Anatomy: muscle tissues
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
functions of muscle tissues
muscle tissues contract in response to a stimulus from the nervous system in order to:
- move material through the body
- move parts of the body and produce movement
- generate heat
excitability
motor signal to contract reaches muscle and initiates a contraction
- muscle cell can respond to a stimulus (electrical impulse)
contractility
muscle contracts and shortens
- in response to stimulus, muscle cell contracts (shortens or attempts to shorten)
extensibility
motor signal to and contraction of muscle stops and muscle is pulled back to resting length (by gravity and/or an antagonist)
- a contraction of the triceps brachii is responsible for pulling (or extending) the biceps brachii
- when contraction ends, muscle cell can be pulled back to resting length
elasticity
muscle is pulled beyond resting length by antagonistic muscles and is able to regain resting length after this stretch
1. muscle has been stretched beyond resting length
2. muscle is able to regain original shape (titin plays a key role)
- muscle cell can be stretched beyond its resting length and then shorten back to resting length
gastrocnemius
- medial head
- lateral head
3 muscle tissue types
1. skeletal muscle
2. cardiac muscle
3. smooth muscle
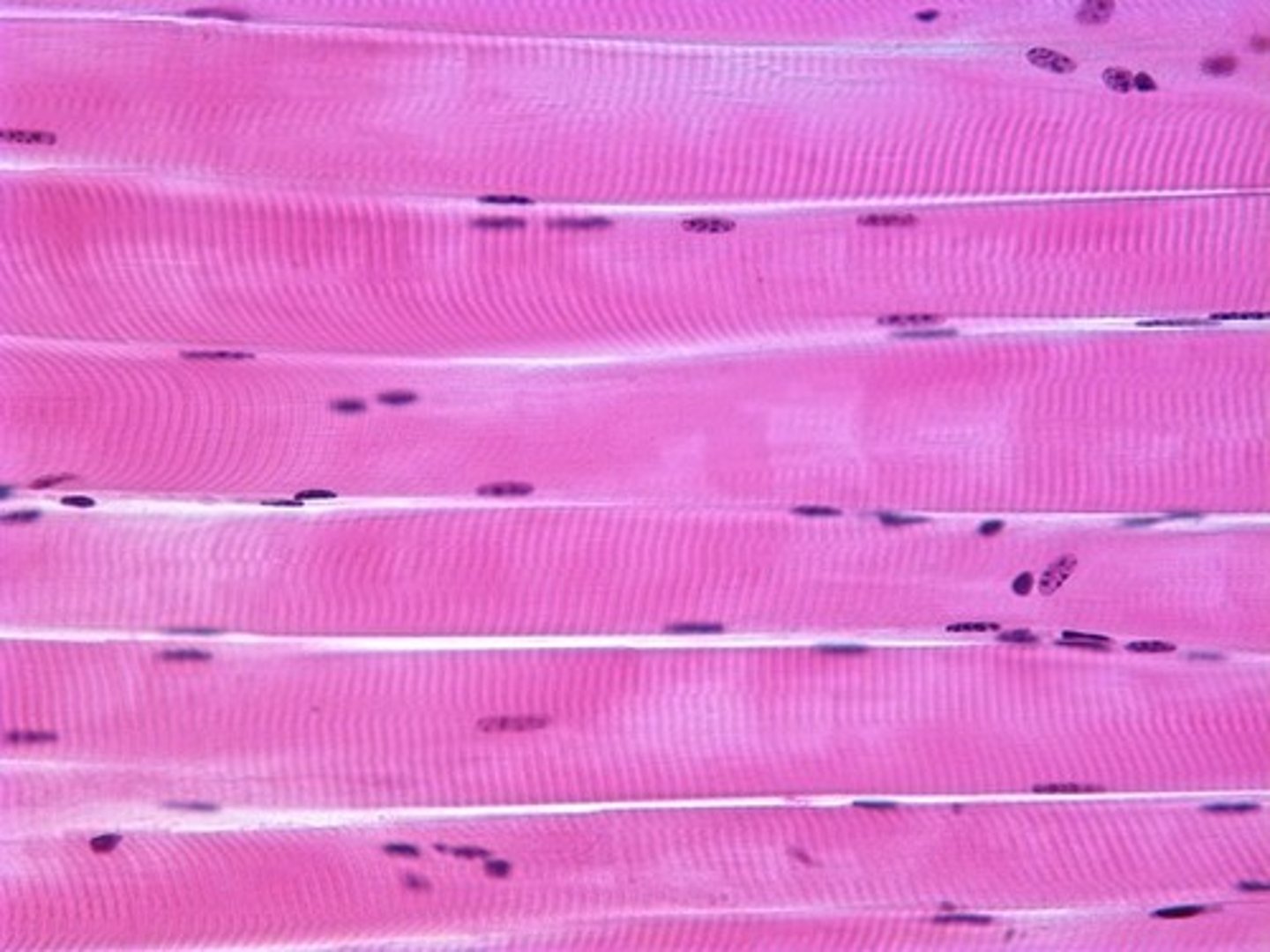
skeletal muscle
- moves the skeleton
- ~40% of body weight
- under voluntary control
- striated
- typically attaches bone -> bone
-> may also attach bone to skin or CT
- 1 muscle fiber can be the length of entire muscle
- can range in length from <1 inch to over a foot
- long, cylindrical, multinucleated cells
cardiac muscle
- only found in heart wall
- under involuntary control
- striated
smooth muscle
- found within the walls of most internal organs
