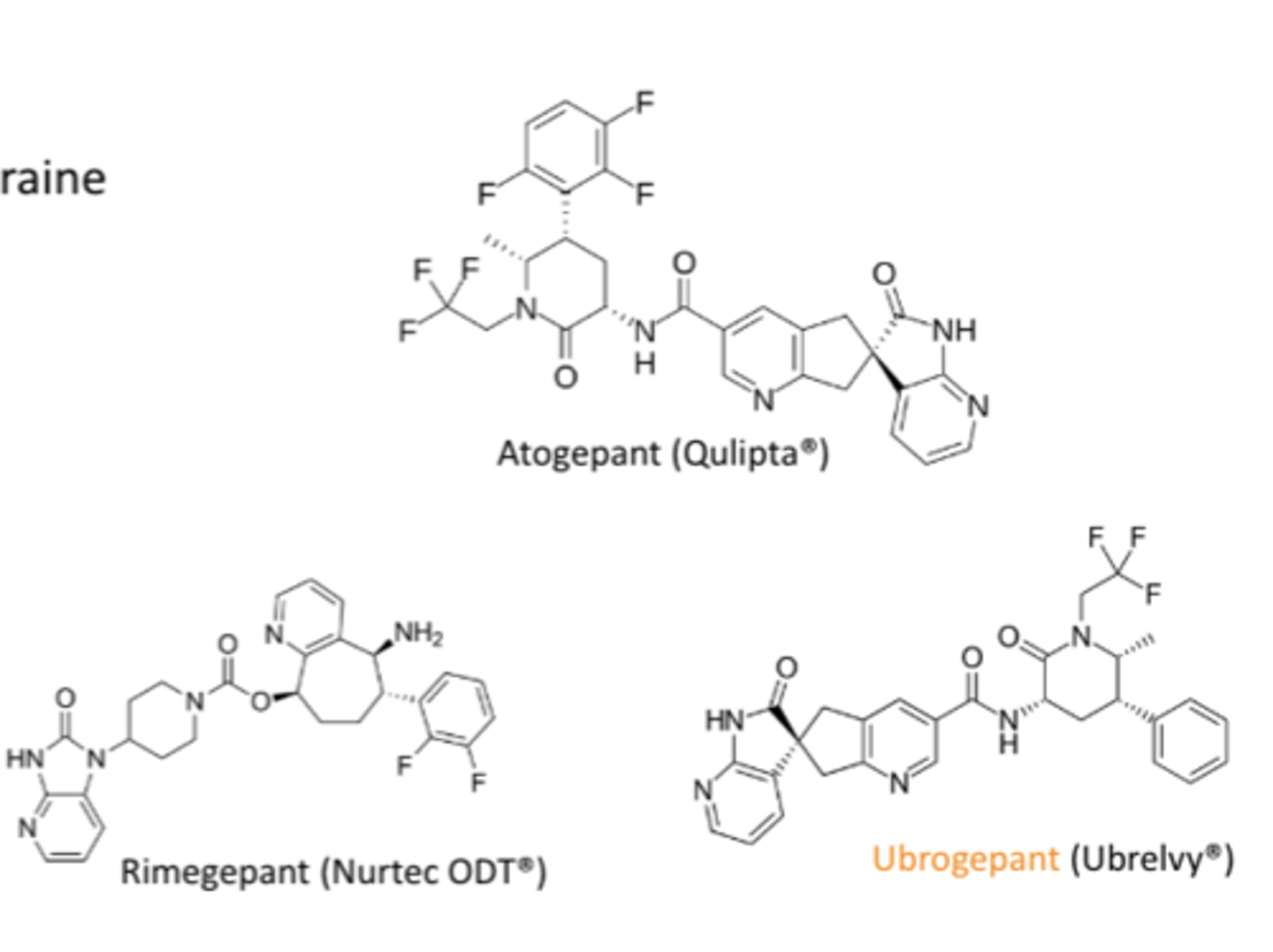
What is a key advantage of the gepants compared to the triptans?*****
They lack the vasoconstrictive effects of the triptans
Topical/local anesthetics
- the "caines"
- capsaicin
- block sodium channels in peripheral sensory neurons, preventing impulse transmission
- for temporary relief of pain or itching
SAR structure of Caines*****
- ester core (benzocaine)
- amide core (lidocaine)
- Hydrophobic/lipophilic portion
- Basic amine/hydrophilic portion
- not ALL compounds fit this SAR model
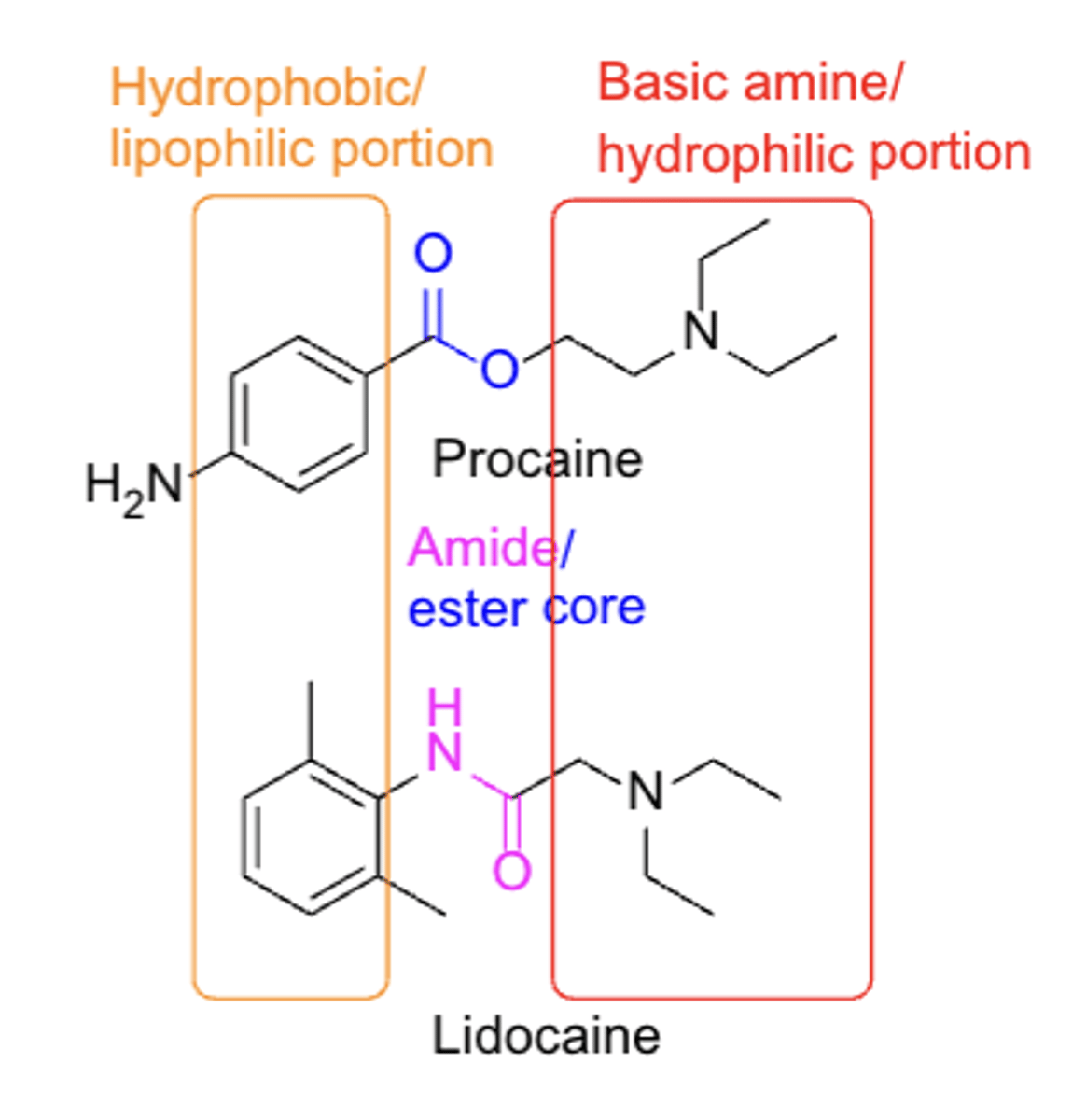
ADMET of topical agents
A: applied topically to mucous membranes or skin, oral BA isnt an issue
M: hydrolysis of ester or amide bonds, N-dealkylation of N-substituted amides
E: primarily in urine
ADRs of topical agents
- convulsions
- CNS depression
- CV effects (especially in amide-based agents)
- methemoglobinemia
