Pulm Clin Med Review
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
What classification of asthma is the following
Symptoms < 2 days per week
Rescue medication < 2 days per week
Nighttime symptoms < 2 times per month
FEV > 80% predicted
FEV1/FVC Normal
Intermitent Asthma
What classification of asthma is the following
Symptoms < 2 days per week
Rescue medication > 2 days per week
Nighttime symptoms 3-4 times per month
FEV > 80% predicted
FEV1/FVC Normal
Mild Asthma
What classification of asthma is the following
Daily symptoms
Rescue Medication Daily
Nighttime symptoms > 1 time per week
FEV1 > 60% but < 80% Predicted
FEV1/FVC Reduced 5%
Moderate Asthma
What classification of asthma is the following
Continual Symptoms
Rescue Medication Several times per day
Nighttime symptoms often > 7 times per week
FEV1 < 60% Predicted
FEV1/FVC Reduced > 5%
Severe Asthma
What white blood cell with be elevated in patients with asthma
Eosinophil
If someone has a predisposed PFT and shows no improvement on a bronchodilator, what might the patient have
COPD
What commonly causes recurrent lung infections of bronchiectasis in patients with cystic fibrosis
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
What does the sweat chloride test used for
Diagnose cystic fibrosis
35 year old patient has chest x-ray that shows emphysemic changes. What is this indicative of?
Alpha 1 Antitrypsin deficiency (b/c shes young)
ICS use can cause what condition in the mouth
Oropharyngeal candidas
What is the most common cause of COPD
Smoking
Chronic Bronchitis and emphysema fall under this umbrella term
COPD
What does this refer to
Sarcoidosis
Silicosis
Asbestosis
Coal Worker’s Pneumoconiosis (Black lung disease)
Idiopathic Fibrosing Interstitial Pneumonia (Pulmonary fibrosis)
Restrictive Lung Diseases
On radiographic imaging, you see a visible pleural line (white line) with no lung marking peripheral to it. What does the patient have?
Pneumothorax
On radiographic imaging, you see that the heart and great vessels are shifted. What does the patient likely have?
Tension pneumothorax
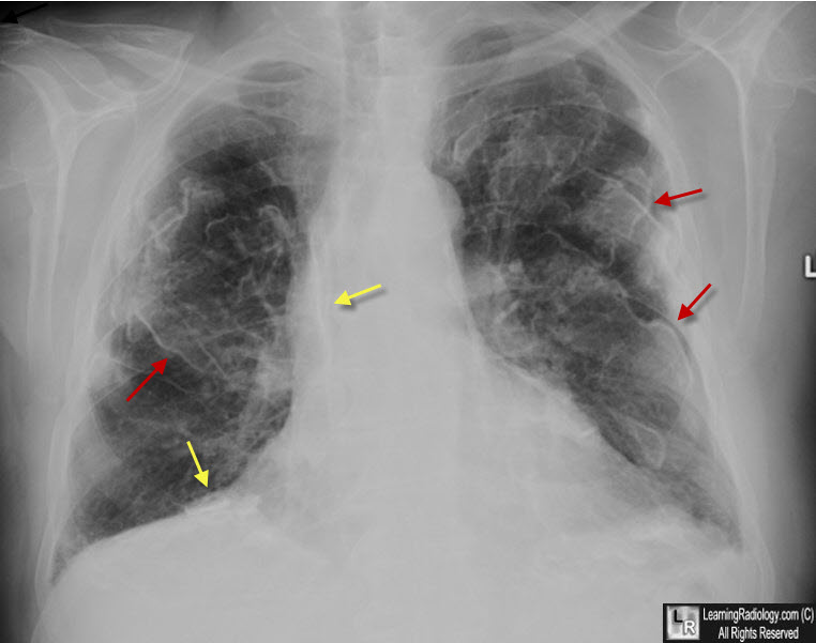
What does this CXR reading indicate
Pleural plaques (MC lower lobes)
“Honeycomb lung” – irregular linear opacities
“Shaggy heart sign”
Indistinct heart borders
Ground glass appearance of lung fields
Mesothelioma (associated with asbestosis) (-the image is specifically asbestosis, but she said mesothelioma can appear similar)
What does this PFT Restrictive Pattern refer to
PFT Restrictive Pattern
FVC ↓
FEV1 ↓ or normal
FEV1/FVC ratio normal
Total Lung capacity ↓
Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD), Sarcoidosis, and Silicosis,
What does this refer to
Restrictive Pattern
FVC ↓
FEV1 ↓ or normal
FEV1/FVC ratio normal or ↑
Total Lung capacity ↓
Lung volumes ↓
Asbestosis
What test is used to determine which type of IDL the patient has
High resolution CT Scan
What pulmonary finding do you expect to find in sarcoidosis
Normal
What does this refer to
Productive cough x 3 months in each of 2 successive years in a patient in whom other causes (such as bronchiectasis) have been excluded
Chronic Bronchitis
What does this refer to
Cyanosis
Nasal flaring
Grunting
Apnea/dyspnea
Retractions
Tachypnea (RR>60 breaths/minute)