- under involuntary control
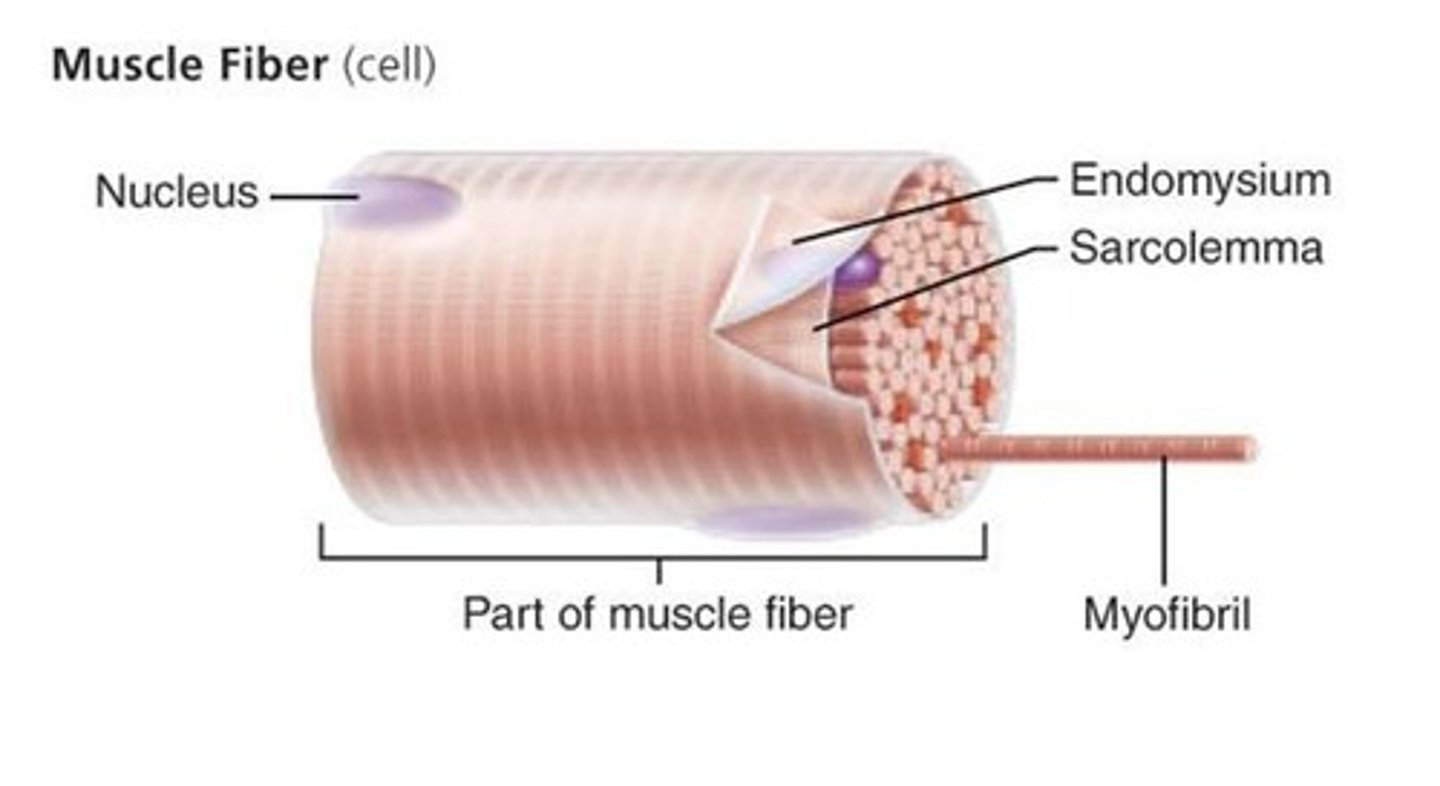
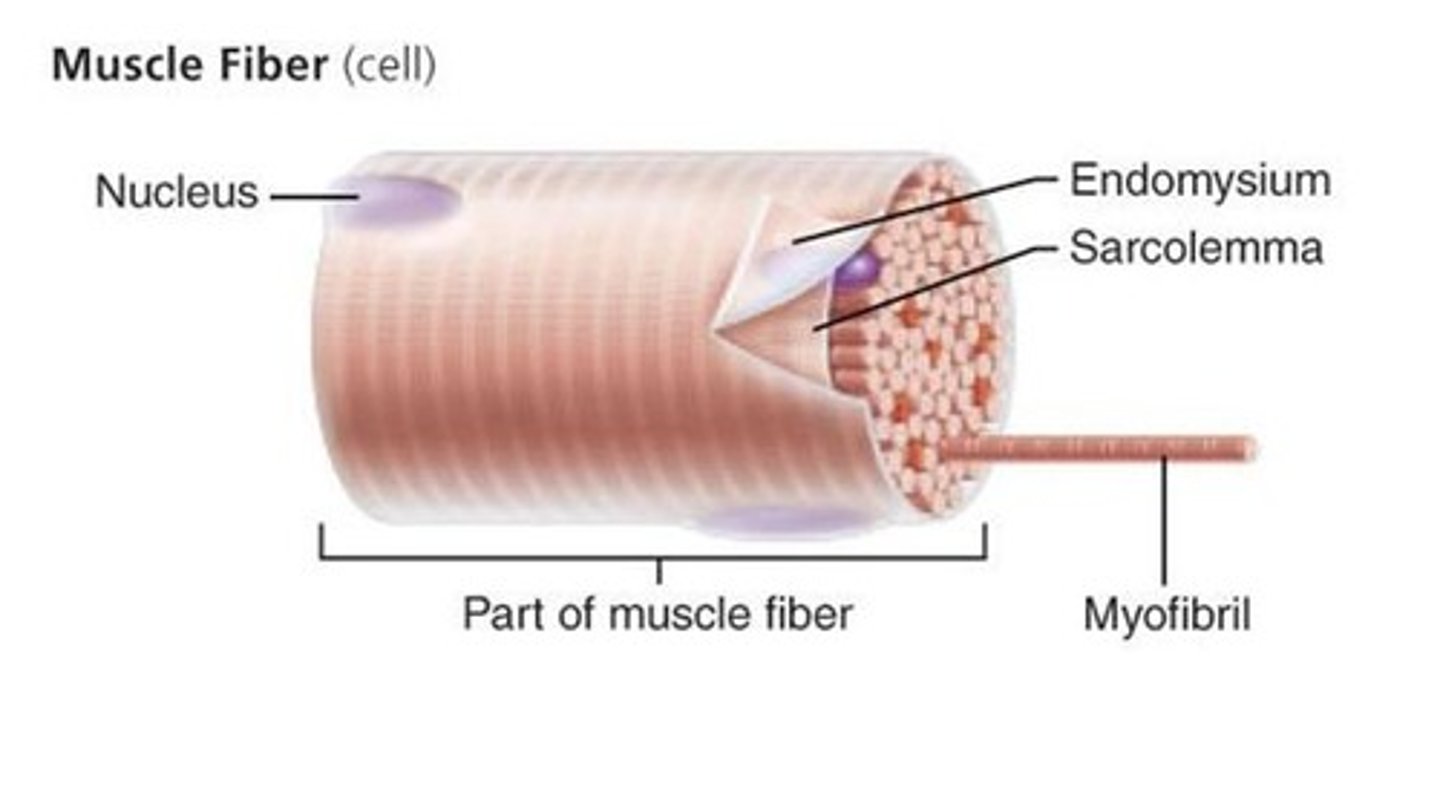
fiber
a muscle cell
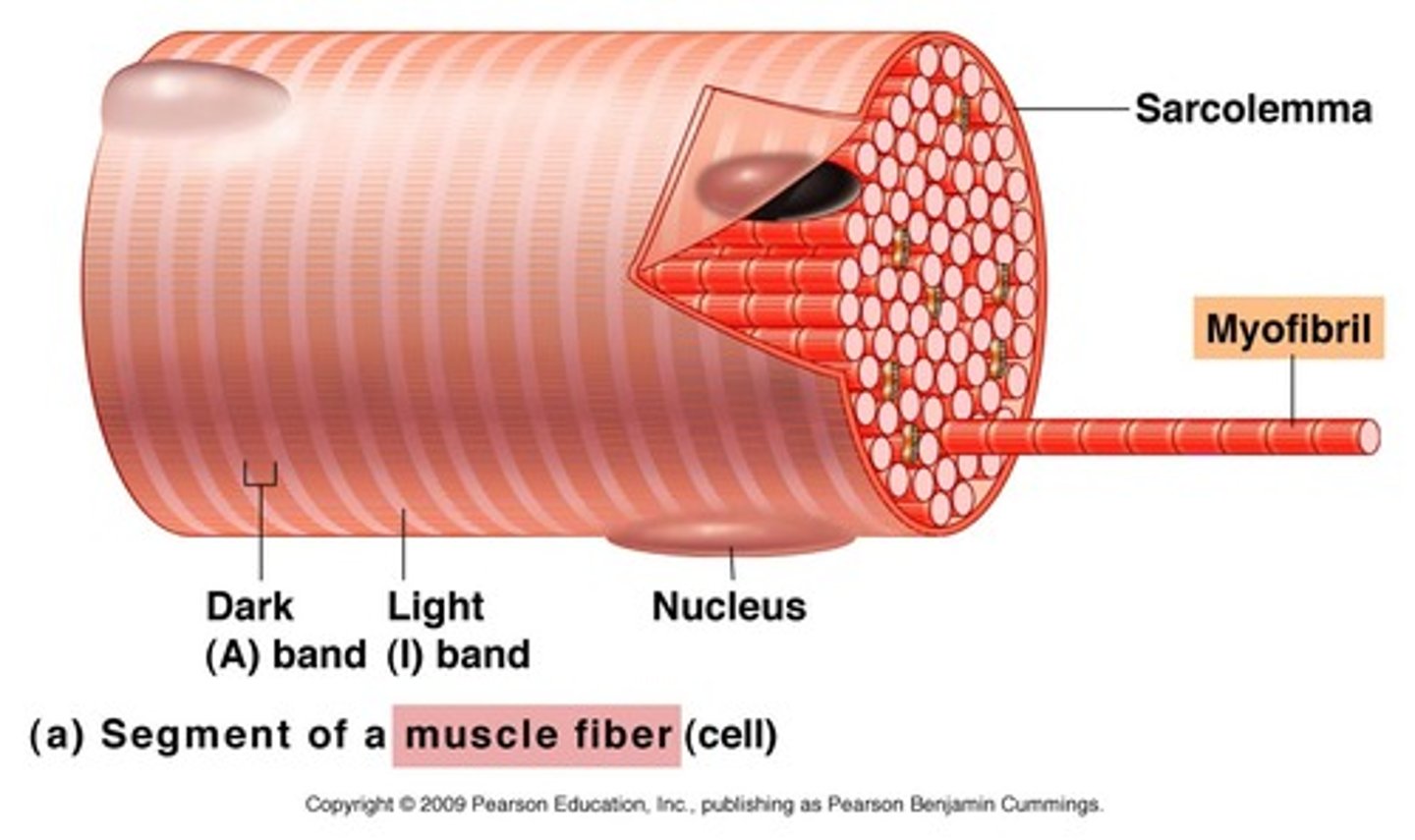
sarcolemma
plasma membrane of a muscle cell
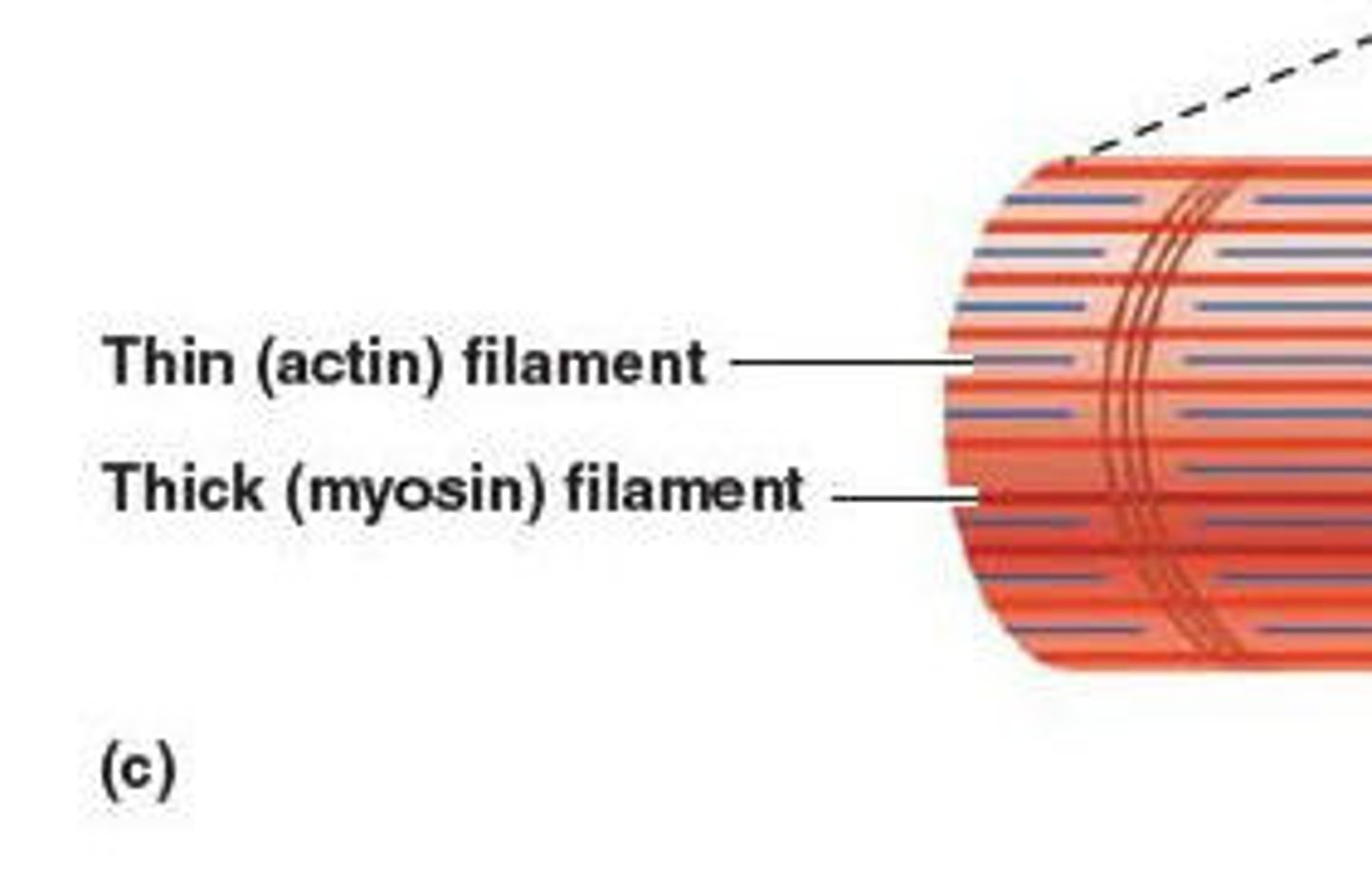
myofilaments
cytoskeletal units
- actin and myosin
- thin (actin) filament
- thick (myosin) filament
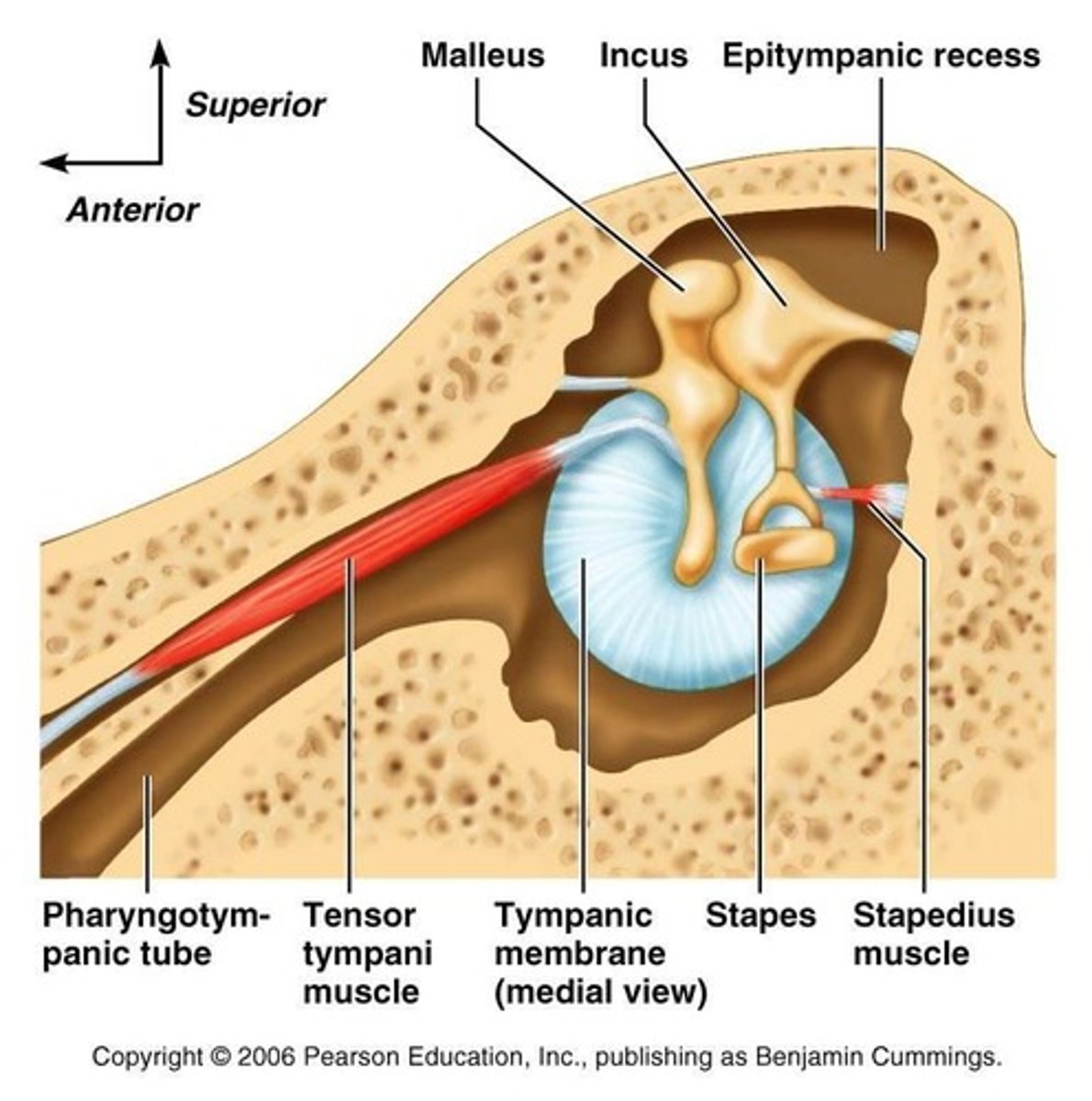
stapedius
shortest skeletal muscle
- in middle ear
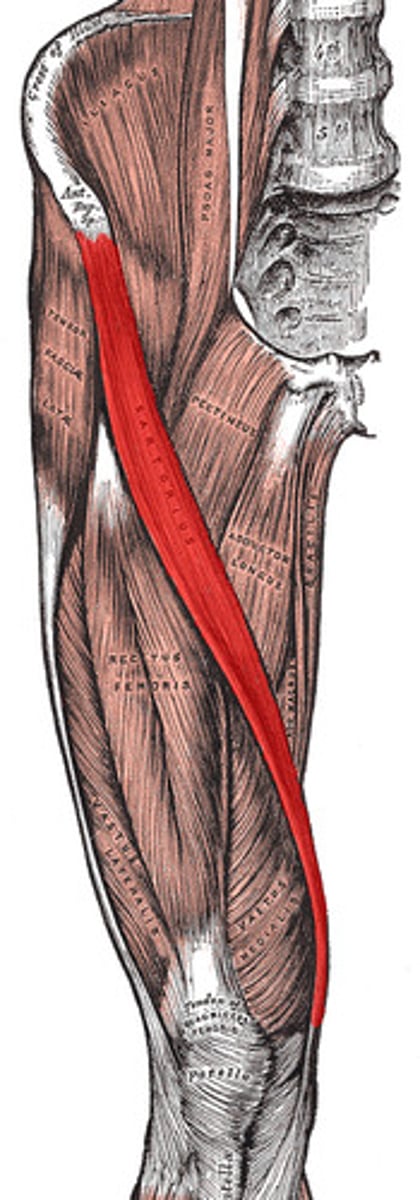
sartorius
longest muscle
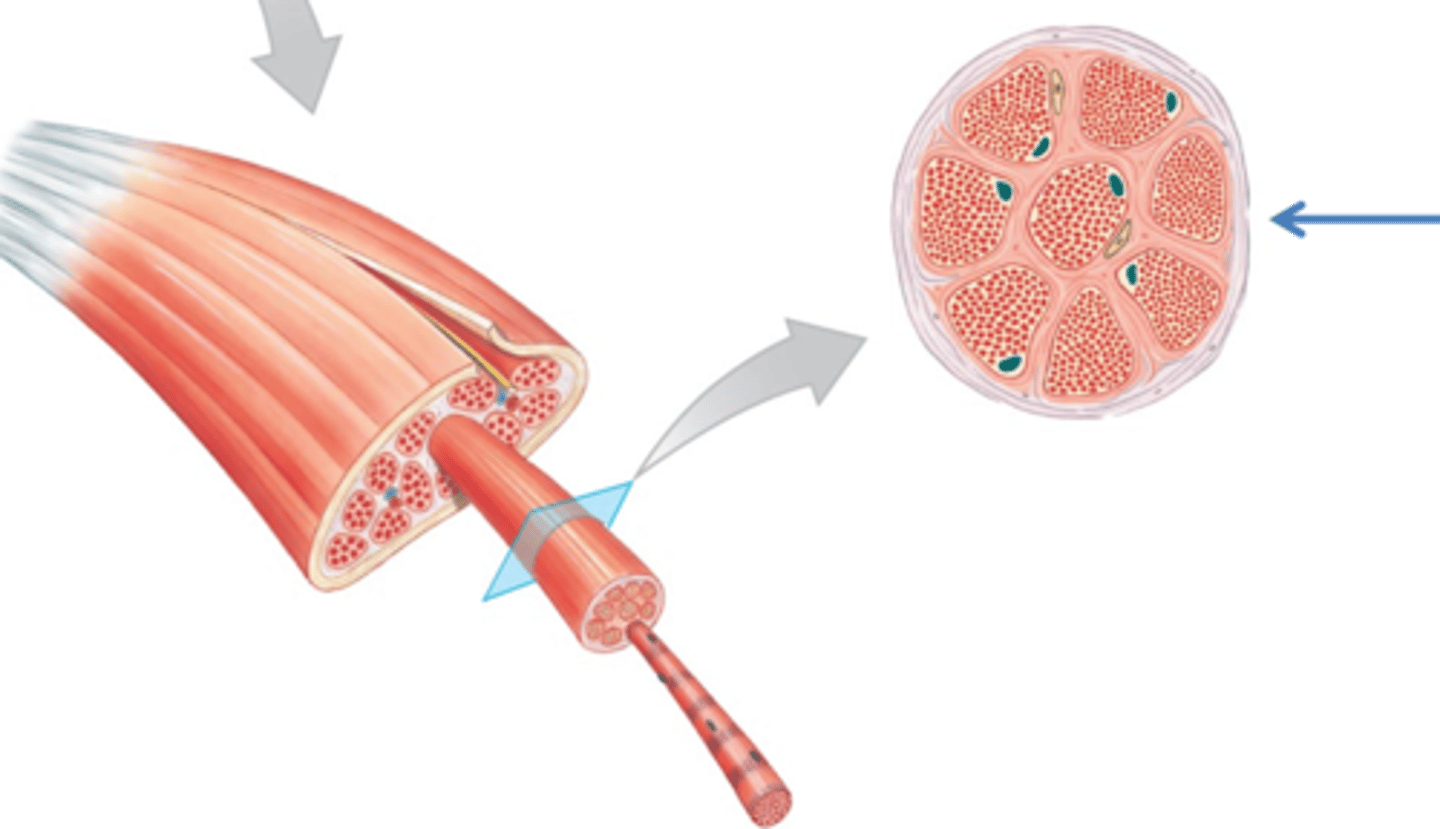
endomysium
loose (areolar) CT surrounding a single muscle fiber
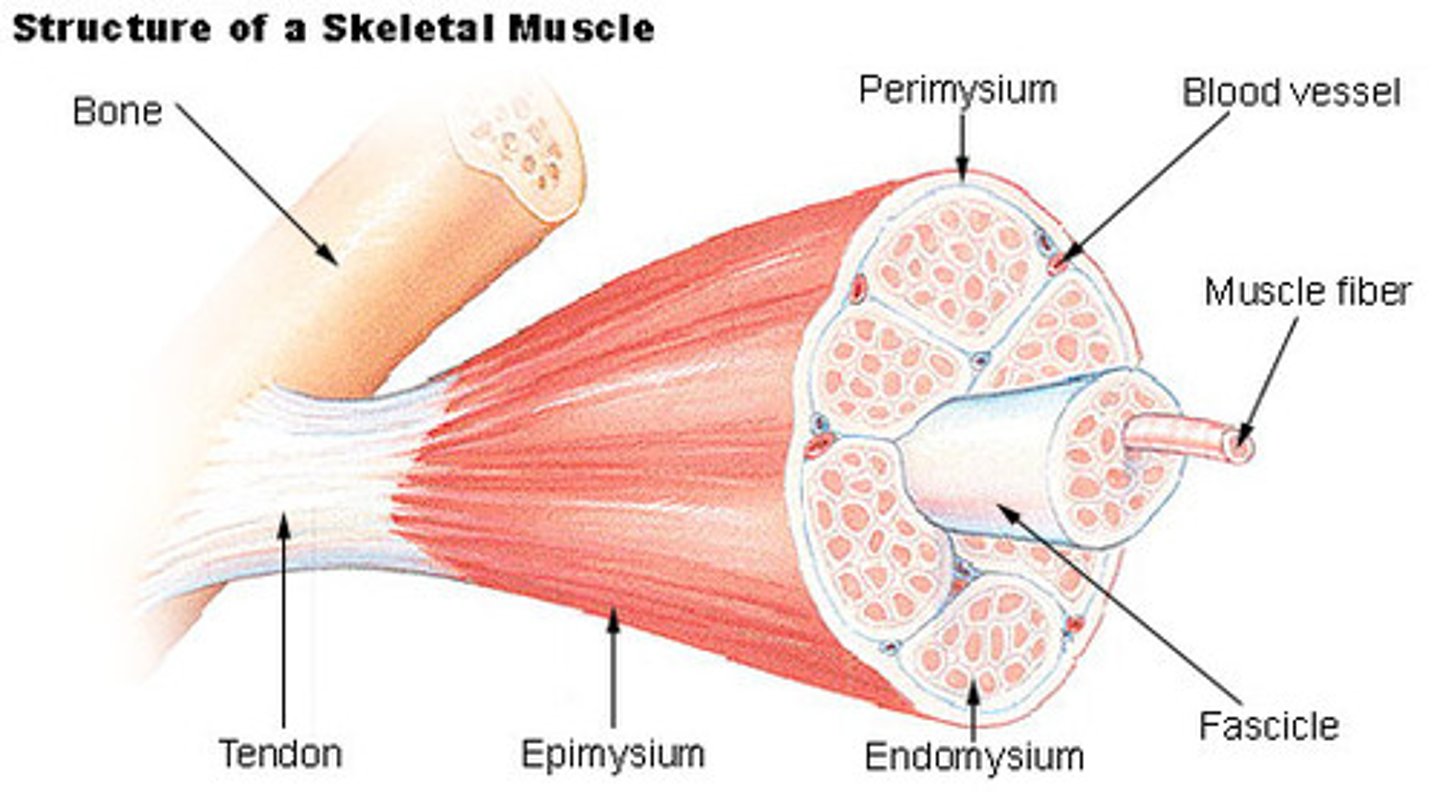
perimysium
dense CT surrounding a muscle fascicle
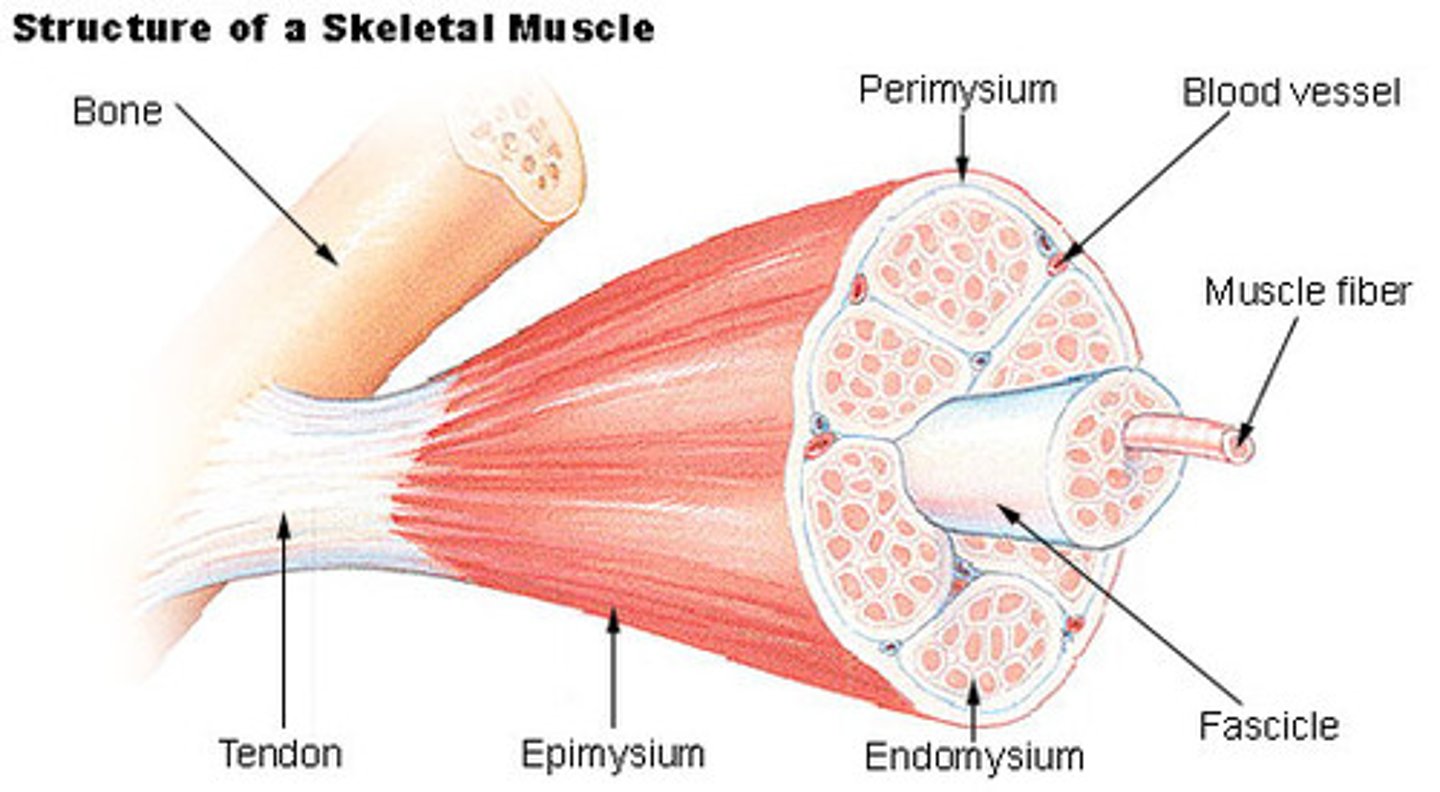
fascicle
collection of muscle fibers
- wrapped by perimysium
epimysium
dense irregular CT surrounding a muscle
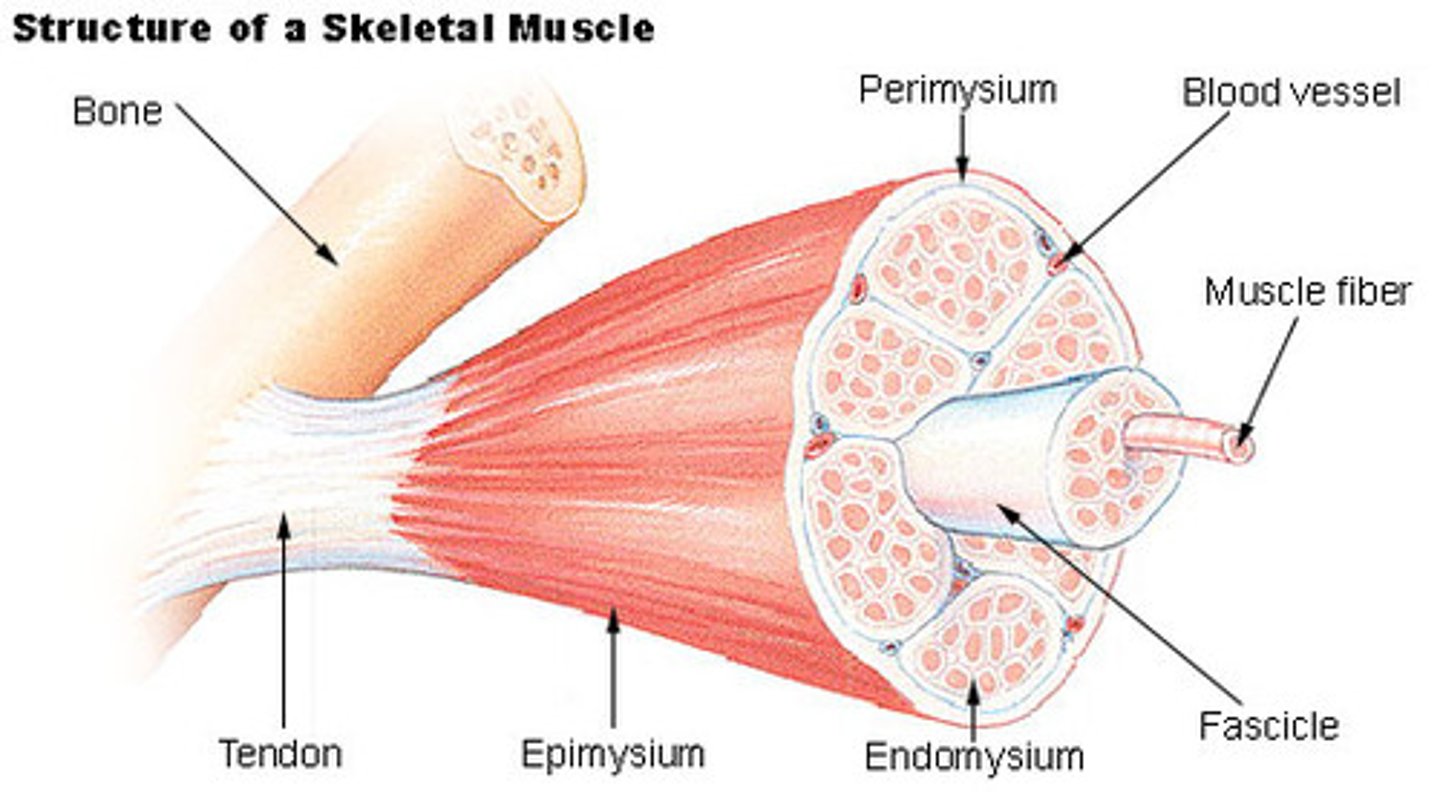
what run through muscle?