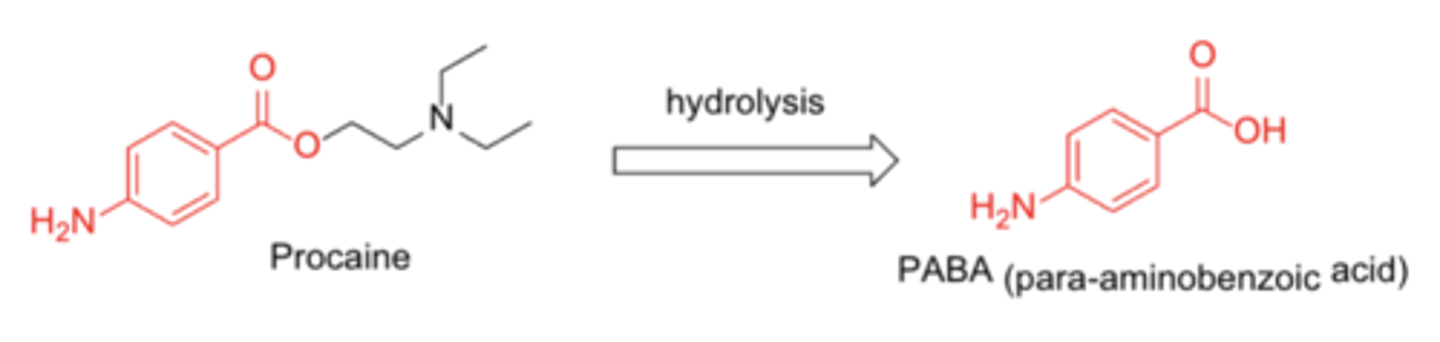
- hypersensitivity to p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA
Precautions of topical agents*****
Patients with a history of hypersensitivity to any local anesthetic (“caine”) agents, especially PABA-based agents
Capsaicin
- topical
- OTC
- anaglesic, but also an irritant (used in many pepper sprays)
- binds to TRPV1 (vanilloid) receptor. Causes depletion of substance P
T/F: Capsaicin works well for arthritis of "deep" joints
FALSE
Capsaicin is typically used as...
add-on therapy w/other agents
Identify which of the agents belong to NSAIDs:
A. Methylprednisolone
B. Aspirin
C. Ibuprofen
D. Celecoxib
E. Pregabalin
B. Aspirin
C. Ibuprofen
D. Celecoxib
T/F: Increasing steric bulk on the N atom flips activity from μ agonist to μantagonist
TRUE
Which metabolite is responsible for the hepatotoxicity of acetaminophen?