Tachycardia (HR>160 beats/minute)
Signs and Symptoms of Infant Respiratory Distress Syndrome
What does this refer to
Dilation and destruction of alveoli
Emphysema
What does this chest x-ray finding indicate
Flattened diaphragm
Panacinar emphysema
Hyperinflatation
Elongated heart
Alpha 1 Antitrypsin Deficiency
What do you need to monitor for a patient with TB
BUN and creatinine
What does this refer
CHF, Cirrhosis of the liver, renal failure, pulmonary failure
Causes of transudative pleural effusion
What does this refer to
Cloudy fluid with protein, WBCs, platelet, and plasma
May have RBC but it would have blood streaking
Characteristics of Exudative Effusion
What is the CC of a patient who has pleural effusion
SOB
How many mL of pleural effusion must be present to be seen on a PA view x-ray
250 mL
How many mL of pleural effusion must be present to be seen on a lateral view x-ray
50 mL
How many mL of pleural effusion is usually present in a symptomatic patient
300 mL
What does this refer to
Pocket of pus due to infection
Empyema
If a pneumothorax causes a shift in the heart and mediastinum what is the dx? Can it be seen on a chest x-ray?
Tension pneumothorax and yes
What activity should be avoided after pneumothorax
Scuba diving
Sarcoidosis and pulmonary fibrosis are examples of…..
Restrictive lung disease
Patient has chronic lung disease and you are getting a CBC, what value do you expect to be elevated?
Hemoglobin and hematocrit
What illness may cause elevated leukocytes
Pneumonia or chronic illness (can be a sign of glycemia or leukemia)
What device is used to help monitor asthma, not diagnose
Peak expiratory flow
What does this refer to
__________ is a standardized method that compares serum and pleural protein and LDH concentrations to differentiate exudative from transudative effusion
Light’s criteria
Light’s criteria is 100% sensitive for diagnosing ________ fluid
Exudative
What does this refer to
Steriling Law with increased hydrostatic pressure or decreased plasma oncotic pressure
Transudative effusion
After an initial PFT, you give a patient with asthma albuterol and repeat the PFT. What do you expect the PFT to do?
Improve
After an initial PFT, you give a patient with asthma albuterol and repeat the PFT. What percent do you expect the PFT to improve by?
12%
What is the purpose of gold standard guideline for COPD
To characterize COPD and determine appropiate treatment
What does this refer to
Located in the parietal space
Nearly always associated with pneumonia
Empyema pus
What specific apparatus can be used in the prevention of occupation or environmental exposure
N95
What does this refer to
Absestos
Silica (sandblasting)
Coal-mining (Black lung)
Smoke (fire-fighters)
Occupational exposures
What is used to determine if the patient needs an anticoagulant?
CHA2DS2-VASc score
According to CHA2DS2-VASc score you need to give a patient an anticoagulant. What would you give them?
Warfarin/Eliquis
If a patient in on an ACEI, what electrolyte should you check routinely
Potassium (causes hypekalemia)
Lung disease over a prolonged period of time can cause what type of heart issue
Cor pulmonale (right heart failure)
You know your patient had lung disease, but are now concerted about their heart, what test are you ordering?