- arteries
- veins
- nerves
arteries
provide oxygen and nutrients
veins
remove cellular waste
nerves
innervate muscle cells
muscle fiber
single muscle cell
sarcoplasm
cytoplasm of a muscle cell
myofibrils
rodlike bundles of actin and myosin that run parallel within the muscle cell
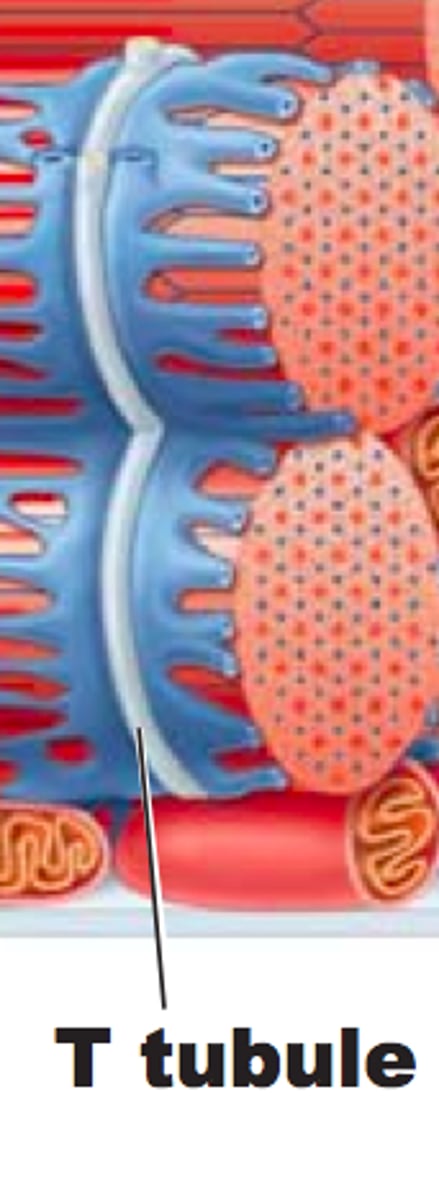
T tubule
extension of sarcolemma that extends into the cell and wraps around myofibrils
- carry electrical stimulus into cell
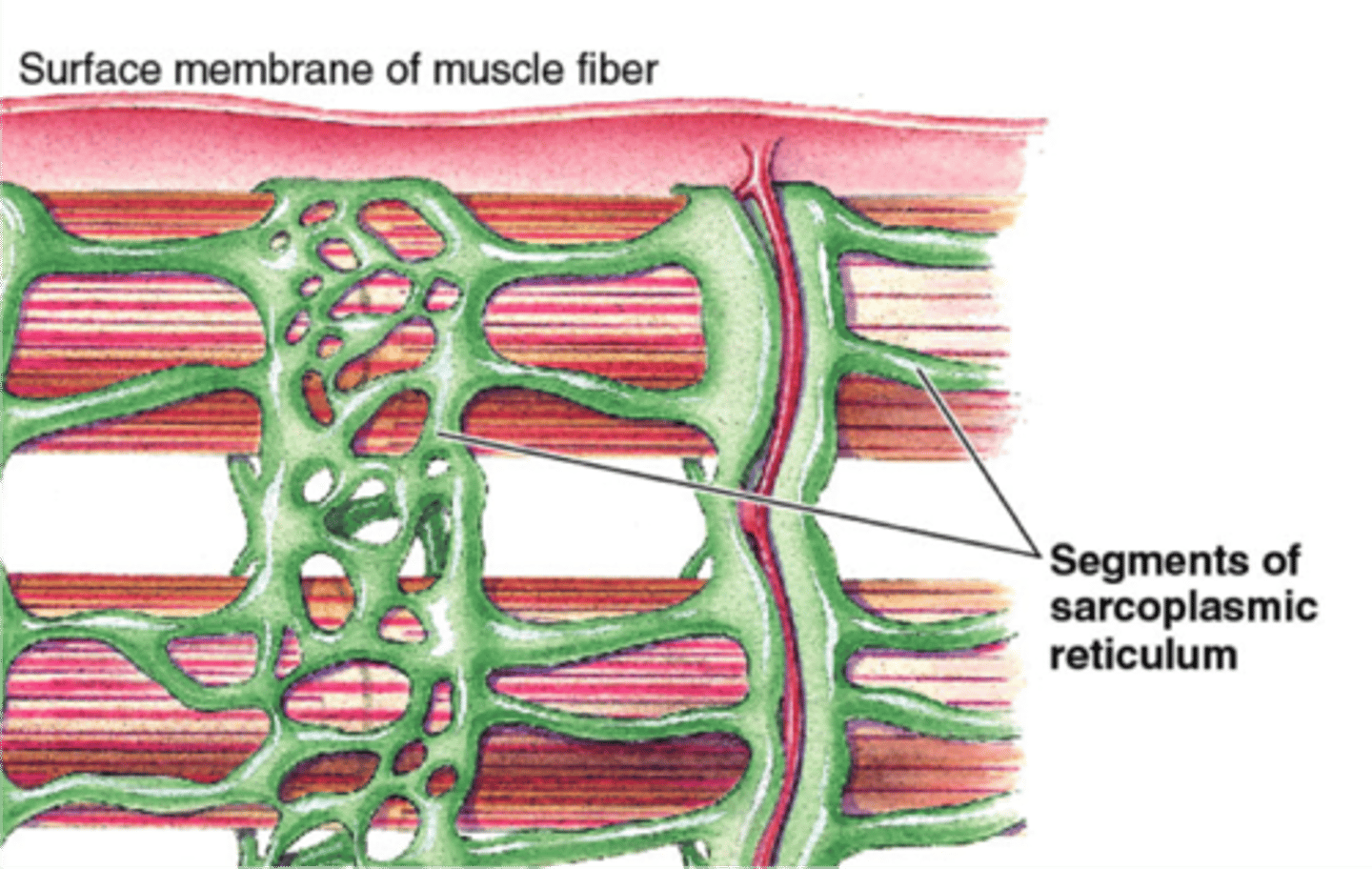
sarcoplasmic reticulum
modified endoplasmic reticulum that stores and pumps calcium ions
structures of a myofibril
- sarcomere
- myofilaments
- Z disc (line)
- A band
- I band
sarcomere
- functional units within a myofibril, repeat the entire length of each myofibril
- organization within each sarcomere gives muscle a striated appearance
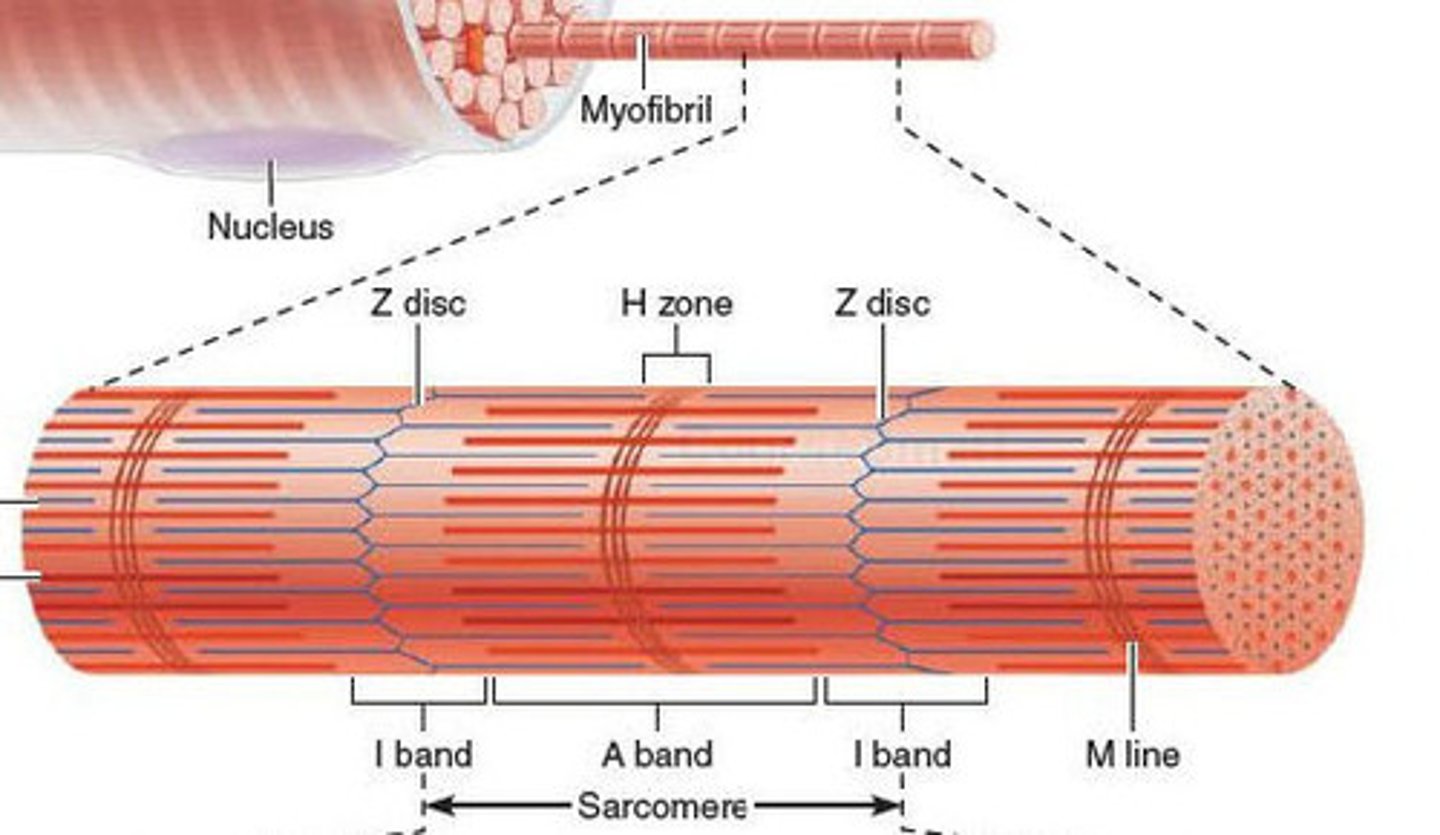
Z disc (line)
protein disc joining adjacent sarcomeres
- associates with T tubule
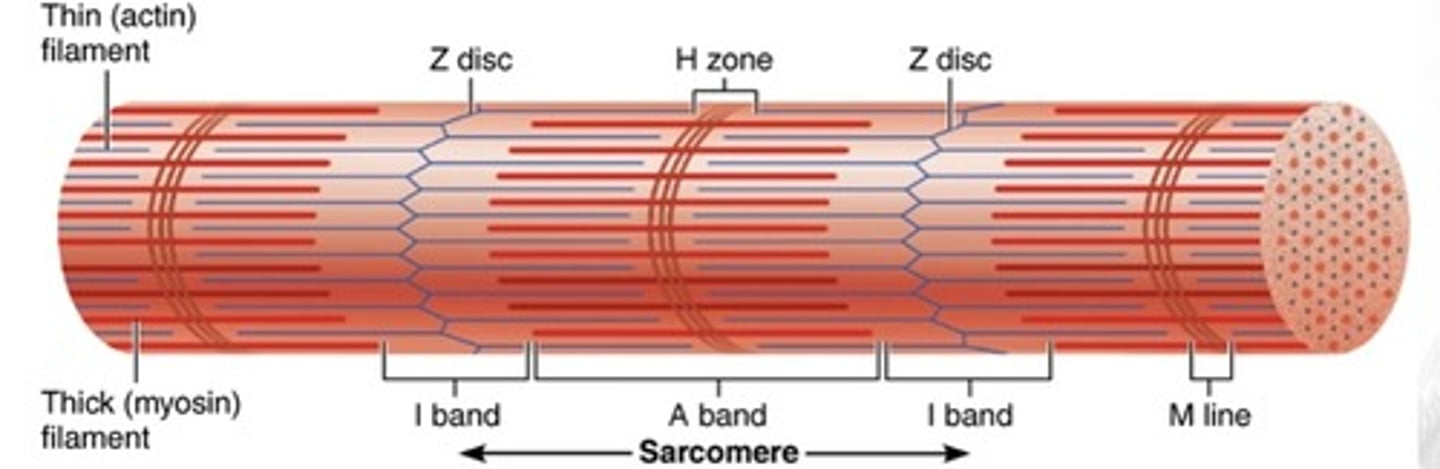
A band
primarily myosin (thick filaments), but some overlapping actin
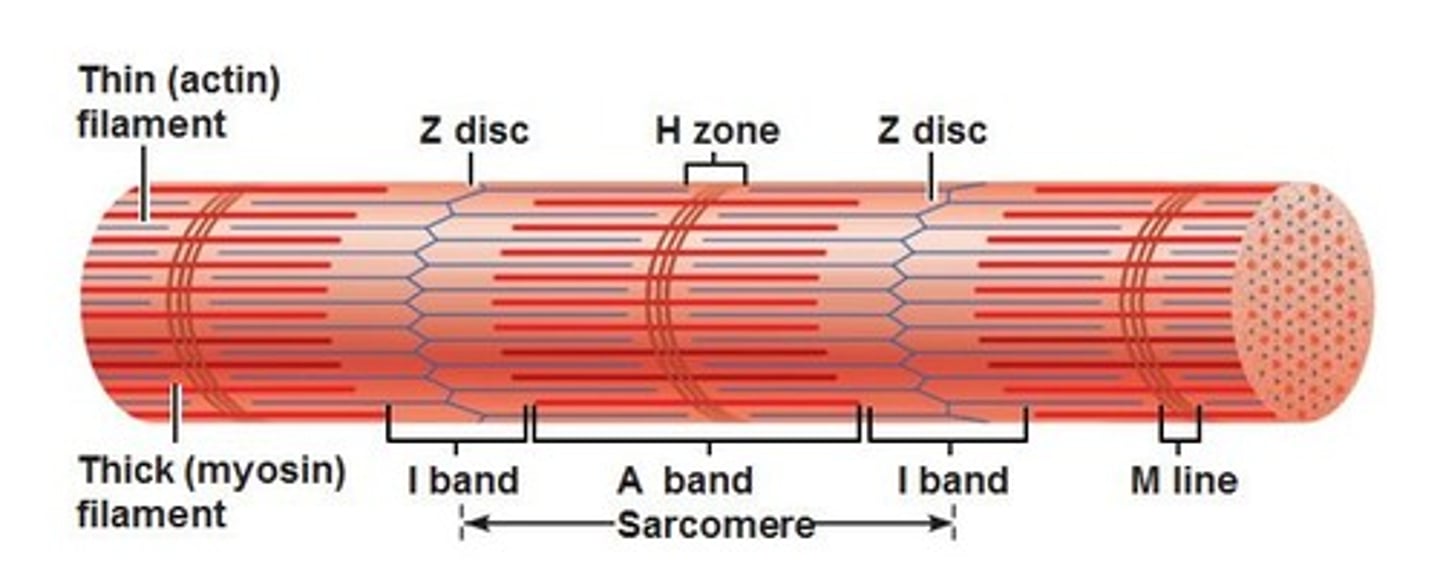
I band
primarily actin (thin filaments)
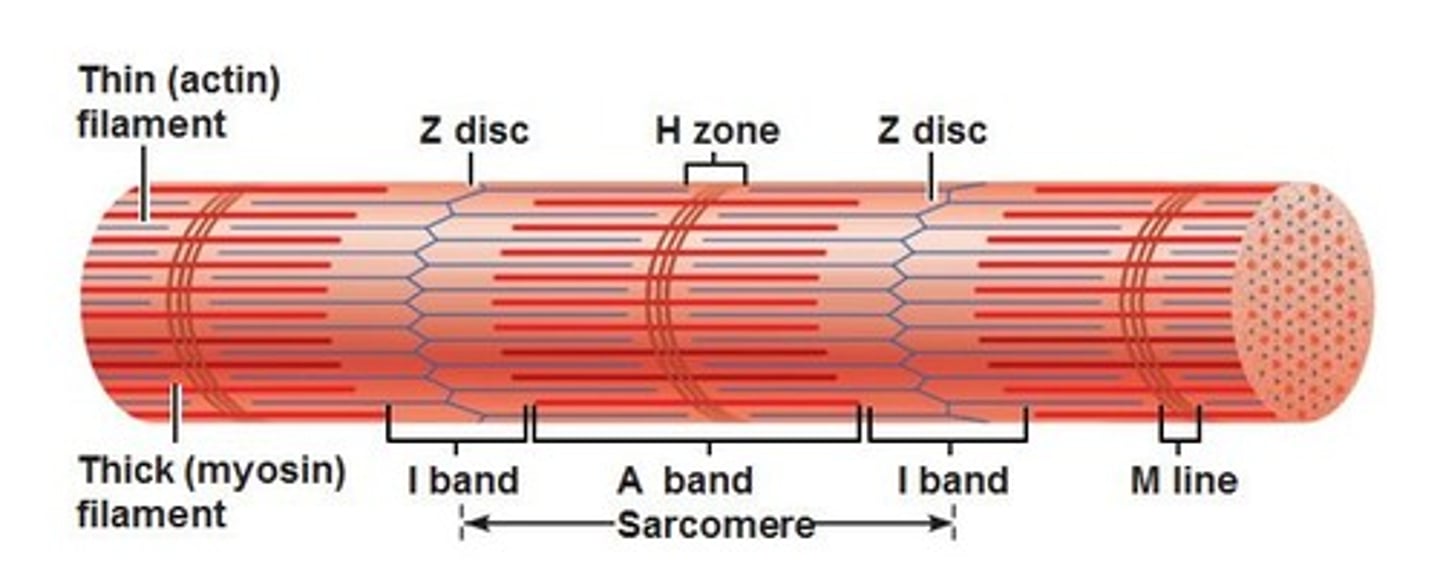
sarcomere shortening
when a contraction occurs, each sarcomere shortens a little, the result adding to the total shortening of the myofibril
- overall shortening of length is about 1/3
titin
large, spring-like protein that attaches Z disc to myosin
- elastic (titin) filaments
which characteristic of skeletal muscle does titin allow for?
elasticity
sliding filament theory
during a contraction, actin and myosin filaments slide across one another
motor units within a muscle
- within a muscle -> muscle fibers work together to perform an action
- changes in force, and fine muscle control are possible because of distinct motor units within a muscle
motor unit
1 motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates
neuron
single nerve cell
force and motor units
- all fibers innervated by a single motor neuron (motor unit) contract at the same time
- activating more motor units within a muscle increases the force exerted by that muscle
large muscles
~2000 fibers/motor unit
smaller muscles
~10 fibers/motor unit
- fine motor control
neuromuscular junction
where neuron (axon terminal) stimulates the muscle cell
what would make a muscle be able to shorten most during a contraction?
longest fibers
what would create the most force during a contraction?
greater number of fibers (strongest)
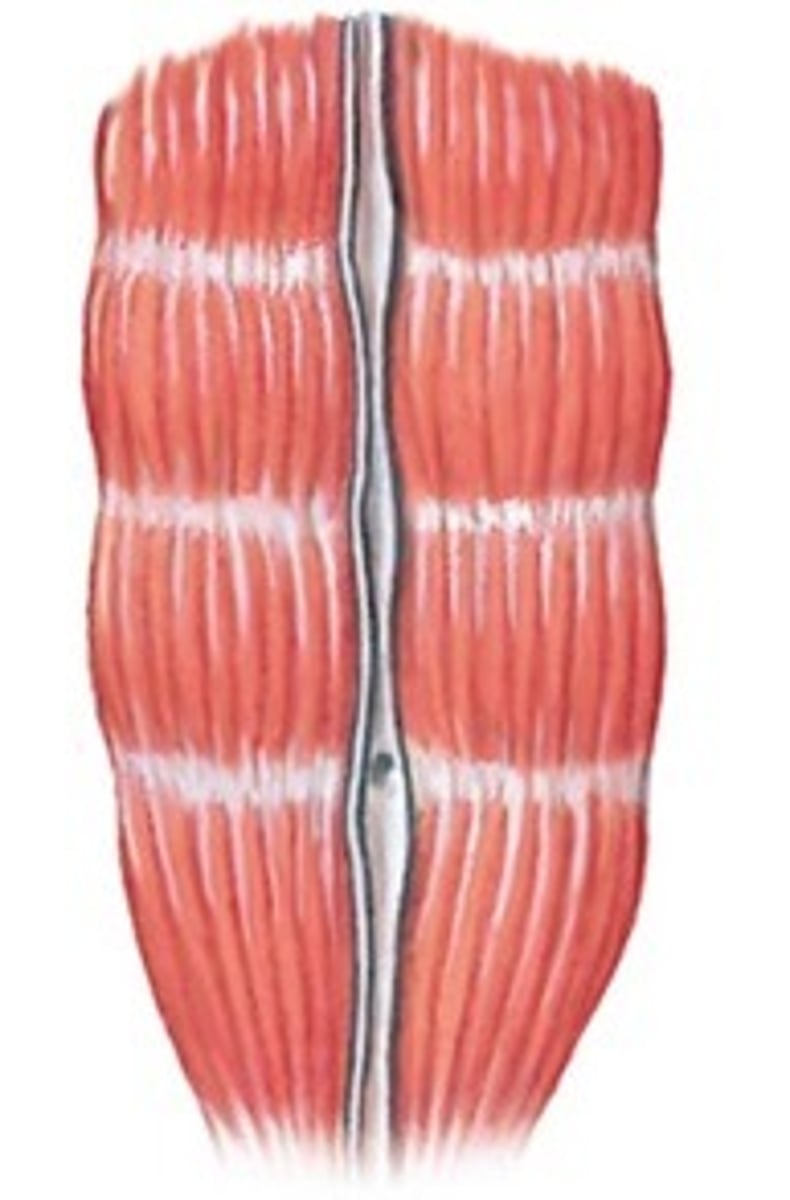
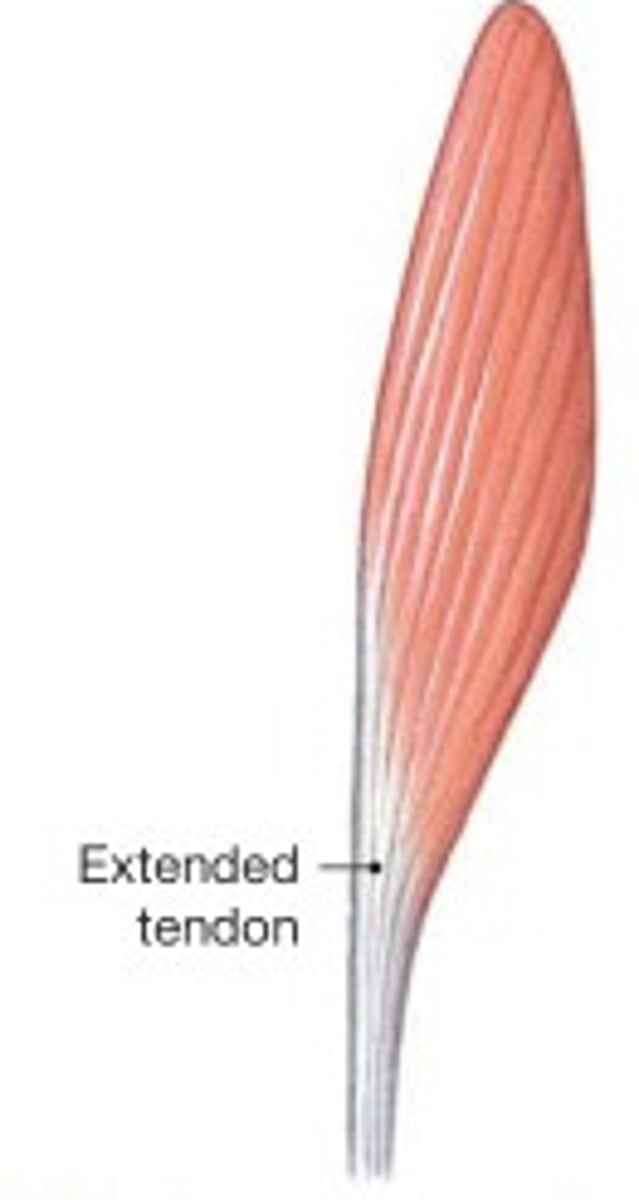
parallel muscles
- muscle fascicles run parallel to axis of muscle
- tendon on either side
- look long and ropelike
- fewer fibers than other types
- longer fibers so able to shorten more

pennate muscles
- tendon runs the whole length of muscle
- fascicles attach to tendon at an angle
- resemble a feather
- 3 subtypes
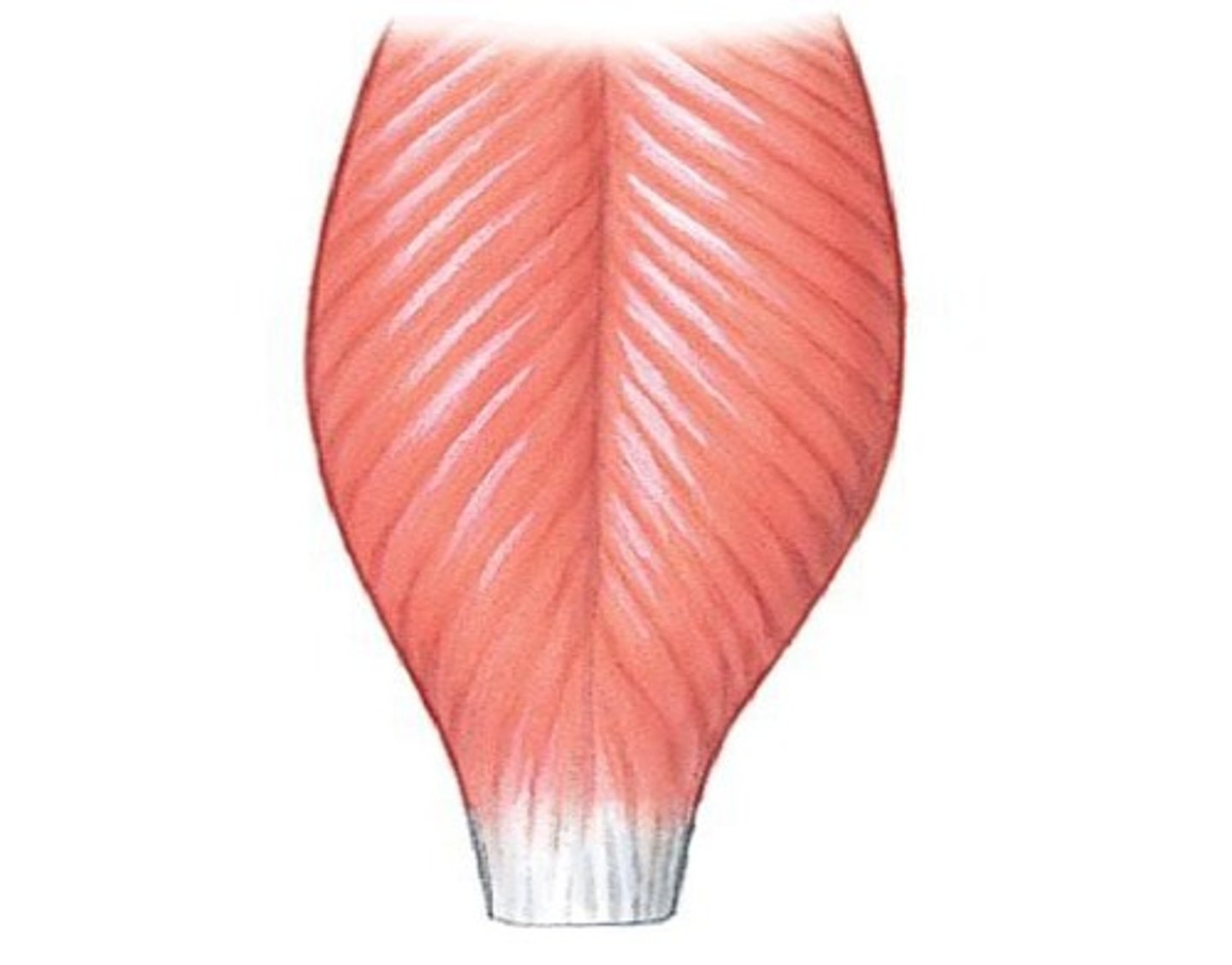
pennate muscles fascicles attach to tendon at an angle
- shorter fibers than parallel muscles
- allows for more fibers so stronger than parallel
subtypes of pennate muscles
1. unipennate
2. bipennate
3. multipennate
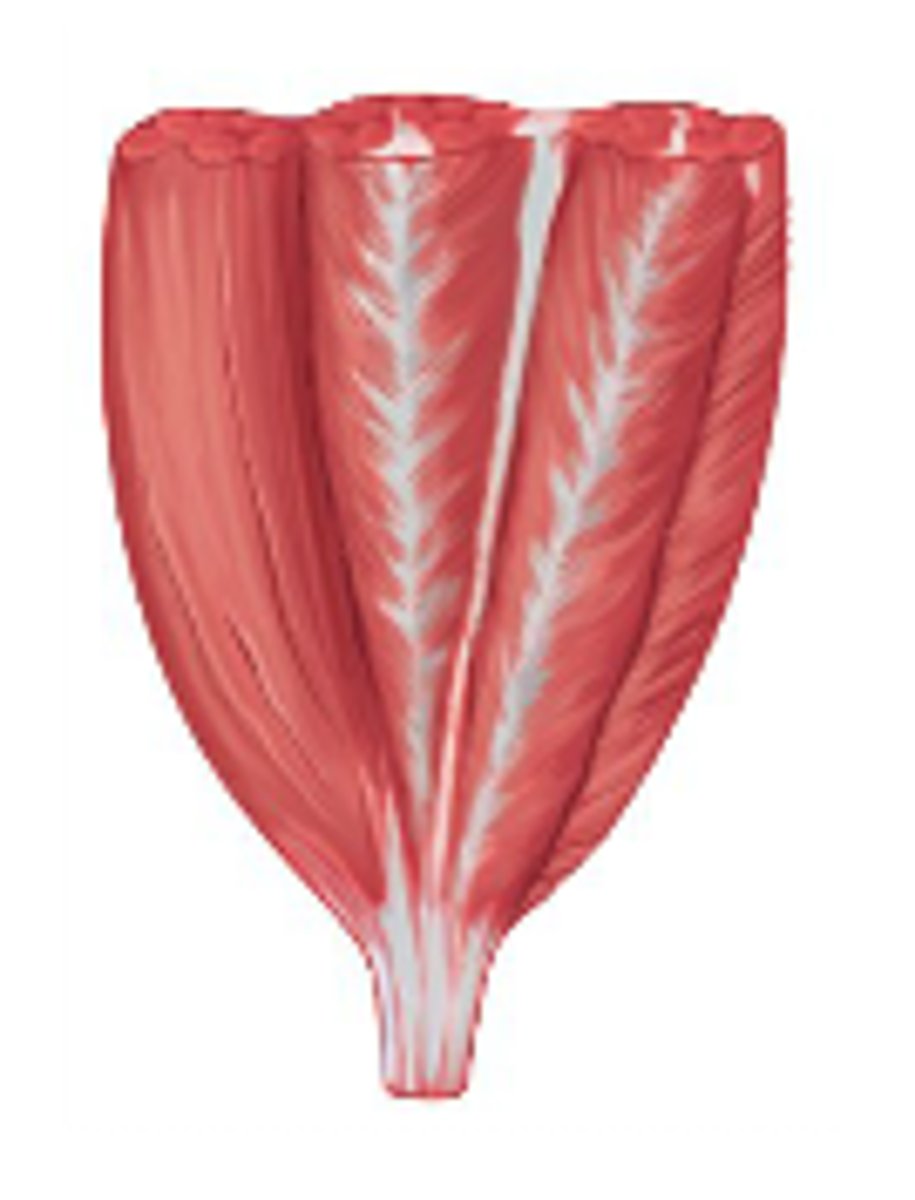
unipennate muscles
fascicles attach to one side of tendon
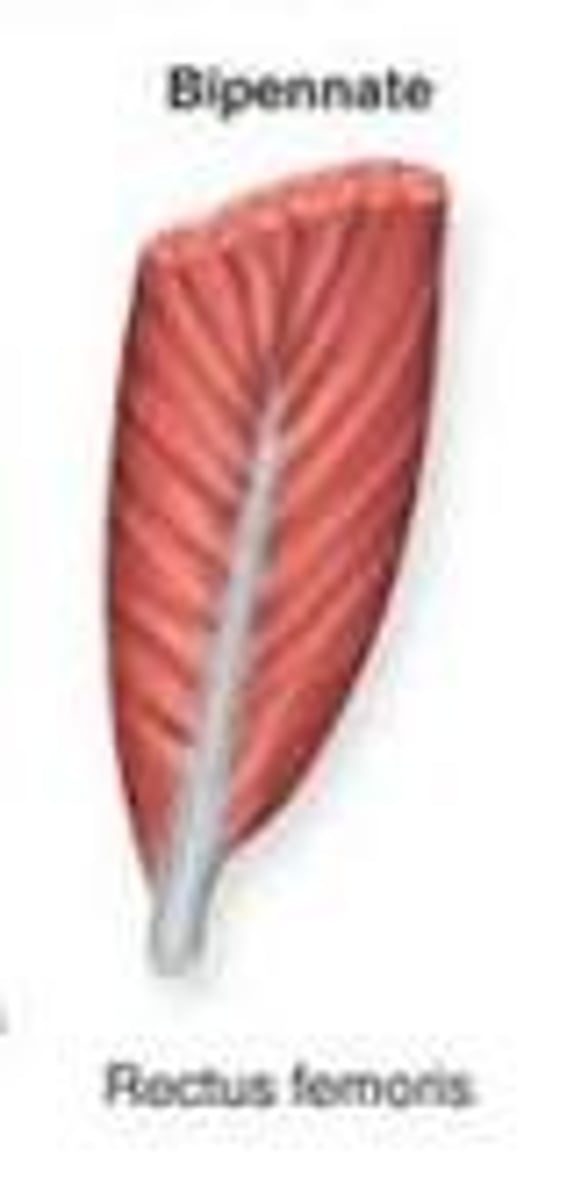
bipennate muscles
fascicles attach to both sides of tendon

multipennate muscles
branching tendon with fascicles attaching at many points
- strongest
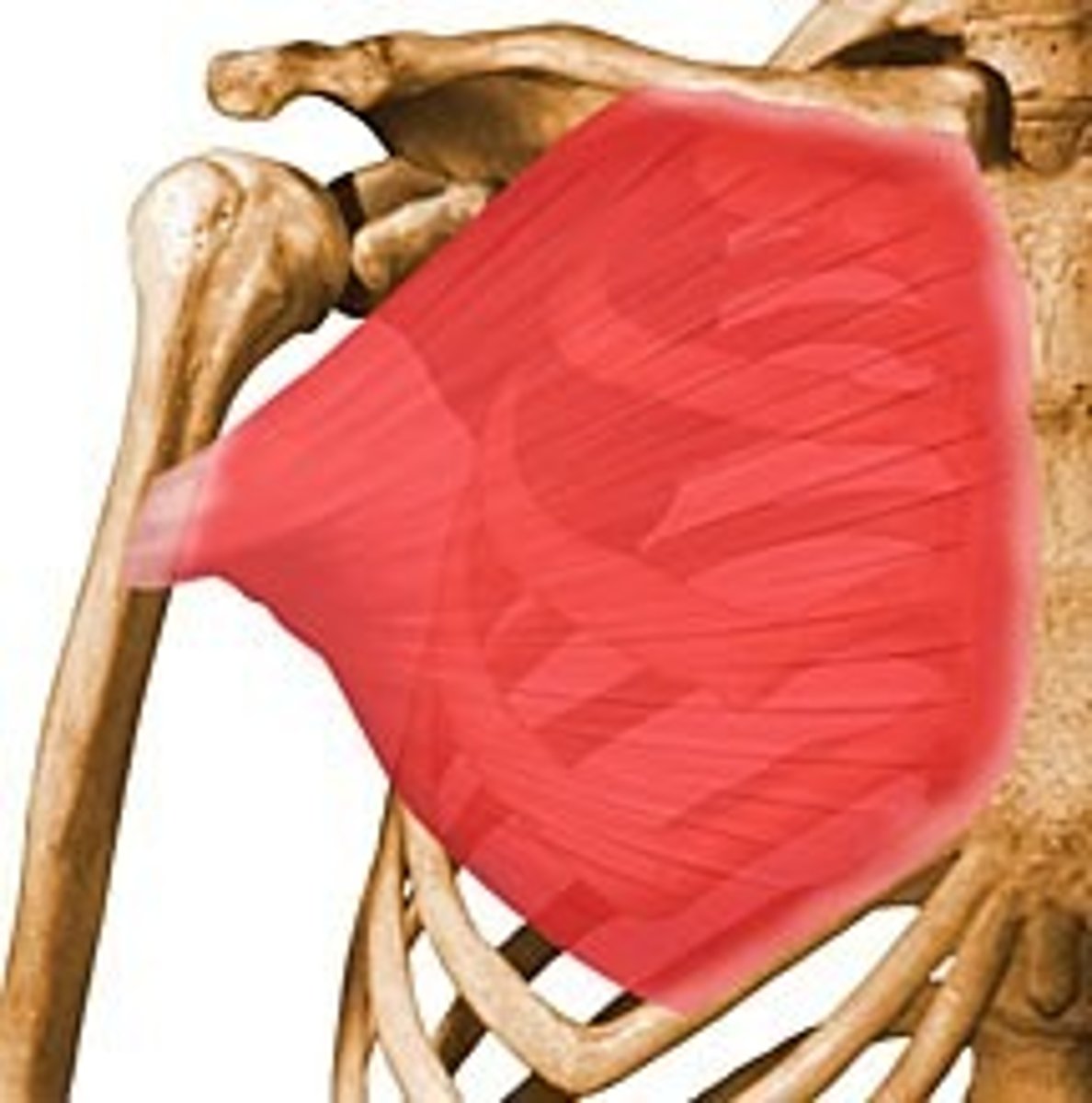