Echocardiogram
What does this refer to
A predictive value that determines the risk of a patient having another MI in the next 14 days
TIMI Score (thrombolysis in myocardial infarction)
What does this refer to
Age
3 or more risk factors for CAD
Known CAD
Aspirin in the past 7 days
Severe Angina
ST segment changes
Increased cardiac biomarkers
TIMI 7 risk factors
What does this refer to
Dyspnea with exercising
Diaphoresis
Dizziness
Nausea
Syncope
Symptoms that are angina equivalent
What is the treatment for bad aortic regurgitation
Valve replacement
What are the 3 cardiac risk equivalent
CAD, PAD, and diabetes
Exudate is confirmed by presenting with at least one of the following criteria. Give me the criteria
Pleural fluid protein/serum protein ratio >0.5
Pleural lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)/serum LDH ratio >0.6
Pleural fluid LDH > two-thirds the upper limits of the laboratory’s normal serum LDH
What does this refer to
Mid to late peaking murmur at the right upper sternal border with diminished A2 and decreased carotid upstroke
Aortic stenosis
What does this refer to
Early, soft decrescendo diastolic murmur at the right upper sternal border best heard leaning forward after expiration
Aortic regurgitation
What does this refer to
Low-pitched, soft rumbling mid to late diastolic murmur heard at the apex; could be associated with a mitral valve opening snap
Mitral stenosis
What does this refer to
Blowing systolic murmur at the apex radiating to the sternal border, axilla, or back
Mitral regurgitation
What does this refer to
FEV1:FVC < 70% (↓)
FEV1 < 80% (↓)
FVC > 80% (normal)
TLC Normal/Increased
RV Normal/Increased (emphysema is reduced)
DLCO Normal (asthma, chronic bronchitis) + reduced (pulmonary fibrosis)