convergent muscles
- origin of muscle is long and broad
- muscle fascicles collected into tendon at insertion
- fan shaped
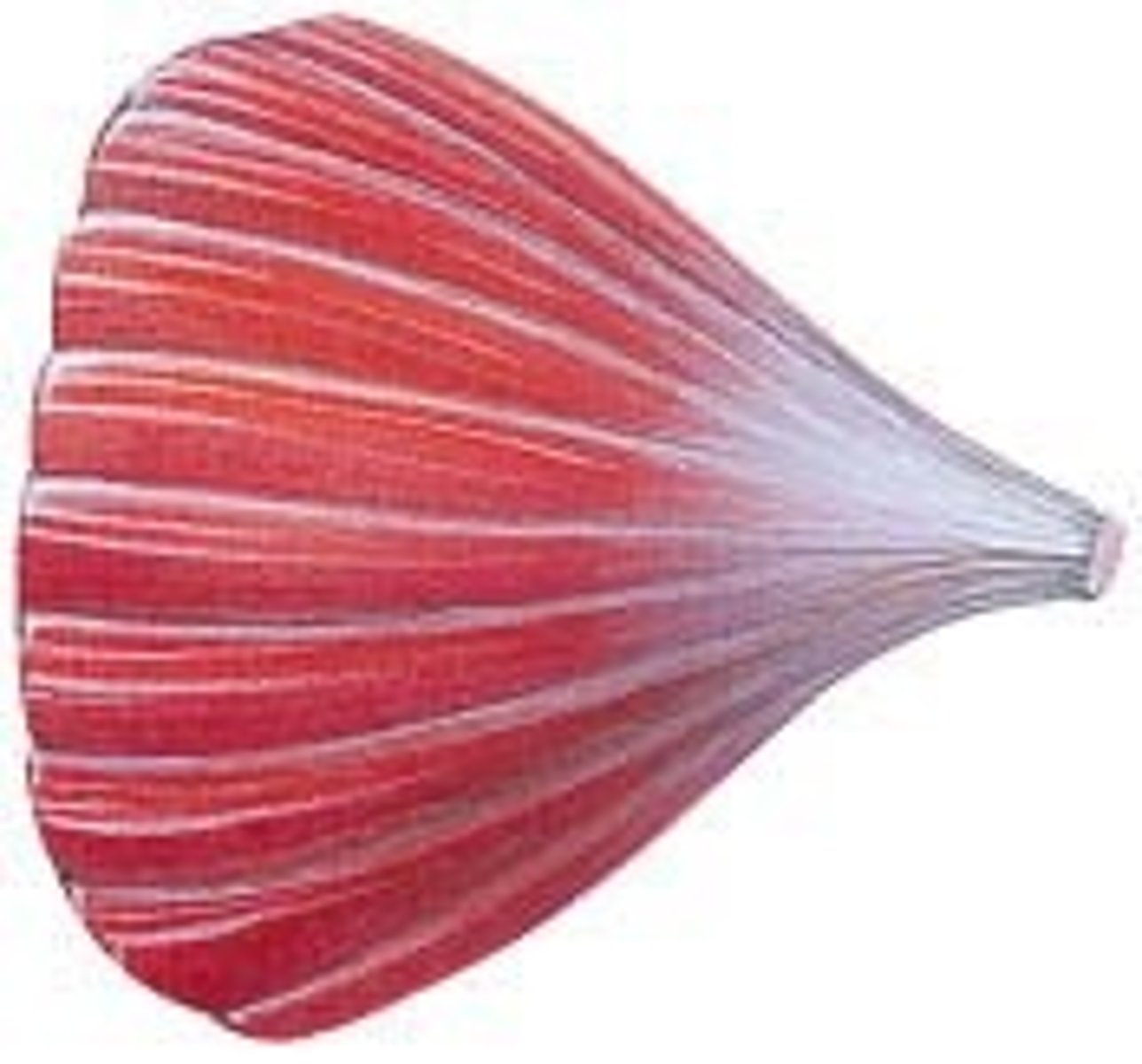

convergent muscles relationship to other muscle types
- more fibers than parallel
- longer fibers than pennate
relative strength of muscles: ranking
pennate > convergent > parallel
relative shortening ability of muscles
parallel > convergent > pennate
circular muscles
- fascicles arranged as a ring
- sphincter muscles
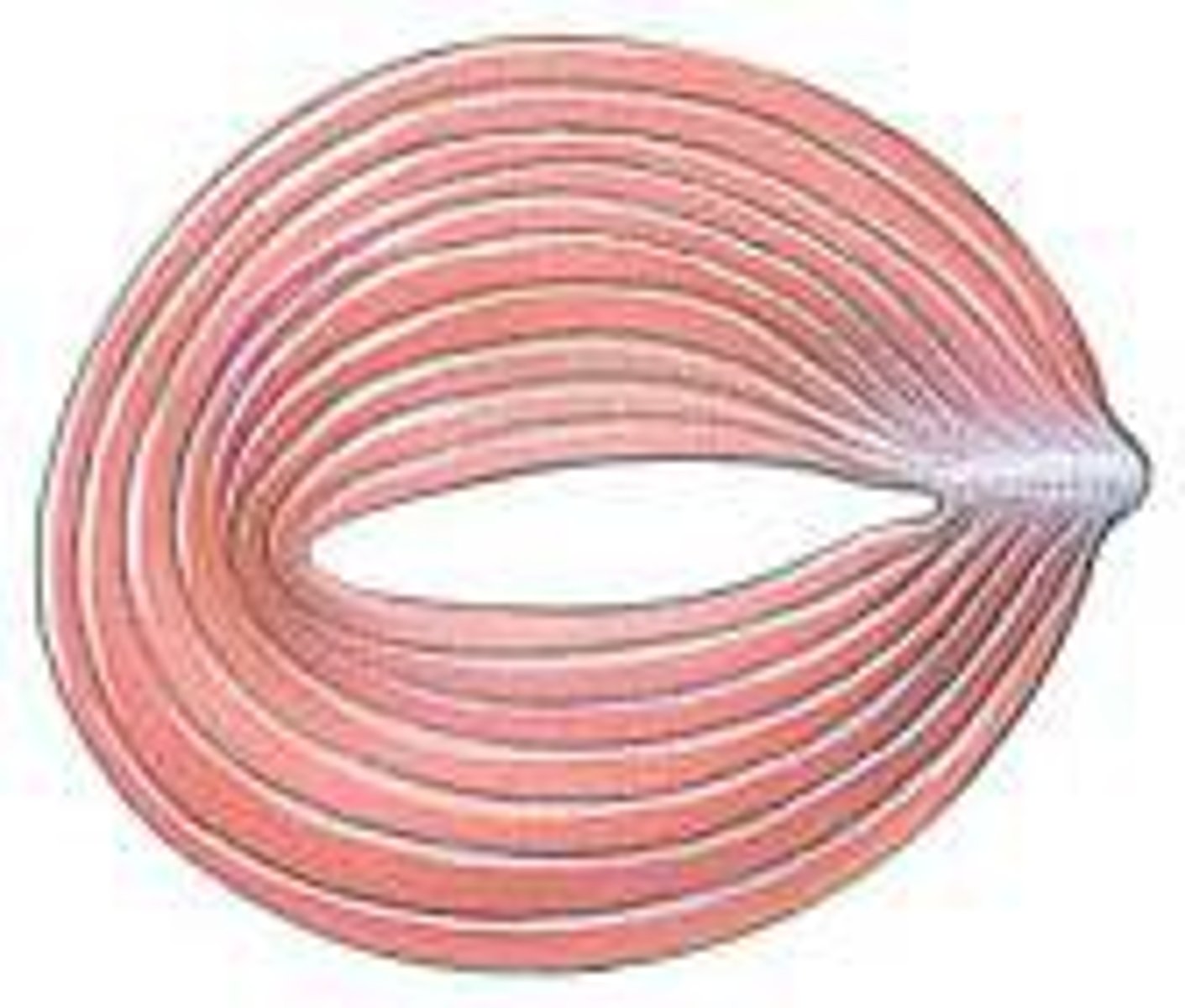

sphincter muscles
when contracted the muscle constricts an orifice (opening) keeping it closed
the pectoralis major is what kind of muscle
convergent
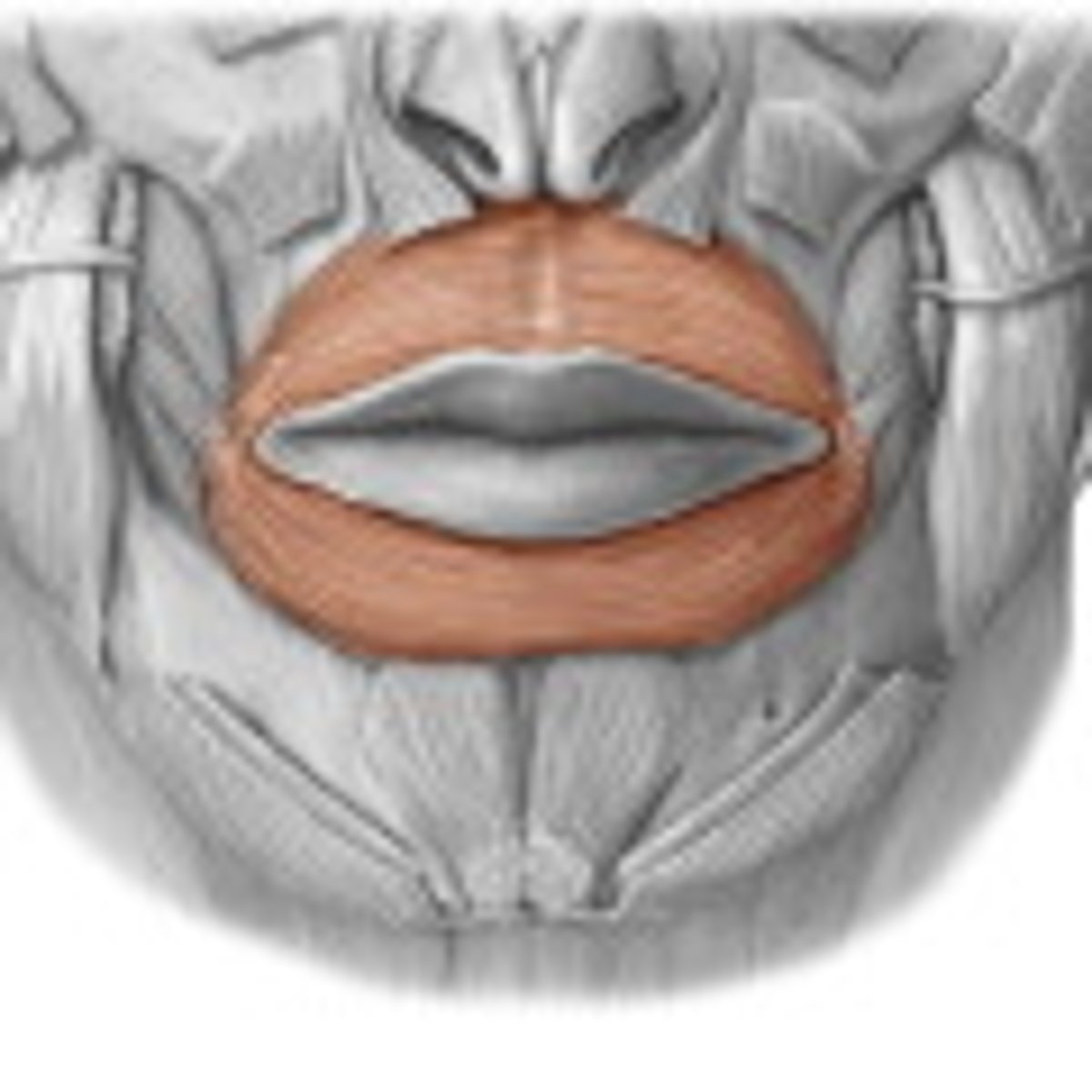
the orbicularis oris is what kind of muscle
circular
the deltoid is what kind of muscle
multipennate
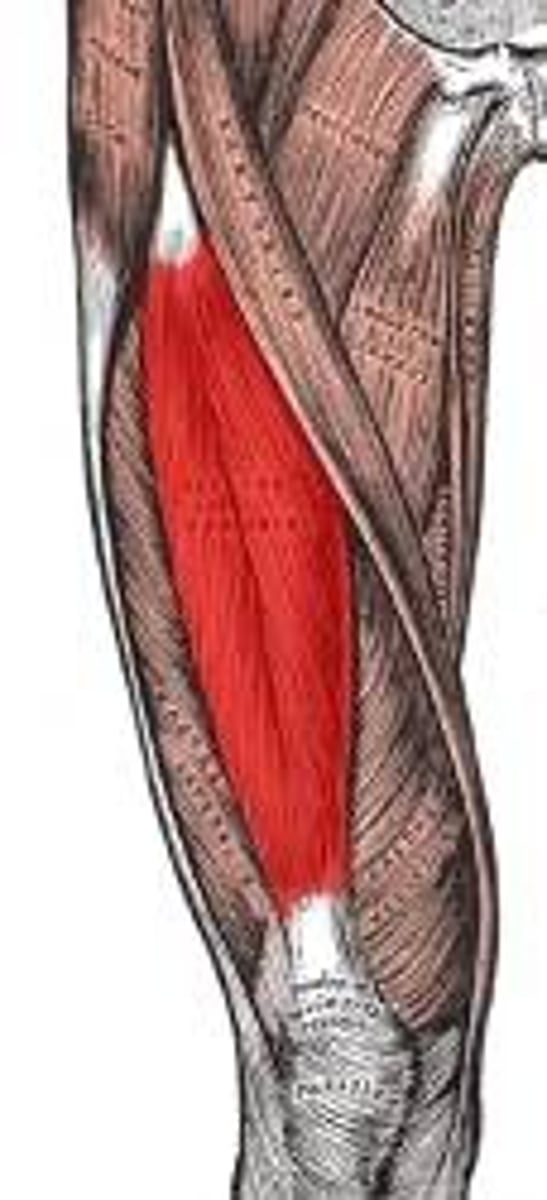
the biceps brachii is what kind of muscle
parallel
the rectus femoris is what kind of muscle
bipennate
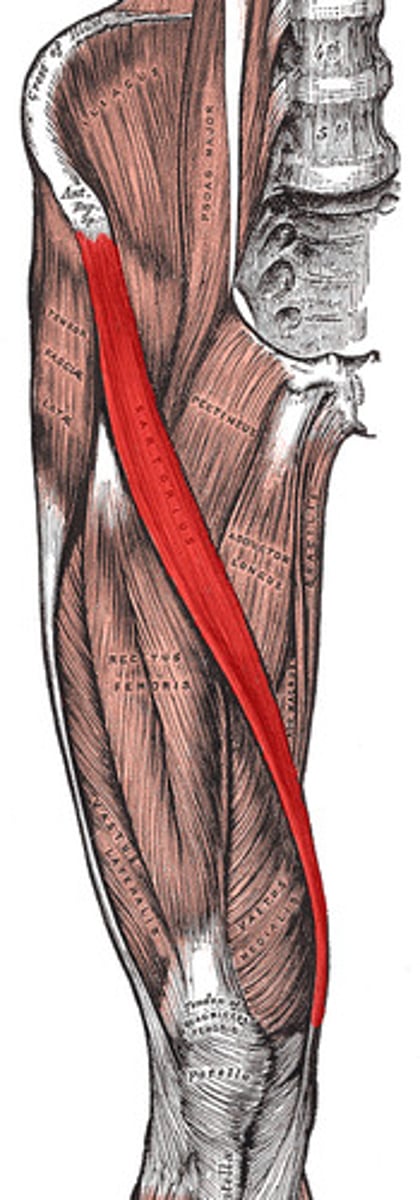
the sartorius is what kind of muscle
parallel
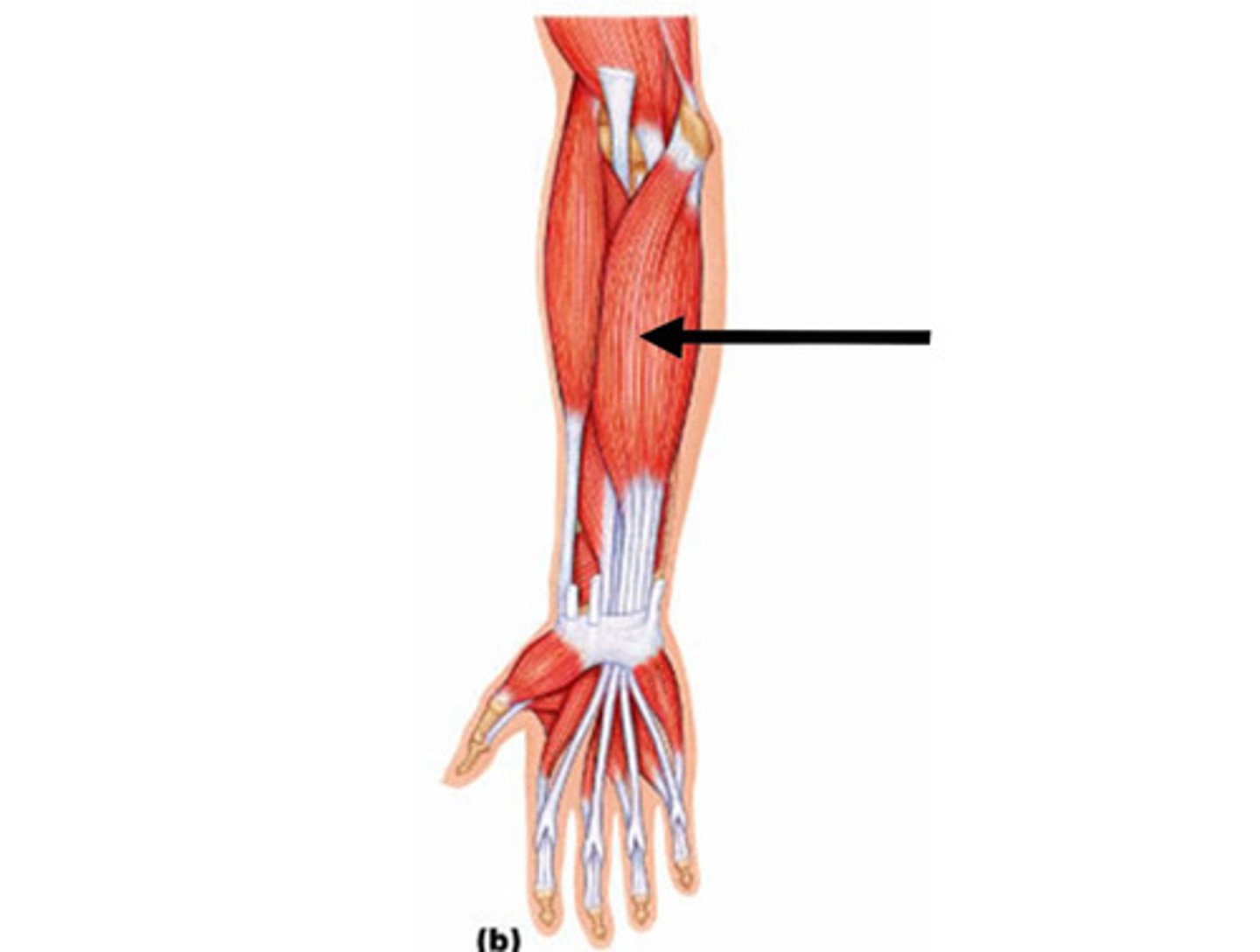
the extensor digitorium longus is what kind of muscle
unipennate
origin
attachment site that is not moved during a muscle action
insertion
attachment site that is moved when muscle shortens
action
the resulting movement of a muscle contraction
tendon
the dense reticular CT that connects muscle to bone
tendons are a dense regular connective tissue. with which structure of bones do you think tendons are continuous?
periosteum (dense irregular CT)
tendons are a dense regular connective tissue. with which structure of muscles do you think tendons are continuous?
epimysium (dense irregular CT)
direct attachment
short, dense regular CT fibers connect muscle to bone
indirect attachment
long, dense, regular CT fibers connect muscle to bone
- ex: tendon and aponeurosis
aponeurosis
flat sheet (different from tendon, which is more rope like)
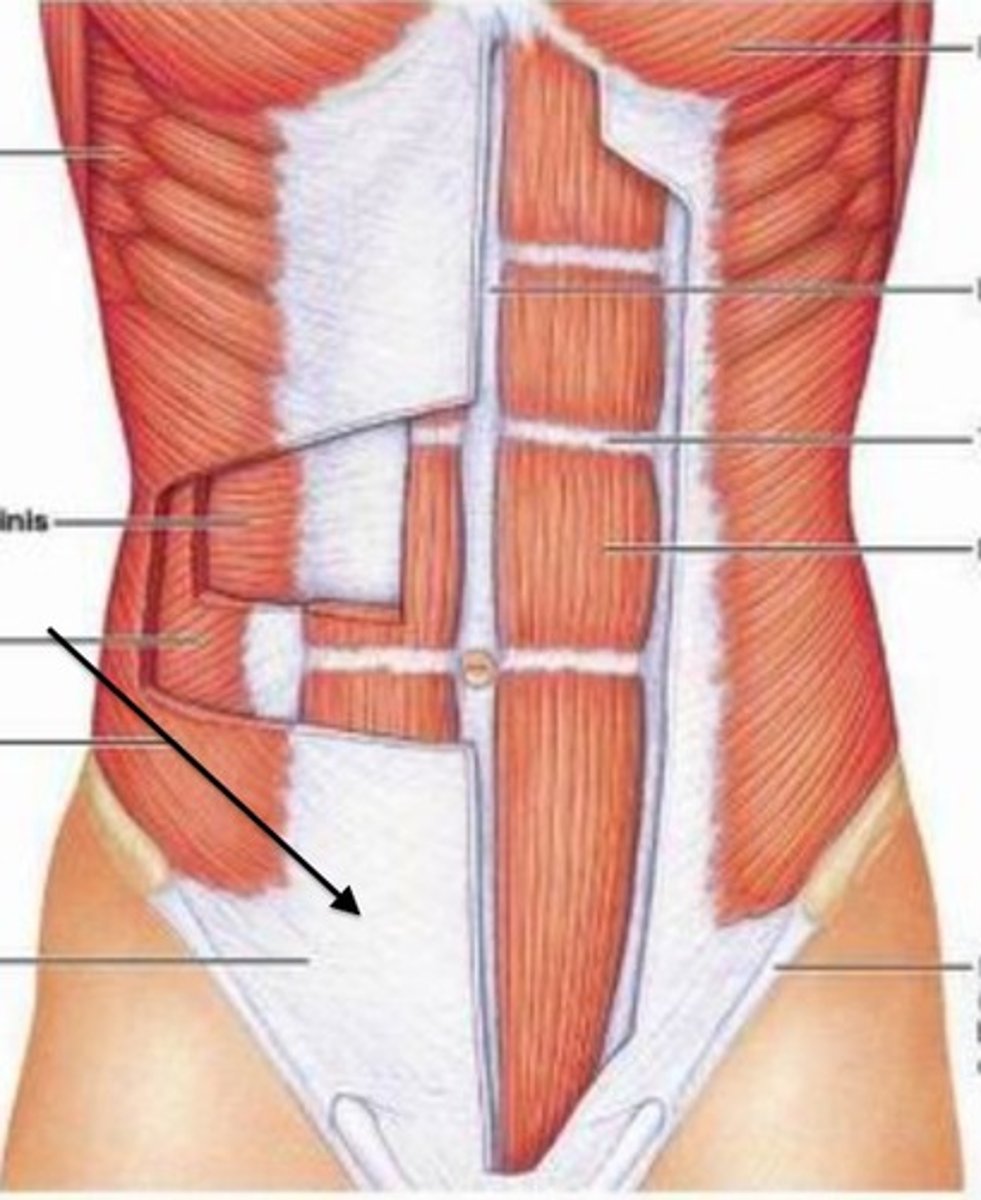
upraised bone markings are visible where?