Obstructive lung disease
What does this refer to
FEV1:FVC >70% (normal)
FEV1 Variable
FVC < 80% (↓)
TLC < 80% (↓)
RV ↓ (parenchymal)
DLCO Normal (Chest wall/neuromuscular) + reduced (emphysema + other cystic lung disease)
Restrictive lung disease
What does this refer to
FEV1:FVC < 70% (↓)
FEV1 < 80% (↓)
FVC < 80% (↓)
TLC Variable
RV variable
Mixed lung disease
What does this refer to
ABG readings:
Cause: hypoventilation (COPD, sedation, neuromuscular disease)
pH: ↓
PaCO2: ↑
Respiratory acidosis
What does this refer to
ABG readings:
Cause: hyperventilation (anxiety, PE, pain)
pH: ↑
PaCO2: ↓
Respiratory alkalosis
What does this refer to
ABG readings:
pH: ↓
HCO₃⁻: ↓
Metabolic acidosis
What normal value does this refer to
7.35-7.45
pH
What normal value does this refer to
35-45
PaCO2
What normal value does this refer to
22-26
HCO3
What’s the answer
pH = 7.23
PCO2 = 54
HCO3 = 22
Respiratory acidosis, no compensation
Whats the answer
pH = 7.38
PCO2 = 59
HCO3 = 34
Respiratory acidosis, fully compensated
What is the answer
pH = 7.28
PCO2 = 41
HCO3 = 19
Metabolic acidosis, no compensation
What does this refer to
pH = 7.30
PCO2 = 50
HCO3 = 29
Partially compensated respiratory acidosis
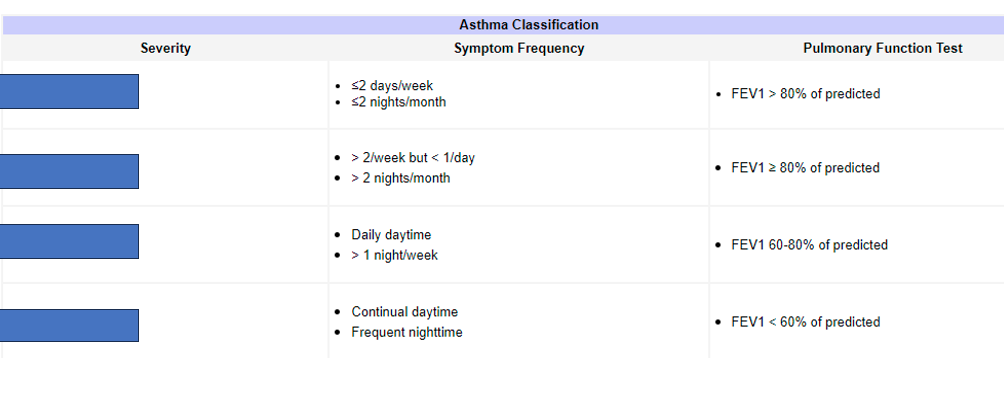
What does the top box refer to
Intermitent
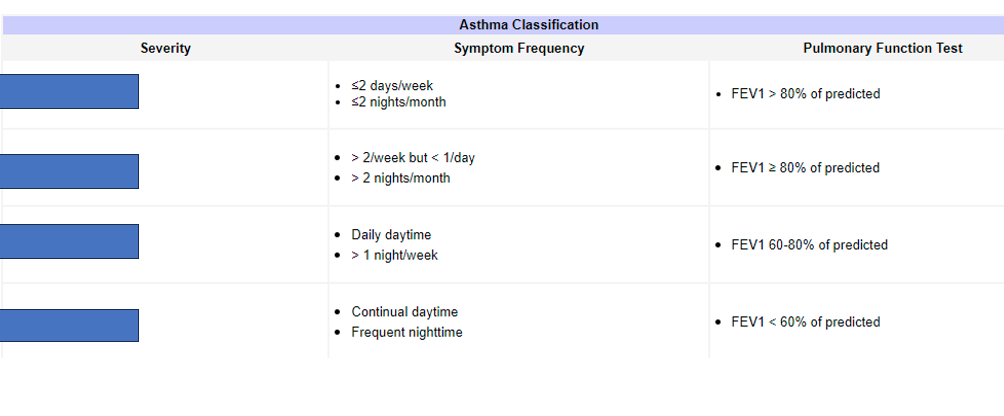
What does the second box refer to
Mild persistent
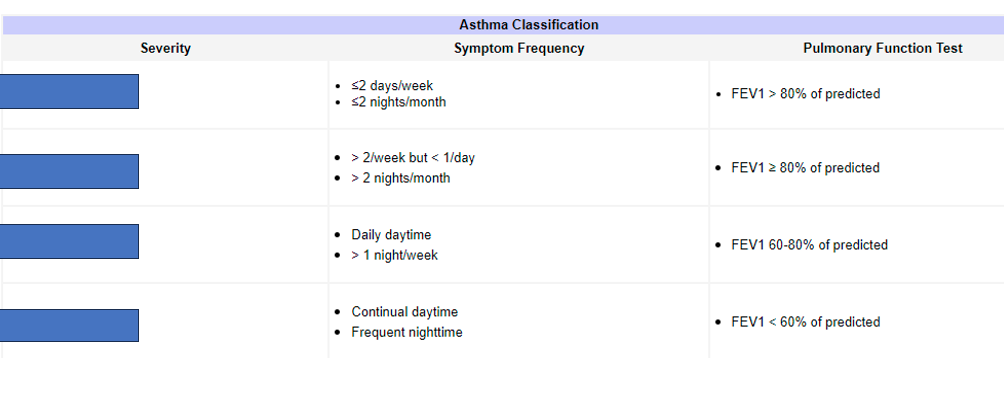
What does the third box refer to
Moderate persistant
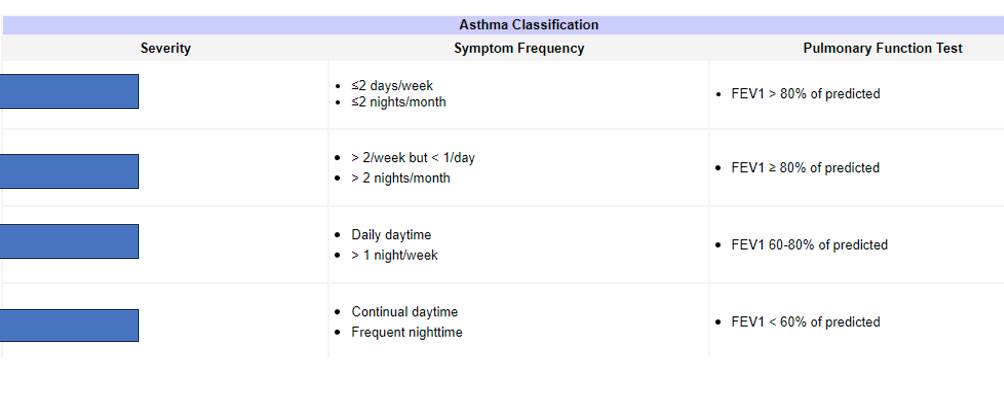
What does the fourth box refer to
Severe persistant
Describe the chamber size that can cause an S4 sound in diastolic HF?
Small chamber (hypertrophy)
Which abnormal heart sound is heard with diastolic HF?
S4