bone where muscles attach
synergists
muscles that work together to perform an action
antagonists
muscles that perform opposite functions
prime mover (agonist)
muscle that is primarily responsible for a movement
fixator
a synergist that assists by holding a bone firmly in place to allow the prime mover to work more effectively
elbow flexion: synergists
biceps brachii, brachialis, and brachioradialis muscles work together to flex elbow
elbow flexion: antagonists
triceps brachii muscle reverses the movement and extends elbow
elbow flexion: prime mover (antagonist)
brachialis muscle is the primary muscle of elbow flexion
elbow flexion: fixator
muscles of scalpula stabilize the shoudler to make elbow flexion more efficient
true statements about muscle fibers
- may be as long as the muscle body
- contain sarcomeres as their contractile unit
- are bundled into fascicles
- contain myofibrils
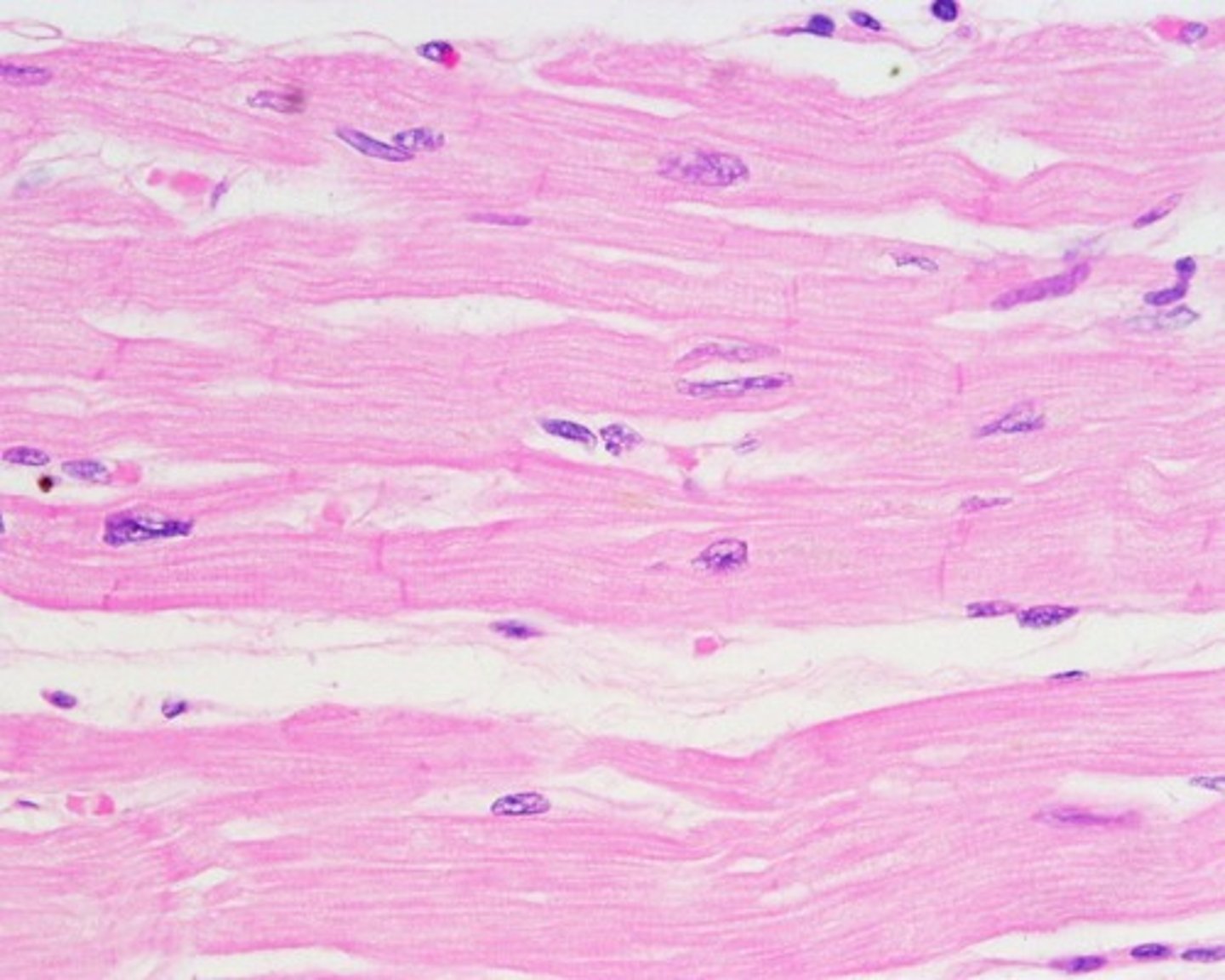
cardiac muscle tissue
thick muscle of heart wall
- striated
- branched
- most cells are uninucleated, but MAY have 2 large nuclei
- cells have some regenerative ability (perhaps 1% a year)
- involuntary
- surrounded by endomysium
- connected at intercalated discs
what type of cellular junction allows cardiac muscle cells to contract in a coordinated fashion?
gap junction
structures of an intercalated disc
- gap junction
- desmosomes
gap junction of an intercalated disc
allow for coordinated contractions by allowing action potentials to quickly spread from cell to cell
desmosomes of an intercalated disc
provide strength, site where intermediate dilaments are attached (fasciae adherens)
inherent rhythmicity (automaticity) of cardiac muscle
- cardiac muscle cells are able to initiate their own contraction without stimulation from the nervous system
- note: our heart does rely on the NS to control things such as heart rate
what type of muscle would you expect to find within the walls of blood vessels?
smooth
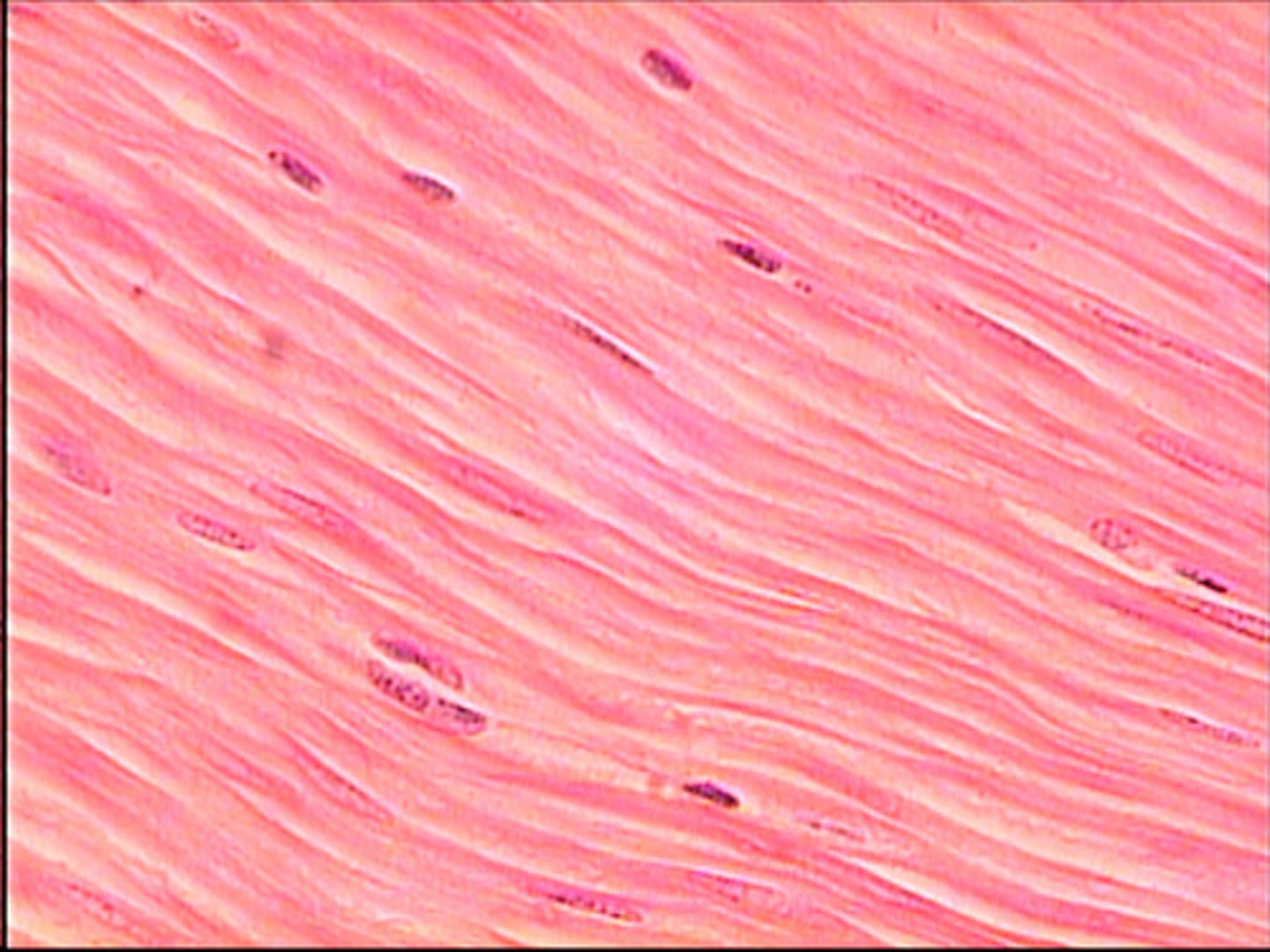
smooth muscle tissue
- small, spindle shaped cells
- uninucleated
- NO striations -> they do contain myofilaments, but they are not arranged into sarcomeres
- each cell covered by endomysium
- involuntary
- regenerate
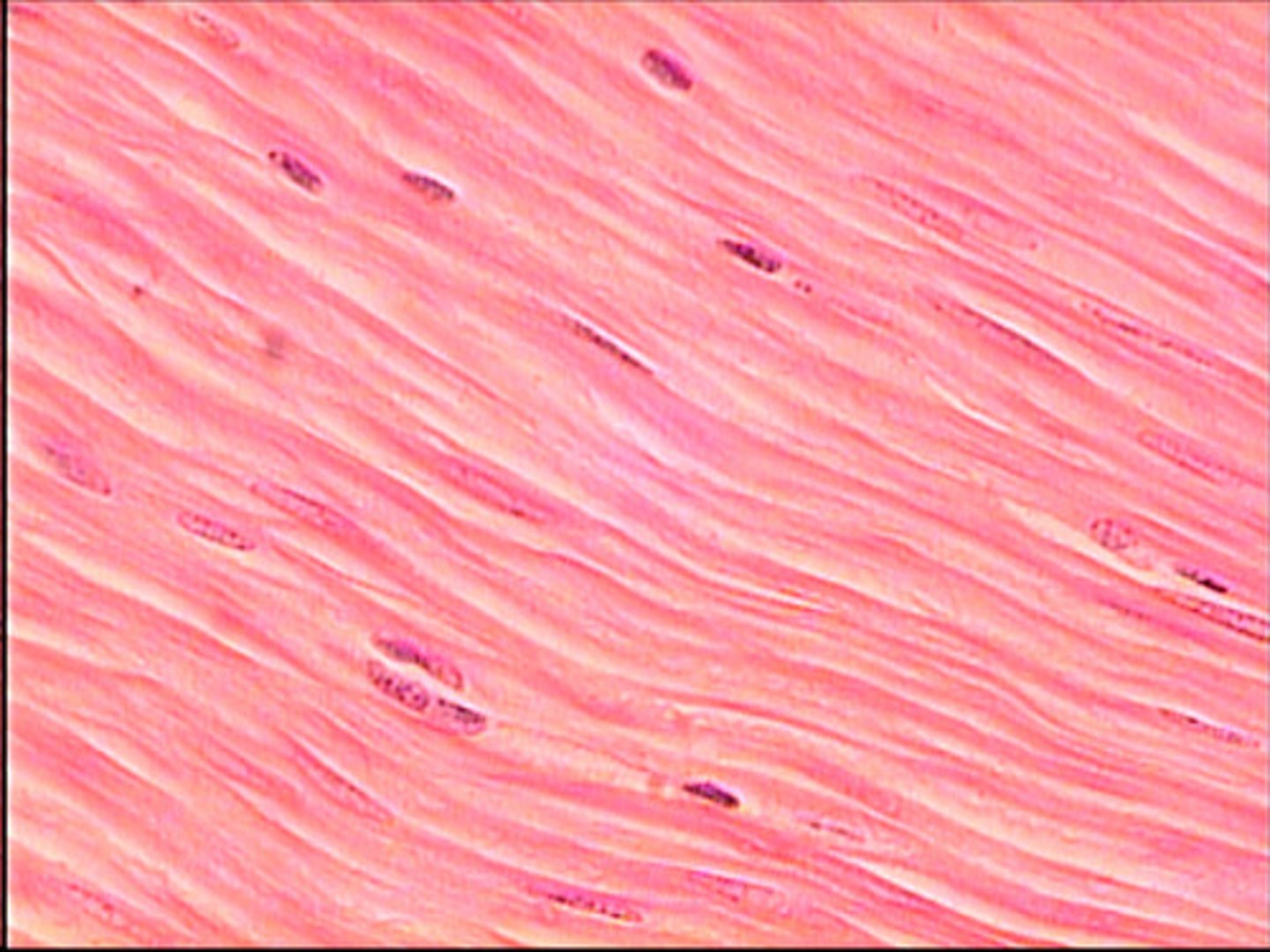
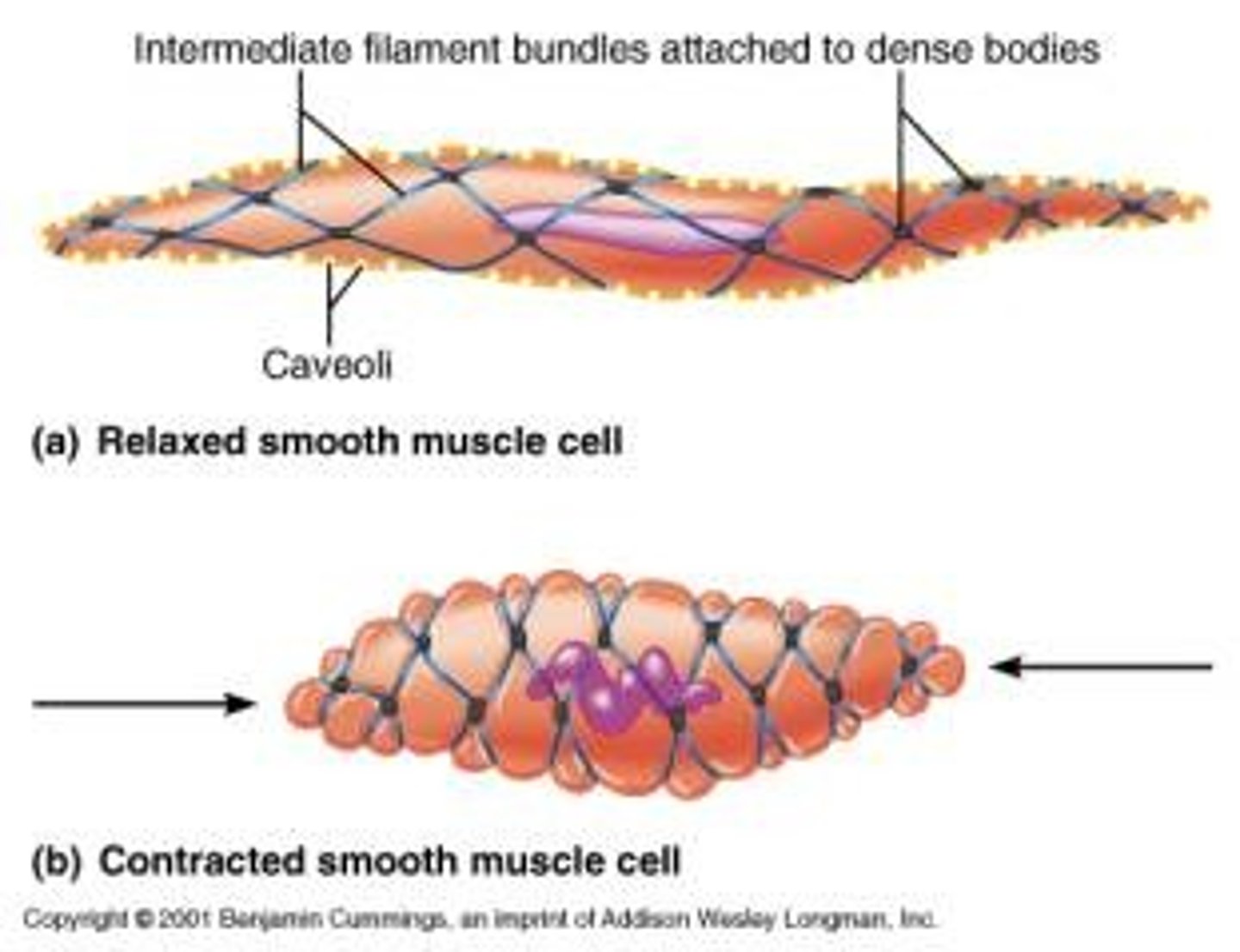
smooth muscle cells
- intermediate filaments anchor actin and myosin
- a contraction involves myosin and actin fibers moving against one another
smooth muscle is typically arranged into two distinct layers:
- circular layer
- longitudinal layer
- layers differ in orientation of cells: typically perpendicular to one another
circular layer of smooth muscle
closest to lumen of organ
longitudinal layer of smooth muscle
wraps around circular layer